Renault FT on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Renault FT (frequently referred to in post-World War I literature as the FT-17, FT17, or similar) was a French light tank that was among the most revolutionary and influential tank designs in history. The FT was the first production
 It is thought possible that Louis Renault began working on the idea as early as 21 December 1915, after a visit from Colonel J. B. E. Estienne. Estienne had drawn up plans for a tracked armoured vehicle based on the Holt caterpillar tractor, and, with permission from General Joffre, approached Renault as a possible manufacturer. Renault declined, saying that his company was operating at full capacity producing war materiel and that he had no experience of tracked vehicles. Estienne later discovered that the Schneider company, were working on a tracked armoured vehicle, which became France's first operational tank, the Schneider CA.
At a later, chance meeting with Renault on 16 July 1916, Estienne asked him to reconsider, which he did. The speed with which the project then progressed to the mock-up stage has led to the theory that Renault had been working on the idea for some time.
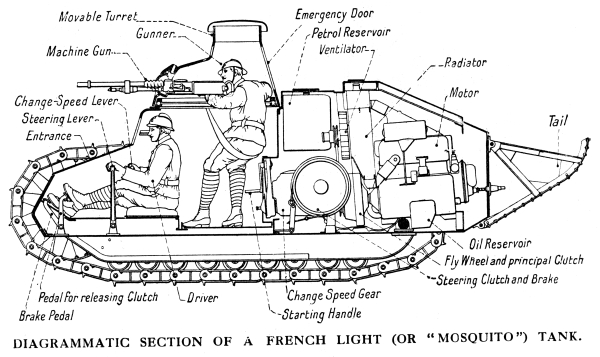
Louis Renault himself conceived the new tank's overall design and set its basic specifications. He imposed a realistic limit to the FT's projected weight, which could not exceed 7 tons. Louis Renault was unconvinced that a sufficient power-to-weight ratio could be achieved with the production engines available at the time to give sufficient mobility to the heavy tank types requested by the military. Renault's most talented industrial designer, Rodolphe Ernst-Metzmaier, generated the FT's detailed execution plans. Charles-Edmond Serre, a long time associate of Louis Renault, organized and supervised the new tank's mass production. The FT's tracks were kept automatically under tension to prevent derailments, while a rounded tail piece facilitated the crossing of trenches. Because the engine had been designed to function normally under any slant, very steep slopes could be negotiated by the Renault FT without loss of power. Effective internal ventilation was provided by the engine's radiator fan, which drew its air through the front crew compartment of the tank and forced it out through the rear engine's compartment.
Renault's design was technically far more advanced than the other two French tanks at the time, namely the Schneider CA1 (1916) and the heavy Saint-Chamond (1917). Nevertheless, Renault encountered some early difficulties in getting his proposal fully supported by Estienne. After the first British use of heavy tanks on 15 September 1916 during the Battle of the Somme, the French military still pondered whether a large number of light tanks would be preferable to a smaller number of superheavy tanks (the later
It is thought possible that Louis Renault began working on the idea as early as 21 December 1915, after a visit from Colonel J. B. E. Estienne. Estienne had drawn up plans for a tracked armoured vehicle based on the Holt caterpillar tractor, and, with permission from General Joffre, approached Renault as a possible manufacturer. Renault declined, saying that his company was operating at full capacity producing war materiel and that he had no experience of tracked vehicles. Estienne later discovered that the Schneider company, were working on a tracked armoured vehicle, which became France's first operational tank, the Schneider CA.
At a later, chance meeting with Renault on 16 July 1916, Estienne asked him to reconsider, which he did. The speed with which the project then progressed to the mock-up stage has led to the theory that Renault had been working on the idea for some time.
Louis Renault himself conceived the new tank's overall design and set its basic specifications. He imposed a realistic limit to the FT's projected weight, which could not exceed 7 tons. Louis Renault was unconvinced that a sufficient power-to-weight ratio could be achieved with the production engines available at the time to give sufficient mobility to the heavy tank types requested by the military. Renault's most talented industrial designer, Rodolphe Ernst-Metzmaier, generated the FT's detailed execution plans. Charles-Edmond Serre, a long time associate of Louis Renault, organized and supervised the new tank's mass production. The FT's tracks were kept automatically under tension to prevent derailments, while a rounded tail piece facilitated the crossing of trenches. Because the engine had been designed to function normally under any slant, very steep slopes could be negotiated by the Renault FT without loss of power. Effective internal ventilation was provided by the engine's radiator fan, which drew its air through the front crew compartment of the tank and forced it out through the rear engine's compartment.
