Rover (space exploration) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A rover (or sometimes planetary rover) is a
A rover (or sometimes planetary rover) is a


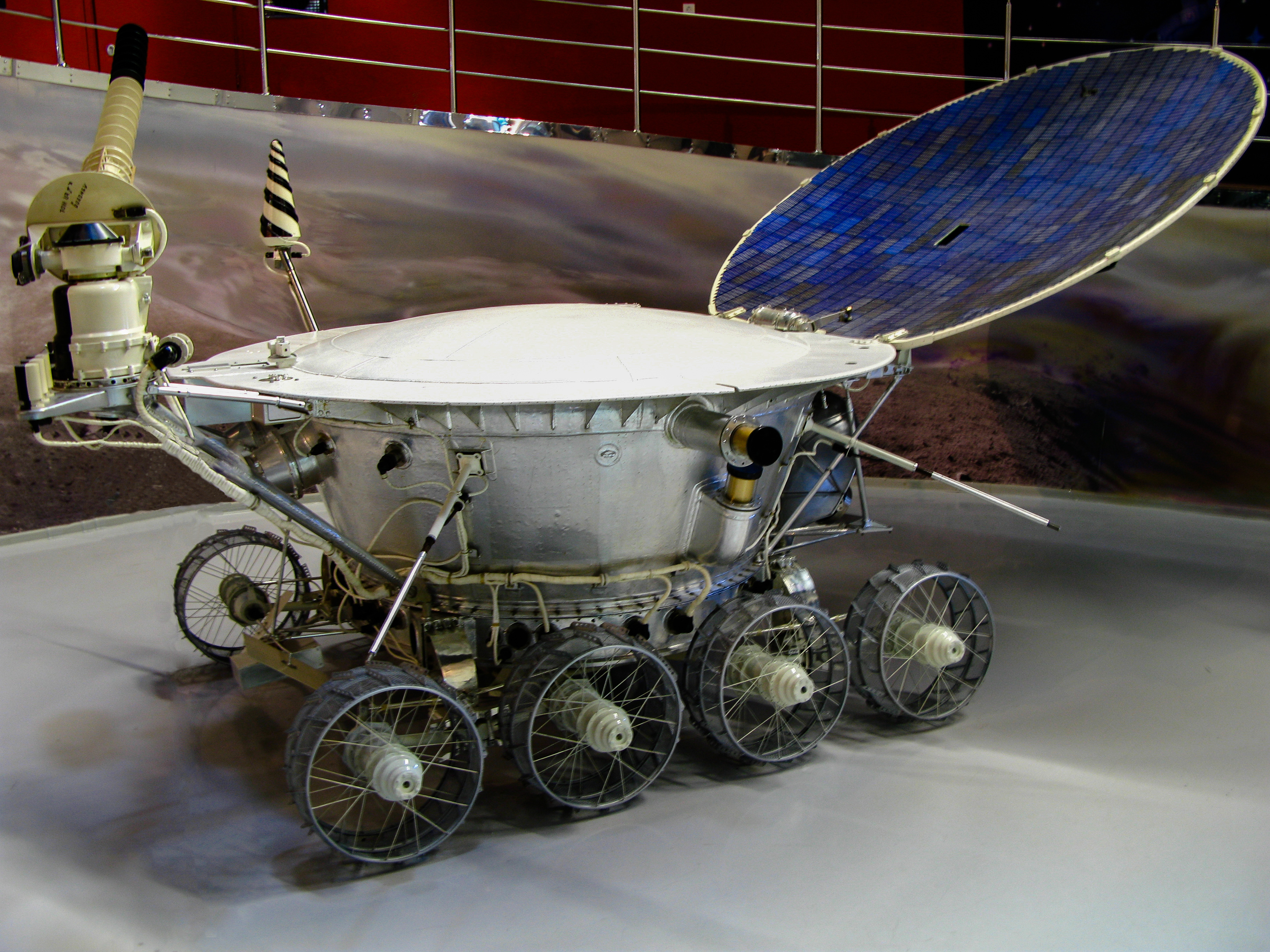 The Lunokhod 1 rover landed on the Moon in November 1970. It was the first roving remote-controlled robot to land on any celestial body. The
The Lunokhod 1 rover landed on the Moon in November 1970. It was the first roving remote-controlled robot to land on any celestial body. The

 The Lunokhod 2 was the second of two unmanned lunar rovers landed on the
The Lunokhod 2 was the second of two unmanned lunar rovers landed on the
 The
The
 ''Spirit'' is a robotic rover on Mars, active from 2004 to 2010. It was one of two rovers of
''Spirit'' is a robotic rover on Mars, active from 2004 to 2010. It was one of two rovers of
 On 26 November 2011, NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission was successfully launched for Mars. The mission successfully landed the robotic ''Curiosity'' rover on the surface of Mars in August 2012. The rover is currently helping to determine whether Mars could ever have supported life, and search for evidence of past or present life on Mars.
