Recovered Territories on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The Recovered Territories or Regained Lands () are the lands east of the Oder-Neisse line that over the centuries were gradually lost by Poland and colonized by the Germans, and that returned to Poland after
The Recovered Territories or Regained Lands () are the lands east of the Oder-Neisse line that over the centuries were gradually lost by Poland and colonized by the Germans, and that returned to Poland after
 The term "Recovered Territories" was officially used for the first time in the Decree of the President of the Republic of 11 October 1938 after the annexation of
The term "Recovered Territories" was officially used for the first time in the Decree of the President of the Republic of 11 October 1938 after the annexation of
''"The Neighbors Respond: The Controversy Over the Jedwabne Massacre in Poland"''
, ed. by Polonsky and Michlic, p. 466 coined in the aftermath of By 1949, the term "Recovered Territories" had been dropped from Polish communist propaganda, but it is still used occasionally in common language.Gregor Thum, ''Die fremde Stadt. Breslau nach 1945'', 2006, p. 298, , On the grounds that those areas should not be regarded as unique territories within the Polish state, the authorities began to refer to them instead as the "Western and Northern Lands".Martin Åberg, Mikael Sandberg, ''Social Capital and Democratisation: Roots of Trust in Post-Communist Poland and Ukraine'', Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2003,
By 1949, the term "Recovered Territories" had been dropped from Polish communist propaganda, but it is still used occasionally in common language.Gregor Thum, ''Die fremde Stadt. Breslau nach 1945'', 2006, p. 298, , On the grounds that those areas should not be regarded as unique territories within the Polish state, the authorities began to refer to them instead as the "Western and Northern Lands".Martin Åberg, Mikael Sandberg, ''Social Capital and Democratisation: Roots of Trust in Post-Communist Poland and Ukraine'', Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2003,
Google Print, p. 51
Wolff and Cordell say that along with the debunking of communist historiography, "the 'recovered territories' thesis ... has been discarded", and that "it is freely admitted in some circles that on the whole 'the recovered territories' had a wholly German character", but that this view has not necessarily been transmitted to the whole of Polish society.Karl Cordell, Stefan Wolff (2005)
''Germany's Foreign Policy Towards Poland and the Czech Republic: Ostpolitik Revisited''
. p. 139. , . "In addition ... it has been relatively easy for Polish historians and others to attempt to debunk communist historiography and present a more balanced analysis of the past – and not only with respect to Germany. It has been controversial, and often painful, but nevertheless it has been done. For example, Poland's acquisition in 1945 of eastern German territories is increasingly presented as the price Germany paid for launching a total war, and then having lost it totally. The 'recovered territories' thesis previously applied in almost equal measures by the communists and Catholic Church has been discarded. Some circles freely admit that on the whole, 'the recovered territories' in fact had a wholly German character. The extent to which this fact transmitted to groups other than the socially and politically engaged is a matter of debate." The term was also used outside Poland. In 1962,
 Several different West Slavic tribes inhabited most of the area of present-day Poland from the 6th century. Duke
Several different West Slavic tribes inhabited most of the area of present-day Poland from the 6th century. Duke  Mieszko's son and successor, Duke Bolesław I Chrobry, upon the 1018
Mieszko's son and successor, Duke Bolesław I Chrobry, upon the 1018
 The
The
 The region of
The region of

 The medieval
The medieval  A small part of northern Greater Poland around the town of Czaplinek was lost to Brandenburg-Prussia in 1668. Bigger portions of Greater Poland were lost in the
A small part of northern Greater Poland around the town of Czaplinek was lost to Brandenburg-Prussia in 1668. Bigger portions of Greater Poland were lost in the
 Lower Silesia was one of the leading regions of medieval Poland.
Lower Silesia was one of the leading regions of medieval Poland.
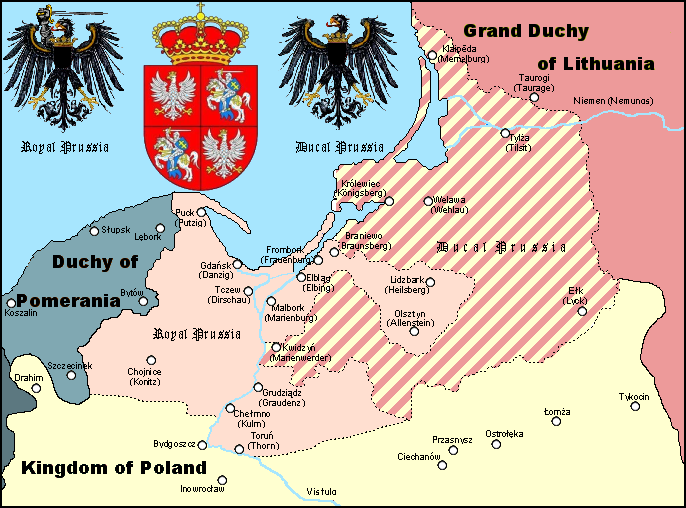 The territories of
The territories of
 Since the time of the
Since the time of the
 During the Polish post-war census of December 1950, data about the pre-war places of residence of the inhabitants as of August 1939 was collected. (In the case of children born between September 1939 and December 1950, their place of residence was reported based on the pre-war places of residence of their mothers.) Thanks to this data it is possible to reconstruct the pre-war geographical origin of the post-war population. Many areas located near the pre-war German border were resettled by people from neighbouring borderland areas of pre-war Poland. For example, Kashubians from the pre-war Polish Corridor settled in nearby areas of German Pomerania adjacent to Polish Pomerania. People from the Poznań region of pre-war Poland settled in East Brandenburg. People from East Upper Silesia moved into the rest of Silesia. And people from
During the Polish post-war census of December 1950, data about the pre-war places of residence of the inhabitants as of August 1939 was collected. (In the case of children born between September 1939 and December 1950, their place of residence was reported based on the pre-war places of residence of their mothers.) Thanks to this data it is possible to reconstruct the pre-war geographical origin of the post-war population. Many areas located near the pre-war German border were resettled by people from neighbouring borderland areas of pre-war Poland. For example, Kashubians from the pre-war Polish Corridor settled in nearby areas of German Pomerania adjacent to Polish Pomerania. People from the Poznań region of pre-war Poland settled in East Brandenburg. People from East Upper Silesia moved into the rest of Silesia. And people from
 The People's Republic had to locate its population inside the new frontiers in order to solidify the hold over the territories. With the
The People's Republic had to locate its population inside the new frontiers in order to solidify the hold over the territories. With the
Google Print, p.79
and to justify the removal of the German inhabitants. Largely excepted from the expulsions of Germans were the "
The "autochthons" not only disliked the subjective and often arbitrary verification process, but they also faced discrimination even after completing it, such as the Polonization of their names. In the Lubusz Voivodeship, Lubusz region (former East Brandenburg), the local authorities conceded already in 1948 that what the PZZ claimed to be a recovered "autochton" Polish population were in fact Germanized migrant workers, who had settled in the region in the late 19th and early 20th centuries – with the exception of one village, Babimost, just across the pre-war border. Great efforts were made to propagate the view of the Piast Concept. It was actively supported by the Catholic Church. The sciences were responsible for the development of this perception of history. In 1945 the Western Institute () was founded to coordinate the scientific activities. Its director, Zygmunt Wojciechowski, characterized his mission as an effort to present the Polish history of the region, and project current Polish reality of these countries upon a historical background. Historical scientists, archaeologists, linguists, art historians and ethnologists worked in an interdisciplinary effort to legitimize the new borders.Gregor Thum, ''Die fremde Stadt. Breslau nach 1945'', 2006, p. 281, , Their findings were popularised in monographs, periodicals, schoolbooks, travel guides, broadcasts and exhibitions. Official maps were drawn showing that the Polish frontiers under the first known Piast princes matched the new ones. According to
File:Oder-neisse.gif, Pre-1945 administrative division (yellow)
File:POLSKA 14-03-1945.png, Projected Polish administration (Okreg I-IV) in March, 1945
File:POLSKA 28-06-1946.png, Integration into the
 People from all over Poland quickly moved in to replace the former German population in a process parallel to the expulsions, with the first settlers arriving in March 1945. These settlers took over farms and villages close to the pre-war frontier while the
People from all over Poland quickly moved in to replace the former German population in a process parallel to the expulsions, with the first settlers arriving in March 1945. These settlers took over farms and villages close to the pre-war frontier while the
 During the
During the  Until the Treaty on the Final Settlement, the West German government regarded the status of the German territories east of the Oder-Neisse rivers as that of areas "temporarily under Polish or Soviet administration". To facilitate wide international acceptance of
Until the Treaty on the Final Settlement, the West German government regarded the status of the German territories east of the Oder-Neisse rivers as that of areas "temporarily under Polish or Soviet administration". To facilitate wide international acceptance of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. This term includes Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (; ), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania, located mostly in north-eastern Germany, with a small portion in no ...
, Lower Silesia, the western part of Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
, Warmia
Warmia ( ; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian subdialect, Warmian: ''Warńija''; Old Prussian language, Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia (reg ...
, Masuria
Masuria ( ; ; ) is an ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian–Masurian Voivodeship (ad ...
, Lubusz Land
Lubusz Land (; ) is a historical region and cultural landscape in Poland and Germany on both sides of the Oder river.
Originally the settlement area of the Lechites, the swampy area was located east of Margraviate of Brandenburg, Brandenburg and ...
and Kłodzko Land
Kłodzko Land (; ; ) is a historical region in southwestern Poland.
The subject of Czech–Polish rivalry in the High Middle Ages, it became a Bohemian domain since the 12th century, although with periods of rule of the Polish Piast dynasty in th ...
. Sometimes the city of Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdań ...
is also included.
The rationale for the term "Recovered" was that these territories formed part of the Polish state, and were lost by Poland in different periods of time. It also referred to the Piast Concept that these territories were part of the traditional Polish homeland under the Piast dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented List of Polish monarchs, Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I of Poland, Mieszko I (–992). The Poland during the Piast dynasty, Piasts' royal rule in Pol ...
(there were their small parts under Poland even after the Piast dynasty ended), after the establishment of the Polish state in 966. Over the centuries, however, they had become predominantly German-speaking through the processes of German eastward settlement (), political expansion (), as well as language shift
Language shift, also known as language transfer, language replacement or language assimilation, is the process whereby a speech community shifts to a different language, usually over an extended period of time. Often, languages that are perceived ...
due to intense Germanisation
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people, and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In l ...
of the local Lechitic and Prussian populations. Therefore, unlike the lands that Poland regained from Germany after World War I under the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
, the Recovered Territories did not contain large Polish-speaking communities at the time of return to Polish jurisdiction. Sizeable Polish minorities existed only in western Upper Silesia and southern Masuria.
