Renault R35 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Renault R35, an abbreviation of ''Char léger Modèle 1935 R'' or R 35, was a French light infantry tank of the
 To save time, Renault based the suspension and running gear on that of the AMR 35 that was designed for the cavalry. It had five wheels at each side, fitted with horizontal leaf springs, like the AMC 35.
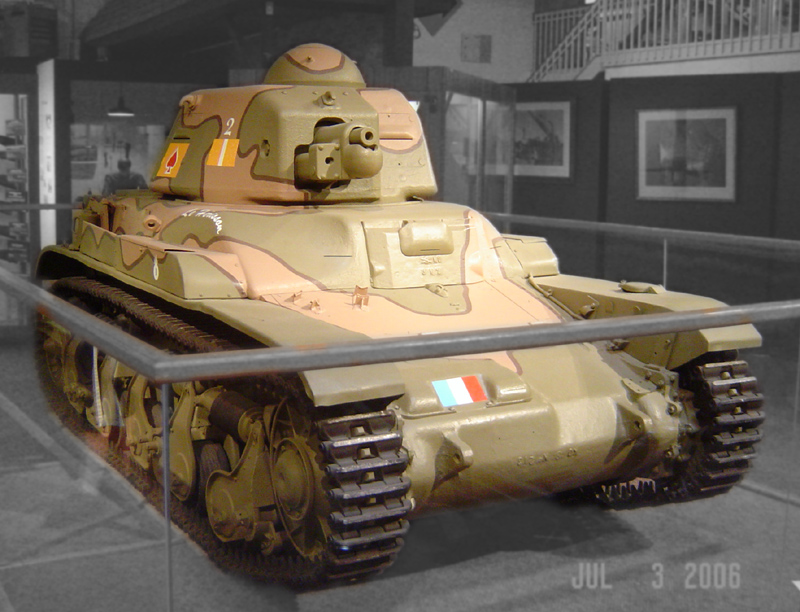
The hull, with a length of 4.02 m, consisted of three cast modules, with a maximum armour thickness of 43 millimetres, that were bolted together. Total weight was 10.6 metric tonnes (9.8 tonnes without fuel and ammunition). The bottom module carried on each side an independently sprung front wheel, two bogies and the driving sprocket at the extreme front. The final drive and differentials were housed at the right in the nose module. It was steered through a Cletrac differential with five gears and by engaging the brakes. The driver was seated somewhat to the left and had two hatches. The Renault V-4 85 hp engine was to the right in the short rear with the self sealing 166 litre fuel tank at its left. It rendered a road speed of 20 km/h and a range of 130 km. Cross-country speed did not exceed 14 km/h and the fuel consumption totaled 212 litre/100 km. From 1940 onward they were fitted with AMX tails to help in trench crossing.
The cast APX hexagonal turret had a 30 mm thick domed rotatable cupola with vertical vision slits (the highest point of 2.13 m) and had to be either hand cranked or moved about by the weight of the commander, the only other crew member. There was sometimes unofficially a seat installed for him but he most often stood. The rear of the turret had a hatch that hinged down that could be used as a seat to improve observation. The earliest vehicles were fitted with the APX-R turret (with the L713 sight) mounting the short Puteaux 37 mm L/21 SA18 gun (the first batches were removed from Renault FT tanks which were then rebuilt as utility vehicles) and the 7.5 mm Châtellerault fortress machine gun. The cannon had a very poor armour penetration: only 12 mm at 500 metres. Afterwards the APX turret with the same cannon but the improved L739 sight and the standard Châtellerault 7.5 mm MAC31 Reibel machine gun was used because of delivery delays of the original weapon. There were also so many delays in the production of the turrets that after the first 380 hulls had been produced in 1936 and only 37 could be fitted with a turret, production was slowed down to 200 annually. The 7.5 mm
To save time, Renault based the suspension and running gear on that of the AMR 35 that was designed for the cavalry. It had five wheels at each side, fitted with horizontal leaf springs, like the AMC 35.
The hull, with a length of 4.02 m, consisted of three cast modules, with a maximum armour thickness of 43 millimetres, that were bolted together. Total weight was 10.6 metric tonnes (9.8 tonnes without fuel and ammunition). The bottom module carried on each side an independently sprung front wheel, two bogies and the driving sprocket at the extreme front. The final drive and differentials were housed at the right in the nose module. It was steered through a Cletrac differential with five gears and by engaging the brakes. The driver was seated somewhat to the left and had two hatches. The Renault V-4 85 hp engine was to the right in the short rear with the self sealing 166 litre fuel tank at its left. It rendered a road speed of 20 km/h and a range of 130 km. Cross-country speed did not exceed 14 km/h and the fuel consumption totaled 212 litre/100 km. From 1940 onward they were fitted with AMX tails to help in trench crossing.
