Racibórz on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Racibórz (german: Ratibor, cz, Ratiboř, szl, Racibōrz) is a city in Silesian Voivodeship in southern
 However, the first confirmed mention of Racibórz was made in 1108 in the ''
However, the first confirmed mention of Racibórz was made in 1108 in the '' From 1299 onwards, Racibórz was ruled by an autonomous city council according to Magdeburg town law. When in 1327 Duke Leszek of Racibórz paid homage to the
From 1299 onwards, Racibórz was ruled by an autonomous city council according to Magdeburg town law. When in 1327 Duke Leszek of Racibórz paid homage to the
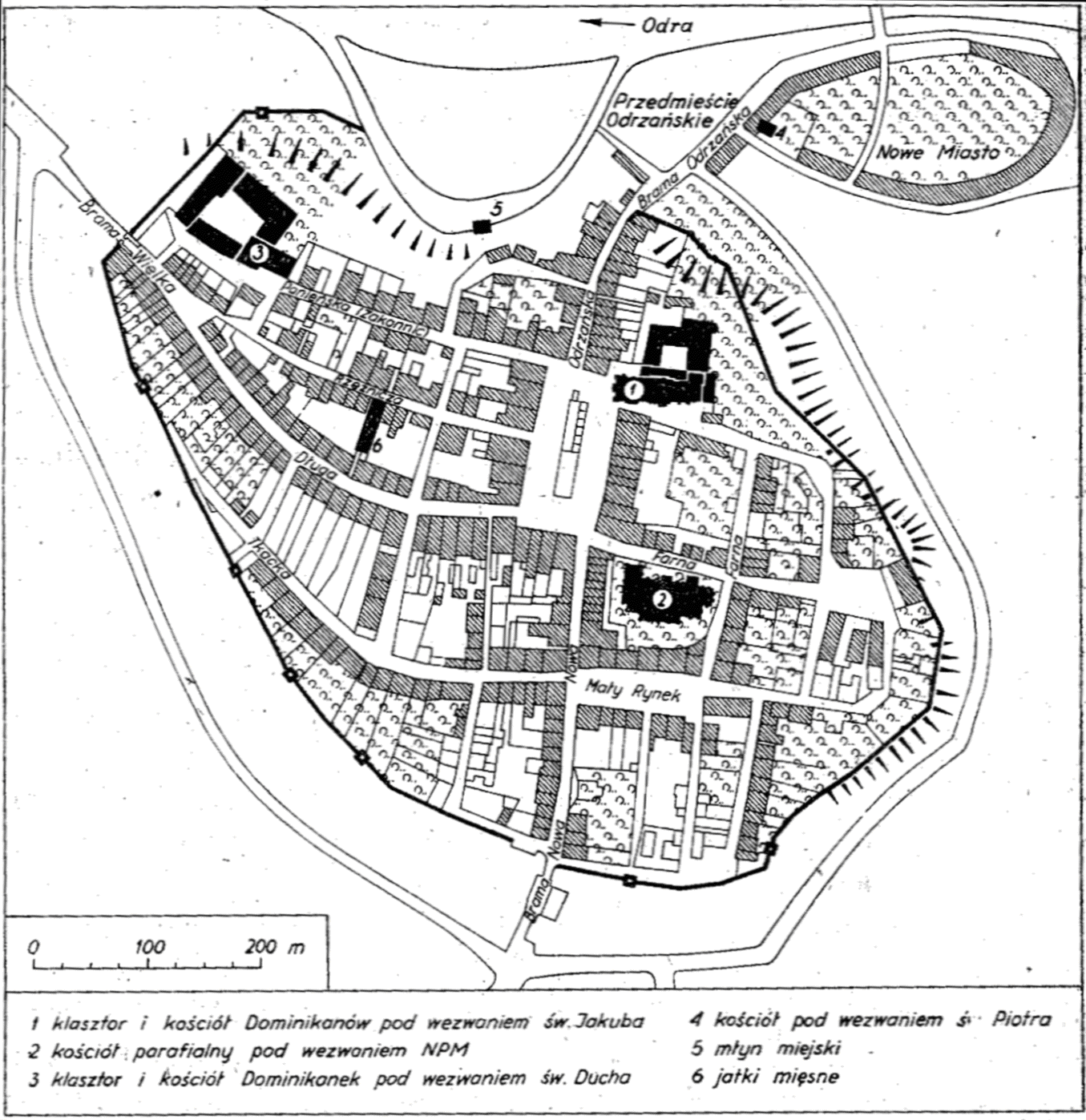 When the last Přemyslid duke Valentin died and was buried in the Dominican church in 1521, Racibórz according to a 1512 inheritance treaty fell to the
When the last Přemyslid duke Valentin died and was buried in the Dominican church in 1521, Racibórz according to a 1512 inheritance treaty fell to the
 During the German
During the German
 The local men's football team is
The local men's football team is
File:Kościół Wniebowzięcia NMP w Raciborzu 12.JPG, Parish church of the Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary
File:Baszta więzienna w Raciborzu 4.JPG, Prison Tower
File:Kościół św. Jakuba w Raciborzu 5.JPG, Saint James church
File:Kaplica zamkowa pw. św. Tomasza Kantuaryjskiego w Raciborzu 2.JPG, Chapel of St. Thomas Becket
File:Kościół św. Jana Chrzciciela w Raciborzu 6.JPG, Church of John the Baptist
File:Sąd Rejonowy w Raciborzu 2.JPG, District Court
Official website
Partnership with German city Leverkusen
Jewish Community in Racibórz
on Virtual Shtetl
{{DEFAULTSORT:Raciborz Cities and towns in Silesian Voivodeship Racibórz County Cities in Silesia
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. It is the administrative seat of Racibórz County
__NOTOC__
Racibórz County ( pl, powiat raciborski) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Silesian Voivodeship, southern Poland, on the Czech border. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polis ...
