Pułtusk on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pułtusk (pronounced ) is a town in northeast
 The town has existed since at least the 10th century. In the
The town has existed since at least the 10th century. In the
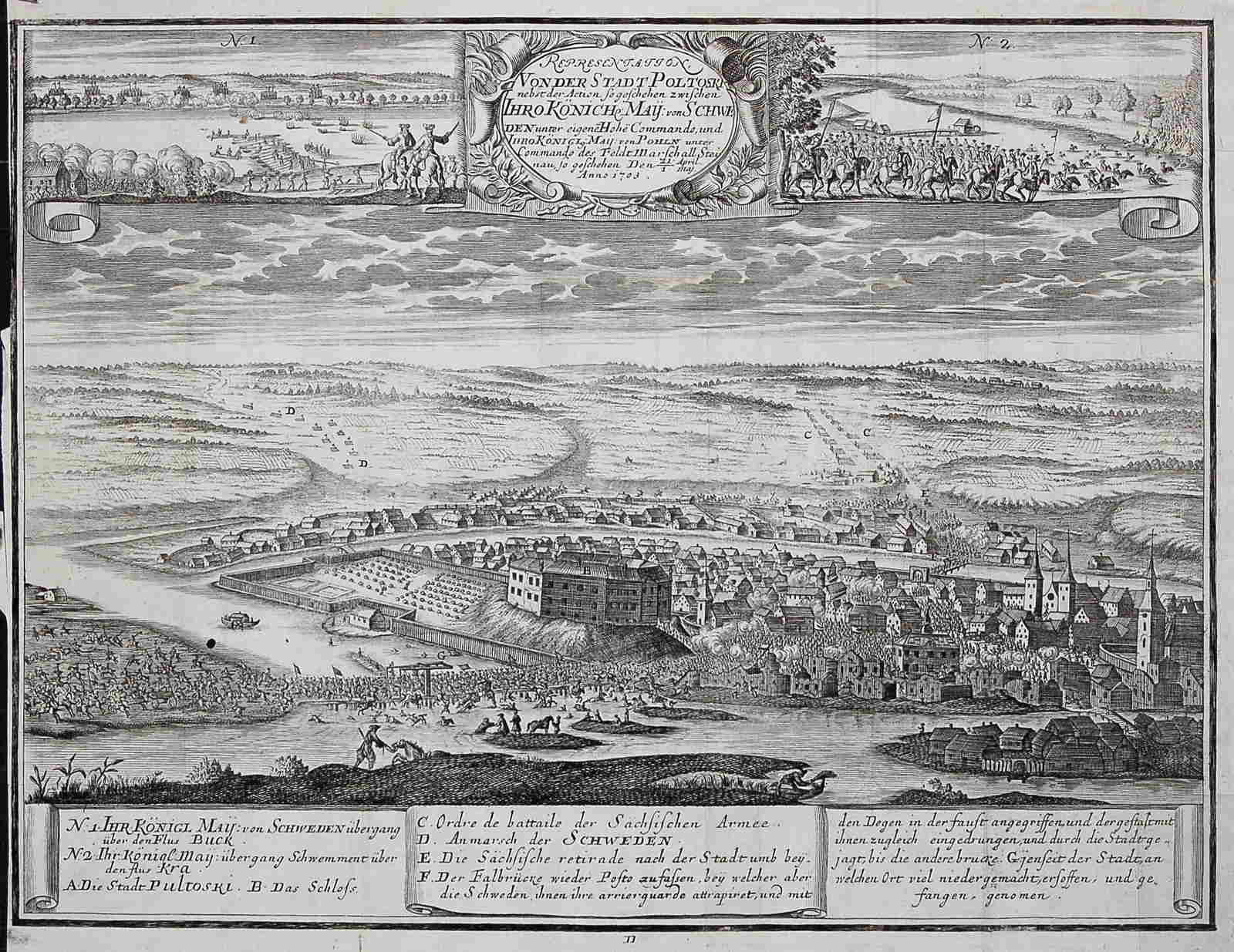 On 21 April 1703 during the
On 21 April 1703 during the
 Another
Another
 The town was reintegrated with Poland, when the country regained independence following World War I in 1918. During the Polish-Soviet War, it was fiercely defended by Poles on August 9-10, 1920, at the eve of the Battle of Warsaw. On August 13, the Russians captured the town, and then they massacred captured Polish soldiers. On August 17, the Polish 9th Infantry Division recaptured the town. In the interbellum the Polish 13th Infantry Regiment was stationed in Pułtusk. In 1931 the town had some 16,800 inhabitants.
