Promised Land on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In the
 The concept of the Promised Land is first mentioned in the
The concept of the Promised Land is first mentioned in the
Abrahamic religions
The term Abrahamic religions is used to group together monotheistic religions revering the Biblical figure Abraham, namely Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The religions share doctrinal, historical, and geographic overlap that contrasts them wit ...
, the "Promised Land" ( ) refers to a swath of territory in the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
that was bestowed upon Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
and his descendants by God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
. In the context of the Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally writt ...
, these descendants are originally understood to have been the Israelites
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age.
Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations ...
, whose forefather was Jacob
Jacob, later known as Israel, is a Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions. He first appears in the Torah, where he is described in the Book of Genesis as a son of Isaac and Rebecca. Accordingly, alongside his older fraternal twin brother E ...
, who was a son of Abraham's son Isaac
Isaac ( ; ; ; ; ; ) is one of the three patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and the Baháʼí Faith. Isaac first appears in the Torah, in wh ...
. The concept of the Promised Land largely overlaps with the Land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine. The definition ...
( Zion) or the Holy Land
The term "Holy Land" is used to collectively denote areas of the Southern Levant that hold great significance in the Abrahamic religions, primarily because of their association with people and events featured in the Bible. It is traditionall ...
in a biblical/religious sense and with Canaan
CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
or Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
in a secular/geographic sense. Although the Book of Numbers
The Book of Numbers (from Biblical Greek, Greek Ἀριθμοί, ''Arithmoi'', , ''Bəmīḏbar'', ; ) is the fourth book of the Hebrew Bible and the fourth of five books of the Jewish Torah. The book has a long and complex history; its final f ...
provides some definition for the Promised Land's boundaries, they are not delineated with precision, but it is universally accepted that the core areas lie in and around Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
. According to the biblical account, the Promised Land was not inherited until the Israelite conquest of Canaan, which took place shortly after the Exodus
The Exodus (Hebrew language, Hebrew: יציאת מצרים, ''Yəṣīʾat Mīṣrayīm'': ) is the Origin myth#Founding myth, founding myth of the Israelites whose narrative is spread over four of the five books of the Torah, Pentateuch (specif ...
.
Biblical narrative
 The concept of the Promised Land is first mentioned in the
The concept of the Promised Land is first mentioned in the Book of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek language, Greek ; ; ) is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its incipit, first word, (In the beginning (phrase), 'In the beginning'). Genesis purpor ...
, which is the first book of the Torah
The Torah ( , "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is also known as the Pentateuch () ...
, which collectively refers to the first five books of the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' God In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
is claimed to have spoken the following promises to . '' God In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
in several verses of Genesis (the first book of the Torah
The Torah ( , "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is also known as the Pentateuch () ...
), which a modern English Bible translates to:
:The LORD had said to Abram, "Leave your country, your people and your father's household and go to the land I will show you." –
:The LORD appeared to Abram and said, "To your offspring r seedI will give this land." –
Later in what is called the covenant of the pieces