Renault's design was technically far more advanced than the other two French tanks at the time, namely the Schneider CA1 (1916) and the heavy Saint-Chamond (1917). Nevertheless, Renault encountered some early difficulties in getting his proposal fully supported by Estienne. After the first British use of heavy tanks on 15 September 1916 during the Battle of the Somme, the French military still pondered whether a large number of light tanks would be preferable to a smaller number of superheavy tanks (the later
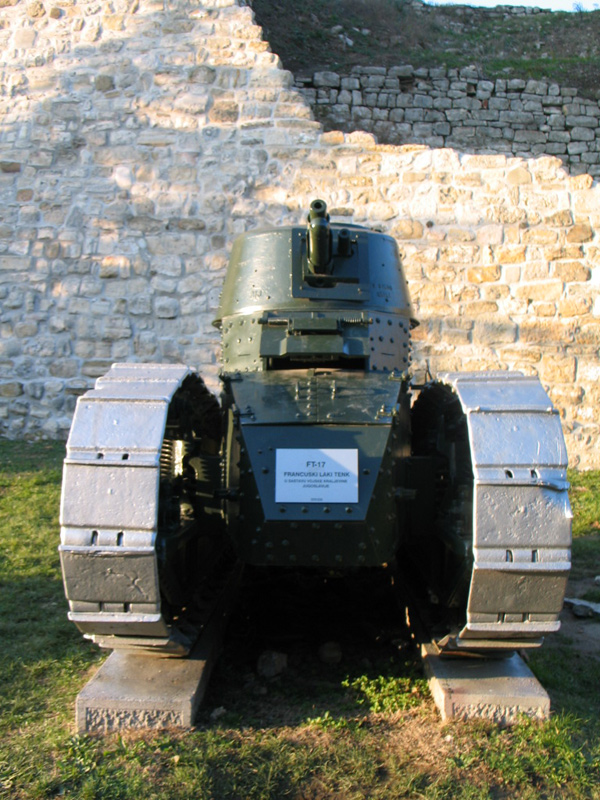 Although it has sometimes been stated that the letters FT stand for the French terms ''faible tonnage'' (low tonnage), ''faible taille'' (small size), ''franchisseur de tranchées'' (trench crosser), o
Although it has sometimes been stated that the letters FT stand for the French terms ''faible tonnage'' (low tonnage), ''faible taille'' (small size), ''franchisseur de tranchées'' (trench crosser), o
''force terrestre'' (land force)
none of these names are correct. Neither was it named the FT 17 or FT-17; nor was there an FT18. The name is derived from the two-letter production code that all new Renault projects were given for internal use: the one available was 'FT'. The prototype was at first referred to as the ''automitrailleuse à chenilles Renault FT modèle 1917''. ''Automitrailleuse à chenilles'' means " armoured car it: motorized machine gunwith tracks." By this stage of the war, ''automitrailleuse'' was the standard word for an armoured car, but by the time the FT was designed there were two other types of French tank in existence and the term ''char d'assaut'' (from the French ''char'' - a cart or wagon, and ''assaut''; attack or assault), soon shortened to ''char'', had at the insistence of Colonel Estienne, already been adopted by the French and was in common use. Once orders for the vehicle had been secured it was the practice at Renault to refer to it as the "FT". The vehicle was originally intended to carry a machine-gun, and was therefore described as a ''char mitrailleur'' - ''mitrailleur'' (from ''mitraille''; grapeshot) had by this time come to mean "machine-gunner". Many sources, predominantly English language accounts, refer to the FT as the "FT 17" or "FT-17." This term is not contemporary, and appears to have arisen post World War One. In Estienne's biography, his granddaughter states, "It is also referred to as the FT 17: the number 17 was added after the war in history books, since it was always referred to at Renault as the FT." Lieutenant-Colonel Paul Malmassari (French tank officer and Doctor of History) states, "The Renault tank never carried the name FT 17 during the First World War, although the initials F.T. seem to appear in August 1917." Some confusion might also have been caused by the fact that the American version of the vehicle, produced in the US under licence from Renault, was designated the M1917. When it was decided to equip the FTs with either cannon or machine-guns, the cannon version was designated ''char canon'' (cannon tank) and the latter, in accordance with French grammar, renamed ''char mitrailleuse'' (machine-gun tank). It is frequently claimed that some of these tanks were designated FT 18. Reasons given for the claim include: it distinguished tanks produced in 1918 from those of 1917; it was applied to FTs armed with cannon as opposed to those with machine-guns; it distinguished FTs with a cast, rounded turret from those with a hexagonal one; it referred to the 18 horsepower engine; it indicated a version to which various modifications had been made. Renault records make no distinction between 1917 and 1918 output; the decision to arm FTs with a 37mm gun was made in April 1917, before any tanks had been manufactured; because of various production difficulties and design requirements, a range of turret types were produced by several manufacturers, but they were all fitted to the basic FT body without any distinguishing reference; all FTs had the same model 18 hp engine. The Renault manual of April 1918 is entitled ''RENAULT CHAR D'ASSAUT 18 HP'', and the illustrations are of the machine-gun version. The official designation was not changed until the 1930s, when the FT was fitted with a 1931 Reibel machine gun and renamed the ''FT modifié 31''. By this time, the French Army was equipped with several other Renault models and it had become necessary to distinguish between the various types.

 The first turret designed for the FT was a circular, cast steel version almost identical to that of the prototype. It was designed to carry a Hotchkiss 8mm machine gun. In April 1917 Estienne decided for tactical reasons that some vehicles should be capable of carrying a small cannon. The 37mm Puteaux gun was chosen, and attempts were made to produce a cast steel turret capable of accommodating it, but they were unsuccessful. The first 150 FTs were for training only, and made of non-hardened steel plus the first model of turret. Meanwhile, the
The first turret designed for the FT was a circular, cast steel version almost identical to that of the prototype. It was designed to carry a Hotchkiss 8mm machine gun. In April 1917 Estienne decided for tactical reasons that some vehicles should be capable of carrying a small cannon. The 37mm Puteaux gun was chosen, and attempts were made to produce a cast steel turret capable of accommodating it, but they were unsuccessful. The first 150 FTs were for training only, and made of non-hardened steel plus the first model of turret. Meanwhile, the
