R-loop on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An R-loop is a three-stranded nucleic acid structure, composed of a DNA: RNA hybrid and the associated non-template single-stranded DNA. R-loops may be formed in a variety of circumstances, and may be tolerated or cleared by cellular components. The term "R-loop" was given to reflect the similarity of these structures to D-loops; the "R" in this case represents the involvement of an RNA
An R-loop is a three-stranded nucleic acid structure, composed of a DNA: RNA hybrid and the associated non-template single-stranded DNA. R-loops may be formed in a variety of circumstances, and may be tolerated or cleared by cellular components. The term "R-loop" was given to reflect the similarity of these structures to D-loops; the "R" in this case represents the involvement of an RNA
 R-looping was first described in 1976. Independent R-looping studies from the laboratories of
R-looping was first described in 1976. Independent R-looping studies from the laboratories of
 An R-loop is a three-stranded nucleic acid structure, composed of a DNA: RNA hybrid and the associated non-template single-stranded DNA. R-loops may be formed in a variety of circumstances, and may be tolerated or cleared by cellular components. The term "R-loop" was given to reflect the similarity of these structures to D-loops; the "R" in this case represents the involvement of an RNA
An R-loop is a three-stranded nucleic acid structure, composed of a DNA: RNA hybrid and the associated non-template single-stranded DNA. R-loops may be formed in a variety of circumstances, and may be tolerated or cleared by cellular components. The term "R-loop" was given to reflect the similarity of these structures to D-loops; the "R" in this case represents the involvement of an RNA moiety
Moiety may refer to:
Chemistry
* Moiety (chemistry), a part or functional group of a molecule
** Moiety conservation, conservation of a subgroup in a chemical species
Anthropology
* Moiety (kinship), either of two groups into which a society is ...
.
In the laboratory, R-loops may also be created by the hybridization
Hybridization (or hybridisation) may refer to:
*Hybridization (biology), the process of combining different varieties of organisms to create a hybrid
*Orbital hybridization, in chemistry, the mixing of atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals
*Nu ...
of mature mRNA with double-stranded DNA under conditions favoring the formation of a DNA-RNA hybrid; in this case, the intron
An intron is any Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of ...
regions (which have been spliced out of the mRNA) form single-stranded DNA loops, as they cannot hybridize with complementary sequence in the mRNA.
History
 R-looping was first described in 1976. Independent R-looping studies from the laboratories of
R-looping was first described in 1976. Independent R-looping studies from the laboratories of Richard J. Roberts
Sir Richard John Roberts (born 6 September 1943) is a British biochemist and molecular biologist. He was awarded the 1993 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Phillip Allen Sharp for the discovery of introns in eukaryotic DNA and the me ...
and Phillip A. Sharp
Phillip Allen Sharp (born June 6, 1944) is an American geneticist and molecular biologist who co-discovered RNA splicing. He shared the 1993 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Richard J. Roberts for "the discovery that genes in eukaryo ...
showed that protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
coding adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from ...
gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s contained DNA sequences that were not present in the mature mRNA. Roberts and Sharp were awarded the Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
in 1993 for independently discovering introns. After their discovery in adenovirus, introns were found in a number of eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
genes such as the eukaryotic ovalbumin gene (first by the O'Malley laboratory, then confirmed by other groups), hexon DNA, and extrachromosomal rRNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribos ...
genes of ''Tetrahymena thermophila
''Tetrahymena thermophila'' is a species of Ciliophora in the family Tetrahymenidae. It is a free living protozoa and occurs in fresh water.
There is little information on the ecology and natural history of this species, but it is the most wide ...
''.
In the mid-1980s, development of an antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of t ...
that binds specifically to the R-loop structure opened the door for immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to spe ...
studies, as well as genome-wide characterization of R-loop formation by DRIP-seq DRIP-seq (DRIP-sequencing) is a technology for genome-wide profiling of a type of DNA-RNA hybrid called an "R-loop". DRIP-seq utilizes a sequence-independent but structure-specific antibody for DNA-RNA immunoprecipitation (DRIP) to capture R-loops ...
.
R-loop mapping
R-loop mapping is a laboratory technique used to distinguish introns fromexon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequen ...
s in double-stranded DNA. These R-loops are visualized by electron microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a hi ...
and reveal intron regions of DNA by creating unbound loops at these regions.
R-loops ''in vivo''
The potential for R-loops to serve as replication primers was demonstrated in 1980. In 1994, R-loops were demonstrated to be present ''in vivo'' through analysis of plasmids isolated from ''E. coli'' mutants carrying mutations intopoisomerase
DNA topoisomerases (or topoisomerases) are enzymes that catalyze changes in the topological state of DNA, interconverting relaxed and supercoiled forms, linked (catenated) and unlinked species, and knotted and unknotted DNA. Topological issues i ...
. This discovery of endogenous
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell.
In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism.
For example, ...
R-loops, in conjunction with rapid advances in genetic sequencing
In genetics and biochemistry, sequencing means to determine the primary structure (sometimes incorrectly called the primary sequence) of an unbranched biopolymer. Sequencing results in a symbolic linear depiction known as a sequence which suc ...
technologies, inspired a blossoming of R-loop research in the early 2000's that continues to this day.