The cast APX hexagonal turret had a 30 mm thick domed rotatable cupola with vertical vision slits (the highest point of 2.13 m) and had to be either hand cranked or moved about by the weight of the commander, the only other crew member. There was sometimes unofficially a seat installed for him but he most often stood. The rear of the turret had a hatch that hinged down that could be used as a seat to improve observation. The earliest vehicles were fitted with the APX-R turret (with the L713 sight) mounting the short Puteaux 37 mm L/21 SA18 gun (the first batches were removed from Renault FT tanks which were then rebuilt as utility vehicles) and the 7.5 mm Châtellerault fortress machine gun. The cannon had a very poor armour penetration: only 12 mm at 500 metres. Afterwards the APX turret with the same cannon but the improved L739 sight and the standard Châtellerault 7.5 mm MAC31 Reibel machine gun was used because of delivery delays of the original weapon. There were also so many delays in the production of the turrets that after the first 380 hulls had been produced in 1936 and only 37 could be fitted with a turret, production was slowed down to 200 annually. The 7.5 mm

 * VIIe Armée
** GBC 510
*** 9eBCC (R 35)
*** 22BCC (R 35)
* Ie Armée
** GBC 515
*** 13BCC ( H 35)
*** 35BCC (R 35)
** GBC 519
*** 38BCC (H 35)
*** 39BCC (R 35)
* IXe Armée
** GBC 518
*** 6eBCC (R 35)
*** 32BCC (R 35)
*** 33BCC (FT)
* IIe Armée
** GBC 503
*** 3eBCC (R 35)
*** 4eBCC (FCM 36)
*** 7eBCC (FCM 36)
* IIIe Armée
** GBC 511
*** 5eBCC (R 35)
*** 12BCC (R 35)
** GBC 513
*** 29BCC (FT)
*** 51BCC (
* VIIe Armée
** GBC 510
*** 9eBCC (R 35)
*** 22BCC (R 35)
* Ie Armée
** GBC 515
*** 13BCC ( H 35)
*** 35BCC (R 35)
** GBC 519
*** 38BCC (H 35)
*** 39BCC (R 35)
* IXe Armée
** GBC 518
*** 6eBCC (R 35)
*** 32BCC (R 35)
*** 33BCC (FT)
* IIe Armée
** GBC 503
*** 3eBCC (R 35)
*** 4eBCC (FCM 36)
*** 7eBCC (FCM 36)
* IIIe Armée
** GBC 511
*** 5eBCC (R 35)
*** 12BCC (R 35)
** GBC 513
*** 29BCC (FT)
*** 51BCC (

 The majority (843) of R35s fell into German hands; 131 were used as such as ''Panzerkampfwagen 35R 731 (f)'', issued to panzer units and mainly used for security duties or driver training, or used on armoured trains; most were later rebuilt as artillery tractors and ammunition carriers after removing the turret.
A considerable number, 174 according to some sources, were converted into a 47 mm tank destroyer to replace the
The majority (843) of R35s fell into German hands; 131 were used as such as ''Panzerkampfwagen 35R 731 (f)'', issued to panzer units and mainly used for security duties or driver training, or used on armoured trains; most were later rebuilt as artillery tractors and ammunition carriers after removing the turret.
A considerable number, 174 according to some sources, were converted into a 47 mm tank destroyer to replace the  Some of the turrets removed from the tanks were used on defensive fighting positions known as "Tobruks". This gave the Tobruk enhanced firepower and the gunner protection from shrapnel and small arms.
Fourteen R 35 tanks, used to train tank drivers, equipped the ''100. Panzer-Ersatz-Bataillon'' (100th Panzer Replacement Battalion) in the German Seventh Army in 1944. On 6 June 1944, they were among the first ''Armee-Reserve'' units sent into combat near
Some of the turrets removed from the tanks were used on defensive fighting positions known as "Tobruks". This gave the Tobruk enhanced firepower and the gunner protection from shrapnel and small arms.
Fourteen R 35 tanks, used to train tank drivers, equipped the ''100. Panzer-Ersatz-Bataillon'' (100th Panzer Replacement Battalion) in the German Seventh Army in 1944. On 6 June 1944, they were among the first ''Armee-Reserve'' units sent into combat near
 The R 35 saw combat in Syrian hands when five R 35s took part in an unsuccessful Syrian Army attack on the
The R 35 saw combat in Syrian hands when five R 35s took part in an unsuccessful Syrian Army attack on the
WWII Vehicles
*
Chars-francais.net
*
1939.pl
{{WWIIRomanianAFVs World War II tanks of France Light tanks of France Military vehicles introduced in the 1930s R35 Vehicles introduced in 1936
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
.
Designed from 1933 onwards and produced from 1936, the type was intended as an infantry support light tank, equipping autonomous tank battalions, that would be allocated to individual infantry divisions to assist them in executing offensive operations. To this end it was relatively well-armoured but slow and lacking a good antitank-capacity, fitted with a short 37 mm gun. At the outbreak of the war, the antitank-role was more emphasized leading to the development and eventual production from April 1940 of a subtype with a more powerful longer gun, the Renault R40. It was planned to shift new production capacity to the manufacture of other, faster, types, but due to the defeat of France the R35/40 remained the most numerous French tank of the war, about 1685 vehicles having been produced by June 1940. At that moment it had also been exported to Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
. For the remainder of the war Germany and its allies would use captured vehicles, some of them rebuilt into tank destroyers.
Development
The development plan of 1926 foresaw the introduction of a ''char d'accompagnement'', a cheap mass-produced light tank to replace theRenault FT
The Renault FT (frequently referred to in post-World War I literature as the FT-17, FT17, or similar) was a French light tank that was among the most revolutionary and influential tank designs in history. The FT was the first production tank to ...
of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
vintage, to make it possible for the standard infantry divisions to execute combined arms
Combined arms is an approach to warfare that seeks to integrate different combat arms of a military to achieve mutually complementary effects (for example by using infantry and armour in an urban environment in which each supports the other) ...
infiltration tactics
In warfare, infiltration tactics involve small independent light infantry forces advancing into enemy rear areas, bypassing enemy frontline strongpoints, possibly isolating them for attack by follow-up troops with heavier weapons. Soldiers ...
, seen as the only viable method of modern offensive warfare left for non-motorised units. The French army did not have the means to motorise more than a few select divisions. In 1930 this plan was replaced by a new one, giving more precise specifications. The first tank to be developed to fulfil its requirements, the Char D1
The Char D1 was an Interwar French light tank.
The French plan of 1926, calling for the creation of a Light Infantry Support Tank, led to the development of the existing Renault NC1 prototype into the Char D1. One hundred and sixty vehicles of t ...
