Romanization (cultural) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Romanization or Latinization (Romanisation or Latinisation), in the historical and cultural meanings of both terms, indicate different historical processes, such as

 Roman names were adopted by some, and the Latin language was spread, which was greatly facilitated by the fact that many cultures were mostly oral (particularly for the
Roman names were adopted by some, and the Latin language was spread, which was greatly facilitated by the fact that many cultures were mostly oral (particularly for the
online
'' Interpretatio'' and the Romanization of Celtic deities. *Mommsen, Theodore. ''The Provinces of the Roman Empire'' Barnes & Noble (re-edition). New York, 2004 *Susanne Pilhofer: "Romanisierung in Kilikien? Das Zeugnis der Inschriften" (''Quellen und Forschungen zur Antiken Welt'' 46), Munich 2006.
acculturation
Acculturation is a process of social, psychological, and cultural change that stems from the balancing of two cultures while adapting to the prevailing culture of the society. Acculturation is a process in which an individual adopts, acquires and ...
, integration and assimilation
Assimilation may refer to:
Culture
* Cultural assimilation, the process whereby a minority group gradually adapts to the customs and attitudes of the prevailing culture and customs
** Language shift, also known as language assimilation, the prog ...
of newly incorporated and peripheral populations by the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
and the later Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
Empire. The term was used in Ancient Roman historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians h ...
and Italian historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians h ...
until the fascist
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and the ...
period, when the various processes were called the " civilizing of barbarians
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by some to be les ...
".
Characteristics

Acculturation
Acculturation is a process of social, psychological, and cultural change that stems from the balancing of two cultures while adapting to the prevailing culture of the society. Acculturation is a process in which an individual adopts, acquires and ...
proceeded from the top down, with the upper classes adopting Roman culture first and the old ways lingering for the longest among peasants in outlying countryside and rural areas. Hostages played an important part in this process, as elite children, from Mauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It stretched from central present-day Algeria westwards to the Atlantic, covering northern present-day Morocco, and southward to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants ...
to Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
, were taken to be raised and educated in Rome.
Ancient Roman historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians h ...
and traditional Italian historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians h ...
confidently identified the different processes involved with a "civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
...
of barbarians
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by some to be les ...
". Modern historians take a more nuanced view: by making their peace with Rome, local elites could make their position more secure and reinforce their prestige. New themes include the study of personal and group values and the construction of identity, which is the personal aspect of ethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introd ...
. The transitions operated differently in different provinces; as Blagg and Millett point out even a Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
may be too broad a canvas to generalize.
One characteristic of cultural Romanization was the creation of many hundreds of Roman coloniae in the territory of the Roman Republic and the subsequent Roman Empire. Until Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
, colonies were created by using retired veteran soldiers, mainly from the Italian peninsula, who promoted Roman customs and laws, with the use of Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
.
It has been estimated that at the beginning of the empire, about 750,000 Italians lived in the provinces. Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
, Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the au ...
and Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
settled many of their veterans in colonies: in Italy, and the provinces. The colonies that were established in Italy until 14 BCE have been studied by Keppie (1983). In his account of the achievements of his long reign, '' Res Gestae Divi Augusti'', Augustus stated that he had settled 120,000 soldiers in twenty colonies in Italy in 31 BCE, then 100,000 men in colonies in Spain and southern Gaul in 14 BCE, followed by another 96,000 in 2 BCE. Brian Campbell also states "From 49 to 32 BCE about 420,000 Italians were recruited", which would thus be the veteran (citizen) stock that was largely sent to the provinces (colonies) during Augustus. The Lex Calpurnia, however, also allowed citizenship to be granted for distinguished bravery. For example, the 1,000 socii from Camerinum after Vercellae 101 BCE (Plutarch Mar. XXXVIII) and the auxiliary (later Legio XXII Deiotariana) after Zela, got Roman citizenship. By the time of Augustus, the legions consisted mostly of ethnic Latins/Italics and Cisalpine Gauls.
