Providence/Stoughton Line on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Providence/Stoughton Line is an

 The
The
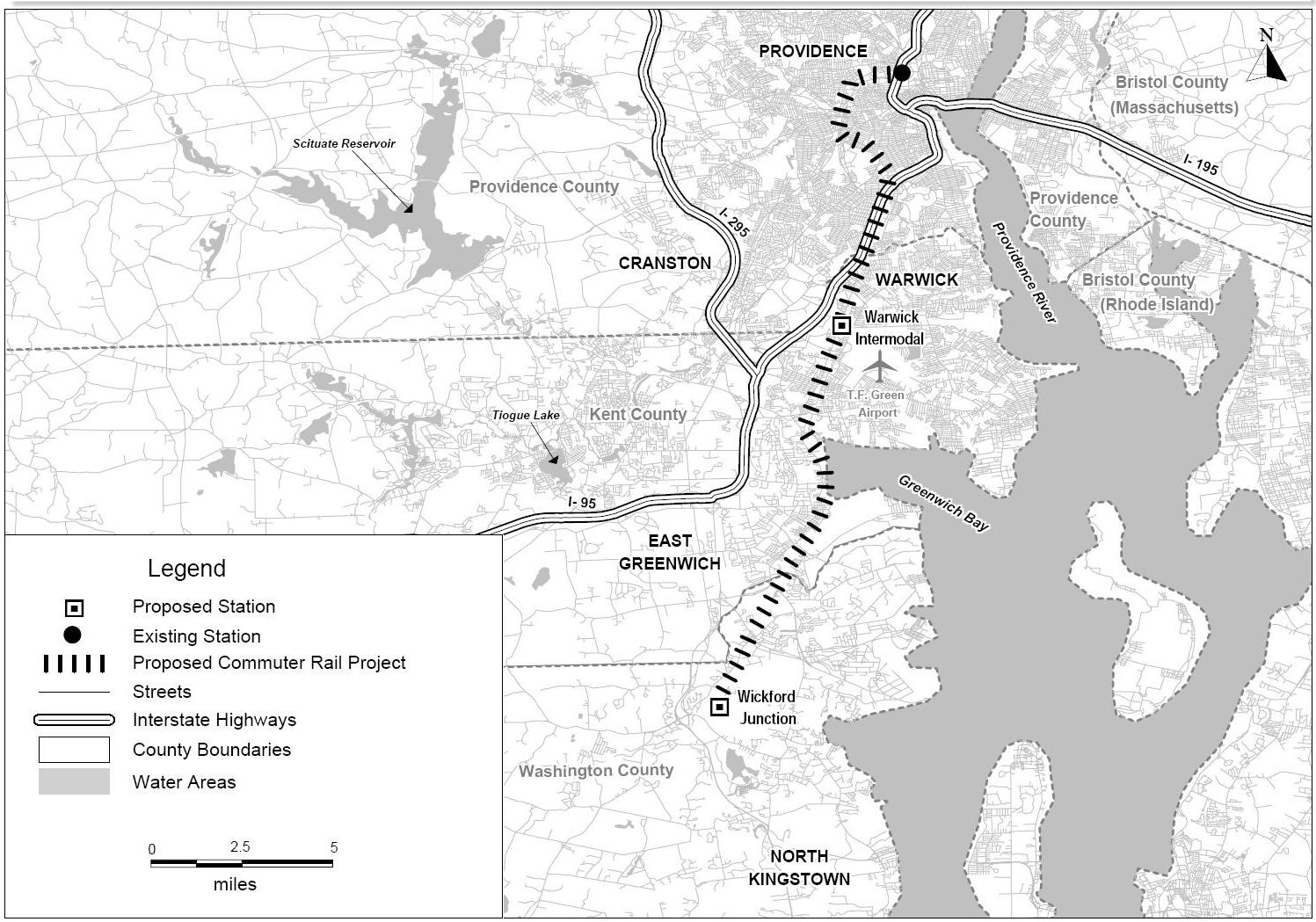 As part of the South County Commuter Rail initiative, a 20-mile extension past Providence to and in Rhode Island is now fully open. The T. F. Green Airport part of the extension opened in December 2010, with Wickford Junction service beginning in April 2012. An infill station at is planned to open on January 23, 2023.
A further 24-mile extension is under consideration by the
As part of the South County Commuter Rail initiative, a 20-mile extension past Providence to and in Rhode Island is now fully open. The T. F. Green Airport part of the extension opened in December 2010, with Wickford Junction service beginning in April 2012. An infill station at is planned to open on January 23, 2023.
