Protein Data bank on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a
 The PDB database is updated weekly ( UTC+0 Wednesday), along with its holdings list. , the PDB comprised:
::134,146 structures in the PDB have a
The PDB database is updated weekly ( UTC+0 Wednesday), along with its holdings list. , the PDB comprised:
::134,146 structures in the PDB have a
The Worldwide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB)
€”parent site to regional hosts (below) *
RCSB Protein Data Bank
(USA) *
PDBe
(Europe) *
PDBj
(Japan) *
BMRB, Biological Magnetic Resonance Data Bank
(USA)
€”documentation on both the PDB and PDBML file formats
—The RCSB's introduction to crystallography
PDBsum Home Page
€”Extracts data from other databases about PDB structures.
€”a PDB mirror especially for searching for nucleic acids
Introductory PDB tutorial sponsored by PDB
PDBe: Quick Tour on EBI Train OnLine
{{Crystallography Biological databases Crystallographic databases Protein structure Science and technology in the United States Bioinformatics Computational biology
database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases s ...
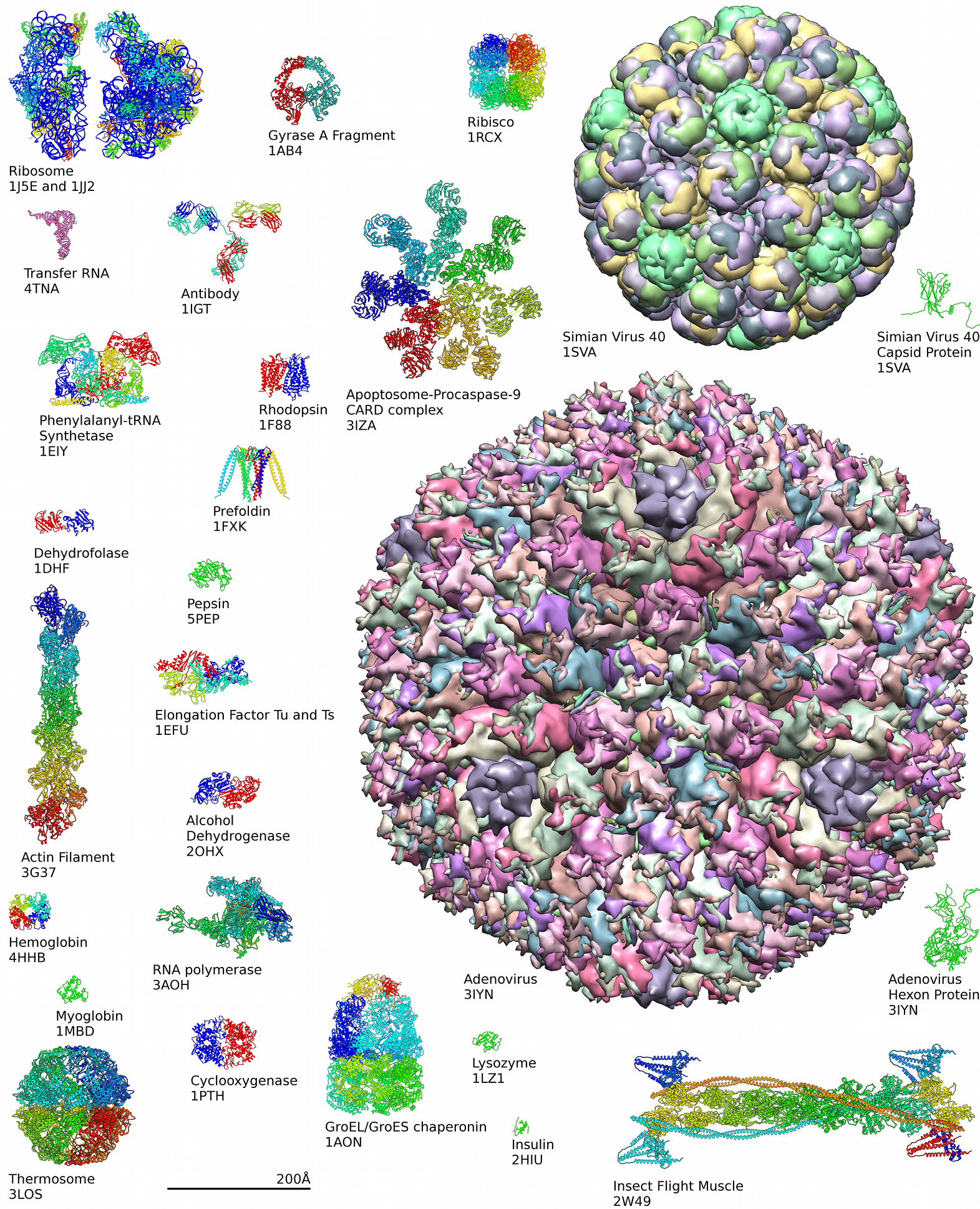
for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules, such as protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s and nucleic acids. The data, typically obtained by X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, or, increasingly, cryo-electron microscopy, and submitted by biologists and biochemists from around the world, are freely accessible on the Internet via the websites of its member organisations (PDBe, PDBj, RCSB, and BMRB). The PDB is overseen by an organization called the Worldwide Protein Data Bank, wwPDB.