However, Romanization did not always result in the extinction of all aspects of native cultures even when there was extensive acculturation. Many non-Latin provincial languages survived the entire period while sustaining considerable Latin influence, including the ancestor languages of Welsh, Albanian, Basque and Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–19 ...
. Where there was language replacement, in some cases, such as Italy, it took place in the early imperial stage, while in others, native languages only totally succumbed to Latin ''after'' the fall of the Empire, as was likely the case with Gaulish. The Gaulish language
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Switze ...
is thought to have survived into the 6th century in France, despite considerable Romanization of the local material culture. The last record of spoken Gaulish deemed to be plausibly credible was when Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (30 November 538 – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of the area that had been previously referred to as Gaul by the Romans. He was born Georgius Floren ...
wrote in the 6th century (c. 560-575) that a shrine in Auvergne
Auvergne (; ; oc, label= Occitan, Auvèrnhe or ) is a former administrative region in central France, comprising the four departments of Allier, Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal and Haute-Loire. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Au ...
which "is called Vasso Galatae in the Gallic tongue" was destroyed and burnt to the ground. Coexisting with Latin, Gaulish helped shape the Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal registers of Latin spoken from the Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve into numerous Romance languages. Its literary counterpa ...
dialects that developed into French, with effects including loanwords and calque
In linguistics, a calque () or loan translation is a word or phrase borrowed from another language by literal word-for-word or root-for-root translation. When used as a verb, "to calque" means to borrow a word or phrase from another language ...
s (including ''oui'', the word for "yes"), sound changes, and influences in conjugation and word order.
Process
The very existence of Romanization is a source of contention among modernarchaeologists
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes ...
. One of the first approaches, which now can be regarded as the "traditional" approach, was taken by Francis Haverfield. He saw this process beginning in primarily post-conquest societies (such as Britain and Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
), where direct Roman policy from the top promoted an increase in the Roman population of the province through the establishment of veteran
A veteran () is a person who has significant experience (and is usually adept and esteemed) and expertise in a particular occupation or field. A military veteran is a person who is no longer serving in a military.
A military veteran that h ...
colonies. The ''coloniae'' would have spoken Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
and been citizens of Rome following their army tenure (See Roman citizenship). Haverfield thus assumes this would have a Romanizing effect upon the native communities.
This thought process, fueled though it was by early 20th century standards of imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic powe ...
and cultural change, forms the basis for the modern understanding of Romanization. However, recent scholarship has devoted itself to providing alternate models of how native populations adopted Roman culture and has questioned the extent to which it was accepted or resisted.
#Non-interventionist model – Native elites were encouraged to increase social standing through association with the powerful conqueror, be it in dress, language, housing or food consumption. This would have provided them with associated power. The establishment of a civil administration system is quickly imposed to solidify the permanence of Roman rule.
#Discrepant identity – No uniformity of identity that can accurately be described as traditional Romanization. Fundamental differences within a province are visible through economics, religion and identity. Not all provincials supported Rome and not all elites wanted to be like the Roman upper classes.
#Acculturation – Aspects of both native and Roman cultures are joined together, as can be seen in the Roman acceptance, and adoption of, non- Classical religious practices. The inclusion of Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kin ...
, Epona, Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Grea ...
and Dolichenus into the pantheon
Pantheon may refer to:
* Pantheon (religion), a set of gods belonging to a particular religion or tradition, and a temple or sacred building
Arts and entertainment Comics
*Pantheon (Marvel Comics), a fictional organization
* ''Pantheon'' (Lone St ...
are evidence.
#Creolization – Romanization occurs as a result of negotiation between different elements of non- egalitarian societies and so material culture is ambiguous.
Legacy
 Roman names were adopted by some, and the Latin language was spread, which was greatly facilitated by the fact that many cultures were mostly oral (particularly for the
Roman names were adopted by some, and the Latin language was spread, which was greatly facilitated by the fact that many cultures were mostly oral (particularly for the Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
s and Iberians
The Iberians ( la, Hibērī, from el, Ἴβηρες, ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (amon ...