 The Renault FT was widely used by French forces in 1918 and by the
The Renault FT was widely used by French forces in 1918 and by the
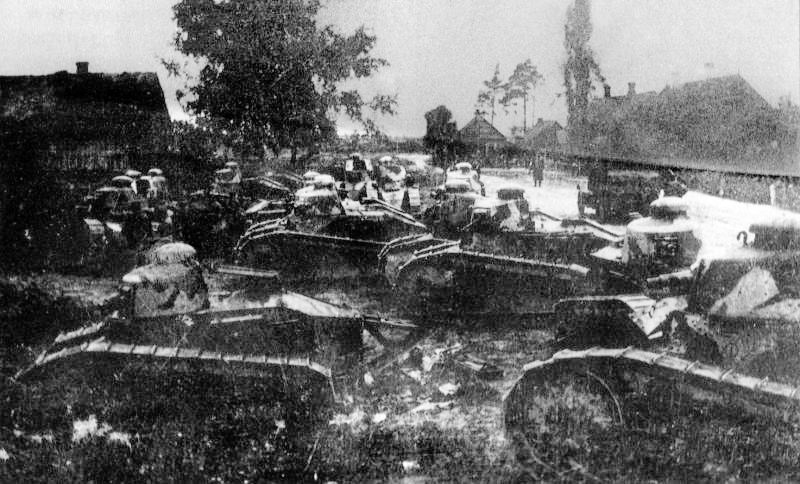 After the end of World War I, Renault FTs were exported to many countries (Belgium, Brazil,
After the end of World War I, Renault FTs were exported to many countries (Belgium, Brazil,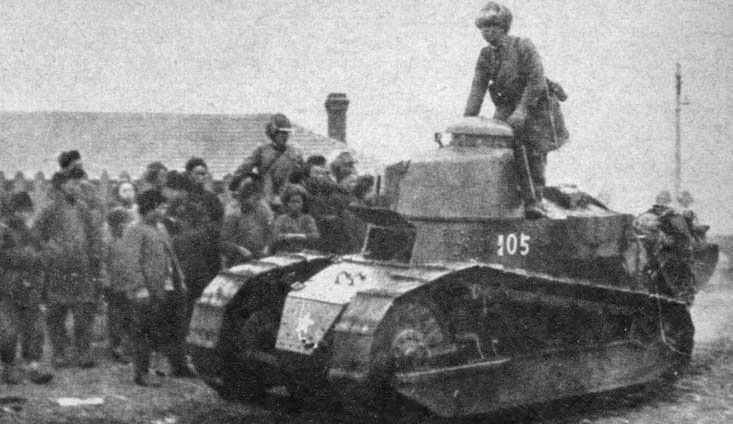  French tanks deployed in
French tanks deployed in
 The fact that several units used the Renault FT gave rise to the popular myth that the French had no modern equipment at all; actually, they had as many modern tanks as the Germans; however, the majority had one-man turrets and were less efficient than German tanks such as the
The fact that several units used the Renault FT gave rise to the popular myth that the French had no modern equipment at all; actually, they had as many modern tanks as the Germans; however, the majority had one-man turrets and were less efficient than German tanks such as the
 The FT was the ancestor of a long line of French tanks: the FT Kégresse, the NC1, the NC2, the
The FT was the ancestor of a long line of French tanks: the FT Kégresse, the NC1, the NC2, the
Tanque Renault F-17 español Rif.jpg, Spanish FT tank in Morocco, 1922
Renault FT-17 in ROC.jpg, Chinese FT tanks
Tankai Renault-FT-17.jpg, Lithuanian FT tanks in 1925
Francouzské tanky Renault vz. 17 čs. armády.gif, Czechoslovak FT tank in 1928
* (some tanks, four discovered by US forces in 2003)
* (54 tanks bought in 1919, used until 1934 in a tank regiment and then used by the Gendarmerie before being scrapped in 1938)
* (12 ''Carros de assalto'', six with 37mm gun, five with 7mm Hotchkiss MGs and one TSF, bought in 1921, later joined by approximatively 28 others, in active service until 1938 and in training service until 1942)
* (~20 FTs, used by the
RenaultTSF.jpg, Renault FT TSF
P003069 Renault FT mod 31 n°66187 near Lisieux, June 1940.jpg, ''FT modifié 31'' destroyed near Lisieux (Normandy) in June 1940
Bundesarchiv Bild 146-1973-035-12, Jugoslawien, zerstörter jugosl. Panzer.jpg, A Yugoslavian M26/27 tank destroyed in the 1941 invasion of Yugoslavia
*''Char canon'': an FT with a 37 mm Puteaux SA18 short-barreled gun: about 3/5 of tanks ordered, about 1/3 of tanks actually produced
*''Char mitrailleuse'': an FT with an 8 mm Hotchkiss M1914 machine gun: about 2/5 of tanks ordered, about 3/5 of tanks produced
*FT 75 BS: a self propelled gun with a short barreled ''Blockhaus Schneider'' 75mm gun: 40 were produced.
*Char signal or TSF: a command tank with a radio. "TSF" stands for ''télégraphie sans fil'' ("wireless"). No armament, three-men crew, 300 ordered, 100 produced.
*FT ''modifié'' 31: upgraded tanks with 7.5 mm Reibel machine gun. After trials from 1929 to 1931, this modification was made in 1933–1934 on 1000 ''chars mitrailleurs'' still in French stocks. This version was sometimes referred to as the "FT 31", though this was not the official name.
* FT ''désarmé'' : French ''char canon'' whose 37mm gun has been removed in the 1930s to arm modern tanks, and used for various purposes:
** ''Pont Bourguignon sur char FT'': FT without turret carrying a light bridge, from an idea of General Louis Ferdinand Bourguignon.
** some were rearmed with an FM 24/29 light machine gun
*FT-''Ko'': Thirteen modified units imported by the
Char Renault FT17 at the Invalides.jpg, Char Renault FT at the
file:Renault FT in Parola tank museum Finland.jpg, Renault FT in Parola Tank Museum procured by Finland in 1919. In service until 1942
Approximately 41 FTs, two ''Russkiy Reno''s, and three FT TSF survive in various museums around the world. Twenty M1917 light tank, M1917s also survive.
Europe:
* Musée des Blindés, Saumur, France. The museum owns three FTs, with two in running order. The inoperable one came from Afghanistan, and is in a static display. Two other tanks from Afghanistan were given to the General George Patton Museum of Leadership, Patton Museum of Cavalry & Armor at Fort Knox, Kentucky. Another one was given to Poland, where it has been renovated and is in running order. The Musée des Blindés also owns an FT TSF.
* Musée de la Grande Guerre, Meaux, Seine-et-Marne, France. One FT ''canon''.
* Musee de l'Armee, Paris, France. One FT
* Glade of the Armistice, near Compiègne, France. One FT
* Bovington Tank Museum, United Kingdom. One FT, an unarmoured training model.
* The Weald Foundation, U.K., has an FT and a TSF. Both restorations finished 2018.
* Royal Museum of the Armed Forces and of Military History, Royal Military Museum, Belgium. One FT is on permanent display.
* National Military Museum, Romania, National Military Museum, Bucharest, Romania. An FT is on permanent outdoor display.
* Military Museum (Belgrade), Belgrade, Serbia. An FT is on permanent outdoor display.
* Parola Tank Museum, Parola, Finland. An FT is on display in the tank hall.
* Musée de l'armée Suisse, Burgdorf, Switzerland. An FT is displayed as the first tank of the Swiss Army, adopted in 1922.
* Museo de Medios Acorazados, El Goloso (Spain). An FT model 1917 under repair.
* Rogaland Krigshistoriske Museum, Stavanger, Norway ()
* Polish Army Museum, Warsaw, Poland. Acquired from Afghanistan in 2012, renovated to running order.