While most regions had long periods of Polish rule, spanning hundreds of years, some regions, when not under Polish rule, were in different times under the authority of the Bohemian (Czech) Kingdom, Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
, Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
, Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
, German Prussia, and the German Reich
German ''Reich'' (, from ) was the constitutional name for the German nation state that existed from 1871 to 1945. The ''Reich'' became understood as deriving its authority and sovereignty entirely from a continuing unitary German ''Volk'' ("na ...
. The western regions became part of various weakened Polish duchies created as a result of the fragmentation of the realm in the 12th and 13th centuries and were then lost to neighbouring Germany.
The great majority of the previous German and Germanized inhabitants fled from these territories in the last year of the Second World War and those who remained were resettled to East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
by the post-war communist authorities, although a small German minority remains in Opolian Silesia. The recovered territories were repopulated with Polish repatriates forced to leave areas of former eastern Poland that had been annexed by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, Poles freed from forced labour in Nazi Germany, with Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
forcibly resettled during Operation Vistula
Operation Vistula (; ) was the codename for the 1947 forced resettlement of close to 150,000 Ukrainians in Poland, Ukrainians (including Rusyns, Boykos, and Lemkos) from the southeastern provinces of People's Republic of Poland, postwar Poland to ...
, and other minorities which settled in Poland after the war, including Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
and Macedonians.
However, contrary to the official declaration that the former German inhabitants of the Recovered Territories had to be removed quickly to house Poles displaced by the Soviet annexation, the Recovered Territories initially faced a severe population shortage. The Soviet-appointed Polish communist authorities that conducted the resettlement also made efforts to denazify and remove traces of German culture, such as place names, monuments and swastikas.
The post-war border between Germany and Poland (the Oder–Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line (, ) is an unofficial term for the Germany–Poland border, modern border between Germany and Poland. The line generally follows the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers, meeting the Baltic Sea in the north. A small portion ...
) was recognized by East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
in 1950 and by West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republi ...
in 1970, and was affirmed by the re-united Germany in the German–Polish Border Treaty of 1990.
Origin and use of the term
 The term "Recovered Territories" was officially used for the first time in the Decree of the President of the Republic of 11 October 1938 after the annexation of
The term "Recovered Territories" was officially used for the first time in the Decree of the President of the Republic of 11 October 1938 after the annexation of Trans-Olza
Trans-Olza (, ; , ''Záolší''; ), also known as Trans-Olza Silesia (), is a territory in the Czech Republic which was disputed between Poland and Czechoslovakia during the Interwar Period. Its name comes from the Olza River.
The history of ...
by the Polish army. It became the official termAn explanation note i''"The Neighbors Respond: The Controversy Over the Jedwabne Massacre in Poland"''
, ed. by Polonsky and Michlic, p. 466 coined in the aftermath of
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
to denote the former eastern territories of Germany
In present-day Germany, the former eastern territories of Germany () refer to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany, i.e. the Oder–Neisse line, which historically had been considered German and which were annexed b ...
that were being handed over to Poland, pending a final peace conference with Germany which eventually never took place. The term "Recovered Territories" is a collective term for different areas with different histories, which can be grouped into three categories:
* Those that once had been part of the Polish state during the rule of the Piasts, many of which later on had been part of various Piast, Griffin
The griffin, griffon, or gryphon (; Classical Latin: ''gryps'' or ''grypus''; Late and Medieval Latin: ''gryphes'', ''grypho'' etc.; Old French: ''griffon'') is a -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk ...
, Jagiellon and Sobieski-ruled duchies, some up to the 17th and 18th century, although often under foreign suzerainty
* Those that had been part of Poland until the 17th century (northernmost part of Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; ), is a Polish Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city in Poland.
The bound ...
, including Czaplinek) or were under Polish suzerainty as fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
s, in the 15th, 16th and 17th centuries (southern Ducal Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (, , ) or Ducal Prussia (; ) was a duchy in the region of Prussia established as a result of secularization of the Monastic Prussia, the territory that remained under the control of the State of the Teutonic Order until t ...
and the Duchy of Opole, which also falls into the category above)
* Territories that had been part of Poland until the Partitions (Warmia
Warmia ( ; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian subdialect, Warmian: ''Warńija''; Old Prussian language, Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia (reg ...
, Malbork Voivodeship, parts of Pomerelia
Pomerelia, also known as Eastern Pomerania, Vistula Pomerania, and also before World War II as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pomerania on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland.
Gdańsk Pomerania is largely c ...
, northern Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; ), is a Polish Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city in Poland.
The bound ...
including Piła, Wałcz, and Złotów
Złotów is a town in northwestern Poland, with a population of 18,303 inhabitants (2011), seat of the Złotów County in the Greater Poland Voivodeship.
The town is located on the river Głomia and is surrounded by five lakes. It is part of the ...
, which were annexed by Prussia in the First Partition of 1772; and Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdań ...
and western parts of Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; ), is a Polish Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city in Poland.
The bound ...
including Międzyrzecz
Międzyrzecz (; , , ) is a town in western Poland, on the Obra (river), Obra and Paklica river, with 17,667 inhabitants (2020). The capital of Gmina Międzyrzecz and Międzyrzecz County. Since the Local Government Reorganization Act of 1998, it ha ...
and Wschowa
Wschowa (pronounced , ) is a town in the Lubusz Voivodeship in western Poland with 13,875 inhabitants (2019). It is the capital of Wschowa County and a significant tourist site containing many important historical monuments. It is part of the his ...
, which followed in the Second Partition of 1793)
The underlying concept was to define post-war Poland as heir to the medieval Piasts' realm,Joanna B. Michlic, ''Poland's Threatening Other: The Image of the Jew from 1880 to the Present'', 2006, pp. 207–208, , Norman Davies, ''God's Playground: A History of Poland in Two Volumes'', 2005, pp. 381ff, , Geoffrey Hosking, George Schopflin, ''Myths and Nationhood'', 1997, p. 153, , which was simplified into a picture of an ethnically homogeneous state that matched post-war borders,Jan Kubik, ''The Power of Symbols Against the Symbols of Power: The Rise of Solidarity and the Fall of State Socialism in Poland'', 1994, pp. 64–65, , as opposed to the later Jagiellon Poland, which was multi-ethnic and located further east. The argument that this territory in fact constituted "old Polish lands"Alfred M. De Zayas, ''Nemesis at Potsdam'', p. 168 seized on a pre-war concept developed by Polish right-wing circles attached to the SN. As cited by One reason for post-war Poland's favoring a Piast rather than a Jagiellon tradition was Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
's refusal to withdraw from the Curzon line and the Allies' readiness to satisfy Poland with German territory instead.Rick Fawn, ''Ideology and national identity in post-communist foreign policies'', 2003, p. 190, , The original argument for awarding formerly German territory to Poland – compensation – was complemented by the argument that this territory in fact constituted former areas of Poland.Joanna B. Michlic, ''Poland's Threatening Other: The Image of the Jew from 1880 to the Present'', 2006, p. 208, , Jan Kubik, ''The Power of Symbols Against the Symbols of Power: The Rise of Solidarity and the Fall of State Socialism in Poland'', 1994, p. 65, , Dmitrow says that "in official justifications for the border shift, the decisive argument that it presented a compensation for the loss of the eastern half of the pre-war Polish territory to the USSR, was viewed as obnoxious and concealed. Instead, a historical argumentation was foregrounded with the dogma, Poland had just returned to 'ancient Piast lands'." Objections to the Allies' decisions and criticism of the Polish politicians' role at Potsdam were censored. In a commentary for Tribune
Tribune () was the title of various elected officials in ancient Rome. The two most important were the Tribune of the Plebs, tribunes of the plebs and the military tribunes. For most of Roman history, a college of ten tribunes of the plebs ac ...
, George Orwell
Eric Arthur Blair (25 June 1903 – 21 January 1950) was an English novelist, poet, essayist, journalist, and critic who wrote under the pen name of George Orwell. His work is characterised by lucid prose, social criticism, opposition to a ...
likened the transfer of German population to transferring the whole of the Irish and Scottish population. Also, the Piasts were perceived to have defended Poland against the Germans, while the Jagiellons' main rival had been the growing Duchy of Moscow, making them a less suitable basis for post-war Poland's Soviet-dominated situation. The People's Republic of Poland
The Polish People's Republic (1952–1989), formerly the Republic of Poland (1947–1952), and also often simply known as Poland, was a country in Central Europe that existed as the predecessor of the modern-day democratic Republic of Poland. ...
under the Polish Workers' Party
The Polish Workers' Party (, PPR) was a communist party in Poland from 1942 to 1948. It was founded as a reconstitution of the Communist Party of Poland (KPP) and merged with the Polish Socialist Party (PPS) in 1948 to form the Polish United W ...
thus supported the idea of Poland based on old Piast lands. The question of the Recovered Territories was one of the few issues that did not divide the Polish Communists and their opposition, and there was unanimity regarding the western border. Even the underground anti-Communist press called for the Piast borders, that would end Germanisation
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people, and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In l ...
and ''Drang nach Osten
(; 'Drive to the East',Ulrich Best''Transgression as a Rule: German–Polish cross-border cooperation, border discourse and EU-enlargement'' 2008, p. 58, Edmund Jan Osmańczyk, Anthony Mango, ''Encyclopedia of the United Nations and Internati ...
''. The official view was that the Poles had always had the inalienable and inevitable right to inhabit the Recovered Territories, even if prevented from doing so by foreign powers. Furthermore, the Piast concept was used to persuade the Allied Powers, who found it difficult to define a Polish "ethnographic territory", to assume that it would be an intolerable injustice to not "give the territories back".
