Proposals for a Jewish state on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
There were several proposals for a Jewish state in the course of
 In 1820, in a precursor to modern
In 1820, in a precursor to modern
 On March 28, 1928, the Presidium of the General Executive Committee of the
On March 28, 1928, the Presidium of the General Executive Committee of the
Jewish Autonomous Region official government website. Retrieved August 30, 2007 On August 20, 1930, the General Executive Committee of the Russian Soviet Republic (
Jewish history
Jewish history is the history of the Jews, and their nation, religion, and culture, as it developed and interacted with other peoples, religions, and cultures. Although Judaism as a religion first appears in Greek records during the Hellenisti ...
between the destruction of ancient Israel
The history of ancient Israel and Judah begins in the Southern Levant during the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age. "Israel" as a people or tribal confederation (see Israelites) appears for the first time in the Merneptah Stele, an inscri ...
and the founding of the modern State of Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. While some of those have come into existence, others were never implemented. The Jewish national homeland usually refers to the State of Israel or the Land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine (see also Isr ...
, depending on political and religious beliefs. Jews and their supporters, as well as their detractors and anti-Semites have put forth plans for Jewish states.
Ararat city (U. S.)
 In 1820, in a precursor to modern
In 1820, in a precursor to modern Zionism
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
, Mordecai Manuel Noah tried to found a Jewish homeland at Grand Island in the Niagara River
The Niagara River () is a river that flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. It forms part of the border between the province of Ontario in Canada (on the west) and the state of New York in the United States (on the east). There are diffe ...
, to be called "Ararat" after Mount Ararat
Mount Ararat or , ''Ararat''; or is a snow-capped and dormant compound volcano in the extreme east of Turkey. It consists of two major volcanic cones: Greater Ararat and Little Ararat. Greater Ararat is the highest peak in Turkey and th ...
, the Biblical resting place of Noah's Ark
Noah's Ark ( he, תיבת נח; Biblical Hebrew: ''Tevat Noaḥ'')The word "ark" in modern English comes from Old English ''aerca'', meaning a chest or box. (See Cresswell 2010, p.22) The Hebrew word for the vessel, ''teva'', occurs twice in ...
. He erected a monument at the island which read "Ararat, a City of Refuge for the Jews, founded by Mordecai M. Noah in the Month of Tishri, 5586 (September, 1825) and in the Fiftieth Year of American Independence." In his ''Discourse on the Restoration of the Jews'', Noah proclaimed his faith that the Jews would return and rebuild their ancient homeland. Noah called on America to take the lead in this endeavor.Selig Adler and Thomas E. Connolly. ''From Ararat to Suburbia: the History of the Jewish Community of Buffalo'' (Philadelphia: the Jewish Publication Society of America, 1960, Library of Congress Number 60-15834) Some have speculated whether Noah's utopian ideas may have influenced Joseph Smith
Joseph Smith Jr. (December 23, 1805June 27, 1844) was an American religious leader and founder of Mormonism and the Latter Day Saint movement. When he was 24, Smith published the Book of Mormon. By the time of his death, 14 years later, h ...
, who founded the Latter Day Saint movement
The Latter Day Saint movement (also called the LDS movement, LDS restorationist movement, or Smith–Rigdon movement) is the collection of independent church groups that trace their origins to a Christian Restorationist movement founded by Jo ...
in Upstate New York a few years later.
British Uganda Program
The BritishUganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The ...
Program was a plan to give a portion of British East Africa
East Africa Protectorate (also known as British East Africa) was an area in the African Great Lakes occupying roughly the same terrain as present-day Kenya from the Indian Ocean inland to the border with Uganda in the west. Controlled by Bri ...
to the Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
ish people as a homeland.
The offer was first made by British Colonial Secretary Joseph Chamberlain
Joseph Chamberlain (8 July 1836 – 2 July 1914) was a British statesman who was first a radical Liberal, then a Liberal Unionist after opposing home rule for Ireland, and eventually served as a leading imperialist in coalition with the C ...
to Theodore Herzl's Zionist group in 1903. He offered of the Mau Plateau in what is today Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
. The offer was a response to pogrom
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russian ...
s against the Jews in Russia, and it was hoped the area could be a refuge from persecution for the Jewish people.
The idea was brought to the World Zionist Organization
The World Zionist Organization ( he, הַהִסְתַּדְּרוּת הַצִּיּוֹנִית הָעוֹלָמִית; ''HaHistadrut HaTzionit Ha'Olamit''), or WZO, is a non-governmental organization that promotes Zionism. It was founded as the ...
's Zionist Congress at its sixth meeting in 1903 in Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (B ...
. There a fierce debate ensued. The African land was described as an "ante-chamber to the Holy Land", but other groups felt that accepting the offer would make it more difficult to establish a Jewish state in Palestine. Before the vote on the matter, the Russian delegation stormed out in opposition. In the end, the motion to consider the plan passed by 295 to 177 votes.
The next year, a three-man delegation was sent to inspect the plateau. Its high elevation gave it a temperate climate, making it suitable for European settlement. However, the observers found a dangerous land filled with lions and other creatures. Moreover, it was populated by a large number of Maasai who did not seem at all amenable to an influx of people coming from Europe.
After receiving this report, Congress decided in 1905 to politely decline the British offer. Some Jews, who viewed this as a mistake, formed the Jewish Territorialist Organization
The Jewish Territorial Organisation, known as the ITO, was a Jewish political movement which first arose in 1903 in response to the British Uganda Offer, but which was institutionalized in 1905. Its main goal was to find an alternative territory ...
with the aim of establishing a Jewish state anywhere.Schreiber, Mordecai. ''The Shengold Jewish Encyclopedia'', 2003. Page 291.
