Rattus rattus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The black rat (''Rattus rattus''), also known as the roof rat, ship rat, or house rat, is a common long-tailed
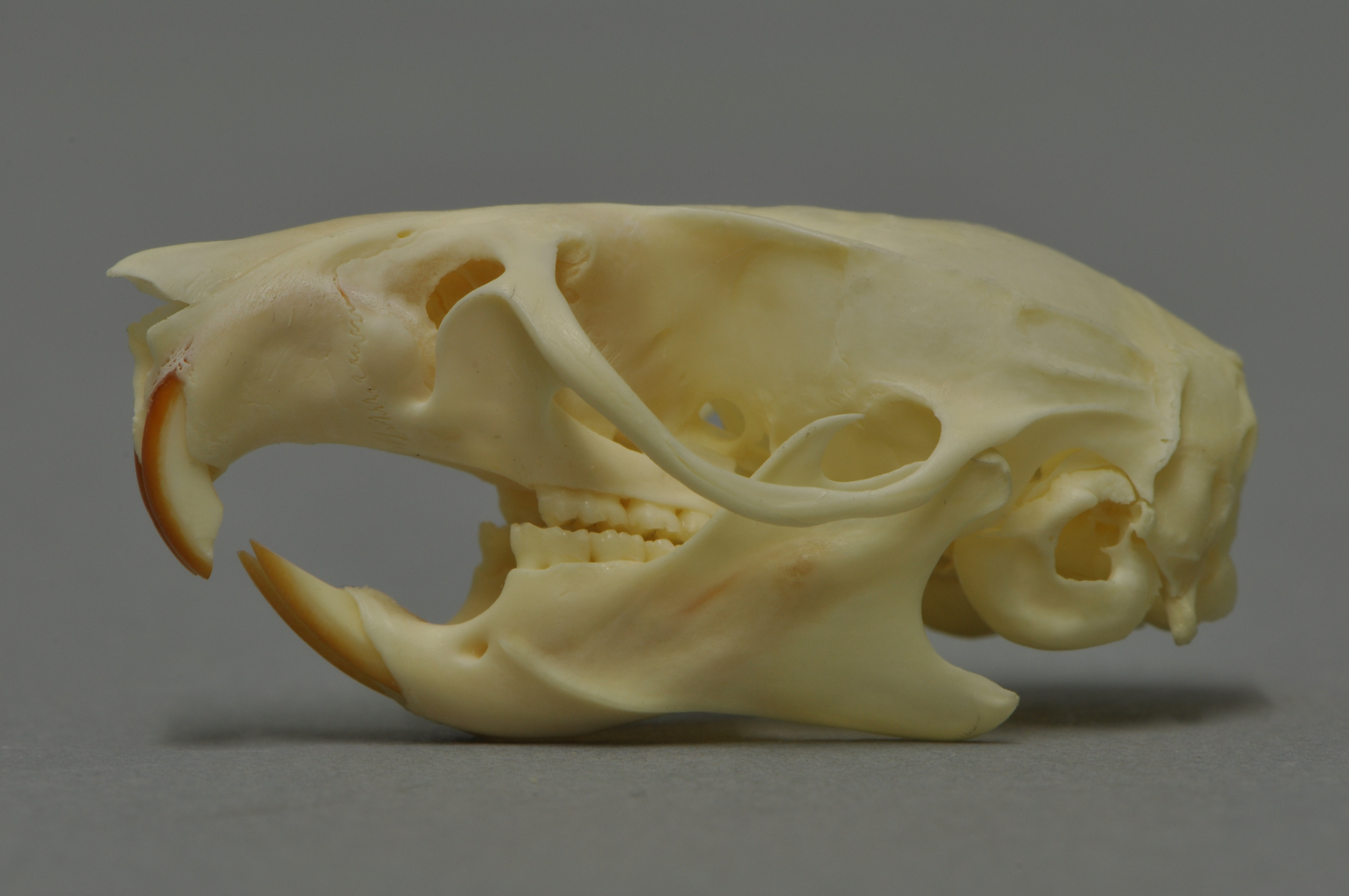

 A typical adult black rat is long, not including a tail, and weighs , depending on the subspecies. Despite its name, the black rat exhibits several colour forms. It is usually black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. In England during the 1920s, several variations were bred and shown alongside domesticated brown rats. This included an unusual green-tinted variety. The black rat also has a scraggly coat of black fur, and is slightly smaller than the brown rat.