.
With Opole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, Ôpole) ;
* Silesian:
** Silesian PLS alphabet: ''Ôpole''
** Steuer's Silesian alphabet: ''Uopole''
* Silesian German: ''Uppeln''
* Czech: ''Opolí''
* Latin: ''Oppelia'', ''Oppolia'', ''Opulia'' is a city l ...
, Racibórz is one of the historic capitals of Upper Silesia, being the residence of the Dukes of Racibórz from 1172 to 1521.
Geography
The city is situated in the southwest of the voivodeship on the upperOder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
river, near the border with the Polish Opole Voivodeship and the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
. The Racibórz Basin (''Kotlina Raciborska'') forms the southeastern extension of the Silesian Lowlands
Silesian Lowlands (or Silesian Plains, pl, Nizina Śląska, cs, Slezská nížina, german: Schlesische Niederung) are lowlands located in Silesia, Poland in Central Europe. A small part is located in the Czech Republic. It is part of the Centra ...
, surrounded by the Opawskie Mountains in the west (part of the Eastern Sudetes
The Eastern Sudetes ( pl, Sudety Wschodnie, cs, Východní Sudety or ''Jesenická oblast'') are the eastern part of the Sudetes mountains on the border of the Czech Republic and Poland. They stretch from the Kłodzko Valley and the Eastern Neis ...
), the Silesian Upland in the north, and the Moravian Gate
The Moravian Gate ( cs, Moravská brána, pl, Brama Morawska, german: Mährische Pforte, sk, Moravská brána) is a geomorphological feature in the Moravian region of the Czech Republic and the Upper Silesia region in Poland. It is formed by the ...
in the south. The town centre is located about southwest of Katowice
Katowice ( , , ; szl, Katowicy; german: Kattowitz, yi, קאַטעוויץ, Kattevitz) is the capital city of the Silesian Voivodeship in southern Poland and the central city of the Upper Silesian metropolitan area. It is the 11th most popu ...
and about southeast of the regional capital Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, r ...
.
As of 2019, the city has a population of approximately 55,000 inhabitants. From 1975 to 1998, it belonged to Katowice Voivodeship.
History
Until the end of the 5th century AD, the lands of the later Racibórz settlement were inhabited by East Germanic Silinger tribes. The town is one of the oldest in Upper Silesia, the site of ahill fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
where the old trade route from the Moravian Gate down to Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
crossed the Oder river. There is a possibility that Racibórz was mentioned in a work of the " Bavarian Geographer" in 845 (this document mentions five strongholds of the Slavic Golensizi
The Golensizi ( pl, Golęszycy, Gołęszycy, Golęszyce, Gołęszyce, Gołężyce, cz, Holasici, german: Golensizen) were a tribe of West Slavs, specifically of the Lechitic tribes (one of the Silesian tribes), living in the Early Middle Ages an ...
(Golenshitse, ''Holasici'' in Czech), a proto-Polish tribe, probably Racibórz was one of them). The name Racibórz is of Slavic origin and probably is derived from the name of one Duke Racibor, the city's founder.
Middle Ages
Gesta principum Polonorum
The ''Gesta principum Polonorum'' (; "''Deeds of the Princes of the Poles''") is the oldest known medieval chronicle documenting the history of Poland from the legendary times until 1113. Written in Latin by an anonymous author, it was most lik ...