Jewish Autonomous Oblast in USSR
 On March 28, 1928, the Presidium of the General Executive Committee of the
On March 28, 1928, the Presidium of the General Executive Committee of the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
passed the decree "On the attaching for Komzet
Komzet (russian: Комитет по земельному устройству еврейских трудящихся, ) was the ''Committee for the Settlement of Toiling Jews on the Land'' (some English sources use the word "working" instead of ...
of free territory near the Amur River in the Far East for settlement of the working Jews." The decree meant that there was "a possibility of establishment of a Jewish administrative territorial unit on the territory of the named region".Establishment and Development of the JARJewish Autonomous Region official government website. Retrieved August 30, 2007 On August 20, 1930, the General Executive Committee of the Russian Soviet Republic (
RSFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
) accepted the decree "On formation of the Birobidzhan
Birobidzhan ( rus, Биробиджа́н, p=bʲɪrəbʲɪˈdʐan; yi, ביראָבידזשאַן, ''Birobidzhan'') is a town and the administrative center of the Jewish Autonomous Oblast, Russia, located on the Trans-Siberian Railway, near th ...
national region in the structure of the Far Eastern Territory". The State Planning Committee considered the Birobidzhan national region as a separate economic unit. In 1932, the first scheduled figures of the region development were considered and authorized.
On May 7, 1934, the Presidium accepted the decree on its transformation in the Jewish Autonomous Region within the Russian Republic. In 1938, with formation of the Khabarovsk Territory, the Jewish Autonomous Region (JAR) was included in its structure.
According to Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet Union, Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as Ge ...
's national policy, each of the national groups that formed the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
would receive a territory in which to pursue cultural autonomy
Minority rights are the normal individual rights as applied to members of racial, ethnic, class, religious, linguistic or gender and sexual minorities, and also the collective rights accorded to any minority group.
Civil-rights movements ...
in a socialist framework. In that sense, it was also a response to two supposed threats to the Soviet state: Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in th ...
, which ran counter to official state policy of atheism
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no d ...
; and Zionism
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
, the creation of the modern State of Israel, which countered Soviet views of nationalism. The idea was to create a new "Soviet Zion", where a proletarian Jewish culture
Jewish culture is the culture of the Jewish people, from its formation in ancient times until the current age. Judaism itself is not a faith-based religion, but an orthoprax and ethnoreligion, pertaining to deed, practice, and identity. Jewis ...
could be developed. Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ve ...
, rather than Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
, would be the national language, and a new socialist literature and arts would replace religion as the primary expression of culture.
Stalin's theory on the National Question held that a group could only be a nation if it had a territory, and since there was no Jewish territory, per se, the Jews were not a nation and did not have national rights. Jewish Communists argued that the way to solve this ideological dilemma was to create a Jewish territory, hence the ideological motivation for the Jewish Autonomous Oblast. Politically, it was also considered desirable to create a Soviet Jewish homeland as an ideological alternative to Zionism and to the theory put forward by Socialist Zionists such as Ber Borochov
Dov Ber Borochov (russian: Дов-Бер Борохов; 3 July 1881 – 17 December 1917) was a Marxist Zionist and one of the founders of the Labor Zionist movement. He was also a pioneer in the study of the Yiddish language.
Biogr ...
that the Jewish Question
The Jewish question, also referred to as the Jewish problem, was a wide-ranging debate in 19th- and 20th-century European society that pertained to the appropriate status and treatment of Jews. The debate, which was similar to other " national ...
could be resolved by creating a Jewish territory in Palestine. Thus Birobidzhan was important for propaganda purposes as an argument against Zionism which was a rival ideology to Marxism
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
among left-wing Jews.
Another important goal of the Birobidzhan project was to increase settlement in the remote Soviet Far East, especially along the vulnerable border with China. In 1928, there was virtually no settlement in the area, while Jews had deep roots in the western half of the Soviet Union, in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
, Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
and Russia proper. In fact, there had initially been proposals to create a Jewish Soviet Republic in the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
or in part of Ukraine but these were rejected because of fears of antagonizing non-Jews in those regions.
The geography and climate of Birobidzhan were harsh, the landscape largely swampland, and any new settlers would have to build their lives from scratch. Some have even claimed that Stalin was also motivated by anti-Semitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
in selecting Birobidzhan; that he wanted to keep the Jews as far away from the centers of power as possible. On the other hand, Ukrainians and Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
ns were reluctant to have a Jewish national home carved out of their territory, even though most Soviet Jews lived there, and there were very few alternative territories without rival national claims to them.
By the 1930s, a massive propaganda campaign was underway to induce more Jewish settlers to move there. Some methods used the standard Soviet propaganda tools of the era and included posters and Yiddish-language novels describing a socialist utopia there. Other methods bordered on the bizarre. In one instance, leaflets promoting Birobidzhan were dropped from an airplane over a Jewish neighborhood in Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
. In another instance, a government-produced Yiddish film called ''Seekers of Happiness
''Seekers of Happiness'' (russian: Искатели счастья, Iskateli schastya) is a Soviet film from 1936 trying to attract Jews to the Jewish Autonomous Oblast (JAO) in the far east of the USSR. It is also known by its alternative name, ...
'' told the story of a Jewish family that fled the Depression in the United States to make a new life for itself in Birobidzhan.
As the Jewish population grew, so did the impact of Yiddish culture on the region. A Yiddish newspaper, the '' Birobidzhaner Shtern'' ("Star of Birobidzhan"), was established; a theater troupe was created; and streets being built in the new city were named after prominent Yiddish authors such as Sholom Aleichem and Y. L. Peretz. The Yiddish language was deliberately bolstered as a basis for efforts to secularize the Jewish population and, despite the general curtailment of this action as described immediately below, the ''Birobidzhaner Shtern'' continues to publish a section in Yiddish.
The Birobidzhan experiment ground to a halt in the mid-1930s, during Stalin's first campaign of purges. Jewish leaders were arrested and executed, and Yiddish schools were shut down. Shortly after this, World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
brought to an abrupt end concerted efforts to bring Jews east.
There was a slight revival in the Birobidzhan idea after the war as a potential home for Jewish refugee
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution.
s. During that time, the Jewish population of the region peaked at almost one-third of the total. But efforts in this direction ended, with the Doctors' plot
The "Doctors' plot" affair, group=rus was an alleged conspiracy of prominent Soviet medical specialists to murder leading government and party officials. It was also known as the case of saboteur doctors or killer doctors. In 1951–1953, a gr ...
, the establishment of Israel as a Jewish state, and Stalin's second wave of purges shortly before his death. Again the Jewish leadership was arrested and efforts were made to stamp out Yiddish culture—even the Judaica collection in the local library was burned. In the ensuing years, the idea of an autonomous Jewish region in the Soviet Union was all but forgotten.
