Rurikids on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Rurik dynasty ( be, Ру́рыкавічы, Rúrykavichy; russian: Рю́риковичи, Ryúrikovichi, ; uk, Рю́риковичі, Riúrykovychi, ; literally "sons/scions of Rurik"), also known as the Rurikid dynasty or Rurikids, was a noble lineage founded by the Varangian prince Rurik, who established himself in Novgorod around the year AD 862. The Rurikids were the ruling
 The Rurikid dynasty was founded in 862 by Rurik, a Varangian prince. The scholarly consensus is that the Rus' people originated in what is currently coastal eastern Sweden around the eighth century and that their name has the same origin as
The Rurikid dynasty was founded in 862 by Rurik, a Varangian prince. The scholarly consensus is that the Rus' people originated in what is currently coastal eastern Sweden around the eighth century and that their name has the same origin as
The Viking World
', ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 4–10 (pp. 6–7). The name ''Rus'' would then have the same origin as the Finnish and
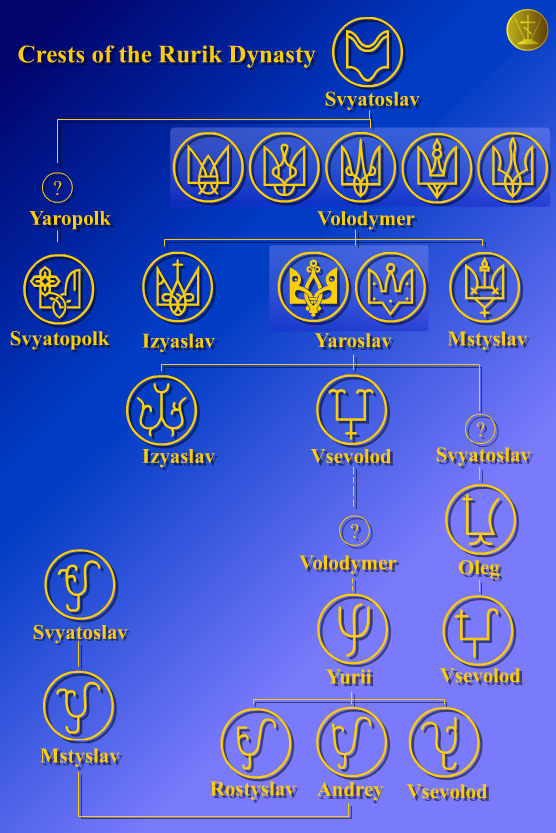 Rurik and his brothers founded a state that later historians called ''Kievan Rus′''. By the middle of the twelfth century, Kievan Rus′ had dissolved into independent principalities, each ruled by a different branch of the Rurik dynasty. The dynasty followed
Rurik and his brothers founded a state that later historians called ''Kievan Rus′''. By the middle of the twelfth century, Kievan Rus′ had dissolved into independent principalities, each ruled by a different branch of the Rurik dynasty. The dynasty followed  According to Jaroslav Pelenski,
This caused the Rurik dynasty to effectively dissolve into several sub-dynasties ruling smaller states in the 10th and 11th centuries. These were the ''Olgoviches'' of
According to Jaroslav Pelenski,
This caused the Rurik dynasty to effectively dissolve into several sub-dynasties ruling smaller states in the 10th and 11th centuries. These were the ''Olgoviches'' of
File:COA Holstein-Gottorp-Romanov chivalric.svg, Arms of the House of Holstein-Gottorp-Romanov
File:RU COA Dolgorukov.svg, Coat of arms of the
dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A ...
of Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas o ...
(after the conquest of Kiev by Oleg of Novgorod in 882) before it finally disintegrated in the mid-13th century, as well as the successor Rus' principalities and Rus' prince republics of Novgorod, Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=pskov-ru.ogg, p=pskof; see also names in other languages) is a city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, located about east of the Estonian border, on the Velikaya River. Population ...
, Vladimir-Suzdal
Vladimir-Suzdal (russian: Владимирско-Су́здальская, ''Vladimirsko-Suzdal'skaya''), also Vladimir-Suzdalian Rus', formally known as the Grand Duchy of Vladimir (1157–1331) (russian: Владимиро-Су́здальс ...