As a result of the German
The town was reintegrated with Poland, when the country regained independence following World War I in 1918. During the Polish-Soviet War, it was fiercely defended by Poles on August 9-10, 1920, at the eve of the Battle of Warsaw. On August 13, the Russians captured the town, and then they massacred captured Polish soldiers. On August 17, the Polish 9th Infantry Division recaptured the town. In the interbellum the Polish 13th Infantry Regiment was stationed in Pułtusk. In 1931 the town had some 16,800 inhabitants.
As a result of the German
Pułtusk Academy of Humanities (Akademia Humanistyczna im. Aleksandra Gieysztora in Pułtusk) * Town Hall * Polonia Castle (now operated as a hotel named ''Dom Polonii'') * ''Ogródek Jordanowski'', one of the first children's playgrounds in Poland * Monument to murdered Jewish residents of Pułtusk. The population of Pułtusk included approximately 9,000 Jews in 1939 before the Holocaust in Poland * Soviet military cemetery
Municipal Website
(Polish)
Pultusk Academy of Humanities
Pultusk student's radio ATENA
Jewish Community in Pułtusk
at Virtual Shtetl
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pultusk Cities and towns in Masovian Voivodeship Pułtusk County Masovian Voivodeship (1526–1795) Warsaw Voivodeship (1919–1939) Holocaust locations in Poland
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, by the river Narew. Located north of Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
in the Masovian Voivodeship
The Masovian Voivodeship, also known as the Mazovia Province ( pl, województwo mazowieckie ) is a voivodeship (province) in east-central Poland, with its capital located in the city of Warsaw, which also serves as the capital of the country. Th ...
, it had a population of about 19,000 . Known for its historic architecture and Europe's longest paved marketplace ( in length), it is a popular weekend destination for the residents of Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
.
Pułtusk is one of the oldest townships in Poland, having received city rights from Duke Siemowit I of Masovia in 1257. Throughout the 15th and 17th centuries, the settlement was a significant economic centre of Masovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centurie ...
. The favourable geographical placement of the town on the Narew, along which goods were transported to the port of Gdańsk on the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
, contributed to the town's importance. Pułtusk was also the site of notable events, such as the Napoleon's 1806 battle, and the world's largest meteorite shower to date in 1868, among others.
History
Middle Ages
 The town has existed since at least the 10th century. In the
The town has existed since at least the 10th century. In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the Castle in Pułtusk was one of the most important defensive forts in northern Masovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centurie ...
against the attacks of Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians ( Old Prussian: ''prūsai''; german: Pruzzen or ''Prußen''; la, Pruteni; lv, prūši; lt, prūsai; pl, Prusowie; csb, Prësowié) were an indigenous tribe among the Baltic peoples that ...
and Lithuanians. According to a legend, the town initially was known as ''Tusk''; however, after a flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrol ...
that destroyed half of the city, it was renamed as Pułtusk (''Pół-'' or ''puł-'' being a Polish prefix for a half). Most historians believe that it was named after a small river known as ''Pełta''.
From the 11th century onwards, the town belonged to the bishops of Płock. Due to a ford
Ford commonly refers to:
* Ford Motor Company, an automobile manufacturer founded by Henry Ford
* Ford (crossing), a shallow crossing on a river
Ford may also refer to:
Ford Motor Company
* Henry Ford, founder of the Ford Motor Company
* Ford F ...
on the river located nearby, Pułtusk became an important centre of trade and commerce. It received its civic charter in 1257, modelled after that of Chełmno
Chełmno (; older en, Culm; formerly ) is a town in northern Poland near the Vistula river with 18,915 inhabitants as of December 2021. It is the seat of the Chełmno County in the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship.