Some scholars, such as Louis Rapoport, Jonathan Brent and Vladimir Naumov, assert that Stalin had devised a plan to deport all of the Jews of the Soviet Union to Birobidzhan much as he had internally deported other national minorities such as the Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
and Volga Germans, forcing them to move thousands of miles from their homes. The Doctors' Plot
The "Doctors' plot" affair, group=rus was an alleged conspiracy of prominent Soviet medical specialists to murder leading government and party officials. It was also known as the case of saboteur doctors or killer doctors. In 1951–1953, a gr ...
may have been the first element of this plan. If so, the plan was aborted by Stalin's death on March 5, 1953.
With the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
and new liberal emigration policies, most of the remaining Jewish population left for Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
and Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. In 1991, the Jewish Autonomous Oblast was transferred from under the jurisdiction of Khabarovsk Krai
Khabarovsk Krai ( rus, Хабаровский край, r=Khabarovsky kray, p=xɐˈbarəfskʲɪj kraj) is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia. It is geographically located in the Russian Far East and is a part of the Far Eastern Federal Distr ...
to the jurisdiction of the Federation, but by then most of the Jews had left and the remaining Jews now constituted less than 2% of the local population. Nevertheless, Yiddish is again taught in the schools, a Yiddish radio station is in operation, and as noted above, the ''Birobidzhaner Shtern'' includes a section in Yiddish.
Fugu plan (Japan)
Despite the little evidence to suggest that the Japanese had ever contemplated a Jewish state or a Jewish autonomous region, RabbiMarvin Tokayer
Marvin Tokayer (born 1936) is an American Rabbi and author who served as a United States Air Force chaplain in Japan. He was later advised by the Lubavitcher Rebbe to return to Japan where he served for eight years as the only rabbi in the country. ...
and Mary Swartz published a book called ''The Fugu Plan'' in 1979. In this partly fictionalized book, Tokayer & Swartz gave the name the to memoranda written in the 1930s Imperial Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent forma ...
proposing settling Jewish refugees escaping Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
-occupied Europe in Japanese territories. Tokayer and Swartz claim that the plan, which was viewed by its proponents as risky but potentially rewarding for Japan, was named after the Japanese word for puffer-fish, a delicacy that can be fatally poisonous if incorrectly prepared.Adam Gamble and Takesato Watanabe. ''A Public Betrayed: An Inside Look at Japanese Media Atrocities and Their Warnings to the West.'' Page 196-197.
Tokayer and Swartz base their claim on statements made by Captain Koreshige Inuzuka. They alleged that such a plan was first discussed in 1934 and then solidified in 1938, supported by notables such as Inuzuka, Ishiguro Shiro and Norihiro Yasue; however, the signing of the Tripartite Pact
The Tripartite Pact, also known as the Berlin Pact, was an agreement between Germany, Italy, and Japan signed in Berlin on 27 September 1940 by, respectively, Joachim von Ribbentrop, Galeazzo Ciano and Saburō Kurusu. It was a defensive milit ...
in 1941 and other events prevented its full implementation. The memorandums were not called The Fugu Plan.
Ben-Ami Shillony Ben-Ami Shillony (born October 28, 1937 (?), Poland) is professor emeritus of Japanese history at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
His wife, until her death, was , professor emerita of French literature at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
S ...
, a professor at the Hebrew University
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI; he, הַאוּנִיבֶרְסִיטָה הַעִבְרִית בִּירוּשָׁלַיִם) is a public university, public research university based in Jerusalem, Israel. Co-founded by Albert Einstein ...
of Jerusalem, confirms that the statements upon which Tokayer and Swartz based their claim were taken out of context and that the translation with which they worked was flawed. Shillony's view is further supported by Kiyoko Inuzuka. In 'The Jews and the Japanese: The Successful Outsiders', he questioned whether the Japanese ever contemplated establishing a Jewish state or a Jewish autonomous region.
Madagascar plan
The Madagascar plan was a suggested policy of theThird Reich
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
government of Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
Germany to forcibly relocate the Jewish population of Europe to the island of Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Afric ...
.Browning, Christopher R. ''The Origins of the Final Solution.'' 2004. Page 81
The evacuation of European Jewry to the island of Madagascar was not a new concept. Henry Hamilton Beamish, Arnold Leese
Arnold Spencer Leese (16 November 1878 – 18 January 1956) was a British fascist politician. Leese was initially prominent as a veterinary expert on camels. A virulent anti-Semite, he led his own fascist movement, the Imperial Fascist League, ...
, Lord Moyne, German scholar Paul de Lagarde
Paul Anton de Lagarde (2 November 1827 – 22 December 1891) was a German biblical scholar and orientalist, sometimes regarded as one of the greatest orientalists of the 19th century. Lagarde's strong support of anti-Semitism, vocal opposition t ...
and the British, French, and Polish governments had all contemplated the idea. Nazi Germany seized upon it, and in May 1940, in his ''Reflections on the Treatment of Peoples of Alien Races in the East'', Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of th ...
declared: "I hope that the concept of Jews will be completely extinguished through the possibility of a large emigration of all Jews to Africa or some other colony."
Although some discussion of this plan had been brought forward from 1938 by other well-known Nazi ideologues, such as Julius Streicher
Julius Streicher (12 February 1885 – 16 October 1946) was a member of the Nazi Party, the '' Gauleiter'' (regional leader) of Franconia and a member of the '' Reichstag'', the national legislature. He was the founder and publisher of the vir ...
, Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German politician, military leader and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which ruled Germany from 1933 to 1 ...
, and Joachim von Ribbentrop
Ulrich Friedrich Wilhelm Joachim von Ribbentrop (; 30 April 1893 – 16 October 1946) was a German politician and diplomat who served as Minister of Foreign Affairs of Nazi Germany from 1938 to 1945.
Ribbentrop first came to Adolf Hitler's not ...
, it was not until June 1940 that the plan was actually set in motion. As victory in France was imminent, it was clear that all French colonies would soon come under German control, and the Madagascar Plan could be realized. It was also felt that a potential peace treaty with Great Britain would put the British navy at Germany's disposal for use in the evacuation.
With Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
's approval, Adolf Eichmann
Otto Adolf Eichmann ( ,"Eichmann"
'' SS. The plan was postponed after the Germans failed to defeat the British in the
 * In 1902, Zionist
* In 1902, Zionist
by Beverley Hooper, Australian Dictionary of Biography, Volume 16, Melbourne University Press, 2002, pp 298–299. Online Ed. published by Australian National University * In 1941 Lord Moyne suggested to
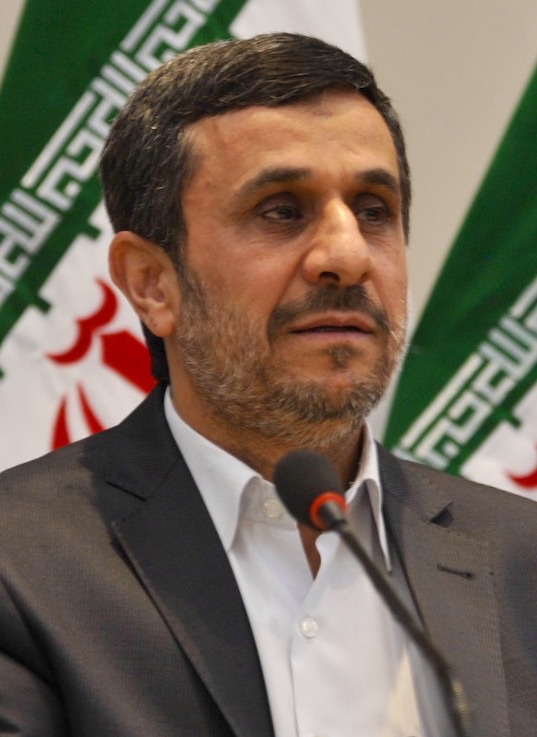 In an interview on Iran's
In an interview on Iran's
IRNA, December 14, 2005."Iranian leader denies Holocaust"
BBC News, December 14, 2005. Retrieved October 23, 2008.CNN
Iranian leader: Holocaust a 'myth'
Article. Retrieved March 30, 2007
Albert Einstein on the Proposal to Create a Jewish Homeland in Peru, 1930
Shapell Manuscript Foundation Zionism Anti-Zionism Settlement schemes Jewish nationalism
'' SS. The plan was postponed after the Germans failed to defeat the British in the
Battle of Britain
The Battle of Britain, also known as the Air Battle for England (german: die Luftschlacht um England), was a military campaign of the Second World War, in which the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) of the Royal Navy defende ...
later in 1940. In 1942, the so-called " Territorial Solution to the Jewish question
The Jewish question, also referred to as the Jewish problem, was a wide-ranging debate in 19th- and 20th-century European society that pertained to the appropriate status and treatment of Jews. The debate, which was similar to other " national ...
" was abandoned in favour of the " Final Solution to the Jewish Question".
British Guiana
A 1939 plan to resettle a modest number of Jewish refugees in British Guiana was shelved at the outbreak of war. In March 1940, the issue of an alternative Jewish Homeland was raised and British Guiana (nowGuyana
Guyana ( or ), officially the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern mainland of South America. Guyana is an indigenous word which means "Land of Many Waters". The capital city is Georgetown. Guyana is bordered by the ...
) was discussed in this context. But the British Government decided that "the problem is at present too problematical to admit of the adoption of a definite policy and must be left for the decision of some future Government in years to come".
Jewish self-governing territory within Italian East Africa
The Italian government during theFascist
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and the ...
period proposed offering to resolve the "Jewish problem" in Europe and in Palestine by resettling Jews into a Jewish self-governing territory within the northwest territory of Italian East Africa
Italian East Africa ( it, Africa Orientale Italiana, AOI) was an Italian colony in the Horn of Africa. It was formed in 1936 through the merger of Italian Somalia, Italian Eritrea, and the newly occupied Ethiopian Empire, conquered in the S ...
that would place them among the Beta Israel
The Beta Israel ( he, בֵּיתֶא יִשְׂרָאֵל, ''Bēteʾ Yīsrāʾēl''; gez, ቤተ እስራኤል, , modern ''Bēte 'Isrā'ēl'', EAE: "Betä Ǝsraʾel", "House of Israel" or "Community of Israel"), also known as Ethiopian Jews ...
Jewish community already living in Italian East Africa. Jews from Europe and Palestine would be resettled to the north-west Ethiopian districts of Gojjam
Gojjam ( ''gōjjām'', originally ጐዛም ''gʷazzam'', later ጐዣም ''gʷažžām'', ጎዣም ''gōžžām'') is a historical province in northwestern Ethiopia, with its capital city at Debre Marqos.
Gojjam's earliest western boundary ex ...
and Begemder
Begemder ( amh, በጌምድር; also known as Gondar or Gonder, alternative name borrowed from its 20th century capital Gondar) was a province in northwest Ethiopia.
Etymology
A plausible source for the name ''Bega'' is that the word means " ...
, along with the Beta Israel community. The proposed Jewish self-governing territory was to be within the Italian Empire
The Italian colonial empire ( it, Impero coloniale italiano), known as the Italian Empire (''Impero Italiano'') between 1936 and 1943, began in Africa in the 19th century and comprised the colonies, protectorates, concessions and dependenci ...
. The Fascist regime at the time showed racialist attitudes towards the Beta Israel Jews of Ethiopia since they are racially black and the Fascist regime deemed whites to be superior to blacks; and racial laws enacted in Italy also applied to the Beta Israel Jews in Italian East Africa that forbade intimate relationships between blacks and whites. Mussolini's plan was never implemented.
Port Davey (Australia)
With the support of the thenPremier of Tasmania
The premier of Tasmania is the head of the executive government in the Australian state of Tasmania. By convention, the leader of the party or political grouping which has majority support in the House of Assembly is invited by the governor of ...
, Robert Cosgrove
Sir Robert Cosgrove (28 December 1884 – 25 August 1969) was an Australian politician who was the 30th and longest-serving Premier of Tasmania. He held office for over 18 years, serving from 1939 to 1947 and from 1948 to 1958. His involv ...
(in office from 1939), Critchley Parker proposed a Jewish settlement at Port Davey
Port Davey is an oceanic inlet located in the south west region of Tasmania, Australia.
Port Davey was named in honour of Thomas Davey, a former Governor of Tasmania. Port Davey is contained within the Port Davey/Bathurst Harbour Marine Na ...
, in south west Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
. Parker surveyed the area, but his death in 1942 put an end to the idea.
Other attempts of Jewish self-governance throughout history
Ancient times
*Adiabene
Adiabene was an ancient kingdom in northern Mesopotamia, corresponding to the northwestern part of ancient Assyria. The size of the kingdom varied over time; initially encompassing an area between the Zab Rivers, it eventually gained control of N ...