, proved to be neither cheap nor particularly light. In 1933, '' Hotchkiss'' offered an alternative solution, the later Hotchkiss H35. For political reasons this proposal was turned into the ''Plan 1933'' and the whole of French industry was in August 1933 invited to propose possible designs. Fourteen companies responded (among which '' Delaunay-Belleville'') and five submitted a prototype: ''Hotchkiss'' itself, the '' Compagnie Général de Construction des Locomotives'', APX, FCM and of course France's prime tank producer: Renault
Groupe Renault ( , , , also known as the Renault Group in English; legally Renault S.A.) is a French multinational automobile manufacturer established in 1899. The company produces a range of cars and vans, and in the past has manufacture ...
. Fearing that his rival Hotchkiss might well replace him as such, Louis Renault hurried to finish a vehicle; construction was soon in such an advanced stage that the changes in specification issued on 21 June 1934, to increase armour thickness from 30 to 40 mm, could not be implemented. On 20 December 1934 Renault was the first to deliver a prototype, with the project name of Renault ZM, to the ''Commission de Vincennes''.
In the spring of 1935 this vehicle was refitted with heavier armour and a standard APX turret, attached by the ''Atelier de Rueil'' between 18 and 25 April. The prototype was still being tested when international tensions increased due to German re-armament
German rearmament (''Aufrüstung'', ) was a policy and practice of rearmament carried out in Germany during the interwar period (1918–1939), in violation of the Treaty of Versailles which required German disarmament after WWI to prevent Germa ...
. This prompted an urgent demand for swifter modernisation of the French tank fleet. The ZM was to be put into production immediately. On 29 April 1935 an order of 300 was made, even before the final model could be finished, at a price of 190,000 French franc
The franc (, ; sign: F or Fr), also commonly distinguished as the (FF), was a currency of France. Between 1360 and 1641, it was the name of coins worth 1 livre tournois and it remained in common parlance as a term for this amount of money. It w ...
per hull (unarmed, without the engine and turret, the overall export price was ca. 1,400,000 francs in 1939, that is ca. 32,000 dollars by 1939 standards).The 190,000 FF price (for the complete hull only: the turret added another 100,000), despite being very low when compared in dollars to other tanks of the epoch, is comparable to many similar prices in other French tank contracts. In 1935 there had been for many years a strong deflation of the dollar, making it very strong against the franc. In addition, this was from 1936 worsened by a deliberate French policy of devaluation until the FF was fixed against the dollar on 9 September 1939 at a 43.8 to 1 rate. These exchange rates did not reflect internal value though: they were an artificial instrument to stimulate French exports. This explains how the French were able to produce the entire R 35 at about 500,000 FF in 1939: the real value of the materials and labour used, was about $30,000, not $12,000, as the franc was undervalued about 2.5 times. The export price was realistic though and did not reflect the lower prices for raw materials France was able to obtain from its colonies. The first series production vehicle was delivered on 4 June 1936 and had to be extensively tested again as it was different from the prototype.
Description
 To save time, Renault based the suspension and running gear on that of the AMR 35 that was designed for the cavalry. It had five wheels at each side, fitted with horizontal leaf springs, like the AMC 35.
The hull, with a length of 4.02 m, consisted of three cast modules, with a maximum armour thickness of 43 millimetres, that were bolted together. Total weight was 10.6 metric tonnes (9.8 tonnes without fuel and ammunition). The bottom module carried on each side an independently sprung front wheel, two bogies and the driving sprocket at the extreme front. The final drive and differentials were housed at the right in the nose module. It was steered through a Cletrac differential with five gears and by engaging the brakes. The driver was seated somewhat to the left and had two hatches. The Renault V-4 85 hp engine was to the right in the short rear with the self sealing 166 litre fuel tank at its left. It rendered a road speed of 20 km/h and a range of 130 km. Cross-country speed did not exceed 14 km/h and the fuel consumption totaled 212 litre/100 km. From 1940 onward they were fitted with AMX tails to help in trench crossing.
The cast APX hexagonal turret had a 30 mm thick domed rotatable cupola with vertical vision slits (the highest point of 2.13 m) and had to be either hand cranked or moved about by the weight of the commander, the only other crew member. There was sometimes unofficially a seat installed for him but he most often stood. The rear of the turret had a hatch that hinged down that could be used as a seat to improve observation. The earliest vehicles were fitted with the APX-R turret (with the L713 sight) mounting the short Puteaux 37 mm L/21 SA18 gun (the first batches were removed from Renault FT tanks which were then rebuilt as utility vehicles) and the 7.5 mm Châtellerault fortress machine gun. The cannon had a very poor armour penetration: only 12 mm at 500 metres. Afterwards the APX turret with the same cannon but the improved L739 sight and the standard Châtellerault 7.5 mm MAC31 Reibel machine gun was used because of delivery delays of the original weapon. There were also so many delays in the production of the turrets that after the first 380 hulls had been produced in 1936 and only 37 could be fitted with a turret, production was slowed down to 200 annually. The 7.5 mm
To save time, Renault based the suspension and running gear on that of the AMR 35 that was designed for the cavalry. It had five wheels at each side, fitted with horizontal leaf springs, like the AMC 35.
The hull, with a length of 4.02 m, consisted of three cast modules, with a maximum armour thickness of 43 millimetres, that were bolted together. Total weight was 10.6 metric tonnes (9.8 tonnes without fuel and ammunition). The bottom module carried on each side an independently sprung front wheel, two bogies and the driving sprocket at the extreme front. The final drive and differentials were housed at the right in the nose module. It was steered through a Cletrac differential with five gears and by engaging the brakes. The driver was seated somewhat to the left and had two hatches. The Renault V-4 85 hp engine was to the right in the short rear with the self sealing 166 litre fuel tank at its left. It rendered a road speed of 20 km/h and a range of 130 km. Cross-country speed did not exceed 14 km/h and the fuel consumption totaled 212 litre/100 km. From 1940 onward they were fitted with AMX tails to help in trench crossing.
