RD-180 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
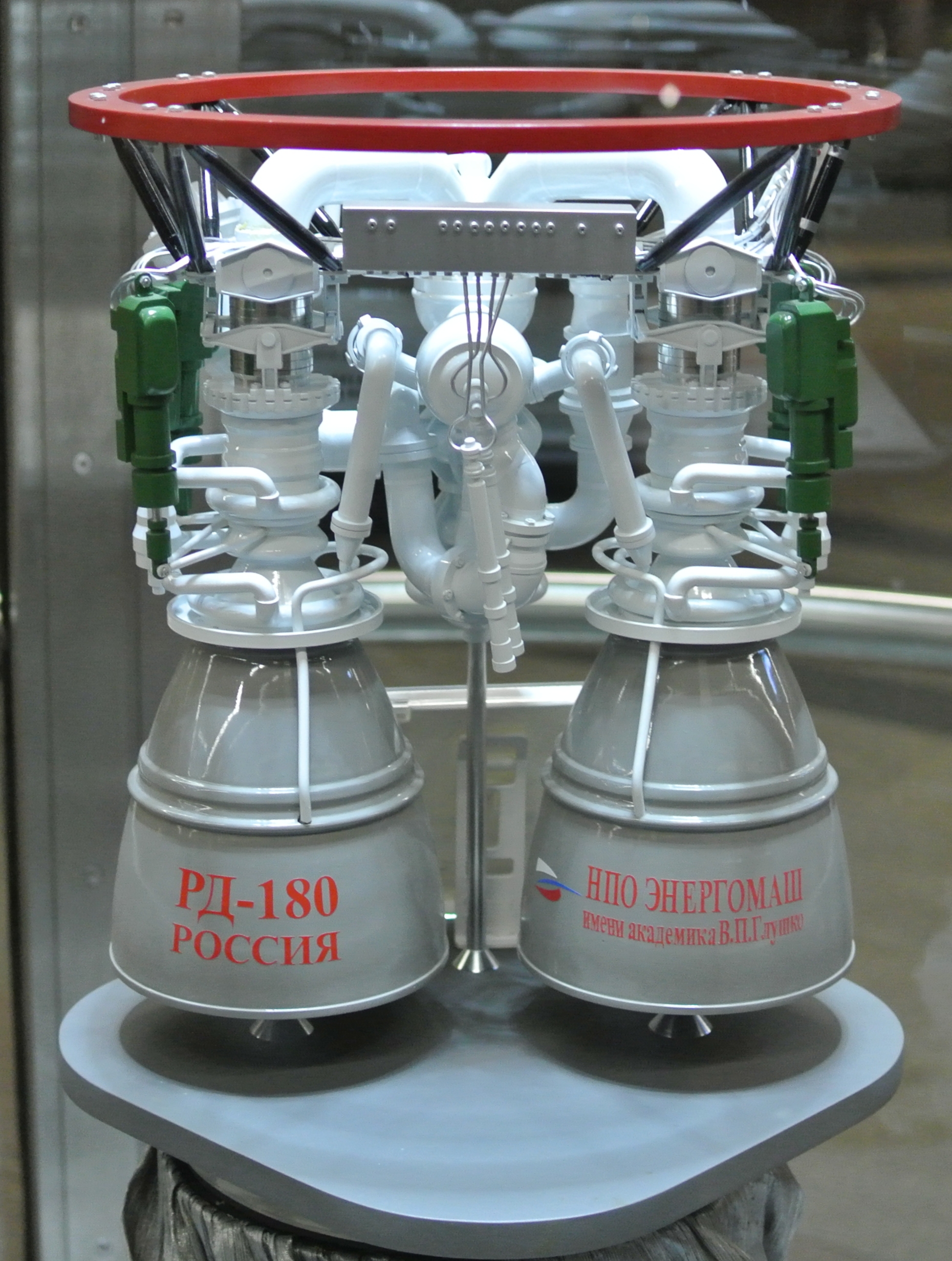 The RD-180 ( rus, РД-180, Ракетный Двигатель-180, Raketnyy Dvigatel-180) is a
The RD-180 ( rus, РД-180, Ракетный Двигатель-180, Raketnyy Dvigatel-180) is a
. In January 2015, Orbital Sciences Corporation have received all the necessary permissions from government bodies for the delivery of 60 engines from NPO Energomash. On 24 December 2015, United Launch Alliance announced that it placed an order for more RD-180 engines to be used by the Atlas V launch vehicle, in addition to 29 engines that the company had ordered before US sanctions against Russia were introduced over Crimea, and just days after the US Congress lifted the ban on the use of Russian engines to get American ships into space.