, Ryazan, Smolensk, Galicia-Volhynia (after 1199), Chernigov, and the Grand Duchy of Moscow (from 1263).
Following the disintegration of Kievan Rus', the most powerful state to eventually arise was the Grand Duchy of Moscow, initially a part of Vladimir-Suzdal
Vladimir-Suzdal (russian: Владимирско-Су́здальская, ''Vladimirsko-Suzdal'skaya''), also Vladimir-Suzdalian Rus', formally known as the Grand Duchy of Vladimir (1157–1331) (russian: Владимиро-Су́здальс ...
, which, along with the Novgorod Republic, established the basis of the modern Russian nation.Excerpted from Ivan III threw off the control of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmen ...
and consolidated the whole of central and northern Rus', ruling it as "Prince of All Rus. Ivan IV assumed the title "Tsar of All Rus and transformed the state into the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
. The Rurik line ruled until 1598, following which they were succeeded by the House of Romanov, after the Time of Troubles.
The Romanovichi branch of the dynasty ruled southwestern Rus' and part of central Rus'. These territories were unified by Roman the Great and his son Daniel Romanovich, who was in 1253 crowned by Pope Innocent IV as king of Galicia–Volhynia. After the line's extinction, the principality was annexed by Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, and the title of its prince eventually passed to the ruler of Austro-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern ...
. According to Ukrainian historiography continuous Rurikid sovereignty from the ninth century to the fourteenth represents part of Ukraine's historical process. In Ukrainian historiography
Prehistoric Ukraine, as a part of the Pontic steppe in Eastern Europe, played an important role in Eurasian cultural contacts, including the spread of the Chalcolithic, the Bronze Age, Indo-European migrations and the domestication of the hor ...
of the 19th century, Ukrainian historiographer Mykhailo Hrushevsky
Mykhailo Serhiiovych Hrushevsky ( uk, Михайло Сергійович Грушевський, Chełm, – Kislovodsk, 24 November 1934) was a Ukrainian academician, politician, historian and statesman who was one of the most important figure ...
, who wrote a book under a similar name, referred to Rus' civilization as Ukraine-Rus'. According to his studies Rus' is not considered to have ended in 1240, but merely to have shifted its centre slightly westward.
As a ruling dynasty, the Rurik dynasty held its own in some parts of Rus' for a total of twenty-one generations in male-line succession, from Rurik (died 879) to Feodor I of Russia (died 1598), a period of more than 700 years. They are one of Europe's oldest royal houses, with numerous existing cadet branch
In history and heraldry, a cadet branch consists of the male-line descendants of a monarch's or patriarch's younger sons ( cadets). In the ruling dynasties and noble families of much of Europe and Asia, the family's major assets— realm, t ...
es.
Origins
 The Rurikid dynasty was founded in 862 by Rurik, a Varangian prince. The scholarly consensus is that the Rus' people originated in what is currently coastal eastern Sweden around the eighth century and that their name has the same origin as
The Rurikid dynasty was founded in 862 by Rurik, a Varangian prince. The scholarly consensus is that the Rus' people originated in what is currently coastal eastern Sweden around the eighth century and that their name has the same origin as Roslagen
Roslagen is the name of the coastal areas of Uppland province in Sweden, which also constitutes the northern part of the Stockholm archipelago.
Historically, it was the name for all the coastal areas of the Baltic Sea, including the eastern p ...
in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
(with the older name being '' Roden'').
According to the prevalent theory, the name ''Rus'', like the Proto-Finnic name for Sweden (''*Ruotsi''), is derived from an Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
term for "the men who row" (''rods-'') as rowing was the main method of navigating the rivers of Eastern Europe, and that it could be linked to the Swedish coastal area of Roslagen
Roslagen is the name of the coastal areas of Uppland province in Sweden, which also constitutes the northern part of the Stockholm archipelago.
Historically, it was the name for all the coastal areas of the Baltic Sea, including the eastern p ...
