Retour des cendres on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The ''retour des cendres'' (literally "return of the ashes", though "ashes" is used here as meaning his mortal remains, as he was not cremated) was the return of the mortal remains of Napoleon I of France from the island of Saint Helena to
The ''retour des cendres'' (literally "return of the ashes", though "ashes" is used here as meaning his mortal remains, as he was not cremated) was the return of the mortal remains of Napoleon I of France from the island of Saint Helena to
 At 7pm on 7 July 1840 the frigate '' Belle Poule'' left
At 7pm on 7 July 1840 the frigate '' Belle Poule'' left
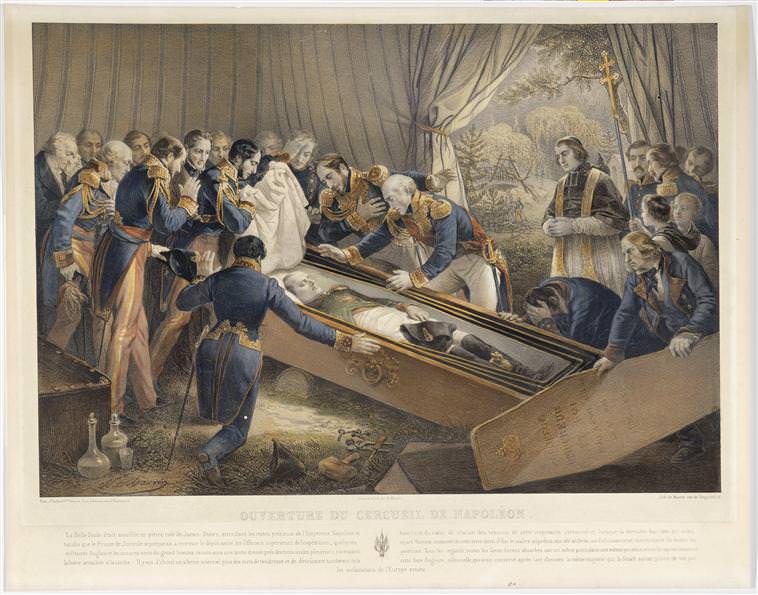 The party returned to the Valley of the Tomb at midnight on 14 October, though Joinville remained on board ship since all the operations up until the coffin's arrival at the embarkation point would be carried out by British soldiers rather than French sailors, and so he felt he could not be present at work that he could not direct. The French section of the party was led by the Count of Rohan-Chabot and included generals Bertrand and Gourgaud, Emmanuel de Las Cases, the Emperor's old servants, Abbé Coquereau, two choirboys, captains Guyet, Charner and Doret, doctor Guillard (chief surgeon of the ''Belle-Poule'') and a lead-worker, Monsieur Leroux. The British section was made up of William Wilde, Colonel Hodson and Mr Scale (members of the island's colonial council), Mr Thomas, Mr Brooke, Colonel Trelawney (the island's artillery commander), naval Lieutenant Littlehales, Captain Alexander (representing Governor Middlemore, who was indisposed, although he eventually arrived accompanied by his son and an aide) and Mr Darling (interior decorator at Longwood during Napoleon's captivity).
By the light of torches, the British soldiers set to work. They removed the grille, then the stones that formed a border to the tomb. The topsoil had already been removed and the French shared among themselves the flowers that had been growing in it. The soldiers then pulled up the three slabs that were closing the pit over. Long efforts were needed to break through the masonry enclosing the coffin. At 9.30 the last slab was raised and the coffin could be seen. Coquereau took some water from the nearby spring, blessed it and sprinkled it over the coffin, before reciting the psalm '' De profundis''. The coffin was raised and transported into a large blue and white striped tent that had been put up the previous day. Then they proceeded to open the bier, in complete silence. The first coffin, of mahogany, had to be sawn off at both ends to get out the second coffin, made of lead, which was then placed within the neo-classical,
The party returned to the Valley of the Tomb at midnight on 14 October, though Joinville remained on board ship since all the operations up until the coffin's arrival at the embarkation point would be carried out by British soldiers rather than French sailors, and so he felt he could not be present at work that he could not direct. The French section of the party was led by the Count of Rohan-Chabot and included generals Bertrand and Gourgaud, Emmanuel de Las Cases, the Emperor's old servants, Abbé Coquereau, two choirboys, captains Guyet, Charner and Doret, doctor Guillard (chief surgeon of the ''Belle-Poule'') and a lead-worker, Monsieur Leroux. The British section was made up of William Wilde, Colonel Hodson and Mr Scale (members of the island's colonial council), Mr Thomas, Mr Brooke, Colonel Trelawney (the island's artillery commander), naval Lieutenant Littlehales, Captain Alexander (representing Governor Middlemore, who was indisposed, although he eventually arrived accompanied by his son and an aide) and Mr Darling (interior decorator at Longwood during Napoleon's captivity).
By the light of torches, the British soldiers set to work. They removed the grille, then the stones that formed a border to the tomb. The topsoil had already been removed and the French shared among themselves the flowers that had been growing in it. The soldiers then pulled up the three slabs that were closing the pit over. Long efforts were needed to break through the masonry enclosing the coffin. At 9.30 the last slab was raised and the coffin could be seen. Coquereau took some water from the nearby spring, blessed it and sprinkled it over the coffin, before reciting the psalm '' De profundis''. The coffin was raised and transported into a large blue and white striped tent that had been put up the previous day. Then they proceeded to open the bier, in complete silence. The first coffin, of mahogany, had to be sawn off at both ends to get out the second coffin, made of lead, which was then placed within the neo-classical, 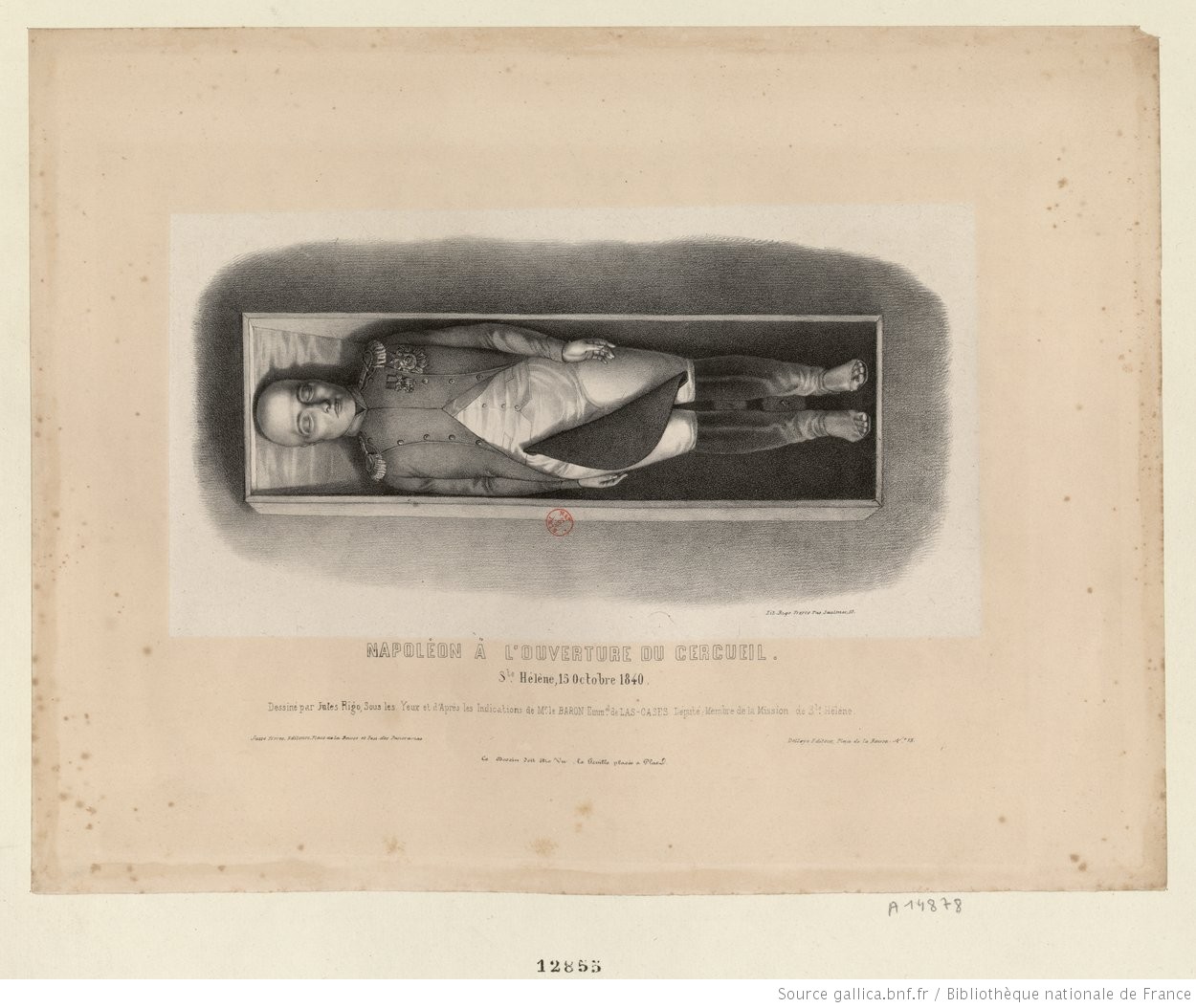 When the lid was lifted what appeared was described by a witness as "a white form – of uncertain shape", which was the only thing visible at first at the light of the torches, briefly sparking fears that the body had decomposed extensively; however, it was discovered that the white satin padding from the coffin lid had detached and fallen over Napoleon's body, covering it like a shroud. Doctor Guillard slowly rolled the satin back, from the feet up: The body laid comfortably in a natural position with the head resting over a cushion while its left forearm and hand laid over his left thigh; Napoleon's face was immediately recognizable and only the sides of the nose seemed to have slightly contracted but overall, the face seemed, on the opinion of the witnesses, peaceful, and his eyes were fully closed, the eyelids even retaining most of the eyelashes; at the same time, the mouth was slightly open, showing three white incisors. As the body became dehydrated, its hairs started to protrude more and more from the skin, making it look as if the hairs had grown; this being a common phenomenon in well-preserved bodies. In Napoleon's case, this phenomenon was most prominently displayed in what would have been his beard and his chin was stippled with the beginnings of a bluish beard. The hands for their part were very white and the fingers were thin and long; the fingernails were still intact and attached to the fingers and they seemed to have grown longer, also protruding because of the dryness of the skin.
Napoleon wore his famous green uniform of the colonel of
