Red Hills (Kansas) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
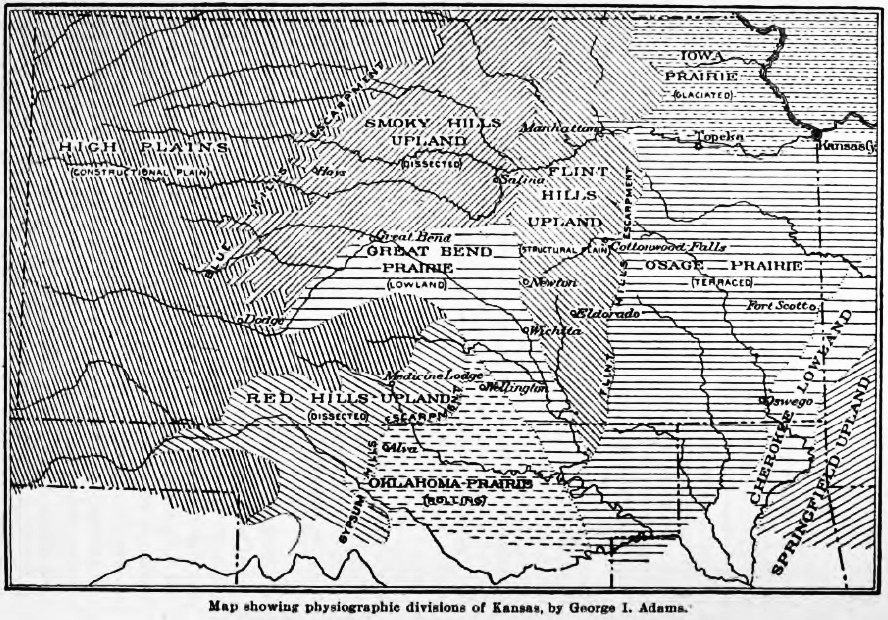 The Red Hills, also referred to as Gypsum Hills, is the name of a United States physiographic region, physiographic region located mostly in Clark County, Kansas, Clark, Comanche County, Kansas, Comanche and Barber County, Kansas, Barber counties in southern and central Kansas. This undulating terrain of red-tinted sediments, a product of the underlying geology, does not fit the conventional description of the Great Plains landscape of Kansas.
The red bed sediments of the Red Hills were deposited in an arid continental Endorheic basin, closed basin that formed within the Pangaean supercontinent during the Permian Period. Water often flooded this basin forming ephemeral Sink (geography), playas of somewhat acidic waters.Benison, K.C. and Goldstein, R.H. 2001. Evaporites and siliciclastics of the Permian Nippewalla Group of Kansas, USA: a case for non-marine deposition in saline lakes and saline pans. Sedimentology 48(1):165-188. The shallow playas were intermittently flooded then dried leaving a mixture of Lake, lacustrine sediments and gypsum evaporites. The red color derives from the oxidation of iron contained within the deposits.
The region is also known as the Gypsum Hills, because of the large natural deposits of gypsum in this area. The dissolution of underlying gypsum beds has led to the formation of sinkholes which are common features within the Red Hills region. Big Basin Prairie Preserve, Big Basin and Little Basin are two well-known sinkholes in western Clark County.
The Red Hills have scenic vistas and some small steep canyons. High points include Mount Nebo (), Mount Jesus () and Mount Lookout (), in Clark County, Kansas.
The Red Hills, also referred to as Gypsum Hills, is the name of a United States physiographic region, physiographic region located mostly in Clark County, Kansas, Clark, Comanche County, Kansas, Comanche and Barber County, Kansas, Barber counties in southern and central Kansas. This undulating terrain of red-tinted sediments, a product of the underlying geology, does not fit the conventional description of the Great Plains landscape of Kansas.
The red bed sediments of the Red Hills were deposited in an arid continental Endorheic basin, closed basin that formed within the Pangaean supercontinent during the Permian Period. Water often flooded this basin forming ephemeral Sink (geography), playas of somewhat acidic waters.Benison, K.C. and Goldstein, R.H. 2001. Evaporites and siliciclastics of the Permian Nippewalla Group of Kansas, USA: a case for non-marine deposition in saline lakes and saline pans. Sedimentology 48(1):165-188. The shallow playas were intermittently flooded then dried leaving a mixture of Lake, lacustrine sediments and gypsum evaporites. The red color derives from the oxidation of iron contained within the deposits.