A further 24-mile extension is under consideration by the


MBTA - Providence/Stoughton Line schedule
{{DEFAULTSORT:Providence Stoughton Line MBTA Commuter Rail
MBTA Commuter Rail
The MBTA Commuter Rail system serves as the commuter rail arm of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority's transportation coverage of Greater Boston in the United States. Trains run over of track to 141 different stations, with 58 stati ...
service in Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut Massachusett_writing_systems.html" ;"title="nowiki/> məhswatʃəwiːsət.html" ;"title="Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət">Massachusett writing systems">məhswatʃəwiːsət'' En ...
and Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
, primarily serving the southwestern suburbs of Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
. Most service runs entirely on the Northeast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston through Providence, New Haven, Stamford, New York City, Philadelphia, Wilmington, ...
between South Station
South Station, officially The Governor Michael S. Dukakis Transportation Center at South Station, is the largest railroad station and intercity bus terminal in Greater Boston and New England's second-largest transportation center after Logan ...
in Boston and Providence station or Wickford Junction station
Wickford Junction is a commuter rail station located in North Kingstown, Rhode Island, United States. It is the southern terminus of the MBTA Commuter Rail Providence/Stoughton Line and serves as a park and ride location for commuters to Provi ...
in Rhode Island, while the Stoughton Branch splits at and terminates at . It is the longest MBTA Commuter Rail line, and the only one that operates outside Massachusetts. The line is the busiest on the MBTA Commuter Rail system, with 17,648 daily boardings in an October 2022 count.
The portion between Boston and Providence was originally built by the Boston and Providence Railroad
The Boston and Providence Railroad was a railroad company in the states of Massachusetts and Rhode Island which connected its namesake cities. It opened in two sections in 1834 and 1835 - one of the first rail lines in the United States - with a ...
between 1834 and 1847. The portion south of Providence was built by the New York, Providence and Boston Railroad
The New York, Providence and Boston Railroad, normally called the Stonington Line, was a major part of the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad between New London, Connecticut and Providence, Rhode Island. It is now part of Amtrak's high-sp ...
in 1837, while the Stoughton Branch was built by the Stoughton Branch Railroad
The Boston and Providence Railroad was a railroad company in the states of Massachusetts and Rhode Island which connected its namesake cities. It opened in two sections in 1834 and 1835 - one of the first rail lines in the United States - with ...
in 1845. The lines were acquired by the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad
The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad , commonly known as The Consolidated, or simply as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in the New England region of the United States from 1872 to December 31, 1968. Founded by the merger of ...
in the 1890s.
The MBTA began subsidizing service in the 1960s, and purchased the infrastructure and rolling stock from Penn Central
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American class I railroad that operated from 1968 to 1976. Penn Central combined three traditional corporate rivals (the Pennsylvania, New York Central and th ...
in 1973. Service was cut back to in 1981, but rush-hour service returned as far as Providence in 1988 under an agreement with the state of Rhode Island. Off-peak service to Rhode Island resumed in 2000. An extension south from Providence opened to in 2010 and to Wickford Junction in 2012. All stations have been made accessible
Accessibility is the design of products, devices, services, vehicles, or environments so as to be usable by people with disabilities. The concept of accessible design and practice of accessible development ensures both "direct access" (i. ...
with high-level platforms. Newer stations like T.F. Green Airport, as well as stations shared with Amtrak, largely have full-length high level platforms; older stations have mostly been retrofitted with "mini-high" platforms one car length long.
History

Boston and Providence Railroad
The Boston and Providence Railroad was a railroad company in the states of Massachusetts and Rhode Island which connected its namesake cities. It opened in two sections in 1834 and 1835 - one of the first rail lines in the United States - with a ...
(B&P) opened between Boston and Sprague Mansion in 1834, and on to Providence in 1835. A new line between Providence and East Junction via Central Falls, shared with the Providence and Worcester Railroad
The Providence and Worcester Railroad is a Class II railroad operating of tracks in Rhode Island, Massachusetts, and Connecticut, as well as New York via trackage rights. The company was founded in 1844 to build a railroad between Providence, ...
south of Central Falls, opened in October 1847. The B&P was leased by the Old Colony Railroad
The Old Colony Railroad (OC) was a major railroad system, mainly covering southeastern Massachusetts and parts of Rhode Island, which operated from 1845 to 1893. Old Colony trains ran from Boston to points such as Plymouth, Fall Ri ...
in 1888; the Old Colony was in turn leased by the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad
The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad , commonly known as The Consolidated, or simply as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in the New England region of the United States from 1872 to December 31, 1968. Founded by the merger of ...
in 1893.