When the lid was lifted what appeared was described by a witness as "a white form – of uncertain shape", which was the only thing visible at first at the light of the torches, briefly sparking fears that the body had decomposed extensively; however, it was discovered that the white satin padding from the coffin lid had detached and fallen over Napoleon's body, covering it like a shroud. Doctor Guillard slowly rolled the satin back, from the feet up: The body laid comfortably in a natural position with the head resting over a cushion while its left forearm and hand laid over his left thigh; Napoleon's face was immediately recognizable and only the sides of the nose seemed to have slightly contracted but overall, the face seemed, on the opinion of the witnesses, peaceful, and his eyes were fully closed, the eyelids even retaining most of the eyelashes; at the same time, the mouth was slightly open, showing three white incisors. As the body became dehydrated, its hairs started to protrude more and more from the skin, making it look as if the hairs had grown; this being a common phenomenon in well-preserved bodies. In Napoleon's case, this phenomenon was most prominently displayed in what would have been his beard and his chin was stippled with the beginnings of a bluish beard. The hands for their part were very white and the fingers were thin and long; the fingernails were still intact and attached to the fingers and they seemed to have grown longer, also protruding because of the dryness of the skin.
Napoleon wore his famous green uniform of the colonel of  All the spectators were in a state of visible shock: Gourgaud, Las Cases, Philippe de Rohan, Marchand and all the servants wept; Bertrand barely fought his tears back. After two minutes' examination, Dr. Guillard proposed that he continue examining the body and open the jars containing the heart and the stomach, in part so that they could confirm or disprove the findings of the autopsy performed by the English when Napoleon died and which had found a perforated ulcer in his stomach. Gourgaud, however, suppressing his tears, became angry and ordered that the coffin be closed at once. The doctor complied and replaced the satin padding, spraying it with a little
All the spectators were in a state of visible shock: Gourgaud, Las Cases, Philippe de Rohan, Marchand and all the servants wept; Bertrand barely fought his tears back. After two minutes' examination, Dr. Guillard proposed that he continue examining the body and open the jars containing the heart and the stomach, in part so that they could confirm or disprove the findings of the autopsy performed by the English when Napoleon died and which had found a perforated ulcer in his stomach. Gourgaud, however, suppressing his tears, became angry and ordered that the coffin be closed at once. The doctor complied and replaced the satin padding, spraying it with a little
 At 8am on Sunday 18 October ''Belle Poule'', ''Favorite'' and ''Oreste'' set sail. ''Oreste'' rejoined the Levant division, whilst the two other ships sailed towards France at full speed, fearful of being attacked. No notable setback occurred to ''Belle Poule'' and ''Favorite'' during the first 13 days of this voyage, though on 31 October they met the merchantman ''Hambourg'', whose captain gave Joinville news of Europe, confirming the news he had received from Doret. The threat of war was confirmed by the Dutch ship ''Egmont'', en route for Batavia. Joinville was sufficiently worried to summon the officers of both his ships to a council of war, to plan precautions to keep the remains out of harm's way should they meet British warships. He had ''Belle Poule'' prepared for possible battle. So that all the ship's guns could be mounted, the temporary cabins set up to house the commission to Saint Helena were demolished and the dividers between them, as well as their furniture, were thrown into the sea – earning the area the nickname "''Lacédémone''". The crew were frequently drilled and called to action stations. Most importantly, he ordered ''Favorite'' to sail away immediately and make for the nearest French port. Joinville was aware that no British warship would attack the ship carrying the body, but also that they would be unlikely to extend the same generosity to ''Favorite''. He doubted, with good reason, that he would be able to save the corvette if she got within range of an enemy ship, without risking his frigate and its precious cargo. Another hypothesis is that ''Favorite'' was the slower ship and would only have held ''Belle Poule'' back if they had been attacked.
On 27 November ''Belle-Poule'' was only 100 leagues from the coasts of France, without having encountered any British patrol. Nonetheless, her commander and crew continued with their precautions – even though these were now unnecessary, because Anglo-French tension had ceased, after France had had to abandon its Egyptian ally and Thiers had been forced to resign.
At 8am on Sunday 18 October ''Belle Poule'', ''Favorite'' and ''Oreste'' set sail. ''Oreste'' rejoined the Levant division, whilst the two other ships sailed towards France at full speed, fearful of being attacked. No notable setback occurred to ''Belle Poule'' and ''Favorite'' during the first 13 days of this voyage, though on 31 October they met the merchantman ''Hambourg'', whose captain gave Joinville news of Europe, confirming the news he had received from Doret. The threat of war was confirmed by the Dutch ship ''Egmont'', en route for Batavia. Joinville was sufficiently worried to summon the officers of both his ships to a council of war, to plan precautions to keep the remains out of harm's way should they meet British warships. He had ''Belle Poule'' prepared for possible battle. So that all the ship's guns could be mounted, the temporary cabins set up to house the commission to Saint Helena were demolished and the dividers between them, as well as their furniture, were thrown into the sea – earning the area the nickname "''Lacédémone''". The crew were frequently drilled and called to action stations. Most importantly, he ordered ''Favorite'' to sail away immediately and make for the nearest French port. Joinville was aware that no British warship would attack the ship carrying the body, but also that they would be unlikely to extend the same generosity to ''Favorite''. He doubted, with good reason, that he would be able to save the corvette if she got within range of an enemy ship, without risking his frigate and its precious cargo. Another hypothesis is that ''Favorite'' was the slower ship and would only have held ''Belle Poule'' back if they had been attacked.