A typical adult black rat is long, not including a tail, and weighs , depending on the subspecies. Despite its name, the black rat exhibits several colour forms. It is usually black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. In England during the 1920s, several variations were bred and shown alongside domesticated brown rats. This included an unusual green-tinted variety. The black rat also has a scraggly coat of black fur, and is slightly smaller than the brown rat.
Photos and video
at ARKive {{Authority control Rattus Rodents of Asia Rodents of Europe Mammals of Azerbaijan Mammals of Nepal Stored-product pests Mammals described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Invasive animal species in Australia
rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are n ...
of the stereotypical rat genus ''Rattus
''Rattus'' is a genus of muroid rodents, all typically called rats. However, the term rat can also be applied to rodent species outside of this genus.
Species and description
The best-known ''Rattus'' species are the black rat (''R. rattus'') ...
'', in the subfamily Murinae. It likely originated in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
, but is now found worldwide.
The black rat is black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. It is a generalist omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nu ...
and a serious pest to farmers because it feeds on a wide range of agricultural crops
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydroponics ...
. It is sometimes kept as a pet. In parts of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, it is considered sacred and respected in the Karni Mata Temple
Karni Mata Temple of Deshnoke (Hindi: करणी माता मंदिर), also known as Madh Deshnoke, is a prominent Hindu temple dedicated to Karni Mata at the town of Deshnoke, located 30 km south of Bikaner, in Rajasthan. It h ...
in Deshnoke
Deshnoke is a City in the Bikaner district of Rajasthan, India.The city is famous for the Karni Mata Temple and was established by Goddess Karni-ji herself who led her followers to this region.
This city will be developed as the Capital of the ...
.
Taxonomy
''Mus rattus'' was thescientific name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bo ...
proposed by Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, ...
in 1758 for the black rat.
Three subspecies were once recognized, but today are considered invalid and are now known to be actually color morphs:
*''Rattus rattus rattus'' – roof rat
*''Rattus rattus alexandrinus'' – Alexandrine rat
*''Rattus rattus frugivorus'' – fruit rat
Characteristics

 A typical adult black rat is long, not including a tail, and weighs , depending on the subspecies. Despite its name, the black rat exhibits several colour forms. It is usually black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. In England during the 1920s, several variations were bred and shown alongside domesticated brown rats. This included an unusual green-tinted variety. The black rat also has a scraggly coat of black fur, and is slightly smaller than the brown rat.
A typical adult black rat is long, not including a tail, and weighs , depending on the subspecies. Despite its name, the black rat exhibits several colour forms. It is usually black to light brown in colour with a lighter underside. In England during the 1920s, several variations were bred and shown alongside domesticated brown rats. This included an unusual green-tinted variety. The black rat also has a scraggly coat of black fur, and is slightly smaller than the brown rat.
Origin
Black rat bone remains dating to the Norman period were discovered in Great Britain. The black rat occurred in prehistoric Europe and in theLevant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
during postglacial periods. The specific origin of the black rat is uncertain due to its disappearance and reintroduction. Evidence such as DNA and bone fragments also indicate that it did not originate in Europe, but migrated from Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
, possibly Malaysia. It probably spread across Europe in the wake of the Roman conquest. Possibly, speciation occurred when it colonized southwestern India, which was the primary country from which Romans obtained their spices. Since the black rat is a passive traveler, it could have easily traveled to Europe during the trading between Rome and the Southwest Asian countries. The black rat in the Mediterranean region differs genetically from its Southeast Asian ancestor by having 38 instead of 42 chromosomes. It is a resilient vector for many diseases because of its ability to hold so many infectious bacteria in its blood. It played a primary role in spreading bacteria contained in fleas on its body, such as the plague bacterium ('' Yersinia pestis'') which is responsible for the Plague of Justinian and the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
.
A study published in 2015 indicates that other Asiatic rodents served as plague reservoirs, from which infections spread as far west as Europe via trade routes, both overland and maritime. Although the black rat was certainly a plague vector in European ports, the spread of the plague beyond areas colonized by rats suggests that the plague was also circulated by humans after reaching Europe.
Diet
Black rats are considered omnivores and eat a wide range of foods, including seeds, fruit, stems, leaves, fungi, and a variety of invertebrates and vertebrates. They are generalists, and thus not very specific in their food preferences, which is indicated by their tendency to feed on any meal provided for cows, swine, chickens, cats, and dogs. They are similar to the tree squirrel in their preference of fruits and nuts. They eat about per day and drink about per day. Their diet is high in water content. They are a threat to many natural habitats because they feed on birds and insects. They are also a threat to many farmers, since they feed on a variety of agricultural-based crops, such as cereals, sugar cane, coconuts, cocoa, oranges, and coffee beans.Distribution and habitat
The black rat originated in India and Southeast Asia, and spread to theNear East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
, and then throughout the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
, reaching Great Britain as early as the 1st century AD. Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common genetic ancestry, common language, or both. Pan and Pfeil (20 ...
subsequently spread it throughout the world. The black rat is again largely confined to warmer areas, having been supplanted by the brown rat (''Rattus norvegicus'') in cooler regions and urban areas. In addition to the brown rat being larger and more aggressive, the change from wooden structures and thatched roofs to bricked and tiled buildings favored the burrowing brown rats over the arboreal black rats. In addition, brown rats eat a wider variety of foods, and are more resistant to weather extremes.