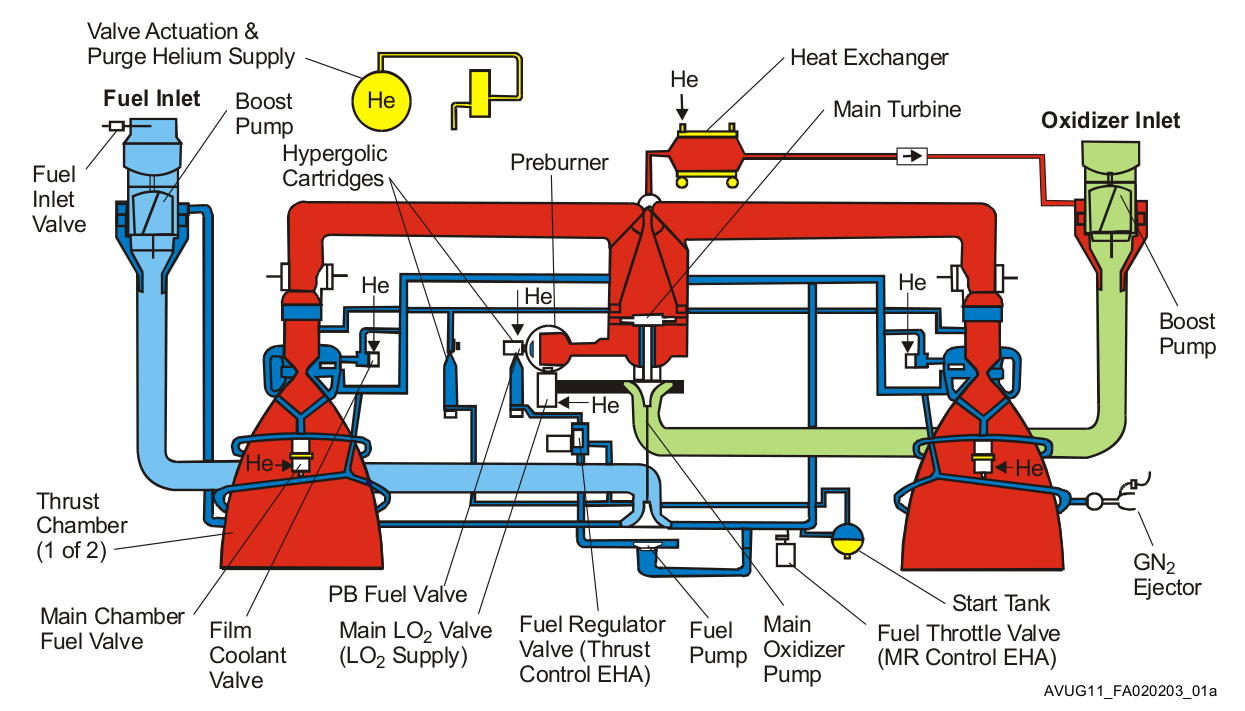 The combustion chambers of the RD-180 share a single turbopump unit, much like in its predecessor, the four-chambered
The combustion chambers of the RD-180 share a single turbopump unit, much like in its predecessor, the four-chambered
Astronautix.com page on RD-180
The Engines That Came In From The Cold!
