Ring-tailed cat on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ringtail (''Bassariscus astutus'') is a mammal of the raccoon family native to arid regions of North America. It is widely distributed and well adapted to disturbed areas. It has been legally trapped for its fur. It is listed as
 These animals are characterized by a long black and white "ringed" tail with 14–16 stripes, which is about the same length as its body.
Ringtails are primarily nocturnal, with large eyes and upright ears that make it easier for them to navigate and forage in the dark. An adept climber, it uses its long tail for balance. The rings on its tail can also act as a distraction for predators. The white rings act as a target, so when the tail rather than the body is caught, the ringtail has a greater chance of escaping.
The claws are short, straight, and semi-retractable, well-suited for climbing.
Smaller than a house cat, it is one of the smallest extant procyonids (only the smallest in the olingo species group average smaller). Its body alone measures and its tail averages from its base. It typically weighs around .
These animals are characterized by a long black and white "ringed" tail with 14–16 stripes, which is about the same length as its body.
Ringtails are primarily nocturnal, with large eyes and upright ears that make it easier for them to navigate and forage in the dark. An adept climber, it uses its long tail for balance. The rings on its tail can also act as a distraction for predators. The white rings act as a target, so when the tail rather than the body is caught, the ringtail has a greater chance of escaping.
The claws are short, straight, and semi-retractable, well-suited for climbing.
Smaller than a house cat, it is one of the smallest extant procyonids (only the smallest in the olingo species group average smaller). Its body alone measures and its tail averages from its base. It typically weighs around .
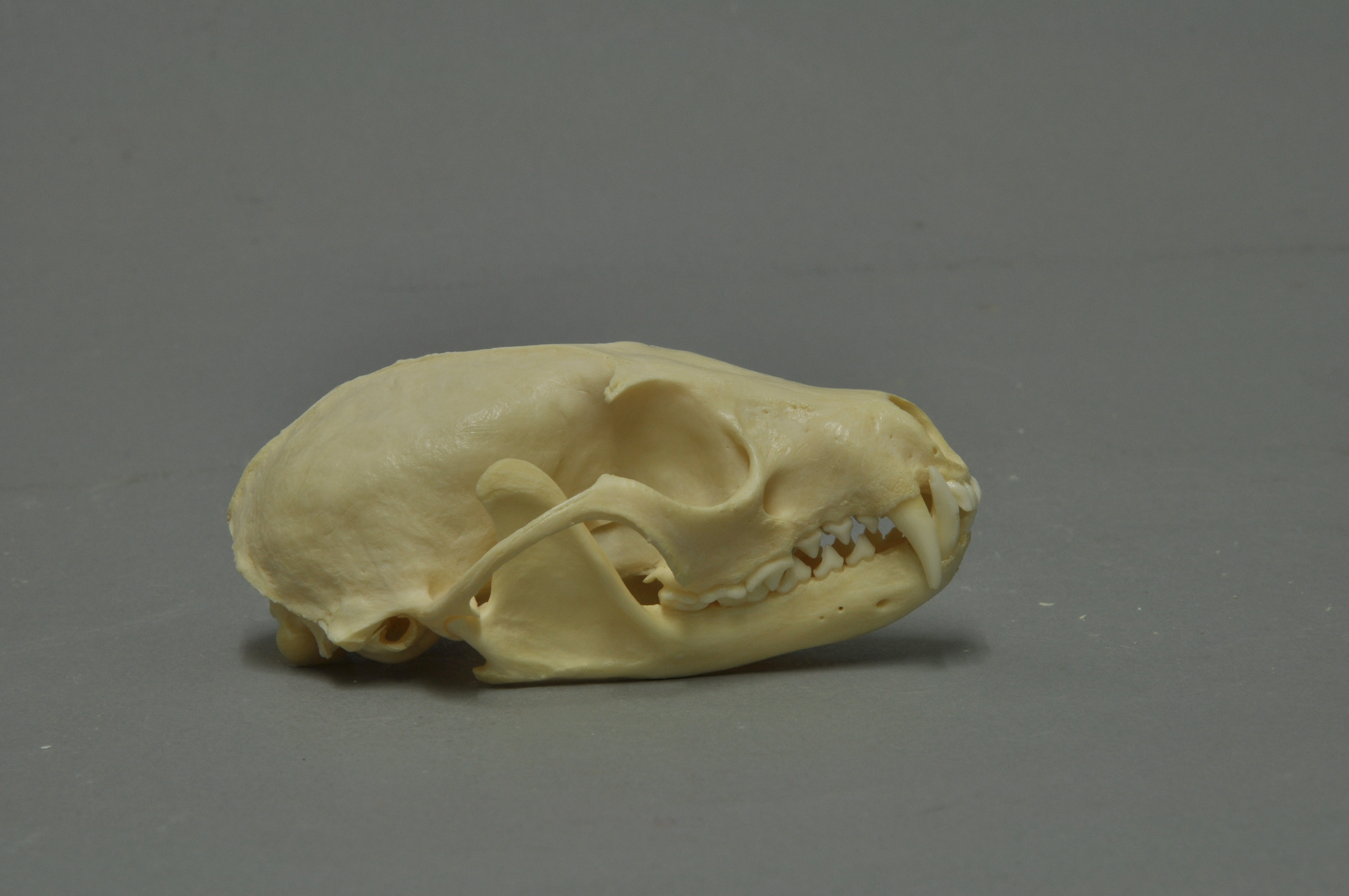 Its dental formula is = 40.
