Progress M-15M on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Progress M-15M (russian: Прогресс М-15М, italic=yes), identified by
 Five Maneuvers were conducted to refine the orbit of Progress M-15M before rendezvous operations started early on 22 April 2012. Progress M-15M docked with the ISS on 22 April 2012 at 14:39 UTC to the Pirs Docking Compartment nadir port. The port was vacated on 19 April 2012 by Progress M-14M. Fully automated rendezvous and docking operations using the Kurs docking system aboard the ISS and the Progress, drove the spacecraft to the linkup at orbital sunset. During the docking the ISS and Progress M-15M were orbiting 400 km above northern
Five Maneuvers were conducted to refine the orbit of Progress M-15M before rendezvous operations started early on 22 April 2012. Progress M-15M docked with the ISS on 22 April 2012 at 14:39 UTC to the Pirs Docking Compartment nadir port. The port was vacated on 19 April 2012 by Progress M-14M. Fully automated rendezvous and docking operations using the Kurs docking system aboard the ISS and the Progress, drove the spacecraft to the linkup at orbital sunset. During the docking the ISS and Progress M-15M were orbiting 400 km above northern
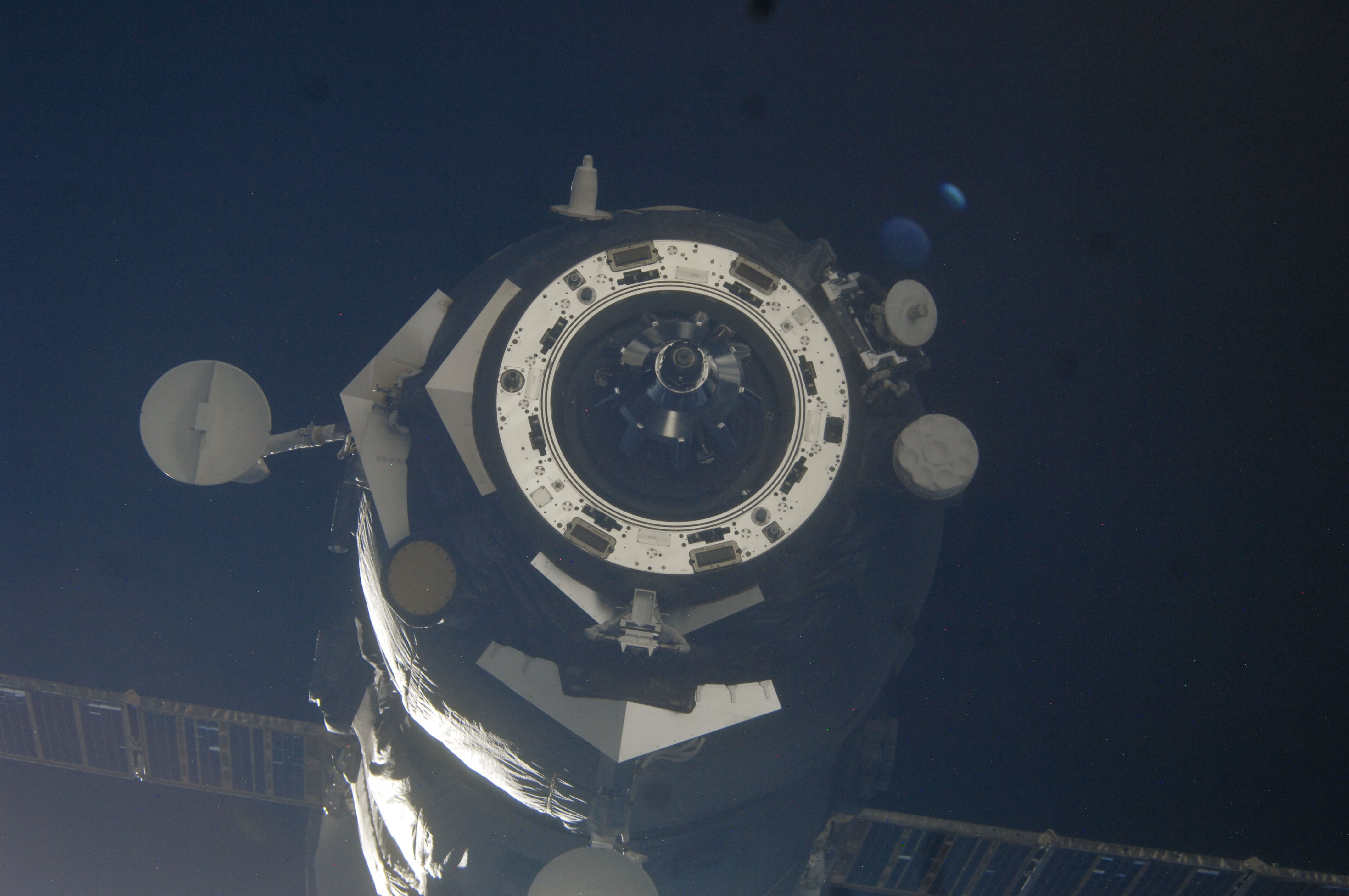 The M-15M spacecraft remained docked to the ISS for 91 days. While docked, its cargo will be off loaded to the ISS and be loaded with trash and unwanted items for disposal.