On 27 November ''Belle-Poule'' was only 100 leagues from the coasts of France, without having encountered any British patrol. Nonetheless, her commander and crew continued with their precautions – even though these were now unnecessary, because Anglo-French tension had ceased, after France had had to abandon its Egyptian ally and Thiers had been forced to resign.
 In the meantime, in October 1840, a new ministry nominally presided over by Marshal
In the meantime, in October 1840, a new ministry nominally presided over by Marshal
 The date for the reburial was set for 15 December. Victor Hugo evoked this day in his ''Les Rayons et les Ombres'':
:"O frozen sky! and sunlight pure! shining bright in history!
:''Funereal triumph, imperial torch!''
:Let the people's memory hold you forever,
:::Day beautiful as glory,
:::Cold as the tomb
Even as far as London, poems commemorating the event were published; one read in part:
:Ah! Luckless to the nations! Luckless day!
:When from Helena's rock they bore away,
:And gave again to France the mouldering bones
:Of him, beneath whose monarchy the thrones
:Of Earth's huge empires shook-that might one,
:The archon of the world-NAPOLEON!
Despite the temperature never rising above 10 degrees Celsius, the crowd of spectators stretching from the
The date for the reburial was set for 15 December. Victor Hugo evoked this day in his ''Les Rayons et les Ombres'':
:"O frozen sky! and sunlight pure! shining bright in history!
:''Funereal triumph, imperial torch!''
:Let the people's memory hold you forever,
:::Day beautiful as glory,
:::Cold as the tomb
Even as far as London, poems commemorating the event were published; one read in part:
:Ah! Luckless to the nations! Luckless day!
:When from Helena's rock they bore away,
:And gave again to France the mouldering bones
:Of him, beneath whose monarchy the thrones
:Of Earth's huge empires shook-that might one,
:The archon of the world-NAPOLEON!
Despite the temperature never rising above 10 degrees Celsius, the crowd of spectators stretching from the  The cortège arrived at the
The cortège arrived at the  General Atthalin stepped forward, bearing on a cushion the sword that Napoleon had worn at Austerlitz and Marengo, which he presented to Louis-Philippe. The king made a strange, recoiling movement, then turned to Bertrand and said: "General, I charge you with placing the Emperor's glorious sword upon his coffin." Overcome with emotion, Bertrand was unable to complete this task, and Gourgaud rushed over and seized the weapon. The king turned to Gourgaud and said: "General Gourgaud, place the Emperor's sword upon the coffin."
In the course of the funeral ceremony, the Paris Opera's finest singers were conducted by Habeneck in a performance of Mozart's '' Requiem''. The ceremony was more worldly than reverent – the deputies were particularly uncomfortable:
General Atthalin stepped forward, bearing on a cushion the sword that Napoleon had worn at Austerlitz and Marengo, which he presented to Louis-Philippe. The king made a strange, recoiling movement, then turned to Bertrand and said: "General, I charge you with placing the Emperor's glorious sword upon his coffin." Overcome with emotion, Bertrand was unable to complete this task, and Gourgaud rushed over and seized the weapon. The king turned to Gourgaud and said: "General Gourgaud, place the Emperor's sword upon the coffin."
In the course of the funeral ceremony, the Paris Opera's finest singers were conducted by Habeneck in a performance of Mozart's '' Requiem''. The ceremony was more worldly than reverent – the deputies were particularly uncomfortable:
 The bearing of the old Marshal Moncey, the governor of the Invalides, somewhat redeemed the impertinence of the court and the politicians. For a fortnight he had been in agony, pressing his doctor to keep him alive at least to complete his role in the ceremony. At the end of the religious ceremony he managed to walk to the catafalque, sprinkled holy water on it and pronounced as the closing words: "And now, let us go home to die".
From 16 to 24 December, the Église des Invalides, illuminated as on the day of the ceremony, remained open to the public. The people had long disbelieved in Napoleon's death and a rumour spread that the tomb was only a
The bearing of the old Marshal Moncey, the governor of the Invalides, somewhat redeemed the impertinence of the court and the politicians. For a fortnight he had been in agony, pressing his doctor to keep him alive at least to complete his role in the ceremony. At the end of the religious ceremony he managed to walk to the catafalque, sprinkled holy water on it and pronounced as the closing words: "And now, let us go home to die".
From 16 to 24 December, the Église des Invalides, illuminated as on the day of the ceremony, remained open to the public. The people had long disbelieved in Napoleon's death and a rumour spread that the tomb was only a
The Second Funeral of Napoleon
by Michael Angelo Titmarsh * A succinct chronology by Albert Benhamou {{italic title July Monarchy Napoleon History of Saint Helena Funerals in France 1840 in France December 1840 events Aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars Louis Philippe I
 The ''retour des cendres'' (literally "return of the ashes", though "ashes" is used here as meaning his mortal remains, as he was not cremated) was the return of the mortal remains of Napoleon I of France from the island of Saint Helena to
The ''retour des cendres'' (literally "return of the ashes", though "ashes" is used here as meaning his mortal remains, as he was not cremated) was the return of the mortal remains of Napoleon I of France from the island of Saint Helena to France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and the burial in Hôtel des Invalides in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
in 1840, on the initiative of Prime Minister Adolphe Thiers and King Louis-Philippe
Louis Philippe (6 October 1773 – 26 August 1850) was King of the French from 1830 to 1848, and the penultimate monarch of France.
As Louis Philippe, Duke of Chartres, he distinguished himself commanding troops during the Revolutionary Wa ...
.
Background
After defeat in theWar of the Sixth Coalition
In the War of the Sixth Coalition (March 1813 – May 1814), sometimes known in Germany as the Wars of Liberation, a coalition of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Spain, the United Kingdom, Portugal, Sweden, and a number of German States defeated F ...
in 1814, Napoleon abdicated as emperor of the French, and was exiled to the Mediterranean island of Elba
Elba ( it, isola d'Elba, ; la, Ilva) is a Mediterranean island in Tuscany, Italy, from the coastal town of Piombino on the Italian mainland, and the largest island of the Tuscan Archipelago. It is also part of the Arcipelago Toscano Nationa ...
. The following year he returned to France, took up the throne, and began the Hundred Days. The powers which had prevailed against him the previous year mobilised against him, and defeated the French in the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armie ...
. Napoleon returned to Paris and abdicated on 22 June 1815. Foiled in his attempt to sail to the United States, he gave himself up to the British, who exiled him to the remote island of St Helena in the south Atlantic Ocean. He died and was buried there in 1821.
Previous attempts
In a codicil to his will, written in exile at Longwood House on St Helena on 16 April 1821, Napoleon had expressed a wish to be buried "on the banks of the Seine, in the midst of the French people hom Iloved so much". On the Emperor's death, Comte Bertrand unsuccessfully petitioned the British government to let Napoleon's wish be granted. He then petitioned the ministers of the newly restored Louis XVIII of France, from whom he did not receive an absolute refusal, instead the explanation that the arrival of the remains in France would undoubtedly be the cause or pretext for political unrest that the government would be wise to prevent or avoid, but that his request would be granted as soon as the situation had calmed and it was safe enough to do so.Course
Political discussions
Initiation
After theJuly Revolution
The French Revolution of 1830, also known as the July Revolution (french: révolution de Juillet), Second French Revolution, or ("Three Glorious ays), was a second French Revolution after the first in 1789. It led to the overthrow of King ...
a petition demanding the remains' reburial in the base of the Colonne Vendôme (on the model of Trajan's ashes, buried in the base of his column in Rome) was refused by the Chambre des Députés on 2 October 1830. However, ten years later, Adolphe Thiers, the new Président du Conseil under Louis-Philippe
Louis Philippe (6 October 1773 – 26 August 1850) was King of the French from 1830 to 1848, and the penultimate monarch of France.
As Louis Philippe, Duke of Chartres, he distinguished himself commanding troops during the Revolutionary Wa ...
and a historian of the French Consulate and First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental E ...