(''Rus-law'') or ''Roden'', as it was known in earlier times.Stefan Brink, 'Who were the Vikings?', in The Viking World
', ed. by Stefan Brink and Neil Price (Abingdon: Routledge, 2008), pp. 4–10 (pp. 6–7). The name ''Rus'' would then have the same origin as the Finnish and
Estonian
Estonian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Estonia, a country in the Baltic region in northern Europe
* Estonians, people from Estonia, or of Estonian descent
* Estonian language
* Estonian cuisine
* Estonian culture
See also
*
...
names for Sweden: ''Ruotsi'' and ''Rootsi''."Russ, adj. and n." OED Online, Oxford University Press, June 2018, www.oed.com/view/Entry/169069. Retrieved 12 January 2021.
The Primary Chronicle gives the following account of how the Rurik dynasty began, dating it to the Byzantine years of the world 6368–6370 (AD 860–862):
There is some ambiguity even in the Primary Chronicle about the specifics of the story, "hence their paradoxical statement 'the people of Novgorod are of Varangian stock, for formerly they were Slovenes. However, archaeological evidence such as " Frankish swords, a sword chape and a tortoiseshell brooch" in the area suggest that there was, in fact, a Scandinavian population during the tenth century at the latest.
History
 Rurik and his brothers founded a state that later historians called ''Kievan Rus′''. By the middle of the twelfth century, Kievan Rus′ had dissolved into independent principalities, each ruled by a different branch of the Rurik dynasty. The dynasty followed
Rurik and his brothers founded a state that later historians called ''Kievan Rus′''. By the middle of the twelfth century, Kievan Rus′ had dissolved into independent principalities, each ruled by a different branch of the Rurik dynasty. The dynasty followed agnatic seniority
Agnatic seniority is a patrilineal principle of inheritance where the order of succession to the throne prefers the monarch's younger brother over the monarch's own sons. A monarch's children (the next generation) succeed only after the males ...
and the ''izgoi
Izgoi is a term that is found in medieval Kievan Rus'. In primary documents, it indicated orphans who were protected by the church. In historiographic writing on the period, the term was meant as a prince in Kievan Rus' who was excluded from succe ...
'' principle. The Rurik dynasty underwent a major schism after the death of Yaroslav the Wise in 1054, dividing into three branches on the basis of descent from three successive ruling Grand Princes: Iziaslav (1024–1078), Sviatoslav
Sviatoslav (russian: Святосла́в, Svjatosláv, ; uk, Святосла́в, Svjatosláv, ) is a Russian and Ukrainian given name of Slavic origin. Cognates include Svetoslav, Svatoslav, , Svetislav. It has a Pre-Christian pagan characte ...
(1027–1076), and Vsevolod Vsevolod or Wsewolod (russian: Все́волод ; uk, Все́волод ) is a Slavic male first name. Its etymology is from Slavic roots 'vse' (all) and 'volodeti' (to rule) and means 'lord-of-everything/everybody', (similar to another princ ...
(1030–1093). In addition, a line of Polotsk princes assimilated themselves with the princes of Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
. In the 10th century the Council of Liubech The Council of Liubech was one of the best documented princely meetings in Kievan Rus' that took place in Liubech (today in Chernihiv Oblast, Ukraine) in 1097. The council ended the (1093–1097) between Svyatopolk II Izyaslavych of Kyiv, Volody ...
made some amendments to a succession rule and divided Ruthenia
Ruthenia or , uk, Рутенія, translit=Rutenia or uk, Русь, translit=Rus, label=none, pl, Ruś, be, Рутэнія, Русь, russian: Рутения, Русь is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin as one of several terms ...
into several autonomous principalities that had equal rights to obtain the Kievan throne.
Vsevolod's line eventually became better known as the Monomakhovichi
Monomakhovichi or House of Monomakh was a major princely branch of the Rurik dynasty, descendants of which managed to inherit practically all princely titles in the Grand Duchy of Kiev. The progenitor of the house is Vladimir II Monomakh (son of V ...
and was the predominant one. The line of Sviatoslav later became known as Olegovychi and often laid claim to the lands of Chernihiv and Severia
Severia or Siveria ( orv, Сѣверія, russian: Северщина, translit=Severshchina, uk, Сіверія or , translit. ''Siveria'' or ''Sivershchyna'') is a historical region in present-day southwest Russia, northern Ukraine, eastern ...