 By 1949, the term "Recovered Territories" had been dropped from Polish communist propaganda, but it is still used occasionally in common language.Gregor Thum, ''Die fremde Stadt. Breslau nach 1945'', 2006, p. 298, , On the grounds that those areas should not be regarded as unique territories within the Polish state, the authorities began to refer to them instead as the "Western and Northern Lands".Martin Åberg, Mikael Sandberg, ''Social Capital and Democratisation: Roots of Trust in Post-Communist Poland and Ukraine'', Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2003,
By 1949, the term "Recovered Territories" had been dropped from Polish communist propaganda, but it is still used occasionally in common language.Gregor Thum, ''Die fremde Stadt. Breslau nach 1945'', 2006, p. 298, , On the grounds that those areas should not be regarded as unique territories within the Polish state, the authorities began to refer to them instead as the "Western and Northern Lands".Martin Åberg, Mikael Sandberg, ''Social Capital and Democratisation: Roots of Trust in Post-Communist Poland and Ukraine'', Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2003, Google Print, p. 51
Wolff and Cordell say that along with the debunking of communist historiography, "the 'recovered territories' thesis ... has been discarded", and that "it is freely admitted in some circles that on the whole 'the recovered territories' had a wholly German character", but that this view has not necessarily been transmitted to the whole of Polish society.Karl Cordell, Stefan Wolff (2005)
''Germany's Foreign Policy Towards Poland and the Czech Republic: Ostpolitik Revisited''
. p. 139. , . "In addition ... it has been relatively easy for Polish historians and others to attempt to debunk communist historiography and present a more balanced analysis of the past – and not only with respect to Germany. It has been controversial, and often painful, but nevertheless it has been done. For example, Poland's acquisition in 1945 of eastern German territories is increasingly presented as the price Germany paid for launching a total war, and then having lost it totally. The 'recovered territories' thesis previously applied in almost equal measures by the communists and Catholic Church has been discarded. Some circles freely admit that on the whole, 'the recovered territories' in fact had a wholly German character. The extent to which this fact transmitted to groups other than the socially and politically engaged is a matter of debate." The term was also used outside Poland. In 1962,
Pope John XXIII
Pope John XXIII (born Angelo Giuseppe Roncalli; 25 November 18813 June 1963) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 28 October 1958 until his death on 3 June 1963. He is the most recent pope to take ...
referred to those territories as the "western lands after centuries recovered", and did not revise his statement, even under pressure of the German embassy. The term is still sometimes considered useful, due to the Polish existence in those lands that was still visible in 1945, by some prominent scholars, such as Krzysztof Kwaśniewski.
History before 1945
Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was Duchy of Poland (966–1025), Duke of Poland from 960 until his death in 992 and the founder of the first unified History of Poland, Polish state, the Civitas Schinesghe. A member of the Piast dynasty, he was t ...
of the Polans, from his stronghold in the Gniezno
Gniezno (; ; ) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. The city is the administrative seat of Gniezno County (''powiat'') ...
area, united various neighboring tribes in the second half of the 10th century, forming the first Polish state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
and becoming the first historically recorded Piast
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of King Casimir III the Great.
Branches of ...
duke. His realm roughly included all of the area of what would later be named the "Recovered Territories", except for the Warmian-Masurian part of Old Prussia and eastern Lusatia
Lusatia (; ; ; ; ; ), otherwise known as Sorbia, is a region in Central Europe, formerly entirely in Germany and today territorially split between Germany and modern-day Poland. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr and Kwisa rivers in the eas ...
.
 Mieszko's son and successor, Duke Bolesław I Chrobry, upon the 1018
Mieszko's son and successor, Duke Bolesław I Chrobry, upon the 1018 Peace of Bautzen
The Peace of Bautzen (; ; ) was a treaty concluded on 30 January 1018, between Holy Roman Emperor Henry II and Bolesław I of Poland which ended a series of Polish-German wars over the control of Lusatia and Upper Lusatia (''Milzenerland'' or ...
expanded the southern part of the realm, but lost control over the lands of Western Pomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
on the Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
coast. After fragmentation, pagan revolts and a Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
n invasion in the 1030s, Duke Casimir I the Restorer (reigned 1040–1058) again united most of the former Piast realm, including Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
and Lubusz Land
Lubusz Land (; ) is a historical region and cultural landscape in Poland and Germany on both sides of the Oder river.
Originally the settlement area of the Lechites, the swampy area was located east of Margraviate of Brandenburg, Brandenburg and ...
on both sides of the middle Oder
The Oder ( ; Czech and ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and its largest tributary the Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through wes ...
River, but without Western Pomerania, which became part of the Polish state again under Bolesław III Wrymouth
Bolesław III Wrymouth (; 20 August 1086 – 28 October 1138), also known as Boleslaus the Wry-mouthed, was the duke of Lesser Poland, Silesia and Sandomierz between 1102 and 1107 and over the whole of Poland between 1107 and 1138. He was the onl ...
from 1116 until 1121, when the noble House of Griffins
The House of Griffin or Griffin dynasty, (; , ; Latin: ''Gryphes''), or House of Pomerania (see ), was a dynasty ruling the Duchy of Pomerania from the 12th century until 1637. The name "Griffins" was used by the dynasty after the 15th century ...
established the Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (; ; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country existed in the Middle Ages between years 1121–11 ...
. On Bolesław's death in 1138, Poland for almost 200 years was subjected to fragmentation, being ruled by Bolesław's sons and by their successors, who were often in conflict with each other. Władysław I the Elbow-high Władysław is a Polish given male name, cognate with Vladislav. The feminine form is Władysława, archaic forms are Włodzisław (male) and Włodzisława (female), and Wladislaw is a variation. These names may refer to:
People Mononym
* Włodzis ...
, crowned King of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of Royal elections in Poland, free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electab ...
in 1320, achieved partial reunification, although the Silesian and Masovian duchies remained independent Piast holdings.
In the course of the 12th to 14th centuries, Germanic, Dutch and Flemish settlers moved into East Central and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
in a migration process known as the ''Ostsiedlung
(, ) is the term for the Early Middle Ages, early medieval and High Middle Ages, high medieval migration of Germanic peoples and Germanisation of the areas populated by Slavs, Slavic, Balts, Baltic and Uralic languages, Uralic peoples; the ...
''. In Pomerania, Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
, Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
and Silesia, the indigenous West Slav (Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs, also known as Elbe Slavs
and more broadly as Wends, is a collective term applied to a number of Lechites, Lechitic (West Slavs, West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germany. The ...
and Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
) or Balt population became minorities in the course of the following centuries, although substantial numbers of the original inhabitants remained in areas such as Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
. In Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; ), is a Polish Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city in Poland.
The bound ...
and in Eastern Pomerania (Pomerelia
Pomerelia, also known as Eastern Pomerania, Vistula Pomerania, and also before World War II as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pomerania on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland.
Gdańsk Pomerania is largely c ...
), German settlers formed a minority.
Despite the loss of several provinces, medieval lawyers of the Kingdom of Poland created a specific claim to all formerly Polish provinces that were not reunited with the rest of the country in 1320. They built on the theory of the '' Corona Regni Poloniae'', according to which the state (the Crown) and its interests were no longer strictly connected with the person of the monarch
A monarch () is a head of stateWebster's II New College Dictionary. "Monarch". Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest ...
. Because of that no monarch could effectively renounce Crown claims to any of the territories that were historically and/or ethnically Polish. Those claims were reserved for the state (the Crown), which in theory still covered all of the territories that were part of, or dependent on, the Polish Crown upon the death of Bolesław III in 1138.
This concept was also developed to prevent from loss of territory after the death of King Casimir III the Great
Casimir III the Great (; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, retaining the title throughout the Galicia–Volhynia Wars. He was the last Polish king fr ...
in 1370, when Louis I of Hungary
Louis I, also Louis the Great (; ; ) or Louis the Hungarian (; 5 March 132610 September 1382), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1342 and King of Poland from 1370. He was the first child of Charles I of Hungary and his wife, Elizabeth of ...
, who ruled Hungary with absolute power, was crowned King of Poland. In the 14th century Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
was one of the greatest powers of Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
, and its influence reached various Balkan
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
principalities and southern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions.
The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or cultu ...
(Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of N ...
). Poland in personal union with Hungary was the smaller, politically weaker and peripheral country. In the Privilege of Koszyce (1374) King Louis I guaranteed that he would not detach any lands from the Polish Kingdom. The concept was not new, as it was inspired by similar Bohemian (Czech) laws ('' Corona regni Bohemiae'').
Some of the territories (such as Pomerelia
Pomerelia, also known as Eastern Pomerania, Vistula Pomerania, and also before World War II as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pomerania on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland.
Gdańsk Pomerania is largely c ...
and Masovia) reunited with Poland during the 15th and 16th centuries. However all Polish monarchs until the end of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic (), was a federation, federative real union between the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania ...
in 1795 had to promise to do everything possible to reunite the rest of those territories with the Crown.
Many significant events in Polish history are associated with these territories, including the victorious battles of Cedynia (972), Niemcza (1017), Psie Pole and Głogów (1109), Grunwald (1410), Oliwa (1627), the lost battles of Legnica
Legnica (; , ; ; ) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River and the Czarna Woda. As well as being the seat of the county, since 1992 the city has been the seat of the Diocese of Legnica. Le ...
(1241) and Westerplatte (1939), the life and work of astronomers Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath who formulated a mathematical model, model of Celestial spheres#Renaissance, the universe that placed heliocentrism, the Sun rather than Earth at its cen ...
(16th century) and Johannes Hevelius
Johannes Hevelius
Some sources refer to Hevelius as Polish:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Some sources refer to Hevelius as German:
*
*
*
*
*of the Royal Society
* (in German also known as ''Hevel''; ; – 28 January 1687) was a councillor and mayor of Danz ...
(17th century), the creation of the oldest Polish-language texts and printings (Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
and the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
era), the creation of the standards and patterns of the Polish literary language (Renaissance era), Polish maritime history, the establishment of one of the first Catholic dioceses in Poland in the Middle Ages (in Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
and Kołobrzeg
Kołobrzeg (; ; ) is a port and spa city in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in north-western Poland with about 47,000 inhabitants (). Kołobrzeg is located on the Parsęta River on the south coast of the Baltic Sea (in the middle of the section ...
), as well as the Polish Reformation in the Renaissance era.
Significant figures were born or lived in these territories. Astronomer Jan of Głogów and scholar Laurentius Corvinus, who were teachers of Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath who formulated a mathematical model, model of Celestial spheres#Renaissance, the universe that placed heliocentrism, the Sun rather than Earth at its cen ...
at the University of Kraków, both hailed from Lower Silesia. Jan Dantyszek (Renaissance poet and diplomat, named the ''Father of Polish Diplomacy'') and Marcin Kromer
Marcin Kromer (Latin: ''Martinus Cromerus''; 11 November 1512 – 23 March 1589) was Prince-Bishop of Warmia (Ermland), a Polish cartographer, diplomat and historian in the Kingdom of Poland and later in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. He w ...