– an ancient kingdom in Mesopotamia with its capital at Arbil was ruled by Jewish converts during the first century.
* Anilai and Asinai – Babylonian-Jewish chieftains.
* Mahoza
Al-Mada'in ( ar, المدائن, , ; ) was an ancient metropolis situated on the Tigris, Tigris River in modern-day Iraq. It was located between the ancient royal centers of Ctesiphon and Seleucia, and was founded by the Sasanian Empire, Sassanid ...
– During the beginning of the sixth century Mar-Zutra II
Mar-Zutra II was a Jewish Exilarch who led a revolt against the Sasanian rulers in 495 CE and achieved seven years of political independence in Mahoza.
Mar-Zutra II became Exilarch of the Jewish community in Babylon at the age of fifteen in 483 CE ...
formed a politically independent state where he ruled from Mahoza, today in central Iraq, for about 7 years.
* Nehardea – the seat of the exilarch
The exilarch was the leader of the Jewish community in Persian Mesopotamia (modern day Iraq) during the era of the Parthians, Sasanians and Abbasid Caliphate up until the Mongol invasion of Baghdad in 1258, with intermittent gaps due to ongoing ...
in Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c ...
.
* Khaybar
KhaybarOther standardized Arabic transliterations: / . Anglicized pronunciation: , . ( ar, خَيْبَر, ) is an oasis situated some north of the city of Medina in the Medina Province of Saudi Arabia. Prior to the rise of Islam in the 7th ...
– a self-governed oasis in Arabia.
* Himyar – there were many Jewish kings at this region of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the north and Oman to the northeast and ...
since 390 CE when a local chieftain named Tub'a Abu Kariba As'ad formed an Empire.
* Kingdom of Semien – a Jewish kingdom in Ethiopia
Middle ages to 19th century
* TheResh Galuta
The exilarch was the leader of the Jewish community in Persian Mesopotamia (modern day Iraq) during the era of the Parthians, Sasanians and Abbasid Caliphate up until the Mongol invasion of Baghdad in 1258, with intermittent gaps due to ongoing ...
or Exilarch exercised considerable authority over the Jewish community in the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
and later the Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
* Makhir of Narbonne and possibly his descendants were acknowledged by the Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippi ...
emperors as ethnarch
Ethnarch (pronounced , also ethnarches, el, ) is a term that refers generally to political leadership over a common ethnic group or homogeneous kingdom. The word is derived from the Greek words ('' ethnos'', "tribe/nation") and (''archon'', " ...
s of western Jewry
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, with their seat at Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in Southern France in the Occitanie region. It lies from Paris in the Aude department, of which it is a sub-prefecture. It is located about from the shores of the ...
* Council of Four Lands – the central body of Jewish authority in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
from 1580 to 1764. Seventy delegates from local '' kehillot'' met to discuss taxation and other issues important to the Jewish community. The "four lands" were Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Großpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest cit ...
, Little Poland, Ruthenia
Ruthenia or , uk, Рутенія, translit=Rutenia or uk, Русь, translit=Rus, label=none, pl, Ruś, be, Рутэнія, Русь, russian: Рутения, Русь is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin as one of several terms ...
and Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
.
* There are unconfirmed reports that Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
, who briefly occupied
' ( Norwegian: ') is a Norwegian political thriller TV series that premiered on TV2 on 5 October 2015. Based on an original idea by Jo Nesbø, the series is co-created with Karianne Lund and Erik Skjoldbjærg. Season 2 premiered on 10 Octobe ...
a foothold in the Levant in 1799 planned a proclamation inviting Jews to create a state. The alleged proclamation was said to have been shelved following his defeat at Acre.
* Principality of Malabar from the eighth century to 1524 the Cochin Jews
Cochin Jews (also known as Malabar Jews or Kochinim, from ) are the oldest group of Jews in India, with roots that are claimed to date back to the time of King Solomon. The Cochin Jews settled in the Kingdom of Cochin in South India, now ...
had an ethnarch ruling over them.
* The Mountain Jews
Mountain Jews or Caucasus Jews also known as Juhuro, Juvuro, Juhuri, Juwuri, Juhurim, Kavkazi Jews or Gorsky Jews ( he, יהודי קווקז ''Yehudey Kavkaz'' or ''Yehudey he-Harim''; russian: Горские евреи, translit=Gorskie Yevrei ...
of remote parts of Daghestan
Dagestan ( ; rus, Дагеста́н, , dəɡʲɪˈstan, links=yes), officially the Republic of Dagestan (russian: Респу́блика Дагеста́н, Respúblika Dagestán, links=no), is a republic of Russia situated in the North Ca ...
in the Caucasus were self-ruling for much of the medieval and early modern period.
* Jarawa Berber tribe on the Maghreb in the seventh century, believed to be Jews, and resisted arabicization under the leadership of Queen Kahina.
* Jodensavanne: an attempt to establish a safe haven for Jews in Surinam.
Modern times
Max Bodenheimer
Max Isidor Bodenheimer ( he, מקס בודנהיימר; 12 March 1865 in Stuttgart – 19 July, 1940 in Jerusalem) was a lawyer and one of the main figures in German Zionism. An associate of Theodor Herzl, he was the first president of the Zioni ...
proposed the idea of the League of East European States The League of East European States or Federation of East European States (german: osteuropäischer Staatenbund) was a 1914 proposal by the German Committee for Freeing of Russian Jews for a German-dominated consociational buffer state to be establi ...
, which would entail the establishment of a buffer state (Pufferstaat) within the Jewish Pale of Settlement
The Pale of Settlement (russian: Черта́ осе́длости, '; yi, דער תּחום-המושבֿ, '; he, תְּחוּם הַמּוֹשָב, ') was a western region of the Russian Empire with varying borders that existed from 1791 to 19 ...
of Russia, composed of the former Polish provinces annexed by Russia.Michlic, Joanna Beata (2006). ''Poland's Threatening Other: The Image of the Jew from 1880 to the Present'', pp. 48, 55–56. University of Nebraska Press. .Blobaum, Robert (2005). ''Anti-Semitism and Its Opponents in Modern Poland'', p. 61. Cornell University Press. .