According to the Hebrew Bible, the covenant of the pieces or covenant between the parts () is an important event in Jewish History. In this central narrative God revealed himself to Abraham and made a covenant with him (in the site known nowadays ...
, a verse is said to describe what are known as "borders of the Land" (''Gevulot Ha-aretz''):
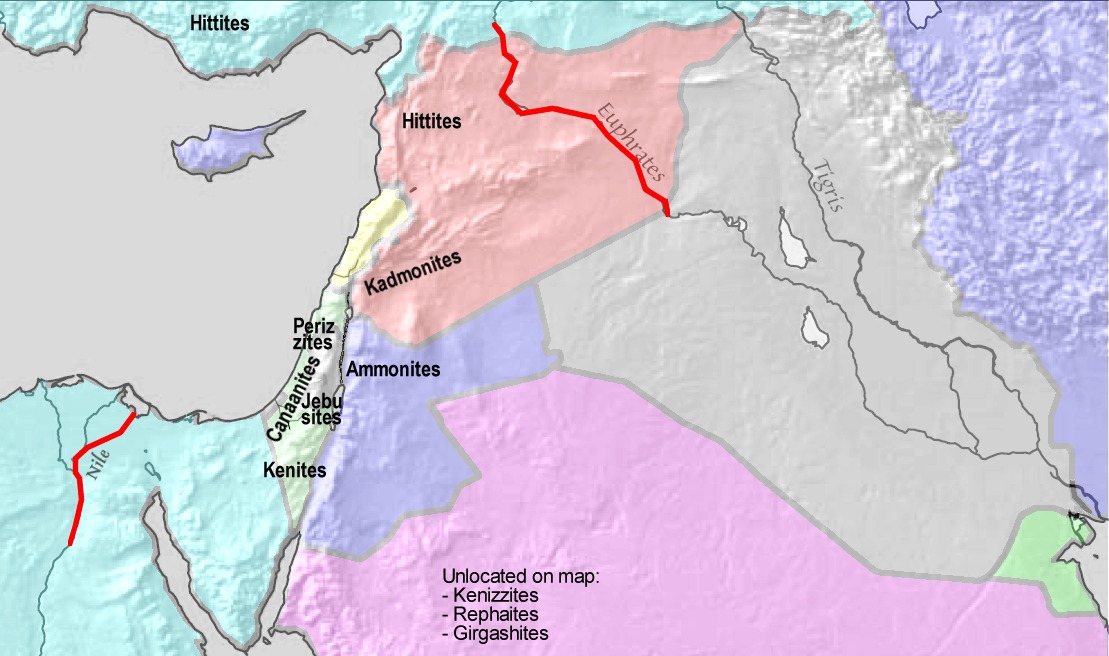
:On that day the Lord made a covenant with Abram and said, "To your descendants I give this land, from the Wadi of Egypt to the great river, the Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
– the land of the Kenites, Kenizzites, Kadmonites, Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
, Perizzites, Rephaites, Amorites
The Amorites () were an ancient Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic-speaking Bronze Age people from the Levant. Initially appearing in Sumerian records c. 2500 BC, they expanded and ruled most of the Levant, Mesopotamia and parts of Eg ...
, Canaanites, Girgashites and Jebusites
The Jebusites (; ) were, according to the Book of Joshua and Books of Samuel from the Hebrew Bible, a Canaanite tribe that inhabited Jerusalem, called Jebus () before the conquest initiated by Joshua (, ) and completed by David (). According to s ...
." –
These allegedly divine promises were given prior to the birth of Abraham's sons. Abraham's family tree includes both the Ishmaelite tribes (the claimed ancestry of Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
and of the Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam () are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets are categorized as messengers (; sing. , ), those who transmit divine revelation, mos ...
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
) through Abraham's first son Ishmael
In the Bible, biblical Book of Genesis, Ishmael (; ; ; ) is the first son of Abraham. His mother was Hagar, the handmaiden of Abraham's wife Sarah. He died at the age of 137. Traditionally, he is seen as the ancestor of the Arabs.
Within Isla ...
and the Israelite tribes (the claimed ancestry of Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
and Samaritans
Samaritans (; ; ; ), are an ethnoreligious group originating from the Hebrews and Israelites of the ancient Near East. They are indigenous to Samaria, a historical region of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah that ...
) through Abraham's second son Isaac
Isaac ( ; ; ; ; ; ) is one of the three patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and the Baháʼí Faith. Isaac first appears in the Torah, in wh ...
.
Subsequent confirmations
God later confirms the promise to Abraham's sonIsaac
Isaac ( ; ; ; ; ; ) is one of the three patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, Islam, and the Baháʼí Faith. Isaac first appears in the Torah, in wh ...
(), and then to Isaac's son Jacob
Jacob, later known as Israel, is a Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions. He first appears in the Torah, where he is described in the Book of Genesis as a son of Isaac and Rebecca. Accordingly, alongside his older fraternal twin brother E ...
() in terms of "the land on which you are lying". Jacob is later renamed "Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
" () and his descendants are called the Children of Israel or the Twelve Tribes of Israel
The Twelve Tribes of Israel ( , ) are described in the Hebrew Bible as being the descendants of Jacob, a Patriarchs (Bible), Hebrew patriarch who was a son of Isaac and thereby a grandson of Abraham. Jacob, later known as Israel (name), Israel, ...
.
The Torah's subsequent Book of Exodus
The Book of Exodus (from ; ''Šəmōṯ'', 'Names'; ) is the second book of the Bible. It is the first part of the narrative of the Exodus, the origin myth of the Israelites, in which they leave slavery in Biblical Egypt through the strength of ...
describes it as "land flowing with milk and honey" () and gives verses on how to treat the prior occupants and marks the borders in terms of the Red Sea
The Red Sea is a sea inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and th ...
, the "Sea of the Philistines
Philistines (; LXX: ; ) were ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan during the Iron Age in a confederation of city-states generally referred to as Philistia.
There is compelling evidence to suggest that the Philistines origi ...
