Proto-Laurasia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the
 Laurentia and Baltica first formed a continental mass known as Proto-Laurasia as part of the supercontinent Columbia which was assembled 2,100—1,800 Mya to encompass virtually all known Archaean continental blocks. Surviving sutures from this assembly are the Trans-Hudson orogen in Laurentia; Nagssugtoqidian orogen in Greenland; the Kola-Karelian (the northwest margin of the Svecokarelian/Svecofennian orogen) and the Volhyn—Central Russia and Pachelma orogenies (across western Russia) in Baltica; and the Akitkan Orogen in Siberia.
Additional Proterozoic crust was accreted 1,800—1,300 Mya, especially along the Laurentia—Greenland—Baltica margin.
Laurentia and Baltica formed a coherent continental mass with southern Greenland and Labrador adjacent to the Arctic margin of Baltica. A magmatic arc extended from Laurentia through southern Greenland to northern Baltica. The breakup of Columbia began 1,600 Mya, including along the western margin of Laurentia and northern margin of Baltica (modern coordinates), and was completed c. 1,300—1,200 Mya, a period during which mafic
Laurentia and Baltica first formed a continental mass known as Proto-Laurasia as part of the supercontinent Columbia which was assembled 2,100—1,800 Mya to encompass virtually all known Archaean continental blocks. Surviving sutures from this assembly are the Trans-Hudson orogen in Laurentia; Nagssugtoqidian orogen in Greenland; the Kola-Karelian (the northwest margin of the Svecokarelian/Svecofennian orogen) and the Volhyn—Central Russia and Pachelma orogenies (across western Russia) in Baltica; and the Akitkan Orogen in Siberia.
Additional Proterozoic crust was accreted 1,800—1,300 Mya, especially along the Laurentia—Greenland—Baltica margin.
Laurentia and Baltica formed a coherent continental mass with southern Greenland and Labrador adjacent to the Arctic margin of Baltica. A magmatic arc extended from Laurentia through southern Greenland to northern Baltica. The breakup of Columbia began 1,600 Mya, including along the western margin of Laurentia and northern margin of Baltica (modern coordinates), and was completed c. 1,300—1,200 Mya, a period during which mafic
 In the vast majority of plate tectonic reconstructions, Laurentia formed the core of the supercontinent Rodinia, but the exact fit of various continents within Rodinia is debated. In some reconstructions, Baltica was attached to Greenland along its Scandinavian or Caledonide margin while
In the vast majority of plate tectonic reconstructions, Laurentia formed the core of the supercontinent Rodinia, but the exact fit of various continents within Rodinia is debated. In some reconstructions, Baltica was attached to Greenland along its Scandinavian or Caledonide margin while
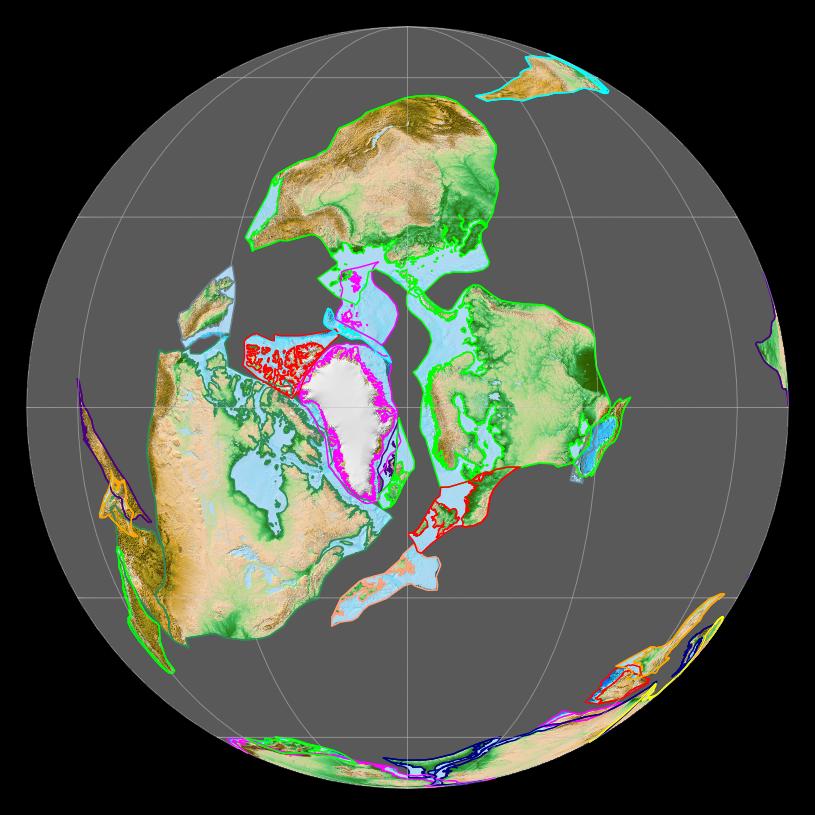
 Laurentia remained almost static near the Equator throughout the early Palaeozoic, separated from Baltica by the up to -wide Iapetus Ocean.
