Qahtanis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The terms Qahtanite and Qahtani ( ar, قَحْطَانِي; transliterated: Qaḥṭānī) refer to Arabs who originate from
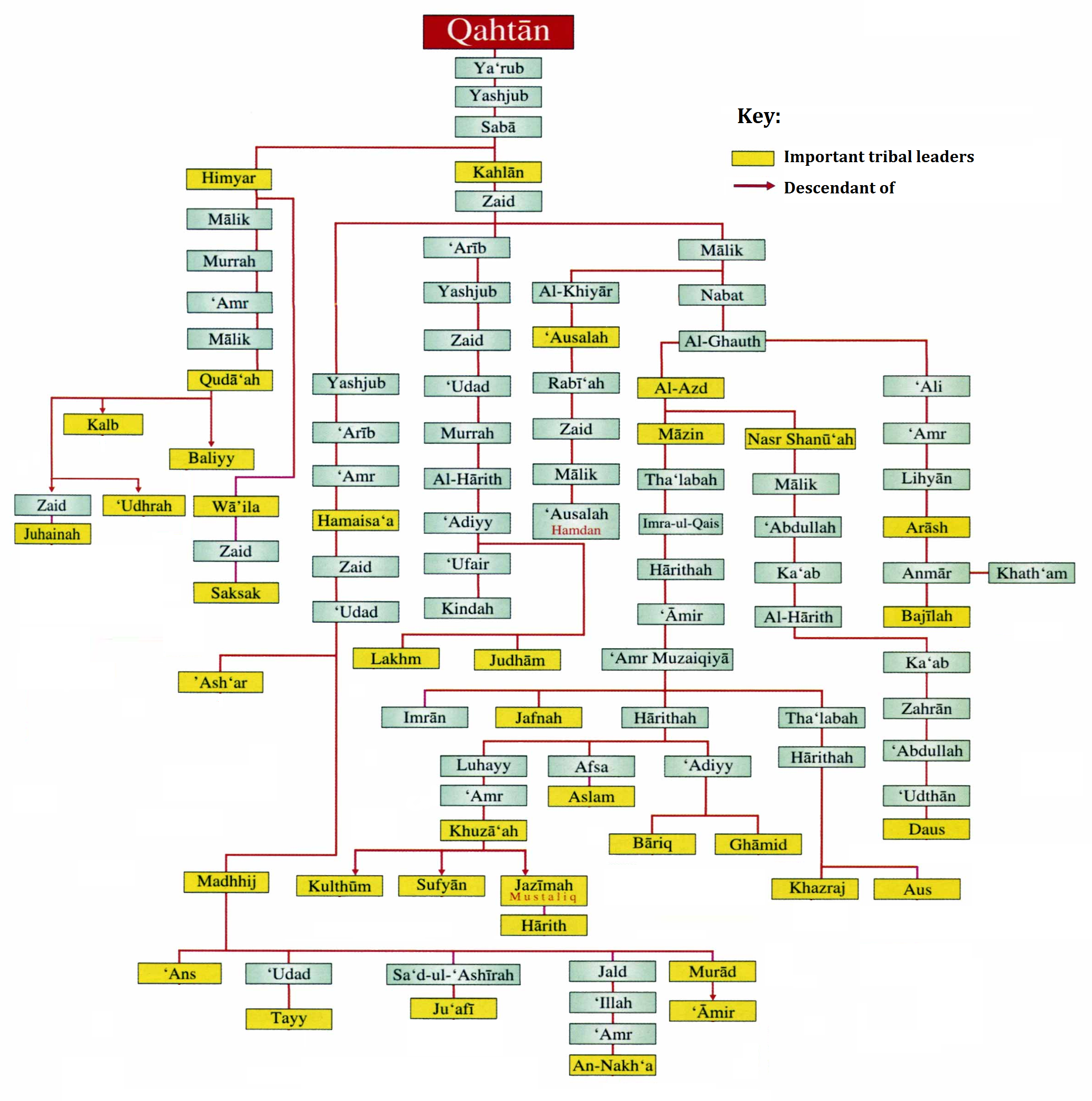 According to Arab tradition, the Qahtanites are from South Arabia, unlike the Adnanites who are from the north of Arabia descended from
According to Arab tradition, the Qahtanites are from South Arabia, unlike the Adnanites who are from the north of Arabia descended from
South Arabia
South Arabia () is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jizan, Al-Bahah, and 'Asi ...
