RGB color model on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
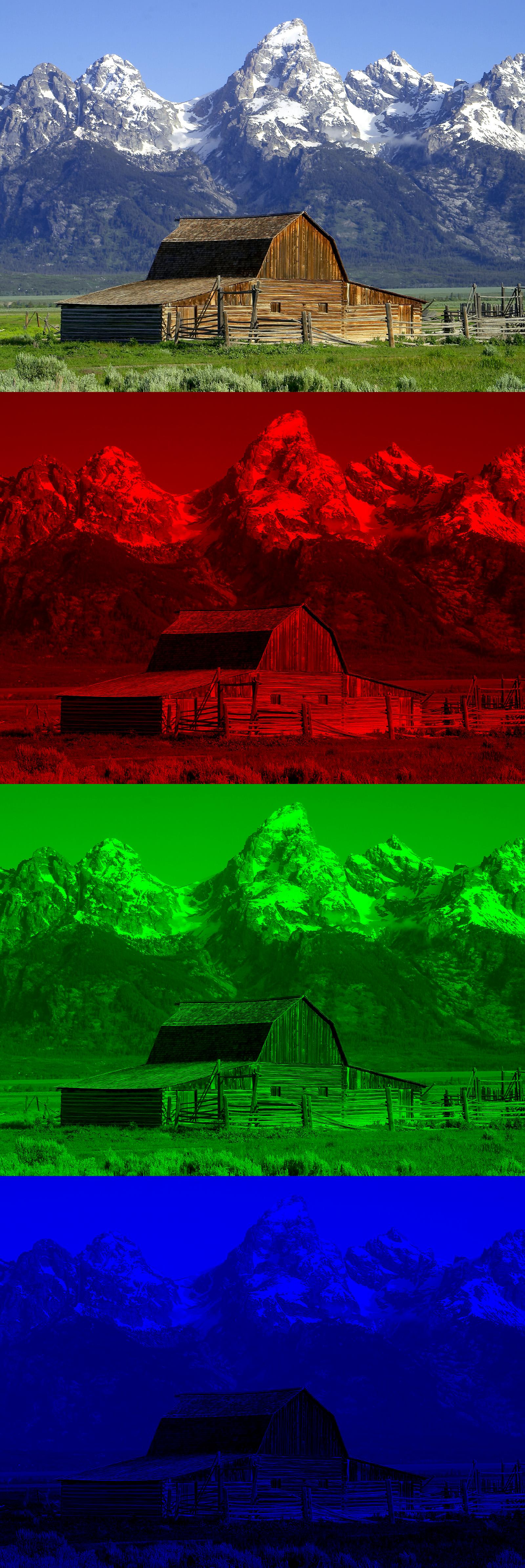 The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red,
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red,
 To form a color with RGB, three light beams (one red, one green, and one blue) must be superimposed (for example by emission from a black screen or by reflection from a white screen). Each of the three beams is called a ''component'' of that color, and each of them can have an arbitrary intensity, from fully off to fully on, in the mixture.
The RGB color model is ''additive'' in the sense that the three light beams are added together, and their light spectra add, wavelength for wavelength, to make the final color's spectrum. This is essentially opposite to the subtractive color model, particularly the
To form a color with RGB, three light beams (one red, one green, and one blue) must be superimposed (for example by emission from a black screen or by reflection from a white screen). Each of the three beams is called a ''component'' of that color, and each of them can have an arbitrary intensity, from fully off to fully on, in the mixture.
The RGB color model is ''additive'' in the sense that the three light beams are added together, and their light spectra add, wavelength for wavelength, to make the final color's spectrum. This is essentially opposite to the subtractive color model, particularly the
 The choice of primary colors is related to the physiology of the
The choice of primary colors is related to the physiology of the
Library of Congress. Such methods lasted until about 1960 using the expensive and extremely complex tri-color carbro
 One common application of the RGB color model is the display of colors on a cathode-ray tube (CRT),
One common application of the RGB color model is the display of colors on a cathode-ray tube (CRT),
 In color television and video cameras manufactured before the 1990s, the incoming light was separated by prisms and filters into the three RGB primary colors feeding each color into a separate video camera tube (or ''pickup tube''). These tubes are a type of cathode-ray tube, not to be confused with that of CRT displays.
With the arrival of commercially viable charge-coupled device (CCD) technology in the 1980s, first, the pickup tubes were replaced with this kind of sensor. Later, higher scale integration electronics was applied (mainly by
In color television and video cameras manufactured before the 1990s, the incoming light was separated by prisms and filters into the three RGB primary colors feeding each color into a separate video camera tube (or ''pickup tube''). These tubes are a type of cathode-ray tube, not to be confused with that of CRT displays.
With the arrival of commercially viable charge-coupled device (CCD) technology in the 1980s, first, the pickup tubes were replaced with this kind of sensor. Later, higher scale integration electronics was applied (mainly by

 A color in the RGB color model is described by indicating how much of each of the red, green, and blue is included. The color is expressed as an RGB triplet (''r'',''g'',''b''), each component of which can vary from zero to a defined maximum value. If all the components are at zero the result is black; if all are at maximum, the result is the brightest representable white.