", and the "River", which a modern English Bible translates to:
: "I will establish your borders from the Red Sea to the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
, and from the desert to the Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
River. I will give into your hands the people who live in the land, and you will drive them out before you. Do not make a covenant with them or with their gods. Do not let them live in your land or they will cause you to sin against me, because the worship of their gods will certainly be a snare to you." –
The Israelites
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age.
Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations ...
lived in a smaller area of former Canaan
CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
ite land and land east of the Jordan River after the legendary prophet Moses
In Abrahamic religions, Moses was the Hebrews, Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites out of slavery in the The Exodus, Exodus from ancient Egypt, Egypt. He is considered the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet in Judaism and Samaritani ...
led the Israelite Exodus out of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
(). The Torah's Book of Deuteronomy
Deuteronomy (; ) is the fifth book of the Torah (in Judaism), where it is called () which makes it the fifth book of the Hebrew Bible and Christian Old Testament.
Chapters 1–30 of the book consist of three sermons or speeches delivered to ...
presents this occupation as their God's fulfillment of the promise (). Moses anticipated that their God might subsequently give the Israelites land reflecting the boundaries of the original promise – if they were obedient to the covenant ().
Interpretations
Jewish interpretation
The concept of the Promised Land is a central religious belief of the Jewish people and a key tenet ofZionism
Zionism is an Ethnic nationalism, ethnocultural nationalist movement that emerged in History of Europe#From revolution to imperialism (1789–1914), Europe in the late 19th century that aimed to establish and maintain a national home for the ...
, the Jewish national movement which established the State of Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
.
Mainstream Jewish tradition regards the promise made to Abraham, Isaac and Jacob as applying to anyone a member of the Jewish people, including proselytes and in turn their descendants and is signified through the ''brit milah'' (rite of circumcision).
Christian interpretation
In theNew Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
, the descent and promise is reinterpreted along religious lines. In the Epistle to the Galatians
The Epistle to the Galatians is the ninth book of the New Testament. It is a letter from Paul the Apostle to a number of Early Christian communities in Galatia. Scholars have suggested that this is either the Galatia (Roman province), Roman pro ...
, Paul the Apostle
Paul, also named Saul of Tarsus, commonly known as Paul the Apostle and Saint Paul, was a Apostles in the New Testament, Christian apostle ( AD) who spread the Ministry of Jesus, teachings of Jesus in the Christianity in the 1st century, first ...
draws attention to the formulation of the promise, avoiding the term "seeds" in the plural (meaning many people), choosing instead "seed," meaning one person, who, he understands to be Jesus
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
(and those united with him). For example, in Galatians 3:16 he notes:
: "The promises were spoken to Abraham and to his seed. Scripture does not say "and to seeds," meaning many people, but "and to your seed," meaning one person, who is Christ."
In Galatians 3:28 –29 Paul goes further, noting that the expansion of the promise from singular to the plural is not based on genetic/physical association, but a spiritual/religious one:
:"There is neither Jew nor Gentile
''Gentile'' () is a word that today usually means someone who is not Jewish. Other groups that claim Israelite heritage, notably Mormons, have historically used the term ''gentile'' to describe outsiders. More rarely, the term is used as a synony ...
, neither slave nor free, neither male nor female, for you are all one in Christ Jesus. If you belong to Christ, then you are Abraham's seed, and heirs according to the promise."
In it is written:
:"It was not through the law that Abraham and his offspring received the promise that he would be heir of the world, but through the righteousness that comes by faith."
German Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Isr ...
commentator Johann Friedrich Karl Keil states that the covenant is through Isaac, but notes that Ishmael
In the Bible, biblical Book of Genesis, Ishmael (; ; ; ) is the first son of Abraham. His mother was Hagar, the handmaiden of Abraham's wife Sarah. He died at the age of 137. Traditionally, he is seen as the ancestor of the Arabs.
Within Isla ...
's descendants have held much of that land through time.
American colonialism
Many European colonists saw America as the "Promised Land", representing a haven from religious conflicts andpersecution
Persecution is the systematic mistreatment of an individual or group by another individual or group. The most common forms are religious persecution, racism, and political persecution, though there is naturally some overlap between these term ...
. For instance, Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should b ...
minister John Cotton's 1630 sermon God's Promise to His Plantation gave colonizers departing England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
to Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
repeated references to the Exodus story, and later German immigrants sang: "America ... is a beautiful land that God promised to Abraham."
In a sermon celebrating independence in 1783, Yale president Ezra Stiles implied Americans were chosen and delivered from bondage to a Promised Land: "the Lord shall have made his American Israel 'high above all nations which he hath made'," reflecting language from Deuteronomy of the promise.
Shawnee/Lenape
The Lenape (, , ; ), also called the Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada.