The M-15M spacecraft remained docked to the ISS for 91 days. While docked, its cargo will be off loaded to the ISS and be loaded with trash and unwanted items for disposal.
 The Progress departed the space station for the second and final time on 30 July 2012 at 21:16 UTC.
The Progress departed the space station for the second and final time on 30 July 2012 at 21:16 UTC.
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
as Progress 47P, is a Progress
Progress is the movement towards a refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. In the context of progressivism, it refers to the proposition that advancements in technology, science, and social organization have resulted, and by extension w ...
spacecraft used by Roskosmos to resupply the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest Modular design, modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos ( ...
during 2012. The fifteenth Progress-M
Progress-M (russian: Прогресс-М, GRAU indices 11F615A55 and 11F615A60), also known as Progress 7K-TGM, is a Russian, previously Soviet spacecraft which is used to resupply space stations. It is a variant of the Progress spacecraft, or ...
11F615A60 spacecraft, it has the serial number
A serial number is a unique identifier assigned incrementally or sequentially to an item, to ''uniquely'' identify it.
Serial numbers need not be strictly numerical. They may contain letters and other typographical symbols, or may consist enti ...
415 and was built by RKK Energia
PAO S. P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia (russian: Ракетно-космическая корпорация «Энергия» им. С. П. Королёва, Raketno-kosmicheskaya korporatsiya "Energiya" im. S. P. Korolyov ...
. It arrived at the ISS in late April to deliver supplies to the Expedition 30
Expedition 30 was the 30th long-duration mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The expedition's first three crew members – Dan Burbank, Anton Shkaplerov and Anatoli Ivanishin – arrived on the ISS aboard Soyuz TMA-22 on 1 ...
crew, and departed the ISS in late July 2012.
It was the 122nd launch to the ISS and the fifth Russian space launch in 2012. It was also the second mission for the Soyuz family of rockets since the beginning of the year.
Launch
The spacecraft was launched on time at 12:50:24 UTC from theBaikonur Cosmodrome
''Baiqoñyr ğaryş ailağy'' rus, Космодром Байконур''Kosmodrom Baykonur''
, image = Baikonur Cosmodrome Soyuz launch pad.jpg
, caption = The Baikonur Cosmodrome's "Gagarin's Start" Soyuz ...
in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
. Ten minutes after liftoff, the Soyuz-U Rocket carrying Progress M-15M successfully delivered the spacecraft to orbit to begin its International Space Station (ISS) Resupply Mission. Progress M-15M was inserted into a 193.68 x 245.52 km x 51.66° inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Ea ...
orbit.
Docking
 Five Maneuvers were conducted to refine the orbit of Progress M-15M before rendezvous operations started early on 22 April 2012. Progress M-15M docked with the ISS on 22 April 2012 at 14:39 UTC to the Pirs Docking Compartment nadir port. The port was vacated on 19 April 2012 by Progress M-14M. Fully automated rendezvous and docking operations using the Kurs docking system aboard the ISS and the Progress, drove the spacecraft to the linkup at orbital sunset. During the docking the ISS and Progress M-15M were orbiting 400 km above northern
Five Maneuvers were conducted to refine the orbit of Progress M-15M before rendezvous operations started early on 22 April 2012. Progress M-15M docked with the ISS on 22 April 2012 at 14:39 UTC to the Pirs Docking Compartment nadir port. The port was vacated on 19 April 2012 by Progress M-14M. Fully automated rendezvous and docking operations using the Kurs docking system aboard the ISS and the Progress, drove the spacecraft to the linkup at orbital sunset. During the docking the ISS and Progress M-15M were orbiting 400 km above northern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. Hooks and latches were engaged a few minutes after docking to firmly secure the spacecraft to the ISS. The Expedition 30
Expedition 30 was the 30th long-duration mission to the International Space Station (ISS). The expedition's first three crew members – Dan Burbank, Anton Shkaplerov and Anatoli Ivanishin – arrived on the ISS aboard Soyuz TMA-22 on 1 ...
crew opened the hatches and entered the Progress later on the day.