These ranges may be quantified in several different ways:
* From 0 to 1, with any fractional value in between. This representation is used in theoretical analyses, and in systems that use
A color in the RGB color model is described by indicating how much of each of the red, green, and blue is included. The color is expressed as an RGB triplet (''r'',''g'',''b''), each component of which can vary from zero to a defined maximum value. If all the components are at zero the result is black; if all are at maximum, the result is the brightest representable white.
These ranges may be quantified in several different ways:
* From 0 to 1, with any fractional value in between. This representation is used in theoretical analyses, and in systems that use
 Since colors are usually defined by three components, not only in the RGB model, but also in other color models such as
Since colors are usually defined by three components, not only in the RGB model, but also in other color models such as
RGB mixer
{{DEFAULTSORT:RGB Color Model 1861 introductions Color space
 The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red,
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combin ...
and blue
Blue is one of the three primary colours in the RYB colour model (traditional colour theory), as well as in the RGB (additive) colour model. It lies between violet and cyan on the spectrum of visible light. The eye perceives blue when ...
primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associ ...
s. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three additive primary colors, red, green, and blue.
The main purpose of the RGB color model is for the sensing, representation, and display of images in electronic systems, such as televisions and computers, though it has also been used in conventional photography
Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is emplo ...
. Before the electronic age
The Information Age (also known as the Computer Age, Digital Age, Silicon Age, or New Media Age) is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during t ...
, the RGB color model already had a solid theory behind it, based in human perception of colors.
RGB is a ''device-dependent'' color model: different devices detect or reproduce a given RGB value differently, since the color elements (such as phosphors or dye
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and ...
s) and their response to the individual red, green, and blue levels vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, or even in the same device over time. Thus an RGB value does not define the same ''color'' across devices without some kind of color management.
Typical RGB input devices are color TV and video cameras, image scanner
An image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting or an object and converts it to a digital image. Commonly used in offices are variations of the desktop ''flatbed scanner'' ...
s, and digital cameras. Typical RGB output devices are TV sets of various technologies ( CRT, LCD, plasma, OLED, quantum dots, etc.), computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations ( computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These prog ...
and mobile phone
A mobile phone, cellular phone, cell phone, cellphone, handphone, hand phone or pocket phone, sometimes shortened to simply mobile, cell, or just phone, is a portable telephone that can make and receive calls over a radio frequency link whi ...
displays, video projectors, multicolor LED displays and large screens such as the Jumbotron. Color printers, on the other hand are not RGB devices, but subtractive color devices typically using the CMYK color model.
Additive colors
 To form a color with RGB, three light beams (one red, one green, and one blue) must be superimposed (for example by emission from a black screen or by reflection from a white screen). Each of the three beams is called a ''component'' of that color, and each of them can have an arbitrary intensity, from fully off to fully on, in the mixture.
The RGB color model is ''additive'' in the sense that the three light beams are added together, and their light spectra add, wavelength for wavelength, to make the final color's spectrum. This is essentially opposite to the subtractive color model, particularly the
To form a color with RGB, three light beams (one red, one green, and one blue) must be superimposed (for example by emission from a black screen or by reflection from a white screen). Each of the three beams is called a ''component'' of that color, and each of them can have an arbitrary intensity, from fully off to fully on, in the mixture.
The RGB color model is ''additive'' in the sense that the three light beams are added together, and their light spectra add, wavelength for wavelength, to make the final color's spectrum. This is essentially opposite to the subtractive color model, particularly the CMY color model
The CMYK color model (also known as process color, or four color) is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation ''CMYK'' refers ...
, that applies to paints, inks, dyes, and other substances whose color depends on ''reflecting'' the light under which we see them. Because of properties, these three colors create white, this is in stark contrast to physical colors, such as dye
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and ...
s which create black when mixed.
Zero intensity for each component gives the darkest color (no light, considered the ''black''), and full intensity of each gives a white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White ...
; the ''quality'' of this white depends on the nature of the primary light sources, but if they are properly balanced, the result is a neutral white matching the system's white point. When the intensities for all the components are the same, the result is a shade of gray, darker or lighter depending on the intensity. When the intensities are different, the result is a colorized hue, more or less saturated depending on the difference of the strongest and weakest of the intensities of the primary colors employed.
When one of the components has the strongest intensity, the color is a hue near this primary color (red-ish, green-ish, or blue-ish), and when two components have the same strongest intensity, then the color is a hue of a secondary color (a shade of cyan, magenta or yellow
Yellow is the color between green and orange on the spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a dominant wavelength of roughly 575585 nm. It is a primary color in subtractive color systems, used in painting or color printing. In th ...
). A secondary color is formed by the sum of two primary colors of equal intensity: cyan is green+blue, magenta is blue+red, and yellow is red+green. Every secondary color is the complement of one primary color: cyan complements red, magenta complements green, and yellow complements blue. When all the primary colors are mixed in equal intensities, the result is white.
The RGB color model itself does not define what is meant by ''red'', ''green'', and ''blue'' colorimetrically, and so the results of mixing them are not specified as absolute, but relative to the primary colors. When the exact chromaticities of the red, green, and blue primaries are defined, the color model then becomes an absolute color space, such as sRGB
sRGB is a standard RGB (red, green, blue) color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission ...
or Adobe RGB
The Adobe RGB (1998) color space or opRGB is a color space developed by Adobe Systems, Inc. in 1998. It was designed to encompass most of the colors achievable on CMYK color printers, but by using RGB primary colors on a device such as a comp ...