. The Izyaslavychi who ruled Turov and Volhynia were eventually replaced by a Monomakhovychi branch.
 According to Jaroslav Pelenski,
This caused the Rurik dynasty to effectively dissolve into several sub-dynasties ruling smaller states in the 10th and 11th centuries. These were the ''Olgoviches'' of
According to Jaroslav Pelenski,
This caused the Rurik dynasty to effectively dissolve into several sub-dynasties ruling smaller states in the 10th and 11th centuries. These were the ''Olgoviches'' of Severia
Severia or Siveria ( orv, Сѣверія, russian: Северщина, translit=Severshchina, uk, Сіверія or , translit. ''Siveria'' or ''Sivershchyna'') is a historical region in present-day southwest Russia, northern Ukraine, eastern ...
who ruled in Chernigov, ''Yuryeviches'' who controlled Vladimir-Suzdal
Vladimir-Suzdal (russian: Владимирско-Су́здальская, ''Vladimirsko-Suzdal'skaya''), also Vladimir-Suzdalian Rus', formally known as the Grand Duchy of Vladimir (1157–1331) (russian: Владимиро-Су́здальс ...
, and ''Romanoviches'' in Galicia-Volhynia.Pelenski, Jaroslaw. ''The Contest for the Legacy of Kievan Rus''. New York: Columbia University Press, 1998. p. 4
Descendants of Sviatoslav II of Kiev
The Olgoviches descended from Oleg I of Chernigov, a son of Sviatoslav II of Kiev and grandson of Yaroslav the Wise. They continued to rule until the early 14th century when they were torn apart by the emergingGrand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was Partitions of Poland, partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire, Habsburg Empire of ...
and Grand Duchy of Moscow. The line continued through Oleg's son Vsevolod II of Kiev, grandson Sviatoslav III of Kiev, great-grandson Vsevolod IV of Kiev and great-great-grandson Michael of Chernigov, from whose sons the extant lines of the Olegoviches are descended, including the Massalsky, Gorchakov, Baryatinsky, Volkonsky and Obolensky, including Repnin.
Descendants of Vsevolod I of Kiev
Vsevolod I of Kiev was the father of Vladimir II Monomakh, giving rise to the name Monomakh for his progeny. Two of Vladimir II's sons were Mstislav I of Kiev andYuri Dolgorukiy
Yuri I Vladimirovich ( rus, Юрий Владимирович, Yuriy Vladimirovich), commonly known as Yuri Dolgorukiy or the Long Arm ( rus, Юрий Долгорукий, Yuriy Dolgorukiy, meaning "Far-Reaching", c. 109915 May 1157) was a Ru ...
.
The Romanoviches (Izyaslavichi of Volhynia) were the line of Roman the Great, descended from Mstislav I of Kiev through his son Iziaslav II of Kiev and his grandson Mstislav II of Kiev, father of Roman the Great. The older Monomakhovychi line that ruled the Principality of Volhynia were eventually crowned kings of Galicia and Volhynia and ruled until 1323. The Romanovychi displaced the older line of Izyaslavychi from Turov and Volhynia as well as Rostyslavychi from Galicia. The last were two brothers of Romanovychi, Andrew
Andrew is the English form of a given name common in many countries. In the 1990s, it was among the top ten most popular names given to boys in English-speaking countries. "Andrew" is frequently shortened to "Andy" or "Drew". The word is derive ...
and Lev II, who ruled jointly and were slain trying to repel Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
incursions. The Polish king, Władysław I the Elbow-high, in his letter to the Pope wrote with regret: "The two last Ruthenian kings, that had been firm shields for Poland from the Tatars, left this world and after their death Poland is directly under Tatar threat." Losing their leadership role, the Rurikids, however, continued to play a vital role in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was Partitions of Poland, partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire, Habsburg Empire of ...
and the later Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
. Most notably, the Ostrogski family held the title of Grand Hetman of Lithuania
Grand may refer to:
People with the name
* Grand (surname)
* Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor
* Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist
* Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper
Places
* Grand, Oklahoma
* Grand, Vosges, village and commun ...
and strove to preserve the Ruthenian language and Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonic ...
in this part of Europe. It is thought that the Drutsk and related princely families may also descend from Roman the Great.