, dreamed of the return of the remains as a grand political ''coup de théâtre'' which would definitively achieve the rehabilitation of the Revolutionary and Imperial periods on which he was engaged in his ''Histoire de la Révolution française'' and ''Histoire du Consulat et de l'Empire''. He also hoped to flatter the left's dreams of glory and restore the reputation of the July Monarchy (whose diplomatic relations with the rest of Europe were then under threat from its problems in Egypt, arising from its support for Muhammad Ali).
It was, nonetheless, Louis-Philippe's policy to try to regain "all the glories of France", to which he had dedicated the Château de Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed ...
, turning it into a museum of French history. Yet he was still reluctant and had to be convinced to support the project against his own doubts. Among the rest of the royal family, the Prince de Joinville did not want to be employed on a job suitable for a "carter" or an "undertaker"; Queen Marie-Amélie adjudged that such an operation would be "fodder for hot-heads"; and their daughter Louise saw it as "pure theatre". In early 1840, the government led by Adolphe Thiers appointed a twelve-member committee () to decide on the location and outline of the funerary monument and select its architect. The committee was chaired by politician Charles de Rémusat
Charles François Marie, Comte de Rémusat (, 13 March 1797 – 6 June 1875), was a French politician and writer.
Biography
He was born in Paris. His father, Auguste Laurent, Comte de Rémusat, whose family came from Toulouse, was chamber ...
and included writers and artists such as Théophile Gautier
Pierre Jules Théophile Gautier ( , ; 30 August 1811 – 23 October 1872) was a French poet, dramatist, novelist, journalist, and art and literary critic.
While an ardent defender of Romanticism, Gautier's work is difficult to classify and rema ...
, David d'Angers
Pierre-Jean David (12 March 1788 – 4 January 1856) was a French sculptor, medalist and active freemason.Initiated in ""Le Père de famille"" Lodge in Angers He adopted the name David d'Angers, following his entry into the studio of the painter ...
and Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres
Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres ( , ; 29 August 1780 – 14 January 1867) was a French Neoclassical painter. Ingres was profoundly influenced by past artistic traditions and aspired to become the guardian of academic orthodoxy against the ...
.
On 10 May 1840 François Guizot, then French ambassador in London, against his own will submitted an official request to the British government, which was immediately approved according to the promise made in 1822. For his part, the British Prime Minister Lord Palmerston
Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston, (20 October 1784 – 18 October 1865) was a British statesman who was twice Prime Minister of the United Kingdom in the mid-19th century. Palmerston dominated British foreign policy during the period ...
privately found the idea nonsensical and wrote about it to his brother, presenting it in the following terms: "Here's a really French idea".
12 May
On 12 May, during discussion of a bill on sugars, the French Interior MinisterCharles de Rémusat
Charles François Marie, Comte de Rémusat (, 13 March 1797 – 6 June 1875), was a French politician and writer.
Biography
He was born in Paris. His father, Auguste Laurent, Comte de Rémusat, whose family came from Toulouse, was chamber ...
mounted the rostrum at the Chambre des Députés and said:
The minister then introduced a bill to authorise "funding of 1 million rancsfor translation of the Emperor Napoleon's mortal remains to the Église des Invalides and for construction of his tomb". This announcement caused a sensation. A heated discussion began in the press, raising all sorts of objections as to the theory and to the practicalities. The town of Saint-Denis petitioned on 17 May that he instead be buried at their basilica, the traditional burial place of French kings.
25–26 May
On 25 and 26 May the bill was discussed in the Chambre. It was proposed byBertrand Clauzel
Bertrand, comte Clauzel (12 December 177221 April 1842) was a Marshal of France. When asked on Saint Helena which of his Generals was the most skillful Napoleon named Clauzel along with Louis-Gabriel Suchet and Étienne Maurice GérardOjala, Jea ...
, an old soldier of the First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental E ...
who had been recalled by the July Monarchy and promoted to Marshal of France
Marshal of France (french: Maréchal de France, plural ') is a French military distinction, rather than a military rank, that is awarded to generals for exceptional achievements. The title has been awarded since 1185, though briefly abolished ( ...
. In the name of the he endorsed the choice of Les Invalides as the burial site, not without discussing the other suggested solutions (besides Saint-Denis, the Arc de Triomphe, the Colonne Vendôme, the Panthéon de Paris and even the Madeleine had been suggested to him). He proposed that the funding be raised to 2 million, that the ship bringing the remains back be escorted by a whole naval squadron and that Napoleon would be the last person to be buried in the Invalides. Speeches were made by the republican critic of the Empire Glais-Bizoin, who stated that "Bonapartist ideas are one of the open wounds of our time; they represent that which is most disastrous for the emancipation of peoples, the most contrary to the independence of the human spirit." The proposal was defended by Odilon Barrot (the future president of Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew ...
's council in 1848), whilst the hottest opponent of it was Lamartine, who found the measure dangerous. Lamartine stated before the debate that "Napoleon's ashes are not yet extinguished, and we're breathing in their sparks". Before the sitting, Thiers tried to dissuade Lamartine from intervening but received the reply "No, Napoleon's imitators must be discouraged." Thiers replied "Oh! But who could think to imitate him today?", only to receive Lamartine's reply that then spread right round Paris – "I do beg your pardon, I meant to say Napoleon's parodists." During the debate Lamartine stated:
In conclusion Lamartine invited France to show that "she id not wishto create out of this ash war, tyranny, legitimate monarchs, pretenders, or even imitators". Hearing this peroration, which was implicitly directed against him, Thiers looked devastated on his bench. Even so, the Chambre was largely favourable and voted through the measures requested, although by 280 votes to 65 it did refuse to raise the funding from 1 to 2 million. The Napoleonic myth was already fully developed and only needed to be crowned. The July Monarchy's official poet Casimir Delavigne
Jean-François Casimir Delavigne (4 April 179311 December 1843) was a French poet and dramatist.
Life and career
Delavigne was born at Le Havre, but was sent to Paris to be educated at the Lycée Napoleon. He read extensively. When, on 20 Marc ...
wrote:
:France, you have seen him again! Your cry of joy, O France,
:::Drowns out the noise of your cannon;
:Your people, a whole people reaching out from your riverbanks,
:::Holds out its arms to Napoleon.
4–6 June
On 4 or 6 June General Bertrand was received by Louis-Philippe, who gave him the Emperor's arms, which were placed in the treasury. Bertrand stated on this occasion: Louis-Philippe replied, with studied formality: This ceremony angered Joseph and Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte, the latter writing in ''The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper '' The Sunday Times'' (f ...
'':
After the arms ceremony Bertrand went to the Hôtel de ville and offered to the president of the Conseil Municipal the council chair that Napoleon had left to the capital – this is now in the Musée Carnavalet.
Arrival at St Helena
 At 7pm on 7 July 1840 the frigate '' Belle Poule'' left
At 7pm on 7 July 1840 the frigate '' Belle Poule'' left Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label= Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is th ...
, escorted by the corvette ''Favorite''. The Prince of Joinville, the king's third son and a career naval officer, was in command of the frigate and the expedition as a whole. Also on board the frigate were Philippe de Rohan-Chabot, an attaché to the French ambassador to the United Kingdom and commissioned by Thiers (wishing to gain reflected glory from any possible part of the expedition) to superintend the exhumation operations; generals Bertrand and Gourgaud; Count Emmanuel de Las Cases (député for Finistère and son of Emmanuel de Las Cases, the author of '' Le Mémorial de Sainte-Hélène''); and five people who had been domestic servants to Napoleon on Saint Helena (Saint-Denis – better known by the name Ali Le Mameluck – Noverraz, Pierron, Archambault and Coursot). Captain Guyet was in command of the corvette, which transported Louis Marchand, Napoleon's chief valet de chambre, who had been with him on Saint Helena. Others on the expedition included Abbé Félix Coquereau (fleet almoner); Charner (Joinville's lieutenant and second in command), Hernoux (Joinville's aide-de-camp), Lieutenant Touchard (Joinville's orderly), General Bertrand's young son Arthur, and ship's doctor Rémy Guillard. Once the bill had been passed, the frigate was adapted to receive Napoleon's coffin: a candlelit chapel was built in the steerage, draped in black velvet embroidered with the Napoleonic symbol of silver bees, with a catafalque at the centre guarded by four gilded wooden eagles.