(Renaissance cartographer, diplomat, historian, music theoretician) were bishops of Warmia. The leading figures of the Polish Enlightenment
The ideas of the Age of Enlightenment in Poland were developed later than in Western Europe, as the Polish bourgeoisie was weaker, and szlachta (nobility) culture (Sarmatism) together with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth political system (Gol ...
are connected with these lands: philosopher, geologist, writer, poet, translator, statesman Stanisław Staszic
Stanisław Wawrzyniec Staszic (baptised 6 November 1755 – 20 January 1826) was a leading figure in the Polish Enlightenment: a Catholic priest, philosopher, geologist, writer, poet, translator and statesman. A physiocrat, monist, pan-Sla ...
and great patron of arts, writer, linguist, statesman and candidate for the Polish crown Adam Kazimierz Czartoryski
Prince Adam Kazimierz Czartoryski (1 December 1734 – 19 March 1823) was an influential Polish aristocrat, writer, literary and theater critic, linguist, traveller and statesman. He was a great patron of arts and a candidate for the Polish cro ...
were both born in these territories, Ignacy Krasicki
Ignacy Błażej Franciszek Krasicki (3 February 173514 March 1801), from 1766 Prince-Bishop of Warmia (in German, ''Ermland'') and from 1795 Archbishop of Gniezno (thus, Primate of Poland), was Poland's leading Polish Enlightenment, Enlightenment ...
(author of the first Polish novel, playwright, nicknamed ''the Prince of Polish Poets'') lived in Warmia
Warmia ( ; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian subdialect, Warmian: ''Warńija''; Old Prussian language, Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia (reg ...
in his adulthood, and brothers Józef Andrzej Załuski and Andrzej Stanisław Załuski
Andrzej Stanisław Kostka Załuski (2 December 1695 – 16 December 1758) was a priest (bishop) in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
In his religious career he held the posts of abbot and later Bishop of Płock (from 1723), bishop of Ł ...
(founders of the Załuski Library in Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
, one of the largest 18th-century book collections in the world) grew up and studied in these territories. Also painters Daniel Schultz, Tadeusz Kuntze and Antoni Blank, as well as composers Grzegorz Gerwazy Gorczycki and Feliks Nowowiejski were born in these lands.
By the time that Poland regained her independence in 1918, Polish activist Dr. Józef Frejlich was already claiming that the lands situated on the right bank of the Oder
The Oder ( ; Czech and ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and its largest tributary the Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through wes ...
river, including inner industrial cities such as Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
, and Baltic ports such as Szczecin
Szczecin ( , , ; ; ; or ) is the capital city, capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the Poland-Germany border, German border, it is a major port, seaport, the la ...
and Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdań ...
, were economic parts of Poland that had to be united with the rest of the "economic territory of Poland" into a united and independent state, as a fundamental condition of the economic revival of Poland after World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
.
After the successful Greater Poland uprising, the cession of Pomerelia
Pomerelia, also known as Eastern Pomerania, Vistula Pomerania, and also before World War II as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pomerania on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland.
Gdańsk Pomerania is largely c ...
to Poland following the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
and the Silesian Uprisings that allowed Poland to obtain a large portion of Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
, the territorial claims of the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I ...
were directed towards the rest of partially Polish speaking Upper Silesia and Masuria
Masuria ( ; ; ) is an ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian–Masurian Voivodeship (ad ...
under German control, as well as the city of Danzig, the Czechoslovakian part of Cieszyn Silesia
Cieszyn Silesia, Těšín Silesia or Teschen Silesia ( ; or ; or ) is a historical region in south-eastern Silesia, centered on the towns of Cieszyn and Český Těšín and bisected by the Olza River. Since 1920 it has been divided betwe ...
and other bordering areas with significant Polish population. The Polish population of these lands was subject to Germanisation
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people, and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In l ...
and intensified repressions, especially after the Nazis came to power in Germany in 1933.
Most of long Germanized Lower Silesia, Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania, Hinder Pomerania, Rear Pomerania or Eastern Pomerania (; ), is a subregion of the historic region of Pomerania in north-western Poland, mostly within the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, while its easternmost parts are within the Po ...
and Eastern Prussia remained undisputed. However, in reaction to Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
's Germany threats to Poland shortly before the outbreak of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Polish nationalists displayed maps of Poland including those ancient Polish territories as well, claiming their intention to recover them.
In the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period, also known as the interbellum (), lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days) – from the end of World War I (WWI) to the beginning of World War II ( ...
the German administration, even before the Nazis took power, conducted a massive campaign of renaming of thousands of placenames, to remove traces of Slavic origin.
Pomerania
Pomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
n (Western Pomeranian) parts of the Recovered Territories came under Polish rule several times from the late 10th century on, when Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was Duchy of Poland (966–1025), Duke of Poland from 960 until his death in 992 and the founder of the first unified History of Poland, Polish state, the Civitas Schinesghe. A member of the Piast dynasty, he was t ...
acquired at least significant parts of them. Mieszko's son Bolesław I established a bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
in the Kołobrzeg
Kołobrzeg (; ; ) is a port and spa city in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in north-western Poland with about 47,000 inhabitants (). Kołobrzeg is located on the Parsęta River on the south coast of the Baltic Sea (in the middle of the section ...
area in 1000–1005/07, before the area was lost again. Despite further attempts by Polish dukes to again control the Pomeranian tribes, this was only partly achieved by Bolesław III in several campaigns lasting from 1116 to 1121. Successful Christian missions ensued in 1124 and 1128; however, by the time of Bolesław's death in 1138, most of West Pomerania (the Griffin-ruled areas) was no longer controlled by Poland. Shortly after, the Griffin Duke of Pomerania, Boguslav I., achieved the integration of Pomerania into the Holy Roman Empire. The easternmost part of later Western Pomerania (including the city of Słupsk
Słupsk (; ; ) is a city with powiat rights located on the Słupia River in the Pomeranian Voivodeship in northern Poland, in the historical region of Pomerania or more specifically in its part known in contemporary Poland as Central Pomerania ...
) in the 13th century was part of Eastern Pomerania, which was re-integrated with Poland, and later on, in the 14th and 15th centuries formed a duchy
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fiefdom, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or Queen regnant, queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important differe ...
, which rulers were vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
s of Jagiellon-ruled Poland. Over the following centuries Western Pomerania was largely Germanized, although a small Slavic Polabian minority remained. Indigenous Slavs and Poles faced discrimination
Discrimination is the process of making unfair or prejudicial distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong, such as race, gender, age, class, religion, or sex ...
from the arriving Germans, who on a local level since the 16th century imposed discriminatory regulations, such as bans on buying goods from Slavs/Poles or prohibiting them from becoming members of craft guilds. The Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (; ; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country existed in the Middle Ages between years 1121–11 ...
under the native Griffin dynasty existed for over 500 years, before it was partitioned between Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
and Brandenburg-Prussia in the 17th century. At the turn of the 20th century there lived about 14,200 persons of Polish mother-tongue in the Province of Pomerania (in the east of Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania, Hinder Pomerania, Rear Pomerania or Eastern Pomerania (; ), is a subregion of the historic region of Pomerania in north-western Poland, mostly within the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, while its easternmost parts are within the Po ...
in the vicinity of the border with the province of West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (; ; ) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and from 1878 to 1919. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1773, formed from Royal Prussia of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonweal ...
), and 300 persons using the Kashubian language
Kashubian () or Cassubian (; ; ) is a West Slavic language belonging to the Lechitic subgroup.Stephen Barbour, Cathie Carmichael, ''Language and Nationalism in Europe'', Oxford University Press, 2000, p.199,
In Poland, it has been an officia ...
(at the Łeba Lake and the Lake Gardno), the total population of the province consisting of almost 1.7 million inhabitants. The Polish communities in many cities of the region, such as Szczecin
Szczecin ( , , ; ; ; or ) is the capital city, capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the Poland-Germany border, German border, it is a major port, seaport, the la ...
and Kołobrzeg, faced intensified repressions after the Nazis
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
came to power in Germany in 1933.
Gdańsk, Lębork and Bytów
 The region of
The region of Pomerelia
Pomerelia, also known as Eastern Pomerania, Vistula Pomerania, and also before World War II as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pomerania on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland.
Gdańsk Pomerania is largely c ...
at the eastern end of Pomerania, including Gdańsk
Gdańsk is a city on the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast of northern Poland, and the capital of the Pomeranian Voivodeship. With a population of 486,492, Data for territorial unit 2261000. it is Poland's sixth-largest city and principal seaport. Gdań ...
(Danzig), was part of Poland since its first ruler Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was Duchy of Poland (966–1025), Duke of Poland from 960 until his death in 992 and the founder of the first unified History of Poland, Polish state, the Civitas Schinesghe. A member of the Piast dynasty, he was t ...
. As a result of the fragmentation of Poland, it was ruled in the 12th and 13th centuries by the Samborides
The Samborides () or House of Sobiesław () were a ruling dynasty in the historic region of Pomerelia. They were first documented about 1155 as governors (''princeps'') in the Eastern Pomeranian lands serving the royal Piast dynasty of Kingdom o ...
, who were (at least initially) more closely tied to the Kingdom of Poland than were the Griffins. After the Treaty of Kępno
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between sovereign states and/or international organizations that is governed by international law. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention ...
in 1282, and the death of the last Samboride in 1294, the region was ruled by kings of Poland for a short period, although also claimed by Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
. After the Teutonic takeover in 1308 the region was annexed to the monastic state of the Teutonic Knights
The State of the Teutonic Order () was a theocratic state located along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea in northern Europe. It was formed by the knights of the Teutonic Order during the early 13th century Northern Crusades in the region ...
.
Most cities of the region joined or sided with the Prussian Confederation, which in 1454 started an uprising against Teutonic rule and asked the Polish King Casimir IV Jagiellon
Casimir IV (Casimir Andrew Jagiellon; ; Lithuanian: ; 30 November 1427 – 7 June 1492) was Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1440 and King of Poland from 1447 until his death in 1492. He was one of the most active Polish-Lithuanian rulers; under ...
to incorporate the region to Poland. After the King agreed and signed the act of incorporation, the Thirteen Years' War broke out, ending in a Polish victory. The Second Peace of Thorn (1466) made Royal Prussia a part of Poland. It had a substantial autonomy and a lot of privileges. It formed the Pomeranian Voivodeship
Pomeranian Voivodeship ( ; ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship, or province, in northwestern Poland. The provincial capital is Gdańsk.
The voivodeship was established on January 1, 1999, out of the former voivodeships of Gdańsk Voivo ...
, located within the province of Royal Prussia in the Kingdom of Poland, as it remained until being annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
in the partitions of 1772 and 1793. A small area in the west of Pomerelia, the Lauenburg and Bütow Land (the region of Lębork
Lębork (; ; ) is a town on the Łeba River, Łeba and Okalica rivers in the Gdańsk Pomerania region in northern Poland. It is the capital of Lębork County in Pomeranian Voivodeship. Its population is 37,000.