In the Late Cambrian, the mid-ocean ridge in the Iapetus Ocean subducted beneath Gondwana which resulted in the opening of a series of large back-arc basins. During the Ordovician, these basins evolved into a new ocean, the
Laurentia remained almost static near the Equator throughout the early Palaeozoic, separated from Baltica by the up to -wide Iapetus Ocean.
In the Late Cambrian, the mid-ocean ridge in the Iapetus Ocean subducted beneath Gondwana which resulted in the opening of a series of large back-arc basins. During the Ordovician, these basins evolved into a new ocean, the
 The subduction of the Iapetus Ocean resulted in the first contact between Laurussia and Gondwana in the Late Devonian and terminated in full collision or the Hercynian/Variscan orogeny in the early Carboniferous (340 Mya). The Variscan orogeny closed the
The subduction of the Iapetus Ocean resulted in the first contact between Laurussia and Gondwana in the Late Devonian and terminated in full collision or the Hercynian/Variscan orogeny in the early Carboniferous (340 Mya). The Variscan orogeny closed the
Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
period) during the breakup of Pangaea, drifting farther north after the split and finally broke apart with the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean
The opening of the North Atlantic Ocean is a geological event that has occurred over millions of years, during which the supercontinent Pangea broke up. As modern-day Europe ( Eurasian plate) and North America ( North American Plate) separated d ...
c. 56 Mya. The name is a portmanteau
A portmanteau word, or portmanteau (, ) is a blend of wordsLaurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
.
Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
, Avalonia, Baltica
Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains.
The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, ...
, and a series of smaller terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust (geology), crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and Accretion (geology), accreted or "Suture (geology), sutured" to crust lying on another pla ...
s, collided in the Caledonian orogeny
The Caledonian orogeny was a mountain-building era recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Mountains, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that ...
c. 400 Ma to form Laurussia (also known as Euramerica, or the Old Red Sandstone Continent). Laurussia then collided with Gondwana to form Pangaea. Kazakhstania
Kazakhstania ( kk, Qazaqstaniya), the Kazakh terranes, or the Kazakhstan Block, is a geological region in Central Asia which consists of the area roughly centered on Lake Balkhash, north and east of the Aral Sea, south of the Siberian craton and ...
and Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
were then added to Pangaea 290–300 Ma to form Laurasia. Laurasia finally became an independent continental mass when Pangaea broke up into Gondwana and Laurasia.
Terminology and origin of the concept
Laurentia, the Palaeozoiccore
Core or cores may refer to:
Science and technology
* Core (anatomy), everything except the appendages
* Core (manufacturing), used in casting and molding
* Core (optical fiber), the signal-carrying portion of an optical fiber
* Core, the centra ...
of North America and continental fragments that now make up part of Europe, collided with Baltica
Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains.
The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, ...
and Avalonia in the Caledonian orogeny
The Caledonian orogeny was a mountain-building era recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Mountains, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that ...
c. 430–420 Mya to form Laurussia. In the Late Carboniferous Laurussia and Gondwana formed Pangaea. Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive region, geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a ...
and Kazakhstania
Kazakhstania ( kk, Qazaqstaniya), the Kazakh terranes, or the Kazakhstan Block, is a geological region in Central Asia which consists of the area roughly centered on Lake Balkhash, north and east of the Aral Sea, south of the Siberian craton and ...
finally collided with Baltica in the Late Permian to form Laurasia.