The PDB is a key in areas of structural biology
Structural biology is a field that is many centuries old which, and as defined by the Journal of Structural Biology, deals with structural analysis of living material (formed, composed of, and/or maintained and refined by living cells) at every le ...
, such as structural genomics
Structural genomics seeks to describe the 3-dimensional structure of every protein encoded by a given genome. This genome-based approach allows for a high-throughput method of structure determination by a combination of experimental and modeling ...
. Most major scientific journals and some funding agencies now require scientists to submit their structure data to the PDB. Many other databases use protein structures deposited in the PDB. For example, SCOP
A (
or ) was a poet as represented in Old English poetry. The scop is the Old English counterpart of the Old Norse ', with the important difference that "skald" was applied to historical persons, and scop is used, for the most part, to designa ...
and CATH classify protein structures, while PDBsum provides a graphic overview of PDB entries using information from other sources, such as Gene ontology
The Gene Ontology (GO) is a major bioinformatics initiative to unify the representation of gene and gene product attributes across all species. More specifically, the project aims to: 1) maintain and develop its controlled vocabulary of gene and ge ...
.
History
Two forces converged to initiate the PDB: a small but growing collection of sets of protein structure data determined by X-ray diffraction; and the newly available (1968) molecular graphics display, theBrookhaven RAster Display Brookhaven may refer to:
Places Canada
* Amesbury, Toronto, also known as Brookhaven-Amesbury, a Toronto neighbourhood
United States
* Brookhaven, Georgia, a city just northeast of Atlanta
** Brookhaven/Oglethorpe (MARTA station), a passenger rail ...
(BRAD), to visualize these protein structures in 3-D. In 1969, with the sponsorship of Walter Hamilton at the Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Upton, Long Island, and was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former U.S. Army base and Japanese internment c ...
, Edgar Meyer (Texas A&M University
Texas A&M University (Texas A&M, A&M, or TAMU) is a public, land-grant, research university in College Station, Texas. It was founded in 1876 and became the flagship institution of the Texas A&M University System in 1948. As of late 2021, T ...
) began to write software to store atomic coordinate files in a common format to make them available for geometric and graphical evaluation. By 1971, one of Meyer's programs, SEARCH, enabled researchers to remotely access information from the database to study protein structures offline. SEARCH was instrumental in enabling networking, thus marking the functional beginning of the PDB.
The Protein Data Bank was announced in October 1971 in Nature New Biology as a joint venture between Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre, UK and Brookhaven National Laboratory, US.
Upon Hamilton's death in 1973, Tom Koeztle took over direction of the PDB for the subsequent 20 years. In January 1994, Joel Sussman of Israel's Weizmann Institute of Science
The Weizmann Institute of Science ( he, מכון ויצמן למדע ''Machon Vaitzman LeMada'') is a public research university in Rehovot, Israel, established in 1934, 14 years before the State of Israel. It differs from other Israeli unive ...
was appointed head of the PDB. In October 1998,
the PDB was transferred to the Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics (RCSB); the transfer was completed in June 1999. The new director was Helen M. Berman
Helen Miriam Berman is a Board of Governors Professor of Chemistry and Chemical Biology at Rutgers University and a former director of the RCSB Protein Data Bank (one of the member organizations of the Worldwide Protein Data Bank). A structural b ...
of Rutgers University (one of the managing institutions of the RCSB, the other being the San Diego Supercomputer Center
The San Diego Supercomputer Center (SDSC) is an organized research unit of the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). SDSC is located at the UCSD campus' Eleanor Roosevelt College east end, immediately north the Hopkins Parking Structure. ...
at UC San Diego
The University of California, San Diego (UC San Diego or colloquially, UCSD) is a public land-grant research university in San Diego, California. Established in 1960 near the pre-existing Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UC San Diego is t ...
). In 2003, with the formation of the wwPDB, the PDB became an international organization. The founding members are PDBe (Europe), RCSB (USA), and PDBj (Japan). The BMRB joined in 2006. Each of the four members of wwPDB can act as deposition, data processing and distribution centers for PDB data. The data processing refers to the fact that wwPDB staff review and annotate each submitted entry. The data are then automatically checked for plausibility (the source code for this validation software has been made available to the public at no charge).
Contents

 The PDB database is updated weekly ( UTC+0 Wednesday), along with its holdings list. , the PDB comprised:
::134,146 structures in the PDB have a
The PDB database is updated weekly ( UTC+0 Wednesday), along with its holdings list. , the PDB comprised:
::134,146 structures in the PDB have a structure factor
In condensed matter physics and crystallography, the static structure factor (or structure factor for short) is a mathematical description of how a material scatters incident radiation. The structure factor is a critical tool in the interpretation ...
file.