The region is also known as the Gypsum Hills, because of the large natural deposits of gypsum in this area. The dissolution of underlying gypsum beds has led to the formation of sinkholes which are common features within the Red Hills region. Big Basin Prairie Preserve, Big Basin and Little Basin are two well-known sinkholes in western Clark County.
The Red Hills have scenic vistas and some small steep canyons. High points include Mount Nebo (), Mount Jesus () and Mount Lookout (), in Clark County, Kansas.
Red Hills Focus Area-U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service
Regions of Kansas Geology of Kansas {{BarberCountyKS-geo-stub
 The Red Hills, also referred to as Gypsum Hills, is the name of a United States physiographic region, physiographic region located mostly in Clark County, Kansas, Clark, Comanche County, Kansas, Comanche and Barber County, Kansas, Barber counties in southern and central Kansas. This undulating terrain of red-tinted sediments, a product of the underlying geology, does not fit the conventional description of the Great Plains landscape of Kansas.
The red bed sediments of the Red Hills were deposited in an arid continental Endorheic basin, closed basin that formed within the Pangaean supercontinent during the Permian Period. Water often flooded this basin forming ephemeral Sink (geography), playas of somewhat acidic waters.Benison, K.C. and Goldstein, R.H. 2001. Evaporites and siliciclastics of the Permian Nippewalla Group of Kansas, USA: a case for non-marine deposition in saline lakes and saline pans. Sedimentology 48(1):165-188. The shallow playas were intermittently flooded then dried leaving a mixture of Lake, lacustrine sediments and gypsum evaporites. The red color derives from the oxidation of iron contained within the deposits.
The region is also known as the Gypsum Hills, because of the large natural deposits of gypsum in this area. The dissolution of underlying gypsum beds has led to the formation of sinkholes which are common features within the Red Hills region. Big Basin Prairie Preserve, Big Basin and Little Basin are two well-known sinkholes in western Clark County.
The Red Hills have scenic vistas and some small steep canyons. High points include Mount Nebo (), Mount Jesus () and Mount Lookout (), in Clark County, Kansas.
The Red Hills, also referred to as Gypsum Hills, is the name of a United States physiographic region, physiographic region located mostly in Clark County, Kansas, Clark, Comanche County, Kansas, Comanche and Barber County, Kansas, Barber counties in southern and central Kansas. This undulating terrain of red-tinted sediments, a product of the underlying geology, does not fit the conventional description of the Great Plains landscape of Kansas.
The red bed sediments of the Red Hills were deposited in an arid continental Endorheic basin, closed basin that formed within the Pangaean supercontinent during the Permian Period. Water often flooded this basin forming ephemeral Sink (geography), playas of somewhat acidic waters.Benison, K.C. and Goldstein, R.H. 2001. Evaporites and siliciclastics of the Permian Nippewalla Group of Kansas, USA: a case for non-marine deposition in saline lakes and saline pans. Sedimentology 48(1):165-188. The shallow playas were intermittently flooded then dried leaving a mixture of Lake, lacustrine sediments and gypsum evaporites. The red color derives from the oxidation of iron contained within the deposits.
The region is also known as the Gypsum Hills, because of the large natural deposits of gypsum in this area. The dissolution of underlying gypsum beds has led to the formation of sinkholes which are common features within the Red Hills region. Big Basin Prairie Preserve, Big Basin and Little Basin are two well-known sinkholes in western Clark County.
The Red Hills have scenic vistas and some small steep canyons. High points include Mount Nebo (), Mount Jesus () and Mount Lookout (), in Clark County, Kansas.
See also
*Big Basin Prairie Preserve *Tallgrass Prairie National Preserve *Flint HillsReferences
External links
Red Hills Focus Area-U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service
Regions of Kansas Geology of Kansas {{BarberCountyKS-geo-stub