At the peak of service around the turn of the century, weekday service included six Boston–Providence local round trips, seven round trips from Taunton and via , 62 Boston– round trips running every 15 minutes, 12 Boston–Dedham round trips via and 24 via , and 11 intercity round trips from beyond Providence. Connections to additional branch line trains were made at , Mansfield, and East Junction. Forest Hills service was soon decimated by the competing Washington Street Elevated
The Washington Street Elevated was an elevated segment of Boston's Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority subway system, comprising the southern stretch of the Orange Line. It ran from Chinatown through the South End and Roxbury, ending i ...
; branch line service declined in the 1920s and 1930s. Further reductions occurred after World War II; cuts in July 1959 reduced Providence service from 12 to nine round trips, Dedham service to one round trip, and Stoughton service to two round trips.
MBTA era
On December 31, 1968, the recently formedPenn Central
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American class I railroad that operated from 1968 to 1976. Penn Central combined three traditional corporate rivals (the Pennsylvania, New York Central and th ...
bought the failing New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad
The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad , commonly known as The Consolidated, or simply as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in the New England region of the United States from 1872 to December 31, 1968. Founded by the merger of ...
. The MBTA bought the section of the Providence–Boston line in Massachusetts, as well as many other lines including the Stoughton Branch, from Penn Central on January 27, 1973. On April 1, 1976 Conrail
Conrail , formally the Consolidated Rail Corporation, was the primary Class I railroad in the Northeastern United States between 1976 and 1999. The trade name Conrail is a portmanteau based on the company's legal name. It continues to do bus ...
took over Penn Central and the commuter rail equipment was sold to the MBTA. Conrail continued to operate the line under contract to the MBTA until 1977, when the Boston and Maine Railroad
The Boston and Maine Railroad was a U.S. Class I railroad in northern New England. Originally chartered in 1835, it became part of what was the Pan Am Railways network in 1983 (most of which was purchased by CSX in 2022).
At the end of 1970 ...
became the sole contractor for all MBTA commuter rail service. Full subsidies by the MBTA for the Providence and Stoughton lines began on September 28, 1976, before which the Federal government helped. On March 31, 1977, the Greater Attleboro Taunton Regional Transit Authority and Rhode Island Department of Transportation began to subsidize service beyond the MBTA district, and Stoughton began to pay to keep its station open, that cost later going to the Brockton Area Transit Authority
Brockton Area Transit Authority, branded as Brockton Area Transit (BAT), is a public, non-profit organization in Massachusetts, charged with providing public transportation to the Brockton area, consisting of the city of Brockton and the adjoini ...
.
On November 3, 1979, the line was closed north of Readville for long-term reconstruction as part of the Southwest Corridor project. All trains began using what is now the Fairmount Line
The Fairmount Line or Dorchester Branch is a line of the MBTA Commuter Rail system in Boston, Massachusetts, USA. Except for a short portion in Milton, it lies entirely within Boston, running southwest from South Station through the neighborh ...
, and special shuttle trains connected South Station to Back Bay. The new line, rebuilt below grade with space for three tracks (the old one had been above grade with room for four tracks), opened on October 5, 1987. The Orange Line shares the corridor between Back Bay and Forest Hills.
After Rhode Island cut back its subsidy, Sunday service was truncated to Attleboro in October 1977, with off-peak and Saturday service following suit in April 1979. On February 20, 1981, the MBTA stopped serving Rhode Island altogether after that state declined to renew its subsidy. On September 17, 1986, Massachusetts and Rhode Island reached an agreement to resume service. Rush-hour
A rush hour (American English, British English) or peak hour (Australian English) is a part of the day during which traffic congestion on roads and crowding on public transport is at its highest. Normally, this happens twice every weekday: on ...
service to Rhode Island was restored on February 1, 1988. On June 20, 1990, a new stop opened in South Attleboro and most trains were extended to the station; regular Sunday service returned in 1992.