* Overloon War Museum, Overloon, Netherlands has a Renault FT bearing German markings. This vehicle was captured in France and subsequently used by the German army to patrol and guard the Volkel airbase during
Chars-francais.net
FT tanks in Czechoslovak Army
Musée des blindés de Saumur
French Renault FT tank
Description and pictures at World War II Vehicles
Char Léger Renault FT Modèle 1917 (video)
Replica Renault FT Tank (video)
Walkaround Renault FT swiss army
FT-17 - The WW1 Tank Used Until the 1980s
{{DEFAULTSORT:Renault FT World War I light tanks World War I tanks of France World War II tanks of France Renault vehicles, FT Light tanks of the interwar period History of the tank Weapons and ammunition introduced in 1917 World War II light tanks Military vehicles introduced in the 1910s Light tanks of France
tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and good battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engi ...
to have its armament within a fully rotating turret.Although a rotating turret had been a feature of some earlier tank designs or prototypes, and had been incorporated in armoured cars
Armored (or armoured) car or vehicle may refer to:
Wheeled armored vehicles
* Armoured fighting vehicle, any armed combat vehicle protected by armor
** Armored car (military), a military wheeled armored vehicle
* Armored car (valuables), an arm ...
for several years, no tank with a turret had entered service. The Renault FT's configuration (crew compartment at the front, engine compartment at the back, and main armament in a revolving turret) became and remains the standard tank layout. Consequently, some armoured warfare
Armoured warfare or armored warfare (mechanized forces, armoured forces or armored forces) (American English; see spelling differences), is the use of armored fighting vehicles in modern warfare. It is a major component of modern methods of ...
historians have called the Renault FT the world's first modern tank.
Over 3,000 Renault FT tanks were manufactured by French industry, most of them in 1918. After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, FT tanks were exported in large numbers. Copies and derivative designs were manufactured in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
( M1917 light tank), in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
( Fiat 3000) and in the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
( T-18 tank). The Renault FT saw combat during the interwar conflicts around the world, but was considered obsolete at the outbreak of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
.
Development
The FT was designed and produced by the Société des Automobiles Renault (Renault Automobile Company), one of France's major manufacturers of motor vehicles then and now. It is thought possible that Louis Renault began working on the idea as early as 21 December 1915, after a visit from Colonel J. B. E. Estienne. Estienne had drawn up plans for a tracked armoured vehicle based on the Holt caterpillar tractor, and, with permission from General Joffre, approached Renault as a possible manufacturer. Renault declined, saying that his company was operating at full capacity producing war materiel and that he had no experience of tracked vehicles. Estienne later discovered that the Schneider company, were working on a tracked armoured vehicle, which became France's first operational tank, the Schneider CA.
At a later, chance meeting with Renault on 16 July 1916, Estienne asked him to reconsider, which he did. The speed with which the project then progressed to the mock-up stage has led to the theory that Renault had been working on the idea for some time.
Louis Renault himself conceived the new tank's overall design and set its basic specifications. He imposed a realistic limit to the FT's projected weight, which could not exceed 7 tons. Louis Renault was unconvinced that a sufficient power-to-weight ratio could be achieved with the production engines available at the time to give sufficient mobility to the heavy tank types requested by the military. Renault's most talented industrial designer, Rodolphe Ernst-Metzmaier, generated the FT's detailed execution plans. Charles-Edmond Serre, a long time associate of Louis Renault, organized and supervised the new tank's mass production. The FT's tracks were kept automatically under tension to prevent derailments, while a rounded tail piece facilitated the crossing of trenches. Because the engine had been designed to function normally under any slant, very steep slopes could be negotiated by the Renault FT without loss of power. Effective internal ventilation was provided by the engine's radiator fan, which drew its air through the front crew compartment of the tank and forced it out through the rear engine's compartment.
Renault's design was technically far more advanced than the other two French tanks at the time, namely the Schneider CA1 (1916) and the heavy Saint-Chamond (1917). Nevertheless, Renault encountered some early difficulties in getting his proposal fully supported by Estienne. After the first British use of heavy tanks on 15 September 1916 during the Battle of the Somme, the French military still pondered whether a large number of light tanks would be preferable to a smaller number of superheavy tanks (the later
It is thought possible that Louis Renault began working on the idea as early as 21 December 1915, after a visit from Colonel J. B. E. Estienne. Estienne had drawn up plans for a tracked armoured vehicle based on the Holt caterpillar tractor, and, with permission from General Joffre, approached Renault as a possible manufacturer. Renault declined, saying that his company was operating at full capacity producing war materiel and that he had no experience of tracked vehicles. Estienne later discovered that the Schneider company, were working on a tracked armoured vehicle, which became France's first operational tank, the Schneider CA.
At a later, chance meeting with Renault on 16 July 1916, Estienne asked him to reconsider, which he did. The speed with which the project then progressed to the mock-up stage has led to the theory that Renault had been working on the idea for some time.
Louis Renault himself conceived the new tank's overall design and set its basic specifications. He imposed a realistic limit to the FT's projected weight, which could not exceed 7 tons. Louis Renault was unconvinced that a sufficient power-to-weight ratio could be achieved with the production engines available at the time to give sufficient mobility to the heavy tank types requested by the military. Renault's most talented industrial designer, Rodolphe Ernst-Metzmaier, generated the FT's detailed execution plans. Charles-Edmond Serre, a long time associate of Louis Renault, organized and supervised the new tank's mass production. The FT's tracks were kept automatically under tension to prevent derailments, while a rounded tail piece facilitated the crossing of trenches. Because the engine had been designed to function normally under any slant, very steep slopes could be negotiated by the Renault FT without loss of power. Effective internal ventilation was provided by the engine's radiator fan, which drew its air through the front crew compartment of the tank and forced it out through the rear engine's compartment.
Renault's design was technically far more advanced than the other two French tanks at the time, namely the Schneider CA1 (1916) and the heavy Saint-Chamond (1917). Nevertheless, Renault encountered some early difficulties in getting his proposal fully supported by Estienne. After the first British use of heavy tanks on 15 September 1916 during the Battle of the Somme, the French military still pondered whether a large number of light tanks would be preferable to a smaller number of superheavy tanks (the later Char 2C
The Char 2C, also known as the FCM 2C, was a French heavy tank, later also seen as a super-heavy tank. It was developed during World War I but not deployed until after the war. It was, in total volume or physical dimensions, the largest operat ...
). On 27 November 1916, Estienne had sent to the French Commander in Chief a personal memorandum proposing the immediate adoption and mass manufacture of a light tank based on the specifications of the Renault prototype. After receiving two large government orders for the FT tank, one in April 1917 and the other in June 1917, Renault was at last able to proceed. His design remained in competition with the superheavy Char 2C until the end of the war.
The prototype was refined during the second half of 1917, but the Renault FT remained plagued by radiator fan belt problems throughout the war. Only 84 were produced in 1917, but 2,697 were delivered to the French army before the Armistice.