''Equinox'', Channel Four Television Corporation, 2000. Documentary video on Russian rocket engine development of the NK-33 and its predecessors for the N1 rocket, the development of the staged combustion cycle, and the eventual 1990s resurgence that led to the RD-180 engine sold to the US launch provider Lockheed Martin for the Atlas III. (NK-33 story starts at 24:15–26:00 (program was shuttered in 1974); the 1990s resurgence and eventual sale of the remaining engines from storage starts at 27:25; first use as RD-180 on a US rocket launch in May 2000.) {{DEFAULTSORT:Rd-180 Rocket engines of Russia Rocket engines using kerosene propellant Rocket engines using the staged combustion cycle Energomash rocket engines
 The RD-180 ( rus, РД-180, Ракетный Двигатель-180, Raketnyy Dvigatel-180) is a
The RD-180 ( rus, РД-180, Ракетный Двигатель-180, Raketnyy Dvigatel-180) is a rocket engine
A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellants as the reaction mass for forming a high-speed propulsive jet of fluid, usually high-temperature gas. Rocket engines are reaction engines, producing thrust by ejecting mass rearward, in accorda ...
designed and built in Russia. It features a dual combustion chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process.
Intern ...
, dual- nozzle design and is fueled by a RP-1/ LOX mixture. The RD-180 is derived from the RD-170/RD-171 line of rocket engines, which were used in the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
Energia launch vehicle and are still in use in the Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
Zenit launch vehicles.
RD-180 engines are also used for the first stage of the American Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas launch vehicle family. It was originally designed by Lockheed Martin, now being operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Lockheed Mart ...
launch vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload ( spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pads, supported by a launch control center and sys ...
, which is being phased out due to the national security implications of being reliant on foreign parts which became of concern after the Russian invasion of Crimea. , Russian supplies and maintenance have been discontinued as the result of trade sanctions caused by the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. A ...
.
History
The roots of the RD-180 rocket engine extend back into the Soviet Energia launch vehicle project. The RD-170, a four-chamber engine, was developed for use on the strap-on boosters for this vehicle, which ultimately was used to lift the Buran orbiter. This engine was scaled down to a two-chamber version by combining the RD-170's combustion devices with half-size turbomachinery. After successful performances in engine tests on a test stand and high-level agreements between the US government and the Russian government, the engines were imported to the US for use on the Lockheed Martin Atlas III, with first flight in 2000. The engine is also used on theUnited Launch Alliance
United Launch Alliance (ULA), legally United Launch Alliance, LLC, is an American spacecraft launch service provider that manufactures and operates a number of rocket vehicles that are capable of launching spacecraft into orbits around Earth, a ...
Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas launch vehicle family. It was originally designed by Lockheed Martin, now being operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Lockheed Mart ...
, the successor to the Atlas III.
The engine has similar design features to the NK-33, which was developed by a different bureau ( Kuznetzov) nearly a decade prior.
2014–2015 availability concerns
Doubts about the reliability of the supply chain for the RD-180 arose following theRussian military intervention in Ukraine
The Russo-Ukrainian War; uk, російсько-українська війна, rosiisko-ukrainska viina. has been ongoing between Russia (alongside Russian separatists in Ukraine) and Ukraine since February 2014. Following Ukraine's Rev ...
in March 2014. For over 13 years since the engine was first used in the Atlas III launch vehicle in 2000, there was never any serious jeopardy to the engine supply, despite an uneven record of US–Russian relations since the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
. But worsening relations between the West and Russia after March 2014 have led to several self inflicted blockages, including a short-lived judicial injunction from the US courts that were unclear on the scope of the US sanctions on importing the Russian engine.
On 13 May 2014, Russian Deputy Prime Minister Dmitry Rogozin announced that "Russia will ban the United States from using Russian-made rocket engines for military launches"—a frequent payload of the ULA Atlas V
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas launch vehicle family. It was originally designed by Lockheed Martin, now being operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Lockheed Mart ...
launch vehicle, which powers its first stage with a single RD-180 engine that is expended after each flight. In response, the US Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Sig ...
has asked the Aerospace Corporation to begin evaluating alternatives for powering the Atlas 5 booster stage with non-RD-180 engines. Early estimates in 2014 were that it would require five or more years to replace the RD-180 on the Atlas V.
Even though the Russian government could cut off the supply to ULA of imported RD-180 engines, the US Congress, with emerging support from the Air Force
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an ...
, has come around to a view that it would not be advantageous to the US government to start up a US production line to produce the RD-180, mainly because it would need a licence from the Russian government. However, the US Congress is advocating for the initiation of a new US hydrocarbon rocket engine program, to field a new engine by 2022.