In 1990, a northbound commuter train was involved in a collision
''A Collision or (3+4=7)'' is the third full-length studio album and sixth album overall by David Crowder Band and the third recorded for sixstepsrecords, released in September 2005. "Foreverandever Etc…" is on the Digital Praise PC game Guita ...
with a northbound '' Night Owl'' train. The accident, which occurred to the west of Back Bay station
Back Bay station (also signed as Back Bay · South End) is an intermodal passenger station in Boston, Massachusetts. It is located just south of Copley Square in Boston's Back Bay and South End neighborhoods. It serves MBTA Commuter Rail and M ...
, injured over four hundred people, although there were no fatalities.
Some off-peak weekday trains were extended to Providence starting on December 11, 2000. On July 24, 2006, the MBTA increased weekday Providence service from 11 to 15 daily round trips. Weekend service to Providence resumed on July 29, and a new layover facility was opened in Pawtucket.
Extensions
 As part of the South County Commuter Rail initiative, a 20-mile extension past Providence to and in Rhode Island is now fully open. The T. F. Green Airport part of the extension opened in December 2010, with Wickford Junction service beginning in April 2012. An infill station at is planned to open on January 23, 2023.
A further 24-mile extension is under consideration by the
As part of the South County Commuter Rail initiative, a 20-mile extension past Providence to and in Rhode Island is now fully open. The T. F. Green Airport part of the extension opened in December 2010, with Wickford Junction service beginning in April 2012. An infill station at is planned to open on January 23, 2023.
A further 24-mile extension is under consideration by the Rhode Island Department of Transportation
The Rhode Island Department of Transportation (RIDOT) is a Rhode Island state government agency charged with design, construction, maintenance and inspection of a wide range of transportation infrastructure. These include 3,300 lane miles of stat ...
. Possible stops include Cranston and East Greenwich
East Greenwich is a New England town, town and the county seat of Kent County, Rhode Island, Kent County, Rhode Island. The population was 14,312 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. East Greenwich is the wealthiest municipality within t ...
, plus existing Amtrak stations in Kingston and Westerly. Rhode Island eventually plans to have its own statewide commuter service along the Northeast Corridor that would connect with MBTA service and an extension of Shore Line East
Shore Line East (SLE) is a commuter rail service which operates along the Northeast Corridor through southern Connecticut, United States. The rail service is a fully owned subsidiary of the Connecticut Department of Transportation (CTDOT) and i ...
. This would be the first commuter service to Westerly since the last state-sponsored train was run in December 1979. A passing siding and new platforms at Kingston, completed in 2017, may enable extension of some trains there in the near term.
Amtrak electrified the Providence Line in 2000, but the MBTA has not utilized this. In 2019, the MBTA had preliminary discussions with Amtrak about leasing Siemens ACS-64 electric locomotives to test on the Providence Line. A section of non-electrified platform sidings at Attleboro, not included in the initial Amtrak electrification, is being electrified in mid-2022 to support future electric MBTA operations. In June 2022, the MBTA indicated plans to pilot electric service on the line using Amtrak locomotives around 2024. Full electric service (including the Stoughton Branch) using battery electric multiple unit
A battery electric multiple unit (BEMU), battery electric railcar or accumulator railcar is an electrically driven multiple unit or railcar whose energy is derived from rechargeable batteries driving the traction motors.
Prime advantages of these ...
s would take place in 2028–29.
Phase 2 of the South Coast Rail
South Coast Rail is a project to build a new southern line of the MBTA Commuter Rail system along several abandoned and freight-only rail lines. The line has been planned to restore passenger rail service between Boston and the cities of Taunton, ...
project, planned to open in 2030, would extend the Stoughton Branch south over the abandoned Dighton and Somerset Railroad
The Dighton and Somerset Railroad, currently referred to as the Dean Street Industrial Track, is a railroad that ran between Fall River and Braintree, Massachusetts. It opened in 1866; from the 1890s to the 1930s and again in the late 1950s, i ...
. It would join Phase 1 (scheduled to open in late 2023) near East Taunton station and replace the section of the Phase 1 route through .
Special event service
In August 1971, the MBTA began operating Boston– and Providence–Foxboro service for events at the newFoxboro Stadium
Foxboro Stadium, originally Schaefer Stadium and later Sullivan Stadium, was an outdoor stadium in the New England region of the United States, located in Foxborough, Massachusetts. It opened in 1971 and served as the home of the New England ...