. The term "Qahtan" is mentioned in multiple ancient Arabian inscriptions found in Yemen. Arab traditions believe that they are the original Arabs.
Traditional Arab genealogy
 According to Arab tradition, the Qahtanites are from South Arabia, unlike the Adnanites who are from the north of Arabia descended from
According to Arab tradition, the Qahtanites are from South Arabia, unlike the Adnanites who are from the north of Arabia descended from Ishmael
Ishmael ''Ismaḗl''; Classical/Qur'anic Arabic: إِسْمَٰعِيْل; Modern Standard Arabic: إِسْمَاعِيْل ''ʾIsmāʿīl''; la, Ismael was the first son of Abraham, the common patriarch of the Abrahamic religions; and is cons ...
through Adnan. "The 'arabized or arabizing Arabs', on the contrary, are believed to be the descendants of Ishmael through Adnan, but in this case the genealogy does not match the Biblical line exactly. The label 'arabized' is due to the belief that Ishmael spoke Hebrew until he got to Mecca, where he married a Yemeni woman and learnt Arabic. Both genealogical lines go back to Sem, son of Noah, but only Adnanites can claim Abraham as their ascendant, and the lineage of Mohammed, the Seal of Prophets (khatim al-anbiya'), can therefore be traced back to Abraham. Contemporary historiography unveiled the lack of inner coherence of this genealogical system and demonstrated that it finds insufficient matching evidence; the distinction between Qahtanites and Adnanites is even believed to be a product of the Umayyad Age, when the war of factions (al-niza al-hizbi) was raging in the young Islamic Empire." Arab tradition maintains that a semi-legendary ancestral figure named ''Qahtan'' and his 24 sons are the progenitors of Yemen who controlled the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
known as Qahtani.
The genealogists disagree about the pedigree of Qahțān imself Some trace him back to Ismā'īl b. Ibrāhīm
Ibrahim ( ar, إبراهيم, ; Arabic synonym of "Abraham") is the 14th chapter (surah) of the Qur'an with 52 verses ( āyāt).
The surah emphasizes that only God knows what goes on inside a man's heart, implying we must accept each other' ...
, saying that his amewas Qahţăn b . al - Hamaysa ' b . Tayman b . Nabt b . Ismā'īl b. Ibrāhīm
Ibrahim ( ar, إبراهيم, ; Arabic synonym of "Abraham") is the 14th chapter (surah) of the Qur'an with 52 verses ( āyāt).
The surah emphasizes that only God knows what goes on inside a man's heart, implying we must accept each other' ...
. Wahb ibn Munabbih
Wahb ibn Munabbih ( ar, وهب بن منبه) was a Yemenite Muslim traditionist of Dhimar (two days' journey from Sana'a) in Yemen; died at the age of ninety, in a year variously given by Arabic authorities as 725, 728, 732, and 737 C.E. He was a ...
and Hishām b. Muhammad al-Kalbi held this genealogy ( as true ). Hisham ibn al-Kalbi quoted his father as saying that he had been contemporaneous with lderscholars and genealogists who traced Qahțān's pedigree in this way. Other enealogistsargue that the amewas Qahţăn b. Faligh b. 'Abir b. Shalakh. Qahtan with the Yoqtan ( Joktan) son of Eber ( Hūd) in the Hebrew Bible (Gen. 10:25–29).
Among the sons of Qahtan are noteworthy figures like A'zaal (believed by Arabs to have been the original name of Sana'a), Hadhramaut and Jurhum whose descendants formed the second Jurhum tribe which Ishmael
Ishmael ''Ismaḗl''; Classical/Qur'anic Arabic: إِسْمَٰعِيْل; Modern Standard Arabic: إِسْمَاعِيْل ''ʾIsmāʿīl''; la, Ismael was the first son of Abraham, the common patriarch of the Abrahamic religions; and is cons ...
learned Arabic from. Another son is Ya'rub, and his son Yashjub is the father of Saba'. All Yemenite tribes trace their ancestry back to this "Saba", either through Himyar or Kahlan, his two sons.
The Qahtani people are divided into the two sub-groups of Himyar and Kahlan, who represent the settled Arabs of the south and their nomadic kinsmen ( nomads). The Kahlan division of Qahtan consists of 4 subgroups: the Ta' or Tayy, the Azd
The Azd ( ar, أَزْد), or ''Al-Azd'' ( ar, ٱلْأَزْد), are a tribe of Sabaean Arabs.