Due to its regional impor ...
( Kulm Law). In 1440 an academy was founded in the town, and it became one of the most influential schools of higher education in the Polish Kingdom. Among its professors were Jakub Wujek
Jakub Wujek (1541 – 27 April 1597, son of Maciej Wujek) was a Polish Jesuit, religious writer, Doctor of Theology, Vice-Chancellor of the Vilnius Academy and translator of the Bible into Polish.
He is well-known for his translation of the Bi ...
and Piotr Skarga
Piotr Skarga (less often Piotr Powęski; 2 February 1536 – 27 September 1612) was a Polish Jesuit, preacher, hagiographer, polemicist, and leading figure of the Counter-Reformation in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Due to his oratoric ...
. By 1595 there were more than 600 students, and their number reached 900 by 1696.
The town was destroyed by Lithuanians in 1262 and 1324. In the 14th century, Pułtusk became the official seat of Płock bishops. The town was again burnt by Lithuanians in 1368, but following the Union of Krewo
In a strict sense, the Union of Krewo or Act of Krėva (also spelled Union of Krevo, Act of Kreva; be, Крэўская унія, translit=Kreŭskaja unija; pl, unia w Krewie; lt, Krėvos sutartis) comprised a set of prenuptial promises made ...
between Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
and Lithuania, the Lithuanian raids were stopped, and the town quickly recovered.
By the 15th century Pułtusk's merchants were among the richest in Poland. The town was granted a privileges of organizing nine grand fairs a year and two small markets a week. The city also gained much profit from exporting wood and grain to Gdańsk, as well as from mead and beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
production.
In around 1405, the Mayor's House, today known as the "Polonia House" or "Polonia Castle", was constructed. In 1449 a Gothic church was added to the city's facilities. In the 16th century the castle was rebuilt by several renowned Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
architects, including Giovanni Battista of Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
and Bartolommeo Berrecci
Bartolomeo Berrecci (1480 Pontassieve, Italy - 1537 Kraków, Poland) was an Italian Renaissance architect who spent most of his career in Poland.
Studies and career in Poland
He learned architecture in Florence, first through apprenticeship ...
, and Giovanni Cini of Siena
Siena ( , ; lat, Sena Iulia) is a city in Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the province of Siena.
The city is historically linked to commercial and banking activities, having been a major banking center until the 13th and 14th centur ...
.
Early modern period
Pułtusk was located in theMasovian Voivodeship
The Masovian Voivodeship, also known as the Mazovia Province ( pl, województwo mazowieckie ) is a voivodeship (province) in east-central Poland, with its capital located in the city of Warsaw, which also serves as the capital of the country. Th ...
in the Greater Poland Province of the Polish Crown. In 1530 the first Masovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centurie ...
n printing house was opened. In 1566 one of the first public theatre
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors or actresses, to present the experience of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The perform ...
s in Poland was established in Pułtusk. In the 16th century the town was visited by many notable individuals, such as King Sigismund III Vasa
Sigismund III Vasa ( pl, Zygmunt III Waza, lt, Žygimantas Vaza; 20 June 1566 – 30 April 1632
N.S.) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1587 to 1632 and, as Sigismund, King of Sweden and Grand Duke of Finland from 1592 to ...
, and poets Jan Kochanowski
Jan Kochanowski (; 1530 – 22 August 1584) was a Polish Renaissance poet who established poetic patterns that would become integral to the Polish literary language. He is commonly regarded as the greatest Polish poet before Adam Mickiewicz.
...
and Maciej Kazimierz Sarbiewski
Maciej Kazimierz Sarbiewski (in Latin, ''Matthias Casimirus Sarbievius''; Lithuanian: ''Motiejus Kazimieras Sarbievijus''; Sarbiewo, Poland, 24 February 1595 Maciej Kazimierz Sarbiewski's biography by Mirosław Korolko in: – 2 April 1640, Wars ...
.
 On 21 April 1703 during the
On 21 April 1703 during the Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swed ...