'' chronicle by the Benedictine monk Gallus Anonymus, at a time when the Polish duke Bolesław III Wrymouth had to ward off the attacks by the forces of Duke Svatopluk of Bohemia invading from the Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The ...
n lands in the south. The Polish rule over the Racibórz area was confirmed in 1137, it was incorporated into the Duchy of Silesia
The Duchy of Silesia ( pl, Księstwo śląskie, german: Herzogtum Schlesien, cs, Slezské knížectví) with its capital at Wrocław was a medieval duchy located in the historic Silesian region of Poland. Soon after it was formed under the Piast ...
according to the Testament of Bolesław III in the following year.
Racibórz was an important center of beer production, and the townspeople enjoyed a privilege that allowed brewing
Brewing is the production of beer by steeping a starch source (commonly cereal grains, the most popular of which is barley) in water and fermenting the resulting sweet liquid with yeast. It may be done in a brewery by a commercial brewer ...
already in the early 12th century. Brewing was an important source of the town's income, and local beer was popular not only in Silesia, but also in neighboring Czechia.
From 1155, Racibórz was the seat of a castellany. The town became the first historical capital of Upper Silesia, when the Duchy of Racibórz was established by the Piast duke Mieszko I Tanglefoot
Mieszko IV Tanglefoot ( pl, Mieszko IV Plątonogi) (c. 1130 – 16 May 1211) was Duke of Kraków and High Duke of Poland from 9 June 1210 until his death one year later. He was also Duke of Silesia from 1163 to 1173 (with his brother as co-ruler) ...
upon the first partition of Silesia in 1172. From 1202 onwards, Duke Mieszko ruled over whole Upper Silesia as Duke of Opole and Racibórz. He had the settlement beneath his residence laid out and the area colonized by Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; ...
merchants, the first coin with the Polish description "MILOST" was issued in Racibórz in 1211. Mieszko's son and successor Duke Casimir I granted the Racibórz citizens municipal privileges in 1217.
In 1241, the Poles led by local Duke Mieszko II the Fat won the Battle of Racibórz during the first Mongol invasion of Poland
The Mongol Invasion of Poland from late 1240 to 1241 culminated in the Battle of Legnica, where the Mongols defeated an alliance which included forces from fragmented Poland and their allies, led by Henry II the Pious, the Duke of Silesia. ...
and the Duke founded a Dominican monastery in the city, where he was buried in 1246. The first Polish national anthem ''Gaude Mater Polonia
''Gaude Mater Polonia'' ( Medieval Latin for "Rejoice, oh Mother Poland"; , Polish: Raduj się, matko Polsko) was one of the most significant medieval Polish hymns, written in Latin between the 13th and the 14th century to commemorate Saint St ...
'' was written ca. 1260–70 in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
by the Dominican brother Wincenty of Kielcza. In 1285 Duke Przemysław of Racibórz
Przemysław of Racibórz ( pl, Przemysław raciborski) (between 21 October 1258 and 12 June 1268 – 7 May 1306) was a Duke of Racibórz since 1282 until his death (until 1290 with his brother as co-ruler).
He was the fourth son of Władysław, ...
granted the Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, r ...
bishop Thomas II Zaremba asylum during his fierce struggle with the Silesian duke Henry IV Probus. In turn, Bishop Thomas donated a college of canons at Racibórz Castle, dedicated to Saint Thomas of Canterbury
Thomas Becket (), also known as Saint Thomas of Canterbury, Thomas of London and later Thomas à Becket (21 December 1119 or 1120 – 29 December 1170), was an English nobleman who served as Lord Chancellor from 1155 to 1162, and then ...
. Duke Przemysław also founded a Dominican nunnery and his daughter Euphemia became its first prior
Prior (or prioress) is an ecclesiastical title for a superior in some religious orders. The word is derived from the Latin for "earlier" or "first". Its earlier generic usage referred to any monastic superior. In abbeys, a prior would be low ...
ess in 1313. Around 1300, the Dominican friar Peregrine of Opole
Peregrine of Opole ( 1260 – ?) was a Silesian Dominican friar. He was twice elected a provincial of his Order and became designated an inquisitor of Wrocław by the pope John XXII.
His major literary achievement is his twofold collection o ...
compiled his ''Sermones de tempore'' and ''Sermones de sanctis'' collections.