Black rat populations can increase exponentially under certain circumstances, perhaps having to do with the timing of the fruiting of the bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, ...
plant, and cause devastation to the plantings of subsistence farmers; this phenomenon is known as '' mautam'' in parts of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
.
Black rats are thought to have arrived in Australia with the First Fleet
The First Fleet was a fleet of 11 ships that brought the first European and African settlers to Australia. It was made up of two Royal Navy vessels, three store ships and six convict transports. On 13 May 1787 the fleet under the command o ...
, and subsequently spread to many coastal regions in the country.
Black rats adapt to a wide range of habitats. In urban areas they are found around warehouses, residential buildings, and other human settlements. They are also found in agricultural areas, such as in barns and crop fields. In urban areas, they prefer to live in dry upper levels of buildings, so they are commonly found in wall cavities and false ceilings. In the wild, black rats live in cliffs, rocks, the ground, and trees. They are great climbers and prefer to live in palms and trees, such as pine trees. Their nests are typically spherical and made of shredded material, including sticks, leaves, other vegetation, and cloth. In the absence of palms or trees, they can burrow into the ground. Black rats are also found around fences, ponds, riverbanks, streams, and reservoirs.
Behaviour and ecology
It is thought that male and female rats have similarly sized home ranges during the winter, but male rats increase the size of their home range during the breeding season. Along with differing between rats of different sex, home range also differs depending on the type of forest in which the black rat inhabits. For example, home ranges in the southern beech forests of theSouth Island
The South Island, also officially named , is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman ...
, New Zealand appear to be much larger than the non-beech forests of the North Island
The North Island, also officially named Te Ika-a-Māui, is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but much less populous South Island by the Cook Strait. The island's area is , making it the world's 14th-larges ...
. Due to the limited number of rats that are studied in home range studies, the estimated sizes of rat home ranges in different rat demographic groups are inconclusive.
Nesting behaviour
Through the usage of tracking devices such as radio transmitters, rats have been found to occupy dens located in trees, as well as on the ground. In Puketi Forest in the Northland Region of New Zealand, rats have been found to form dens together. Rats appear to den and forage in separate areas in their home range depending on the availability of food resources. Research shows that, in New South Wales, the black rat prefers to inhabit lower leaf litter of forest habitat. There is also an apparent correlation between the canopy height and logs and the presence of black rats. This correlation may be a result of the distribution of the abundance of prey as well as available refuges for rats to avoid predators. As found inNorth Head, New South Wales
North Head is an Australian National Heritage listed headland which includes the North Head Quarantine Station and has been symbolically regarded by ships arriving in Australia since 1788 as the entrance to Port Jackson, New South Wales
...
, there is positive correlation between rat abundance, leaf litter cover, canopy height, and litter depth. All other habitat variables showed little to no correlation. While this species' relative, the brown (Norway) rat prefers to nest near the ground of a building the black rat will prefer the upper floors and roof. Because of this habit they have been given the common name roof rat.
Foraging behaviour
The black rat displays flexibility in its foraging behaviour. It is a predatory species and adapts to different micro-habitats. It often meets and forages together in close proximity within and between sexes. It tends to forage after sunset. If the food cannot be eaten quickly, it searches for a place to carry and hoard to eat at a later time. Although it eats a broad range of foods, it is a highly selective feeder; only a restricted selection of the foods is dominating. When offered a wide diversity of foods, it eats only a small sample of each. This allows to monitoring the quality of foods that are present year round, such as leaves, as well as seasonal foods, such as herbs and insects. This method of operating on a set of foraging standards ultimately determines the final composition of its meals. Also, by sampling the available food in an area, it maintains a dynamic food supply, balance its nutrient intake, and avoids intoxication by secondary compounds.Diseases
Black rats (or theirectoparasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
s) can carry a number of pathogens, of which bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium ('' Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as wel ...
(via the Oriental rat flea), typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposure. ...