A series of continental blocks that now form East and Southeast Asia were later added to Laurasia.
In 1904–1909 Austrian geologist Eduard Suess
Eduard Suess (; 20 August 1831 - 26 April 1914) was an Austrian geologist and an expert on the geography of the Alps. He is responsible for hypothesising two major former geographical features, the supercontinent Gondwana (proposed in 1861) and t ...
proposed that the continents in the Southern Hemisphere were once merged into a larger continent called Gondwana. In 1915 German meteorologist Alfred Wegener
Alfred Lothar Wegener (; ; 1 November 1880 – November 1930) was a German climatologist, geologist, geophysicist, meteorologist, and polar researcher.
During his lifetime he was primarily known for his achievements in meteorology and ...
proposed the existence of a supercontinent called Pangaea. In 1937 South African geologist Alexander du Toit
Alexander Logie du Toit FRS ( ; 14 March 1878 – 25 February 1948) was a geologist from South Africa and an early supporter of Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift.
Early life and education
Du Toit was born in Newlands, Cape Town in ...
proposed that Pangaea was divided into two larger landmasses, Laurasia in the Northern Hemisphere and Gondwana in the Southern Hemisphere, separated by the Tethys Ocean.
"Laurussia" was defined by Swiss geologist Peter Ziegler
Peter Alfred Ziegler (2 November 1928 – 19 July 2013) was a Swiss geologist, who made contributions to the understanding of the geological evolution of Europe and the North Atlantic borderlands, of intraplate tectonics and of plate tectoni ...
in 1988 as the merger between Laurentia and Baltica along the northern Caledonian suture. The "Old Red Continent" is an informal name often used for the Silurian-Carboniferous deposits in the central landmass of Laurussia.
Several earlier supercontinents proposed and debated in the 1990s and later (e.g. Rodinia, Nuna, Nena) included earlier connections between Laurentia, Baltica, and Siberia. These original connections apparently survived through one and possibly even two Wilson Cycle
The Wilson Cycle is a model that describes the opening and closing of ocean basins and the subduction and divergence of tectonic plates during the assembly and disassembly of supercontinents. A classic example of the Wilson Cycle is the opening a ...
s, though their intermittent duration and recurrent fit is debated.
Proto-Laurasia
Pre–Rodinia
dike swarm
A dike swarm (American spelling) or dyke swarm (British spelling) is a large geological structure consisting of a major group of parallel, linear, or radially oriented magmatic dikes intruded within continental crust or central volcanoes ...
s were emplaced, including MacKenzie
Mackenzie, Mckenzie, MacKenzie, or McKenzie may refer to:
People
* Mackenzie (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name)
* Mackenzie (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name)
* Clan Mackenzie, a S ...
and Sudbury in Laurentia.
Traces left by large igneous province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation ...
s provide evidences for continental mergers during this period. Those related to Proto-Laurasia includes:
* 1,750 Mya extensive magmatism in Baltica, Sarmatia
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th c ...
(Ukraine), southern Siberia, northern Laurentia, and West Africa indicate these cratons were linked to each other;
* a 1,630–1,640 Mya-old continent composed of Siberia, Laurentia, and Baltica is suggested by sills in southern Siberia that can be connected to the Melville Bugt dyke swarm in western Greenland; and
* a major large igneous province 1,380 Mya during the breakup of the Nuna/Columbia supercontinent connects Laurentia, Baltica, Siberia, Congo, and West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
.
Rodinia
 In the vast majority of plate tectonic reconstructions, Laurentia formed the core of the supercontinent Rodinia, but the exact fit of various continents within Rodinia is debated. In some reconstructions, Baltica was attached to Greenland along its Scandinavian or Caledonide margin while
In the vast majority of plate tectonic reconstructions, Laurentia formed the core of the supercontinent Rodinia, but the exact fit of various continents within Rodinia is debated. In some reconstructions, Baltica was attached to Greenland along its Scandinavian or Caledonide margin while Amazonia
The Amazon rainforest, Amazon jungle or ; es, Selva amazónica, , or usually ; french: Forêt amazonienne; nl, Amazoneregenwoud. In English, the names are sometimes capitalized further, as Amazon Rainforest, Amazon Forest, or Amazon Jungle. ...
was docked along Baltica's Tornquist margin. Australia and East Antarctica were located on Laurentia's western margin.