 From 1299 onwards, Racibórz was ruled by an autonomous city council according to Magdeburg town law. When in 1327 Duke Leszek of Racibórz paid homage to the
From 1299 onwards, Racibórz was ruled by an autonomous city council according to Magdeburg town law. When in 1327 Duke Leszek of Racibórz paid homage to the Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
king John of Bohemia
John the Blind or John of Luxembourg ( lb, Jang de Blannen; german: link=no, Johann der Blinde; cz, Jan Lucemburský; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King o ...
, his duchy became a Bohemian
Bohemian or Bohemians may refer to:
*Anything of or relating to Bohemia
Beer
* National Bohemian, a brand brewed by Pabst
* Bohemian, a brand of beer brewed by Molson Coors
Culture and arts
* Bohemianism, an unconventional lifestyle, origin ...
fiefdom. The Bohemian feudal suzerainty, confirmed in the 1335 Treaty of Trentschin, led to the seizure of Racibórz as a reverted fief, when the line of the Silesian Piasts became extinct upon Duke Leszek's death in 1336. The next year King John enfeoffed Leszek's brother-in-law Duke Nicholas II of Opava
Nicholas II of Opava (also: ''Nicholas II of Troppau'', ''Nicholas II of Ratibór''; cz, Mikuláš II. Opavský; 1288 – 8 December 1365) was Duke of Opava (german: Troppau) from 1318 to 1365 and Duke of Ratibór from 1337 to 1365 and Burgrav ...
with the duchy, which from that time on was ruled by the Opava cadet branch of the Bohemian Přemyslid dynasty
The Přemyslid dynasty or House of Přemyslid ( cs, Přemyslovci, german: Premysliden, pl, Przemyślidzi) was a Bohemian royal dynasty that reigned in the Duchy of Bohemia and later Kingdom of Bohemia and Margraviate of Moravia (9th century–1 ...
and incorporated into the Lands of the Bohemian Crown
The Lands of the Bohemian Crown were a number of incorporated states in Central Europe during the medieval and early modern periods connected by feudal relations under the Bohemian kings. The crown lands primarily consisted of the Kingdom o ...
. The Racibórz citizens retained their autonomy and the town developed to an important commercial centre for the region with significant cloth, tanning and brewing
Brewing is the production of beer by steeping a starch source (commonly cereal grains, the most popular of which is barley) in water and fermenting the resulting sweet liquid with yeast. It may be done in a brewery by a commercial brewer ...
industries.
Modern Era
 When the last Přemyslid duke Valentin died and was buried in the Dominican church in 1521, Racibórz according to a 1512 inheritance treaty fell to the
When the last Přemyslid duke Valentin died and was buried in the Dominican church in 1521, Racibórz according to a 1512 inheritance treaty fell to the Opole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, Ôpole) ;
* Silesian:
** Silesian PLS alphabet: ''Ôpole''
** Steuer's Silesian alphabet: ''Uopole''
* Silesian German: ''Uppeln''
* Czech: ''Opolí''
* Latin: ''Oppelia'', ''Oppolia'', ''Opulia'' is a city l ...
dukes Jan II the Good, also a vassal of Bohemian king. As he himself left no male heirs, his lands fell back to the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
king Ferdinand I. With Opole, Racibórz was temporarily given in pawn to the Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, also , german: Haus Hohenzollern, , ro, Casa de Hohenzollern) is a German royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenb ...
margraves of Ansbach and to the royal Polish House of Vasa. The town's economy suffered from the devastations in the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of batt ...
. In 1683, on his way to the Battle of Vienna
The Battle of Vienna; pl, odsiecz wiedeńska, lit=Relief of Vienna or ''bitwa pod Wiedniem''; ota, Beç Ḳalʿası Muḥāṣarası, lit=siege of Beç; tr, İkinci Viyana Kuşatması, lit=second siege of Vienna took place at Kahlenberg Mo ...
, Polish King John III Sobieski
John III Sobieski ( pl, Jan III Sobieski; lt, Jonas III Sobieskis; la, Ioannes III Sobiscius; 17 August 1629 – 17 June 1696) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1674 until his death in 1696.
Born into Polish nobility, Sobi ...
stopped in Racibórz, which he called a ''beautiful and fortified town'' in a letter to his wife Queen Marie Casimire.
After the First Silesian War in 1742, Racibórz was ceded to the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
under Frederick the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Sil ...
. With most of the Silesian territory it was incorporated into the Province of Silesia
The Province of Silesia (german: Provinz Schlesien; pl, Prowincja Śląska; szl, Prowincyjŏ Ślōnskŏ) was a province of Prussia from 1815 to 1919. The Silesia region was part of the Prussian realm since 1740 and established as an official p ...
in 1815 and the town became the administrative seat of a ''Landkreis
In all German states, except for the three city states, the primary administrative subdivision higher than a '' Gemeinde'' (municipality) is the (official term in all but two states) or (official term in the states of North Rhine-Westphalia ...