The voyage lasted 93 days and, due to the youth of some of its crews, turned into a tourist trip, with the Prince dropping anchor at Cadiz for four days, Madeira for two days and Tenerife for four days, while 15 days of balls and festivities were held at Bahia, Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
. The two ships finally reached Saint Helena on 8 October and in the roadstead found the French brig ''Oreste'', commanded by Doret, who had been one of the ensigns who had come up with a daring plan at île d'Aix to get Napoleon away on a lugger after Waterloo and who would later become a capitaine de corvette. Doret had arrived at Saint Helena to pay his last respects to Napoleon but he also brought worrying news – the Egyptian incident, combined with Thiers' aggressive policy, were very close to causing a diplomatic rupture between France and the United Kingdom. Joinville knew that the ceremony would be respected but began to fear he would be intercepted by British ships on the return trip.
The mission disembarked the following day and went to Plantation House, where the island's governor, Major-General George Middlemore was waiting for them. After a long interview with Joinville (with the rest of the mission waiting impatiently in the lounge), Middlemore appeared before the rest of the mission and announced "Gentlemen, the Emperor's mortal remains will be handed over to you on Thursday 15 October". The mission then set off for Longwood, via the Valley of the Tomb (or Geranium Valley). Napoleon's tomb was in a solitary spot, covered by three slabs placed level with the soil. This very simple monument was surrounded by an iron grille, solidly fixed on a base and shaded by a weeping willow, with another such tree lying dead by its side. All this was surrounded by a wooden fence and very close by was a spring whose fresh and clear water Napoleon had enjoyed. At the gate to the enclosure, Joinville dismounted, bared his head and approached the iron grille, followed by the rest of the mission. In a deep silence they contemplated the severe and bare tomb. After half an hour Joinville remounted and the expedition continued on its way. Lady Torbet, owner of the land where the tomb was sited, had set up a booth to sell refreshments for the few pilgrims to the tomb and was unhappy about the exhumation since it would eliminate her already small profits from it. They then went in pilgrimage to Longwood, which was in a very ruinous state – the furniture had disappeared, many walls were covered with graffiti, Napoleon's bedroom had become a stable where a farmer pastured his beasts and got a little extra income by guiding visitors around it. The sailors from ''Oreste'' grabbed the billiard table, which had been spared by the goats and sheep, and carried off the tapestry and anything else they could carry, all the while being loudly shouted at by the farmer with demands for compensation.
Exhumation
 The party returned to the Valley of the Tomb at midnight on 14 October, though Joinville remained on board ship since all the operations up until the coffin's arrival at the embarkation point would be carried out by British soldiers rather than French sailors, and so he felt he could not be present at work that he could not direct. The French section of the party was led by the Count of Rohan-Chabot and included generals Bertrand and Gourgaud, Emmanuel de Las Cases, the Emperor's old servants, Abbé Coquereau, two choirboys, captains Guyet, Charner and Doret, doctor Guillard (chief surgeon of the ''Belle-Poule'') and a lead-worker, Monsieur Leroux. The British section was made up of William Wilde, Colonel Hodson and Mr Scale (members of the island's colonial council), Mr Thomas, Mr Brooke, Colonel Trelawney (the island's artillery commander), naval Lieutenant Littlehales, Captain Alexander (representing Governor Middlemore, who was indisposed, although he eventually arrived accompanied by his son and an aide) and Mr Darling (interior decorator at Longwood during Napoleon's captivity).
By the light of torches, the British soldiers set to work. They removed the grille, then the stones that formed a border to the tomb. The topsoil had already been removed and the French shared among themselves the flowers that had been growing in it. The soldiers then pulled up the three slabs that were closing the pit over. Long efforts were needed to break through the masonry enclosing the coffin. At 9.30 the last slab was raised and the coffin could be seen. Coquereau took some water from the nearby spring, blessed it and sprinkled it over the coffin, before reciting the psalm '' De profundis''. The coffin was raised and transported into a large blue and white striped tent that had been put up the previous day. Then they proceeded to open the bier, in complete silence. The first coffin, of mahogany, had to be sawn off at both ends to get out the second coffin, made of lead, which was then placed within the neo-classical,
The party returned to the Valley of the Tomb at midnight on 14 October, though Joinville remained on board ship since all the operations up until the coffin's arrival at the embarkation point would be carried out by British soldiers rather than French sailors, and so he felt he could not be present at work that he could not direct. The French section of the party was led by the Count of Rohan-Chabot and included generals Bertrand and Gourgaud, Emmanuel de Las Cases, the Emperor's old servants, Abbé Coquereau, two choirboys, captains Guyet, Charner and Doret, doctor Guillard (chief surgeon of the ''Belle-Poule'') and a lead-worker, Monsieur Leroux. The British section was made up of William Wilde, Colonel Hodson and Mr Scale (members of the island's colonial council), Mr Thomas, Mr Brooke, Colonel Trelawney (the island's artillery commander), naval Lieutenant Littlehales, Captain Alexander (representing Governor Middlemore, who was indisposed, although he eventually arrived accompanied by his son and an aide) and Mr Darling (interior decorator at Longwood during Napoleon's captivity).
By the light of torches, the British soldiers set to work. They removed the grille, then the stones that formed a border to the tomb. The topsoil had already been removed and the French shared among themselves the flowers that had been growing in it. The soldiers then pulled up the three slabs that were closing the pit over. Long efforts were needed to break through the masonry enclosing the coffin. At 9.30 the last slab was raised and the coffin could be seen. Coquereau took some water from the nearby spring, blessed it and sprinkled it over the coffin, before reciting the psalm '' De profundis''. The coffin was raised and transported into a large blue and white striped tent that had been put up the previous day. Then they proceeded to open the bier, in complete silence. The first coffin, of mahogany, had to be sawn off at both ends to get out the second coffin, made of lead, which was then placed within the neo-classical, ebony
Ebony is a dense black/brown hardwood, coming from several species in the genus '' Diospyros'', which also contains the persimmons. Unlike most woods, ebony is dense enough to sink in water. It is finely textured and has a mirror finish when ...
coffin that had been brought for it from France. General Middlemore and Lieutenant Touchard then arrived and presented themselves, before the party proceeded to unsolder the lead coffin. The coffin inside this, again of mahogany, was remarkably well-preserved. Its screws were removed with difficulty. It was then possible to open, with infinite care, the final coffin, made of tin.
 When the lid was lifted what appeared was described by a witness as "a white form – of uncertain shape", which was the only thing visible at first at the light of the torches, briefly sparking fears that the body had decomposed extensively; however, it was discovered that the white satin padding from the coffin lid had detached and fallen over Napoleon's body, covering it like a shroud. Doctor Guillard slowly rolled the satin back, from the feet up: The body laid comfortably in a natural position with the head resting over a cushion while its left forearm and hand laid over his left thigh; Napoleon's face was immediately recognizable and only the sides of the nose seemed to have slightly contracted but overall, the face seemed, on the opinion of the witnesses, peaceful, and his eyes were fully closed, the eyelids even retaining most of the eyelashes; at the same time, the mouth was slightly open, showing three white incisors. As the body became dehydrated, its hairs started to protrude more and more from the skin, making it look as if the hairs had grown; this being a common phenomenon in well-preserved bodies. In Napoleon's case, this phenomenon was most prominently displayed in what would have been his beard and his chin was stippled with the beginnings of a bluish beard. The hands for their part were very white and the fingers were thin and long; the fingernails were still intact and attached to the fingers and they seemed to have grown longer, also protruding because of the dryness of the skin.