; see RGB color space for more details.
Physical principles for the choice of red, green, and blue
 The choice of primary colors is related to the physiology of the
The choice of primary colors is related to the physiology of the human eye
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm.
...
; good primaries are stimuli that maximize the difference between the responses of the cone cells of the human retina to light of different wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tr ...
s, and that thereby make a large color triangle.
The normal three kinds of light-sensitive photoreceptor cells in the human eye (cone cells) respond most to yellow (long wavelength or L), green (medium or M), and violet (short or S) light (peak wavelengths near 570 nm, 540 nm and 440 nm, respectively). The difference in the signals received from the three kinds allows the brain to differentiate a wide gamut
In color reproduction, including computer graphics and photography, the gamut, or color gamut , is a certain ''complete subset'' of colors. The most common usage refers to the subset of colors which can be accurately represented in a given circ ...
of different colors, while being most sensitive (overall) to yellowish-green light and to differences between hues in the green-to-orange region.
As an example, suppose that light in the orange range of wavelengths (approximately 577 nm to 597 nm) enters the eye and strikes the retina. Light of these wavelengths would activate both the medium and long wavelength cones of the retina, but not equally—the long-wavelength cells will respond more. The difference in the response can be detected by the brain, and this difference is the basis of our perception of orange. Thus, the orange appearance of an object results from light from the object entering our eye and stimulating the different cones simultaneously but to different degrees.
Use of the three primary colors is not sufficient to reproduce ''all'' colors; only colors within the color triangle defined by the chromaticities of the primaries can be reproduced by additive mixing of non-negative amounts of those colors of light.
History of RGB color model theory and usage
The RGB color model is based on the Young–Helmholtz theory of trichromatic color vision, developed by Thomas Young andHermann von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Associat ...
in the early to mid-nineteenth century, and on James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish mathematician and scientist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and ligh ...
's color triangle that elaborated that theory (circa 1860).
Photography
The first experiments with RGB in early color photography were made in 1861 by Maxwell himself, and involved the process of combining three color-filtered separate takes. To reproduce the color photograph, three matching projections over a screen in a dark room were necessary. The additive RGB model and variants such as orange–green–violet were also used in theAutochrome Lumière
The Autochrome Lumière was an early color photography process patented in 1903 by the Lumière brothers in France and first marketed in 1907. Autochrome was an additive color "mosaic screen plate" process. It was the principal color photogr ...
color plates and other screen-plate technologies such as the Joly color screen and the Paget process
The Paget process was an early colour photography process patented in Britain in 1912 by G.S. Whitfield and first marketed by the Paget Prize Plate Company in 1913. A paper-based Paget process was also briefly sold. Both were discontinued in the ...
in the early twentieth century. Color photography by taking three separate plates was used by other pioneers, such as the Russian Sergey Prokudin-Gorsky
Sergey Mikhaylovich Prokudin-Gorsky ( rus, Сергей Михайлович Прокудин-Горский, p=sʲɪrˈɡʲej mʲɪxəjɫəvʲɪtɕ prəkudʲin ˈɡorskʲɪj, a=ru-Prokudin-Gorskii.ogg; – September 27, 1944) was a Ru ...
in the period 1909 through 1915.Photographer to the Tsar: Sergei Mikhailovich Prokudin-GorskiiLibrary of Congress. Such methods lasted until about 1960 using the expensive and extremely complex tri-color carbro
Autotype
Autotype is a function in some computer applications or programs, typically those containing forms, which fills in a field once you have typed in the first few letters. Most of the time, such as in a web browser, the entries that appear in the li ...
process.
When employed, the reproduction of prints from three-plate photos was done by dyes or pigments using the complementary CMY model, by simply using the negative plates of the filtered takes: reverse red gives the cyan plate, and so on.
Television
Before the development of practical electronic TV, there were patents on mechanically scanned color systems as early as 1889 inRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
. The color TV
Color television or Colour television is a television transmission technology that includes color information for the picture, so the video image can be displayed in color on the television set. It improves on the monochrome or black-and-white t ...
pioneer John Logie Baird
John Logie Baird FRSE (; 13 August 188814 June 1946) was a Scottish inventor, electrical engineer, and innovator who demonstrated the world's first live working television system on 26 January 1926. He went on to invent the first publicly dem ...
demonstrated the world's first RGB color transmission in 1928, and also the world's first color broadcast in 1938, in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
. In his experiments, scanning and display were done mechanically by spinning colorized wheels.
The Columbia Broadcasting System (CBS) began an experimental RGB field-sequential color system in 1940. Images were scanned electrically, but the system still used a moving part: the transparent RGB color wheel rotating at above 1,200 rpm in synchronism with the vertical scan. The camera and the cathode-ray tube (CRT) were both monochromatic. Color was provided by color wheels in the camera and the receiver.
More recently, color wheels have been used in field-sequential projection TV receivers based on the Texas Instruments monochrome DLP imager.
The modern RGB shadow mask technology for color CRT displays was patented by Werner Flechsig in Germany in 1938.