''. In the 18th century, Racibórz belonged to the tax inspection region of Prudnik. The mediate Lordship of Ratibor was acquired by Elector William I of Hesse in 1812, succeeded by Landgrave Victor Amadeus of Hesse-Rotenburg in 1821 and Prince Victor of Hohenlohe-Schillingsfürst in 1834, who was vested with the title of a "Duke of Ratibor" by King Frederick William IV of Prussia in 1840. At that time, Ratibor had already lost its status as a residential town, while the princes held court in the secularised monastery of Rudy (then officially ''Groß Rauden''). In the 19th century, Prussian policies increased the Germanisation
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In lin ...
. Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in ...
smuggled large amounts of gunpowder through the town to the Russian Partition of Poland during the January Uprising
The January Uprising ( pl, powstanie styczniowe; lt, 1863 metų sukilimas; ua, Січневе повстання; russian: Польское восстание; ) was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at ...
in 1863. Ratibor became part of the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
in 1871.
20th century
According to the Prussian census of 1910, the city of Ratibor had a population of 38,424, of which around 60% spoke German, 30% spoke Polish and 10% were bilingual. AfterWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, the Upper Silesian plebiscite
The Upper Silesia plebiscite was a plebiscite mandated by the Versailles Treaty and carried out on 20 March 1921 to determine ownership of the province of Upper Silesia between Weimar Germany and Poland. The region was ethnically mixed with bot ...
was held in 1921, in which 90.9% of votes in Ratibor town were for Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
and 9.1% were for Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. Consequently, the town remained in Germany, as part of the Prussian Province of Upper Silesia
The Province of Upper Silesia (german: Provinz Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ''Provinz Oberschläsing''; szl, Prowincyjŏ Gōrny Ślōnsk; pl, Prowincja Górny Śląsk) was a province of the Free State of Prussia from 1919 to 1945. It comprise ...
, and became a border town, while the present-day district of Brzezie, lying east of the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
was reintegrated with Poland. Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
increasingly persecuted local Polish activists since 1937. In May 1939, the Germans searched the local branch of the Union of Poles in Germany
Union of Poles in Germany ( pl, Związek Polaków w Niemczech, german: Bund der Polen in Deutschland e.V.) is an organisation of the Polish minority in Germany, founded in 1922. In 1924, the union initiated collaboration between other minorities, ...
and arrested both its secretary Leon Czogała and Ludwika Linderówna, activist of the local Association of Polish Women. In June 1939, the Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one orga ...
seized the headquarters of local Polish organizations, which was then handed over to the Hitler Youth
The Hitler Youth (german: Hitlerjugend , often abbreviated as HJ, ) was the youth organisation of the Nazi Party in Germany. Its origins date back to 1922 and it received the name ("Hitler Youth, League of German Worker Youth") in July 1926. ...
, while the Polish library and documents were confiscated.
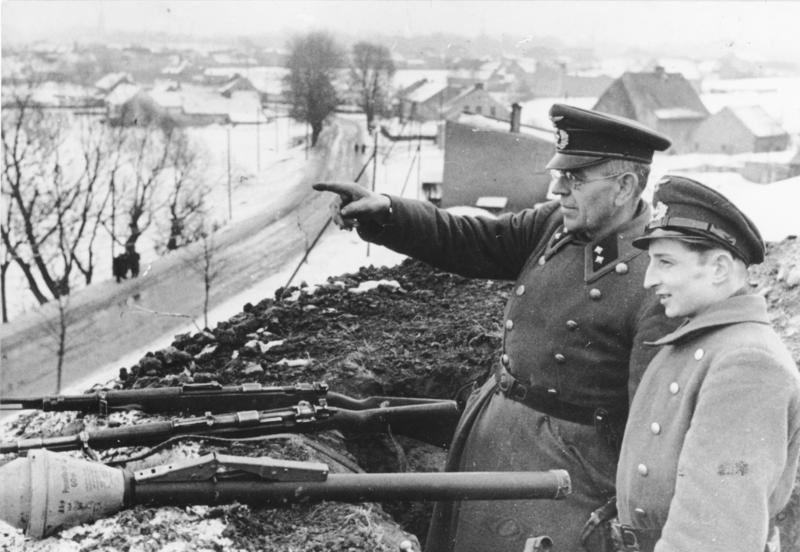
 During the German
During the German invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week af ...