Siberia was located near but at some distance from Laurentia's northern margin in most reconstructions.
In the reconstruction of some Russian geologists, however, the southern margin (modern coordinates) of Siberia merged with the northern margin of Laurentia, and these two continents broke up along what is now the -long Central Asian Foldbelt no later than 570 Mya and traces of this breakup can still be found in the Franklin dike swarm in northern Canada and the Aldan Shield in Siberia.
The Proto-Pacific opened and Rodinia began to breakup during the Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is prec ...
(c. 750–600 Mya) as Australia-Antarctica (East Gondwana) rifted from the western margin of Laurentia, while the rest of Rodinia (West Gondwana and Laurasia) rotated clockwise and drifted south. Earth subsequently underwent a series of glaciations – the Varanger (c. 650 Mya, also known as Snowball Earth) and the Rapitan and Ice Brook glaciations (c. 610-590 Mya) – both Laurentia and Baltica were located south of 30°S, with the South Pole located in eastern Baltica, and glacial deposits from this period have been found in Laurentia and Baltica but not in Siberia.
A mantle plume (the Central Iapetus Magmatic Province) forced Laurentia and Baltica to separate ca. 650–600 Mya and the Iapetus Ocean opened between them. Laurentia then began to move quickly () north towards the Equator where it got stuck over a cold spot in the Proto-pacific. Baltica remained near Gondwana in southern latitudes into the Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya.
T ...
.
Pannotia
Laurentia, Baltica, and Siberia remained connected to each other within the short-lived, Precambrian- Cambrian supercontinent Pannotia or Greater Gondwana. At this time a series of continental blocks – Peri-Gondwana – that now form part of Asia, theCathaysia
Cathaysia was a microcontinent or a group of terranes that rifted off Gondwana during the Late Paleozoic. They mostly correspond to modern territory of China, which were split into the North China and South China blocks.
Terminology
The terms " ...
n terranes – Indochina, North China, and South China – and Cimmerian
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into Wes ...
terranes – Sibumasu, Qiangtang, Lhasa
Lhasa (; Lhasa dialect: ; bo, text=ལྷ་ས, translation=Place of Gods) is the urban center of the prefecture-level Lhasa City and the administrative capital of Tibet Autonomous Region in Southwest China. The inner urban area of Lhas ...
, Afghanistan, Iran, and Turkey – were still attached to the Indian–Australian margin of Gondwana. Other blocks that now form part of southwestern Europe and North America from New England to Florida were still attached to the African-South American margin of Gondwana.
This northward drift of terranes across the Tethys also included the Hunic terranes, now spread from Europe to China.
Pannotia broke apart in the late Precambrian into Laurentia, Baltica, Siberia, and Gondwana. A series of continental blocks – the Cadomian–Avalonian, Cathaysian, and Cimmerian terranes – broke away from Gondwana and began to drift north.
Euramerica/Laurussia

Rheic Ocean
The Rheic Ocean was an ocean which separated two major palaeocontinents, Gondwana and Laurussia (Laurentia- Baltica-Avalonia). One of the principal oceans of the Palaeozoic, its sutures today stretch from Mexico to Turkey and its closure result ...
, which separated a series of terranes – Avalonia, Carolinia, and Armorica
Armorica or Aremorica (Gaulish: ; br, Arvorig, ) is the name given in ancient times to the part of Gaul between the Seine and the Loire that includes the Brittany Peninsula, extending inland to an indeterminate point and down the Atlantic Coast ...
– from Gondwana.
Avalonia rifted from Gondwana in the Early Ordovician and collided with Baltica near the Ordovician–Silurian boundary (480–420 Mya). Baltica-Avalonia was then rotated and pushed north towards Laurentia. The collision between these continents closed the Iapetus Ocean and formed Laurussia, also known as Euramerica. Another historical term for this continent is the Old Red Continent or Old Red Sandstone Continent, in reference to abundant red beds of the Old Red Sandstone
The Old Red Sandstone is an assemblage of rocks in the North Atlantic region largely of Devonian age. It extends in the east across Great Britain, Ireland and Norway, and in the west along the northeastern seaboard of North America. It also exte ...
during the Devonian. The continent covered including several large Arctic continental blocks.