Napoleon wore his famous green uniform of the colonel of
When the lid was lifted what appeared was described by a witness as "a white form – of uncertain shape", which was the only thing visible at first at the light of the torches, briefly sparking fears that the body had decomposed extensively; however, it was discovered that the white satin padding from the coffin lid had detached and fallen over Napoleon's body, covering it like a shroud. Doctor Guillard slowly rolled the satin back, from the feet up: The body laid comfortably in a natural position with the head resting over a cushion while its left forearm and hand laid over his left thigh; Napoleon's face was immediately recognizable and only the sides of the nose seemed to have slightly contracted but overall, the face seemed, on the opinion of the witnesses, peaceful, and his eyes were fully closed, the eyelids even retaining most of the eyelashes; at the same time, the mouth was slightly open, showing three white incisors. As the body became dehydrated, its hairs started to protrude more and more from the skin, making it look as if the hairs had grown; this being a common phenomenon in well-preserved bodies. In Napoleon's case, this phenomenon was most prominently displayed in what would have been his beard and his chin was stippled with the beginnings of a bluish beard. The hands for their part were very white and the fingers were thin and long; the fingernails were still intact and attached to the fingers and they seemed to have grown longer, also protruding because of the dryness of the skin.
Napoleon wore his famous green uniform of the colonel of chasseur
''Chasseur'' ( , ), a French term for "hunter", is the designation given to certain regiments of French and Belgian light infantry () or light cavalry () to denote troops trained for rapid action.
History
This branch of the French Army orig ...
s which was perfectly preserved; his chest was still crossed by the red ribbon of the Légion d'Honneur, but all other decorations and medals over the uniform were slightly tarnished. His hat laid sideways across his thighs. The boots he wore had cracked at the seams, showing his four smaller toes in each foot.
 All the spectators were in a state of visible shock: Gourgaud, Las Cases, Philippe de Rohan, Marchand and all the servants wept; Bertrand barely fought his tears back. After two minutes' examination, Dr. Guillard proposed that he continue examining the body and open the jars containing the heart and the stomach, in part so that they could confirm or disprove the findings of the autopsy performed by the English when Napoleon died and which had found a perforated ulcer in his stomach. Gourgaud, however, suppressing his tears, became angry and ordered that the coffin be closed at once. The doctor complied and replaced the satin padding, spraying it with a little
All the spectators were in a state of visible shock: Gourgaud, Las Cases, Philippe de Rohan, Marchand and all the servants wept; Bertrand barely fought his tears back. After two minutes' examination, Dr. Guillard proposed that he continue examining the body and open the jars containing the heart and the stomach, in part so that they could confirm or disprove the findings of the autopsy performed by the English when Napoleon died and which had found a perforated ulcer in his stomach. Gourgaud, however, suppressing his tears, became angry and ordered that the coffin be closed at once. The doctor complied and replaced the satin padding, spraying it with a little creosote
Creosote is a category of carbonaceous chemicals formed by the distillation of various tars and pyrolysis of plant-derived material, such as wood or fossil fuel. They are typically used as preservatives or antiseptics.
Some creosote types were ...
as a preservative before putting back on the original tin lid (though without re-soldering it) and the original mahogany lid. The original lead coffin was then re-soldered.
The original lead coffin and its contents were then placed into a new ebony coffin with combination lock that had been brought from France. This ebony coffin, made in Paris, was 2.56m long, 1.05m wide and 0.7m deep. Its design imitated classical Roman coffins. The lid bore the sole inscription "Napoléon" in gold letters. Each of the four sides was decorated with the letter N in gilded bronze and there were six strong bronze rings for handles. On the coffin were also inscribed the words "Napoléon Empereur mort à Sainte-Hélène le 05 Mai 1821 (Napoleon, Emperor, died at St Helena on 05 May 1821)".
After the combination lock had been closed, the ebony coffin was placed in a new oak coffin, designed to protect that of ebony. Then this mass, totalling 1,200 kilos, was hoisted by 43 gunners onto a solid hearse, draped in black with four plumes of black feathers at each corner and drawn with great difficulty by four horses caparisoned in black. The coffin was covered with a large (4.3m by 2.8m) black pall made of single piece of velvet sown with golden bees and bearing eagles surmounted by imperial crowns at its corners as well as a large silver cross. The ladies of Saint Helena offered to the French commissioner the tricolour flags that would be used in the ceremony and which they had made with their own hands, and the imperial flag that would be flown by ''Belle Poule''.
Transfer to ''Belle Poule''
At 3.30, in driving rain, with the citadel and ''Belle Poule'' firing alternate gun salutes, the cortège slowly moved along under the command of Middlemore. Count Bertrand, Baron Gourgaud, Baron Las Cases the younger and Marchand walked holding the corners of the pall. A detachment of militia brought up the rear, followed by a crowd of people, while the forts fired their cannon on every minute. Reaching Jamestown, the procession marched between two ranks of garrison soldiers with arms reversed. The French ships lowered their launches, with that of ''Belle Poule'', ornamented with gilded eagles, carrying Joinville. At 5.30 the funeral procession stopped at the end of the jetty. Middlemore, old and ill, walked painfully over to Joinville. Their brief conversation, more or less in French, marked the point at which the remains were officially handed over to France. With infinite caution, the heavy coffin was placed in the launch. The French ships (up until then showing signs of mourning) hoisted their colours and all the ships present fired their guns. On ''Belle Poule'' 60 men were paraded, drums beat a salute and funeral airs were played. The coffin was hoisted onto the deck and its oak envelope was taken off. Coquereau gave absolution and Napoleon had returned to French territory. At 6.30 the coffin was placed in a candlelit chapel, ornamented with military trophies, on the stern of the ship. At 10 the following day mass was said on deck, then the coffin was lowered into the candlelit chapel in the steerage, while the frigate's band played. Once this had been done, each officer received a commemorative medal. The sailors divided up among themselves the oak coffin and the dead willow that had been taken away from the Valley of the Tomb.Return from St Helena
 At 8am on Sunday 18 October ''Belle Poule'', ''Favorite'' and ''Oreste'' set sail. ''Oreste'' rejoined the Levant division, whilst the two other ships sailed towards France at full speed, fearful of being attacked. No notable setback occurred to ''Belle Poule'' and ''Favorite'' during the first 13 days of this voyage, though on 31 October they met the merchantman ''Hambourg'', whose captain gave Joinville news of Europe, confirming the news he had received from Doret. The threat of war was confirmed by the Dutch ship ''Egmont'', en route for Batavia. Joinville was sufficiently worried to summon the officers of both his ships to a council of war, to plan precautions to keep the remains out of harm's way should they meet British warships. He had ''Belle Poule'' prepared for possible battle. So that all the ship's guns could be mounted, the temporary cabins set up to house the commission to Saint Helena were demolished and the dividers between them, as well as their furniture, were thrown into the sea – earning the area the nickname "''Lacédémone''". The crew were frequently drilled and called to action stations. Most importantly, he ordered ''Favorite'' to sail away immediately and make for the nearest French port. Joinville was aware that no British warship would attack the ship carrying the body, but also that they would be unlikely to extend the same generosity to ''Favorite''. He doubted, with good reason, that he would be able to save the corvette if she got within range of an enemy ship, without risking his frigate and its precious cargo. Another hypothesis is that ''Favorite'' was the slower ship and would only have held ''Belle Poule'' back if they had been attacked.
On 27 November ''Belle-Poule'' was only 100 leagues from the coasts of France, without having encountered any British patrol. Nonetheless, her commander and crew continued with their precautions – even though these were now unnecessary, because Anglo-French tension had ceased, after France had had to abandon its Egyptian ally and Thiers had been forced to resign.