, which started World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the '' Einsatzgruppe I'' entered the town on September 4, 1939, to commit atrocities against Poles. In September 1939, the Germans confiscated assets of the local Polish bank, and carried out mass arrests of prominent Poles, including the chairman of the local "Sokół" Polish Gymnastic Society, the editor-in-chief
An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies.
The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ...
of local Polish newspaper ''Dziennik Raciborski'', the chairman of the local Polish bank and activists of the Association of Polish Women. During the war, the Germans operated a Nazi prison, a '' Polenlager'' forced labour camp for Poles, a forced labour camp for Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, and six labour subcamps of the Stalag VIII-B/344 prisoner-of-war camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured by a belligerent power in time of war.
There are significant differences among POW camps, internment camps, and military prisons. ...
in the town, and three labour subcamps of Stalag VIII-B/344 in the present-day district of Brzezie. In 1945, two German-conducted death marches
A death march is a forced march of prisoners of war or other captives or deportees in which individuals are left to die along the way. It is distinguished in this way from simple prisoner transport via foot march. Article 19 of the Geneva Convent ...
of prisoners of the Auschwitz concentration camp
Auschwitz concentration camp ( (); also or ) was a complex of over 40 concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. I ...
and its subcamps passed through the town towards the Gross-Rosen concentration camp
, known for =
, location =
, built by =
, operated by =
, commandant =
, original use =
, construction =
, in operation = Summer of 1940 – 14 February 1945
, gas cham ...
and Opava. In the final stages of the war, it was initially spared by the Red Army Vistula–Oder Offensive but occupied and devastated on 30 March 1945. After end of the war, in June 1945, the army of Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
briefly entered into the town and Czechoslovakia officially claimed the area of Racibórz and Głubczyce
Głubczyce ( cs, Hlubčice or sparsely ''Glubčice'', german: Leobschütz, Silesian German: ''Lischwitz'') is a town in Opole Voivodeship in southern Poland, near the border with the Czech Republic. It is the administrative seat of Głubczyce C ...
(''Ratibořsko'' and ''Hlubčicko'') because of having a substantial Czech minority (see border conflicts between Poland and Czechoslovakia
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders ca ...
). At the same time the expulsion of Germans
Expulsion or expelled may refer to:
General
* Deportation
* Ejection (sports)
* Eviction
* Exile
* Expeller pressing
* Expulsion (education)
* Expulsion from the United States Congress
* Extradition
* Forced migration
* Ostracism
* Persona non ...
started, while the town became wholly part of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
as defined at the Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris P ...
. The German CDU politician Herbert Hupka
Herbert Hupka (August 15, 1915 – August 24, 2006) was a German journalist, politician (SPD and later the CDU), and advocate for the Germans expelled from neighbouring countries after the Second World War.
Early life
Hupka was born in a ...
at the end of his life promoted reconciliation between the former German inhabitants, including himself, and the new Polish settlers and administration of Racibórz. In 1997, a flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrol ...
devastated the town.
Climate
Racibórz has anoceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
: ''Cfb'') using the isotherm or a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
(Köppen climate classification: ''Dfb'') using the isotherm.
Districts
*Centrum *Nowe Zagrody *Ocice *Stara Wieś *Miedonia *Ostróg *Markowice *Płonia * Brzezie *Sudół *Studzienna *OboraCulture
The officially protected traditional beverage from Racibórz is localbeer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
, which is produced in various styles (as designated by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Poland).
Sports
 The local men's football team is
The local men's football team is KP Unia Racibórz
KP Unia Racibórz is a football club from Racibórz, Silesian Voivodeship, Silesia, Poland.
History As part of a sports club
Unia Racibórz was founded on 27 April 1946 as a men's team. Its initial name was ''Klub Sportowy Plania Racibórz''. The ...
. It competes in the lower leagues, however, it played in the Polish top division in the past. Defunct women's football club RTP Unia Racibórz
RTP Unia Racibórz was a women's football club from Racibórz, Poland. The club won five national championships, three Polish Cups and participated in the UEFA Women's Champions League.
History As part of a sports club
Unia Racibórz was founded ...
was also based in the town. It played in Poland's top division, and won five consecutive national championships from 2009 to 2013.
Notable people
*Wawrzyniec z Raciborza
Wawrzyniec z Raciborza (1381–1448) was an Upper Silesian theologian, active in Kraków, Poland.
1381 births
1448 deaths
People from Racibórz
Polish Roman Catholic theologians
{{Poland-reli-bio-stub ...
