Qāf on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Qoph ( Phoenician Qōp  ) is the nineteenth
) is the nineteenth  is derived from the Phoenician letter, and derivations from Aramaic include
is derived from the Phoenician letter, and derivations from Aramaic include
 The origin of the glyph shape of ''qōp'' (
The origin of the glyph shape of ''qōp'' ( ) is uncertain. It is usually suggested to have originally depicted either a
) is uncertain. It is usually suggested to have originally depicted either a
 The Arabic letter is named '. It is written in several ways depending in its position in the word:
Traditionally in the scripts of the Maghreb it is written with a single dot, similarly to how the letter '' fā'' ف is written in Mashreqi scripts:
It is usually transliterated into Latin script as ''q'', though some scholarly works use ''ḳ''.
The Arabic letter is named '. It is written in several ways depending in its position in the word:
Traditionally in the scripts of the Maghreb it is written with a single dot, similarly to how the letter '' fā'' ف is written in Mashreqi scripts:
It is usually transliterated into Latin script as ''q'', though some scholarly works use ''ḳ''.

Are There Scribal Errors In The Qur'ân?
see ' on a traffic sign written which is written elsewhere as , Retrieved 2011-August-27
letter
Letter, letters, or literature may refer to:
Characters typeface
* Letter (alphabet), a character representing one or more of the sounds used in speech; any of the symbols of an alphabet.
* Letterform, the graphic form of a letter of the alphabe ...
of the Semitic scripts
Proto-Sinaitic (also referred to as Sinaitic, Proto-Canaanite when found in Canaan, the North Semitic alphabet, or Early Alphabetic) is considered the earliest trace of alphabetic writing and the common ancestor of both the Ancient South Arabian ...
. Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in ...
Qop Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
Qof , Syriac Syriac may refer to:
*Syriac language, an ancient dialect of Middle Aramaic
*Sureth, one of the modern dialects of Syriac spoken in the Nineveh Plains region
* Syriac alphabet
** Syriac (Unicode block)
** Syriac Supplement
* Neo-Aramaic languages a ...
Qōp̄ ܩ and Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
.
Its original sound value was a West Semitic emphatic stop, presumably . In Hebrew numerals, it has the numerical value of 100.
Origins
 The origin of the glyph shape of ''qōp'' (
The origin of the glyph shape of ''qōp'' (sewing needle
A sewing needle, used for hand-sewing, is a long slender tool with a pointed tip at one end and a hole (or ''eye'') to hold the sewing thread. The earliest needles were made of bone or wood; modern needles are manufactured from high carbon steel ...
, specifically the eye of a needle (Hebrew and Aramaic both refer to the eye of a needle), or the back of a head and neck (''qāf'' in Arabic meant "nape
The nape is the back of the neck. In technical anatomical/medical terminology, the nape is also called the nucha (from the Medieval Latin rendering of the Arabic , "spinal marrow"). The corresponding adjective is ''nuchal'', as in the term ''nu ...
").
According to an older suggestion, it may also have been a picture of a monkey and its tail (the Hebrew means "monkey").
Besides Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in ...
''Qop'', which gave rise to the letter in the Semitic abjads used in classical antiquity,
Phoenician ''qōp'' is also the origin of the Latin letter Q and Greek Ϙ (''qoppa'') and Φ (''phi'').
Hebrew Qof
The ''Oxford Hebrew-English Dictionary'' transliterates the letter Qoph () as ' or '; and, when word-final, it may be transliterated as '. The English spellings of Biblical names (as derived fromLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
via Biblical Greek
Koine Greek (; Koine el, ἡ κοινὴ διάλεκτος, hē koinè diálektos, the common dialect; ), also known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek or New Testament Greek, was the common supra-reg ...
) containing this letter may represent it as ''c'' or ''k'', e.g. ''Cain'' for Hebrew ''Qayin'', or ''Kenan'' for ''Qena'an'' (Genesis 4:1, 5:9).
Pronunciation
In modern Israeli Hebrew the letter is also called '. The letter represents ; i.e., no distinction is made between Qof and Kaph (in modern Hebrew). However, many historical groups have made that distinction, with Qof being pronounced byIraqi Jews
The history of the Jews in Iraq ( he, יְהוּדִים בָּבְלִים, ', ; ar, اليهود العراقيون, ) is documented from the time of the Babylonian captivity c. 586 BC. Iraqi Jews constitute one of the world's oldest and mo ...
and other Mizrahim, or even as by Yemenite Jews
Yemenite Jews or Yemeni Jews or Teimanim (from ''Yehudei Teman''; ar, اليهود اليمنيون) are those Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Is ...
under the influence of Yemeni Arabic
Yemeni Arabic is a cluster of varieties of Arabic spoken in Yemen, southwestern Saudi Arabia and the Horn of Africa. It is generally considered a very conservative dialect cluster, having many classical features not found across most of the Ara ...