, a decisive battle was fought in Pułtusk, where the Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
army under Charles XII
Charles XII, sometimes Carl XII ( sv, Karl XII) or Carolus Rex (17 June 1682 – 30 November 1718 O.S.), was King of Sweden (including current Finland) from 1697 to 1718. He belonged to the House of Palatinate-Zweibrücken, a branch line of ...
defeated and captured a large part of the Saxon army under Graf von Steinau. Although the town and the castle were initially conquered by Polish forces, they were later recaptured by the Swedish army, which looted and destroyed it.
After the Partitions of Poland, the town was annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
. The Polish forces of General Antoni Madaliński stationed in Pułtusk in 1794 declined to obey Prussian orders and started their march towards Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
. This marked the start of the Kościuszko Uprising. Prussian rule lasted only a few years.
Under the partitions
Battle of Pułtusk
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
was fought on 26 December 1806, between forces of Imperial Russia and Imperial France. The battle became so famous that its name is inscribed on the Arc de Triomphe in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
. After the fall of Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
in 1809, Pułtusk became the temporary capital of the Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw ( pl, Księstwo Warszawskie, french: Duché de Varsovie, german: Herzogtum Warschau), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during ...
. After the fall of Napoléon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
, the town became part of so-called Congress Poland within the Russian Partition
The Russian Partition ( pl, zabór rosyjski), sometimes called Russian Poland, constituted the former territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that were annexed by the Russian Empire in the course of late-18th-century Partitions of Po ...
of Poland.
During the November Uprising, the town changed hands several times. In 1831 Russian forces were carrying a cholera epidemic when they entered the town, resulting in high fatalities. Pułtusk inhabitants took part also in the January Uprising. Afterwards the town was utterly destroyed and Russian officials sent many prominent citizens to Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
and internal exile. On 30 January 1868 a meteorite fell in Pułtusk. It was one of the biggest to fall in Europe. Large chunks ( each) were acquired by the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
, which has them on display in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
.
Although, the first Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
settled in the town in the 15th century, the Jewish community only started to flourish in the 19th century after a large influx of Jews. At the start of the 19th century, about 120 Jews lived in the city. Others lived in shtetls outside the city. Throughout the 19th century, though, the Jewish population increased rapidly to nearly 7,000 in the mid-19th century as a result of Russian discriminatory policies and the expulsion of Jews from Russia to Russian-controlled Congress Poland (see ''Pale of Settlement
The Pale of Settlement (russian: Черта́ осе́длости, '; yi, דער תּחום-המושבֿ, '; he, תְּחוּם הַמּוֹשָב, ') was a western region of the Russian Empire with varying borders that existed from 1791 to 19 ...
'').
The great fire in 1875 destroyed most of the city. It was depicted by Nobel Laureate Henryk Sienkiewicz in his novel ''Quo Vadis'' as the great fire of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
.
By the year 1900, around 6,000 Jews lived in Pułtusk. Many had migrated to nearby Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
before and after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. Others emigrated to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. Following the war, the Jewish population rose to about 7,500 and accounted for roughly half of the total population of the town.
During the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
Pultusk was the scene of another battle on 13 July 1915 when German forces attempted to cross the river Narew at Pułtusk. The 40th Infantry Division and the 50th Infantry Division of the imperial Russian Army successfully prevented them.
Interbellum and World War II
 The town was reintegrated with Poland, when the country regained independence following World War I in 1918. During the Polish-Soviet War, it was fiercely defended by Poles on August 9-10, 1920, at the eve of the Battle of Warsaw. On August 13, the Russians captured the town, and then they massacred captured Polish soldiers. On August 17, the Polish 9th Infantry Division recaptured the town. In the interbellum the Polish 13th Infantry Regiment was stationed in Pułtusk. In 1931 the town had some 16,800 inhabitants.
As a result of the German
The town was reintegrated with Poland, when the country regained independence following World War I in 1918. During the Polish-Soviet War, it was fiercely defended by Poles on August 9-10, 1920, at the eve of the Battle of Warsaw. On August 13, the Russians captured the town, and then they massacred captured Polish soldiers. On August 17, the Polish 9th Infantry Division recaptured the town. In the interbellum the Polish 13th Infantry Regiment was stationed in Pułtusk. In 1931 the town had some 16,800 inhabitants.