* In the early 20th century Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
and El Arish
ʻArish or el-ʻArīsh ( ar, العريش ' , ''Hrinokorura'') is the capital and largest city (with 164,830 inhabitants ) of the North Sinai Governorate of Egypt, as well as the largest city on the entire Sinai Peninsula, lying on the Medit ...
on the Sinai Peninsula in Egypt and its environs were proposed as a site for Jewish settlement by Herzl Herzl is both a given name and a surname. Notable people with the name include:
Given name:
*Herzl Berger
*Herzl Bodinger
*Herzl Rosenblum
* Herzl Yankl Tsam
Surname:
*Theodor Herzl
See also
*Mount Herzl
Mount Herzl ( he, הַר הֶרְצְ� ...
.
* Several proposals for a Jewish "republic" under Arab or Transjordanian suzerainty were put forward by the Hashemite
The Hashemites ( ar, الهاشميون, al-Hāshimīyūn), also House of Hashim, are the royal family of Jordan, which they have ruled since 1921, and were the royal family of the kingdoms of Hejaz (1916–1925), Syria (1920), and Iraq (1921� ...
kings of Hejaz
The Hejaz (, also ; ar, ٱلْحِجَاز, al-Ḥijāz, lit=the Barrier, ) is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. It includes the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif, and Baljurashi. It is also known as the "Western Prov ...
and emirs of Transjordan; the closest these proposals came to fruition was the Faisal–Weizmann Agreement, which proved to be impossible to implement subsequent to the division of the Levant into League of Nations Mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administ ...
s.
* Eastern Arabia
Eastern Arabia, historically known as al-Baḥrayn ( ar, البحرين) until the 18th century, is a region stretched from Basra to Khasab along the Persian Gulf coast and included parts of modern-day Bahrain, Kuwait, Eastern Saudi Arabia, Unite ...
A Russian Jewish doctor residing in France named Dr M. L. Rothstein proposed the establishment of a Jewish state in al-Hasa modern day Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
in September 1917.
*Jewish autonomy in Crimea
Jewish autonomy in Crimea was a project in the Soviet Union to create an autonomous region for Jews in the Crimean peninsula carried out during the 1920s and 1930s. Following the WWII and the creation of the Jewish Autonomous Oblast in the ...
* Sosúa
Sosúa is a beach town in the Puerto Plata province of the Dominican Republic. Located approximately from the Gregorio Luperón International Airport in San Felipe de Puerto Plata.
The town is divided into three sectors: ''El Batey'', which i ...
is a town located in the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
, in 1938 the Dominican dictator Rafael Leónidas Trujillo gave permission to 500 European Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
(mainly Austrians and Germans) to settle in the village of Sosúa. The Jews did build a synagogue and a museum there. They also created a cheese and dairy factory still in existence today.
* Moisés Ville (Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ve ...
: מאָזעסוויל) is a small town (comuna) in the province of Santa Fe, Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
, it was founded on October 23, 1889, by Eastern European and Russian Jews, escaping pogrom
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russian ...
s and persecution.
* Salonika
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
in the Ottoman Empire was populated mainly by Sephardim
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
with Judeo-Spanish
Judaeo-Spanish or Judeo-Spanish (autonym , Hebrew script: , Cyrillic: ), also known as Ladino, is a Romance language derived from Old Spanish. Originally spoken in Spain, and then after the Edict of Expulsion spreading through the Ottoman Emp ...
as the main language. After its incorporation to the Kingdom of Greece
The Kingdom of Greece ( grc, label= Greek, Βασίλειον τῆς Ἑλλάδος ) was established in 1832 and was the successor state to the First Hellenic Republic. It was internationally recognised by the Treaty of Constantinople, wh ...
, it remained very Jewish until the arrival of Greek refugees from Anatolia in the 1920s.
* Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and share ...
– In 1935, British Zionist
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
journalist Leo Elton traveled to Albania, apparently at his own initiative, to see if it would be possible to establish a Jewish national entity there. It seems the only surviving trace of his voyage is his report 10 years later to Hebrew University
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (HUJI; he, הַאוּנִיבֶרְסִיטָה הַעִבְרִית בִּירוּשָׁלַיִם) is a public university, public research university based in Jerusalem, Israel. Co-founded by Albert Einstein ...
's first president, Judah Leib Magnes. The document rests in the Central Archive for the History of the Jewish People at the university's Givat Ram
Givat Ram ( he, גִּבְעַת רָם) is a neighborhood in central Jerusalem. It is the site of Kiryat HaMemshala (Hebrew: קריית הממשלה, ''lit.'' Government complex), which includes many of Israel's most important national instituti ...
campus in Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
. Elton's journey was spurred on by the increasing persecution of German Jews two years into the Nazi regime and Britain's refusal to increase the quotas on Jewish immigration to Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
. Elton writes that he first read of the idea in British newspapers reporting that the Albanian government welcomed Jewish immigration.
* The Kimberley Plan was a failed plan by the Freeland League, led by Isaac Nachman Steinberg, to resettle Jewish refugees from Europe in the Kimberley region in Australia before and during the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europ ...
.Steinberg, Isaac Nachman (1888–1957)by Beverley Hooper, Australian Dictionary of Biography, Volume 16, Melbourne University Press, 2002, pp 298–299. Online Ed. published by Australian National University * In 1941 Lord Moyne suggested to
David Ben-Gurion
David Ben-Gurion ( ; he, דָּוִד בֶּן-גּוּרִיּוֹן ; born David Grün; 16 October 1886 – 1 December 1973) was the primary national founder of the State of Israel and the first prime minister of Israel. Adopting the nam ...
that Jewish refugees could be resettled in East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
after Germany was defeated and the area's German inhabitants were expelled. Ben-Gurion responded that "the only way to get Jews to go o East Prussiawould be with machine guns."
* Kiryas Joel, New York – a town composed largely of Yiddish-speaking Hasidic
Hasidism, sometimes spelled Chassidism, and also known as Hasidic Judaism ( Ashkenazi Hebrew: חסידות ''Ḥăsīdus'', ; originally, "piety"), is a Jewish religious group that arose as a spiritual revival movement in the territory of conte ...
Jews affiliated with the Satmar dynasty.
* Kiryas Tosh, Boisbriand, Quebec
Boisbriand is an off-island suburb of Montreal, in southwestern Quebec, Canada, on the north shore of the Rivière des Mille Îles in the Thérèse-De Blainville Regional County Municipality.