Naming
 Although it has sometimes been stated that the letters FT stand for the French terms ''faible tonnage'' (low tonnage), ''faible taille'' (small size), ''franchisseur de tranchées'' (trench crosser), o
Although it has sometimes been stated that the letters FT stand for the French terms ''faible tonnage'' (low tonnage), ''faible taille'' (small size), ''franchisseur de tranchées'' (trench crosser), o''force terrestre'' (land force)
none of these names are correct. Neither was it named the FT 17 or FT-17; nor was there an FT18. The name is derived from the two-letter production code that all new Renault projects were given for internal use: the one available was 'FT'. The prototype was at first referred to as the ''automitrailleuse à chenilles Renault FT modèle 1917''. ''Automitrailleuse à chenilles'' means " armoured car it: motorized machine gunwith tracks." By this stage of the war, ''automitrailleuse'' was the standard word for an armoured car, but by the time the FT was designed there were two other types of French tank in existence and the term ''char d'assaut'' (from the French ''char'' - a cart or wagon, and ''assaut''; attack or assault), soon shortened to ''char'', had at the insistence of Colonel Estienne, already been adopted by the French and was in common use. Once orders for the vehicle had been secured it was the practice at Renault to refer to it as the "FT". The vehicle was originally intended to carry a machine-gun, and was therefore described as a ''char mitrailleur'' - ''mitrailleur'' (from ''mitraille''; grapeshot) had by this time come to mean "machine-gunner". Many sources, predominantly English language accounts, refer to the FT as the "FT 17" or "FT-17." This term is not contemporary, and appears to have arisen post World War One. In Estienne's biography, his granddaughter states, "It is also referred to as the FT 17: the number 17 was added after the war in history books, since it was always referred to at Renault as the FT." Lieutenant-Colonel Paul Malmassari (French tank officer and Doctor of History) states, "The Renault tank never carried the name FT 17 during the First World War, although the initials F.T. seem to appear in August 1917." Some confusion might also have been caused by the fact that the American version of the vehicle, produced in the US under licence from Renault, was designated the M1917. When it was decided to equip the FTs with either cannon or machine-guns, the cannon version was designated ''char canon'' (cannon tank) and the latter, in accordance with French grammar, renamed ''char mitrailleuse'' (machine-gun tank). It is frequently claimed that some of these tanks were designated FT 18. Reasons given for the claim include: it distinguished tanks produced in 1918 from those of 1917; it was applied to FTs armed with cannon as opposed to those with machine-guns; it distinguished FTs with a cast, rounded turret from those with a hexagonal one; it referred to the 18 horsepower engine; it indicated a version to which various modifications had been made. Renault records make no distinction between 1917 and 1918 output; the decision to arm FTs with a 37mm gun was made in April 1917, before any tanks had been manufactured; because of various production difficulties and design requirements, a range of turret types were produced by several manufacturers, but they were all fitted to the basic FT body without any distinguishing reference; all FTs had the same model 18 hp engine. The Renault manual of April 1918 is entitled ''RENAULT CHAR D'ASSAUT 18 HP'', and the illustrations are of the machine-gun version. The official designation was not changed until the 1930s, when the FT was fitted with a 1931 Reibel machine gun and renamed the ''FT modifié 31''. By this time, the French Army was equipped with several other Renault models and it had become necessary to distinguish between the various types.
Production
France
About half of all FTs were manufactured in Renault's factory at Boulogne-Billancourt near Paris, with the remainder subcontracted to other companies. Of the original order for 3,530, Renault accounted for 1,850 (52%),Berliet
Berliet was a French manufacturer of automobiles, buses, trucks and military vehicles among other vehicles based in Vénissieux, outside of Lyon, France. Founded in 1899, and apart from a five-year period from 1944 to 1949 when it was put into 'a ...
800 (23%), SOMUA
Somua, an acronym for ''Société d'outillage mécanique et d'usinage d'artillerie'', was a French company that manufactured machinery and vehicles. A subsidiary of Schneider-Creusot, Somua was based in Saint-Ouen, a suburb of Paris.
Overview
...
(a subsidiary of Schneider & Cie) 600 (17%), and Delaunay-Belleville 280 (8%). When the order was increased to 7,820 in 1918, production was distributed in roughly the same proportion. Louis Renault agreed to waive royalties for all French manufacturers of the FT.
United States
When the US entered the war in April 1917, its army was short of heavy matériel, and had no tanks at all. Because of the wartime demands on French industry, it was decided that the quickest way to supply the American forces with sufficient armour was to manufacture the FT in the US. A requirement of 4,400 of a modified version, the M1917, was decided on, with delivery expected to begin in April, 1918. By June 1918, US manufacturers had failed to produce any, and delivery dates were put back until September. France therefore agreed to lend 144 FTs, enough to equip two battalions. No M1917s reached the American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) until the war was over.Turret
 The first turret designed for the FT was a circular, cast steel version almost identical to that of the prototype. It was designed to carry a Hotchkiss 8mm machine gun. In April 1917 Estienne decided for tactical reasons that some vehicles should be capable of carrying a small cannon. The 37mm Puteaux gun was chosen, and attempts were made to produce a cast steel turret capable of accommodating it, but they were unsuccessful. The first 150 FTs were for training only, and made of non-hardened steel plus the first model of turret. Meanwhile, the
The first turret designed for the FT was a circular, cast steel version almost identical to that of the prototype. It was designed to carry a Hotchkiss 8mm machine gun. In April 1917 Estienne decided for tactical reasons that some vehicles should be capable of carrying a small cannon. The 37mm Puteaux gun was chosen, and attempts were made to produce a cast steel turret capable of accommodating it, but they were unsuccessful. The first 150 FTs were for training only, and made of non-hardened steel plus the first model of turret. Meanwhile, the Berliet
Berliet was a French manufacturer of automobiles, buses, trucks and military vehicles among other vehicles based in Vénissieux, outside of Lyon, France. Founded in 1899, and apart from a five-year period from 1944 to 1949 when it was put into 'a ...
Company had produced a new design, a polygonal turret of riveted plate, which was simpler to produce than the early cast steel turret. It was given the name "omnibus", since it could easily be adapted to mount either the Hotchkiss machine gun or the Puteaux 37mm with its telescopic sight. This turret was fitted to production models in large numbers. In 1918 ''Forges et aciéries Paul Girod'' produced a successful circular turret which was mostly cast with some rolled parts. The Girod turret was also an "omnibus" design. Girod supplied it to all the companies producing the FT, and in the later stages of the war it became more commonplace than the Berliet turret. The turret sat on a circular ball-bearing race, and could easily be rotated by the gunner/commander or be locked in position with a handbrake.