The Lenape's historica ...
scholar Steven Newcomb argued in his 2008 book ''Pagans in the Promised Land: Decoding the Doctrine of Christian Discovery'' that Christendom
The terms Christendom or Christian world commonly refer to the global Christian community, Christian states, Christian-majority countries or countries in which Christianity is dominant or prevails.SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christen ...
's discovery doctrine was also the same claim of "the right to kill and plunder non-Christians" found in this covenant tradition, whereby "the Lord" in Deuteronomy told his chosen people how they were to "utterly destroy" the "many nations before thee" when "He" brought them into the land "He" had discovered and promised to "His" "Chosen People" to "possess", and that this "right" was woven into US law through the 1823 Johnson v. McIntosh Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
ruling.
= Mormonism
=Mormonism
Mormonism is the theology and religious tradition of the Latter Day Saint movement of Restorationism, Restorationist Christianity started by Joseph Smith in Western New York in the 1820s and 1830s. As a label, Mormonism has been applied to va ...
teaches that the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
is the Biblical promised land, the U.S. Constitution divinely inspired, and Mormons
Mormons are a Religious denomination, religious and ethnocultural group, cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's d ...
God's chosen people.
Muslim interpretation
1st century Roman–Jewish historianFlavius Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; , ; ), born Yosef ben Mattityahu (), was a History of the Jews in the Roman Empire, Roman–Jewish historian and military leader. Best known for writing ''The Jewish War'', he was born in Jerusalem—then part of the Judaea ...
postulated that Ishmael was the founder of the Arab race. And according to Muslim tradition, Islam's founding prophet Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
was a Hanif (true monotheistic believer of the religion of Abraham). His tribe, the Quraysh
The Quraysh () are an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe who controlled Mecca before the rise of Islam. Their members were divided into ten main clans, most notably including the Banu Hashim, into which Islam's founding prophet Muhammad was born. By ...
, traces its ancestry to Ishmael
In the Bible, biblical Book of Genesis, Ishmael (; ; ; ) is the first son of Abraham. His mother was Hagar, the handmaiden of Abraham's wife Sarah. He died at the age of 137. Traditionally, he is seen as the ancestor of the Arabs.
Within Isla ...
.
Palestinian interpretation
SomePalestinians
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenou ...
claim partial descent from the Israelites and Maccabees
The Maccabees (), also spelled Machabees (, or , ; or ; , ), were a group of Jews, Jewish rebel warriors who took control of Judea, which at the time was part of the Seleucid Empire. Its leaders, the Hasmoneans, founded the Hasmonean dynasty ...
, as well as from other peoples who have lived in the region."(With reference to Palestinians in Ottoman times) Although proud of their Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
heritage and ancestry, the Palestinians
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenou ...
considered themselves to be descended not only from Arab conquerors of the seventh century but also from indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
who had lived in the country since time immemorial, including the ancient Hebrews
The Hebrews (; ) were an ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic-speaking people. Historians mostly consider the Hebrews as synonymous with the Israelites, with the term "Hebrew" denoting an Israelite from the nomadic era, which pre ...
and the Canaanites before them. Acutely aware of the distinctiveness of Palestinian history, the Palestinians saw themselves as the heirs of its rich associations." Walid Khalidi, 1984, ''Before Their Diaspora: A Photographic History of the Palestinians, 1876–1948''. Institute for Palestine Studies
African-American spirituals
African-American spirituals invoke the imagery of the "Promised Land" asheaven
Heaven, or the Heavens, is a common Religious cosmology, religious cosmological or supernatural place where beings such as deity, deities, angels, souls, saints, or Veneration of the dead, venerated ancestors are said to originate, be throne, ...
or paradise
In religion and folklore, paradise is a place of everlasting happiness, delight, and bliss. Paradisiacal notions are often laden with pastoral imagery, and may be cosmogonical, eschatological, or both, often contrasted with the miseries of human ...
and as an escape from slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
, which could often only be reached by death. The imagery and term also appear elsewhere in popular culture
Popular culture (also called pop culture or mass culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of cultural practice, practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as popular art
, in sermons, and in speeches such as Martin Luther King Jr.'s 1968 " I've Been to the Mountaintop", in which he said:
f. pop art
F is the sixth letter of the Latin alphabet.
F may also refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* F or f, the number 15 (number), 15 in hexadecimal and higher positional systems
* ''p'F'q'', the hypergeometric function
* F-distributi ...
or mass art, sometimes contraste ...I just want to do God's will. And He's allowed me to go up to the mountain. And I've looked over. And I've seen the Promised Land. I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight, that we, as a people, will get to the Promised Land. So I'm happy, tonight. I'm not worried about anything. I'm not fearing any man. Mine eyes have seen the glory of the coming of the Lord.