). Anyone who wanted to deal (through writing) with the bureaucracy and/or with the Roman market had to write in Latin. The extent of the adoption is subject to ongoing debate, as the native languages were certainly spoken after the conquests. Moreover, in the eastern half of the Empire, Latin had to compete with Greek, which largely kept its position as lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
and even spread to new areas. Latin became prominent in certain areas around new veteran colonies like Berytus
) or Laodicea in Canaan (2nd century to 64 BCE)
, image = St. George's Cathedral, Beirut.jpg
, image_size =
, alt =
, caption = Roman ruins of Berytus, in front of Saint George Greek Orthodox Cathedral in moder ...
.
The ancient tribal laws were replaced by Roman law
Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the '' Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor J ...
, with its institutions of property rights.
Typically-Roman institutions, such as public baths, the imperial cult and gladiator
A gladiator ( la, gladiator, "swordsman", from , "sword") was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gla ...
fights, were adopted.
Gradually, the conquered would see themselves as Romans. The process was supported by the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
and then by the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
.
The entire process was facilitated by the Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
origin of most of the languages and by the similarity of the gods of many ancient cultures. They also already had had trade relations and contacts with one another through the seafaring Mediterranean cultures like the Phoenicians
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their his ...
and the Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
.
Romanization was largely effective in the western half of the empire, where native civilizations were weaker. In the Hellenized east, ancient civilizations like those of Ancient Egypt, Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
, The Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
, Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous so ...
and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, effectively resisted all but its most superficial effects. When the Empire was divided, the east, with mainly Greek culture, was marked by the increasing strength of specifically Greek culture and language to the detriment of the Latin language and other Romanizing influences, but its citizens continued to regard themselves as Romans.
While Britain certainly was Romanized, its approximation to the Roman culture seems to have been smaller than that of Gaul. The most romanized regions, as demonstrated by Dott. Bernward Tewes and Barbara Woitas of the computing center of the Catholic University Eichstätt-Ingolstadt, were Italy, the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
, Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
, southern Germany and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, str ...
.
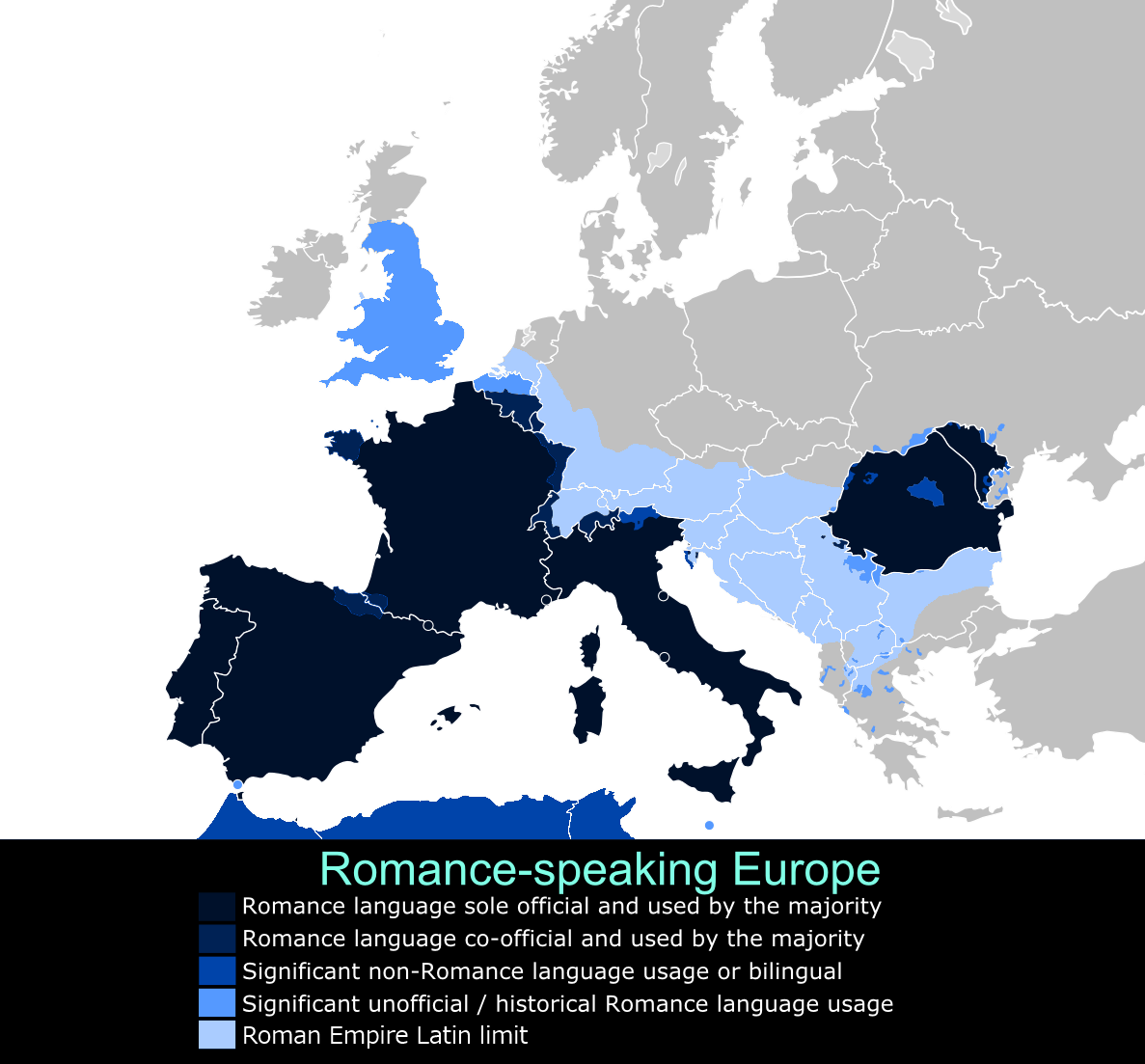
Romanization in most of those regions remains such a powerful cultural influence in most aspects of life today that they are described as "Latin countries" and "Latin American countries". That is most evident in European countries in which Romance languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language ...
are spoken and former colonies that have inherited the languages and other Roman influences. According to Theodor Mommsen
Christian Matthias Theodor Mommsen (; 30 November 1817 – 1 November 1903) was a German classical scholar, historian, jurist, journalist, politician and archaeologist. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest classicists of the 19th centur ...
, cultural Romanization was more complete in those areas that developed a "neolatin language" (like Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese, and Romanian). The same process later developed in the recent centuries' colonial empires.
Example
* Britain *Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
* Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
* Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hi ...
* Illyria
In classical antiquity, Illyria (; grc, Ἰλλυρία, ''Illyría'' or , ''Illyrís''; la, Illyria, ''Illyricum'') was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by numerous tribes of people collectively known as the Illyr ...
* Thrace and Moesia
Heritage
* Latinization of names * List of cities founded by the Romans *Spread of the Latin script
This article discusses the geographic spread of the Latin script throughout history, from its archaic beginnings in Latium to the dominant writing system on Earth in modernity.
The Latin letters' ancestors are found in the Phoenician, Greek a ...
* Historiography of Romanization
See also
*Romanitas
''Romanitas'' is the collection of political and cultural concepts and practices by which the Romans defined themselves. It is a Latin word, first coined in the third century AD, meaning "Roman-ness" and has been used by modern historians as sho ...
* Roman citizenship
* Latin Rights
Notes
References
* *Francisco Marco Simón, "Religion and Religious Practices of the Ancient Celts of the Iberian Peninsula" in ''e-Keltoi: The Celts in the Iberian Peninsula'', 6 287–345online
'' Interpretatio'' and the Romanization of Celtic deities. *Mommsen, Theodore. ''The Provinces of the Roman Empire'' Barnes & Noble (re-edition). New York, 2004 *Susanne Pilhofer: "Romanisierung in Kilikien? Das Zeugnis der Inschriften" (''Quellen und Forschungen zur Antiken Welt'' 46), Munich 2006.
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Romanization Society of ancient Rome Ancient Roman culture