The
Its dental formula is = 40.
The
Least Concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as evaluated as not being a focus of species conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wild. T ...
on the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biol ...
.
It is also known as the ringtail cat, ring-tailed cat, miner's cat or bassarisk, and is sometimes called a cacomistle, though this term seems to be more often used to refer to '' Bassariscus sumichrasti''.
The ringtail is the state mammal of Arizona.
Description
The ringtail is black to dark brown in color with pale underparts. The animal has a pointed muzzle with long whiskers, similar to that of a fox (its Latin name means ‘clever little fox’) and its body resembles that of a cat. The ringtailed's face resembles a mask as dark brown and black hair surround its eyes. These animals are characterized by a long black and white "ringed" tail with 14–16 stripes, which is about the same length as its body.
Ringtails are primarily nocturnal, with large eyes and upright ears that make it easier for them to navigate and forage in the dark. An adept climber, it uses its long tail for balance. The rings on its tail can also act as a distraction for predators. The white rings act as a target, so when the tail rather than the body is caught, the ringtail has a greater chance of escaping.
The claws are short, straight, and semi-retractable, well-suited for climbing.
Smaller than a house cat, it is one of the smallest extant procyonids (only the smallest in the olingo species group average smaller). Its body alone measures and its tail averages from its base. It typically weighs around .
These animals are characterized by a long black and white "ringed" tail with 14–16 stripes, which is about the same length as its body.
Ringtails are primarily nocturnal, with large eyes and upright ears that make it easier for them to navigate and forage in the dark. An adept climber, it uses its long tail for balance. The rings on its tail can also act as a distraction for predators. The white rings act as a target, so when the tail rather than the body is caught, the ringtail has a greater chance of escaping.
The claws are short, straight, and semi-retractable, well-suited for climbing.
Smaller than a house cat, it is one of the smallest extant procyonids (only the smallest in the olingo species group average smaller). Its body alone measures and its tail averages from its base. It typically weighs around .
ankle
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular joi ...
joint is flexible and is able to rotate over 180 degrees, making the animal an agile climber. The long tail provides balance for negotiating narrow ledges and limbs, even allowing individuals to reverse directions by performing a cartwheel. Ringtails also can ascend narrow passages by stemming (pressing all feet on one wall and their back against the other or pressing both right feet on one wall and both left feet on the other), and wider cracks or openings by ricocheting between the walls.
As adults, these mammals lead solitary lives, generally coming together only to mate. A typical call is a very loud, plaintive bark. They produce a variety of sounds, including clicks and chatters reminiscent of raccoons.
Ringtails have been reported to exhibit fecal marking behavior as a form of intraspecific communication to define territory boundaries or attract potential mates. It has been suggested that ringtails use feces as a way to mark territory. In 2003, a study in Mexico City found that ringtails tended to defecate in similar areas in a seemingly nonrandom pattern, mimicking that of other carnivores that utilized excretions to mark territories.
Ringtails prefer a solitary existence but may share a den or be found mutually grooming one another. They exhibit limited interaction except during the breeding season, which occurs in the early spring. Ringtails can survive for long periods on water derived from food alone, and have urine which is more concentrated than any other mammal studied, an adaptation that allows for maximum water retention.
Reproduction
Ringtails mate in the spring. The gestation period is 45–50 days, during which the male will procure food for the female. There will be 2–4 kits in a litter. The cubs open their eyes after one month, and will hunt for themselves after four months. They reach sexual maturity at 10 months. The ringtail's lifespan in the wild is about seven years.Range and habitat
The ringtail is commonly found in rocky desert habitats, where it nests in the hollows of trees or abandoned wooden structures. It has been found throughout theGreat Basin Desert
The Great Basin Desert is part of the Great Basin between the Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada and the Wasatch Range. The desert is a geographical region that largely overlaps the Great Basin shrub steppe defined by the World Wildlife Fund, a ...
, which stretches over several states (Nevada, Utah, California, Idaho, and Oregon) as well as the Sonoran Desert
The Sonoran Desert ( es, Desierto de Sonora) is a desert in North America and ecoregion that covers the northwestern Mexican states of Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur, as well as part of the southwestern United States (in Ariz ...
in Arizona, and the Chihuahuan Desert
The Chihuahuan Desert ( es, Desierto de Chihuahua, ) is a desert ecoregion designation covering parts of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. It occupies much of far West Texas, the middle to lower Rio Grande Valley and the lo ...
in New Mexico, Texas, and northern Mexico. The ringtail also prefers rocky habitats associated with water, such as the riparian canyons, cave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea ...
s, or mine shafts.