On 26 November 2011, NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission was successfully launched for Mars. The mission successfully landed the robotic ''Curiosity'' rover on the surface of Mars in August 2012. The rover is currently helping to determine whether Mars could ever have supported life, and search for evidence of past or present life on Mars.
 The ''Perseverance'' rover of the
The ''Perseverance'' rover of the

 A rover (or sometimes planetary rover) is a
A rover (or sometimes planetary rover) is a planetary surface
A planetary surface is where the solid or liquid material of certain types of astronomical objects contacts the atmosphere or outer space. Planetary surfaces are found on solid objects of planetary mass, including terrestrial planets (includi ...
exploration
Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians.
Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most ...
device designed to move across the solid surface on a planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
or other planetary mass celestial bodies
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often us ...
. Some rovers have been designed as land vehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles (motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles (trains, trams), wat ...
s to transport members of a human spaceflight
Human spaceflight (also referred to as manned spaceflight or crewed spaceflight) is spaceflight with a crew or passengers aboard a spacecraft, often with the spacecraft being operated directly by the onboard human crew. Spacecraft can also be ...
crew; others have been partially or fully autonomous robot
An autonomous robot is a robot that acts without recourse to human control. The first autonomous robots environment were known as Elmer and Elsie, which were constructed in the late 1940s by W. Grey Walter. They were the first robots in history ...
s. Rovers are typically created to land on another planet (other than Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
) via a lander
Lander may refer to:
Media and entertainment
* ''Lander'' (computer game), computer game published by Psygnosis in 1999
* ''Lander'' (game demo), the 3D game demo provided with the Acorn Archimedes computer
* Lander (Transformers), a fiction ...
-style spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, ...
, tasked to collect information about the terrain, and to take crust samples such as dust, soil, rocks, and even liquids. They are essential tools in space exploration
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the exploration of space is carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration though is conducted both by uncrewed robo ...
.
Features
Rovers arrive on spacecraft and are used in conditions very distinct from those on the Earth, which makes some demands on their design.Reliability
Rovers have to withstand high levels of acceleration, high and low temperatures,pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country a ...
, dust, corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engi ...
, cosmic rays
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our ...
, remaining functional without repair for a needed period of time.

Autonomy
Rovers which land on celestial bodies far from the Earth, such as the Mars Exploration Rovers, cannot be remotely controlled in real-time since the speed at which radio signals travel is far too slow for ''real-time'' or ''near-real-time'' communication. For example, sending a signal from Mars to Earth takes between 3 and 21 minutes. These rovers are thus capable of operating autonomously with little assistance from ground control as far asnavigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation ...
and data acquisition Data acquisition is the process of sampling signals that measure real-world physical conditions and converting the resulting samples into digital numeric values that can be manipulated by a computer. Data acquisition systems, abbreviated by the acro ...
are concerned, although they still require human input for identifying promising targets in the distance to which to drive, and determining how to position itself to maximize solar energy. Giving a rover some rudimentary visual identification capabilities to make simple distinctions can allow engineers to speed up the reconnaissance. During the NASA Sample Return Robot Centennial Challenge, a rover, named ''Cataglyphis'', successfully demonstrated autonomous navigation, decision-making, and sample detection, retrieval, and return capabilities.
Non-wheeled approaches
Other rover designs that do not use wheeled approaches are possible. Mechanisms that utilize "walking" on robotic legs, hopping, rolling, etc. are possible. For example,Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is conside ...
researchers have proposed "Hedgehog", a small cube
In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.