At 8am on Sunday 18 October ''Belle Poule'', ''Favorite'' and ''Oreste'' set sail. ''Oreste'' rejoined the Levant division, whilst the two other ships sailed towards France at full speed, fearful of being attacked. No notable setback occurred to ''Belle Poule'' and ''Favorite'' during the first 13 days of this voyage, though on 31 October they met the merchantman ''Hambourg'', whose captain gave Joinville news of Europe, confirming the news he had received from Doret. The threat of war was confirmed by the Dutch ship ''Egmont'', en route for Batavia. Joinville was sufficiently worried to summon the officers of both his ships to a council of war, to plan precautions to keep the remains out of harm's way should they meet British warships. He had ''Belle Poule'' prepared for possible battle. So that all the ship's guns could be mounted, the temporary cabins set up to house the commission to Saint Helena were demolished and the dividers between them, as well as their furniture, were thrown into the sea – earning the area the nickname "''Lacédémone''". The crew were frequently drilled and called to action stations. Most importantly, he ordered ''Favorite'' to sail away immediately and make for the nearest French port. Joinville was aware that no British warship would attack the ship carrying the body, but also that they would be unlikely to extend the same generosity to ''Favorite''. He doubted, with good reason, that he would be able to save the corvette if she got within range of an enemy ship, without risking his frigate and its precious cargo. Another hypothesis is that ''Favorite'' was the slower ship and would only have held ''Belle Poule'' back if they had been attacked.
On 27 November ''Belle-Poule'' was only 100 leagues from the coasts of France, without having encountered any British patrol. Nonetheless, her commander and crew continued with their precautions – even though these were now unnecessary, because Anglo-French tension had ceased, after France had had to abandon its Egyptian ally and Thiers had been forced to resign.
Arrival in France
 In the meantime, in October 1840, a new ministry nominally presided over by Marshal
In the meantime, in October 1840, a new ministry nominally presided over by Marshal Nicolas Soult
Marshal General Jean-de-Dieu Soult, 1st Duke of Dalmatia, (; 29 March 1769 – 26 November 1851) was a French general and statesman, named Marshal of the Empire in 1804 and often called Marshal Soult. Soult was one of only six officers in Frenc ...
but in reality headed by François Guizot succeeded Thiers's cabinet in an attempt to resolve the crisis Thiers had provoked with the United Kingdom over the Middle East. This new arrangement gave rise to fresh hostile comment in the press as to the "''retour des cendres''":
Fearful of being overthrown thanks to the "''retour''" initiative (the future Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew ...
had just attempted a coup d'État) yet unable to abandon it, the government decided to rush it to a conclusion – as Victor Hugo
Victor-Marie Hugo (; 26 February 1802 – 22 May 1885) was a French Romantic writer and politician. During a literary career that spanned more than sixty years, he wrote in a variety of genres and forms. He is considered to be one of the great ...
commented, "It was pressed into finishing it." The interior minister, Comte Duchâtel, affirmed that "Whether the preparations are ready or not, the funeral ceremony will take place on 15 December, whatever weather should happen or arise."
Everyone in Paris and its suburbs was conscripted to get the preparations done as quickly as possible, with the coffin's return voyage being faster than expected and internal political problems having caused considerable delays. From the Pont de Neuilly to Les Invalides, papier-mâché structures were set up which would line the funeral procession, though these were slapped together only late on the night before the ceremony.
The funeral carriage itself, resplendently gilded and richly draped, was 10 m high, 5.8m wide, 13 m long, weighed 13 tonnes and was drawn by four groups of four richly caparisoned horses. It had four massive gilded wheels, on whose axles rested a thick tabular base. This supported a second base, rounded at the front and forming a semi-circular platform on which were set a group of genii supporting Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
's crown. At the back of this rose a dais, like an ordinary pedestal, on which stood a smaller pedestal in the shape of a quadrangle. Finally: 14 statues, larger than life and gilded all over, held up a vast shield on their heads, above which was placed a model of Napoleon's coffin; this whole ensemble was veiled in a long purple crêpe
A crêpe or crepe ( or , , Quebec French: ) is a very thin type of pancake. Crêpes are usually one of two varieties: ''sweet crêpes'' () or ''savoury galettes'' (). They are often served with a wide variety of fillings such as cheese, ...
, sown with gold bees. The back of the car was made up of a trophy of flags, palms and laurels, with the names of Napoleon's main victories.
To avoid any revolutionary outbreak, the government (which had already insisted on the remains being buried with full military honours in Les Invalides) ordered that the ceremony would be strictly military, dismissing the civil cortège and thus infuriating the law and medical students who were to have formed it. Eventually, the students protested in '' Le National'':
"Children of the new generations, he law and medical studentsdo not understand the exclusive cult that gives in to force of arms, in the absence of the civil institutions that are the foundation of liberty. he studentsdo not prostrate themselves before the spirit of invasion and conquest, but, at the moment when our nationality seems to be demeaned, the schools had wished to pay homage by their presence to the man who was from the outset the energetic and glorious representative of this nationality." The diplomatic corps gathered at the British embassy in Paris and decided to abstain from participating in the ceremony due to their antipathy to Napoleon as well as to Louis-Philippe.
On 30 November ''Belle-Poule'' entered the roadstead of Cherbourg, and six days later the remains were transferred to the steamer ''la Normandie''. Reaching Le Havre, and then on to Val-de-la-Haye
Val-de-la-Haye () is a commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Normandy region in north-western France.
Geography
A forestry and light industrial village situated by the banks of the Seine, some southwest of Rouen on the D 51 road. A ...
, near Rouen, where the coffin was transferred to ''la Dorade 3'' for carrying further up the Seine, on whose banks people had gathered to pay homage to Napoleon. On 14 December ''la Dorade 3'' moored at Courbevoie in the northwest of Paris.
Reburial
 The date for the reburial was set for 15 December. Victor Hugo evoked this day in his ''Les Rayons et les Ombres'':
:"O frozen sky! and sunlight pure! shining bright in history!
:''Funereal triumph, imperial torch!''
:Let the people's memory hold you forever,
:::Day beautiful as glory,
:::Cold as the tomb
Even as far as London, poems commemorating the event were published; one read in part:
:Ah! Luckless to the nations! Luckless day!
:When from Helena's rock they bore away,
:And gave again to France the mouldering bones
:Of him, beneath whose monarchy the thrones
:Of Earth's huge empires shook-that might one,
:The archon of the world-NAPOLEON!
Despite the temperature never rising above 10 degrees Celsius, the crowd of spectators stretching from the
The date for the reburial was set for 15 December. Victor Hugo evoked this day in his ''Les Rayons et les Ombres'':
:"O frozen sky! and sunlight pure! shining bright in history!
:''Funereal triumph, imperial torch!''
:Let the people's memory hold you forever,
:::Day beautiful as glory,
:::Cold as the tomb
Even as far as London, poems commemorating the event were published; one read in part:
:Ah! Luckless to the nations! Luckless day!
:When from Helena's rock they bore away,
:And gave again to France the mouldering bones
:Of him, beneath whose monarchy the thrones
:Of Earth's huge empires shook-that might one,
:The archon of the world-NAPOLEON!
Despite the temperature never rising above 10 degrees Celsius, the crowd of spectators stretching from the Pont de Neuilly
The Pont de Neuilly (English: Bridge of Neuilly) is a road and rail bridge carrying the Route nationale 13 (N13) and Paris Métro Line 1 which crosses the Seine between the right bank of Neuilly-sur-Seine and Courbevoie and Puteaux on the left b ...
to the Invalides
The Hôtel des Invalides ( en, "house of invalids"), commonly called Les Invalides (), is a complex of buildings in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France, containing museums and monuments, all relating to the military history of France, as ...
was huge. Some houses' rooftops were covered with people. Respect and curiosity won out over irritation, and the biting cold cooled all restlessness in the crowd. Under pale sunlight after snow, the plaster statues and gilded-card ornaments produced an ambiguous effect upon Hugo: "the niggardly clothing the grandiose". Hugo also wrote:
 The cortège arrived at the
The cortège arrived at the Invalides
The Hôtel des Invalides ( en, "house of invalids"), commonly called Les Invalides (), is a complex of buildings in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France, containing museums and monuments, all relating to the military history of France, as ...
around 1:30, and at 2 pm it reached the gate of honour. The king and all France's leading statesmen were waiting in the royal chapel, the Église du Dôme. Joinville was to make a short speech, but nobody had remembered to forewarn him – he contented himself with a sabre salute and the king mumbled a few unintelligible words. '' Le Moniteur'' described the scene as best it could:
 General Atthalin stepped forward, bearing on a cushion the sword that Napoleon had worn at Austerlitz and Marengo, which he presented to Louis-Philippe. The king made a strange, recoiling movement, then turned to Bertrand and said: "General, I charge you with placing the Emperor's glorious sword upon his coffin." Overcome with emotion, Bertrand was unable to complete this task, and Gourgaud rushed over and seized the weapon. The king turned to Gourgaud and said: "General Gourgaud, place the Emperor's sword upon the coffin."