The cast APX hexagonal turret had a 30 mm thick domed rotatable cupola with vertical vision slits (the highest point of 2.13 m) and had to be either hand cranked or moved about by the weight of the commander, the only other crew member. There was sometimes unofficially a seat installed for him but he most often stood. The rear of the turret had a hatch that hinged down that could be used as a seat to improve observation. The earliest vehicles were fitted with the APX-R turret (with the L713 sight) mounting the short Puteaux 37 mm L/21 SA18 gun (the first batches were removed from Renault FT tanks which were then rebuilt as utility vehicles) and the 7.5 mm Châtellerault fortress machine gun. The cannon had a very poor armour penetration: only 12 mm at 500 metres. Afterwards the APX turret with the same cannon but the improved L739 sight and the standard Châtellerault 7.5 mm MAC31 Reibel machine gun was used because of delivery delays of the original weapon. There were also so many delays in the production of the turrets that after the first 380 hulls had been produced in 1936 and only 37 could be fitted with a turret, production was slowed down to 200 annually. The 7.5 mm machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles) ar ...
's spent cartridges (from a total of 2,400) went down a chute through a hole in the floor. The tank carried 42 armour piercing and 58 high explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An ...
rounds.
The R 35 at first had no radio, except for the second battalion of the ''507e Régiment de Chars de Combat'' (of Charles de Gaulle), but the R 40 had the ER 54 installed. However, this added to the already heavy task load of the commander, who also acted as gunner and loader.
Renault R40 and projects
In 1937 it had become obvious the original suspension system was unreliable and ineffective. After many trials it was replaced in the 1940 production run, after the 1540 vehicles had been built with the original design, by an AMX system using twelve wheels fitted with six vertical springs (AMX was the new name of the military division of Renault nationalised on 2 December 1936). About the same time the radio and a much more powerful gun were introduced. The long-barrelled L/35 37 mm SA38 in the adapted cast APX-R1 turret (with L767 sight) gave it an effective anti-tank capacity: 40 mm at 500 metres. The new combination was named the ''Char léger modèle 1935 R modifié 1939'' but is more commonly known as the Renault R40. It was delivered in time to equip one battalion of the Polish 10th Armoured Cavalry Brigade of the Polish Army in France and the last two French tank battalions to be formed. It was intended to fit the R 40 with the welded FCM turret in the second half of 1940, while refitting all existing R 35s with the longer SA 38 gun and bringing R 40 production levels up to 120 per month for the duration of the war. From January 1940, the vehicles of light tank unit commanders were gradually uparmed with the longer gun; but as absolute priority was given to tanks serving in armoured divisions, which were of the Hotchkiss type, of the 273 platoon, company and battalion commanders eligible in Renault units, only a few if any received this "R 39". The only official possible exception to the rule that Hotchkiss tanks had to be modified first was made on 12 February 1940 when it was ordered to replace the turrets of 24 Infantry tanks, without specifying the type, present in depot or driver schools in order to obtain older turrets to be fitted on R 35 export vehicles. In the same period a crash programme was executed to produce 200,000 armour piercing rounds per month for the shorter gun, as there had been only minimal stocks of this ammunition type. Several projects were based on the R 35 such as a number offascine
A fascine is a rough bundle of brushwood or other material used for strengthening an earthen structure, or making a path across uneven or wet terrain. Typical uses are protecting the banks of streams from erosion, covering marshy ground and so ...
carriers: these had frames or other contraptions mounted over the hull or turret with a fascine in them that could be dropped to fill trenches.
Operational history
The R35 was intended to replace the Renault FT as standard light infantry tank from the summer of 1936, but even by May 1940 not enough conscripts had been retrained and therefore eight battalions of the older tank had to be kept operational. On 1 September 1939, at the outbreak of war, 975 vehicles had been delivered out of 1070 produced; 765 were fielded by tank battalions in France, 49 used for drive training, 33 were in depot and 45 present in the colonies. Of a total order for 2,300 at least 1,601 had been produced until 1 June 1940 — the numbers for that month are lacking — of which 245 had been exported: to Poland (50), Turkey (100; two batches of fifty each in February and March 1940), Romania (41 from an order for 200), and Yugoslavia (54). It is likely that the tanks exported to Yugoslavia (in April 1940) are not included under the 1,601 total and that overall production was 1,685; serial numbers known to be actually used indicate a production of at least 1670 vehicles.Poland
As the threat of war became apparent and the production rate of Polish 7TP tank was insufficient, it was decided to buy vehicles abroad. Poles were most interested in FrenchSOMUA S35
The SOMUA S35 was a French cavalry tank of the Second World War. Built from 1936 until 1940 to equip the armoured divisions of the Cavalry, it was for its time a relatively agile medium-weight tank, superior in armour and armament to its Frenc ...
tanks, but the proposal was refused by the French government. In 1938 the Polish Army bought one (according to other sources, two or three) R35 tank for testing. After a series of tests it was found that the design was disappointing: the engine was overheating, the suspension was tough, and armament insufficient. In April 1939 it was finally decided to buy a hundred R35 tanks as an emergency measure. The first shipment of fifty (other sources lower the number to 49) arrived in Poland in July 1939, along with three Hotchkiss H35 tanks bought for testing. In August they were mostly put into service with the Łuck
Lutsk ( uk, Луцьк, translit=Lutsk}, ; pl, Łuck ; yi, לוצק, Lutzk) is a city on the Styr River in northwestern Ukraine. It is the administrative center of the Volyn Oblast (province) and the administrative center of the surrounding L ...
-based 12th Armoured Battalion. At the beginning of the Invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week aft ...
45 (or 46) tanks formed the core of the newly created 21st Light Tank Battalion that was part of the general reserve of the Commander in Chief. The unit was to defend the Romanian Bridgehead
__NOTOC__
The Romanian Bridgehead ( pl, Przedmoście rumuńskie; ro, Capul de pod român) was an area in southeastern Poland that is now located in Ukraine. During the invasion of Poland in 1939 at the start of the Second World War), the Polish ...
