Religious denominations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
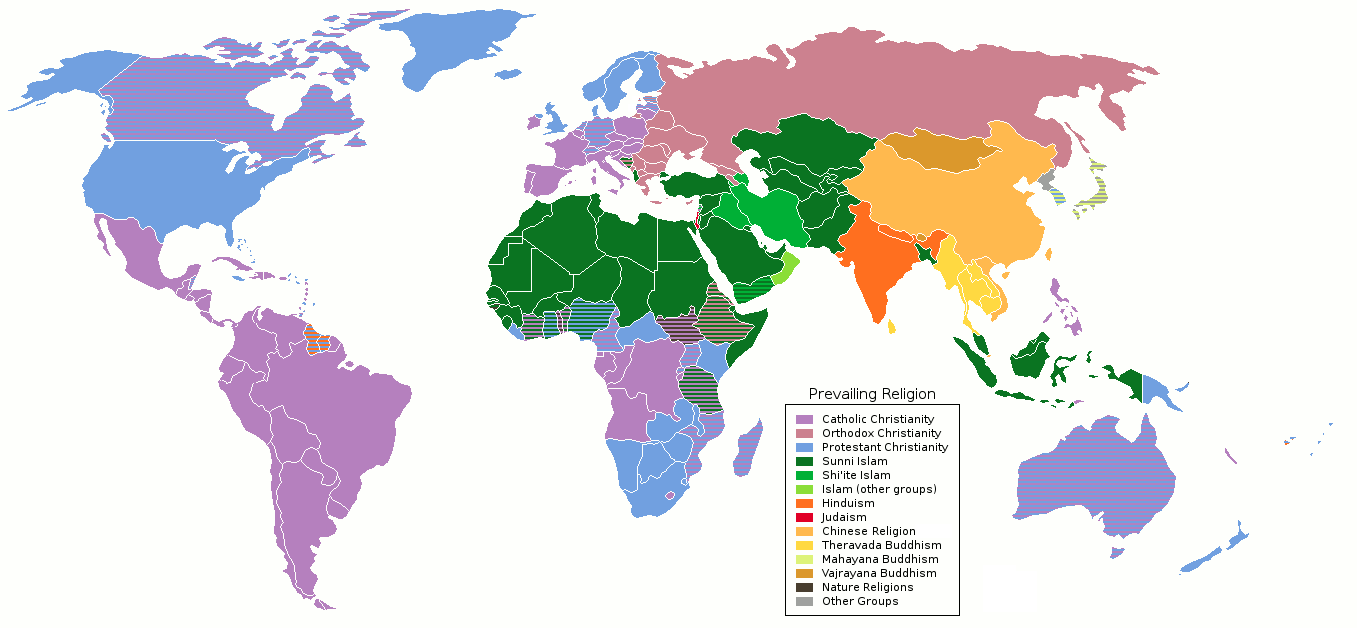 A religious denomination is a subgroup within a
A religious denomination is a subgroup within a
BBC News, 17 October 2010
Independent News, New Zealand, Press Release: Department Of Corrections, 13 December 2007 Military organizations that do not have large numbers of members from several individual smaller but related denominations will routinely hold multi-denominational religious services, often generically called "
ABC News (US), MARK NIESSE 26 December 2010 New chapel heralds more North Fort Hood construction
First U.S. Army, Sgt. 1st Class Gail Braymen, 19 July 2010
 A religious denomination is a subgroup within a
A religious denomination is a subgroup within a religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
that operates under a common name and tradition among other activities.
The term refers to the various Christian denomination
A Christian denomination is a distinct Religion, religious body within Christianity that comprises all Church (congregation), church congregations of the same kind, identifiable by traits such as a name, particular history, organization, leadersh ...
s (for example, Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
, Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, and the many varieties of Protestantism
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
). It is also used to describe the five major branches of Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
(Karaite Judaism
Karaite Judaism () or Karaism (, sometimes spelt Karaitism (; ''Yahadut Qara'it''); also spelt Qaraite Judaism, Qaraism or Qaraitism) is a Jewish religious movement characterized by the recognition of the written Torah alone as its supreme ...
, Orthodox, Conservative, Reform, and Reconstructionist). Within Islam, it can refer to the branches or sects (such as Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a dis ...
, Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
), as well as their various subdivisions such as sub-sects, schools of jurisprudence, schools of theology and religious movements.
The world's largest religious denominations are Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disag ...
and Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
.
Christianity
AChristian denomination
A Christian denomination is a distinct Religion, religious body within Christianity that comprises all Church (congregation), church congregations of the same kind, identifiable by traits such as a name, particular history, organization, leadersh ...
is a generic term for a distinct religious body identified by traits such as a common name, structure, leadership and doctrine. Individual bodies, however, may use alternative terms to describe themselves, such as church or fellowship. Divisions between one group and another are defined by doctrine and church authority; issues such as the biblical interpretation, the authority of apostolic succession, eschatology, and papal primacy often separate one denomination from another. Groups of denominations often sharing broadly similar beliefs, practices and historical ties are known as branches of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
.