Personal computers
Personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or te ...
s of the late 1970s and early 1980s, such as the Apple II
The Apple II (stylized as ) is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Jerry Manock developed the design of Apple II's foam-m ...
and VIC-20, used composite video. The Commodore 64 and the Atari 8-bit family used S-Video
S-Video (also known as separate video, Y/C, and erroneously Super-Video ) is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video, typically at 525 lines or 625 lines. It encodes video luma and chrominance on two separate chann ...
derivatives. IBM introduced a 16-color scheme (four bits—one bit each for red, green, blue, and intensity) with the Color Graphics Adapter (CGA) for its IBM PC in 1981, later improved with the Enhanced Graphics Adapter (EGA) in 1984. The first manufacturer of a truecolor graphics card for PCs (the TARGA) was Truevision in 1987, but it was not until the arrival of the Video Graphics Array (VGA) in 1987 that RGB became popular, mainly due to the analog signals in the connection between the adapter and the monitor
Monitor or monitor may refer to:
Places
* Monitor, Alberta
* Monitor, Indiana, town in the United States
* Monitor, Kentucky
* Monitor, Oregon, unincorporated community in the United States
* Monitor, Washington
* Monitor, Logan County, West ...
which allowed a very wide range of RGB colors. Actually, it had to wait a few more years because the original VGA cards were palette-driven just like EGA, although with more freedom than VGA, but because the VGA connectors were analog, later variants of VGA (made by various manufacturers under the informal name Super VGA) eventually added true-color. In 1992, magazines heavily advertised true-color Super VGA hardware.
RGB devices
RGB and displays
 One common application of the RGB color model is the display of colors on a cathode-ray tube (CRT),
One common application of the RGB color model is the display of colors on a cathode-ray tube (CRT), liquid-crystal display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but ...
(LCD), plasma display
A plasma display panel (PDP) is a type of flat panel display that uses small cells containing plasma: ionized gas that responds to electric fields. Plasma televisions were the first large (over 32 inches diagonal) flat panel displays to be rele ...
, or organic light emitting diode (OLED) display such as a television, a computer's monitor, or a large scale screen. Each pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device.
In most digital display devices, pixels are the ...
on the screen is built by driving three small and very close but still separated RGB light sources. At common viewing distance, the separate sources are indistinguishable, which tricks the eye to see a given solid color. All the pixels together arranged in the rectangular screen surface conforms the color image.
During digital image processing each pixel can be represented in the computer memory
In computing, memory is a device or system that is used to store information for immediate use in a computer or related computer hardware and digital electronic devices. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the term '' primary storag ...
or interface hardware (for example, a '' graphics card'') as binary values for the red, green, and blue color components. When properly managed, these values are converted into intensities or voltages via gamma correction
Gamma correction or gamma is a nonlinear operation used to encode and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following power-law expression:
: V_\tex ...
to correct the inherent nonlinearity of some devices, such that the intended intensities are reproduced on the display.
The Quattron released by Sharp uses RGB color and adds yellow as a sub-pixel, supposedly allowing an increase in the number of available colors.
Video electronics
RGB is also the term referring to a type ofcomponent video
Component video is an analog video signal that has been split into two or more component channels. In popular use, it refers to a type of component analog video (CAV) information that is transmitted or stored as three separate signals. Compo ...
signal used in the video
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) sy ...
electronics industry. It consists of three signals—red, green, and blue—carried on three separate cables/pins. RGB signal formats are often based on modified versions of the RS-170 and RS-343 standards for monochrome video. This type of video signal is widely used in Europe since it is the best quality signal that can be carried on the standard SCART
SCART (also known as or , especially in France, 21-pin EuroSCART in marketing by Sharp in Asia, Euroconector in Spain, EuroAV or EXT, or EIA Multiport in the United States, as an EIA interface) is a French-originated standard and associated 21- ...
connector. This signal is known as RGBS (4 BNC/ RCA terminated cables exist as well), but it is directly compatible with RGBHV used for computer monitors (usually carried on 15-pin cables terminated with 15-pin D-sub or 5 BNC connectors), which carries separate horizontal and vertical sync signals.
Outside Europe, RGB is not very popular as a video signal format; S-Video takes that spot in most non-European regions. However, almost all computer monitors around the world use RGB.
Video framebuffer
A framebuffer is a digital device for computers which stores data in the so-called ''video memory'' (comprising an array ofVideo RAM
Dual-ported video RAM, or VRAM, is a dual-ported variant of dynamic RAM (DRAM), which was once commonly used to store the framebuffer in graphics adapters. Note that most computers and game consoles do not use this form of memory, and dual-port ...
or similar chips). This data goes either to three digital-to-analog converters (DACs) (for analog monitors), one per primary color or directly to digital monitors. Driven by software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
At the lowest programming level, executable code consist ...
, the CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, a ...
(or other specialized chips) write the appropriate byte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable uni ...
s into the video memory to define the image. Modern systems encode pixel color values by devoting eight bits to each of the R, G, and B components. RGB information can be either carried directly by the pixel bits themselves or provided by a separate color look-up table (CLUT) if indexed color graphic modes are used.
