Roman Gradual on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The ''Roman Gradual'' (Latin: ''Graduale Romanum'') is an official liturgical book of the Roman Rite of the
The ''Roman Gradual'' (Latin: ''Graduale Romanum'') is an official liturgical book of the Roman Rite of the
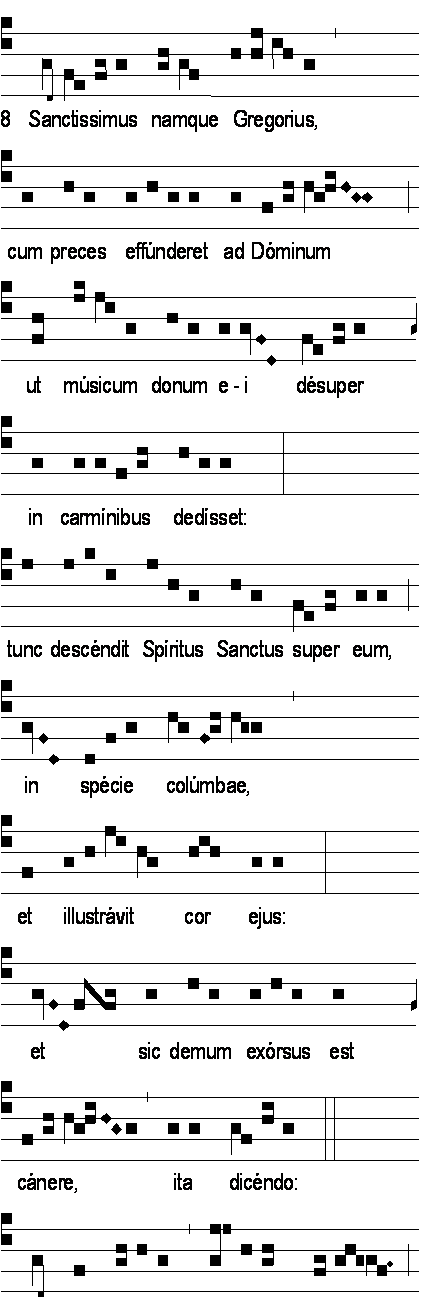 The Roman Gradual includes the
*
The Roman Gradual includes the
*
Jeffrey Tucker: The Real Catholic Songbook
* Bergeron, Katherine. Decadent enchantments: the revival of Gregorian chant at Solesmes. Berkeley : University of California Press, c1998. .
 The ''Roman Gradual'' (Latin: ''Graduale Romanum'') is an official liturgical book of the Roman Rite of the
The ''Roman Gradual'' (Latin: ''Graduale Romanum'') is an official liturgical book of the Roman Rite of the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
containing chants, including the proper
Proper may refer to:
Mathematics
* Proper map, in topology, a property of continuous function between topological spaces, if inverse images of compact subsets are compact
* Proper morphism, in algebraic geometry, an analogue of a proper map for ...
and many more, for use in Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
.
The latest edition of 1974 takes account of the 1970 revision of the ''Roman Missal
The Roman Missal ( la, Missale Romanum) is the title of several missals used in the celebration of the Roman Rite. Along with other liturgical books of the Roman Rite, the Roman Missal contains the texts and rubrics for the celebration of th ...
''.
In 1979, the ''Graduale Triplex: The Roman Gradual With the Addition of Neums from Ancient Manuscripts'' ( in English (1985), in Latin) was published. It added reproductions of the neume
A neume (; sometimes spelled neum) is the basic element of Western and Eastern systems of musical notation prior to the invention of five-line staff notation.
The earliest neumes were inflective marks that indicated the general shape but not nec ...
s from ancient manuscripts placed above and below the later notation.