As a result of the German invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week aft ...
, which started World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
in September 1939, Pułtusk was occupied by the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
and incorporated into Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. Already on September 12-13, 1939, the '' Einsatzgruppe V'' entered the town to commit atrocities against the population. Nazi Germany operated a police prison, court prison and forced labour camp in the town. The German police carried out executions of Poles in the local prison in November and December 1939. During the German occupation, approximately 50% of the city's inhabitants, mostly Jews, were expelled or deported, some to Nazi concentration camps
From 1933 to 1945, Nazi Germany operated more than a thousand concentration camps, (officially) or (more commonly). The Nazi concentration camps are distinguished from other types of Nazi camps such as forced-labor camps, as well as con ...
. In 1941-1945 it was renamed in German as ''Ostenburg'', to erase traces of Polish origin. On December 17, 1942, the Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one orga ...
carried out a public execution of four members of the Home Army
The Home Army ( pl, Armia Krajowa, abbreviated AK; ) was the dominant resistance movement in German-occupied Poland during World War II. The Home Army was formed in February 1942 from the earlier Związek Walki Zbrojnej (Armed Resistance) est ...
, the leading Polish resistance organization. In the battle for Pułtusk during later World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, over 16,000 soldiers of the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army ( Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, afte ...
were killed. As a result of the battle, approximately 85% of the city was destroyed.
On September 7, 1939, the city became under the control of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. On September 27, the Germans deported most of the Jews to concentration camps. Some eventually made their way to the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
border but many died in the camps. In the 21st century, descendants of Pułtusk Jewry are found mainly in Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, and Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
.
Modern times
In 1950, arail line
Rail terminology is a form of technical terminology. The difference between the American term ''railroad'' and the international term ''railway'' (used by the International Union of Railways and English-speaking countries outside the United Sta ...
connecting Pułtusk with Nasielsk Railway Station was built.
In 1975, the Science Center of the Mazovian Center for Scientific Research was opened in the town.
In 1993, Pułtusk hosted the first ever biennial meeting of the World International Advisory Committee of UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
's Memory of the World Programme
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, ...
to discuss and inscribe items onto the Register.
Points of interest
Currently Pułtusk is one of the most picturesque towns ofMasovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centurie ...
. Located on the Narew river, it is one of the most popular weekend places for residents of Warsaw. Points of interest include:
* Collegiate Church of Annunciation
* Small Gothic church with unique Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
stuccos
* The Old Town market (reputedly the longest market square in Europe) Nasze Miasto - Pułtusk (History of Pułtusk)Pułtusk Academy of Humanities (Akademia Humanistyczna im. Aleksandra Gieysztora in Pułtusk) * Town Hall * Polonia Castle (now operated as a hotel named ''Dom Polonii'') * ''Ogródek Jordanowski'', one of the first children's playgrounds in Poland * Monument to murdered Jewish residents of Pułtusk. The population of Pułtusk included approximately 9,000 Jews in 1939 before the Holocaust in Poland * Soviet military cemetery
Education
* Pułtusk Academy of HumanitiesSports
The local football club is Nadnarwianka Pułtusk. It competes in the lower leagues.International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Pułtusk is twinned with: *Ganderkesee
Ganderkesee (Northern Low Saxon: ''Gannerseer'') is a municipality in Oldenburg district, in Lower Saxony, Germany.
Geography
Ganderkesee is located on the northern edge of a nature park called "Wildeshauser Geest". The northernmost part of the c ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
* Montmorency, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
* New Britain, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
* Senica, Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
* Szerencs
Szerencs is a town in Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county, Northern Hungary. It lies away from Miskolc, and away from Budapest. It has about 9,100 inhabitants.
History
Szerencs grew into a town where the Great Plain and the Zemplén mountains meet. ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
Notes and references
External links
Municipal Website
(Polish)
Pultusk Academy of Humanities
Pultusk student's radio ATENA
Jewish Community in Pułtusk
at Virtual Shtetl
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pultusk Cities and towns in Masovian Voivodeship Pułtusk County Masovian Voivodeship (1526–1795) Warsaw Voivodeship (1919–1939) Holocaust locations in Poland