Regulation of R-loop formation and resolution
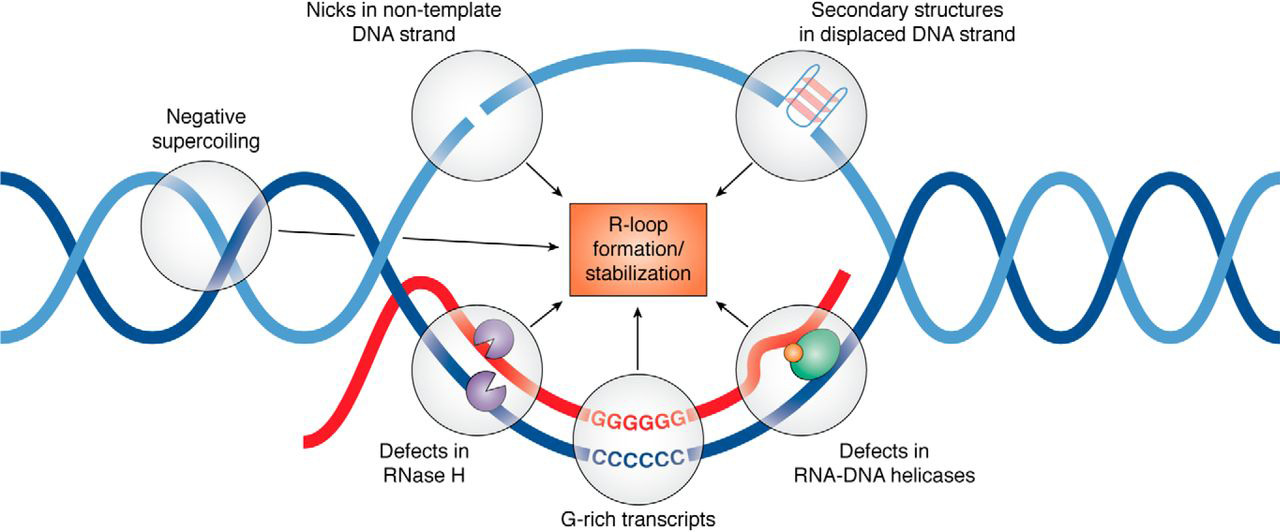
RNaseH enzymes are the primary proteins responsible for the dissolution of R-loops, acting to degrade the RNA moiety in order to allow the two complementary DNA strands to anneal. Research over the past decade has identified more than 50 proteins that appear to influence R-loop accumulation, and while many of them are believed to contribute by sequestering or processing newly transcribed RNA to prevent re-annealing to the template, mechanisms of R-loop interaction for many of these proteins remain to be determined.Roles of R-loops in genetic regulation
R-loop formation is a key step inimmunoglobulin class switching
Immunoglobulin class switching, also known as isotype switching, isotypic commutation or class-switch recombination (CSR), is a biological mechanism that changes a B cell's production of immunoglobulin from one type to another, such as from the ...
, a process that allows activated B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted o ...
s to modulate antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of t ...
production. They also appear to play a role in protecting some active promoters from methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These ...
. The presence of R-loops can also inhibit transcription. Additionally, R-loop formation appears to be associated with “open” chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important ...
, characteristic of actively transcribed regions.
R-loops as genetic damage
When unscheduled R-loops form, they can cause damage by a number of different mechanisms. Exposed single-stranded DNA can come under attack by endogenous mutagens, including DNA-modifying enzymes such as activation-induced cytidine deaminase, and can block replication forks to induce fork collapse and subsequent double-strand breaks. As well, R-loops may induce unscheduled replication by acting as aprimer
Primer may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Primer'' (film), a 2004 feature film written and directed by Shane Carruth
* ''Primer'' (video), a documentary about the funk band Living Colour
Literature
* Primer (textbook), a te ...
.
R-loop accumulation has been associated with a number of diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 4 (ALS4), ataxia oculomotor apraxia type 2 (AOA2), Aicardi–Goutières syndrome
Aicardi–Goutières syndrome (AGS), which is completely distinct from the similarly named Aicardi syndrome, is a rare, usually early onset childhood, inflammatory disorder most typically affecting the brain and the skin (neurodevelopmental disor ...
, Angelman syndrome
Angelman syndrome or Angelman's syndrome (AS) is a genetic disorder that mainly affects the nervous system. Symptoms include a small head and a specific facial appearance, severe intellectual disability, developmental disability, limited to no ...
, Prader–Willi syndrome
Prader–Willi syndrome (PWS) is a genetic disorder caused by a loss of function of specific genes on chromosome 15. In newborns, symptoms include weak muscles, poor feeding, and slow development. Beginning in childhood, those affected become ...
, and cancer.
R-loops, Introns and DNA damage
Intron
An intron is any Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of ...
s are non-coding regions within gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
s that are transcribed along with the coding regions of genes, but are subsequently removed from the primary RNA transcript by splicing. Actively transcribed regions of DNA often form R-loops that are vulnerable to DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
. Introns reduce R-loop formation and DNA damage in highly expressed yeast genes. Genome-wide analysis showed that intron-containing genes display decreased R-loop levels and decreased DNA damage compared to intron-less genes of similar expression in both yeast and humans. Inserting an intron within an R-loop prone gene can also suppress R-loop formation and recombination. Bonnet et al. (2017) speculated that the function of introns in maintaining genetic stability may explain their evolutionary maintenance at certain locations, particularly in highly expressed genes.
See also
*DRIP-seq DRIP-seq (DRIP-sequencing) is a technology for genome-wide profiling of a type of DNA-RNA hybrid called an "R-loop". DRIP-seq utilizes a sequence-independent but structure-specific antibody for DNA-RNA immunoprecipitation (DRIP) to capture R-loops ...
* Ribonuclease H
Ribonuclease H (abbreviated RNase H or RNH) is a family of non-sequence-specific endonuclease enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of RNA in an RNA/ DNA substrate via a hydrolytic mechanism. Members of the RNase H family can be found in nearl ...
* Immunoglobulin class switching
Immunoglobulin class switching, also known as isotype switching, isotypic commutation or class-switch recombination (CSR), is a biological mechanism that changes a B cell's production of immunoglobulin from one type to another, such as from the ...
* DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritan ...
References
{{reflist DNA RNA splicing