Hinduism
InHinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, the major deity or philosophical belief identifies a denomination, which also typically has distinct cultural and religious practices. The major denominations include Shaivism
Shaivism (; sa, शैवसम्प्रदायः, Śaivasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Supreme Being. One of the largest Hindu denominations, it incorporates many sub-traditions rangi ...
, Shaktism
Shaktism ( sa, शाक्त, , ) is one of several major Hindu denominations, wherein the metaphysical reality is considered metaphorically a woman and Shakti ( Mahadevi) is regarded as the supreme godhead. It includes many goddesses, al ...
, Vaishnavism
Vaishnavism ( sa, वैष्णवसम्प्रदायः, Vaiṣṇavasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu denominations along with Shaivism, Shaktism, and Smartism. It is also called Vishnuism since it considers Vishnu as ...
and Smartism.
Islam
A bottom-up report byPew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C.
It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and th ...
suggests that 25% of Muslims surveyed globally self-identified as non-denominational Muslims. Historically
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
, Islam was divided into three major sects well known as Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a dis ...
, Khawarij
The Kharijites (, singular ), also called al-Shurat (), were an Islamic sect which emerged during the First Fitna (656–661). The first Kharijites were supporters of Ali who rebelled against his acceptance of arbitration talks to settle the ...
and Shī‘ah. Nowadays, Sunnis
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word ''Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagree ...
constitute about 90% of the overall Muslim population while the Shi'as are around 10%. Today, many of the Shia sects are extinct. The major surviving Imamah- Muslim Sects are Usulism ''(with nearly more than 8.5%),'' Nizari Ismailism
The Nizaris ( ar, النزاريون, al-Nizāriyyūn, fa, نزاریان, Nezāriyān) are the largest segment of the Ismaili Muslims, who are the second-largest branch of Shia Islam after the Twelvers. Nizari teachings emphasize independent ...
''(with nearly more than 1%),'' Alevism
Alevism or Anatolian Alevism (; tr, Alevilik, ''Anadolu Aleviliği'' or ''Kızılbaşlık''; ; az, Ələvilik) is a local Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Alevi Islamic ( ''bāṭenī'') teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, w ...
''(with slightly more than 0.5% but less than 1%According to Krisztina Kehl-Bodrogi, ''Syncretistic Religious Communities in the Near East'' edited by her, B. Kellner-Heinkele, & A. Otter-Beaujean. Leiden: Brill, 1997.).'' The other existing groups include Zaydi Shi'a of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and ...
whose population is nearly more than 0.5% of the world's Muslim population, Musta’li Ismaili ''(with nearly 0.1% whose Taiyabi
Tayyibi Isma'ilism is the only surviving sect of the Musta'li branch of Isma'ilism, the other being the extinct Hafizi branch. Followers of Tayyibi Isma'ilism are found in various Bohra communities: Dawoodi, Sulaymani, and Alavi.
The Tayyibi ...
adherents reside in Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
state in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
and Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former c ...
city in Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
. There are also significant diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
populations in Europe, North America, the Far East and East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
),'' and Ibadis from the Kharijites
The Kharijites (, singular ), also called al-Shurat (), were an Islamic sect which emerged during the First Fitna (656–661). The first Kharijites were supporters of Ali who rebelled against his acceptance of arbitration talks to settle the ...
whose population has diminished to a level below 0.15%. On the other hand, new Muslim sects like African American Muslims, Ahmadi Muslims
Ahmadiyya (, ), officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community or the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ, ar, الجماعة الإسلامية الأحمدية, al-Jamāʿah al-Islāmīyah al-Aḥmadīyah; ur, , translit=Jamā'at Aḥmadiyyah Musl ...
''(with nearly around 1%),'' non-denominational Muslims, Quranist Muslims.''Destined Encounters - Page 203, Sury Pullat - 2014 of the world's total Muslim population)'' were later independently developed.
Judaism
Jewish religious movements, sometimes called "denominations" or "branches", include different groups which have developed among Jews from ancient times. Today, the main division is between the Orthodox, Reform and Conservative lines, with several smaller movements alongside them. This threefold denominational structure is mainly present in the United States, while in Israel the fault lines are between the religious Orthodox and the non-religious. The movements differ in their views on various issues. These issues include the level of observance, the methodology for interpreting and understandingJewish law
''Halakha'' (; he, הֲלָכָה, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical comman ...
, biblical authorship, textual criticism
Textual criticism is a branch of textual scholarship, philology, and of literary criticism that is concerned with the identification of textual variants, or different versions, of either manuscripts or of printed books. Such texts may range in da ...
and the nature or role of the messiah
In Abrahamic religions, a messiah or messias (; ,
; ,
; ) is a saviour or liberator of a group of people. The concepts of ''mashiach'', messianism, and of a Messianic Age originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible, in which a ''mashiach'' i ...
(or messianic age). Across these movements there are marked differences in liturgy
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. ''Liturgy'' can also be used to refer specifically to public worship by Christians. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and partic ...
, especially in the language in which services are conducted, with the more traditional movements emphasizing Hebrew. The sharpest theological division occurs between Orthodox and non-Orthodox Jews who adhere to other denominations, such that the non-Orthodox movements are sometimes referred to collectively as the "liberal denominations" or "progressive streams."