The Rostislaviches were the line of Rostislav I of Kiev, another son of Mstislav I of Kiev, who was Prince of Smolensk and a progenitor of the lines descending from the princes of Smolensk and Yaroslavl.
The Shakhovskoy
The House of Shakhovskoy (alt. ''Shahovskoy'', ''Shahovskoi'', uk, Шаховської, russian: Шаховской, french: Chakhovskoï, german: Schachowskoi, it, Šachovskoj) is the name of a princely Russian family descending from the Rur ...
s were founded by Konstantin "Shakh" Glebovich, Prince of Yaroslavl, and traces its lineage to Rostislav I of Kiev through his son Davyd Rostislavich. This branch also descends cognatically of Ivan I of Moscow
Iván I Danilovich Kalitá (Russian: Ива́н I Данилович Калита́; 1 November 1288 – 31 March 1340 or 1341Basil Dmytryshyn, ''Medieval Russia:A source book, 850-1700'', (Academic International Press, 2000), 194.) was Grand D ...
, through the latter's daughter Evdokia Ivanovna Moskovskaya (1314–1342), who married , Prince of Yaroslavl (died 1345). They were the great-grandparents of Andrey and Yuriy, the first Shakhovskoy princes. This is possibly the most senior extant branch of the Rurikids, with many Shakhovskoys living outside of Russia after having fled during the Russian Revolution.
The Yuryeviches were founded by Yuriy Dolgorukiy
Yuri I Vladimirovich ( rus, Юрий Владимирович, Yuriy Vladimirovich), commonly known as Yuri Dolgorukiy or the Long Arm ( rus, Юрий Долгорукий, Yuriy Dolgorukiy, meaning "Far-Reaching", c. 109915 May 1157) was a Rur ...
, the founder of Moscow and spread vastly in the north-east. Yuri's son Vsevolod the Big Nest was Prince of Vladimir-Suzdal
Vladimir-Suzdal (russian: Владимирско-Су́здальская, ''Vladimirsko-Suzdal'skaya''), also Vladimir-Suzdalian Rus', formally known as the Grand Duchy of Vladimir (1157–1331) (russian: Владимиро-Су́здальс ...
, a precursor state to the Grand Principality of Moscow and thus of the Russian Empire. Vsevolod's son Konstantin of Rostov was Prince of Rostov and the progenitor of various Rostov princely lines. Another son, Ivan Vsevolodich, was Prince of Starodub and progenitor of a number of extant lines, most notably the Gagarin line.
Vsevolod's son Yaroslav II of Vladimir was the father of Alexander Nevsky, whose son Daniel of Moscow sired the ruling house of Moscow until the end of the 16th century.
Beginning with the reign of Ivan the Terrible, the Muscovite branch used the title "Tsar of All Russia" and ruled over the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
. The death in 1598 of Tsar Feodor I ended the rule of the Rurik dynasty. The dynasty was briefly revived in the person of Vasili IV of Russia, a descendant of Shuyskiy line of the Rurik dynasty, but he died without issue. The unstable period known as the Time of Troubles followed Feodor's death and lasted until 1613.
In that year, Mikhail I ascended the throne, founding the Romanov dynasty that would rule until 1762 and as Holstein-Gottorp-Romanov until the revolutions of 1917. Tsar Mikhail's father Patriarch Filaret of Moscow was descended from the Rurik dynasty through the female line. His mother, Evdokiya Gorbataya-Shuyskaya, was a Rurikid princess from the Shuysky branch, daughter of Alexander Gorbatyi-Shuisky. Tsar Mikhail's first wife Maria Dolgorukova
Maria Vladimirovna Dolgorukova (''Мария Владимировна Долгорукова'' in Russian) (1601 – 17 January 1625) was a Tsaritsa of Russia as the first spouse of Tsar Michael I of Russia.