(1381–1448), Roman Catholic theologian
* Joseph Freiherr von Eichendorff (1788–1857), Prussian poet, playwright
*Julius Reinhold Friedlander
Julius Reinhold Friedlander (1803–1839) was a German-American educator. He was the founder of the Pennsylvania Institution for the Instruction of the Blind in Philadelphia, which later became the Overbrook School for the Blind.
Biography
Juli ...
(1803–1839), educator, founder of the Pennsylvania Institution for the Instruction of the Blind
The Overbrook School for the Blind in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania was established in 1832. Its present site, in the city's Overbrook neighborhood, was acquired in 1890. Along with the Pennsylvania School for the Deaf, the Western Pennsylvania S ...
* Ludwig Traube (1818–1876), German physician
* Moritz Traube (1826–1894), German chemist
*Paul Guttmann
Paul Guttmann (9 September 1834 in Ratibor ( pl, Racibórz) – 24 May 1893 in Berlin) was a German pathologist.
He studied medicine in Berlin, Würzburg and Vienna, earning his doctorate in 1858. From 1859 he worked in Berlin, where he later b ...
(1834–1893), German pathologist
*Hermann Traube
Hermann Traube (September 24, 1860 – January 29, 1913) was a German mineralogist born in Ratibor, Silesia (presently Racibórz, Poland). He was the son of chemist Moritz Traube (1826-1894).
He studied at the Universities of Leipzig, Heide ...
(1860–1913), German mineralogist
*Johannes Thiele Johannes Thiele may refer to:
*Johannes Thiele (zoologist)
*Johannes Thiele (chemist)
Friedrich Karl Johannes Thiele (May 13, 1865 – April 17, 1918) was a German chemist and a prominent professor at several universities, including those in ...
(1865–1918), German chemist
*Wilhelm Traube
Wilhelm Traube (10 January 1866 – 28 September 1942) was a German chemist.
Biography
Traube was born at Ratibor (Racibórz) in Prussian Silesia, a son of the famous private scholar Moritz Traube.
After studying law for a short time, he ...
(1866–1942), German chemist
*Else Berg
Else Berg (19 February 1877, Ratibor – 19 November 1942, Auschwitz) was a German-born Dutch painter of Jewish descent; associated with the Bergense School. She was married to the Dutch painter, Mommie Schwarz. She and her husband were both mu ...
(1877–1942), German-Dutch painter
*Arthur Löwenstamm
Arthur Löwenstamm (also spelt Loewenstamm) (20 December 1882– 22 April 1965) was a Jewish theologian, writer and rabbi in Berlin and in London, where he came in 1939 as a refugee from Nazi Germany.
He was the last rabbi of the Jewish ...
(1882–1965), rabbi
*Augustin Souchy
Augustin Souchy Bauer (28 August 1892 – 1 January 1984) was a German anarchist, antimilitarist, labor union official and journalist. He traveled widely and wrote extensively about the Spanish Civil War and intentional communities. He was bor ...
(1892–1984), German anarchist
*Fritz Otto Bernert
'' Oberleutnant'' Fritz Otto Bernert (commonly called Otto) (6 March 1893 – 18 October 1918) was a leading German fighter ace of World War I. After being invalided from infantry duty after his fourth wound, Bernert joined the aviation branch. Aft ...
(1893–1918), German fighter ace of World War I
*Willibald Borowietz
__NOTOC__
Willibald Borowietz (17 September 1893 – 1 July 1945) was a German general during World War II who commanded several divisions. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross, Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak ...
(1893–1945), Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
general
*Gertrud Arndt
Gertrud Arndt (''née'' Hantschk; 20 September 1903 – 10 July 2000) was a German photographer and designer associated with the Bauhaus movement. She is remembered for her pioneering series of self-portraits from around 1930.
Biography
Born G ...
(1903–2000), German photographer
*Günther Friedländer
Günther Friedländer (April 8, 1902 – May 25, 1975) was a German pharmacist, botanist, pharmacognosist, food chemist, an industrialist of medical products, and the founder of Teva Pharmaceutical Industries.
Biography
Günther Friedlä ...
(1912–1920), Founder of Teva Pharmaceuticals
*Herbert Kutscha
Herbert Kutscha (24 April 1917 – 19 September 2003 ) was a German Luftwaffe fighter ace and recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross during World War II. The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross was awarded to recognise extreme battle ...
(1917–2003), German Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabt ...
fighter ace
*Hannes Rosenow
Hannes Rosenow (5 May 1925 in Ratibor – 28 July 2000 in Munich) was a German portrait and landscape painter.
Biography
After his graduation from the gymnasium in Ratibor in Upper Silesia, military draft and release from military internment ...