In June 2014, Aerojet Rocketdyne proposed that the US Federal government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a f ...
"fund an all-new, U.S.-sourced rocket propulsion system", the thrust kerosene/ LOX AR-1 rocket engine. , Aerojet's early projection was that the cost of each engine would be under per pair of engines—not including the up to estimated development cost to be funded by the US Government. Aerojet believed that the AR-1 could replace the RD-180 in the US Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle
National Security Space Launch (NSSL) — formerly Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) from 1994 to 2019 — is a program of the United States Space Force (USSF) intended to assure access to space for United States Department of Defense and o ...
fleet, and that it would be more affordable.
On 21 August 2014, the U.S. Air Force released an official request for information (RFI) for a replacement for the RD-180. The RFI seeks information on "booster propulsion and/or launch system material options that could deliver cost-effective, commercially-viable solutions for current and future National Security Space (NSS) launch requirements. Air Force Space Command (AFSPC) is considering an acquisition strategy to stimulate the commercial development of booster propulsion systems and/or launch systems for Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle
National Security Space Launch (NSSL) — formerly Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) from 1994 to 2019 — is a program of the United States Space Force (USSF) intended to assure access to space for United States Department of Defense and o ...
(EELV)-class spacelift applications." The day before, the United Launch Alliance
United Launch Alliance (ULA), legally United Launch Alliance, LLC, is an American spacecraft launch service provider that manufactures and operates a number of rocket vehicles that are capable of launching spacecraft into orbits around Earth, a ...
had taken delivery of two RD-180s, the first since the Russian annexation of Crimea. It is not clear when or if the replacement of the RD-180 would start, and the RFI asked input for several options including similarity to the Russian engine, whether it would come in a new configuration and the use of "alternative launch vehicles" for the EELV mission.
In 2014, RD-Amross were selling the RD-180s (to ULA) for $23.4m each.Reuters ''In Pentagon deal with Russians, big profit for tiny Florida firm'' nov 2014. In January 2015, Orbital Sciences Corporation have received all the necessary permissions from government bodies for the delivery of 60 engines from NPO Energomash. On 24 December 2015, United Launch Alliance announced that it placed an order for more RD-180 engines to be used by the Atlas V launch vehicle, in addition to 29 engines that the company had ordered before US sanctions against Russia were introduced over Crimea, and just days after the US Congress lifted the ban on the use of Russian engines to get American ships into space.
US production of the RD-180
United Launch Alliance (ULA) announced in February 2015 that it was considering undertaking US production of the Russian RD-180 engine at the Decatur, Alabama, rocket stage manufacturing facility. The US-manufactured engines would be used only for government civil (NASA) and commercial launches, and would not be used for US military launches. This potential project is a backup plan to the new engine development work that ULA is undertaking withBlue Origin
Blue Origin, LLC is an American private spaceflight, privately funded aerospace manufacturer and sub-orbital spaceflight services company headquartered in Kent, Washington. Founded in 2000 by Jeff Bezos, the founder and executive chairman of Am ...
on the BE-4
The Blue Engine 4 or BE-4 is an oxygen-rich liquefied-methane-fueled staged-combustion rocket engine under development by Blue Origin. The BE-4 is being developed with private and public funding. The engine has been designed to produce of thr ...
.
Under RD AMROSS, Pratt & Whitney is licensed to produce the RD-180 in the United States. Originally, production of the RD-180 in the US was scheduled to begin in 2008, but this did not happen. According to a 2005 GAO Assessment of Selected Major Weapon Programs, Pratt & Whitney planned to start building the engine in the United States with a first military launch by 2012. This, too, did not happen. In 2014, the Defense Department estimated that it would require approximately $1 billion and five years to begin US domestic manufacture of the RD-180 engine.
Overall, by April 14, 2021 Energomash
The Energomash Corporation (Cyrillic: "Энергомаш") was a Russian power engineering company. Energomash manufactures small cogeneration plants as well as a wide variety of components for the energy industry
The energy industry is the to ...
has delivered 122 RD-180 rocket engines to the United States over more than 20 years of cooperation.