In the course of the funeral ceremony, the Paris Opera's finest singers were conducted by Habeneck in a performance of Mozart's '' Requiem''. The ceremony was more worldly than reverent – the deputies were particularly uncomfortable:
General Atthalin stepped forward, bearing on a cushion the sword that Napoleon had worn at Austerlitz and Marengo, which he presented to Louis-Philippe. The king made a strange, recoiling movement, then turned to Bertrand and said: "General, I charge you with placing the Emperor's glorious sword upon his coffin." Overcome with emotion, Bertrand was unable to complete this task, and Gourgaud rushed over and seized the weapon. The king turned to Gourgaud and said: "General Gourgaud, place the Emperor's sword upon the coffin."
In the course of the funeral ceremony, the Paris Opera's finest singers were conducted by Habeneck in a performance of Mozart's '' Requiem''. The ceremony was more worldly than reverent – the deputies were particularly uncomfortable:
 The bearing of the old Marshal Moncey, the governor of the Invalides, somewhat redeemed the impertinence of the court and the politicians. For a fortnight he had been in agony, pressing his doctor to keep him alive at least to complete his role in the ceremony. At the end of the religious ceremony he managed to walk to the catafalque, sprinkled holy water on it and pronounced as the closing words: "And now, let us go home to die".
From 16 to 24 December, the Église des Invalides, illuminated as on the day of the ceremony, remained open to the public. The people had long disbelieved in Napoleon's death and a rumour spread that the tomb was only a
The bearing of the old Marshal Moncey, the governor of the Invalides, somewhat redeemed the impertinence of the court and the politicians. For a fortnight he had been in agony, pressing his doctor to keep him alive at least to complete his role in the ceremony. At the end of the religious ceremony he managed to walk to the catafalque, sprinkled holy water on it and pronounced as the closing words: "And now, let us go home to die".
From 16 to 24 December, the Église des Invalides, illuminated as on the day of the ceremony, remained open to the public. The people had long disbelieved in Napoleon's death and a rumour spread that the tomb was only a cenotaph
A cenotaph is an empty tomb or a monument erected in honour of a person or group of people whose remains are elsewhere. It can also be the initial tomb for a person who has since been reinterred elsewhere. Although the vast majority of cenot ...
. It was claimed that on St Helena the commission had found only an empty coffin and that the British had secretly sent the body to London for an autopsy; and yet another rumour was that in 1870 the Emperor's mortal remains had been removed from the Invalides to save them from being captured in the Franco-Prussian War and had never been returned. Hugo wrote that, though the actual body was there, the people's good sense was not amiss:
Political failure
The return of the remains had been intended to boost the image of the July Monarchy and to provide a tinge of glory to its organisers, Thiers and Louis-Philippe. Thiers had spotted the rise of the French infatuation with the First Empire that would go on to become the Napoleonic myth. He also thought that returning the remains would seal the new spirit of accord between France and the United Kingdom even though the Egyptian affair was beginning to agitate Europe. As for Louis-Philippe he would be disappointed in his hope to use the remains' return to give additional legitimacy to his monarchy, which was rickety and indifferent to the French people. The great majority of the French, excited by the return of the remains of one whom they had come to see as a martyr, felt betrayed that they had been unable to render him the homage that they had wished. Hence, the government began to fear rioting and took every possible measure to prevent the people from assembling. Accordingly, the cortège had been mostly riverborne and had spent little time in towns outside Paris. In Paris, only important personages were present at the ceremony. Worse, the lack of respect shown by most of the politicians shocked public opinion and revealed a rift between the people and their government. The "retour" also did not prevent France from losing its diplomatic war with the United Kingdom. France was forced to give up supporting its Egyptian ally. Thiers, losing his way in aggressive policies, was ridiculed, and the king was compelled to dismiss him even before ''Belle Poule'' arrived. Thiers had managed to push through the return of the remains but was unable to profit from that success.Monument
In April 1840 the organized a competition in which 81 architects participated, whose projects were exhibited in the recently completed Palais des Beaux-Arts. After a protracted process, Louis Visconti was selected as project architect in 1842 and finalized his design around mid-1843. Visconti created a circular hollow beneath the dome, as a kind of open crypt. At its center is a massive sarcophagus which has often been described as made of red porphyry, including in the ''Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various t ...
'' as of mid-2021, but is actually a purple quartzite from a geological region known as Shoksha, near Lake Onega
Lake Onega (; also known as Onego, rus, Оне́жское о́зеро, r=Onezhskoe ozero, p=ɐˈnʲɛʂskəɪ ˈozʲɪrə; fi, Ääninen, Äänisjärvi; vep, Änine, Änižjärv) is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Repu ...
in Russian Karelia. The sarcophagus rests upon a base of green granite from the Vosges: These quarries were located in the Karelian region of the Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
which then belonged to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
and were under the suzerainty of Tsar Nicholas I of Russia
, house = Romanov-Holstein-Gottorp
, father = Paul I of Russia
, mother = Maria Feodorovna (Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg)
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Gatchina Palace, Gatchina, Russian Empire
, death_date = ...
; the French ended up paying around 200,000 francs for the stones, borne by the French government. That green granite block rests, in turn, upon a slab of black marble, 5.5m x 1.2m x 0.65m, quarried at Sainte-Luce and transported to Paris with great difficulty.
The monument took years to complete, not least because of the exceptional requirements for the stone to be used. The Russian quartzite, intended as an echo of the porphyry used for late Roman imperial burials, was quarried in 1848 upon Tsar Nicholas I's special permission by Italian engineer Giovanni Bujatti, and shipped via Kronstadt
Kronstadt (russian: Кроншта́дт, Kronshtadt ), also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt or Kronštádt (from german: link=no, Krone for " crown" and ''Stadt'' for "city") is a Russian port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city ...
and Le Havre to Paris, where it arrived on 10 January 1849. The sarcophagus was then sculpted by marbler A. Seguin using innovative steam-machinery techniques. It was almost finished by December 1853, but the final stages were delayed by the sudden death of Visconti that month and by Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew ...
's alternative project to move his uncle's resting place to the Basilica of Saint-Denis
The Basilica of Saint-Denis (french: Basilique royale de Saint-Denis, links=no, now formally known as the ) is a large former medieval abbey church and present cathedral in the commune of Saint-Denis, a northern suburb of Paris. The building ...
, which he renounced after having commissioned plans for it from Eugène Viollet-le-Duc.
On 2 April 1861, Napoleon's coffin was transferred from the chapel of Saint-Jérôme, where it had lain since 1840. The transfer was accompanied only by an intimate ceremony: present were the Emperor Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew ...
, Empress Eugénie, the Prince Imperial Napoléon Eugène, other related princes, government ministers and senior officials of the crown.
Sources
* * Arthur Bertrand, ''Lettres sur l’expédition de Sainte-Hélène en 1840'', Paris, Paulin, 1841 * Abbé Félix Coquereau, ''Souvenirs du voyage à Sainte-Hélène'', Paris, H. Delloye, 1841 * Emmanuel de Las Cases, ''Journal écrit à bord de la frégate La Belle Poule'', Paris, H. Delloye, 1841 * Philippe de Rohan-Chabot, ''Les Cinq Cercueils de l’Empereur, souvenirs inédits'', préface de René de Chambrun, Paris, France-Empire, 1985Bibliography
* * * * * * *Notes
External links
The Second Funeral of Napoleon
by Michael Angelo Titmarsh * A succinct chronology by Albert Benhamou {{italic title July Monarchy Napoleon History of Saint Helena Funerals in France 1840 in France December 1840 events Aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars Louis Philippe I