Description
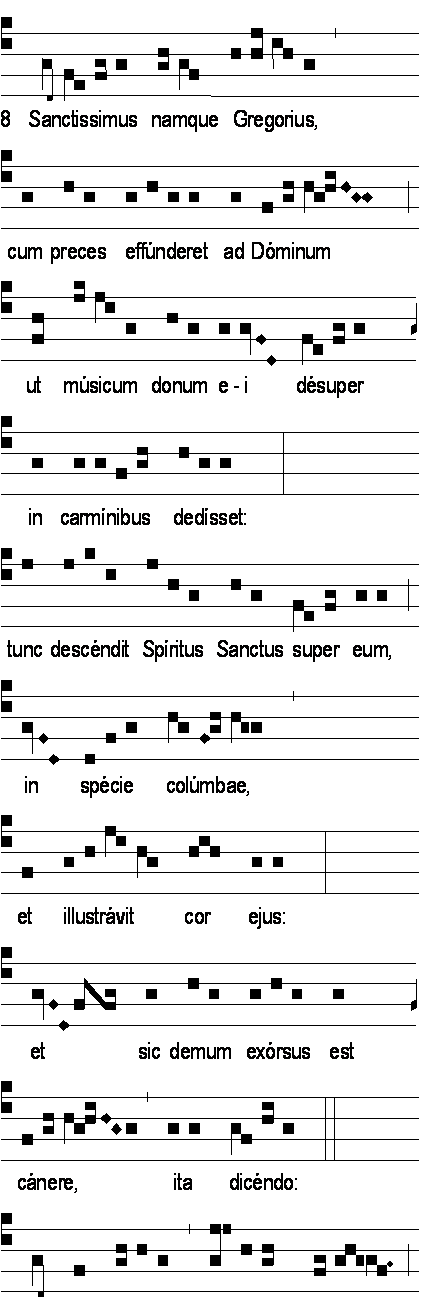 The Roman Gradual includes the
*
The Roman Gradual includes the
* Introit
The Introit (from Latin: ''introitus'', "entrance") is part of the opening of the liturgy, liturgical celebration of the Eucharist for many Christian denominations. In its most complete version, it consists of an antiphon, Psalms, psalm verse and ' ...
(entrance chant: antiphon with verses),
* the Gradual
The gradual ( la, graduale or ) is a chant or hymn in the Mass, the liturgical celebration of the Eucharist in the Catholic Church, and among some other Christians. It gets its name from the Latin (meaning "step") because it was once chanted ...
psalm (a meditative psalm chant, this may be replaced with a simpler responsorial psalm
Responsorial psalmody primarily refers to the placement and use of the Psalm within the readings at a Christian service of the Eucharist. The Psalm chosen in such a context is often called the responsorial psalm. Although often associated with ...
except when the Mass is celebrated "in Cantu" according to the rubrics of the accompanying document Ordo Cantus Missae), or an additional Alleluia
Alleluia (derived from the Hebrew ''Hallelujah'', meaning "Praise Yahweh") is a Latin phrase in Christianity used to give praise to God. In Christian worship, Alleluia is used as a liturgical chant in which that word is combined with verses of ...
verse during Eastertide
Eastertide (also known as Eastertime or the Easter season) or Paschaltide (also known as Paschaltime or the Paschal season) is a festal season in the liturgical year of Christianity that focuses on celebrating the Resurrection of Jesus Christ. ...
,
* the Sequence Hymn (obligatory on Easter
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the '' Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samuel ...
and Pentecost, optional on Corpus Christi and Our Lady of Sorrows
Our Lady of Sorrows ( la, Beata Maria Virgo Perdolens), Our Lady of Dolours, the Sorrowful Mother or Mother of Sorrows ( la, Mater Dolorosa, link=no), and Our Lady of Piety, Our Lady of the Seven Sorrows or Our Lady of the Seven Dolours are names ...
),
* the Alleluia
Alleluia (derived from the Hebrew ''Hallelujah'', meaning "Praise Yahweh") is a Latin phrase in Christianity used to give praise to God. In Christian worship, Alleluia is used as a liturgical chant in which that word is combined with verses of ...
chant, or the tract during Lent,
* the offertory chant,
* and the Communion antiphon.
It includes a selection of chants that are normally published in a companion volume known as the Kyriale
The Kyriale is a collection of Gregorian chant settings for the Ordinary of the Mass. It contains eighteen Masses (each consisting of the Kyrie, Gloria xcluded from Masses intended for weekdays/ferias and Sundays in Advent and Lent Sanctus, and ...
, a collection of chants for the Order of Mass: the Kyrie, Gloria, Credo, Sanctus, and Agnus Dei.
There have been and are other Graduals, apart from the Roman Gradual. For instance, the Dominican Order had its own rite of Mass and its own Gradual: "Graduale juxta ritum sacri ordinis praedicatorum" (Gradual according to the rite of the Sacred Order of Preachers).
Structure of the 1974 edition
The 1974 Roman Gradual is arranged into 8 major sections: # Praenotanda (Rubrics) # Proprium de Tempore (Proper of Seasons) # Communia (Commons) # Proprium de Sanctis (Proper of Saints) # Missae Rituales ad Diversa et Votivae (Ritual and Votive Masses) # Cantus in Ordine Missae Occurrentes (Chants Occurring in Order of Mass, including theKyriale
The Kyriale is a collection of Gregorian chant settings for the Ordinary of the Mass. It contains eighteen Masses (each consisting of the Kyrie, Gloria xcluded from Masses intended for weekdays/ferias and Sundays in Advent and Lent Sanctus, and ...
).