In areas with a bountiful source of water, as many as 50 ringtails/sq. mile (20/km²) have been found. Ranging from , the territories of male ringtails occasionally intersect with several females.
The ringtail is found in the southwestern United States in southern Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, eastern Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
, Oklahoma, Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
, Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
, southern Nevada
Southern Nevada (SNV) is a region and the southern portion of the U.S. state of Nevada which includes the Las Vegas Valley. It also includes the areas in and around Pahrump and Pioche. Tonopah and Hawthorne are sometimes also referred to as part ...
, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
and Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
. In Mexico it ranges from the northern desert state of Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mex ...
to Oaxaca
Oaxaca ( , also , , from nci, Huāxyacac ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca), is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of Mexico. It is ...
. Its distribution overlaps that of ''B. sumichrasti'' in the Mexican states of Guerrero
Guerrero is one of the 32 states that comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo and its largest city is Acapulcocopied from article, GuerreroAs of 2020, Guerrero the pop ...
, Oaxaca
Oaxaca ( , also , , from nci, Huāxyacac ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca), is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of Mexico. It is ...
, and Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
.
Fossils assigned to ''B. astutus'' dating back to the early Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Washington.
File:Bassariscus.jpg, Two ringtails
File:Bassariscus astutus (ringtail)-11297651994.jpg, Ringtail den
File:Squaw-ringtail-28112.jpg, Ringtail in Phoenix, Arizona
File:Bassaris astuta - 1700-1880 - Print - Iconographia Zoologica - Special Collections University of Amsterdam - UBA01 IZ22400145.tif, ''Bassaris astuta'' print from ''Iconographia Zoologica'' (1700–1880)
Diet
Small vertebrates such aspasserine birds
A passerine () is any bird of the Order (biology), order Passeriformes (; from Latin 'sparrow' and '-shaped'), which includes more than half of all bird species. Sometimes known as perching birds, passerines are distinguished from other order ...
, rats, mice, squirrels, rabbits, snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
s, lizards, frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is ...
s, and toads are the most important foods during winters. However, the ringtail is omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nut ...
, as are all procyonids. Berries and insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three ...
s are important in the diet year-round, and become the primary part of the diet in spring and summer, along with other fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particu ...
.
As an omnivore the ringtail enjoys a variety of foods in its diet, the majority of which is made up of animal matter. Insects and small mammals such as rabbits, mice, rats and ground squirrels are some examples of the ringtail's carnivorous tendencies. Occasionally the ringtail will also eat fish, lizards, birds, snakes and carrion. The ringtail also enjoys juniper, hack and black berries, persimmon, prickly pear, and fruit in general. They have even been observed partaking from birdseed feeders, hummingbird feeders, sweet nectar or sweetened water.
The results of a study of scat from ringtails on Isla San José, Baja California Sur, showed that the ringtail tended to prey on whatever was most abundant during each respective season. During the spring the ringtail's diet consisted largely of insects, showing up in about 50% of the analyzed feces. Small rodents, snakes, and some lizards were also present. Plant matter was presented in large amounts, around 59% of the collected feces contained some type of plant, with fruits of '' Phaulothamnus'', '' Lycium'', and ''Solanum
''Solanum'' is a large and diverse genus of flowering plants, which include three food crops of high economic importance: the potato, the tomato and the eggplant (aubergine, brinjal). It is the largest genus in the nightshade family Solanaceae ...
'' most common. The large amount of ironwood seeds and leaves demonstrated that these fleshy fruits were an obvious favorite of the ringtail.
Ecology
Foxes, coyotes,raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of ...
s, bobcats, hawks, and owl
Owls are birds from the order Strigiformes (), which includes over 200 species of mostly solitary and nocturnal birds of prey typified by an upright stance, a large, broad head, binocular vision, binaural hearing, sharp talons, and feathers a ...
s opportunistically prey upon ringtails of all ages, though predominantly on younger, more vulnerable specimens. Also occasional prey to coatis, lynxes, and mountain lions, the ringtail is rather adept at avoiding predators. The ringtail's success in deterring potential predators is largely attributed to its ability to excrete musk when startled or threatened. The main predators of the ringtail are the great horned owl and the red-tailed hawk.
Ringtails have occasionally been hunted for their pelts, but the fur is not especially valuable. Fur trapping has slowed down considerably, but current population sizes and growth rates remain unclear.
Tameability
Ringtail are said to be easily tamed / habituated to humans, and can make an affectionate pet and effective mouser. Miners and settlers once kept pet ringtails to keep their cabins free of vermin; hence, the common name of "miner's cat".References
Further reading
*External links
* * {{Taxonbar, from=Q632701 Procyonidae Carnivorans of North America Mammals of Mexico Mammals of the United States Fauna of the Baja California Peninsula Fauna of the Southwestern United States Fauna of the Mojave Desert Fauna of the Colorado Desert Fauna of the Sonoran Desert Fauna of the Great Basin Mammals described in 1830 Symbols of Arizona