History Middle Ages
The region fo ...
and Bytów
Bytów (; ; ) is a town in the Gdańsk Pomerania region of northern Poland with 16,730 inhabitants as of December 2021. It is the capital of Bytów County in the Pomeranian Voivodeship.
In the early Middle Ages a fortified stronghold stood nea ...
) was granted to the rulers of Pomerania as a Polish fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
, before being reintegrated with Poland in 1637, and later on, again transformed into a Polish fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
, which it remained until the First Partition, when three quarters of Royal Prussia's urban population were German-speaking Protestants.
After Poland regained independence in 1918, a large part of Pomerelia was reintegrated with Poland, as the so-called Polish Corridor, and so was not part of the post-war so-called Recovered Territories.
Lubusz Land and parts of Greater Poland
 The medieval
The medieval Lubusz Land
Lubusz Land (; ) is a historical region and cultural landscape in Poland and Germany on both sides of the Oder river.
Originally the settlement area of the Lechites, the swampy area was located east of Margraviate of Brandenburg, Brandenburg and ...
on both sides of the Oder River up to the Spree in the west, including Lubusz (Lebus
Lebus () is a historic town in the Märkisch-Oderland District of Brandenburg, Germany. It is the administrative seat of ''Amt'' ("collective municipality") Amt Lebus, Lebus. The town, located on the west bank of the Oder river at the border with ...
) itself, also formed part of Mieszko's realm. In the period of fragmentation of Poland the Lubusz Land was in different periods part of the Greater Poland and Silesian provinces of Poland. Poland lost Lubusz when the Silesian duke Bolesław II Rogatka sold it to the Ascanian margraves of Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
in 1249. The Bishopric of Lebus, established by Polish Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth
Bolesław III Wrymouth (; 20 August 1086 – 28 October 1138), also known as Boleslaus the Wry-mouthed, was the duke of Lesser Poland, Silesia and Sandomierz between 1102 and 1107 and over the whole of Poland between 1107 and 1138. He was the onl ...
, remained a suffragan of the Archdiocese of Gniezno until 1424, when it passed under the jurisdiction of the Archbishopric of Magdeburg
The Archbishopric of Magdeburg was a Catholic Church, Latin Catholic archdiocese (969–1552) and Prince-Bishopric, Prince-Archbishopric (1180–1680) of the Holy Roman Empire centered on the city of Magdeburg on the Elbe River.
Planned since 95 ...
. The Lubusz Land was part of the Lands of the Bohemian (Czech) Crown from 1373 to 1415.
Brandenburg also acquired the castellany of Santok
Santok (German : ''Zantoch'') is a village in Gorzów County, Lubusz Voivodeship, in western Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Santok.
Geography
Santok is located at the confluence of the Noteć and W ...
, which formed part of the Duchy of Greater Poland
The Duchy of Greater Poland was a district principality in Greater Poland that was a fiefdom of the Kingdom of Poland. It was formed in 1138 from the territories of the Kingdom of Poland, following its fragmentation started by the testament of ...
, from Duke Przemysł I of Greater Poland
Przemysł I (4 June 1221 – 4 June 1257), a member of the Piast dynasty, was Duke of Greater Poland from 1239 until his death, from 1241 with his brother Bolesław the Pious as co-ruler. He was able to re-acquire large parts of Greater Poland, ...
and made it the nucleus of their Neumark
The Neumark (), also known as the New March () or as East Brandenburg (), was a region of the Margraviate of Brandenburg and its successors located east of the Oder River in territory which became part of Poland in 1945 except some villages o ...
("New March") region. In the following decades Brandenburg annexed further parts of northwestern Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; ), is a Polish Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city in Poland.
The bound ...
. Later on, Santok was briefly recaptured by the Poles several times. Of the other cities, King Casimir III the Great
Casimir III the Great (; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, retaining the title throughout the Galicia–Volhynia Wars. He was the last Polish king fr ...
recovered Wałcz in 1368. The lost parts of Greater Poland were part of the Lands of the Bohemian (Czech) Crown from 1373 to 1402, when despite an agreement between the Luxembourg dynasty of Bohemia and the Jagiellons
The Jagiellonian ( ) or Jagellonian dynasty ( ; ; ), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty (), the House of Jagiellon (), or simply the Jagiellons (; ; ), was the name assumed by a cadet branch of the Lithuanian ducal dynasty of Gediminids upon rec ...
of Poland on the sale of the region to Poland, it was sold to the Teutonic Order
The Teutonic Order is a religious order (Catholic), Catholic religious institution founded as a military order (religious society), military society in Acre, Israel, Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Sa ...
. During the Polish–Teutonic War (1431–35) several towns of the region rebelled against the Order to join Poland, among them Choszczno/Arnswalde, Neuwedell and Falkenburg. The present-day Polish Lubusz Voivodeship
Lubusz Voivodeship ( ) is a voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship (province) in western Poland with a population of 972,140. Its regional capitals are Gorzów Wielkopolski and Zielona Góra. The region is characterized by a landscape of forests, lake ...
comprises most of the former Brandenburgian Neumark territory east of the Oder.
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partition (politics), partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place between 1772 and 1795, toward the end of the 18th century. They ended the existence of the state, resulting in the eli ...
: the northern part with Piła and Wałcz in the First Partition and the remainder, including the western part with Międzyrzecz
Międzyrzecz (; , , ) is a town in western Poland, on the Obra (river), Obra and Paklica river, with 17,667 inhabitants (2020). The capital of Gmina Międzyrzecz and Międzyrzecz County. Since the Local Government Reorganization Act of 1998, it ha ...
and Wschowa
Wschowa (pronounced , ) is a town in the Lubusz Voivodeship in western Poland with 13,875 inhabitants (2019). It is the capital of Wschowa County and a significant tourist site containing many important historical monuments. It is part of the his ...
in the Second Partition. During Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
ic times the Greater Poland territories formed part of the Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw (; ; ), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a First French Empire, French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during the Napoleonic Wars. It initially comprised the ethnical ...
, but after the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
Prussia reclaimed them as part of the Grand Duchy of Posen
The Grand Duchy of Posen (; ) was part of the Kingdom of Prussia, created from Prussian Partition, territories annexed by Prussia after the Partitions of Poland, and formally established following the Congress of Vienna in 1815. On 9 February 1 ...
(Poznań), later Province of Posen
The Province of Posen (; ) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1848 to 1920, occupying most of the historical Greater Poland. The province was established following the Greater Poland Uprising (1848), Poznań Uprisi ...
. After , those parts of the former Province of Posen and of West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (; ; ) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and from 1878 to 1919. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 1773, formed from Royal Prussia of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonweal ...
that were not restored as part of the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I ...
were administered as Grenzmark Posen-Westpreußen (the German Province of Posen–West Prussia) until 1939.
Silesia
Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
was one of three main cities of the Medieval Polish Kingdom, according to the 12th-century chronicle '' Gesta principum Polonorum''. Henry I the Bearded
Henry the Bearded (, ; c. 1165/70 – 19 March 1238) was a Polish duke from the Piast dynasty.
He was Dukes of Silesia, Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1201, Seniorate Province, Duke of Kraków and List of Polish monarchs, High Duke of all Kin ...
granted town rights
Town privileges or borough rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium. The city law customary in Central Europe probably dates back to Italian models, which in turn were oriented towards the tradition ...
for the first time in the history of Poland in 1211 to the Lower Silesian town of Złotoryja
Złotoryja (; , ; Latin: ''Aureus Mons'', ''Aurum'') is a historic town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship in southwestern Poland, the administrative seat of Złotoryja County, and of the smaller Gmina Złotoryja. Złotoryja is the first town in Pola ...
. The '' Book of Henryków'', containing the oldest known written sentence in Polish, was created in Lower Silesia. The first Polish-language printed text was published in Wrocław by Głogów-born Kasper Elyan, who is regarded as the first Polish printer. Burial sites of Polish monarchs are located in Wrocław, Trzebnica
Trzebnica (Polish pronunciation: ; , ) is a town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship in west-central Poland. It is the seat of Trzebnica County, and of the smaller administrative district (gmina) called Gmina Trzebnica. It lies within the eastern Trzebni ...
and Legnica
Legnica (; , ; ; ) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River and the Czarna Woda. As well as being the seat of the county, since 1992 the city has been the seat of the Diocese of Legnica. Le ...
.
Piast dukes continued to rule Silesia following the 12th-century fragmentation of Poland
The period of rule by the Piast dynasty between the 10th and 14th centuries is the first major stage of the history of Poland, history of the Polish state. The dynasty was founded by a series of dukes listed by the chronicler Gall Anonymous in t ...
. The Silesian Piasts
The Silesian Piasts were the elder of four lines of the Polish Piast dynasty beginning with Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), eldest son of Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth, Bolesław III of Poland. By Bolesław's Testament of Bolesław III Krzy ...
retained power in most of the region until the early 16th century, the last ( George William, duke of Legnica
Legnica (; , ; ; ) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River and the Czarna Woda. As well as being the seat of the county, since 1992 the city has been the seat of the Diocese of Legnica. Le ...
) dying in 1675. Some Lower Silesian duchies were also under the rule of Polish Jagiellons
The Jagiellonian ( ) or Jagellonian dynasty ( ; ; ), otherwise the Jagiellon dynasty (), the House of Jagiellon (), or simply the Jagiellons (; ; ), was the name assumed by a cadet branch of the Lithuanian ducal dynasty of Gediminids upon rec ...
( Głogów) and Sobieskis (Oława
Oława (, , ) is a historic town in south-western Poland with 33,029 inhabitants (2019). It is situated in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, within the Wrocław metropolitan area. It is the seat of Oława County and of the smaller administrative distri ...
), and part of Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
, the Duchy of Opole, found itself back under Polish rule in the mid-17th century, when the Habsburgs pawned the duchy to the Polish Vasas. The Roman Catholic Diocese of Wrocław, established in 1000 as one of Poland's oldest dioceses, remained a suffragan of the Archbishopric of Gniezno until 1821.