A CLUT is a specialized RAM that stores R, G, and B values that define specific colors. Each color has its own address (index)—consider it as a descriptive reference number that provides that specific color when the image needs it. The content of the CLUT is much like a palette of colors. Image data that uses indexed color specifies addresses within the CLUT to provide the required R, G, and B values for each specific pixel, one pixel at a time. Of course, before displaying, the CLUT has to be loaded with R, G, and B values that define the palette of colors required for each image to be rendered. Some video applications store such palettes in PAL files ( ''Age of Empires'' game, for example, uses over half-a-dozen) and can combine CLUTs on screen.
;RGB24 and RGB32
This indirect scheme restricts the number of available colors in an image CLUT—typically 256-cubed (8 bits in three color channel
Color digital images are made of pixels, and pixels are made of combinations of primary colors represented by a series of code. A channel in this context is the grayscale image of the same size as a color image, made of just one of these primary ...
s with values of 0–255)—although each color in the RGB24 CLUT table has only 8 bits representing 256 codes for each of the R, G, and B primaries, making 16,777,216 possible colors. However, the advantage is that an indexed-color image file can be significantly smaller than it would be with only 8 bits per pixel for each primary.
Modern storage, however, is far less costly, greatly reducing the need to minimize image file size. By using an appropriate combination of red, green, and blue intensities, many colors can be displayed. Current typical display adapters use up to 24-bits of information for each pixel: 8-bit per component multiplied by three components (see the Numeric representations section below (24bits = 2563, each primary value of 8 bits with values of 0–255). With this system, 16,777,216 (2563 or 224) discrete combinations of R, G, and B values are allowed, providing millions of different (though not necessarily distinguishable) hue, saturation and lightness shades. Increased shading has been implemented in various ways, some formats such as .png and .tga
Truevision TGA, often referred to as TARGA, is a raster graphics file format created by Truevision Inc. (now part of Avid Technology). It was the native format of TARGA and VISTA boards, which were the first graphic cards for IBM-compatibl ...
files among others using a fourth greyscale
In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a grayscale image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample representing only an ''amount'' of light; that is, it carries only intensity information. Gr ...
color channel as a masking layer, often called RGB32.
For images with a modest range of brightnesses from the darkest to the lightest, eight bits per primary color provides good-quality images, but extreme images require more bits per primary color as well as the advanced display technology. For more information see High Dynamic Range
High dynamic range (HDR) is a dynamic range higher than usual, synonyms are wide dynamic range, extended dynamic range, expanded dynamic range.
The term is often used in discussing the dynamic range of various signals such as images, videos, au ...
(HDR) imaging.
Nonlinearity
In classic CRT devices, the brightness of a given point over thefluorescent
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, ...
screen due to the impact of accelerated electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
s is not proportional to the voltages applied to the electron gun control grids, but to an expansive function of that voltage. The amount of this deviation is known as its gamma
Gamma (uppercase , lowercase ; ''gámma'') is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 3. In Ancient Greek, the letter gamma represented a voiced velar stop . In Modern Greek, this letter r ...
value (), the argument for a power law function, which closely describes this behavior. A linear response is given by a gamma value of 1.0, but actual CRT nonlinearities have a gamma value around 2.0 to 2.5.
Similarly, the intensity of the output on TV and computer display devices is not directly proportional to the R, G, and B applied electric signals (or file data values which drive them through digital-to-analog converters). On a typical standard 2.2-gamma CRT display, an input intensity RGB value of (0.5, 0.5, 0.5) only outputs about 22% of full brightness (1.0, 1.0, 1.0), instead of 50%. To obtain the correct response, a gamma correction
Gamma correction or gamma is a nonlinear operation used to encode and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following power-law expression:
: V_\tex ...
is used in encoding the image data, and possibly further corrections as part of the color calibration process of the device. Gamma affects black-and-white
Black-and-white (B&W or B/W) images combine black and white in a continuous spectrum, producing a range of shades of grey.
Media
The history of various visual media began with black and white, and as technology improved, altered to color. ...
TV as well as color. In standard color TV, broadcast signals are gamma corrected.
RGB and cameras
Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professional ...
), simplifying and even removing the intermediate optics, thereby reducing the size of home video cameras and eventually leading to the development of full camcorder
A camcorder is a self-contained portable electronic device with video and recording as its primary function. It is typically equipped with an articulating screen mounted on the left side, a belt to facilitate holding on the right side, hot-sw ...
s. Current webcam
A webcam is a video camera which is designed to record or stream to a computer or computer network. They are primarily used in videotelephony, livestreaming and social media, and security. Webcams can be built-in computer hardware or peripher ...
s and mobile phone
A mobile phone, cellular phone, cell phone, cellphone, handphone, hand phone or pocket phone, sometimes shortened to simply mobile, cell, or just phone, is a portable telephone that can make and receive calls over a radio frequency link whi ...
s with cameras are the most miniaturized commercial forms of such technology.
Photographic digital cameras that use a CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSF ...
or CCD image sensor often operate with some variation of the RGB model. In a Bayer filter arrangement, green is given twice as many detectors as red and blue (ratio 1:2:1) in order to achieve higher luminance resolution than chrominance
Chrominance (''chroma'' or ''C'' for short) is the signal used in video systems to convey the color information of the picture (see YUV color model), separately from the accompanying luma signal (or Y' for short). Chrominance is usually represen ...
resolution. The sensor has a grid of red, green, and blue detectors arranged so that the first row is RGRGRGRG, the next is GBGBGBGB, and that sequence is repeated in subsequent rows. For every channel, missing pixels are obtained by interpolation in the demosaicing process to build up the complete image. Also, other processes used to be applied in order to map the camera RGB measurements into a standard RGB color space as sRGB.