The cube is the only ...
-shaped rover that can controllably hop—or even spin out of a sandy sinkhole by corkscrewing upward to escape—for surface exploration of low gravity celestial bodies.
History

Lunokhod 0 (No.201)
The Soviet rover was intended to be the first roving remote-controlledrobot
A robot is a machine—especially one programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the control may be embedded within. Robots may be ...
on the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, but crashed during a failed start of the launcher 19 February 1969.
Lunokhod 1
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
launched Lunokhod 1 aboard the Luna 17 spacecraft on November 10, 1970, and it entered lunar orbit on November 15. The spacecraft soft-landed in the Sea of Rains region on November 17. The lander had dual ramps from which Lunokhod 1 could descend to the lunar surface, which it did at 06:28 UT. From November 17, 1970, to November 22, 1970, the rover drove 197 m, and during 10 communication sessions returned 14 close up pictures of the Moon and 12 panoramic views. It also analyzed the lunar soil. The last successful communications session with Lunokhod 1 was on September 14, 1971. Having worked for 11 months,
Lunokhod 1 held the durability record for space rovers for more than 30 years, until a new record was set by the Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, '' Spirit'' and '' Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rovers to explore the Martian surface ...
s.
Apollo Lunar Roving Vehicle

NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
included Lunar Roving Vehicle
The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is a battery-powered four-wheeled rover used on the Moon in the last three missions of the American Apollo program ( 15, 16, and 17) during 1971 and 1972. It is popularly called the Moon buggy, a play on the ...
s in three Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
missions: Apollo 15
Apollo 15 (July 26August 7, 1971) was the ninth crewed mission in the United States' Apollo program and the fourth to land on the Moon. It was the first J mission, with a longer stay on the Moon and a greater focus on science than ear ...
(which landed on the Moon July 30, 1971), Apollo 16
Apollo 16 (April 1627, 1972) was the tenth human spaceflight, crewed mission in the United States Apollo program, Apollo space program, administered by NASA, and the fifth and penultimate to Moon landing, land on the Moon. It was the second o ...
(which landed April 21, 1972), and Apollo 17
Apollo 17 (December 7–19, 1972) was the final mission of NASA's Apollo program, the most recent time humans have set foot on the Moon or traveled beyond low Earth orbit. Commander Gene Cernan and Lunar Module Pilot Harrison Schmitt walke ...
(which landed December 11, 1972).
Lunokhod 2
 The Lunokhod 2 was the second of two unmanned lunar rovers landed on the
The Lunokhod 2 was the second of two unmanned lunar rovers landed on the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
as part of the Lunokhod program. The rover became operational on the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
on January 16, 1973.
It was the second roving remote-controlled robot
A robot is a machine—especially one programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the control may be embedded within. Robots may be ...
to land on any celestial body. The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
launched Lunokhod 2 aboard the Luna 21 spacecraft on January 8, 1973, and the spacecraft soft-landed in the eastern edge of the Mare Serenitatis region on January 15, 1973. Lunokhod 2 descended from the lander's dual ramps to the lunar surface at 01:14 UT on January 16, 1973. Lunokhod 2 operated for about four months, covered of terrain, including hilly upland areas and rilles, and sent back 86 panoramic images and over 80,000 TV pictures. Based on wheel rotations Lunokhod 2 was thought to have covered but Russian scientists at the Moscow State University of Geodesy and Cartography (MIIGAiK) have revised that to an estimated distance of about based on Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter ( LRO) images of the lunar surface. Subsequent discussions with their American counterparts ended with an agreed-upon final distance of , which has stuck since.
PrOP-M
The Soviet Mars 2 and Mars 3 landers each had a small 4.5 kg Mars rover on board, which would have moved across the surface on skis while connected to the lander with a 15-meter umbilical. Two small metal rods were used for autonomous obstacle avoidance, as radio signals from Earth would have taken too long to drive the rovers using remote control. The rover was planned to be placed on the surface after landing by a manipulator arm and to move in the field of view of the television cameras and stop to make measurements every 1.5 meters. The rover tracks in the Martian soil would also have been recorded to determine material properties. Because of the crash landing of Mars 2 and the communication failure (15 seconds post landing) of Mars 3, neither rover was deployed.Lunokhod 3
The Soviet rover was intended to be the third roving remote-controlled robot on the Moon in 1977. The mission was canceled due to lack of launcher availability and funding, although the rover was built.Marsokhod
The Marsokhod was a Soviet rover (hybrid, with both controls telecommand and automatic) aimed at Mars, part of theMars 4NM
The Mars program was a series of uncrewed spacecraft launched by the Soviet Union between 1960 and 1973. The spacecraft were intended to explore Mars, and included flyby probes, landers and orbiters.