The first German colonists arrived in the late 12th century, and large-scale German settlement started in the early 13th century during the reign of Henry I (Duke of Silesia from 1201 to 1238). After the era of German colonisation, the Polish language still predominated in Upper Silesia and in parts of Lower and Middle Silesia north of the Odra river. Here the Germans who arrived during the Middle Ages became mostly Polonized; Germans dominated in large cities and Poles mostly in rural areas. The Polish-speaking territories of Lower and Middle Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
, commonly described until the end of the 19th century as the ''Polish side'', were mostly Germanized in the 18th and 19th centuries, except for some areas along the northeastern frontier. The province came under the control of Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages, medieval and History of the Czech lands, early modern monarchy in Central Europe. It was the pr ...
in the 14th century and was briefly under Hungarian rule in the 15th century. Silesia passed to the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
of Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
in 1526, and Prussia's Frederick the Great
Frederick II (; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was the monarch of Prussia from 1740 until his death in 1786. He was the last Hohenzollern monarch titled ''King in Prussia'', declaring himself ''King of Prussia'' after annexing Royal Prussia ...
conquered most of it in 1742. A part of Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
became part of Poland after World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and the Silesian Uprisings, but the bulk of Silesia formed part of the post-1945 Recovered Territories.
Warmia and Masuria
 The territories of
The territories of Warmia
Warmia ( ; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian subdialect, Warmian: ''Warńija''; Old Prussian language, Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia (reg ...
and Masuria
Masuria ( ; ; ) is an ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian–Masurian Voivodeship (ad ...
were originally inhabited by pagan Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians were a Balts, Baltic people that inhabited the Prussia (region), region of Prussia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea between the Vistula Lagoon to the west and the Curonian Lagoon ...
, until the conquest by the Teutonic Knights
The Teutonic Order is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to t ...
in the 13th and 14th centuries. In order to repopulate the conquered areas, Poles from neighboring Masovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( ) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the largest city and Płock being the capital of the region . Throughout the ...
, called Masurians (''Mazurzy''), were allowed to settle here (hence the name Masuria
Masuria ( ; ; ) is an ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian–Masurian Voivodeship (ad ...
). During an uprising against the Teutonic Order most towns of the region joined or sided with the Prussian Confederation, at the request of which King Casimir IV Jagiellon
Casimir IV (Casimir Andrew Jagiellon; ; Lithuanian: ; 30 November 1427 – 7 June 1492) was Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1440 and King of Poland from 1447 until his death in 1492. He was one of the most active Polish-Lithuanian rulers; under ...
signed the act of incorporation of the region into the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland (; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a monarchy in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval period from 1025 until 1385.
Background
The West Slavs, West Slavic tribe of Polans (western), Polans who lived in what i ...
(1454). After the Second Peace of Thorn (1466) Warmia
Warmia ( ; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian subdialect, Warmian: ''Warńija''; Old Prussian language, Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia (reg ...
was confirmed to be incorporated to Poland, while Masuria
Masuria ( ; ; ) is an ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian–Masurian Voivodeship (ad ...
became part of a Polish fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
, first as part of the Teutonic state, and from 1525 as part of the secular Ducal Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (, , ) or Ducal Prussia (; ) was a duchy in the region of Prussia established as a result of secularization of the Monastic Prussia, the territory that remained under the control of the State of the Teutonic Order until t ...
. Then it would become one of the leading centers of Polish Lutheranism, while Warmia, under the administration of prince-bishop
A prince-bishop is a bishop who is also the civil ruler of some secular principality and sovereignty, as opposed to '' Prince of the Church'' itself, a title associated with cardinals. Since 1951, the sole extant prince-bishop has been the ...
s remained one of the most overwhelmingly Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
regions of Poland.
Polish suzerainty over Masuria
Masuria ( ; ; ) is an ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian–Masurian Voivodeship (ad ...
ended in 1657/1660 as a result of the Deluge
A deluge is a large downpour of rain, often a flood.
The Deluge refers to the flood narrative in the biblical book of Genesis.
Deluge or Le Déluge may also refer to:
History
*Deluge (history), the Swedish and Russian invasion of the Polish-L ...
and Warmia was annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
in the First Partition of Poland
The First Partition of Poland took place in 1772 as the first of three partitions that eventually ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The growth of power in the Russian Empire threatened the Kingdom of Prussia an ...
(1772). Both regions formed the southern part of the province of East Prussia
East Prussia was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's ...
, established in 1773.
All of Warmia and most of Masuria remained part of Germany after World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and the re-establishment of independent Poland. During the 1920 East Prussian Plebiscite, the districts east of the Vistula
The Vistula (; ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest in Europe, at in length. Its drainage basin, extending into three other countries apart from Poland, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra i ...
within the region of Marienwerder (Kwidzyn), along with all of the Allenstein Region (Olsztyn) and the district of Oletzko voted to be included within the province of East Prussia and thus became part of Weimar Germany. All of the region as the southern part of the province of East Prussia became part of Poland after World War II, with northern East Prussia going to the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
to form the Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast () is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russian Federation. It is a Enclave and exclave, semi-exclave on the Baltic Sea within the Baltic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, surrounded by Pola ...
.
Polish minorities already living in the Recovered Territories
 Since the time of the
Since the time of the Piast dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented List of Polish monarchs, Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I of Poland, Mieszko I (–992). The Poland during the Piast dynasty, Piasts' royal rule in Pol ...
, which unified many of the western Slavic tribes and ruled Poland from the 10th to the 14th centuries, ethnic Poles continued to live in these territories under foreign rule, including Bohemian, Hungarian, Austrian, Prussian, and from 1871 German, this despite the Germanization process (''Ostsiedlung
(, ) is the term for the Early Middle Ages, early medieval and High Middle Ages, high medieval migration of Germanic peoples and Germanisation of the areas populated by Slavs, Slavic, Balts, Baltic and Uralic languages, Uralic peoples; the ...
''), which began in the 13th century with the arrival of German, Dutch and Flemish colonists to Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
and Pomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
at the behest of the feudal Silesian Piasts
The Silesian Piasts were the elder of four lines of the Polish Piast dynasty beginning with Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), eldest son of Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth, Bolesław III of Poland. By Bolesław's Testament of Bolesław III Krzy ...
and the House of Griffins
The House of Griffin or Griffin dynasty, (; , ; Latin: ''Gryphes''), or House of Pomerania (see ), was a dynasty ruling the Duchy of Pomerania from the 12th century until 1637. The name "Griffins" was used by the dynasty after the 15th century ...
. Likewise, in the 14th, 15th and 16th century many Polish settlers from Mazovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( ) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the largest city and Płock being the capital of the region . Throughout the ...
migrated into the southern portions of the Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (, , ) or Ducal Prussia (; ) was a duchy in the region of Prussia established as a result of secularization of the Monastic Prussia, the territory that remained under the control of the State of the Teutonic Order until t ...
.
Before the outbreak of war, regions of Masuria
Masuria ( ; ; ) is an ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian–Masurian Voivodeship (ad ...
, Warmia
Warmia ( ; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian subdialect, Warmian: ''Warńija''; Old Prussian language, Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia (reg ...
and Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
still contained significant ethnic Polish populations, and in many areas the Poles constituted a majority of the inhabitants. According to the 1939 Nazi German census, the territories were inhabited by 8,855,000 people, including a Polish minority in the territories' easternmost parts.Piotr Eberhardt
Piotr Eberhardt (December 27, 1935 – September 10, 2020) was a Polish geographer, a professor at the Polish Academy of Sciences and author of studies in the field of demography and population geography. His works included the ethnic problems of ...
, Jan Owsinski, ''Ethnic Groups and Population Changes in Twentieth-century Central-Eastern Europe: History, Data, Analysis'', 2003, pp.142ff, , However these data, concerning ethnic minorities, that came from the census conducted during the reign of the NSDAP
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party ( or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported the ideology of Nazism. Its precursor, the German Workers ...
(Nazi Party) is usually not considered by historians and demographers as trustworthy but as drastically falsified. Therefore, while this German census placed the number of Polish-speakers and bilinguals below 700,000 people, Polish demographers have estimated that the actual number of Poles in the former German East was between 1.2 and 1.3 million. In the 1.2 million figure, approximately 850,000 were estimated for the Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
n regions, 350,000 for southern East Prussia
East Prussia was a Provinces of Prussia, province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1871); following World War I it formed part of the Weimar Republic's ...
and 50,000 for the rest of the territories.
Under German rule, these communities faced discrimination and oppression. In 1924, an association of national minorities was founded in Germany, also representing the Polish minority. Jan Baczewski from Warmia
Warmia ( ; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian subdialect, Warmian: ''Warńija''; Old Prussian language, Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia (reg ...
, member of the Landtag of Prussia
The Landtag of Prussia () was the representative assembly of the Kingdom of Prussia implemented in 1849, a bicameralism, bicameral legislature consisting of the upper Prussian House of Lords, House of Lords (''Herrenhaus'') and the lower Prussian ...
, initiated a law allowing the founding of schools for national minorities. In 1938, the Nazi government changed thousands of place-names (especially of cities and villages) of Polish origin to newly invented German place-names; about 50% of the existing names were changed in that year alone. Also, undercover operatives were sent to spy on Polish communities. Information was gathered on who sent their children to Polish schools, or bought Polish books and newspapers. Polish schools, printing presses, headquarters of Polish institutions as well as private homes and shops owned by Poles were routinely attacked by members of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS). Although, thousands of Poles were forcefully migrated or voluntarily migrated to these lands during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
Also, small isolated enclaves of ethnic Poles could be found in Pomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
, Lubusz Land
Lubusz Land (; ) is a historical region and cultural landscape in Poland and Germany on both sides of the Oder river.
Originally the settlement area of the Lechites, the swampy area was located east of Margraviate of Brandenburg, Brandenburg and ...
and Lower Silesia. These included scattered villages which remained ethnically Polish and large cities such as Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
(''Breslau''), Szczecin
Szczecin ( , , ; ; ; or ) is the capital city, capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the Poland-Germany border, German border, it is a major port, seaport, the la ...
(''Stettin'') and Zielona Góra
Zielona Góra (; ''Green Mountain''; ) is the largest city in Lubusz Voivodeship, located in western Poland, with 140,403 inhabitants (). The region is closely associated with vineyards and holds an annual Zielona Góra Wine Fest, Wine Fest. Zie ...
(''Grünberg in Schlesien'') which contained small Polish communities.