Multi-denominational
The term "multi-denominational" may describe (for example) a religious event that includes several religious denominations from sometimes unrelated religious groups. Manycivic
Civic is something related to a city or municipality. It also can refer to multiple other things:
General
*Civics, the science of comparative government
*Civic engagement, the connection one feels with their larger community
*Civic center, a comm ...
events include religious portions led by representatives from several religious denominations to be as inclusive or representational as possible of the expected population or audience. For example: the Sunday thanksgiving
Thanksgiving is a national holiday celebrated on various dates in the United States, Canada, Grenada, Saint Lucia, Liberia, and unofficially in countries like Brazil and Philippines. It is also observed in the Netherlander town of Leiden ...
mass at Campamento Esperanza (English: Camp Hope
Camp Hope is a volunteer base camp located in a former school in St. Bernard Parish, Louisiana. Camp Hope has welcomed people from all over the United States and all over the world who have come to participate in the massive recovery efforts of S ...
) in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
, where services were led by both a Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in partic ...
and by an Evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual expe ...
preacher during the Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
an 2010 Copiapó mining accident
The 2010 Copiapó mining accident, also known then as the "Chilean mining accident", began on 5 August 2010, with a cave-in at the San José copper–gold mine, located in the Atacama Desert north of the regional capital of Copiapó, in nort ...
.Chile mine: Rescued men attend service of thanksBBC News, 17 October 2010
Chaplains
A chaplain is, traditionally, a cleric (such as a minister, priest, pastor, rabbi, purohit, or imam), or a lay representative of a religious tradition, attached to a secular institution (such as a hospital, prison, military unit, intel ...
- frequently ordained
Ordination is the process by which individuals are consecrated, that is, set apart and elevated from the laity class to the clergy, who are thus then authorized (usually by the denominational hierarchy composed of other clergy) to perform ...
clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
of any religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
- are often assigned to secular organizations to provide spiritual support to its members who may belong to any of many different religions or denominations. Many of these chaplains, particularly those serving with the military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
or other large secular organizations, are specifically trained to minister to members of many different faiths, even faiths with opposing religious ideology
An ideology is a set of beliefs or philosophies attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely epistemic, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones." Formerly applied pri ...
from that of the chaplain's own faith.Christmas in Prison - A Quiet OneIndependent News, New Zealand, Press Release: Department Of Corrections, 13 December 2007 Military organizations that do not have large numbers of members from several individual smaller but related denominations will routinely hold multi-denominational religious services, often generically called "
Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
" Sunday services, so minority Protestant denominations are not left out or unserved.Obamas Make Rare Trip to Church While in HawaiiABC News (US), MARK NIESSE 26 December 2010 New chapel heralds more North Fort Hood construction
First U.S. Army, Sgt. 1st Class Gail Braymen, 19 July 2010
See also
* Attempted schisms in the Baháʼí Faith *Christian denomination
A Christian denomination is a distinct Religion, religious body within Christianity that comprises all Church (congregation), church congregations of the same kind, identifiable by traits such as a name, particular history, organization, leadersh ...
* Ecumenism
Ecumenism (), also spelled oecumenism, is the concept and principle that Christians who belong to different Christian denominations should work together to develop closer relationships among their churches and promote Christian unity. The adjec ...
* Hindu denominations
Hindu denominations, '' sampradayas'', traditions, movements, and sects are traditions and sub-traditions within Hinduism centered on one or more gods or goddesses, such as Vishnu, Shiva, Shakti and so on. The term ''sampradaya'' is used for bra ...
* Interfaith dialogue
* Islamic schools and branches
Islamic schools and branches have different understandings of Islam. There are many different sects or denominations, schools of Islamic jurisprudence, and schools of Islamic theology, or '' ʿaqīdah'' (creed). Within Islamic groups themselves ...
* Jain schools and branches
* Jewish religious movements
Jewish religious movements, sometimes called " denominations", include different groups within Judaism which have developed among Jews from ancient times. Today, the most prominent divisions are between traditionalist Orthodox movements (includi ...
* Mansions of Rastafari
* Non-denominational
A non-denominational person or organization is one that does not follow (or is not restricted to) any particular or specific religious denomination.
Overview
The term has been used in the context of various faiths including Jainism, Baháʼí Fait ...
* Religious syncretism
* Schism
A schism ( , , or, less commonly, ) is a division between people, usually belonging to an organization, movement, or religious denomination. The word is most frequently applied to a split in what had previously been a single religious body, suc ...
* Schools of Buddhism
The schools of Buddhism are the various institutional and doctrinal divisions of Buddhism that have existed from ancient times up to the present. The classification and nature of various doctrinal, philosophical or cultural facets of the schoo ...
* Sects of Sikhism
* Shinto sects and schools
, the folk religion of Japan, developed a diversity of schools and sects, outbranching from the original Ko-Shintō (ancient Shintō) since Buddhism was introduced into Japan in the sixth century.
Early period schools and groups
The main Shinto s ...
* Sociological classifications of religious movements
* Taoist schools
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Religious Denomination