Service history
World War I
 The Renault FT was widely used by French forces in 1918 and by the
The Renault FT was widely used by French forces in 1918 and by the American Expeditionary Forces
The American Expeditionary Forces (A. E. F.) was a formation of the United States Army on the Western Front of World War I. The A. E. F. was established on July 5, 1917, in France under the command of General John J. Pershing. It fought along ...
(AEF) on the Western Front in the later stages of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
Its battlefield debut occurred on 31 May 1918, east of the Forest of Retz, east of Chaudun, between Ploisy and Chazelles, during the Third Battle of the Aisne. This engagement, with 30 tanks, successfully broke up a German advance, but in the absence of infantry support, the vehicles later withdrew. From then on, gradually increasing numbers of FTs were deployed, together with smaller numbers of the older Schneider CA1 and Saint-Chamond tanks. As the war had become a war of movement during mid-1918, during the Hundred Days Offensive, the lighter FTs were often transported on heavy trucks and special trailers rather than by rail on flat cars. Estienne had initially proposed to overwhelm the enemy defences using a "swarm" of light tanks, a tactic that was eventually successfully implemented. Beginning in late 1917, the Entente allies were attempting to outproduce the Central Powers in all respects, including artillery, tanks, and chemical weapons. Consequently, a goal was set of manufacturing 12,260 FT tanks (7,820 in France and 4,440 in the United States) before the end of 1919.It played a leading role in the offensives of 1918, when it received the popular name of "Victory Tank".
The British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
used 24 FTs for command and liaison duties, usually with the gun removed.
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
received 3 FTs in June 1918, but they did not see action and no other tanks were received until the end of the war.
Interwar period
 After the end of World War I, Renault FTs were exported to many countries (Belgium, Brazil,
After the end of World War I, Renault FTs were exported to many countries (Belgium, Brazil, Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, Estonia, Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
, Iran, Japan, Lithuania, the Netherlands, Poland, Romania, Spain, Switzerland, Turkey, and Yugoslavia). Renault FT tanks were used by most nations having armoured forces, generally as their prominent tank type.
They were used in anti-Soviet conflicts such as the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
, Polish-Soviet War and Estonian War of Independence. On 5 February 1920 Estonia purchased nine vehicles from France.
 French tanks deployed in
French tanks deployed in Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, c ...
were given to the Chinese Fengtian Army of Zhang Zuolin
Zhang Zuolin (; March 19, 1875 June 4, 1928), courtesy name Yuting (雨亭), nicknamed Zhang Laogang (張老疙瘩), was an influential Chinese bandit, soldier, and warlord during the Warlord Era in China. The warlord of Manchuria from 1916 to ...
in 1919. 14 more Renaults were bought in 1924 and 1925. These tanks saw action to protect the border from the Soviets in the 1920s and against the warlord
A warlord is a person who exercises military, economic, and political control over a region in a country without a strong national government; largely because of coercive control over the armed forces. Warlords have existed throughout much of h ...
Wu Peifu
Wu Peifu or Wu P'ei-fu (; April 22, 1874 – December 4, 1939) was a major figure in the struggles between the warlords who dominated Republican China from 1916 to 1927.
Early career
Born in Shandong Province in eastern China, Wu initi ...
in 1926. After the Japanese invasion of Manchuria
The Empire of Japan's Kwantung Army invaded Manchuria on 18 September 1931, immediately following the Mukden Incident. At the war's end in February 1932, the Japanese established the puppet state of Manchukuo. Their occupation lasted until the ...
, nearly all were handed over to the Manchukuo Imperial Army
The Manchukuo Imperial Army ( zh, s=滿洲國軍, p=Mǎnzhōuguó jūn) was the ground force of the military of the Empire of Manchukuo, a puppet state established by Imperial Japan in Manchuria, a region of northeastern China. The force was pri ...
.
Renault tanks were also used in colonial conflicts, for instance crushing a revolt in Italian Libya
Libya ( it, Libia; ar, ليبيا, Lībyā al-Īṭālīya) was a colony of the Fascist Italy located in North Africa, in what is now modern Libya, between 1934 and 1943. It was formed from the unification of the colonies of Italian Cyrenaica ...
in 1919. The French Army sent a company of FT tanks to Syria during the Great Druze Revolt. In Brazil, the FT tanks were used by the Old Republic to crush various revolts between 1924 and 1927 and by Vargas forces against the Constitutionalist Revolution
The Constitutionalist Revolution of 1932 (sometimes also referred to as Paulista War or Brazilian Civil War) is the name given to the uprising of the population of the Brazilian state of São Paulo against the Brazilian Revolution of 1930 whe ...
.
During the Rif War
The Rif War () was an armed conflict fought from 1921 to 1926 between Spain (joined by France in 1924) and the Berber tribes of the mountainous Rif region of northern Morocco.
Led by Abd el-Krim, the Riffians at first inflicted several de ...
, after the Annual disaster, the Spanish Army ordered 10 FT armed with Hotchkiss machine guns and 1 ''char TSF'' to supplement a first Renault bought in 1919. These tanks formed a company deployed from 1921. After a first failure, they proved to be very effective and six more were delivered in 1925. The Spanish FT were the first tanks in history to take part in an amphibious assault, the Alhucemas landing
The Alhucemas landing ( es, Desembarco de Alhucemas; also known as Al Hoceima landing) was a landing operation which took place on 8 September 1925 at Alhucemas by the Spanish Army and Navy and, in lesser numbers, an allied French naval and ae ...
. The French Army deployed two battalions of FT during the war, including one company of tanks with Kégresse tracks. After the end of the war, the French tanks remained in North Africa to finish the "pacification" of Morocco in the Atlas Mountains. When the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, link ...
broke, half of the Renault crews remained loyal to the Spanish Republic while the others joined the rebels. France later sent 32 FTs to the Republicans; the number of FTs sold to the Republicans by Poland is unclear; estimates vary between 16 and 94.
World War II and after
Renault FT tanks were also fielded in limited numbers duringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, in Poland, Finland, France, Greece, Romania and the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 ...
