Regenerative medicine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
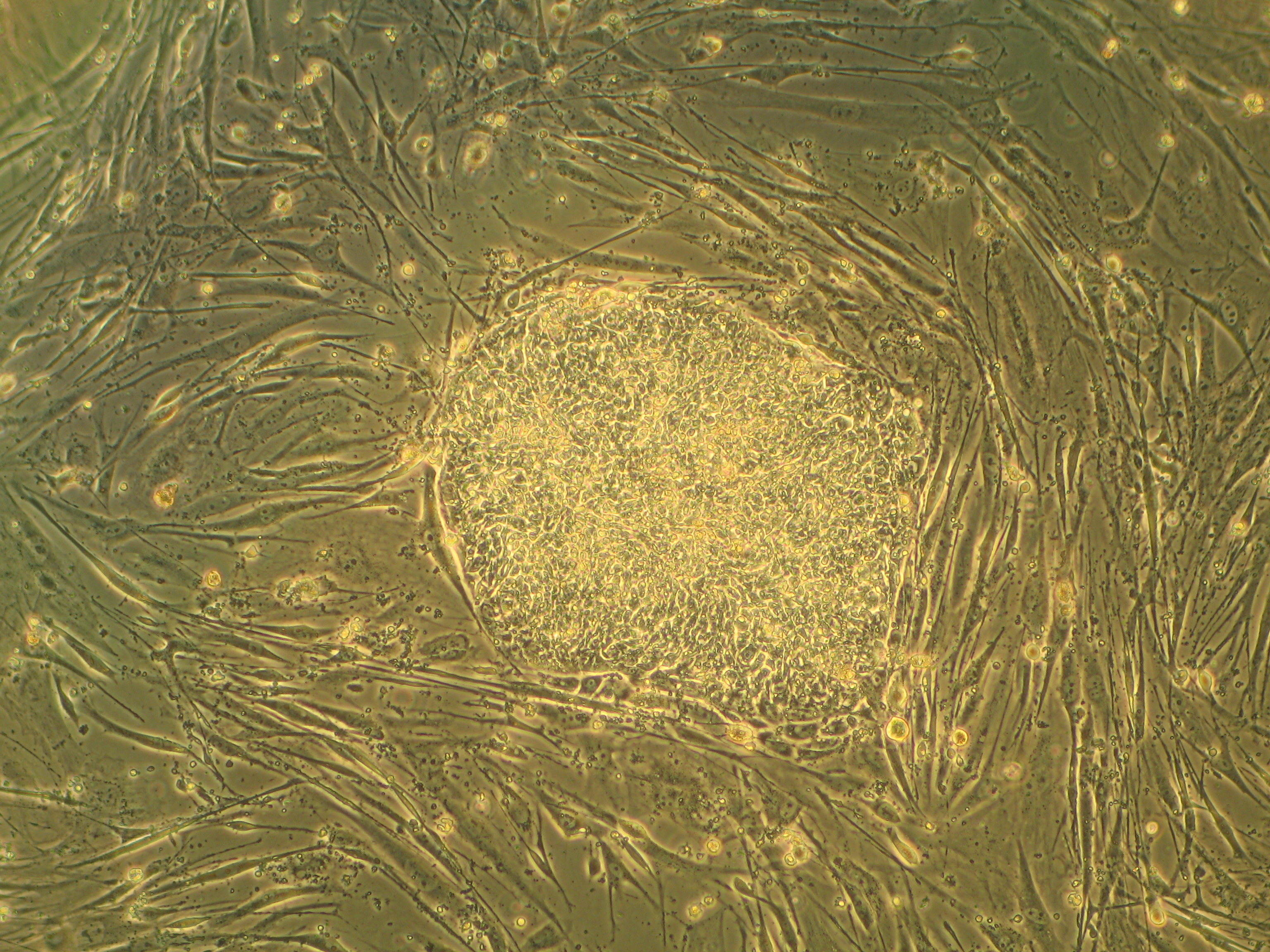 Regenerative medicine deals with the "process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human or animal cells, tissues or organs to restore or establish normal function". This field holds the promise of engineering damaged tissues and organs by stimulating the body's own repair mechanisms to functionally heal previously irreparable tissues or organs.