RGB and scanners
In computing, animage scanner
An image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting or an object and converts it to a digital image. Commonly used in offices are variations of the desktop ''flatbed scanner'' ...
is a device that optically scans images (printed text, handwriting, or an object) and converts it to a digital image which is transferred to a computer. Among other formats, flat, drum and film scanners exist, and most of them support RGB color. They can be considered the successors of early telephotography
Wirephoto, telephotography or radiophoto is the sending of pictures by telegraph, telephone or radio.
Édouard Belin's Bélinographe of 1913, which scanned using a photocell and transmitted over ordinary phone lines, formed the basis for the W ...
input devices, which were able to send consecutive scan lines as analog amplitude modulation signals through standard telephonic lines to appropriate receivers; such systems were in use in press since the 1920s to the mid-1990s. Color telephotographs were sent as three separated RGB filtered images consecutively.
Currently available scanners typically use CCD or contact image sensor
Contact image sensors (CIS) are image sensors used in flatbed scanners almost in direct contact with the object to be scanned. Charge-coupled devices (CCDs), the other kind of sensor often used in scanners, use mirrors to bounce light to a stati ...
(CIS) as the image sensor, whereas older drum scanners use a photomultiplier tube as the image sensor. Early color film scanners used a halogen lamp and a three-color filter wheel, so three exposures were needed to scan a single color image. Due to heating problems, the worst of them being the potential destruction of the scanned film, this technology was later replaced by non-heating light sources such as color LEDs.
Numeric representations
 A color in the RGB color model is described by indicating how much of each of the red, green, and blue is included. The color is expressed as an RGB triplet (''r'',''g'',''b''), each component of which can vary from zero to a defined maximum value. If all the components are at zero the result is black; if all are at maximum, the result is the brightest representable white.
These ranges may be quantified in several different ways:
* From 0 to 1, with any fractional value in between. This representation is used in theoretical analyses, and in systems that use
A color in the RGB color model is described by indicating how much of each of the red, green, and blue is included. The color is expressed as an RGB triplet (''r'',''g'',''b''), each component of which can vary from zero to a defined maximum value. If all the components are at zero the result is black; if all are at maximum, the result is the brightest representable white.
These ranges may be quantified in several different ways:
* From 0 to 1, with any fractional value in between. This representation is used in theoretical analyses, and in systems that use floating point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can ...
representations.
* Each color component value can also be written as a percentage, from 0% to 100%.
* In computers, the component values are often stored as unsigned integer numbers in the range 0 to 255, the range that a single 8-bit byte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable uni ...
can offer. These are often represented as either decimal or hexadecimal numbers.
* High-end digital image equipment are often able to deal with larger integer ranges for each primary color, such as 0..1023 (10 bits), 0..65535 (16 bits) or even larger, by extending the 24-bits (three 8-bit values) to 32-bit, 48-bit, or 64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit CPUs and ALUs are those that are based on processor registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. A ...
units (more or less independent from the particular computer's word size).
For example, brightest saturated red is written in the different RGB notations as:
::
In many environments, the component values within the ranges are not managed as linear (that is, the numbers are nonlinearly related to the intensities that they represent), as in digital cameras and TV broadcasting and receiving due to gamma correction, for example. Linear and nonlinear transformations are often dealt with via digital image processing. Representations with only 8 bits per component are considered sufficient if gamma correction
Gamma correction or gamma is a nonlinear operation used to encode and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following power-law expression:
: V_\tex ...
is used.
Following is the mathematical relationship between RGB space to HSI space (hue, saturation, and intensity: HSI color space):
If , then .
Color depth
The RGB color model is one of the most common ways to encode color in computing, and several different digital representations are in use. The main characteristic of all of them is the quantization of the possible values per component (technically a ''sample
Sample or samples may refer to:
Base meaning
* Sample (statistics), a subset of a population – complete data set
* Sample (signal), a digital discrete sample of a continuous analog signal
* Sample (material), a specimen or small quantity of ...
'' ) by using only integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign ( −1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the languag ...
numbers within some range, usually from 0 to some power of two minus one (2''n'' − 1) to fit them into some bit groupings. Encodings of 1, 2, 4, 5, 8 and 16 bits per color are commonly found; the total number of bits used for an RGB color is typically called the color depth.