With the Caledonian orogeny completed Laurussia was delimited thus:
* The eastern margin were the Barents Shelf and Moscow Platform;
* the western margin were the western shelves of Laurentia, later affected by the Antler orogeny
The Antler orogeny was a tectonic event that began in the early Late Devonian with widespread effects continuing into the Mississippian and early Pennsylvanian. Most of the evidence for this event is in Nevada but the limits of its reach are un ...
;
* the northern margin was the Innuitian- Lomonosov orogeny which marked the collision between Laurussia and the Arctic Craton;
* and the southern margin was a Pacific-style active margin
Active may refer to:
Music
* ''Active'' (album), a 1992 album by Casiopea
* Active Records, a record label
Ships
* ''Active'' (ship), several commercial ships by that name
* HMS ''Active'', the name of various ships of the British Royal ...
where the northward directed subduction of the ocean floor between Gondwana and Laurussia pushed continental fragments towards the latter.
During the Devonian (416-359 Mya) the combined landmass of Baltica and Avalonia rotated around Laurentia, which remained static near the Equator. The Laurentian warm, shallow seas and on shelves a diverse assemblage of benthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the ...
s exceeding . The Old Red Sandstone
The Old Red Sandstone is an assemblage of rocks in the North Atlantic region largely of Devonian age. It extends in the east across Great Britain, Ireland and Norway, and in the west along the northeastern seaboard of North America. It also exte ...
Continent stretched across northern Laurentia and into Avalonia and Baltica but for most of the Devonian a narrow seaway formed a barrier where the North Atlantic would later open. Tetrapods evolved from fish in the Late Devonian, with the oldest known fossils from Greenland. Low sea-levels during the Early Devonian produced natural barriers in Laurussia which resulted in provincialism
Parochialism is the state of mind, whereby one focuses on small sections of an issue rather than considering its wider context. More generally, it consists of being narrow in scope. In that respect, it is a synonym of " provincialism". It may, p ...
within the benthic fauna. In Laurentia the Transcontinental Arch divided brachiopod
Brachiopods (), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of trochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, w ...
s into two provinces, with one of them confined to a large embayment west of the Appalachians. By the Middle Devonian, these two provinces had been united into one and the closure of the Rheic Ocean finally united faunas across Laurussia. High plankton productivity from the Devonian-Carboniferous boundary resulted in anoxic event
Oceanic anoxic events or anoxic events ( anoxia conditions) describe periods wherein large expanses of Earth's oceans were depleted of dissolved oxygen (O2), creating toxic, euxinic (anoxic and sulfidic) waters. Although anoxic events have not ...
s that left black shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especia ...
s in the basins of Laurentia.
Pangaea
 The subduction of the Iapetus Ocean resulted in the first contact between Laurussia and Gondwana in the Late Devonian and terminated in full collision or the Hercynian/Variscan orogeny in the early Carboniferous (340 Mya). The Variscan orogeny closed the
The subduction of the Iapetus Ocean resulted in the first contact between Laurussia and Gondwana in the Late Devonian and terminated in full collision or the Hercynian/Variscan orogeny in the early Carboniferous (340 Mya). The Variscan orogeny closed the Rheic Ocean
The Rheic Ocean was an ocean which separated two major palaeocontinents, Gondwana and Laurussia (Laurentia- Baltica-Avalonia). One of the principal oceans of the Palaeozoic, its sutures today stretch from Mexico to Turkey and its closure result ...
(between Avalonia and Armorica) and the Proto-Tethys Ocean (between Armorica and Gondwana) to form the supercontinent Pangaea. The Variscan orogeny is complex and the exact timing and the order of the collisions between involved microcontinents has been debated for decades.
Pangaea was completely assembled by the Permian except for the Asian blocks. The supercontinent was centred on the Equator during the Triassic and Jurassic, a period that saw the emergence of the Pangaean megamonsoon. Heavy rainfall resulted in high groundwater tables, in turn resulting in peat formation and extensive coal deposits.