The Hasidic community of Kiryas Tosh is located ...
- a town composed largely of Yiddish-speaking Hasidic Jews affiliated with the Tosh
Tosh may refer to:
People
* Tosh (surname)
* Tosh (nickname)
* Tosh Townend (born 1985), professional skateboarder
* Tosh Van der Sande (born 1990), Belgian professional cyclist
Places
* Tosh, Himachal Pradesh, India; a village
* Kiryas ...
dynasty.
* Qırmızı Qəsəbə
Qırmızı Qəsəbə (, ), translated as "Red Town" (russian: Красная Слобода, ; he, , ), is a village and municipality in the Quba District of Azerbaijan. It has a population of approximately 3,598 people. Outside of Israel and th ...
– The town is the primary settlement of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
's population of Mountain Jews
Mountain Jews or Caucasus Jews also known as Juhuro, Juvuro, Juhuri, Juwuri, Juhurim, Kavkazi Jews or Gorsky Jews ( he, יהודי קווקז ''Yehudey Kavkaz'' or ''Yehudey he-Harim''; russian: Горские евреи, translit=Gorskie Yevrei ...
, who make up the population of approximately 4,000.
* Sitka, Alaska
russian: Ситка
, native_name_lang = tli
, settlement_type = Consolidated city-county, Consolidated city-borough
, image_skyline = File:Sitka 84 Elev 135.jpg
, image_caption = Downtown Sitka in 1984
...
– a plan for Jews to settle the Sitka area in Alaska, the Slattery Report
The Slattery Report, officially titled ''The Problem of Alaskan Development'', was produced by the United States Department of the Interior under President Franklin D. Roosevelt's secretary Harold L. Ickes in 1939–40. It was named after Undersecr ...
, was proposed by U.S. President Franklin Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
's Secretary of the Interior Secretary of the Interior may refer to:
* Secretary of the Interior (Mexico)
* Interior Secretary of Pakistan
* Secretary of the Interior and Local Government (Philippines)
* United States Secretary of the Interior
See also
*Interior ministry
An ...
Harold L. Ickes
Harold LeClair Ickes ( ; March 15, 1874 – February 3, 1952) was an American administrator, politician and lawyer. He served as United States Secretary of the Interior for nearly 13 years from 1933 to 1946, the longest tenure of anyone to hold th ...
in 1939 but turned down. An alternate history
Alternate history (also alternative history, althist, AH) is a genre of speculative fiction of stories in which one or more historical events occur and are resolved differently than in real life. As conjecture based upon historical fact, alte ...
of the proposal where Jews do settle in Sitka is the subject of author Michael Chabon
Michael Chabon ( ;
born May 24, 1963) is an American novelist, screenwriter, columnist, and short story writer. Born in Washington, DC, he spent a year studying at Carnegie Mellon University before transferring to the University of Pittsburgh, gr ...
's novel ''The Yiddish Policemen's Union
''The Yiddish Policemen's Union'' is a 2007 novel by American author Michael Chabon. The novel is a detective story set in an alternative history version of the present day, based on the premise that during World War II, a temporary settlement ...
''.
* Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
– Vietnamese government officials in 2005 told Israeli officials of a plan discussed between Ho Chi Minh
(: ; born ; 19 May 1890 – 2 September 1969), commonly known as (' Uncle Hồ'), also known as ('President Hồ'), (' Old father of the people') and by other aliases, was a Vietnamese revolutionary and statesman. He served as P ...
and Moshe Dayan
Moshe Dayan ( he, משה דיין; 20 May 1915 – 16 October 1981) was an Israeli military leader and politician. As commander of the Jerusalem front in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, Chief of Staff of the Israel Defense Forces (1953–1958) dur ...
to invite Jews to live in the country. No documentation of the offer and discussion has yet been made available. In 1966, David Ben-Gurion reported that Ho Chi Minh had suggested to him (in Paris in 1946) that he form a government in exile in North Vietnam. He turned down the offer, saying that "for obvious reasons, this was unacceptable."
Proposals for a second Jewish state
Following the creation of the State of Israel, the goal of establishing a Jewish state was achieved. However, since then, there have been some proposals for a second Jewish state, in addition to Israel: * ManyIsraeli settlers
Israeli may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the State of Israel
* Israelis, citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel
* Modern Hebrew, a language
* ''Israeli'' (newspaper), published from 2006 to 2008
* Guni Israeli (b ...
in the West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
have mulled declaring independence as the State of Judea
The State of Judea ( he, מְדִינַת יְהוּדָה, ''Medīnat Yəhuda'') is a proposed halachic state in the West Bank put forward by Israeli Jewish settlers. After the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) declared the existence ...
should Israel ever withdraw from the West Bank. The idea first surfaced following the PLO's declaration of a Palestinian state in 1988. Some settler activists feared that Israel would bow to international pressure and withdraw from the West Bank, and sought to lay the groundwork for a Halachic state in the West Bank should this come to pass. In January 1989, several hundred activists met and announced their intention to create such a state in the event of Israeli withdrawal. The idea has been raised multiple times since.
* In May 2007, Israeli art student Ronen Eidelman, who was studying in Germany at the time, launched the "Medinat Weimar" movement, a satirical
Satire is a genre of the visual, literary, and performing arts, usually in the form of fiction and less frequently non-fiction, in which vices, follies, abuses, and shortcomings are held up to ridicule, often with the intent of shaming or ...
political movement for the establishment of a second Jewish state in Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million.
Erfurt is the capital and lar ...
, Germany, with Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
as its capital.
Proposals for alternative Jewish homelands and anti-Zionism
Among early Zionists, there was some consideration given to alternatives outside of the Middle East as a temporary measure. Later as a prevailing strain ofanti-Zionism
Anti-Zionism is opposition to Zionism. Although anti-Zionism is a heterogeneous phenomenon, all its proponents agree that the creation of the modern State of Israel, and the movement to create a sovereign Jewish state in the region of Palestin ...
puts forth an opposition to Israel's existence in the Middle East, a smaller wing of anti-Zionism focuses upon the circumstances of the resulting region-wide conflict which followed Israel's Jewish settlement and 1948 declaration of independence; this ideology proposes the hypothetical resettlement of the entire Jewish Israeli population in another isolated region of the world outside the Middle East.