Undocking and decay
 The M-15M spacecraft remained docked to the ISS for 91 days. While docked, its cargo will be off loaded to the ISS and be loaded with trash and unwanted items for disposal.
The M-15M spacecraft remained docked to the ISS for 91 days. While docked, its cargo will be off loaded to the ISS and be loaded with trash and unwanted items for disposal.
Kurs-NA test
Kurs is the system used by Progress spacecraft for automated rendezvous and docking with the space station. In addition to its current Kurs-A antennas, Progress M-15M was also fitted with a new antenna system known as Kurs-NA. The first Progress M-15M docking to the space station used the traditional Kurs-A. It was decided as such to ensure that Progress' cargo would not go wasted, should the new Kurs-NA system fail. Kurs-NA system is more power efficient than its predecessor, Kurs-A. It also replaces the function of five existing Kurs-A antennas into one antenna, thus allowing for the removal of four antennas from future Progress and Soyuz spacecraft. Getting rid of these antennas will reduce the risk of a docking failure as some are deployed post-launch and one is retracted prior to docking since it extends forward of the Progress docking interface.First undocking and failed redocking
On 22 July 2012, Progress M-15M undocked from the Pirs Docking Compartment and tried to perform a re-rendezvous two days later to test the new Kurs-NA navigation antenna. The undocking from the space station's Pirs compartment occurred around 20:27 UTC. The undocking occurred 410 km over easternMongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
. The redocking was scheduled for 01:57 UTC on 24 July 2012. However it was aborted after equipment aboard the Progress spacecraft failed a self-test.
The problem occurred at 01:23 UTC while the KURS-NA system was being activated. The issue forced the spacecraft into a passive abort mode as designed under safety protocols. At the time of the abort ISS and Progress were flying 15 km apart. Two orbits after the abort, Russian flight controllers commanded the automated rendezvous system to re-activate for the collection of data. A second redocking attempt had to be delayed till 28 July 2012 to de-conflict with the arrival of the Japanese Kounotori 3
Kounotori 3 ( ja, こうのとり3号機; English: "white stork" ), also known as HTV-3, was the third flight of the Japanese H-II Transfer Vehicle. It was launched on 21 July 2012 to resupply the International Space Station (ISS) aboard the H ...
spacecraft at the ISS on 27 July 2012.
A likely cause for the aborted rendezvous was pointed at lower than expected temperatures on Progress M-15M. As a solution to the issue, Russian engineers turned on all available heaters on the spacecraft, which kept Progress M-15M at a constant 22°, which in turn resulted in Kurs-NA activating successfully, paving the way for the second docking attempt.
Second successful dedocking
When Kurs-NA was successfully activated at 23:00 UTC on 28 July 2012, it locked on to the passive Kurs-P on the Zvezda service module of the ISS. The re-rendezvous, fly-around and docking to the space station's Pirs compartment successfully occurred at around 01:00 UTC on 29 July 2012. During the time of the docking the ISS and the Progress was flying above theEarth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
to the west of New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the wide Torres ...
.
Final departure from the ISS
 The Progress departed the space station for the second and final time on 30 July 2012 at 21:16 UTC.
The Progress departed the space station for the second and final time on 30 July 2012 at 21:16 UTC.
Experiments
Progress M-15M will conduct two experiments: Khlopushka, from 6-14 August 2012, and Radar-Progress, from 15-20 August 2012. At the completion of the Radar-Progress experiment, Progress M-15M will de-orbit for a destructive re-entry over thePacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
.
Cargo
Progress M-15M was packed with 2703 pounds of equipment, food, clothing, life support system gear (dry cargo), 1988 pounds of propellant to replenish reservoirs that feed the Russian maneuvering thrusters, 926 pounds of water and some 50 kg ofoxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
and air.
Among the cargo items inside the Progress, there was a special present for the Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, who arrived at the ISS on 15 May 2012 and is expected to celebrate his 54th birthday in orbit on 21 June 2012.
References
{{Orbital launches in 2012 Progress (spacecraft) missions Spacecraft launched in 2012 Spacecraft which reentered in 2012 Spacecraft launched by Soyuz-U rockets Supply vehicles for the International Space Station