In an interview on August 26, 2021 ULA's CEO Tory Bruno said that three or four RD-180s are installed on Atlas V rockets for upcoming missions, and the rest are sitting in a warehouse. “We took early delivery, if you will, with the RD-180, so I can end that relationship and not be dependent upon ussiabecause that’s what Congress asked us to do”, he said. In all, the US has taken delivery of 122 RD-180 engines from Energomash
The Energomash Corporation (Cyrillic: "Энергомаш") was a Russian power engineering company. Energomash manufactures small cogeneration plants as well as a wide variety of components for the energy industry
The energy industry is the to ...
, generating billions in revenue for Russia’s space program.
Replacement for the RD-180 engine on US Atlas launch vehicle
As a result of the geopolitical and USpolitical
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studi ...
considerations as 2014 progressed, United Launch Alliance initiated an effort to consider the possible replacement of the Russian-supplied RD-180 engine used on the first-stage booster of the ULA Atlas V. Formal study contracts were issued in June 2014 to a number of US rocket-engine suppliers.
In September 2014, ULA announced that it has entered into a partnership with Blue Origin
Blue Origin, LLC is an American private spaceflight, privately funded aerospace manufacturer and sub-orbital spaceflight services company headquartered in Kent, Washington. Founded in 2000 by Jeff Bezos, the founder and executive chairman of Am ...
to develop the BE-4
The Blue Engine 4 or BE-4 is an oxygen-rich liquefied-methane-fueled staged-combustion rocket engine under development by Blue Origin. The BE-4 is being developed with private and public funding. The engine has been designed to produce of thr ...
LOX/methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
engine to replace the RD-180 on a new first-stage booster that would succeed the Atlas V. At the time, the engine was already in its third year of development by Blue Origin, and ULA expected the new stage and engine to start flying no earlier than 2019. Two of the -thrust BE-4 engines will be used on the new launch vehicle booster.
Dynetics and Aerojet Rocketdyne (AJR) have also offered their AR1 hydrocarbon-fueled rocket engine as replacement of the RD-180. ULA CEO Tory Bruno has said in early 2015 that both the AR-1 option and the US manufacture of the RD-180 by ULA under license are backup options to the primary option ULA is pursuing with the Blue Origin BE-4 engine.
By March 2016, the US Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Sig ...
had signed development contracts with AJR and Blue Origin to provide funding toward engine development for both engines.
, the first Vulcan flight with new engines is expected to fly in 2022.
As of May 25, 2020 (20 years since the first launch of the Atlas LV with RD-180), 116 engines have been delivered to the USA, 90 launches have taken place, all of them are recognized as successful.
Design and specifications
 The combustion chambers of the RD-180 share a single turbopump unit, much like in its predecessor, the four-chambered
The combustion chambers of the RD-180 share a single turbopump unit, much like in its predecessor, the four-chambered RD-170
The RD-170 ( rus, РД-170, Ракетный Двигатель-170, Raketnyy Dvigatel-170) is the world's most powerful and heaviest liquid-fuel rocket engine. It was designed and produced in the Soviet Union by NPO Energomash for use with the ...
. The RD-180 is fueled by an RP-1/ LOX mixture and uses an extremely efficient, high-pressure staged combustion cycle. The engine runs with an oxidizer-to-fuel ratio of 2.72 and employs an oxygen-rich preburner, unlike typical fuel-rich US designs. The thermodynamics of the cycle allow an oxygen-rich preburner to give a greater power-to-weight ratio, but with the drawback that high-pressure, high-temperature gaseous oxygen must be transported throughout the engine. The movements of the engine nozzles are controlled by four hydraulic actuators. The engine can be throttled from 47% to 100% of nominal thrust.
Applications
During the early 1990s, General Dynamics Space Systems Division (later purchased by Lockheed Martin) acquired the rights to use the RD-180 in theEvolved Expendable Launch Vehicle
National Security Space Launch (NSSL) — formerly Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) from 1994 to 2019 — is a program of the United States Space Force (USSF) intended to assure access to space for United States Department of Defense and o ...