Regenerative medicine also includes the possibility of growing tissues and organs in the laboratory and implanting them when the body cannot heal itself. When the cell source for a regenerated organ is derived from the patient's own tissue or cells, the challenge of organ
Regenerative medicine deals with the "process of replacing, engineering or regenerating human or animal cells, tissues or organs to restore or establish normal function". This field holds the promise of engineering damaged tissues and organs by stimulating the body's own repair mechanisms to functionally heal previously irreparable tissues or organs.
Regenerative medicine also includes the possibility of growing tissues and organs in the laboratory and implanting them when the body cannot heal itself. When the cell source for a regenerated organ is derived from the patient's own tissue or cells, the challenge of organ
 Regenerative medicine has been studied by dentists to find ways that damaged teeth can be repaired and restored to obtain natural structure and function. Dental tissues are often damaged due to tooth decay, and are often deemed to be irreplaceable except by synthetic or metal dental fillings or crowns, which requires further damage to be done to the teeth by drilling into them to prevent the loss of an entire tooth.
Researchers from King's College London have created a drug called Tideglusib that claims to have the ability to regrow dentin, the second layer of the tooth beneath the enamel which encases and protects the pulp (often referred to as the nerve).
Animal studies conducted on mice in Japan in 2007 show great possibilities in regenerating an entire tooth. Some mice had a tooth extracted and the cells from bioengineered tooth germs were implanted into them and allowed to grow. The result were perfectly functioning and healthy teeth, complete with all three layers, as well as roots. These teeth also had the necessary ligaments to stay rooted in its socket and allow for natural shifting. They contrast with traditional dental implants, which are restricted to one spot as they are drilled into the jawbone.
A person's baby teeth are known to contain stem cells that can be used for regeneration of the dental pulp after a root canal treatment or injury. These cells can also be used to repair damage from periodontitis, an advanced form of gum disease that causes bone loss and severe gum recession. Research is still being done to see if these stem cells are viable enough to grow into completely new teeth. Some parents even opt to keep their children's baby teeth in special storage with the thought that, when older, the children could use the stem cells within them to treat a condition.
Regenerative medicine has been studied by dentists to find ways that damaged teeth can be repaired and restored to obtain natural structure and function. Dental tissues are often damaged due to tooth decay, and are often deemed to be irreplaceable except by synthetic or metal dental fillings or crowns, which requires further damage to be done to the teeth by drilling into them to prevent the loss of an entire tooth.
Researchers from King's College London have created a drug called Tideglusib that claims to have the ability to regrow dentin, the second layer of the tooth beneath the enamel which encases and protects the pulp (often referred to as the nerve).
Animal studies conducted on mice in Japan in 2007 show great possibilities in regenerating an entire tooth. Some mice had a tooth extracted and the cells from bioengineered tooth germs were implanted into them and allowed to grow. The result were perfectly functioning and healthy teeth, complete with all three layers, as well as roots. These teeth also had the necessary ligaments to stay rooted in its socket and allow for natural shifting. They contrast with traditional dental implants, which are restricted to one spot as they are drilled into the jawbone.
A person's baby teeth are known to contain stem cells that can be used for regeneration of the dental pulp after a root canal treatment or injury. These cells can also be used to repair damage from periodontitis, an advanced form of gum disease that causes bone loss and severe gum recession. Research is still being done to see if these stem cells are viable enough to grow into completely new teeth. Some parents even opt to keep their children's baby teeth in special storage with the thought that, when older, the children could use the stem cells within them to treat a condition.