, but was divided after the Soviet invasion of Poland of 17 September. Late September the unit was withdrawn to defend the Romanian Bridgehead
__NOTOC__
The Romanian Bridgehead ( pl, Przedmoście rumuńskie; ro, Capul de pod român) was an area in southeastern Poland that is now located in Ukraine. During the invasion of Poland in 1939 at the start of the Second World War), the Polish ...
. Subsequently, 34 tanks were withdrawn to Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
. Six tanks were attached to the 10th Motorized Cavalry Brigade in Stanisławów (today Ivano-Frankivsk); they forced their way through Kolomyia and three vehicles crossed the Hungarian border. The remaining tanks - four R35s and three H35s - were put into service with the improvised ''Dubno'' Operational Group
{{Unreferenced, date=October 2008
Operational Group ( pl, Grupa Operacyjna, abbreviated GO) was the highest level of tactical division of the Polish Army before and during World War II and the invasion of Poland. It was corps-sized, although variou ...
and took part in the battles of Krasne on 19 September (with the Soviets) and Kamionka Strumiłowa (with the Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
), during which all were destroyed. The second shipment of R35s did not reach Poland prior to the outbreak of World War II. They were diverted by the French to Syria.
Romania
As part of a rearmament program of the late 1930s,Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
sought to obtain a license for the local manufacture of two hundred French Renault R35 infantry tanks. By early 1938, negotiations for establishing a factory for the production of R35 tanks had reached an advanced state. By this time France's own demands for rearmament prohibited further development, however. In August and September 1939, as a stopgap measure, forty-one R35s were supplied to the Royal Romanian Army. These tanks served as the principal tank of the newly formed 2nd Armoured Regiment. At the end of September 1939, an additional thirty-four brand new R35s passed into Romanian hands when the Polish 21st Light Tank Battalion (''Batalion Czołgów Lekkich'', or BCL) chose internment over capture following the German conquest of Poland and fled over the Romanian border. With seventy-five tanks on strength, the 2nd Armoured Regiment expanded into two battalions.
After the Battle of Stalingrad, the Romanians decided that the R 35s required significant improvement of their anti-tank capacity. At first, the turret of an R 35 of the 2nd Tank Regiment of the 1st Tank Division was swapped for the turret of a captured Soviet T-26
The T-26 tank was a Soviet light tank used during many conflicts of the Interwar period and in World War II. It was a development of the British Vickers 6-Ton tank and was one of the most successful tank designs of the 1930s until its light ...
. Ultimately, at the beginning of 1943, it was decided to keep the thicker armor of the French turret. Thus, the 45 mm gun of the T-26 was adopted as a replacement for the original 37 mm gun. The Soviet gun was attached to the French turret with the help of an extension which contained the recoil mechanism of the 45 mm piece. The downside to this was that, following these modifications, there was no longer enough space in the turret to keep the coaxial machine gun, which was thus removed. A Romanian-produced 47 mm Schneider gun was also proposed. The upgraded tanks were adopted as tank destroyers under the designation ''Vânătorul de care R35'' (VDC 35; meaning "R35 tank hunter"), with thirty R35s converted until June 1944 by the Leonida factory in Bucharest. The Soviet 45 mm guns were taken from captured T-26 and BT-7 tanks. They were refurbished at the Army Arsenal in Târgoviște while the new gun mounts containing the recoil mechanism were made at the Concordia Works in Ploiești
Ploiești ( , , ), formerly spelled Ploești, is a city and county seat in Prahova County, Romania. Part of the historical region of Muntenia, it is located north of Bucharest.
The area of Ploiești is around , and it borders the Blejoi commune ...
. These vehicles served until the end of the war. A significant amount of the original French-made parts, from both the original and converted R35 tanks, was replaced by Romanian-produced spares in 1941-1942. Romanian factories produced drive sprocket
A sprocket, sprocket-wheel or chainwheel is a profiled wheel with teeth that mesh with a roller chain, chain, Caterpillar track, track or other perforated or indented material. The name 'sprocket' applies generally to any wheel upon which radial ...
s, drive shafts, tracks, new metal-rimmed road wheels and cylinder heads
In an internal combustion engine, the cylinder head (often abbreviated to simply "head") sits above the cylinders and forms the roof of the combustion chamber.
In sidevalve engines, the head is a simple sheet of metal; whereas in more modern ove ...
. The wheels were designed locally to be ten times more durable. Added to these were the gun mounts for the 45 mm guns, added as turret extensions, which contained the recoil mechanism. Thus, the Romanian-converted R35 had significant Romanian-manufactured parts in its hull, transmission and turret.
There were sixty R35 tanks in the Romanian inventory on 19 July 1944, thirty of which had been rearmed with 45 mm guns.
The only surviving part of a VDC R35 is a turret owned by a private collector from Slovakia.