Life
Maria Dolgorukova was born to b ...
was of Rurikid stock but their marriage produced no children. Emperor Peter III in 1762 brought fresh Rurikid blood to the Romanovs: he and his wife Catherine the Great
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anha ...
both descended from the Rurik dynasty. (Catherine the Great descended from a daughter of Yaroslav I (978–1054) through her maternal grandfather, Christian August of Holstein-Gottorp.)
Trade
In the early days of the Rurikid dynasty, the Kievan Rus' mainly traded with other tribes inEastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
and Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and S ...
. "There was little need for complex social structures to carry out these exchanges in the forests north of the steppes. So long as the entrepreneurs operated in small numbers and kept to the north, they did not catch the attention of observers or writers." The Rus' also had strong trading ties to Byzantium, particularly in the early 900s, as treaties in 911 and 944 indicate. These treaties deal with the treatment of runaway Byzantine slaves and limitations on the amounts of certain commodities such as silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from th ...
that could be bought from Byzantium. The Rus' used log rafts floated down the Dnieper River
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
by Slavic tribes for the transport of goods, particularly slaves to Byzantium.
Skirmish with Byzantium
One of the largest military accomplishments of the Rurikid dynasty was the attack on Byzantium in 960. Pilgrims of the Rus' had been making the journey from Kiev toConstantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
for many years, and Constantine Porphyrogenitus, the Emperor of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, believed that this gave them significant information about the arduous parts of the journey and where travelers were most at risk, as would be pertinent for an invasion. This route took travelers through domain of the Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: Печенег(и), uk, Печеніг(и), hu, Besenyő(k), gr, Πατζινάκοι, Πετσενέγοι, Πατζινακίται, ka, პა� ...
, journeying mostly by river. In June 941, the Rus' staged a naval ambush on Byzantine forces, making up for their smaller numbers with small, maneuverable boats. These boats were ill-equipped for the transportation of large quantities of treasure, suggesting that looting was not the goal. The raid was led, according to the Primary Chronicle, by a king called Igor. Three years later, the treaty of 944 stated that all ships approaching Byzantium must be preceded by a letter from the Rurikid prince stating the number of ships and assuring their peaceful intent. This not only indicates fear of another surprise attack, but an increased Kievan presence in the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
.
Legacy
Russian andUkrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
historians have debated for many years about the legacy of the Rurikid dynasty. The Russian view sees the Principality of Moscow ruled by the Rurikid dynasty as the sole heir to the Kievan Rus' civilization, this view is "resting largely on religious-ecclesiastical and historical claims" because Russia was ruled by the Rurikid dynasty until 16th century, while Ukraine was not defined as a state until 20th century. This view started in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
as ruled by the original Rurikid dynasty between the 1330s and the late 1850s. The Ukrainian view was formulated much later, between the 1840s and the end of the 1930s in Eastern Austria, and views the Ukrainian descendants of the Rurikid dynasty as its only true successors. The Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
theory was a modified version of the Russian which "allotted equal rights to the Kievan inheritance to the Three Slavic peoples, that is the Russians, the Ukrainians, and the Belorussians
, native_name_lang = be
, pop = 9.5–10 million
, image =
, caption =
, popplace = 7.99 million
, region1 =
, pop1 = 600,000–768,000
, region2 =
, pop2 ...
", but later elevated the Russian nation as the elder brother to give the others "needed guidance in revolutionary struggles and socialist construction."
There are currently various extant branches of the Rurikids, for instance: the Houses of Shakhovskoy
The House of Shakhovskoy (alt. ''Shahovskoy'', ''Shahovskoi'', uk, Шаховської, russian: Шаховской, french: Chakhovskoï, german: Schachowskoi, it, Šachovskoj) is the name of a princely Russian family descending from the Rur ...
, Gagarin, and Lobanov-Rostovsky. Whose some of the representatives are: Prince Dmitriy Mikhailovich Shakhovskoy (born 1934), Prince Dmitri Andreevich Gagarin (born 1973) and Prince Nikita Lobanov-Rostovsky (born 1935), a descendant of Prince Konstantin Vasilyevich of Rostov. The three of them are of the Monomakhovichi
Monomakhovichi or House of Monomakh was a major princely branch of the Rurik dynasty, descendants of which managed to inherit practically all princely titles in the Grand Duchy of Kiev. The progenitor of the house is Vladimir II Monomakh (son of V ...
branch. While the Shakhovskoys claim descent from Mstislav I of Kiev, the Gagarins, and the Lobanov-Rostovskys are descendants of Vsevolod III of Vladimir, which makes the Shakhovskoys the most senior.