Regenerative Medicine
gives more details about Regenerative Stem Cells. * * Kevin Strange and Viravuth Yin, "A Shot at Regeneration: A once abandoned drug compound shows an ability to rebuild organs damaged by illness and injury", ''
transplant rejection
Transplant rejection occurs when transplanted tissue is rejected by the recipient's immune system, which destroys the transplanted tissue. Transplant rejection can be lessened by determining the molecular similitude between donor and recipient ...
via immunological mismatch is circumvented. This approach could alleviate the problem of the shortage of organs available for donation.
Some of the biomedical approaches within the field of regenerative medicine may involve the use of stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
s. Examples include the injection of stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
s or progenitor cells obtained through directed differentiation ( cell therapies); the induction of regeneration by biologically active molecules administered alone or as a secretion by infused cells (immunomodulation therapy); and transplantation of ''in vitro'' grown organs and tissues (tissue engineering
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of Cell (biology), cells, engineering, Materials science, materials methods, and suitable biochemistry, biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintai ...
).
History
The ancient Greeks postulated whether parts of the body could be regenerated in the 700s BC. Skin grafting, invented in the late 19th century, can be thought of as the earliest major attempt to recreate bodily tissue to restore structure and function. Advances in transplanting body parts in the 20th century further pushed the theory that body parts could regenerate and grow new cells. These advances led to tissue engineering, and from this field, the study of regenerative medicine expanded and began to take hold. This began with cellular therapy, which led to the stem cell research that is widely being conducted today. The first cell therapies were intended to slow the aging process. This began in the 1930s with Paul Niehans, a Swiss doctor who was known to have treated famous historical figures such as Pope Pius XII, Charlie Chaplin, and king Ibn Saud of Saudi Arabia. Niehans would inject cells of young animals (usually lambs or calves) into his patients in an attempt to rejuvenate them. In 1956, a more sophisticated process was created to treat leukemia by inserting bone marrow from a healthy person into a patient with leukemia. This process worked mostly due to both the donor and receiver in this case being identical twins. Nowadays, bone marrow can be taken from people who are similar enough to the patient who needs the cells to prevent rejection. The term "regenerative medicine" was first used in a 1992 article on hospital administration by Leland Kaiser. Kaiser's paper closes with a series of short paragraphs on future technologies that will impact hospitals. One paragraph had "Regenerative Medicine" as a bold print title and stated, "A new branch of medicine will develop that attempts to change the course of chronic disease and in many instances will regenerate tired and failing organ systems." The term was brought into the popular culture in 1999 by William A. Haseltine when he coined the term during a conference on Lake Como, to describe interventions that restore to normal function that which is damaged by disease, injured by trauma, or worn by time. Haseltine was briefed on the project to isolate human embryonic stem cells and embryonic germ cells atGeron Corporation
Geron Corporation is a biotechnology company located in Foster City, California, which specializes in developing and commercializing therapeutic products for cancer that inhibit telomerase.
Company information
Geron, based in Foster City, Cal ...
in collaboration with researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
and Johns Hopkins School of Medicine
The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine (JHUSOM) is the medical school of Johns Hopkins University, a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1893, the School of Medicine shares a campus with the Johns Hopkins Hospi ...
. He recognized that these cells' unique ability to differentiate into all the cell types of the human body ( pluripotency) had the potential to develop into a new kind of regenerative therapy. Explaining the new class of therapies that such cells could enable, he used the term "regenerative medicine" in the way that it is used today: "an approach to therapy that ... employs human genes, proteins and cells to re-grow, restore or provide mechanical replacements for tissues that have been injured by trauma, damaged by disease or worn by time" and "offers the prospect of curing diseases that cannot be treated effectively today, including those related to aging".
Later, Haseltine would go on to explain that regenerative medicine acknowledges the reality that most people, regardless of which illness they have or which treatment they require, simply want to be restored to normal health. Designed to be applied broadly, the original definition includes cell and stem cell therapies, gene therapy, tissue engineering, genomic medicine, personalized medicine, biomechanical prosthetics, recombinant proteins, and antibody treatments. It also includes more familiar chemical pharmacopeia—in short, any intervention that restores a person to normal health. In addition to functioning as shorthand for a wide range of technologies and treatments, the term “regenerative medicine” is also patient friendly. It solves the problem of confusing or intimidating language discourage to patients.