France
On 10 May 1940, on the eve of the German invasion, in mainland France the R 35 equipped 21 battalions, each fielding 45 vehicles. This gave 945 R 35/R 40 tanks in the French front line units. Of these, 900 were originally allocated at Army level in ''Groupements de Bataillons de Chars'' consisting of several battalions:
 * VIIe Armée
** GBC 510
*** 9eBCC (R 35)
*** 22BCC (R 35)
* Ie Armée
** GBC 515
*** 13BCC ( H 35)
*** 35BCC (R 35)
** GBC 519
*** 38BCC (H 35)
*** 39BCC (R 35)
* IXe Armée
** GBC 518
*** 6eBCC (R 35)
*** 32BCC (R 35)
*** 33BCC (FT)
* IIe Armée
** GBC 503
*** 3eBCC (R 35)
*** 4eBCC (FCM 36)
*** 7eBCC (FCM 36)
* IIIe Armée
** GBC 511
*** 5eBCC (R 35)
*** 12BCC (R 35)
** GBC 513
*** 29BCC (FT)
*** 51BCC (
* VIIe Armée
** GBC 510
*** 9eBCC (R 35)
*** 22BCC (R 35)
* Ie Armée
** GBC 515
*** 13BCC ( H 35)
*** 35BCC (R 35)
** GBC 519
*** 38BCC (H 35)
*** 39BCC (R 35)
* IXe Armée
** GBC 518
*** 6eBCC (R 35)
*** 32BCC (R 35)
*** 33BCC (FT)
* IIe Armée
** GBC 503
*** 3eBCC (R 35)
*** 4eBCC (FCM 36)
*** 7eBCC (FCM 36)
* IIIe Armée
** GBC 511
*** 5eBCC (R 35)
*** 12BCC (R 35)
** GBC 513
*** 29BCC (FT)
*** 51BCC (Char 2C
The Char 2C, also known as the FCM 2C, was a French heavy tank, later also seen as a super-heavy tank. It was developed during World War I but not deployed until after the war. It was, in total volume or physical dimensions, the largest operat ...
)
** GBC 520
*** 23BCC (R 35)
*** 30BCC (FT)
** GBC 532
*** 43BCC (R 35)
* IVe Armée
** GBC 502
*** 20BCC (R 35)
*** 24BCC (R 35)
** GBC 504
*** 10BCC (R 35)
*** 343 CAC (FT)
*** 344 CAC (FT)
* Ve Armée
** GBC 501
*** 1rBCC (R 35)
*** 2eBCC (R 35)
*** 31BCC (FT)
** GBC 508
*** 21BCC (R 35)
*** 34BCC (R 35)
** GBC 517
*** 19BCC (Char D2
The Char D2 was a French medium tank of the interwar period.
In 1930, at a time the Char D1 had not even entered production, the Renault company agreed to build a better armoured version called the Char D2. By not using old-fashioned rivets, it ...
)
* VIIIe Armée
** GBC 506
*** 16BCC (R 35)
*** 36BCC (FT)
*** 17BCC (R 35)
*** 18BCC (FT)
* Armée des Alpes
** GBC 514
*** Bataillon de Chars des Troupes Coloniales (FT)
These pure tank units had no organic infantry or artillery component and thus had to cooperate with infantry divisions. However, 135 R35s (2, 24 and the new 44 BCC) were allocated on 15 May to the provisional 4th DCR (''Division Cuirassée''). Two more new battalions, the 40th and 48th ''Bataillion de Chars de Combat'', though still not having completed training, were used to reinforce 2nd DCR, the first equipped with 15 R35s and 30 R40s, the second with 16 R35s and 29 R40s bringing the total organic strength to 1035. In addition the 1st and 2nd Tank Battalion of the Polish 10th Armoured Cavalry Brigade, at first training with Renault FTs, were equipped with 17 R35s and about 24 R40s in late May; in June the R40s had been given back but replaced by 28 new ones. At the same time 1, 6, 25, 34 and 39 BCC were used to reconstitute 1DCR, 10 BCC reinforced 3DCR and 25 BCC was reconstituted with 21 R35s and 24 (ex-Polish) R40s. As about 300 tanks from the materiel reserve were issued to these units as well, around 800 of the 1440 available R35s ended up in armoured divisions after all.
French colonies
Two R35 battalions (63 and 68 BCC) with 45 and 50 tanks respectively were in Syria, a Frenchmandate territory
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for adminis ...
, and 30 were in Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
, 26 serving with 62 BCC and four in depot. The tanks in Syria would fight during the allied invasion of that mandate territory in 1941 and then partly be taken over by the Free French
Free France (french: France Libre) was a political entity that claimed to be the legitimate government of France following the dissolution of the Third Republic. Led by French general , Free France was established as a government-in-exile ...
''1e CCC'', those in North Africa during Operation Torch in November 1942.
Germany

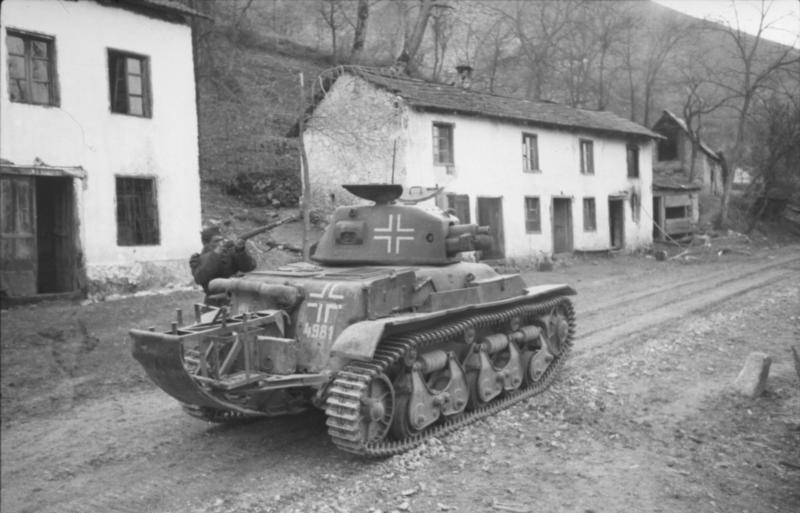
 The majority (843) of R35s fell into German hands; 131 were used as such as ''Panzerkampfwagen 35R 731 (f)'', issued to panzer units and mainly used for security duties or driver training, or used on armoured trains; most were later rebuilt as artillery tractors and ammunition carriers after removing the turret.
A considerable number, 174 according to some sources, were converted into a 47 mm tank destroyer to replace the
The majority (843) of R35s fell into German hands; 131 were used as such as ''Panzerkampfwagen 35R 731 (f)'', issued to panzer units and mainly used for security duties or driver training, or used on armoured trains; most were later rebuilt as artillery tractors and ammunition carriers after removing the turret.