Geometric representation
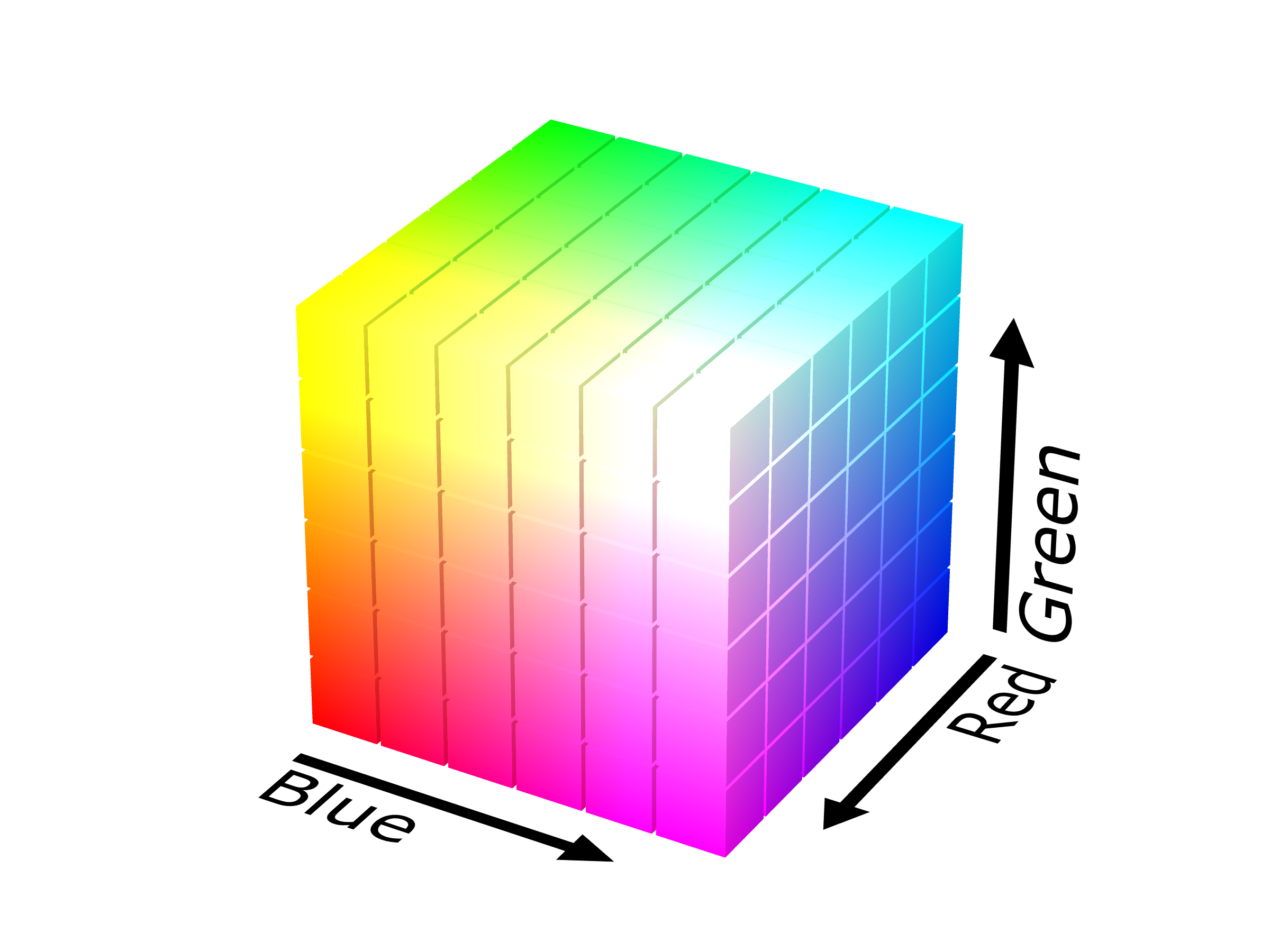
 Since colors are usually defined by three components, not only in the RGB model, but also in other color models such as
Since colors are usually defined by three components, not only in the RGB model, but also in other color models such as CIELAB
The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'' , is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination (abbreviated CIE) in 1976. (Referring to CIELAB as "Lab" without asterisks should be avoided to prevent confusio ...
and Y'UV
YUV is a color model typically used as part of a color image pipeline. It encodes a color image or video taking human perception into account, allowing reduced bandwidth for chrominance components, compared to a "direct" RGB-representation. Hi ...
, among others, then a three-dimensional
Three-dimensional space (also: 3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a geometric setting in which three values (called '' parameters'') are required to determine the position of an element (i.e., point). This is the inform ...
volume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). ...
is described by treating the component values as ordinary Cartesian coordinates in a Euclidean space
Euclidean space is the fundamental space of geometry, intended to represent physical space. Originally, that is, in Euclid's ''Elements'', it was the three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, but in modern mathematics there are Euclidea ...
. For the RGB model, this is represented by a cube using non-negative values within a 0–1 range, assigning black to the origin at the vertex (0, 0, 0), and with increasing intensity values running along the three axes up to white at the vertex (1, 1, 1), diagonally opposite black.
An RGB triplet (''r'',''g'',''b'') represents the three-dimensional coordinate of the point of the given color within the cube or its faces or along its edges. This approach allows computations of the color similarity of two given RGB colors by simply calculating the distance
Distance is a numerical or occasionally qualitative measurement of how far apart objects or points are. In physics or everyday usage, distance may refer to a physical length or an estimation based on other criteria (e.g. "two counties over"). ...
between them: the shorter the distance, the higher the similarity. Out-of-gamut computations can also be performed this way.