(1925-2000), German painter
* Claus Ogerman (1930–2016), German–American musician
*Hubert Kostka
Hubert Jerzy Kostka (born 27 May 1940 in Ratibor) is a retired Polish football goalkeeper. Kostka participated in the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich, where Poland won the men's football tournament. Kostka is not only a successful player, he ...
(born 1940), footballer
*Marek Migalski
Dr Marek Henryk Migalski (born 14 January 1969 in Racibórz) is a Polish politician, Member of the European Parliament, political scientist, and columnist. A member of Poland Comes First (PjN), Migalski was elected to the European Parliament at ...
(born 1969), politician, Member of the European Parliament
A Member of the European Parliament (MEP) is a person who has been elected to serve as a popular representative in the European Parliament.
When the European Parliament (then known as the Common Assembly of the ECSC) first met in 1952, its ...
, political scientist, and columnist
*Ryszard Wolny
Ryszard Marcin Wolny (born 24 March 1969 in Racibórz) is a Polish wrestler and Olympic champion in Greco-Roman wrestling.
Olympics
Wolny has competed in five Olympics, from 1988 to 2004. At the 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta
...
(born 1969), wrestler and Olympic champion
*Arkadiusz Mularczyk
Arkadiusz Mularczyk
• Born 4/2/1971 in Racibórz, Poland
• Graduated with a Masters in Law from the Jagiellonian University, Kraków in 1996.
• Local councillor in Nowy Sacz from 1992-2002.
• Postgraduate studies at the Helsinki Foun ...
(born 1971), politician
*Magdalena Walach
Magdalena Walach (born 13 May 1976) is a Polish film and theater actress. In 1999 she completed studies at the Ludwik Solski Academy for the Dramatic Arts in Kraków. She is a member of the Bagatela Theatre acting company. Walach is married t ...
(born 1976), actress
* Michał Kamiński (born 1987), volleyball player
*Artur Noga
Artur Noga (born 2 May 1988 in Racibórz) is a Polish athlete. He mainly competes in the 110 metres hurdles. He finished 5th at the 2008 Summer Olympics
The 2008 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXIX Olympiad () and also know ...
(born 1988), athlete
* Sebastian Tyrała (born 1988), Polish-German footballer
*Justyna Święty-Ersetic
Justyna Święty-Ersetic (; born 3 December 1992) is a Polish sprinter specialising in the 400 metres. She was the 2018 European champion and a two-time European Indoor Championship medallist in this event. Święty-Ersetic won many medals ...
(born 1992), sprinter
*Łukasz Moneta
Łukasz Moneta (born 13 May 1994) is a Polish professional footballer who plays as a left midfielder for Ruch Chorzów.
Club career
He made his league debut on 2 August 2014 in an Ekstraklasa match against Górnik Zabrze.
Career statistics
Clu ...
(born 1994), footballer
*Denis Kudla (wrestler)
''For the American professional tennis player, see Denis Kudla.''
Denis Maksymilian Kudla (born 24 December 1994) is a German Greco-Roman wrestling, Greco-Roman wrestler. He won a bronze medal at the 2016 European Wrestling Championships. Kudla ...
(born 1994), German wrestler
Twin towns – sister cities
Racibórz is twinned with: * Kędzierzyn-Koźle, Poland * Leverkusen, Germany * Opava, Czech Republic *Roth Roth may refer to:
Places
Germany
* Roth (district), in Bavaria, Germany
** Roth, Bavaria, capital of that district
** Roth (electoral district), a federal electoral district
* Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany:
** Roth an der Our, in the district ...
, Germany
* Tysmenytsia
Tysmenytsia ( uk, Ти́смениця, translit=Tysmenycia; pl, Tyśmienica) is a city in Ivano-Frankivsk Raion, Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast of western Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Tysmenytsia urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukr ...
, Ukraine
* Villeneuve-d'Ascq, France
* Zugló (Budapest), Hungary
Former twin towns:
* Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad ( ; rus, Калининград, p=kəlʲɪnʲɪnˈɡrat, links=y), until 1946 known as Königsberg (; rus, Кёнигсберг, Kyonigsberg, ˈkʲɵnʲɪɡzbɛrk; rus, Короле́вец, Korolevets), is the largest city and ...
, Russia (terminated in 2022 due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine)
Gallery
References
External links
Official website
Partnership with German city Leverkusen
Jewish Community in Racibórz
on Virtual Shtetl
{{DEFAULTSORT:Raciborz Cities and towns in Silesian Voivodeship Racibórz County Cities in Silesia