. Providence service ended early in the 1973 season due to insufficient ridership; Boston service ended that October. Boston service via the Franklin Line resumed in 1986. It was rerouted over the Providence/Stoughton Line in 1989, with intermediate stops at Back Bay, Hyde Park, Route 128, Canton Junction, Sharon, and Mansfield; a reverse move was made at Mansfield to access the Framingham Secondary
The Framingham Secondary (formerly the Framingham Subdivision) is a railroad line in the U.S. state of Massachusetts. The line runs from Mansfield northwest to Framingham along a former New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad line. Its south e ...
. Boston–Foxboro service was again rerouted over the Franklin Line in 1995. Providence–Foxboro event service resumed for the 1997 season, with intermediate stops at South Attleboro, Attleboro, and Mansfield. Event service was extended to T.F. Green Airport in 2012, but cut back to Providence in 2019.
COVID-19 pandemic
Substantially reduced schedules were in effect from March 16 to June 23, 2020. Service changes effective November 2, 2020, shifted some peak service to off-peak, providing 60-minute all-day headways between Providence and Boston. Reduced schedules were again put in effect on December 14, 2020. As part of a schedule change on January 23, 2021, Sunday morning Boston–Providence service began operation for the first time since the New Haven era. On February 26, 2021,South Attleboro station
South Attleboro station is an MBTA Commuter Rail Providence/Stoughton Line station in Attleboro, Massachusetts. It is located under Newport Avenue (Attleboro), Newport Avenue (Route 1A) in the South Attleboro, Massachusetts, South Attleboro neig ...
was temporarily closed due to structural deterioration. Full service was restored on April 5, 2021. As part of that schedule change, all Providence/Stoughton Line trains began stopping at Ruggles station
Ruggles station is an intermodal transfer station in Boston, Massachusetts. It serves Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) rapid transit, bus, and commuter rail services and is located at the intersection of Ruggles and Tremont st ...
after an additional platform there was completed. Additionally, the final Providence-bound train on weekdays began stopping at Forest Hills station to provide a transfer to a shuttle train to Needham. During the closure of the Orange Line from August 19 to September 18, 2022, additional Providence/Stoughton Line trains stopped at Forest Hills. One of these trains – a midday Providence outbound – continued to stop after September 19. Daily ridership reached 17,648 in October 2022 – 69% of pre-COVID ridership.
Service
, weekday service has 20 Boston–Providence round trips, half of which run to Wickford Junction, and 16 Boston–Stoughton round trips. Weekend service has nine Boston–Providence round trips, with no Wickford Junction or Stoughton service. The main branch forms the far northern leg of Amtrak's Northeast Corridor. All ''Acela Express
The ''Acela'' ( ; originally the ''Acela Express'' until September 2019) is Amtrak's flagship service along the Northeast Corridor (NEC) in the Northeastern United States between Washington, D.C. and Boston via 13 intermediate stops, inclu ...
'' trains and all ''Northeast Regional
The ''Northeast Regional'' is an intercity rail service operated by Amtrak in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic United States. In the past it has been known as the ''NortheastDirect'', ''Acela Regional'', or ''Regional''. It is Amtrak's busi ...
'' routes between Boston and New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
run along this line. South Station, Back Bay, Route 128 and Providence have long ranked among the busiest Amtrak stations in the country. With fast and frequent MBTA and Amtrak service, the Providence-Boston share of the Northeast Corridor is one of the busiest rail lines in the country.
Ownership and financing
The MBTA owns the section from Boston to the Rhode Island border (called the Attleboro Line), while Amtrak owns all track in Rhode Island. The entire line is part of theNortheast Corridor
The Northeast Corridor (NEC) is an electrified railroad line in the Northeast megalopolis of the United States. Owned primarily by Amtrak, it runs from Boston through Providence, New Haven, Stamford, New York City, Philadelphia, Wilmington, ...
.
As part of the 1988 Pilgrim Partnership Agreement, Rhode Island provides capital funding (including some of its federal formula funds) for MBTA expansion in the state. Massachusetts (through the MBTA) provides the operating subsidy for MBTA Commuter Rail
The MBTA Commuter Rail system serves as the commuter rail arm of the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority's transportation coverage of Greater Boston in the United States. Trains run over of track to 141 different stations, with 58 stati ...
service in return. Rhode Island also pays Amtrak to allow the MBTA to use its tracks.
Station listing

Stoughton Branch
References
External links
MBTA - Providence/Stoughton Line schedule
{{DEFAULTSORT:Providence Stoughton Line MBTA Commuter Rail