Branches
* Izyaslavichi of Polotsk, princes of Polotsk * Izyaslavichi of Turov, princes of Turiv and Volhynia *Monomakhovichi
Monomakhovichi or House of Monomakh was a major princely branch of the Rurik dynasty, descendants of which managed to inherit practically all princely titles in the Grand Duchy of Kiev. The progenitor of the house is Vladimir II Monomakh (son of V ...
, princes of Pereyaslav
** Izyaslavichi of Monomakh, princes of Volhynia, kings of Rus (senior branch)
** Rostislavichi, princes of Smolensk (middle branch)
** Yurievichi, princes of Vladimir-Suzdal, Grand Princes of Moscow (junior branch)
**Shakhovskoy
The House of Shakhovskoy (alt. ''Shahovskoy'', ''Shahovskoi'', uk, Шаховської, russian: Шаховской, french: Chakhovskoï, german: Schachowskoi, it, Šachovskoj) is the name of a princely Russian family descending from the Rur ...
, princes of Yaroslavl (senior extant branch)
** Lobanov-Rostovsky, princes of Rostov (middle extant branch)
** Gagarin, princes of Starodub-on-the-Klyazma (junior extant branch)
** Khilkov, princes of Starodub-on-the-Klyazma (junior extant branch)
* Mosalsky, princes of Mosalsky (Massalsky)
* Olgovichi, princes of Chernihiv
* Rostislavichi of Halych, princes of Halych
* Kropotkin, princes Kropotkin (extant)
* Rzhesvsky, non-titled (extant)
* Putyatin, princes Putyatin (extant)
* Obolensky, princes Obolensky (extant)
**Dolgorukov
The House of Dolgorukov () is a princely Russian family of Rurikid stock. They are a cadet branch of the Obolenskiy family (until 1494 the rulers of Obolensk, one of the Upper Oka Principalities) and as such claiming patrilineal descent from ...
, princes Dolgorukov (extant; cadet branch of the Obolensky family)
* Gorchakov, princes Gorchakov (extant)
*Vadbosky, a branch of the princes Belozersky (extant)
*Volkonsky, a branch of the princes of Tarusa (extant)
*Possibly the Wiśniowiecki family, a branch of the House of Zbaraski 200px, Korybut coat of arms
The House of Zbaraski was a princely family of Ruthenian origin in the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland domiciled in Volhynia (today Ukraine). The name is derived from the town of Zbarazh, the core of their dominions ...
(extinct)
Family tree (from Rurik to Vladimir I)
Wives and children of Vladimir I (1)
Wives and children of Vladimir I (2)
Wives and children of Vladimir I (3)
Yurievich branch
The following shows the descent of the leading (historically most powerful) branch of the Russian Rurikids, being the descendants of Yuri I Dolgorukiy ("Long-Armed"), sixth son of Vladimir II Monomakh: * Vladimir the Great * Yaroslav the Wise, son of Vladimir I the Great * Vsevolod I of Kiev, son of Yaroslav the Wise * Vladimir II Monomakh, son of Vsevolod I of Kiev * Yuri I Dolgorukiy, son of Vladimir II Monomakh The lineage from Yuri I onwards is given in the table belowFamily tree
Gallery
Dolgoruky
The House of Dolgorukov () is a princely Russian family of Rurikid stock. They are a cadet branch of the Obolenskiy family (until 1494 the rulers of Obolensk, one of the Upper Oka Principalities) and as such claiming patrilineal descent fro ...
family
File:RU COA Beloselsky-Belozersky.svg, Coat of arms of the Belosselsky-Belozersky family
The Belosselsky-Belozersky princely and Rurikid family is an aristocratic Russian family that descends in a direct male line from the Earliest Kievan Rus rulers and later of the medieval sovereigns of the Principality of Beloozero.