# Appendix (Containing hymns and litanies)
# Missae Propriae Ordinis Sancti Benedicti (Mass Propers of the Order of Saint Benedict)
History
Originally the book was called an ''antiphonale missarum'' ("Antiphonal
An antiphonary or antiphonal is one of the liturgical books intended for use (i.e. in the liturgical choir), and originally characterized, as its name implies, by the assignment to it principally of the antiphons used in various parts of the ...
of the Mass"). Graduals, like the later Cantatory, may have originally included only the responsorial items, the Gradual, Alleluia
Alleluia (derived from the Hebrew ''Hallelujah'', meaning "Praise Yahweh") is a Latin phrase in Christianity used to give praise to God. In Christian worship, Alleluia is used as a liturgical chant in which that word is combined with verses of ...
, and Tract.
In 1908 a revised edition of the Roman Gradual was published. In it Pope Pius X gave official approval to the work of the monastery of Solesmes, founded in the 1830s by Dom Guéranger, was done by Dom Pothier in restoring Gregorian chant to its purity by removing the alterations it had undergone in the centuries immediately preceding. The work had involved much research and study.
That edition of the Roman Gradual was the basis also of a more general compilation of chants known as the Liber Usualis
The ''Liber Usualis'' is a book of commonly used Gregorian chants in the Catholic tradition, compiled by the monks of the Abbey of Solesmes in France. According to Willi Apel, the chants in the ''Liber Usualis'' originated in the 11th century.Ap ...
. This was not an official liturgical book, but it contained all the chants of the Roman Gradual, as well as other chants and hymns and instructions on the proper way to sing them.
In 1974, after the Second Vatican Council
The Second Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the , or , was the 21st ecumenical council of the Roman Catholic Church. The council met in St. Peter's Basilica in Rome for four periods (or sessions), each lasting between 8 and ...
an edition of the Roman Gradual based on that of 1908 was issued. While the melodies remained unchanged, there was a relocation of pieces to fit the revised Roman Missal
The Roman Missal ( la, Missale Romanum) is the title of several missals used in the celebration of the Roman Rite. Along with other liturgical books of the Roman Rite, the Roman Missal contains the texts and rubrics for the celebration of th ...
and calendar. Some chants were replaced by ancient ones rediscovered after 1908. A simpler gradual for small churches or inexperienced choirs was published in 1967 and 1975, as the Graduale Simplex
Graduale simplex ("Simple Gradual") is a gradual in Latin and in Gregorian, published by the Vatican in 1967 following the Second Vatican Council, so that the use of Gregorian chant can adapt to smaller parishes and churches or to those who lack e ...
.
In 2011 (Part 1 De dominicis et festis) and 2018 (Part 2 De feriis et sanctis) the ''Graduale novum'' was published by
Christian Dostal, Johannes Berchmans Göschl, Cornelius Pouderoijen, Franz Karl Praßl, Heinrich Rumphorst, and Stephan Zippe, members of the melodic restitution group of AISCGre (International Society for the Study of Gregorian Chant). It claims to be a Editio magis critica iuxta according to SC 117.
Despite an initial disappearance of the use of the Roman Gradual from many parishes following the Second Vatican Council
The Second Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the , or , was the 21st ecumenical council of the Roman Catholic Church. The council met in St. Peter's Basilica in Rome for four periods (or sessions), each lasting between 8 and ...
, often done out of a misunderstanding that Gregorian Chant had been abrogated or otherwise discouraged, its use has become increasingly popular in recent years. Parishes which celebrate the Mass according to the 1970 Roman Missal
The Roman Missal ( la, Missale Romanum) is the title of several missals used in the celebration of the Roman Rite. Along with other liturgical books of the Roman Rite, the Roman Missal contains the texts and rubrics for the celebration of th ...
, whether fully in Latin or a vernacular language, have begun to utilize the chants of the Gradual. This has been encouraged by the most recent Popes
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
, including Pope Francis
Pope Francis ( la, Franciscus; it, Francesco; es, link=, Francisco; born Jorge Mario Bergoglio, 17 December 1936) is the head of the Catholic Church. He has been the bishop of Rome and sovereign of the Vatican City State since 13 March 2013. ...
who has encouraged the presence of a Schola Cantorum in every parish so that at least one Mass might be celebrated with the Church's official music.
Bibliography and external links
* Abbaye Saint-Pierre de Solesmes. Graduale Romanum. Desclée & Co., Tournai, Belgium 1974.Jeffrey Tucker: The Real Catholic Songbook
* Bergeron, Katherine. Decadent enchantments: the revival of Gregorian chant at Solesmes. Berkeley : University of California Press, c1998. .
References
{{Authority control Roman Rite liturgical books Catholic liturgical music Mass in the Catholic Church