A considerable number, 174 according to some sources, were converted into a 47 mm tank destroyer to replace the Panzerjäger I
The Panzerjäger I ("English: tank hunter number 1") was the first German ''panzerjäger'' (a self-propelled anti-tank gun, or "tank destroyer") to see service in the Second World War. All mounted the Czech Škoda-built 4.7 cm KPÚV vz. 38 (Ge ...
: the ''4,7 cm PaK(t) auf Panzerkampfwagen 35R(f) ohne Turm''. The tank destroyer version had the turret replaced with an armoured superstructure mounting a 47mm kanon P.U.V. vz. 36 (Škoda A6) anti-tank gun. The vehicles were converted by Alkett between May to October 1941 to try and make an equivalent vehicle to the Panzerjäger I. The result was not as successful as the Panzerjäger I, mainly due to the slow speed of the R 35 and the overloaded chassis. A few were deployed in Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
, most were deployed in occupied territories, such as the Channel Islands
The Channel Islands ( nrf, Îles d'la Manche; french: îles Anglo-Normandes or ''îles de la Manche'') are an archipelago in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two Crown Dependencies: the Bailiwick of Jersey, ...
, The Netherlands (with Pz.Jg.Abt.657, part of Pz Kompanie 224) and France. They fought in the battles for Normandy with ''Schnelle Brigade 30'' in 1944 (five attached to the 3rd company, ''Schnelle Abteilung 517''), and around Arnhem
Arnhem ( or ; german: Arnheim; South Guelderish: ''Èrnem'') is a city and municipality situated in the eastern part of the Netherlands about 55 km south east of Utrecht. It is the capital of the province of Gelderland, located on both ban ...
with Pz.Jg.Abt. 657. Other possible users include 346 Inf. Div. in Normandy and 59th Inf. Div who fought the 101st Airborne during Operation Market Garden.
Sainte-Mère-Église
Sainte-Mère-Église () is a commune in the northwestern French department of Manche, in Normandy. On 1 January 2016, the former communes of Beuzeville-au-Plain, Chef-du-Pont, Écoquenéauville and Foucarville were merged into Sainte-Mère-Ég ...
to oppose the American airborne landings in Normandy
The U.S. airborne landings in Normandy were the first U.S. combat operations during Operation Overlord, the invasion of Normandy by the Western Allies on June 6, 1944, during World War II. Around 13,100 American paratroopers of the 82nd and 1 ...
. Supporting a counterattack by the 1057th Grenadier Regiment, R35s penetrated the command post of the U.S. 1st Battalion 505th Parachute Infantry Regiment
The 505th Parachute Infantry Regiment (505th PIR), originally the 505th Infantry Regiment, is an airborne infantry regiment of the United States Army, one of four infantry regiments of the 82nd Airborne Division of the United States Army, with ...
before being destroyed by bazooka
Bazooka () is the common name for a man-portable recoilless anti-tank rocket launcher weapon, widely deployed by the United States Army, especially during World War II. Also referred to as the "stovepipe", the innovative bazooka was among the ...
fire.
Italy
The Royal Italian Army received 124 R35s with which the 4th Tank Infantry Regiment formed two battalions. The two battalions were assigned to the 131st Tank Infantry Regiment, which was deployed in January 1942 toSicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
. There, the regiment's CI Tank Battalion "R35" was assigned to the XII Army Corps defending the island's West, while the regiment with the CII Tank Battalion "R35" joined the XVI Army Corps defending the island's South. It used some of its R35s in defence
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense indus ...
of Gela
Gela (Sicilian and ; grc, Γέλα) is a city and (municipality) in the Autonomous Region of Sicily, Italy; in terms of area and population, it is the largest municipality on the southern coast of Sicily. Gela is part of the Province of Ca ...
on Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
against US Rangers
United States Army Rangers, according to the US Army's definition, are personnel, past or present, in any unit that has the official designation "Ranger". The term is commonly used to include graduates of the US Army Ranger School, even if t ...
. 5th Battalion, East Yorkshire Regiment was attacked by five R35s as it advanced towards Sortino
Sortino ( Sicilian: ''Sciurtinu'') is a town and '' comune'' in the Province of Syracuse, Sicily ( Italy). It is located in the Anapo river valley.
The Necropolis of Pantalica, part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site of "Syracuse and the Roc ...
; four were quickly knocked out but the fifth drove right through the battalion and carried on until it was knocked out by a 105 mm self-propelled gun near Floridia
Floridia (; scn, Ciuriḍḍia ; from Latin "day of Flora" or the adjective ''floridus'' "florid") is a town and ''comune'' in the Province of Syracuse, Sicily (Italy).
Geography
Floridia lies west of Syracuse. Its principal industries are ...
.
Other forces during the Second World War
Some of the tanks that Germany captured were given or sold to Germany's allies:Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
received about forty.
Three Polish vehicles in late 1939 found their way to Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
.
During the Syria-Lebanon Campaign, the Australian 2/6th Cavalry Commando Regiment's 'A' Squadron used four R35s that had been captured from the Vichy French.
Switzerland took over twelve R 35s that had fled from France.
After the German victory over Yugoslavia in 1941, the Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia ( sh, Nezavisna Država Hrvatska, NDH; german: Unabhängiger Staat Kroatien; it, Stato indipendente di Croazia) was a World War II-era puppet state of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. It was established in p ...
took over some R35s that had not been destroyed when fighting ''11. Panzerdivision'' on 13 and 14 April.