During the Cambrian and Early Ordovician, when wide oceans separated all major continents, only pelagic marine organisms, such as plankton, could move freely across the open ocean and therefore the oceanic gaps between continents are easily detected in the fossil records of marine bottom dwellers and non-marine species. By the Late Ordovician, when continents were pushed closer together closing the oceanic gaps, benthos
Benthos (), also known as benthon, is the community of organisms that live on, in, or near the bottom of a sea, river, lake, or stream, also known as the benthic zone.ostracod
Ostracods, or ostracodes, are a class of the Crustacea (class Ostracoda), sometimes known as seed shrimp. Some 70,000 species (only 13,000 of which are extant) have been identified, grouped into several orders. They are small crustaceans, typi ...
s and fishes remained isolated. As Laurussia formed during the Devonian and Pangaea formed, fish species in both Laurussia and Gondwana began to migrate between continents and before the end of the Devonian similar species were found on both sides of what remained of the Variscan barrier.
The oldest tree fossils are from the Middle Devonian pteridophyte Gilboa forest
Gilboa Fossil Forest, New York, United States, is a petrified forest and one of the oldest known forests. Located near the Gilboa Dam in Schoharie County, New York, the region is home to tree trunks from the Devonian period. The fossils, some of t ...
in central Laurussia (today New York, United States).
In the late Carboniferous, Laurussia was centred on the Equator and covered by tropical rainforests, commonly referred to as the coal forest
Coal forests were the vast swathes of wetlands that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous ( Pennsylvanian) and Permian times.Cleal, C. J. & Thomas, B. A. (2005). "Palaeozoic tropical rainforests and their e ...
. By the Permian, the climate had become arid and these rainforests collapsed, lycopsid
Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants known as lycopods, lycophytes or other terms including the component lyco-. Members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts. They have dichotomously branching s ...
s (giant mosses) were replaced by treeferns. In the dry climate a detritivorous fauna – including ringed worms, molluscs
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estim ...
, and some arthropods – evolved and diversified, alongside other arthropods who were herbivorous and carnivorous, and tetrapods – insectivores and piscivore
A piscivore () is a carnivorous animal that eats primarily fish. The name ''piscivore'' is derived . Piscivore is equivalent to the Greek-derived word ichthyophage, both of which mean "fish eater". Fish were the diet of early tetrapod evoluti ...
s such as amphibians and early amniotes.
Laurasia
During the Carboniferous–Permian Siberia, Kazakhstan, and Baltica collided in theUralian orogeny
The Uralian orogeny refers to the long series of linear deformation and mountain building events that raised the Ural Mountains, starting in the Late Carboniferous and Permian periods of the Palaeozoic Era, 323–299 and 299–251 million years ag ...
to form Laurasia.
The Palaezoic-Mesozoic transition was marked by the reorganisation of Earth's tectonic plates which resulted in the assembly of Pangaea, and eventually its break-up. Caused by the detachment of subducted mantle slabs, this reorganisation resulted in rising mantle plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hot ...
s that produced large igneous province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation ...
s when they reached the crust. This tectonic activity also resulted in the Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic (P–T, P–Tr) extinction event, also known as the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian Extinction and colloquially as the Great Dying, formed the boundary between the Permian and Triassic geologic periods, as ...
. Tentional stresses across Eurasia developed into a large system of rift basins (Urengoy, East Uralian-Turgay and Khudosey) and flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reac ...
s in the West Siberian Basin, the Pechora Basin, and South China.
Laurasia and Gondwana were equal in size but had distinct geological histories. Gondwana was assembled before the formation of Pangaea, but the assembly of Laurasia occurred during and after the formation of the supercontinent. These differences resulted in different patterns of basin formation and transport of sediments. East Antarctica was the highest ground within Pangaea and produced sediments that were transported across eastern Gondwana but never reached Laurasia. During the Palaeozoic, c. 30–40% of Laurasia but only 10–20% of Gondwana was covered by shallow marine water.