(EELV) and the Atlas program. As these programs were conceived to support United States Government launches, as well as commercial launches, it was also arranged for the RD-180 to be co-produced by Pratt & Whitney. However, all production to date has taken place in Russia. The engine is currently sold by a joint venture between the Russian developer and producer of the engine NPO Energomash
NPO Energomash “V. P. Glushko” is a major Russian rocket engine manufacturer. The company primarily develops and produces liquid propellant rocket engines. Energomash originates from the Soviet design bureau OKB-456, which was founded in 1 ...
and Pratt & Whitney, called RD Amross.
The RD-180 was first deployed on the Atlas IIA-R vehicle, which was the Atlas IIA
Atlas II was a member of the Atlas family of launch vehicles, which evolved from the successful Atlas missile program of the 1950s. The Atlas II was a direct evolution of the Atlas I, featuring longer first stage tanks, higher-performing engine ...
vehicle with the Russian (hence the R) engine replacing the previous main engine. This vehicle was later renamed the Atlas III. An additional development program was undertaken to certify the engine for use on the modular Common Core Booster
The Common Core Booster (CCB) is an American rocket stage, which is used as the first stage of the Atlas V rocket as part of its modular design. It was also intended that two additional CCBs would be used as boosters on the Atlas V Heavy, however ...
primary stage of the Atlas V rocket.
Prospective uses
RD-180 was proposed to be used with a new family of Rus-M Russian space launch vehicles, proposed by Roskosmos contractors, but the program was canceled by the Russian Space Agency in October 2011. In March 2010, Jerry Grey, a consultant to theAmerican Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics
The American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) is a professional society for the field of aerospace engineering. The AIAA is the U.S. representative on the International Astronautical Federation and the International Council of ...
and Universities Space Research Association and a former professor of aerospace engineering at Princeton University
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the ...
, suggested using the RD-180 for a prospective NASA heavy-lift launch vehicle. For those who might be concerned about too much reliance on Russia, he pointed out that RD Amross was "very close to producing a U.S.-built version of the RD-180, and with some infusion of NASA funding could be manufacturing that engine (and perhaps even a thrust equivalent of the RD-170) in a few years".
Prospective alternative
In February 2010, despite the availability of necessary documentation and legal rights for producing RD-180 in the United States,NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
was considering development of an indigenous core-stage engine that would be "capable of generating high levels of thrust approximately equal to or exceeding the performance of the Russian-built engine". NASA desired to produce a fully operational engine by 2020 or sooner, depending on partnership with the U.S. Defense Department. In 2021, NASA stopped buying new engines due to the planned retirement of Atlas V rocket.
2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On February 24, 2022, Russia began a large-scale military invasion of Ukraine. Six days later on March 2, 2022, as Russia continued the invasion, they formally announced an end of all sales and support of the RD-180 engines to the United States, in retaliation for sanctions placed on Russia by the US for the Ukraine attack.See also
* Comparison of orbital rocket engines * Staged combustion cycle used in engine * RD-191 derivative engine being developed for theAngara rocket
The Angara rocket family (Russian: Ангара) is a family of launch vehicles being developed by the Moscow-based Khrunichev State Research and Production Space Center. The launch vehicles are to put between and into low Earth orbit and are ...
* RD-0124 used in the Soyuz-2.1b
* RD-107 used in the R-7 Semyorka missiles and Soyuz FG
* RD-58 upper stage RP-1/ LOX engine used in the N-1 rocket, derivatives used in the Proton and Zenit rockets
References
External links
Astronautix.com page on RD-180
The Engines That Came In From The Cold!
''Equinox'', Channel Four Television Corporation, 2000. Documentary video on Russian rocket engine development of the NK-33 and its predecessors for the N1 rocket, the development of the staged combustion cycle, and the eventual 1990s resurgence that led to the RD-180 engine sold to the US launch provider Lockheed Martin for the Atlas III. (NK-33 story starts at 24:15–26:00 (program was shuttered in 1974); the 1990s resurgence and eventual sale of the remaining engines from storage starts at 27:25; first use as RD-180 on a US rocket launch in May 2000.) {{DEFAULTSORT:Rd-180 Rocket engines of Russia Rocket engines using kerosene propellant Rocket engines using the staged combustion cycle Energomash rocket engines