Origin of the post-war population according to 1950 census
 During the Polish post-war census of December 1950, data about the pre-war places of residence of the inhabitants as of August 1939 was collected. (In the case of children born between September 1939 and December 1950, their place of residence was reported based on the pre-war places of residence of their mothers.) Thanks to this data it is possible to reconstruct the pre-war geographical origin of the post-war population. Many areas located near the pre-war German border were resettled by people from neighbouring borderland areas of pre-war Poland. For example, Kashubians from the pre-war Polish Corridor settled in nearby areas of German Pomerania adjacent to Polish Pomerania. People from the Poznań region of pre-war Poland settled in East Brandenburg. People from East Upper Silesia moved into the rest of Silesia. And people from
During the Polish post-war census of December 1950, data about the pre-war places of residence of the inhabitants as of August 1939 was collected. (In the case of children born between September 1939 and December 1950, their place of residence was reported based on the pre-war places of residence of their mothers.) Thanks to this data it is possible to reconstruct the pre-war geographical origin of the post-war population. Many areas located near the pre-war German border were resettled by people from neighbouring borderland areas of pre-war Poland. For example, Kashubians from the pre-war Polish Corridor settled in nearby areas of German Pomerania adjacent to Polish Pomerania. People from the Poznań region of pre-war Poland settled in East Brandenburg. People from East Upper Silesia moved into the rest of Silesia. And people from Masovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( ) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the largest city and Płock being the capital of the region . Throughout the ...
and the Suwałki Region
Suwałki Region ( ; ) is a historical region around the city of Suwałki in northeastern Poland near the border with Lithuania. It encompasses the powiats of Augustów, Suwałki, and Sejny, and roughly corresponds to the southern part of the for ...
moved into adjacent Masuria
Masuria ( ; ; ) is an ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian–Masurian Voivodeship (ad ...
. Poles expelled from former Polish territories in the east (today mainly parts of Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
, Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
) settled in large numbers everywhere in the Recovered Territories (but many of them also settled in central Poland).
Polonization of the Recovered Territories
 The People's Republic had to locate its population inside the new frontiers in order to solidify the hold over the territories. With the
The People's Republic had to locate its population inside the new frontiers in order to solidify the hold over the territories. With the Kresy
Eastern Borderlands (), often simply Borderlands (, ) was a historical region of the eastern part of the Second Polish Republic. The term was coined during the interwar period (1918–1939). Largely agricultural and extensively multi-ethnic with ...
annexed by the Soviet Union, Poland was effectively moved westwards and its area reduced by almost 20% (from ). Millions of non-Poles – mainly Germans from the Recovered Territories, as well as some Ukrainians in the east – were to be expelled from the new Poland, while large numbers of Poles needed to be resettled having been expelled from the Kresy. The expellees were termed "repatriates". The result was the largest exchange of population in European history.
The picture of the new western and northern territories being recovered Piast territory was used to forge Polish settlers and "repatriates" arriving there into a coherent community loyal to the new regime,Martin Åberg, Mikael Sandberg, ''Social Capital and Democratisation: Roots of Trust in Post-Communist Poland and Ukraine'', Ashgate Publishing, Ltd., 2003, Google Print, p.79
and to justify the removal of the German inhabitants. Largely excepted from the expulsions of Germans were the "
autochthons
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
", close to three million ethnically Polish/Slavic inhabitants of Masuria
Masuria ( ; ; ) is an ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian–Masurian Voivodeship (ad ...
( Masurs), Pomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
( Kashubians, Slovincians) and Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
(Silesians
Silesians (; Silesian German: ''Schläsinger'' ''or'' ''Schläsier''; ; ; ) is both an ethnic as well as a geographical term for the inhabitants of Silesia, a historical region in Central Europe divided by the current national boundaries o ...
). The Polish government aimed to retain as many autochthons as possible, as their presence on former German territory was used to indicate the intrinsic "Polishness" of the area and justify its incorporation into the Polish state as "recovered" territories. "Verification" and "national rehabilitation" processes were set up to reveal a "dormant Polishness" and determine who was redeemable as a Polish citizen. Few were actually expelled.Tomasz Kamusella in Prauser and Reeds (eds), ''The Expulsion of the German communities from Eastern Europe'', p.28, EUI HEC 2004/The "autochthons" not only disliked the subjective and often arbitrary verification process, but they also faced discrimination even after completing it, such as the Polonization of their names. In the Lubusz Voivodeship, Lubusz region (former East Brandenburg), the local authorities conceded already in 1948 that what the PZZ claimed to be a recovered "autochton" Polish population were in fact Germanized migrant workers, who had settled in the region in the late 19th and early 20th centuries – with the exception of one village, Babimost, just across the pre-war border. Great efforts were made to propagate the view of the Piast Concept. It was actively supported by the Catholic Church. The sciences were responsible for the development of this perception of history. In 1945 the Western Institute () was founded to coordinate the scientific activities. Its director, Zygmunt Wojciechowski, characterized his mission as an effort to present the Polish history of the region, and project current Polish reality of these countries upon a historical background. Historical scientists, archaeologists, linguists, art historians and ethnologists worked in an interdisciplinary effort to legitimize the new borders.Gregor Thum, ''Die fremde Stadt. Breslau nach 1945'', 2006, p. 281, , Their findings were popularised in monographs, periodicals, schoolbooks, travel guides, broadcasts and exhibitions. Official maps were drawn showing that the Polish frontiers under the first known Piast princes matched the new ones. According to
Norman Davies
Ivor Norman Richard Davies (born 8 June 1939) is a British and Polish historian, known for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland and the United Kingdom. He has a special interest in Central and Eastern Europe and is UNESCO Profes ...
, the young post-war generation received education informing them that the boundaries of the People's Republic were the same as those on which the Polish nation had developed for centuries. Furthermore, they were instructed that the Polish "Motherland" has always been in the same location, even when "occupied" for long periods of time by foreigners or as political boundaries shifted.Norman Davies, ''God's Playground: A History of Poland in Two Volumes'', 2005, p. 386, , Because the Recovered Territories had been under German and Prussian rule for many centuries, many events of this history were perceived as part of "foreign" rather than "local" history in post-war Poland. Polish scholars thus concentrated on the Polish aspects of the territories: medieval Piast history of the region, the cultural, political and economic bonds to Poland, the history of the Polish-speaking population in Prussia and the "Drang nach Osten" as a historical constant since the Middle Ages.
Voivodeships of Poland
A voivodeship ( ; ; plural: ) is the highest-level Administrative divisions of Poland, administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly tran ...
as of June, 1946
File:Northern and Western Territories.PNG, Present-day administrative division of Poland, Western and Northern Lands in dark green
Removal of Germans and traces of German habitation
The Communist authorities of the Polish People's Republic and some Polish citizens desired to erase all traces of German rule. The "Recovered Territories" after the transfer still contained a substantial German population. The Polish administration set up a "Ministry for the Recovered Territories", headed by the then deputy prime ministerWładysław Gomułka
Władysław Gomułka (; 6 February 1905 – 1 September 1982) was a Polish Communist politician. He was the ''de facto'' leader of Polish People's Republic, post-war Poland from 1947 until 1948, and again from 1956 to 1970.
Born in 1905 in ...
.Karl Cordell, Andrzej Antoszewski, ''Poland and the European Union'', 2000, p.167, , A "Bureau for Repatriation" was to supervise and organize the expulsions and resettlements. According to the national census of 14 February 1946, the population of Poland still included 2,288,300 Germans, of which 2,036,439—nearly 89 per cent—lived in the ''Recovered Territories''. By this stage Germans still constituted more than 42 per cent of the inhabitants of these regions, since their total population according to the 1946 census was 4,822,075. However, by 1950 there were only 200,000 Germans remaining in Poland, and by 1957 that number fell to 65,000. While the estimates of how many Germans remained vary, a constant German exodus took place even after the expulsions. Between 1956 and 1985, 407,000 people from Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
and about 100,000 from Warmia-Masuria declared German nationality and left for Germany. In the early 1990s, after the Polish Communist regime had collapsed 300,000-350,000 people declared themselves German.
The flight and expulsion of the remaining Germans in the first post-war years presaged a broader campaign to remove signs of former German rule.
More than 30,000 German placenames were replaced with PolishDan Diner, Raphael Gross, Yfaat Weiss, ''Jüdische Geschichte als allgemeine Geschichte'', p.164 or Polonized medieval Slavic ones.Gregor Thum, ''Die fremde Stadt. Breslau nach 1945'', 2006, p.344, , Tomasz Kamusella and Terry Sullivan in Karl Cordell, ''Ethnicity and Democratisation in the New Europe'', 1999, pp.175ff, , Previous Slavic and Polish names used before German settlements had been established; in the cases when one was absent either the German name was translated or new names were invented. In January 1946, a Committee for Settling of Place Names was set up to assign new official toponyms. The German language was banned from public schools, government media and church services. Many German monuments, graveyards, buildings or entire ensembles of buildings were demolished. Objects of art were moved to other parts of the country. German inscriptions were erased, including those on religious objects, in churches and in cemeteries. In Ziemia Lubuska "Socialist competitions" were organized to search and destroy final German traces.
Historian John Kulczycki argues that the Communist authorities discovered that forging an ethnically homogeneous Poland in the Recovered Territories was quite complicated, for it was difficult to differentiate German speakers who were "really" Polish and those who were not. The government used criteria that involved explicit links to Polish ethnicity, as well the person's conduct. Local verification commissions had wide latitude in determining who was or was not Polish and should remain. Their decisions were based on the nationalist assumption that an individual's national identity is a lifetime "ascriptive" characteristic acquired at birth and not easily changed. However people who "betrayed" their Polish heritage by their political words or actions were excluded from the Polish nation. Everyone else was labelled as "Polish" and had to remain in their "native" land – even if they wanted to emigrate to Germany.
Resettlement of the Territories
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
was still advancing. In addition to the settlers, other Poles went for "szaber" or looting expeditions, soon affecting all former eastern territories of Germany
In present-day Germany, the former eastern territories of Germany () refer to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany, i.e. the Oder–Neisse line, which historically had been considered German and which were annexed b ...