, Weil's disease, toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by '' Toxoplasma gondii'', an apicomplexan. Infections with toxoplasmosis are associated with a variety of neuropsychiatric and behavioral conditions. Occasionally, people may have a few weeks or mont ...
and trichinosis
Trichinosis, also known as trichinellosis, is a parasitic disease caused by roundworms of the '' Trichinella'' type. During the initial infection, invasion of the intestines can result in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Migration of ...
are the best known. It has been hypothesized that the displacement of black rats by brown rats led to the decline of the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
. This theory has, however, been deprecated, as the dates of these displacements do not match the increases and decreases in plague outbreaks.
Rats serve as outstanding vectors for transmittance of diseases because they can carry bacteria and viruses in their systems. A number of bacterial diseases are common to rats, and these include '' Streptococcus pneumoniae'', '' Corynebacterium kutsheri,'' '' Bacillus piliformis'', ''Pasteurella pneumotropica
__NOTOC__
''Pasteurella'' is a genus of Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic bacteria. ''Pasteurella'' species are nonmotile and pleomorphic, and often exhibit bipolar staining ("safety pin" appearance). Most species are catalase- and oxidase- ...
'', and ''Streptobacillus moniliformis
''Streptobacillus moniliformis'' is a non-motile, Gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium that is a member of the family Leptotrichiaceae. The genome of ''S. moniliformis'' is one of two completed sequences of the order Fusobacteriales. Its name c ...
'', to name a few. All of these bacteria are disease causing agents in humans. In some cases, these diseases are incurable.
Predators
The black rat is prey to cats and owls in domestic settings. In less urban settings, rats are preyed on by weasels, foxes, and coyotes. These predators have little effect on the control of the black rat population because black rats are agile and fast climbers. In addition to agility, the black rat also uses its keen sense of hearing to detect danger and quickly evade mammalian and avian predators.As an invasive species
Damage caused
After ''Rattus rattus'' was introduced into the northern islands of New Zealand, they fed on the seedlings, adversely affecting the ecology of the islands. Even after eradication of ''R. rattus'', the negative effects may take decades to reverse. When consuming these seabirds and seabird eggs, these rats reduce the pH of the soil. This harms plant species by reducing nutrient availability in soil, thus decreasing the probability of seed germination. For example, research conducted by Hoffman et al. indicates a large impact on 16 indigenous plant species directly preyed on by ''R. rattus''. These plants displayed a negative correlation in germination and growth in the presence of black rats. Rats prefer to forage in forest habitats. In theOgasawara islands
The Bonin Islands, also known as the , are an archipelago of over 30 subtropical and tropical islands, some directly south of Tokyo, Japan and northwest of Guam. The name "Bonin Islands" comes from the Japanese word ''bunin'' (an archaic read ...
, they prey on the indigenous snails and seedlings. Snails that inhabit the leaf litter of these islands showed a significant decline in population on the introduction of ''Rattus rattus''. The black rat shows a preference for snails with larger shells (greater than 10 mm), and this led to a great decline in the population of snails with larger shells. A lack of prey refuges makes it more difficult for the snail to avoid the rat.
Complex pest
The black rat is a complex pest, defined as one that influences the environment in both harmful and beneficial ways. In many cases, after the black rat is introduced into a new area, the population size of some native species declines or goes extinct. This is because the black rat is a good generalist with a wide dietaryniche
Niche may refer to:
Science
*Developmental niche, a concept for understanding the cultural context of child development
* Ecological niche, a term describing the relational position of an organism's species
*Niche differentiation, in ecology, the ...
and a preference for complex habitats; this causes strong competition for resources among small animals. This has led to the black rat completely displacing many native species in Madagascar, the Galapagos, and the Florida Keys. In a study by Stokes ''et al.'', habitats suitable for the native bush rat, ''Rattus fuscipes
The bush rat or Australian bush rat (''Rattus fuscipes'') is a small Australian nocturnal animal. It is an omnivore and one of the most common indigenous species of rat on the continent, found in many heathland areas of Victoria and New So ...
'', of Australia are often invaded by the black rat and are eventually occupied by only the black rat. When the abundances of these two rat species were compared in different micro-habitats
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
, both were found to be affected by micro-habitat disturbances, but the black rat was most abundant in areas of high disturbance; this indicates it has a better dispersal ability.
Despite the black rat's tendency to displace native species, it can also aid in increasing species population numbers and maintaining species diversity. The bush rat, a common vector for spore dispersal of truffles
A truffle is the fruiting body of a subterranean ascomycete fungus, predominantly one of the many species of the genus ''Tuber''. In addition to ''Tuber'', many other genera of fungi are classified as truffles including '' Geopora'', '' Pe ...