Asian blocks
During the assembly of Pangaea Laurasia grew as continental blocks broke off Gondwana's northern margin; pulled by old closing oceans in front of them and pushed by new opening oceans behind them. During the Neoproterozoic-Early Paleozoic break-up of Rodinia the opening of the Proto-Tethys Ocean split the Asian blocks – Tarim, Qaidam, Alex, North China, and South China – from the northern shores of Gondwana (north of Australia in modern coordinates) and the closure of the same ocean reassembled them along the same shores 500–460 Mya resulting in Gondwana at its largest extent. The break-up of Rodinia also resulted in the opening of the long-lived Paleo-Asian Ocean between Baltica and Siberia in the north and Tarim and North China in the south. The closure of this ocean is preserved in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt, the largest orogen on Earth. North China, South China, Indochina, and Tarim broke off Gondwana during the Silurian-Devonian; Palaeo-Tethys opened behind them. Sibumasu and Qiantang and other Cimmerian continental fragments broke off in the Early Permian. Lhasa, West Burma, Sikuleh, southwest Sumatra, West Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo broke off during the Late Triassic-Late Jurassic. During the Carboniferous and Permian, Baltica first collided with Kazakhstania and Siberia, then North China with Mongolia and Siberia. By the middle Carboniferous, however, South China had already been in contact with North China long enough to allow floral exchange between the two continents. The Cimmerian blocks rifted from Gondwana in the Late Carboniferous. In the early Permian, the Neo-Tethys Ocean opened behind the Cimmerian terranes (Sibumasu, Qiantang, Lhasa) and, in the late Carboniferous, the Palaeo-Tethys Ocean closed in front. The eastern branch of the Palaeo-Tethys Ocean, however, remained opened while Siberia was added to Laurussia and Gondwana collided with Laurasia. When the eastern Palaeo-Tethys closed 250–230 Mya, a series of Asian blocks – Sibumasu, Indochina, South China, Qiantang, and Lhasa – formed a separate southern Asian continent. This continent collided 240–220 Mya with a northern continent – North China, Qinling, Qilian, Qaidam, Alex, and Tarim – along the Central China orogen to form a combined East Asian continent. The northern margins of the northern continent collided with Baltica and Siberia 310–250 Ma, and thus the formation of the East Asian continent marked Pangaea at its greatest extent. By this time, the rifting of western Pangaea had already begun.Flora and fauna
Pangaea split in two as the Tethys Seaway opened between Gondwana and Laurasia in the Late Jurassic. The fossil record, however, suggests the intermittent presence of a Trans-Tethys land bridge, though the location and duration of such a land bridge remains enigmatic.Pine trees
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garde ...
evolved in the early Mesozoic c. 250 Mya and the pine genus originated in Laurasia in the Early Cretaceous c. 130 Mya in competition with faster growing flowering plants
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
. Pines adapted to cold and arid climates in environments where the growing season was shorter or wildfire common; this evolution limited pine range to between 31° and 50° north and resulted in a split into two subgenera: ''Strobus
'' Pinus'', the pines, is a genus of approximately 111 extant tree and shrub species. The genus is currently split into two subgenera: subgenus ''Pinus'' (hard pines), and subgenus ''Strobus'' (soft pines). Each of the subgenera have been furthe ...
'' adapted to stressful environments and ''Pinus
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden ...
'' to fire-prone landscapes. By the end of the Cretaceous pines were established across Laurasia, from North America to East Asia.
From the Triassic to the Early Jurassic, before the break-up of Pangaea, archosaurs (crurotarsans, pterosaurs and dinosaurs including birds) had a global distribution, especially crurotarsans, the group ancestral to the crocodilians
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period (Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
. This cosmopolitanism ended as Gondwana fragmented and Laurasia was assembled. Pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 ...
diversity reach a maximum in the Late Jurassic—Early Cretaceous and plate tectonic didn't affect the distribution of these flying reptiles. Crocodilian ancestors also diversified during the Early Cretaceous but were divided into Laurasian and Gondwanan populations; true crocodilians evolved from the former. The distribution of the three major groups of dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s – the sauropods
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
, theropods
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally ca ...
, and ornithischians – was similar that of the crocodilians. East Asia remained isolated with endemic species including psittacosaurs (horned dinosaurs) and Ankylosauridae
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known Ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Pa ...
(club-tailed, armoured dinosaurs).
Meanwhile, mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur o ...
slowly settled in Laurasia from Gondwana in the Triassic, the latter of which was the living area of their Permian ancestors
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder or a forebear, is a parent or ( recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from w ...