The term regenerative medicine is increasingly conflated with research on stem cell therapies. Some academic programs and departments retain the original broader definition while others use it to describe work on stem cell research.
From 1995 to 1998 Michael D. West
Michael D. West (born in Niles, Michigan on 28 April 1953) is an American biogerontologist, and a pioneer in stem cells, cellular aging and telomerase. He is the founder and CEO of AgeX Therapeutics,
a startup focused on the field of experim ...
, PhD, organized and managed the research between Geron Corporation
Geron Corporation is a biotechnology company located in Foster City, California, which specializes in developing and commercializing therapeutic products for cancer that inhibit telomerase.
Company information
Geron, based in Foster City, Cal ...
and its academic collaborators James Thomson at the University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United Stat ...
and John Gearhart of Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hemisphere. It consi ...
that led to the first isolation of human embryonic stem and human embryonic germ cells, respectively.
In March 2000, Haseltine, Antony Atala, M.D., Michael D. West, Ph.D., and other leading researchers founded ''E-Biomed: The Journal of Regenerative Medicine''. The peer-reviewed journal facilitated discourse around regenerative medicine by publishing innovative research on stem cell therapies, gene therapies, tissue engineering, and biomechanical prosthetics. The Society for Regenerative Medicine, later renamed the Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Biology Society, served a similar purpose, creating a community of like-minded experts from around the world.
In June 2008, at the Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, Professor Paolo Macchiarini and his team, of the University of Barcelona
The University of Barcelona ( ca, Universitat de Barcelona, UB; ; es, link=no, Universidad de Barcelona) is a public university located in the city of Barcelona, Catalonia, in Spain. With 63,000 students, it is one of the biggest universities i ...
, performed the first tissue engineered trachea (wind pipe) transplantation. Adult stem cells were extracted from the patient's bone marrow, grown into a large population, and matured into cartilage cells, or chondrocyte
Chondrocytes (, from Greek χόνδρος, ''chondros'' = cartilage + κύτος, ''kytos'' = cell) are the only cells found in healthy cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and prote ...
s, using an adaptive method originally devised for treating osteoarthritis. The team then seeded the newly grown chondrocytes, as well as epithelial cells, into a decellularised (free of donor cells) tracheal segment that was donated from a 51-year-old transplant donor who had died of cerebral hemorrhage. After four days of seeding, the graft was used to replace the patient's left main bronchus. After one month, a biopsy elicited local bleeding, indicating that the blood vessels had already grown back successfully.
In 2009, the SENS Foundation
The SENS Research Foundation is a non-profit organization that does research programs and public relations work for the application of regenerative medicine to aging. It was founded in 2009, located in Mountain View, California, USA. The organ ...
was launched, with its stated aim as "the application of regenerative medicine – defined to include the repair of living cells and extracellular material in situ – to the diseases and disabilities of ageing". In 2012, Professor Paolo Macchiarini and his team improved upon the 2008 implant by transplanting a laboratory-made trachea seeded with the patient's own cells.
On September 12, 2014, surgeons at the Institute of Biomedical Research and Innovation Hospital in Kobe, Japan, transplanted a 1.3 by 3.0 millimeter sheet of retinal pigment epithelium cells, which were differentiated from iPS cells through directed differentiation, into an eye of an elderly woman, who suffers from age-related macular degeneration.
In 2016, Paolo Macchiarini was fired from Karolinska University in Sweden due to falsified test results and lies. The TV-show Experimenten aired on Swedish Television and detailed all the lies and falsified results.