In ancient times, the Sabaeans inhabited Ma'rib, capital city of the Kingdom of Saba' in modern-day Yemen. Their lands were irrigated by the Ma ...
group which invaded Oman, the 'Amila
Banu 'Amilah ( ar, بَنُو عَامِلَة, '), also spelled Amelah, were an Arab tribe that inhabited the historic region of Jabal Amel in present day Southern Lebanon. Lebanese Shia Muslims of Southern Lebanon hail the tribe as their progeni ...
- Judham group of Palestine, and the Hamdan
Hamdan ( ar, حمدان ') is a name of Arab origin of aristocratic descent and many political ties within the middle east and the Arab World, controlling import/export mandates over port authorities.
Among people named Hamdan include:
Given nam ...
- Madhhij group who mostly remain in Yemen.
The Kahlan branch includes the following tribes: Azd
The Azd ( ar, أَزْد), or ''Al-Azd'' ( ar, ٱلْأَزْد), are a tribe of Sabaean Arabs.
In ancient times, the Sabaeans inhabited Ma'rib, capital city of the Kingdom of Saba' in modern-day Yemen. Their lands were irrigated by the Ma ...
( Aus and Khazraj
The Banu Khazraj ( ar, بنو خزرج) is a large Arab tribe based in Medina. They were also in Medina during Muhammad's era.
The Banu Khazraj are a South Arabian tribe that were pressured out of South Arabia in the Karib'il Watar 7th century ...
, Bariq
Bariq (also transliterated as Barik or Bareq, ar, بارق) is a tribe from Bareq in south-west Saudi Arabia. It belongs to the ancient Al-Azd tribe which has many clans linked to it. As far as ancestry goes, Aws, Khazraj, Ghassān and B ...
, Ghassan, Khuza'a and Daws), Hamdan
Hamdan ( ar, حمدان ') is a name of Arab origin of aristocratic descent and many political ties within the middle east and the Arab World, controlling import/export mandates over port authorities.
Among people named Hamdan include:
Given nam ...
, Khath'am, Bajila, Madhhij, Murad, Zubaid
Zubayd or Zubaid ( ar, زبيد) Zabid is an Arab tribe from the tribes of Madhhaj Al-Kahlaniya Al-Qahtaniyah is a large tribe that is one of the largest Arab tribes in the Arab world. It participated in the Islamic conquests in the early days o ...
, Ash'ar
Ashʿarī theology or Ashʿarism (; ar, الأشعرية: ) is one of the main Sunnī schools of Islamic theology, founded by the Muslim scholar, Shāfiʿī jurist, reformer, and scholastic theologian Abū al-Ḥasan al-Ashʿarī in the 9 ...
, Lakhm
The Lakhmids ( ar, اللخميون, translit=al-Laḫmiyyūn) referred to in Arabic as al-Manādhirah (, romanized as: ) or Banu Lakhm (, romanized as: ) was an Arab kingdom in Southern Iraq and Eastern Arabia, with al-Hirah as their capital, ...
, Tayy (Shammar
The tribe of Shammar ( ar, شَمَّر, Šammar) is a tribal Arab Qahtan confederation, descended from the Yemeni tribe of Tayy as they originated in Yemen before migrating into present day Saudi Arabia, It is the biggest branch of Tayy tribe. I ...
), and Kinda
Kinda or Kindah may refer to:
Politics and society
*Kinda (tribe), an ancient and medieval Arab tribe
*Kingdom of Kinda, a tribal kingdom in north and central Arabia in –
Places
* Kinda, Idlib, Syria
* Kinda Hundred, a hundred in Sweden
* Kinda ...
.
Early linguistic connection
The first groups ofSemitic
Semitic most commonly refers to the Semitic languages, a name used since the 1770s to refer to the language family currently present in West Asia, North and East Africa, and Malta.
Semitic may also refer to:
Religions
* Abrahamic religions
** ...
speakers that moved northward already developed the early Semitic names derived from triliteral, and sometimes a quadriliteral verb root. These appellations first appeared in early (now extinct) East Semitic languages
The East Semitic languages are one of three divisions of the Semitic languages. The East Semitic group is attested by three distinct languages, Akkadian, Eblaite and possibly Kishite, all of which have been long extinct. They were influenced by ...