.
Qoph is consistently transliterated into classical Greek with the unaspirated〈κ〉/k/, while Kaph (both its allophones) is transliterated with the aspirated〈χ〉/kʰ/. Thus Qoph was unaspirated /k/ where Kaph was /kʰ/, this distinction is no longer present. Further we know that Qoph is one of the emphatic consonants through comparison with other Semitic languages, and most likely was ejective /kʼ/. In Arabic the emphatics are pharyngealised and this causes a preference for back vowels, this is not shown in Hebrew orthography. Though the gutturals show a preference for certain vowels, Hebrew emphatics do not in Tiberian Hebrew (the Hebrew dialect recorded with vowels) and therefore were most likely not pharyngealised, but ejective, pharyngealisation being a result of Arabisation.
Numeral
Qof in Hebrew numerals represents the number 100. Sarah is described inGenesis Rabba
Genesis Rabbah (Hebrew: , ''B'reshith Rabba'') is a religious text from Judaism's classical period, probably written between 300 and 500 CE with some later additions. It is a midrash comprising a collection of ancient rabbinical homiletical inter ...
as , literally "At Qof years of age, she was like Kaph years of age in sin", meaning that when she was 100 years old, she was as sinless as when she was 20.
Arabic Qāf
 The Arabic letter is named '. It is written in several ways depending in its position in the word:
Traditionally in the scripts of the Maghreb it is written with a single dot, similarly to how the letter '' fā'' ف is written in Mashreqi scripts:
It is usually transliterated into Latin script as ''q'', though some scholarly works use ''ḳ''.
The Arabic letter is named '. It is written in several ways depending in its position in the word:
Traditionally in the scripts of the Maghreb it is written with a single dot, similarly to how the letter '' fā'' ف is written in Mashreqi scripts:
It is usually transliterated into Latin script as ''q'', though some scholarly works use ''ḳ''.
Pronunciation
According toSibawayh
Sibawayh ( ar, سِيبَوَيْهِ ' or ; fa, سِیبُویه ' ; c. 760–796), whose full name is Abu Bishr Amr ibn Uthman ibn Qanbar al-Basri (, '), was a Persian leading grammarian of Basra and author of the earliest book on Arabic ...
, author of the first book on Arabic grammar, the letter is pronounced voiced
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds (usually consonants). Speech sounds can be described as either voiceless (otherwise known as ''unvoiced'') or voiced.
The term, however, is used to refer ...
(''maǧhūr''), although some scholars argue, that Sibawayh's term ''maǧhūr'' implies lack of aspiration rather than voice. As noted above, Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA), terms used mostly by linguists, is the variety of standardized, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries; occasionally, it also ref ...
has the voiceless uvular plosive
The voiceless uvular plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. It is pronounced like a voiceless velar plosive , except that the tongue makes contact not on the soft palate but on the uvula. The symbol in th ...
as its standard pronunciation of the letter, but dialectical pronunciations vary as follows:
The three main pronunciations:
*: in most of Tunisia, Algeria and Morocco, Southern and Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
Yemen and parts of Oman, Northern Iraq, parts of the Levant (especially the Alawite and Druze dialects). In fact, it is so characteristic of the Alawites and the Druze that Levantines invented a verb "yqaqi" /jqæqi/ that means "speaking with a /q/". However, most other dialects of Arabic will use this pronunciation in learned words that are borrowed from Standard Arabic into the respective dialect or when Arabs speak Modern Standard Arabic.
*: in most of the Arabian Peninsula, Northern and Eastern
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
Yemen and parts of Oman, Southern Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
, some parts within Jordan, eastern Syria and southern Palestine, Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south.
In ancient E ...
(''Ṣaʿīd''), Sudan, Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
, Mauritania and to lesser extent in some parts of Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, and Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
but it is also used partially across those countries in some words.
*: in most of the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, as well as some North African towns such as Tlemcen
Tlemcen (; ar, تلمسان, translit=Tilimsān) is the second-largest city in northwestern Algeria after Oran, and capital of the Tlemcen Province. The city has developed leather, carpet, and textile industries, which it exports through the p ...
and Fez.
Other pronunciations:
*: In Sudanese and some forms of Yemeni
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
, even in loanwords from Modern Standard Arabic or when speaking Modern Standard Arabic.
*: In rural Palestinian
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
it is often pronounced as a voiceless velar plosive
The voiceless velar plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound used in almost all spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is k.
The sound is a ver ...
, even in loanwords from Modern Standard Arabic or when speaking Modern Standard Arabic.