, has been extirpated from many micro-habitats of Australia. In the absence of a vector, the diversity of truffle species would be expected to decline. In a study in New South Wales, Australia it was found that, although the bush rat consumes a diversity of truffle species, the black rat consumes as much of the diverse fungi as the natives and is an effective vector for spore dispersal. Since the black rat now occupies many of the micro-habitats that were previously inhabited by the bush rat, the black rat plays an important ecological role in the dispersal of fungal spores. By eradicating the black rat populations in Australia, the diversity of fungi would decline, potentially doing more harm than good.
Control methods
Large-scale rat control programs have been taken to maintain a steady level of the invasive predators in order to conserve the native species in New Zealand such as kokako andmohua Mohua may refer to:
* Golden Bay / Mohua, a bay at the northwest end of New Zealand's South Island
*Yellowhead (bird) or mohua, a small bird endemic to the South Island of New Zealand
*The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs
The Ministry of Ho ...
. Pesticides, such as pindone and 1080 ( sodium fluoroacetate), are commonly distributed via aerial spray by helicopter as a method of mass control on islands infested with invasive rat populations. Bait, such as brodifacoum, is also used along with coloured dyes (used to deter birds from eating the baits) in order to kill and identify rats for experimental and tracking purposes. Another method to track rats is the use of wired cage traps, which are used along with bait, such as rolled oats and peanut butter, to tag and track rats to determine population sizes through methods like mark-recapture and radio-tracking. Tracking tunnels (coreflute tunnels containing an inked card) are also commonly used monitoring devices, as are chew-cards containing peanut butter. Poison control methods are effective in reducing rat populations to nonthreatening sizes, but rat populations often rebound to normal size within months. Besides their highly adaptive foraging behavior and fast reproduction, the exact mechanisms for their rebound is unclear and are still being studied.
In 2010, the Sociedad Ornitológica Puertorriqueña (Puerto Rican Bird Society) and the Ponce Yacht and Fishing Club launched a campaign to eradicate the black rat from the Isla Ratones (Mice Island) and Isla Cardona
Isla Cardona, also known as Sor Isolina Ferré Island, is a small, uninhabited island located 1.30 nautical miles south of the mainland Puerto Rico, Puerto Rican shore across from Barrio Playa (Ponce), Playa, on the west side of the entrance to ...
(Cardona Island) islands off the municipality of Ponce, Puerto Rico
Ponce (, , , ) is both a city and a municipality on the southern coast of Puerto Rico. The city is the seat of the municipal government.
Ponce, Puerto Rico's most populated city outside the San Juan metropolitan area, was founded on 12 August 1 ...
.
Decline in population
''Rattus rattus'' populations were common in Great Britain, but began to decline after the introduction of the brown rat in the 18th century. ''R. rattus'' populations remained common in seaports and major cities until the late 19th century, but have been decreased due to rodent control and sanitation measures. The Shiant Islands in theOuter Hebrides
The Outer Hebrides () or Western Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar or or ("islands of the strangers"); sco, Waster Isles), sometimes known as the Long Isle/Long Island ( gd, An t-Eilean Fada, links=no), is an island chain off the west coas ...
in Scotland are often cited as the last remaining wild population of ''R. rattus'' left in Britain but evidence demonstrates that populations survive on other islands (e.g. Inchcolm) and in localised areas of the British mainland. Recent National Biodiversity Network data show populations around the U.K., particularly in ports and port towns. This is supported by anecdotal records from London and Liverpool.
As of winter 2015 the Shiant Isles Recovery Project (a joint initiative between RSPB and Scottish Natural Heritage) is underway to eradicate ''Rattus rattus'' populations on the islands.
See also
*Karni Mata Temple
Karni Mata Temple of Deshnoke (Hindi: करणी माता मंदिर), also known as Madh Deshnoke, is a prominent Hindu temple dedicated to Karni Mata at the town of Deshnoke, located 30 km south of Bikaner, in Rajasthan. It h ...
, Deshnoke, Rajasthan, India.
* Polynesian rat
The Polynesian rat, Pacific rat or little rat (''Rattus exulans''), known to the Māori as ''kiore'', is the third most widespread species of rat in the world behind the brown rat and black rat. The Polynesian rat originated in Southeast Asia, a ...
* Urban plague
References
Further reading
*List of books and articles about rats
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby union ...
External links
Photos and video
at ARKive {{Authority control Rattus Rodents of Asia Rodents of Europe Mammals of Azerbaijan Mammals of Nepal Stored-product pests Mammals described in 1758 Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Invasive animal species in Australia