Colors in web-page design
Initially, the limited color depth of most video hardware led to a limited color palette of 216 RGB colors, defined by the Netscape Color Cube. The web-safe color palette consists of the 216 (63) combinations of red, green, and blue where each color can take one of six values (in hexadecimal): #00, #33, #66, #99, #CC or #FF (based on the 0 to 255 range for each value discussed above). These hexadecimal values = 0, 51, 102, 153, 204, 255 in decimal, which = 0%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 100% in terms of intensity. This seems fine for splitting up 216 colors into a cube of dimension 6. However, lacking gamma correction, the perceived intensity on a standard 2.5 gamma CRT / LCD is only: 0%, 2%, 10%, 28%, 57%, 100%. See the actual web safe color palette for a visual confirmation that the majority of the colors produced are very dark. With the predominance of 24-bit displays, the use of the full 16.7 million colors of the HTML RGB color code no longer poses problems for most viewers. ThesRGB
sRGB is a standard RGB (red, green, blue) color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission ...
color model (a ''device-independent'' color space) for HTML
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaS ...
was formally adopted as an Internet standard in HTML 3.2, though it had been in use for some time before that. All images and colors are interpreted as being sRGB (unless another color space is specified) and all modern displays can display this color space (with color management being built in into browsers or operating systems).
The syntax in CSS
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language such as HTML or XML (including XML dialects such as SVG, MathML or XHTML). CSS is a cornerstone technolo ...
is:
rgb(#,#,#)
where # equals the proportion of red, green, and blue respectively. This syntax can be used after such selectors as "background-color:" or (for text) "color:".
Wide gamut color is possible in modern CSS, but only the Safari browser supports it.
For example, a color on the DCI-P3 color space can be indicated as :
color(display-p3 # # #)
where # equals the proportion of red, green, and blue in 0.0 to 1.0 respectively
Color management
Proper reproduction of colors, especially in professional environments, requires color management of all the devices involved in the production process, many of them using RGB. Color management results in several transparent conversions between device-independent (sRGB
sRGB is a standard RGB (red, green, blue) color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web. It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission ...
, XYZ, L*a*b*
The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'' , is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination (abbreviated CIE) in 1976. (Referring to CIELAB as "Lab" without asterisks should be avoided to prevent confusio ...
) and device-dependent color space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital represen ...
s (RGB and others, as CMYK for color printing) during a typical production cycle, in order to ensure color consistency throughout the process. Along with the creative processing, such interventions on digital images can damage the color accuracy and image detail, especially where the gamut is reduced. Professional digital devices and software tools allow for 48 bpp ( bits per pixel) images to be manipulated (16 bits per channel), to minimize any such damage.
ICC profile compliant applications, such as Adobe Photoshop, use either the Lab color space
The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'' , is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination (abbreviated CIE) in 1976. (Referring to CIELAB as "Lab" without asterisks should be avoided to prevent confusio ...
or the CIE 1931 color space as a ''Profile Connection Space'' when translating between color spaces.
RGB model and luminance–chrominance formats relationship
All luminance–chrominance formats used in the different TV and video standards such asYIQ
YIQ is the color space used by the analog NTSC color TV system, employed mainly in North and Central America, and Japan.
''I'' stands for ''in-phase'', while ''Q'' stands for ''quadrature'', referring to the components used in quadrature amplitud ...
for NTSC
The first American standard for analog television broadcast was developed by National Television System Committee (NTSC)National Television System Committee (1951–1953), Report and Reports of Panel No. 11, 11-A, 12–19, with Some supplement ...
, YUV for PAL, YDBDR for SECAM
SECAM, also written SÉCAM (, ''Séquentiel de couleur à mémoire'', French for ''color sequential with memory''), is an analog color television system that was used in France, some parts of Europe and Africa, and Russia. It was one of th ...
, and YPBPR for component video use color difference signals, by which RGB color images can be encoded for broadcasting/recording and later decoded into RGB again to display them. These intermediate formats were needed for compatibility with pre-existent black-and-white TV formats. Also, those color difference signals need lower data bandwidth compared to full RGB signals.
Similarly, current high-efficiency digital color image data compression schemes such as JPEG
JPEG ( ) is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by digital photography. The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and imag ...
and MPEG store RGB color internally in YCBCR format, a digital luminance–chrominance format based on YPBPR. The use of YCBCR also allows computers to perform lossy
In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data compression methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data si ...
subsampling with the chrominance channels (typically to 4:2:2 or 4:1:1 ratios), which reduces the resultant file size.
See also
*CMY color model
The CMYK color model (also known as process color, or four color) is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation ''CMYK'' refers ...
* CMYK color model
* Color theory
* Colour banding
* Complementary colors
* DCI-P3 – a common RGB color space
* List of color palettes
* ProPhoto RGB color space
* RG color models
An RG color model is a dichromatic color model represented by red and green primary colors. The name of the pair of models comes from the initials of the two primary colors: red and green. The model may be either additive or subtractive. The prima ...
* RGBA color model
* scRGB
scRGB is a wide color gamut RGB color space created by Microsoft and HP that uses the same color primaries and white/black points as the sRGB color space but allows coordinates below zero and greater than one. The full range is −0.5 through j ...
* TSL color space TSL color space (Tint, Saturation and Lightness ) is a perceptual color space which defines color as tint (the degree to which a stimulus can be described as similar to or different from another stimuli that are described as red, green, blue, yellow ...
References
External links
RGB mixer
{{DEFAULTSORT:RGB Color Model 1861 introductions Color space