, although they were already obsolete. In May 1940, the French Army still had seven front-line battalions, each equipped with 63 FTs, one under-strength battalion as well as three independent companies, each with 10, for a total organic strength of 504. 105 more were in service in the colonies of Morocco and Algeria and 58 in French Levant, Madagascar and Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
. Some FT tanks had also been buried within the ground and encased in concrete to supplement the Maginot Line.
 The fact that several units used the Renault FT gave rise to the popular myth that the French had no modern equipment at all; actually, they had as many modern tanks as the Germans; however, the majority had one-man turrets and were less efficient than German tanks such as the
The fact that several units used the Renault FT gave rise to the popular myth that the French had no modern equipment at all; actually, they had as many modern tanks as the Germans; however, the majority had one-man turrets and were less efficient than German tanks such as the Panzer III
The ''Panzerkampfwagen III'', commonly known as the Panzer III, was a medium tank developed in the 1930s by Germany, and was used extensively in World War II. The official German ordnance designation was Sd.Kfz. 141. It was intended to fight ot ...
and IV. The French suffered from strategic and tactical weaknesses rather than from equipment deficiencies, although many of the French tanks were also markedly slow (unlike the German tanks of the time). When the best French units were cut off by the German drive to the English Channel, around 390 FTs, previously used for training or stored in depots, joined the 184 to 192 FTs in service with internal security units. The Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
captured 1,704 FTs. They used about 100 for airfield defence and about 650 for patrolling occupied Europe. Some were used by the Germans in 1944 for street-fighting in Paris, but by this time they were hopelessly out of date.
Vichy France
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its te ...
used Renault FTs against Allied invasion forces during Operation Torch in Morocco and Algeria. The French tanks were no match for the newly arrived American M4 Sherman and M3 Stuart tanks. The last combat of the French Army FTs was during the Japanese invasion of French Indochina
The was a short undeclared military confrontation between Japan and France in northern French Indochina. Fighting lasted from 22 to 26 September 1940; the same time as the Battle of South Guangxi in the Sino-Japanese War, which was the main ...
, when a section defended the Hue fortress.
The last "combat" use may have been in the 1980s during the Soviet–Afghan War
The Soviet–Afghan War was a protracted armed conflict fought in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from 1979 to 1989. It saw extensive fighting between the Soviet Union and the Afghan mujahideen (alongside smaller groups of anti-Sovie ...
, when some FTs were reportedly used as pillboxes or roadblocks.
Derivatives
 The FT was the ancestor of a long line of French tanks: the FT Kégresse, the NC1, the NC2, the
The FT was the ancestor of a long line of French tanks: the FT Kégresse, the NC1, the NC2, the Char D1
The Char D1 was an Interwar French light tank.
The French plan of 1926, calling for the creation of a Light Infantry Support Tank, led to the development of the existing Renault NC1 prototype into the Char D1. One hundred and sixty vehicles of t ...
, and the Char D2
The Char D2 was a French medium tank of the interwar period.
In 1930, at a time the Char D1 had not even entered production, the Renault company agreed to build a better armoured version called the Char D2. By not using old-fashioned rivets, it ...
. The Italians produced the FIAT 3000, a moderately close copy of the FT, as their standard tank.
The Soviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
captured 14 burnt-out Renaults from White Russian forces and rebuilt them at the Krasnoye Sormovo Factory in 1920. Nearly 15 exact copies, called "Russki Renoe", were produced in 1920–1922, but they were never used in battle because of many technical problems. In 1928–1931, the first completely Soviet-designed tank was the T-18, a derivative of the Renault with sprung suspension.
Operators
Fengtian clique
The Fengtian clique () was one of several opposing military factions that constituted the early Republic of China during its Warlord Era. It was named after Fengtian Province (now Liaoning), and operated from a territorial base comprising the th ...
and then by the Northeastern Army)
* (12 former Yugoslav tanks used by the Ustaše Militia
The Ustaše (), also known by anglicised versions Ustasha or Ustashe, was a Croatian fascist and ultranationalist organization active, as one organization, between 1929 and 1945, formally known as the Ustaša – Croatian Revolutionary Move ...
and 12 others by the Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
against the partisans)
* (seven tanks, bought in 1921-1923 and used until 1933)
* (four FTs with gun and eight FT with machine guns, bought in 1924 and used until 1940)
* (34 tanks, used since 1919)
*
* (captured)
* (some tanks received from France in 1924, actual delivery disputed)
* (13 tanks, some used alongside Renault NC1s in Manchuria in 1932)
* (seven FTs in 1919 and many more Fiat 3000s)
* (12 FTs with Maxim machine guns, bought in 1923)
* (ex-Chinese tanks from 1931, with some Japanese or French tanks later supplied)
* (one FT with Schwarzlose machine gun, used for trials)
* (one ex-American tank, used 1936-1940)
*
* (74-76 Renault FTs, including 40 tanks with 37mm guns, bought in 1919, used by the ''Regiment 1 Care de Lupta'' and during WW2 by an internal security battalion)
* Russian White movement
*
* (18 FTs delivered from France between 1919 and 1925 and 48 others delivered from France and Poland to the Spanish Republic)
* (one tank bought for trials in 1923)
* (two tanks bought in 1921 and three others in 1939 for training the infantry to the tanks)
* (one company of Renault FT, received from France in 1921 or 1928)
* (24 on loan in 1918, for command and reconnaissance. Returned after War.)
*
*
Variants
Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor o ...
in 1919, armed with either the 37mm SA18 cannon or machine guns; used in combat in the Manchurian Incident and subsequently for training
* M1917: US-built copy. 950 built, 374 of which were gun tanks and fifty of which were radio tanks. During World War II the Canadian Army purchased 236 redundant M1917s for training purposes.
*''Russkiy Reno'': the "Russian Renault", the first Soviet tank, produced at Krasnoye Sormovo. A close copy. 17 units were produced. Also known as "Tank M" or "KS tank".
*Renault FT CWS: the Renault FT CWS or ''Zelazny'' ("iron") tanks were built in Poland for use as training vehicles only (Polish combat tanks were French manufactured). These tanks used spare French engines and components. The hulls and turrets were manufactured to French specifications in all other respects. Around 27 CWS FT tanks were built. CWS is the abbreviation for ''Centralne Warsztaty Samochodowe'' (translated as "Central Workshops for Motor vehicles" or "Central Truck Workshop"), a plant in Warsaw which performed maintenance and depot level repair.