Marginal pronunciations:
*: In some positions in Najdi Najdi may refer to:
*People of Najd
* Najdi (surname)
* Najdi Arabic, a variety of the Arabic language,
* Najdi (sheep), a breed of sheep
*Najdi!
Najdi! ( mk, Најди!, meaning "Find!") is a search engine specialized in Republic of Macedonia ...
, though this pronunciation is fading in favor of .
*: Optionally in Iraqi and in Gulf Arabic
Gulf Arabic ( ' local pronunciation: or ', local pronunciation: ) is a variety of the Arabic language spoken in Eastern Arabia around the coasts of the Persian Gulf in Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, southern Iraq, eastern Sa ...
, it is sometimes pronounced as a voiced postalveolar affricate
The voiced palato-alveolar sibilant affricate, voiced post-alveolar affricate or voiced domed postalveolar sibilant affricate, is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The sound is transcribed in the International Phonetic ...
, even in loanwords from Modern Standard Arabic or when speaking Modern Standard Arabic.
* ~ : in Sudanese and some Yemeni dialects ( Yafi'i), and sometimes in Gulf Arabic
Gulf Arabic ( ' local pronunciation: or ', local pronunciation: ) is a variety of the Arabic language spoken in Eastern Arabia around the coasts of the Persian Gulf in Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, southern Iraq, eastern Sa ...
by Persian influence, even in loanwords from Modern Standard Arabic or when speaking Modern Standard Arabic.
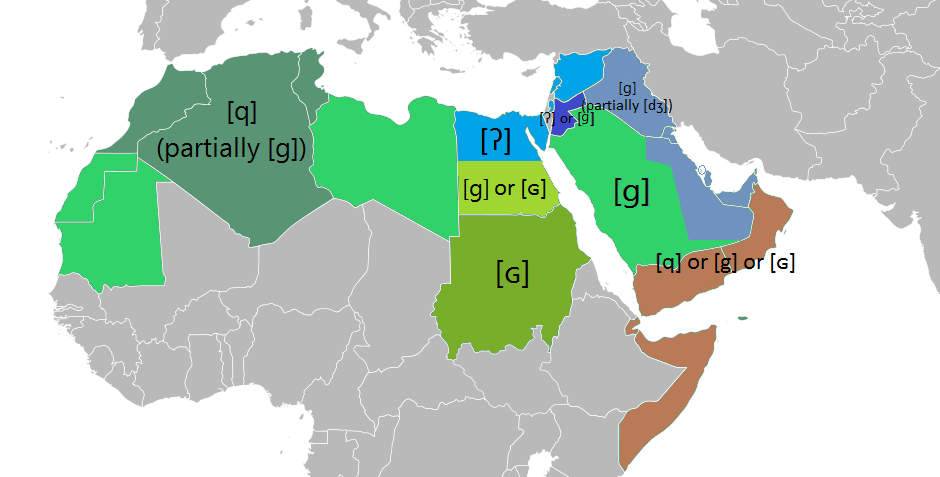
Velar Gāf
It is not well known when the pronunciation of Qāf as a velar occurred or the probability of it being connected to the pronunciation of Jīm as an affricate , but the Arabian peninsula which is the homeland of the Arabic language, there are two sets of pronunciations, either the represents a and represents a which is the main pronunciation in most of the peninsula except for western and southernYemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
and parts of Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is situated on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, and spans the mouth of ...
where represents a and represents a .
The Standard Arabic (MSA) combination of as a and as a does not occur in any natural modern dialect in the Arabian peninsula, which shows a strong correlation between the palatalization of to and the pronunciation of the as a as shown in the table below:

Maghrebi variant
The Maghrebi style of writing ' is different: having only a single point (dot) above; when the letter is isolated or word-final, it may sometimes become unpointed. The earliest Arabic manuscripts show ' in several variants: pointed (above or below) or unpointed. Then the prevalent convention was having a point above for ' and a point below for '; this practice is now only preserved in manuscripts from the Maghribi, with the exception of Libya and Algeria, where theMashriq
The Mashriq ( ar, ٱلْمَشْرِق), sometimes spelled Mashreq or Mashrek, is a term used by Arabs to refer to the eastern part of the Arab world, located in Western Asia and eastern North Africa. Poetically the "Place of Sunrise", th ...
i form (two dots above: ) prevails.
Within Maghribi texts, there is no possibility of confusing it with the letter ', as it is instead written with a dot underneath () in the Maghribi script.Muhammad Ghoniem, M S M Saifullah, cAbd ar-Rahmân Robert Squires & cAbdus SamadAre There Scribal Errors In The Qur'ân?
see ' on a traffic sign written which is written elsewhere as , Retrieved 2011-August-27
Unicode
References
External links
{{Northwest Semitic abjad Arabic letters Hebrew letters Phoenician alphabet