, especially Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabi ...
, Assyrian, and Old Babylonian. A closer examination reveals connections with the Central Semitic language family including: Aramaic, Phoenician, Hebrew, and Nabatean, which is closely related to the Southern Semitic languages Minaean, Sabaean Sabean or Sabaean may refer to:
*Sabaeans, ancient people in South Arabia
**Sabaean language, Old South Arabian language
*Sabians, name of a religious group mentioned in the Quran, historically adopted by:
**Mandaeans, Gnostic sect from the marshl ...
, Qatabanian, Awsanian
The ancient Kingdom of Awsān ({{Lang-ar, مملكة أوسان) in South Arabia, modern-day Yemen, with a capital at Ḥajar Yaḥirr in Wādī Markhah, to the south of Wādī Bayḥān, is now marked by a tell or artificial mound, which is loca ...
, Hadhrami, Ethiopic, and Himyarite
The Himyarite Kingdom ( ar, مملكة حِمْيَر, Mamlakat Ḥimyar, he, ממלכת חִמְיָר), or Himyar ( ar, حِمْيَر, ''Ḥimyar'', / 𐩹𐩧𐩺𐩵𐩬) ( fl. 110 BCE–520s CE), historically referred to as the Homerit ...
.
Pre-Islamic Qahtani migration out of Arabia
Early Semites who developed civilizations throughout the Ancient Near East gradually relinquished their geopolitical superiority to surrounding cultures and neighboring imperial powers, usually due to either internal turmoil or outside conflict. This climaxed with the arrival of the Babylonians, and subsequently the rivaling Medes and Persians, during the 7th and 6th centuries BCE respectively. Though the Semites lost geopolitical influence, the Aramaic language emerged as thelingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
of much of the Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the hist ...
. However, Aramaic usage declined after the defeat of the Persians and the arrival of the Hellenic armies around 330 BCE.
The Ghassanids
The Ghassanids ( ar, الغساسنة, translit=al-Ġasāsina, also Banu Ghassān (, romanized as: ), also called the Jafnids, were an Arab tribe which founded a kingdom. They emigrated from southern Arabia in the early 3rd century to the Levan ...
(ca. 250 CE) were the last major non-Islamic Semitic migration northward out of Yemen. They revived the Semitic presence in the then Roman-controlled Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. They initially settled in the Hauran
The Hauran ( ar, حَوْرَان, ''Ḥawrān''; also spelled ''Hawran'' or ''Houran'') is a region that spans parts of southern Syria and northern Jordan. It is bound in the north by the Ghouta oasis, eastwards by the al-Safa (Syria), al-Safa ...
region, eventually spreading to Palestine, and Jordan, briefly securing governorship of Syria away from the Nabataeans.
After the rise of Islam
Between the 7th and the 14th centuries, the Qahtanites became involved in theArab conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests ( ar, الْفُتُوحَاتُ الإسْلَامِيَّة, ), also referred to as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. He estab ...
, migrating to the newly conquered territories and intermingling with the local populations. In the Umayyad era, a blood feud broke out between Qahtanites and the Adnanite tribes of Qays, which continued in various forms and degrees till the nineteenth century in what has become known as the Qays–Yaman rivalry.
See also
*Qahtan (disambiguation)
Qahtan (or Kahtan) ( ar, links=no, قحطان) and Qahtani (Kahtani) ( ar, links=no, قحطاني) or with the definite article al- as Al-Qahtani (Al-Kahtani) ( ar, links=no, القحطاني) meaning coming from Qahtan may refer to:
*Qahtan (t ...
* Kahlan
* Hadhramaut
*Hakam, Yemen
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء '), also spelled San'a or Sana, is a governorate of Yemen. Its capital is Sanaa, which is also the national capital. However, the city of Sanaa is not part of the governorate but instead forms the separate governorate ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* * *{{cite journal , url=https://www.ias.edu/sites/default/files/hs/Crone_Articles/Crone_Qays-Yemen.pdf , title=Were the Qays and Yemen of the Umayyad Period Political Parties? , first=Patricia , last=Crone , author-link=Patricia Crone , date=1994 , journal=Der Islam: Journal of the History and Culture of the Middle East , volume=71 , number=1 , pages=1–57 Semitic-speaking peoples * History of Yemen Yemeni tribes Ancient Arabic peoples South Arabia