*Renault M26/27: a development of the FT with a different suspension and Kégresse rubber tracks; a number were used in Yugoslavia and five in Poland.
* FIAT 3000: an Italian derivation.
* T-18: A Soviet derivation with sprung suspension and Fiat engines.
* Polish gas tank: A Polish modification built in the ''Wojskowy Instytut Gazowy'' ("Military Gas Institute") and tested on the Rembertów proving ground on 5 July 1926. Instead of a turret, the tank had twin gas cylinders. It was designed to create smoke screens, but could also be used for chemical attacks. Only one was produced.
* Renault FT AC: A December 1939 plan to convert France's obsolete FTs into tank destroyers. The tank never left the drawing board. It was designed to have a 47mm APX anti-tank gun instead of the turret.
Surviving vehicles
Musée de l'Armée
The Musée de l'Armée (; "Army Museum") is a national military museum of France located at Les Invalides in the 7th arrondissement of Paris. It is served by Paris Métro stations Invalides, Varenne and La Tour-Maubourg
The Musée de l'Armée ...
Bovington 179 FT-17 1.jpg, FT at The Tank Museum, Bovington Tank Museum
BrazilianFT-17-FView.JPG, A Brazilian army FT received in 1921
Renault FT-17 w Muzeum Wojska Polskiego.jpg, Renault FT in Polish Army Museum
Renault FT17 National Military Museum Bucharest.JPG, Romanian armored fighting vehicle production during World War II, Romanian-used FT at the National Military Museum, Romania, National Military Museum, Bucharest
Renault FT-17 at Overloon War Museum.jpg, German-captured FT at the Overloon War Museum, Overloon
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
.
* Two full-scale, working replicas of Renault FTs were built from scratch by an enthusiast, the late Robert Tirczakowski for Jerzy Hoffman's 2011 film ''Battle of Warsaw 1920''.
North America:
* U.S. Army Armor and Cavalry Collection, Fort Benning, Georgia in the United States. In 2003, two FT tanks, one would have mounted a 37mm cannon and the other an 8mm mg, were discovered in Kabul by Major Robert Redding. With permission from the Afghan government, the two tanks were transferred to the United States, where one of them, a machine gun tank, was restored and originally put on display in the General George Patton Museum of Leadership, Patton Museum of Cavalry & Armor, until the Armor Branch collection was transferred to Fort Benning. This FT is currently on display in the Armor Gallery of the NIM. The Armor Collection currently is restoring the other FT, 37mm gun tank. A previous FT at Fort Knox was transferred to US Army Heritage & Education Center at Carlisle Barracks, Pennsylvania.
* Louisiana State Military Museum at Jackson Barracks in New Orleans, Louisiana. An FT was inundated by floodwaters of Hurricane Katrina in 2005. It was restored by the Museum of the American G.I. and has been returned to display.
* National World War I Museum, located at Liberty Memorial, Kansas City, Missouri. An FT, damaged by German artillery.
* An FT is on static display at the US Army Heritage and Education Center at Carlisle Barracks, Pennsylvania.
* A hybrid FT/M-1917 is displayed in a life-sized diorama at Fort George G. Meade Museum, Maryland.
* The Museum of the American G.I. in College Station, Texas has a completely original, fully functional, fully operational FT with functional 37mm main gun. The tank saw service during the war and exhibits minor battle damage on some track segments.
South America:
* Museu Militar Conde de Linhares in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. One FT.
* Museu Eduardo André Matarazzo, Bebedouro, Brazil. One FT is on permanent display
Australia:
*Australian War Memorial, Canberra. One FT at the Treloar storage and conservation annexe in Mitchell, Australian Capital Territory
See also
* G-numbers, part of former US cataloging system for military vehicles * Tanks of FranceNotes
References
Further reading
* Ayres, Leonard P. (1919), ''The War with Germany. A Statistical Summary'', Washington, Government Printing Office. p. 80 (Tanks) * * Crowell, Benedict (1919) ''America's Munitions 1917-1918'', Chapter 8 : ''Tanks'', Washington Government Printing Office. * * Dingli, Laurent ( 2000 ), ''Louis Renault '', Grandes Biographies, Flammarion. * Estienne Mondet, Arlette, ( 2010 ),'' Le general J.B.E. Estienne . Pere des Chars '', L'Harmattan, Paris, * * * Gougaud, Alain, (1987) ''L'Aube de la Gloire: Les auto mitrailleuses et les chars francais pendant la Grande Guerre, Histoire technique et militaire'', Societe Ocebur (Guides Muller), . * Hatry, Gilbert, ( 1978 ), '' Renault Usine de Guerre '', Eds. Lafourcade, Paris, -. A full chapter is dedicated to the industrial production history of the Renault FT * * Jurkiewiecz, Bruno, (2008) ''Les Chars Francais au Combat 1917–1918'', (over 150 illustrations) ECPAD/YSEC, BP 405 27405 Louviers Cedex France. A compatible DVD of period films demonstrating the French WW I tanks, including the Renault FT, is attached to this book. * Malmassari, Paul (2009) ''Les Chars de la Grande Guerre''. "14-18 Le Magazine de la Grande Guerre" . * Ortholan, Henri, ( 2008 ),'' La Guerre des Chars''. Bernard Giovangeli Editeur, Paris, * Perre, J. (1940) ''Batailles et Combats des Chars Francais: La bataille defensive Avril-Juillet 1918''. Second Tome. Charles Lavauzelle & Cie. * * * * ''Renault Char d'Assaut 18 HP, Notice descriptive et Reglement de Manoeuvre et d'Entretien''( Avril 1918 ). A.Omeyer, 26 Boulevard Beaumarchais, Paris 11eme. 68 pages and 15 plates. This is the original Renault factory complete user's manual for the "FT tank". It can be consulted on line at "scribd.com" (World Digital Library)External links
Chars-francais.net
FT tanks in Czechoslovak Army
Musée des blindés de Saumur
French Renault FT tank
Description and pictures at World War II Vehicles
Char Léger Renault FT Modèle 1917 (video)
Replica Renault FT Tank (video)
Walkaround Renault FT swiss army
FT-17 - The WW1 Tank Used Until the 1980s
{{DEFAULTSORT:Renault FT World War I light tanks World War I tanks of France World War II tanks of France Renault vehicles, FT Light tanks of the interwar period History of the tank Weapons and ammunition introduced in 1917 World War II light tanks Military vehicles introduced in the 1910s Light tanks of France