Origins
The f ...
File:RU COA Kropotkin.svg, Coat of arms of the Kropotkin family
{{Infobox noble house, name=Princes Kropotkin, native_name=Князья Кропоткины, native_name_lang=Ru, coat_of_arms=RU_COA_Kropotkin.svg, coat_of_arms_size=150px, coat_of_arms_caption=Arms of Princes Kropotkin, image=POL_COA_Jełowicki_ ...
File:Coat of Arms of Aladin.jpg, Coat of arms of the families of Monastyrev stock is composed of Smolensk and Belozersk emblems.
File:Coats of arms of the house of Gagarin.svg, Gagarin family
The House of Gagarin (russian: Гага́рин) is the name of a Russian princely family descending from sovereign rulers of Starodub-on-the-Klyazma.
Origins
The descendant of the Great Prince Vladimir Svyatoslavich, the Christianizer of Ru ...
/ Khilkoff
The House of Khilkoff or Khilkov (russian: Хилков) is a Rurikid princely family descending from sovereign rulers of Starodub-on-the-Klyazma. The descendant of the Great Prince Vladimir Svyatoslavich, the Christianizer of Russia, Prince I ...
Coat of arms
File:Golitsyn dukes v1 p2.png, Coat of arms of the Golitsyn family
File:Gorchakov arms.jpg, Coat of arms of the Gorchakov family
File:RU COA Mosalsky XV, 2.jpg, Coat of arms of the Mosalsky family
File:Herb Ostrogski.jpg, Coat of arms of the Ostrogski
The House of Ostrogski ( pl, Ostrogscy, lt, Ostrogiškiai, ua, Острозькі - ''Ostroz'ki'') was one of the more prominent families in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The ...
family
File:Repnin coat.jpg, The Obolensky – Repnin coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its ...
is composed of the emblems of Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
and Chernigov.
File:RU COA Romodanowski.png, Coat of arms of the Romodanowski family
File:RU COA Shujski.png, Coat of arms of the Shuyski family
File:RU_COA_Tatischev_II,_17.png, Coat of arms of the Tatischev family
image:POL COA Korybut.svg, Korybut coat of arms
Korybut is a Polish coat of arms. It was used by the Princely House of Wiśniowiecki-Zbaraski and several branches of the House of Nieświcki in the times of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
Notable bearers
Notable bearers of this coat of arm ...
See also
* Rulers of Kievan Rus' * Shum Gora *Grand Prince of Tver The title of Prince of Tver was borne by the head of the branch of the Rurikid dynasty that ruled the Principality of Tver. In 1247 Tver was allocated to Grand Prince Alexander Nevsky, and became an independent principality. In 1252, the principal ...
*Knyaz
, or ( Old Church Slavonic: Кнѧзь) is a historical Slavic title, used both as a royal and noble title in different times of history and different ancient Slavic lands. It is usually translated into English as prince or duke, dependi ...
*Symbols of the Rurikids
Throughout the early Middle Ages, the Rurikid knyazes of the Kievan Rus' used unique symbols to denote property rights over various items. They are depicted on punches, seals, and coins of the Rurikids. In contrast to Western European heraldry, w ...
References
Further reading
* Bibliography of the history of the Early Slavs and Rus' *Bibliography of Russian history (1223–1613)
This is a select bibliography of post World War II English language books (including translations) and journal articles about the history of Russia and its borderlands from the Mongol invasions until 1613. Book entries may have references to rev ...
*List of Slavic studies journals
This is a list of notable and independent English language peer-reviewed academic journals related to Slavic studies. Journals should be published by major universities, professional associations, national or regional historical societies, or no ...
{{Authority control
Rurik Dynasty
The Rurik dynasty ( be, Ру́рыкавічы, Rúrykavichy; russian: Рю́риковичи, Ryúrikovichi, ; uk, Рю́риковичі, Riúrykovychi, ; literally "sons/scions of Rurik"), also known as the Rurikid dynasty or Rurikids, was ...
1598 disestablishments
States and territories established in the 860s
862 establishments
Russian monarchy
Ukrainian monarchy