. They split in two groups, with one returning to Gondwana (and stayed there after Pangaea split) while the other
In phenomenology, the terms the Other and the Constitutive Other identify the other human being, in their differences from the Self, as being a cumulative, constituting factor in the self-image of a person; as acknowledgement of being real; h ...
staying in Laurasia (until further descendants switched to Gondwana starting from the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
).
In the early Eocene a peak in global warming led to a pan-Arctic fauna with alligators and amphibians present north of the Arctic Circle. In the early Palaeogene, landbridges still connected continents, allowing land animals to migrate between them. On the other hand, submerged areas occasionally divided continents: the Turgai Sea
The Turgai Sea, also known as the Turgay Sea, Turgai Strait, Obik Sea, Ural Sea or West Siberian Sea, was a large shallow body of salt water (an epicontinental or epeiric sea) during the Mesozoic through Cenozoic Eras. It extended north of the pre ...
separated Europe and Asia from the Middle Jurassic to the Oligocene and as this sea or strait dried out, a massive faunal interchange took place and the resulting extinction event in Europe is known as the ''Grande Coupure
Grande means "large" or "great" in many of the Romance languages. It may also refer to:
Places
* Grande, Germany, a municipality in Germany
* Grande Communications, a telecommunications firm based in Texas
* Grande-Rivière (disambiguation)
* Ar ...
''.
The Coraciiformes
The Coraciiformes are a group of usually colourful birds including the kingfishers, the bee-eaters, the rollers, the motmots, and the todies. They generally have syndactyly, with three forward-pointing toes (and toes 3 & 4 fused at their base) ...
(an order of birds including kingfishers) evolved in Laurasia. While this group now has a mostly tropical distribution, they originated in the Arctic in the late Eocene c. 35 Mya from where they diversified across Laurasia and farther south across the Equator.
The placental mammal group of Laurasiatheria
Laurasiatheria ("laurasian beasts") is a superorder of placental mammals that groups together true insectivores ( eulipotyphlans), bats ( chiropterans), carnivorans, pangolins ( pholidotes), even-toed ungulates ( artiodactyls), odd-toed ungulat ...
is named after Laurasia.
Final split
In the Triassic–Early Jurassic (c. 200 Mya), the opening of the CentralAtlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
was preceded by the formation of a series of large rift basins, such as the Newark Basin
The Newark Basin is a sediment-filled rift basin located mainly in northern New Jersey but also stretching into south-eastern Pennsylvania and southern New York. It is part of the system of Eastern North America Rift Basins.
Geology
Approximat ...
, between eastern North America, from what is today the Gulf of Mexico to Nova Scotia, and in Africa and Europe, from Morocco to Greenland.
By spreading had begun in the North Atlantic between the Rockall Plateau
The Rockall Trough ( gd, Clais Sgeir Rocail) is a deep-water bathymetric feature to the northwest of Scotland and Ireland, running roughly from southwest to northeast, flanked on the north by the Rockall Plateau and to the south by the Porcu ...
, a continental fragment sitting on top of the Eurasian Plate, and North America. By 56 Mya Greenland had become an independent plate, separated from North America by the Labrador Sea-Baffin Bay Rift. By 33 Mya spreading had ceased in the Labrador Sea and relocated to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The opening of the North Atlantic Ocean
The opening of the North Atlantic Ocean is a geological event that has occurred over millions of years, during which the supercontinent Pangea broke up. As modern-day Europe ( Eurasian plate) and North America ( North American Plate) separated d ...
had effectively broken Laurasia in two.
See also
*Laurasiatheria
Laurasiatheria ("laurasian beasts") is a superorder of placental mammals that groups together true insectivores ( eulipotyphlans), bats ( chiropterans), carnivorans, pangolins ( pholidotes), even-toed ungulates ( artiodactyls), odd-toed ungulat ...
* Laurasiformes
References
Notes
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control Former supercontinents Historical continents Carboniferous paleogeography Permian paleogeography Mesozoic paleogeography Paleocene paleogeography Natural history of North America Mesozoic North America Geology of Greenland Geology of North America Geology of Europe Geology of Asia Natural history of Europe Natural history of Asia