::10,289 structures have an NMR restraint file.
::4,814 structures in the PDB have a chemical shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of an atomic nucleus relative to a standard in a magnetic field. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure o ...
s file.
::4,718 structures in the PDB have a 3DEM map file deposited in EM Data Bank
Most structures are determined by X-ray diffraction, but about 10% of structures are determined by protein NMR. When using X-ray diffraction, approximations of the coordinates of the atoms of the protein are obtained, whereas using NMR, the distance between pairs of atoms of the protein is estimated. The final conformation of the protein is obtained from NMR by solving a distance geometry Distance geometry is the branch of mathematics concerned with characterizing and studying sets of points based ''only'' on given values of the distances between pairs of points. More abstractly, it is the study of semimetric spaces and the isom ...
problem. After 2013, a growing number of proteins are determined by cryo-electron microscopy. Clicking on the numbers in the linked external table displays examples of structures determined by that method.
For PDB structures determined by X-ray diffraction that have a structure factor file, their electron density map may be viewed. The data of such structures is stored on the "electron density server".
Historically, the number of structures in the PDB has grown at an approximately exponential rate, with 100 registered structures in 1982, 1,000 structures in 1993, 10,000 in 1999, and 100,000 in 2014.
File format
The file format initially used by the PDB was called the PDB file format. The original format was restricted by the width of computer punch cards to 80 characters per line. Around 1996, the "macromolecular Crystallographic Information file" format, mmCIF, which is an extension of the CIF format was phased in. mmCIF became the standard format for the PDB archive in 2014. In 2019, the wwPDB announced that depositions for crystallographic methods would only be accepted in mmCIF format. An XML version of PDB, called PDBML, was described in 2005. The structure files can be downloaded in any of these three formats, though an increasing number of structures do not fit the legacy PDB format. Individual files are easily downloaded into graphics packages from Internet URLs: * For PDB format files, use, e.g.,http://www.pdb.org/pdb/files/4hhb.pdb.gz http://pdbe.org/download/4hhb http://www.pdb.org/pdb/files/4hhb.xml.gz http://pdbe.org/pdbml/4hhb 4hhb" is the PDB identifier. Each structure published in PDB receives a four-character alphanumeric identifier, its PDB ID. (This is not a unique identifier for biomolecules, because several structures for the same molecule—in different environments or conformations—may be contained in PDB with different PDB IDs.)
Viewing the data
The structure files may be viewed using one of several free and open source computer programs, including Jmol,Pymol
PyMOL is an open source but proprietary molecular visualization system created by Warren Lyford DeLano. It was commercialized initially by DeLano Scientific LLC, which was a private software company dedicated to creating useful tools that becom ...
, VMD, Molstar and Rasmol. Other non-free, shareware programs include ICM-Browser, MDL Chime
MDL ''Chime'' was a free plugin used by web browsers to display the three-dimensional structures of molecules. and was based on the RasMol code.
Chime was used by a wide range of biochemistry web sites for the visualization of macromolecules ...
, UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera (or simply Chimera) is an extensible program for interactive visualization and analysis of molecular structures and related data, including density maps, supramolecular assemblies, sequence alignments, docking results, trajectories, a ...
, Swiss-PDB Viewer, StarBiochem (a Java-based interactive molecular viewer with integrated search of protein databank), Sirius, and VisProt3DS (a tool for Protein Visualization in 3D stereoscopic view in anaglyph and other modes), and Discovery Studio. The RCSB PDB website contains an extensive list of both free and commercial molecule visualization programs and web browser plugins.
See also
*Crystallographic database A crystallographic database is a database specifically designed to store information about the structure of molecules and crystals. Crystals are solids having, in all three dimensions of space, a regularly repeating arrangement of atoms, ions, or ...
* Protein structure
Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers specifically polypeptides formed from sequences of amino acids, the monomers of the polymer. A single amino acid monom ...
* Protein structure prediction
Protein structure prediction is the inference of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence—that is, the prediction of its secondary and tertiary structure from primary structure. Structure prediction is different ...
* Protein structure database
* PDBREPORT lists all anomalies (also errors) in PDB structures
* PDBsum—extracts data from other databases about PDB structures
* Proteopedia—a collaborative 3D encyclopedia of proteins and other molecules
References
External links
The Worldwide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB)
€”parent site to regional hosts (below) *
RCSB Protein Data Bank
(USA) *
PDBe
(Europe) *
PDBj
(Japan) *
BMRB, Biological Magnetic Resonance Data Bank
(USA)
€”documentation on both the PDB and PDBML file formats
—The RCSB's introduction to crystallography
PDBsum Home Page
€”Extracts data from other databases about PDB structures.
€”a PDB mirror especially for searching for nucleic acids
Introductory PDB tutorial sponsored by PDB
PDBe: Quick Tour on EBI Train OnLine
{{Crystallography Biological databases Crystallographic databases Protein structure Science and technology in the United States Bioinformatics Computational biology