Pulse sequence on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
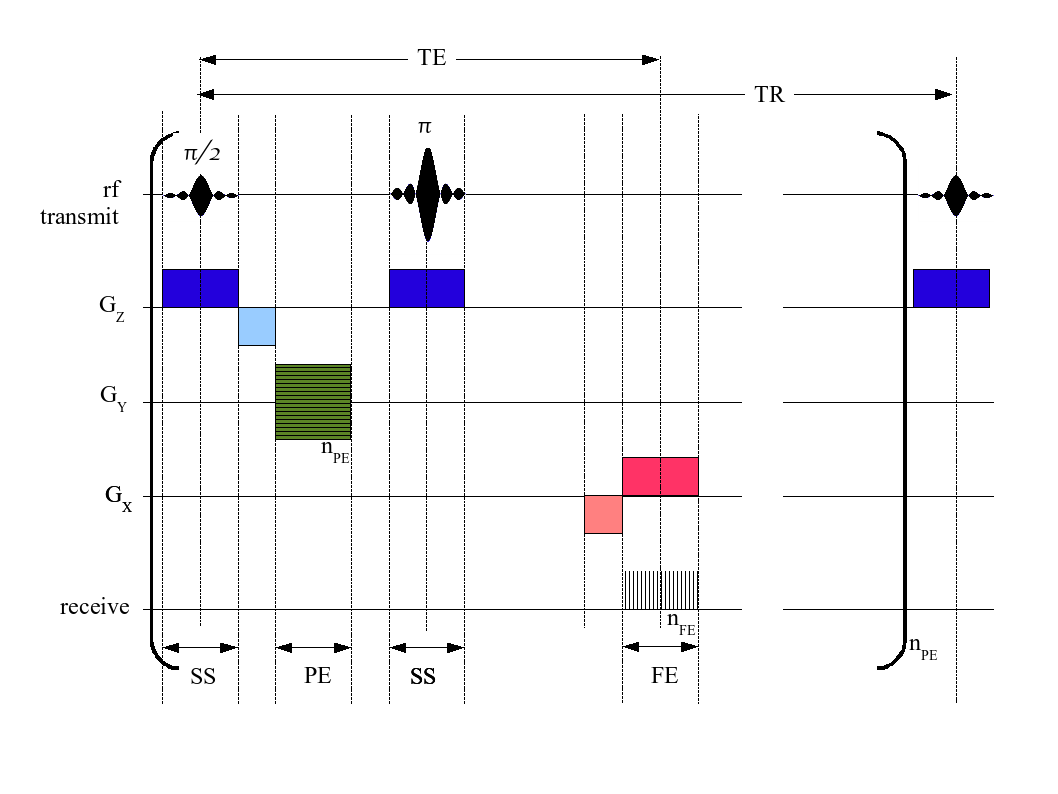

 In Fourier transform NMR spectroscopy and imaging, a pulse sequence describes a series of
In Fourier transform NMR spectroscopy and imaging, a pulse sequence describes a series of
Pulse sequences
in the online textbook
The Basics of NMR
(by Joseph Hornak) Nuclear magnetic resonance


 In Fourier transform NMR spectroscopy and imaging, a pulse sequence describes a series of
In Fourier transform NMR spectroscopy and imaging, a pulse sequence describes a series of radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the up ...
pulses applied to the sample, such that the free induction decay is related to the characteristic frequencies of the desired signals. After applying a Fourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed ...
, the signal can be represented in the frequency domain as the NMR spectrum
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei. The sample is placed in a magnetic fiel ...
. In magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
, additional '' gradient pulses'' are applied by switching magnetic fields that exhibit a space-dependent gradient which can be used to reconstruct spatially resolved images after applying Fourier transforms.
The outcome of pulse sequences is often analyzed using the product operator formalism
In NMR spectroscopy, the product operator formalism is a method used to determine the outcome of pulse sequences in a rigorous but straightforward way. With this method it is possible to predict how the bulk magnetization evolves with time under th ...
.
See also
* Spin echo *Insensitive nuclei enhanced by polarization transfer Insensitive nuclei enhancement by polarization transfer (INEPT) is a signal enhancement method used in NMR spectroscopy. It involves the transfer of nuclear spin polarization from spins with large Boltzmann population differences to nuclear spins ...
* MRI sequenceReferences
{{reflistExternal links
Pulse sequences
in the online textbook
The Basics of NMR
(by Joseph Hornak) Nuclear magnetic resonance