Research
Widespread interest and funding for research on regenerative medicine has prompted institutions in the United States and around the world to establish departments and research institutes that specialize in regenerative medicine including: The Department of Rehabilitation and Regenerative Medicine atColumbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
, the Institute for Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine at Stanford University
Stanford University, officially Leland Stanford Junior University, is a private research university in Stanford, California. The campus occupies , among the largest in the United States, and enrolls over 17,000 students. Stanford is conside ...
, the Center for Regenerative and Nanomedicine at Northwestern University
Northwestern University is a private research university in Evanston, Illinois. Founded in 1851, Northwestern is the oldest chartered university in Illinois and is ranked among the most prestigious academic institutions in the world.
Charte ...
, the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, and the British Heart Foundation Centers of Regenerative Medicine at the University of Oxford
, mottoeng = The Lord is my light
, established =
, endowment = £6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019)
, budget = £2.145 billion (2019–20)
, chancellor ...
. In China, institutes dedicated to regenerative medicine are run by the Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS); ), known by Academia Sinica in English until the 1980s, is the national academy of the People's Republic of China for natural sciences. It has historical origins in the Academia Sinica during the Republi ...
, Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University (; abbr. THU) is a national public research university in Beijing, China. The university is funded by the Ministry of Education.
The university is a member of the C9 League, Double First Class University Plan, Projec ...
, and the Chinese University of Hong Kong, among others.
In dentistry
Extracellular matrix
Extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide s ...
materials are commercially available and are used in reconstructive surgery
Reconstructive surgery is surgery performed to restore normal appearance and function to body parts malformed by a disease or medical condition.
Description
Reconstructive surgery is a term with training, clinical, and reimbursement implicat ...
, treatment of chronic wound A chronic wound is a wound that does not heal in an orderly set of stages and in a predictable amount of time the way most wounds do; wounds that do not heal within three months are often considered chronic.
Chronic wounds seem to be detained in one ...
s, and some orthopedic surgeries; as of January 2017 clinical studies were under way to use them in heart surgery to try to repair damaged heart tissue.
The use of fish skin with its natural constituent of omega 3, has been developed by an Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
ic company Kereceis. Omega 3 is a natural anti-inflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs remedy pain by reducing inflammation as o ...
, and the fish skin material acts as a scaffold for cell regeneration. In 2016 their product ''Omega3 Wound'' was approved by the FDA for the treatment of chronic wounds and burns. In 2021 the FDA gave approval for ''Omega3 Surgibind'' to be used in surgical applications including plastic surgery.
Cord blood
Though uses of cord blood beyond blood and immunological disorders is speculative, some research has been done in other areas. Any such potential beyond blood and immunological uses is limited by the fact that cord cells arehematopoietic
Haematopoiesis (, from Greek , 'blood' and 'to make'; also hematopoiesis in American English; sometimes also h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cell ...
stem cells (which can differentiate only into blood cells), and not pluripotent Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
stem cells (such as embryonic stem cells, which can differentiate into any type of tissue). Cord blood has been studied as a treatment for diabetes. However, apart from blood disorders, the use of cord blood for other diseases is not a routine clinical modality and remains a major challenge for the stem cell community.
Along with cord blood, Wharton's jelly and the cord lining have been explored as sources for mesenchymal stem cells
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) also known as mesenchymal stromal cells or medicinal signaling cells are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteoblasts (bone cells), chondrocytes (cartilage c ...
(MSC), and as of 2015 had been studied in vitro, in animal models, and in early stage clinical trials for cardiovascular diseases, as well as neurological deficits, liver diseases, immune system diseases, diabetes, lung injury, kidney injury, and leukemia.
See also
References
Further reading
Non-technical further reading
Regenerative Medicine
gives more details about Regenerative Stem Cells. * * Kevin Strange and Viravuth Yin, "A Shot at Regeneration: A once abandoned drug compound shows an ability to rebuild organs damaged by illness and injury", ''
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it ...
'', vol. 320, no. 4 (April 2019), pp. 56–61.
Technical further reading
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Regenerative Medicine Vertebrate developmental biology Emerging technologies Regenerative biomedicine Tissue engineering