Early Mars spacecraft were small, and launc ...
and scheduled to commence after 1973 (according to the plans of 1970). It was to be launched by a N1 rocket, which never flew successfully.
''Sojourner''
 The
The Mars Pathfinder
''Mars Pathfinder'' (''MESUR Pathfinder'') is an American robotic spacecraft that landed a base station with a roving probe on Mars in 1997. It consisted of a lander, renamed the Carl Sagan Memorial Station, and a lightweight, wheeled robot ...
mission included ''Sojourner'', the first rover to successfully deploy on another planet. NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
, the space agency of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, launched Mars Pathfinder on 4 December 1996; it landed on Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
in a region called Chryse Planitia on 4 July 1997. From its landing until the final data transmission on 27 September 1997, Mars Pathfinder returned 16,500 images from the lander and 550 images from ''Sojourner'', as well as data from more than 15 chemical analyses of rocks and soil and extensive data on winds and other weather factors.
Beagle 2 Planetary Undersurface Tool
Beagle 2
The ''Beagle 2'' is an inoperative British Mars lander that was transported by the European Space Agency's 2003 ''Mars Express'' mission. It was intended to conduct an astrobiology mission that would have looked for evidence of past life on Mar ...
was designed to explore Mars with a small "mole" (Planetary Undersurface Tool, or PLUTO), to be deployed by the arm. PLUTO had a compressed spring mechanism designed to enable it to move across the surface at a rate of 20 mm per second and to burrow into the ground, collecting a subsurface sample in a cavity in its tip. Beagle 2 failed while attempting to land on Mars in 2003.
Mars Exploration Rover ''Spirit''
 ''Spirit'' is a robotic rover on Mars, active from 2004 to 2010. It was one of two rovers of
''Spirit'' is a robotic rover on Mars, active from 2004 to 2010. It was one of two rovers of NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
's ongoing Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, '' Spirit'' and '' Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rovers to explore the Martian surface ...
mission. It landed successfully on Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
at 04:35 Ground UTC on January 4, 2004, three weeks before its twin, '' Opportunity'' (MER-B), landed on the other side of the planet. Its name was chosen through a NASA-sponsored student essay competition. The rover became stuck in late 2009, and its last communication with Earth was sent on March 22, 2010.
Chang'e 3's Yutu Rover
Chang'e 3
Chang'e 3 (; ) is a robotic lunar exploration mission operated by the China National Space Administration (CNSA), incorporating a robotic lander and China's first lunar rover. It was launched in December 2013 as part of the second phase of t ...
is a Chinese Moon mission that includes a robotic lunar rover ''Yutu'', named after the pet rabbit of Chang'e
Chang'e ( ; , alternatively rendered as Chang-Er or Ch‘ang-o), originally known as Heng'e, is the Chinese goddess of the Moon. She is the subject of several legends in Chinese mythology, most of which incorporate several of the following elem ...
, the goddess of the Moon in Chinese mythology. Launched in 2013 with the Chang'e 3
Chang'e 3 (; ) is a robotic lunar exploration mission operated by the China National Space Administration (CNSA), incorporating a robotic lander and China's first lunar rover. It was launched in December 2013 as part of the second phase of t ...
mission, it is China's first lunar rover, the first soft landing on the Moon since 1976 and the first rover to operate there since the Soviet Lunokhod 2 ceased operations on 11 May 1973. It was deployed on the Moon on December 14, 2013, and the rover encountered operational difficulties toward the end of the second lunar day after surviving and recovering successfully the first 14-day lunar night (about a month on the Moon), and was unable to move after the end of the second lunar night, though it continued to gather useful information for some months afterward. In October 2015, ''Yutu'' set the record for the longest operational period for a rover on the Moon. On 31 July 2016, ''Yutu'' ceased to operate after a total of 31 months, well beyond its original expected lifespan of three months.