. On 30 March 1945, the Gdańsk Voivodeship was established as the first administrative Polish unit in the "recovered" territories. While the Germans were interned and expelled, close to 5 million settlersKarl Cordell, Andrzej Antoszewski, ''Poland and the European Union'', 2000, p.168, , : gives 4.55 million in the first years were either attracted or forced to settle the areas between 1945 and 1950. An additional 1,104,000 people had declared Polish nationality and were allowed to stay (851,000 of those in Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
), bringing up the number of Poles to 5,894,600 as of 1950. The settlers can be grouped according to their background:
*settlers from Central Poland moving voluntarily (the majority)
*Poles that had been freed from forced labor in Nazi Germany (up to two million)
*so-called "repatriants": Poles expelled from the areas east of the new Polish-Soviet border were preferably settled in the new western territories, where they made up 26% of the population (up to two million)
*non-Poles forcibly resettled during the Operation Vistula
Operation Vistula (; ) was the codename for the 1947 forced resettlement of close to 150,000 Ukrainians in Poland, Ukrainians (including Rusyns, Boykos, and Lemkos) from the southeastern provinces of People's Republic of Poland, postwar Poland to ...
in 1947. Large numbers of Ukrainians were forced to move from south-eastern Poland under a 1947 Polish government operation aimed at dispersing, and therefore assimilating, those Ukrainians who had not been expelled eastward already, throughout the newly acquired territories. Belarusians living around the area around Białystok were also pressured into relocating to the formerly German areas for the same reasons. This scattering of members of non-Polish ethnic groups throughout the country was an attempt by the Polish authorities to dissolve the unique ethnic identity of groups like the Ukrainians, Belarusians and Lemkos
Lemkos (; ; ; ) are an ethnic group inhabiting the Lemko Region (; ) of Carpathian Rus', an ethnographic region in the Carpathian Mountains and foothills spanning Ukraine, Slovakia, and Poland.
Lemkos are often considered to be a sub-group of ...
, and broke the proximity and communication necessary for strong communities to form.
*Tens of thousands of Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
Holocaust
The Holocaust (), known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (), was the genocide of History of the Jews in Europe, European Jews during World War II. From 1941 to 1945, Nazi Germany and Collaboration with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy ...
-survivors, most of them " repatriates" from the East, settled mostly in Lower Silesia, creating Jewish cooperatives and institutions – the largest communities were founded in Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
(Breslau, Lower Silesia), Szczecin
Szczecin ( , , ; ; ; or ) is the capital city, capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the Poland-Germany border, German border, it is a major port, seaport, the la ...
(Stettin, Pomerania
Pomerania ( ; ; ; ) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship, West Pomeranian, Pomeranian Voivod ...
) and Wałbrzych
Wałbrzych (; ; or ''Walmbrich''; or ) is a city located in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in southwestern Poland, seat of Wałbrzych County. Wałbrzych lies approximately southwest of the voivodeship capital Wrocław and about from the Czec ...
(Waldenburg, Lower Silesia). However most of them left Poland in 1968 due to the Polish 1968 political crisis.
*Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
and Macedonians, refugees of the Greek Civil War (around 10,000 people)
Polish and Soviet newspapers and officials encouraged Poles to relocate to the west – "the land of opportunity". These new territories were described as a place where opulent villas abandoned by fleeing Germans waited for the brave; fully furnished houses and businesses were available for the taking. In fact, the areas were devastated by the war, the infrastructure largely destroyed, suffering high crime rates and looting by gangs. It took years for civil order to be established.
In 1970, the Polish population of the Northern and Western territories for the first time caught up to the pre-war population level (8,711,900 in 1970 vs 8,855,000 in 1939). In the same year, the population of the other Polish areas also reached its pre-war level (23,930,100 in 1970 vs 23,483,000 in 1939).
Today the population of the territories is predominantly Polish, although a small German minority still exists in a few places, including Olsztyn
Olsztyn ( , ) is a city on the Łyna River in northern Poland. It is the capital of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, and is a city with powiat rights, city with county rights. The population of the city was estimated at 169,793 residents
Olsz ...
, Masuria
Masuria ( ; ; ) is an ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian–Masurian Voivodeship (ad ...
, and Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
, particularly in Opole Voivodeship
Opole Voivodeship ( , , ), is the smallest and least populated voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship (province) of Poland. The province's name derives from that of the region's capital and largest city, Opole. It is part of Silesia. A relatively lar ...
(the area of Opole
Opole (; ; ; ) is a city located in southern Poland on the Oder River and the historical capital of Upper Silesia. With a population of approximately 127,387 as of the 2021 census, it is the capital of Opole Voivodeship (province) and the seat of ...
, Strzelce Opolskie, Prudnik
Prudnik (, , , ) is a town in southern Poland, located in the southern part of Opole Voivodeship near the border with the Czech Republic. It is the administrative seat of Prudnik County and Gmina Prudnik. Its population numbers 21,368 inhabitant ...
, Kędzierzyn-Koźle and Krapkowice
Krapkowice (; ; ) is a town in southern Poland with 16,301 inhabitants (2019), situated in the Opole Voivodeship, straddling both banks of the Oder River at the point where it joins with the Osobłoga. It is the regional capital of Krapkowice Cou ...
).
Role of the Recovered Territories in the Communists' rise to power
The Communist government, not democratically legitimized, sought to legitimize itself through anti-German propaganda. The German "revanchism" was played up as a permanent German threat, with the Communists being the only guarantors and defenders of Poland's continued possession of the "Recovered Territories". Gomułka asserted that:The western territories are one of the reasons the government has the support of the people. This neutralizes various elements and brings people together. Westward expansion and agricultural reform will bind the nation with the state. Any retreat would weaken our domestic position.The redistribution of "ownerless property" among the people by the regime brought it broad-based popular sympathy. After the Second World War, the Soviet Union annexed the Polish territory of the
Kresy
Eastern Borderlands (), often simply Borderlands (, ) was a historical region of the eastern part of the Second Polish Republic. The term was coined during the interwar period (1918–1939). Largely agricultural and extensively multi-ethnic with ...
—located east of the Curzon line—and encouraged or forced ethnic minorities in these parts of Poland, including ethnic Poles, to move west. In the framework of the campaign, Soviets exhibited posters in public places with messages such as,
Legal status of the territories
 During the
During the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
the official position in the First World
The concept of the First World was originally one of the " Three Worlds" formed by the global political landscape of the Cold War, as it grouped together those countries that were aligned with the Western Bloc of the United States. This groupin ...
was that the concluding document of the Potsdam Conference was not an international treaty
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between sovereign states and/or international organizations that is governed by international law. A treaty may also be known as an international agreement, protocol, covenant, convention ...
, but a mere memorandum
A memorandum (: memorandums or memoranda; from the Latin ''memorandum'', "(that) which is to be remembered"), also known as a briefing note, is a Writing, written message that is typically used in a professional setting. Commonly abbreviation, ...
. It regulated the issue of the German eastern border, which was to be the Oder-Neisse line, but the final article of the memorandum said that the final status of the German state and therefore its territories were subject to a separate peace treaty between Germany and the Allies of World War II
The Allies, formally referred to as the United Nations from 1942, were an international Coalition#Military, military coalition formed during World War II (1939–1945) to oppose the Axis powers. Its principal members were the "Four Policeme ...
. During the period from 1945 to 1990 two treaties between Poland and both East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
and West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republi ...
were signed concerning the German-Polish border. In 1950, the German Democratic Republic and the People's Republic of Poland
The Polish People's Republic (1952–1989), formerly the Republic of Poland (1947–1952), and also often simply known as Poland, was a country in Central Europe that existed as the predecessor of the modern-day democratic Republic of Poland. ...
signed the Treaty of Zgorzelec
The Treaty of Zgorzelec (Full title ''The Agreement Concerning the Demarcation of the Established and the Existing Polish-German State Frontier'', also known as the ''Treaty of Görlitz'' and ''Treaty of Zgorzelic'') between the People's Repub ...
, recognizing the Oder-Neisse line, officially designated by the Communists as the "Border of Peace and Friendship". On 7 December 1970, the Treaty of Warsaw between the Federal Republic of Germany and Poland was signed concerning the Polish western border. Both sides committed themselves to nonviolence and accepted the existing ''de facto'' border—the Oder-Neisse line. However a final treaty was not signed until 1990 as the " Treaty on the Final Settlement With Respect to Germany".
German reunification
German reunification () was the process of re-establishing Germany as a single sovereign state, which began on 9 November 1989 and culminated on 3 October 1990 with the dissolution of the East Germany, German Democratic Republic and the int ...
in 1990, the German political establishment recognized the " facts on the ground" and accepted the clauses in the Treaty on the Final Settlement whereby Germany renounced all claims to territory east of the Oder-Neisse line. This allowed the treaty to be negotiated quickly and for unification of democratic West Germany and socialist East Germany to go ahead quickly.
In accordance with a duty imposed on Germany by the Treaty on the Final Settlement, in the same year, 1990, Germany signed a separate treaty with Poland, the German-Polish Border Treaty, confirming the two countries' present borders.
The signature and ratification of the border treaty between Germany and Poland formalized in international law the recognition of the existing border and put an end to all qualified German claims.
See also
*Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany
Following the Invasion of Poland at the beginning of World War II, nearly a quarter of the entire territory of the Second Polish Republic was Areas annexed by Nazi Germany, annexed by Nazi Germany and placed directly under the German civil ad ...
*Territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union
Seventeen days after the German invasion of Poland in 1939, which marked the beginning of the Second World War, the Soviet Union entered the eastern regions of Poland (known as the ) and annexed territories totalling with a population of 13,299 ...
* Kaliningrad question
* History of German settlement in Central and Eastern Europe
*Former eastern territories of Germany
In present-day Germany, the former eastern territories of Germany () refer to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany, i.e. the Oder–Neisse line, which historically had been considered German and which were annexed b ...
*Territorial changes of Poland after World War II
At the end of World War II, Poland underwent major changes to the location of its international border. In 1945, after the defeat of Nazi Germany, the Oder–Neisse line became its western border, resulting in gaining the Recovered Territorie ...
*Territorial evolution of Poland
Poland is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus, and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian Enclave and exclave, exclave, ...
*Polish nationalism
Polish nationalism () is a nationalism which asserts that the Polish people are a nation and which affirms the cultural unity of Poles. British historian of Poland Norman Davies defines nationalism as "a doctrine ... to create a nation by arous ...
*Irredentism
Irredentism () is one State (polity), state's desire to Annexation, annex the territory of another state. This desire can be motivated by Ethnicity, ethnic reasons because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to or the same as the ...
* Poland A and B
*Polonization
Polonization or Polonisation ()In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэяй. Польскі ...
*Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, German people, people, and German culture, culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nati ...
*Russification
Russification (), Russianisation or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians adopt Russian culture and Russian language either voluntarily or as a result of a deliberate state policy.
Russification was at times ...
Sources
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * Kończal, Kornelia (2023), ''Post-German Spaces'', in: Yifat Gutman und Jenny Wüstenberg (ed.): The Routledge Handbook of Memory Activism, London and New York, Routledge, p. 345–349. {{Borders of Poland Aftermath of World War II in Germany Aftermath of World War II in Poland Borders of Germany Borders of Poland Deportation Historical geography of Germany Germany–Poland relations Poland in World War II Polish irredentism Stalinism in Poland Territorial evolution of Germany Annexation Post–World War II forced migrations