Syria and Lebanon
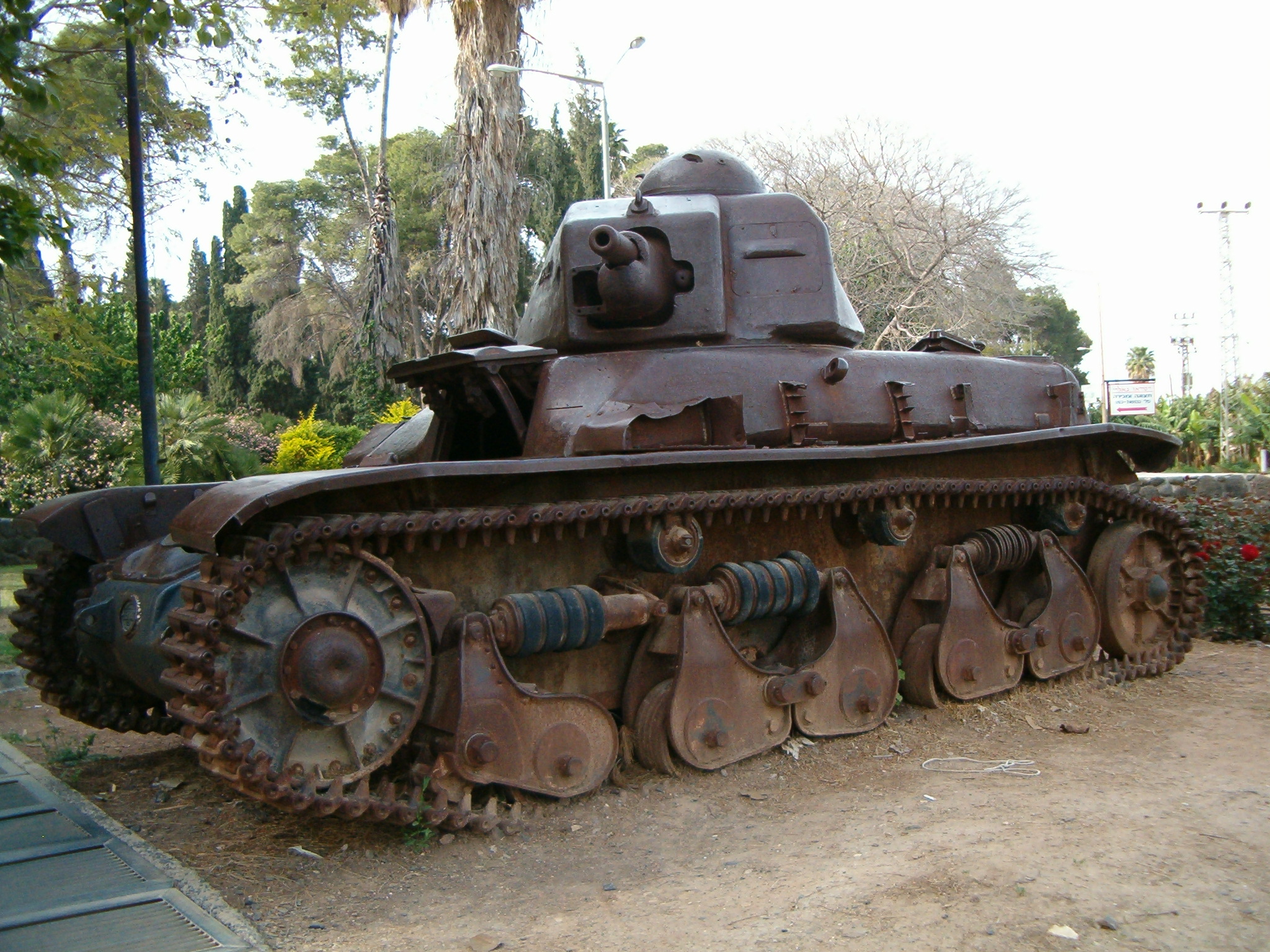
 The R 35 saw combat in Syrian hands when five R 35s took part in an unsuccessful Syrian Army attack on the
The R 35 saw combat in Syrian hands when five R 35s took part in an unsuccessful Syrian Army attack on the Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
kibbutz Degania Alef in the Galilee on 20 May 1948. The kibbutz defenders, armed with a 20 mm anti-tank gun and Molotov cocktail
A Molotov cocktail (among several other names – ''see other names'') is a hand thrown incendiary weapon constructed from a frangible container filled with flammable substances equipped with a fuse (typically a glass bottle filled with fla ...
s, managed to knock out three R 35s, causing the remaining forces to retreat. One of the disabled R 35s remains near the kibbutz today as a memorial of the 1947–1949 Palestine war. A 1991 IDF probe proved that this R35 had been knocked out by a PIAT
The Projector, Infantry, Anti Tank (PIAT) Mk I was a British man-portable anti-tank weapon developed during the Second World War. The PIAT was designed in 1942 in response to the British Army's need for a more effective infantry anti-tank weapon ...
round.
The Lebanese Army also incorporated a number of R 35s. Some of the Lebanese vehicles had been rebuilt with a British 40 mm Ordnance QF 2-pounder
The Ordnance QF 2-pounder ( QF denoting "quick firing"), or simply "2 pounder gun", was a British anti-tank gun and vehicle-mounted gun employed in the Second World War.
It was the main anti-tank weapon of the artillery units in the Battle o ...
gun, seeing action in the 1958 Lebanon crisis
The 1958 Lebanon crisis (also known as the Lebanese Civil War of 1958) was a political crisis in Lebanon caused by political and religious tensions in the country that included a United States military intervention. The intervention lasted for aro ...
.
Postwar France
Some R 35s served after the war in the Gendarmerie, as "R 39s" refitted with SA 38 guns. They were phased out from 1951 in favour of the Sherman tank.See also
* Tanks in FranceReferences
Literature
Pascal Danjou, 2005, ''Renault R35/R40'', Editions du Barbotin, BallainvilliersExternal links
WWII Vehicles
*
Chars-francais.net
*
1939.pl
{{WWIIRomanianAFVs World War II tanks of France Light tanks of France Military vehicles introduced in the 1930s R35 Vehicles introduced in 1936