Mars Exploration Rover ''Opportunity''
''Opportunity'' is a robotic rover on the planet Mars, active from 2004 to early 2019. Launched fromEarth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
on July 7, 2003, it landed on the Martian Meridiani Planum on January 25, 2004, at 05:05 Ground UTC (about 13:15 local time), three weeks after its twin '' Spirit'' (MER-A) touched down on the other side of the planet. On July 28, 2014, NASA announced that ''Opportunity'', after having traveled over on the planet Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
, has set a new "off-world" record as the rover having driven the greatest distance, surpassing the previous record held by the Soviet Union's Lunokhod 2 rover that had traveled . ( related image)
Active rover missions
Active Mars rover locations in context
Mars Science Laboratory Rover ''Curiosity''
 On 26 November 2011, NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission was successfully launched for Mars. The mission successfully landed the robotic ''Curiosity'' rover on the surface of Mars in August 2012. The rover is currently helping to determine whether Mars could ever have supported life, and search for evidence of past or present life on Mars.
On 26 November 2011, NASA's Mars Science Laboratory mission was successfully launched for Mars. The mission successfully landed the robotic ''Curiosity'' rover on the surface of Mars in August 2012. The rover is currently helping to determine whether Mars could ever have supported life, and search for evidence of past or present life on Mars.
''Yutu-2'' (Chang'e 4 rover)
Chinese mission launched 7 December 2018, landed and deployed rover 3 January 2019 on the far side of the Moon. It was the first ever rover that operates on the far side of the Moon. In December 2019, ''Yutu 2'' broke the lunar longevity record, previously held by the Soviet Union's '' Lunokhod 1'' rover, which operated on the lunar surface for eleven lunar days (321 Earth days) and traversed a total distance of . In February 2020, Chinese astronomers reported, for the first time, a high-resolution image of a lunar ejecta sequence, and, as well, direct analysis of its internal architecture. These were based on observations made by the Lunar Penetrating Radar (LPR) on board the ''Yutu-2'' rover while studying the far side of the Moon.Mars 2020 ''Perseverance'' rover
 The ''Perseverance'' rover of the
The ''Perseverance'' rover of the Mars 2020
Mars 2020 is a Mars rover mission forming part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program that includes the rover '' Perseverance'', the small robotic, coaxial helicopter '' Ingenuity'', and associated delivery vehicles. Mars 2020 was launched from ...
mission is a Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
rover developed by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
which was launched in 2020 and landed on Mars on February 18, 2021. It is intended to investigate an astrobiologically relevant ancient environment on Mars, investigate its surface geological processes and history, including the assessment of its past habitability and potential for preservation of biosignature
A biosignature (sometimes called chemical fossil or molecular fossil) is any substance – such as an element, isotope, or molecule – or phenomenon that provides scientific evidence of past or present life. Measurable attribute ...
s within accessible geological materials.
Tianwen-1 ''Zhurong''
Tianwen-1, a CNSA project, launched on July 23, 2020, and successfully reached Mars orbit on February 10, 2021. The Zhurong rover landed on Mars on May 14, 2021, and was deployed from lander on 22 May 2021. It will conduct scientific missions.Planned rover missions
Chandrayaan 3
Chandrayaan-3 is a proposed mission by India, consisting of a lunar lander and a rover. It would be a re-attempt to demonstrate soft landing, following the failure of Chandrayaan-2's ''Vikram'' lander.ExoMars ''Rosalind Franklin''
The European Space Agency (ESA) has designed and carried out early prototyping and testing of the ''Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Elsie Franklin (25 July 192016 April 1958) was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose work was central to the understanding of the molecular structures of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), RNA (ribonucleic acid), viruses, ...
'' rover. , the rover is scheduled for launch in late 2022.
See also
* List of rovers on extraterrestrial bodies * Google Lunar X Prize * Lander (spacecraft) * LORAX * Lunar rover * Mars rover ( Crewed) * '' Tank on the Moon'', 2007 documentary filmReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rover (Space Exploration) Off-road vehicles Spacecraft Soviet inventions Russian inventions Space robots