Proposed deportation of Israelis to Central Europe
Prominent anti-Zionists includingAzzam Tamimi
Azzam Tamimi (sometimes spelled Azam Tamimi; born 1955, Hebron, West Bank) is a British-Palestinian Jordanian academic and political activist affiliated with the Muslim Brotherhood. He is currently a freelance presenter at Alhiwar TV Channel. He ...
and Helen Thomas have proposed sending the Jews in Israel to Europe or the United States.
In January 2006, Tamimi wrote that creation of the state of Israel "was a solution to a European problem and the Palestinians are under no obligation to be the scapegoats for Europe's failure to recognise the Jews as human beings entitled to inalienable rights. Hamas, like all Palestinians, refuses to be made to pay for the criminals who perpetrated the Holocaust. However, Israel is a reality and that is why Hamas is willing to deal with that reality in a manner that is compatible with its principles."
In 2010 after being asked by Rabbi David Nesenoff on camera for comments on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, Helen Thomas, a Lebanese-American journalist and correspondent for United Press International
United Press International (UPI) is an American international news agency whose newswires, photo, news film, and audio services provided news material to thousands of newspapers, magazines, radio and television stations for most of the 2 ...
, suggested that Jews should "get the hell out of Palestine" and go back to Poland, Germany "And America and everywhere else. Why push people out of there who have lived there for centuries?". The resulting uproar led to an initial apology and her resignation from UPI, but she defended her comments in other venues afterward.
Mahmud Ahmadinejad's proposal for a Jewish state
 In an interview on Iran's
In an interview on Iran's Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
channel ' Al-Alam' on December 8, 2005, Iranian President Mahmud Ahmadinejad
Mahmoud Ahmadinejad ( fa, محمود احمدینژاد, Mahmūd Ahmadīnežād ), born Mahmoud Sabbaghian ( fa, محمود صباغیان, Mahmoud Sabbāghyān, 28 October 1956),
said that if Germany and Austria feel responsible for the massacre of Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, they should host a state of Israel on their own soil. Speaking at a news conference, Ahmadinejad said most Jews in Israel "have no roots in Palestine, but they are holding the destiny of Palestine in their hands and allow themselves to kill the Palestinian people", adding:
On December 14, 2005, in Zahedan, Iran, Ahmadinejad said: "People in Palestine are getting killed every day by the new rulers of Palestine. As a consequence of the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europ ...
, the Europeans took land from the Palestinians for a Jewish state. I don't care whether the Holocaust took place or not, but it is illogical to give a piece of Palestine for compensation. Some people make an awful fuss about that Holocaust, make a myth
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narrat ...
of it."Polling only solution to Palestine problem, PresidentIRNA, December 14, 2005."Iranian leader denies Holocaust"
BBC News, December 14, 2005. Retrieved October 23, 2008.CNN
Iranian leader: Holocaust a 'myth'
Article. Retrieved March 30, 2007
Criticism
Such proposals to remove Jews from Israel/Palestine (or, at least, to claim another territory as a better homeland for the Jewish people than Israel) have been criticized as contradicting of both the corporate right toself-determination
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a '' jus cogens'' rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It sta ...
and indigenous land rights. Furthermore, suggestions or demands for Jewish people to move back to Central Europe are seen as implicitly targeting or minimizing the history of persecution against Ashkenazi Jews in Central Europe (including, among other events, the Final Solution
The Final Solution (german: die Endlösung, ) or the Final Solution to the Jewish Question (german: Endlösung der Judenfrage, ) was a Nazi plan for the genocide of individuals they defined as Jews during World War II. The "Final Solution to th ...
enacted by the German Nazi Party). Yoram Dori, an op-ed writer at ''The Jerusalem Post
''The Jerusalem Post'' is a broadsheet newspaper based in Jerusalem, founded in 1932 during the British Mandate of Palestine by Gershon Agron as ''The Palestine Post''. In 1950, it changed its name to ''The Jerusalem Post''. In 2004, the pap ...
'', reproached Helen Thomas for wanting to "exile us back to the inferno, as if nothing happened 65 years ago in Europe, as if our hands have not been stretched out for peace since the establishment of the state." Richard Cohen, op-ed writer for ''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large n ...
'', described Thomas' comments as "revealing how very little she knew", citing post-World War II Polish violence against Polish Jews returning to their home villages from Displaced persons camp
A refugee camp is a temporary settlement built to receive refugees and people in refugee-like situations. Refugee camps usually accommodate displaced people who have fled their home country, but camps are also made for internally displaced peo ...
s.
Finally, there are millions of Mizrahi Jews
Mizrahi Jews ( he, יהודי המִזְרָח), also known as ''Mizrahim'' () or ''Mizrachi'' () and alternatively referred to as Oriental Jews or ''Edot HaMizrach'' (, ), are a grouping of Jewish communities comprising those who remained ...
and Sephardi Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
that hail from countries other than the traditional Central European countries that the proposals believe Jews should go back to. In his autobiographical novel '' A Tale of Love and Darkness'', Israeli writer Amos Oz
Amos Oz ( he, עמוס עוז; born Amos Klausner; 4 May 1939 – 28 December 2018) was an Israeli writer, novelist, journalist, and intellectual. He was also a professor of Hebrew literature at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. From 1967 onw ...
recounted his father's account of how the walls in Europe were covered in graffiti saying "Jews, go to Palestine" but when he reached Palestine, the walls were scrawled with the words "Jews, get out of Palestine."
See also
* Halachic state *Jewish homeland
A homeland for the Jewish people is an idea rooted in Jewish history, religion, and culture. The Jewish aspiration to return to Zion, generally associated with divine redemption, has suffused Jewish religious thought since the destruction ...
* Jewish settlement in the Japanese Empire
* List of Jewish states and dynasties
* Proposals for a Palestinian state
The history of the State of Palestine describes the creation and evolution of the State of Palestine in the West Bank and Gaza Strip.
During the Mandatory period, numerous plans of partition of Palestine were proposed but without the agreeme ...
* Territorialism
Territorialism can refer to:
* Animal territorialism, the animal behavior of defending a geographical area from intruders
* Environmental territorialism, a stance toward threats posed toward individuals, communities or nations by environmental even ...
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Albert Einstein on the Proposal to Create a Jewish Homeland in Peru, 1930
Shapell Manuscript Foundation Zionism Anti-Zionism Settlement schemes Jewish nationalism
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
Lists of proposals