Boundaries from the Book of Numbers
:Boundaries of the 'Promised Land' given in theBook of Numbers
The Book of Numbers (from Biblical Greek, Greek Ἀριθμοί, ''Arithmoi'', , ''Bəmīḏbar'', ; ) is the fourth book of the Hebrew Bible and the fourth of five books of the Jewish Torah. The book has a long and complex history; its final f ...
(chapter 34)
::The South border. —(v. 3) "Then your ''south'' quarter shall be from the wilderness of Zin along by the coast of Edom, and your ''south border'' shall be the outmost coast of the salt sea eastward : (v. 4) And your border shall turn from the south to the ''ascent of Akrabbim'', and pass on to Zin : and the going forth thereof shall be from the south to Kadesh-barnea, and shall go on to Hazar-addar, and pass on to Azmon : (v. 5) And the border shall fetch a compass from Azmon unto the river of Egypt, and the goings out of it shall be at the sea."
::The Western border. —(v. 6) "And as for the ''western border'', ye shall even have the great sea for a border : this shall be your west border."
::The North border. —(v. 7) "And this shall be your ''north border'' : from the great sea ye shall point out for you mount Hor : (v. 8) From mount Hor ye shall point out your border unto the entrance of Hamath ; and the goings forth of the border shall be to Zedad : (v 9) And the border shall go on to Ziphron, and the goings out of it shall be at Hazar-enan : this shall be your north border."
::The East border. —(v. 10) "And ye shall point out your ''east border'' from Hazar-enan to Shepham : (v. 11) And the coast shall go down from Shepham to ''Riblah'', on the east side of Ain ; and the border shall descend, and shall reach unto the side of the ''sea of Chinnereth'' eastward : (v. 12) And the border shall go down to Jordan, and the goings out of it shall be at the salt sea : this shall be your land ''with the coasts thereof'' round about."
:Boundaries of the 'Promised Land' given by Jerome
Jerome (; ; ; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was an early Christian presbyter, priest, Confessor of the Faith, confessor, theologian, translator, and historian; he is commonly known as Saint Jerome.
He is best known ...
c.400
::You may delineate the Promised Land of Moses
In Abrahamic religions, Moses was the Hebrews, Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites out of slavery in the The Exodus, Exodus from ancient Egypt, Egypt. He is considered the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet in Judaism and Samaritani ...
from the Book of Numbers (ch. 34): as bounded on the south by the desert tract called Sina, between the Dead Sea and the city of Kadesh-barnea, hich is located with the Arabah to the east">Arabah.html" ;"title="hich is located with the Arabah">hich is located with the Arabah to the eastand continues to the west, as far as the river of Egypt, that discharges into the open sea near the city of Arish">Rhinocolara; as bounded on the west by the sea along the coasts of Palestine, Phoenicia, Coele-Syria, and Cilicia; as bounded on the north by the circle formed by the Taurus Mountains and Zephyrium and extending to Hamath, called Epiphany-Syria; as bounded on the east by the city of Hippos, Israel, Antioch Hippos and Lake Kinneret, now called Sea of Galilee, Tiberias, and then the Jordan River which discharges into the salt sea, now called the Dead Sea.
* 1845: Salomon Munk, ''Palestine, Description Géographique, Historique et Archéologique," in "L'Univers Pittoresque'':
Under the name ''Palestine'', we comprehend the small country formerly inhabited by the Israelites, and which is today part of Acre and Damascus pachalics. It stretched between 31 and 33° N. latitude and between 32 and 35° degrees E. longitude, an area of about 1300 . Some zealous writers, to give the land of the Hebrews some political importance, have exaggerated the extent of Palestine; but we have an authority for us that one can not reject. St. Jerome, who had long traveled in this country, said in his letter to Dardanus (ep. 129) that the northern boundary to that of the southern, was a distance of 160 Roman miles, which is about 55 . He paid homage to the truth despite his fears, as he said himself, of availing the ''Promised Land'' to pagan mockery, "" (Latin: "I am embarrassed to say the breadth of the promised land, lest we seem to have given the heathen an opportunity of blaspheming").
Footnotes
See also
References
General sources
* {{Zionism Hebrew Bible regions Abraham African-American cultural history Book of Genesis Canaan Hebrew Bible places Hebrew Bible words and phrases Land of Israel Zionism Mythical utopias Religious nationalism Phrases related to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict