Prinz Adalbert-class cruiser on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ''Prinz Adalbert'' class was a group of two
 The First Naval Law in Germany, passed in 1898, envisioned a force of twelve
The First Naval Law in Germany, passed in 1898, envisioned a force of twelve
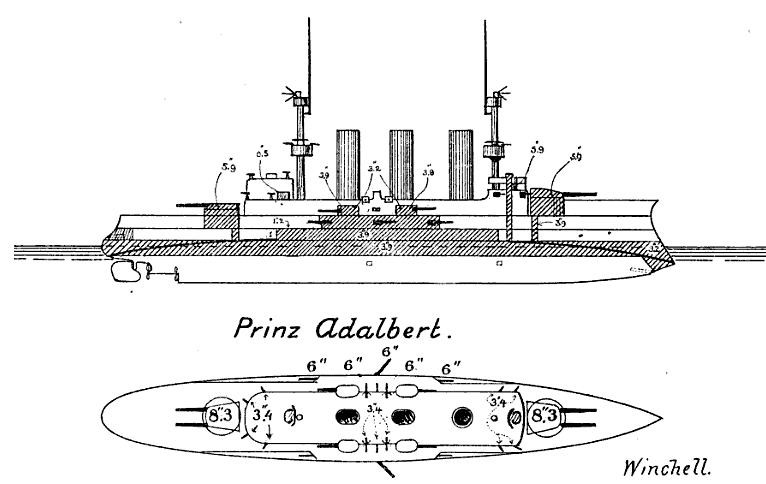 The ships of the ''Prinz Adalbert'' class were long at the waterline and
The ships of the ''Prinz Adalbert'' class were long at the waterline and
armored cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship and fast eno ...
s built for the German ''Kaiserliche Marine
{{italic title
The adjective ''kaiserlich'' means "imperial" and was used in the German-speaking countries to refer to those institutions and establishments over which the ''Kaiser'' ("emperor") had immediate personal power of control.
The term wa ...
'' (Imperial Navy) under the terms of the Second Naval Law. Two ships of the class were built, and , between 1900 and 1904. The two ships were heavily based on the previous armored cruiser, , with a series of incremental improvements. Their armor layout was revised slightly to improve internal protection and their main battery consisted of four guns instead of the two carried by ''Prinz Heinrich''. The new ships also received more powerful propulsion systems, making them slightly faster. ''Prinz Adalbert'' spent her peacetime career as a gunnery training ship
A training ship is a ship used to train students as sailors. The term is mostly used to describe ships employed by navies to train future officers. Essentially there are two types: those used for training at sea and old hulks used to house classr ...
while ''Friedrich Carl'' initially served as the flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the fi ...
of the fleet's reconnaissance forces. By 1909, she had been replaced by more modern cruisers and joined ''Prinz Adalbert'' as a training vessel.
Following the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in July 1914, both vessels were mobilized
Mobilization is the act of assembling and readying military troops and supplies for war. The word ''mobilization'' was first used in a military context in the 1850s to describe the preparation of the Prussian Army. Mobilization theories and ...
; ''Friedrich Carl'' was assigned to the cruiser squadron in the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
and was quickly sunk by Russian naval mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive device placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Unlike depth charges, mines are deposited and left to wait until they are triggered by the approach of, or contact with, any ...
s off Memel in November, though most of her crew was safely evacuated. ''Prinz Adalbert'' initially served in the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
, supporting the Raid on Yarmouth
The Raid on Yarmouth, on 3 November 1914, was an attack by the Imperial German Navy on the British North Sea port and town of Great Yarmouth. German shells only landed on the beach causing little damage to the town, after German ships laying m ...
in November 1914 before transferring to the Baltic to replace her lost sister. ''Prinz Adalbert'' had little better luck, being torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, su ...
ed by British submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s twice in 1915, the first, in July, caused serious damage and necessitated lengthy repairs. The second, in October, caused an internal magazine
A magazine is a periodical publication, generally published on a regular schedule (often weekly or monthly), containing a variety of content. They are generally financed by advertising, purchase price, prepaid subscriptions, or by a combinatio ...
explosion that destroyed the ship and killed almost her entire crew. Six-hundred and seventy-two men were killed, the greatest single loss of life for the German Navy in the Baltic during the war; there were only three survivors of her sinking.
Design
 The First Naval Law in Germany, passed in 1898, envisioned a force of twelve
The First Naval Law in Germany, passed in 1898, envisioned a force of twelve armored cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship and fast eno ...
s intended for overseas service in the German colonies. However, the German Navy required cruisers for operations with the fleet as well, and attempted to design ships that could fulfill both roles, primarily due to budget constraints. The first product of the 1898 Naval Law, , was an alteration of an earlier vessel, , equipped with fewer guns and thinner but more comprehensive armor in a trade-off for higher speed and lower cost. According to the law, one large cruiser was to be built per year, so work began immediately on a follow-on vessel to fulfill the requirement.
The subsequent design—that of the ''Prinz Adalbert'' class—was prepared in 1899–1900, and was an improvement on ''Prinz Heinrich''. The basic hull size and shape remained largely identical, but modifications were made to the armament and armor layout. Four quick-firing guns in twin turrets were substituted for the pair of slower guns mounted singly on the older vessel, as the design staff had by that time begun to question the wisdom of limiting the heavy gun battery to just two guns. The 21 cm caliber would remain the standard for all subsequent armored cruiser designs. The ships' secondary battery
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or prima ...
was kept largely the same as that of ''Prinz Heinrich'', apart from the addition of another pair of guns.
Armor thickness remained similar in strength to that of ''Prinz Heinrich'', though it was made more comprehensive, the primary improvement being to the upper belt, which was connected to the main battery barbette
Barbettes are several types of gun emplacement in terrestrial fortifications or on naval ships.
In recent naval usage, a barbette is a protective circular armour support for a heavy gun turret. This evolved from earlier forms of gun protection ...
s by oblique armored bulkheads. The deck thickness was also increased, and a new propulsion system that was about 10 percent more powerful than ''Prinz Heinrich''s increased the ships' top speed by compared to the earlier vessel.
General characteristics
 The ships of the ''Prinz Adalbert'' class were long at the waterline and
The ships of the ''Prinz Adalbert'' class were long at the waterline and overall
Overalls, also called bib-and-brace overalls or dungarees, are a type of garment usually used as protective clothing when working. The garments are commonly referred to as a "pair of overalls" by analogy with "pair of trousers".
Overalls were ...
, and had a beam of . The ships were designed to displace , but at full load
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into wei ...
displaced up to ; they had a draft of forward and aft. The ships' hulls were constructed from transverse and longitudinal steel frames, over which the steel hull plates were rivet
A rivet is a permanent mechanical fastener. Before being installed, a rivet consists of a smooth cylindrical shaft with a head on one end. The end opposite to the head is called the ''tail''. On installation, the rivet is placed in a punched ...
ed. The vessels contained fourteen watertight compartment
A compartment is a portion of the space within a ship defined vertically between decks and horizontally between bulkheads. It is analogous to a room within a building, and may provide watertight subdivision of the ship's hull important in retain ...
s and a double bottom
A double hull is a ship Hull (watercraft), hull design and construction method where the bottom and sides of the ship have two complete layers of watertight hull surface: one outer layer forming the normal hull of the ship, and a second inner hull ...
that extended for 60 percent of the length of the hull. The designers reverted to the use of two heavy military mast
__NOTOC__
M
...
s that had been discarded in ''Prinz Heinrich''s design.
The German navy regarded the vessels as good sea boats, with gentle motion when the ships' lower fuel bunkers were full. The ships were responsive to commands from the helm, and steering was controlled with a single rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally aircraft, air or watercraft, water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to ...
. They lost up to 60 percent speed with the rudder hard over, but suffered only minimal speed loss in heavy seas. The ships' casemate guns were placed too low, which rendered them exceedingly wet even in a slight swell. They had a transverse metacentric height
The metacentric height (GM) is a measurement of the initial static stability of a floating body. It is calculated as the distance between the centre of gravity of a ship and its metacentre. A larger metacentric height implies greater initial stab ...
of . The ships had a standard crew of 35 officers and 551 enlisted men, though when serving as a squadron flagship this could be augmented by another 9 officers and 44 enlisted men. The ships were equipped with several boats, including a pair of picket boat
A picket boat is a type of small naval craft. These are used for harbor patrol and other close inshore work, and have often been carried by larger warships as a ship's boat. They range in size between 30 and 55 feet.
Patrol boats, or any craft en ...
s, a launch, a pinnace
Pinnace may refer to:
* Pinnace (ship's boat), a small vessel used as a tender to larger vessels among other things
* Full-rigged pinnace
The full-rigged pinnace was the larger of two types of vessel called a pinnace in use from the sixteenth ...
, two cutters, two yawl
A yawl is a type of boat. The term has several meanings. It can apply to the rig (or sailplan), to the hull type or to the use which the vessel is put.
As a rig, a yawl is a two masted, fore and aft rigged sailing vessel with the mizzen mast p ...
s, and two dinghies
A dinghy is a type of small boat, often carried or towed by a larger vessel for use as a tender. Utility dinghies are usually rowboats or have an outboard motor. Some are rigged for sailing but they differ from sailing dinghies, which ...
.
''Prinz Adalbert'' and ''Friedrich Carl'' were powered by three vertical 3-cylinder triple expansion engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be tr ...
s; the center shaft drove a three-bladed screw
A screw and a bolt (see '' Differentiation between bolt and screw'' below) are similar types of fastener typically made of metal and characterized by a helical ridge, called a ''male thread'' (external thread). Screws and bolts are used to fa ...
in diameter, while the two outboard shafts powered four-bladed screws in diameter. The engines were supplied with steam by fourteen coal-fired Dürr water-tube boiler
A high pressure watertube boiler (also spelled water-tube and water tube) is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-gene ...
s produced by ''Düsseldorf-Ratinger Röhrenkesselfabrik'', which were ducted into three funnels
A funnel is a tube or pipe that is wide at the top and narrow at the bottom, used for guiding liquid or powder into a small opening.
Funnels are usually made of stainless steel, aluminium, glass, or plastic. The material used in its construc ...
. Compared to those on earlier German cruisers, the propeller shafts were shortened and better faired into the hull lines to reduce the amount of drag they induced, and they were made self-supporting; these changes were incorporated into all future cruisers and battleships built by the ''Kaiserliche Marine''.
The propulsion system was rated at for ''Prinz Adalbert'' and for ''Friedrich Carl'' and top speeds of and , respectively. Both ships reached higher horsepower figures on trials
In law, a trial is a coming together of parties to a dispute, to present information (in the form of evidence) in a tribunal, a formal setting with the authority to adjudicate claims or disputes. One form of tribunal is a court. The tribunal, w ...
, though their speeds were not significantly improved. The ships were designed to carry of coal, though storage could be increased to . This enabled a maximum range of up to at a cruising speed of . Electrical power was supplied by four generators with a total output of at 110 volts
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Definit ...
.
Armament
''Prinz Adalbert'' and ''Friedrich Carl'' were armed with amain battery
A main battery is the primary weapon or group of weapons around which a warship is designed. As such, a main battery was historically a gun or group of guns, as in the broadsides of cannon on a ship of the line. Later, this came to be turreted ...
of four SK L/40 guns in two twin turrets, one on either end of the main superstructure
A superstructure is an upward extension of an existing structure above a baseline. This term is applied to various kinds of physical structures such as buildings, bridges, or ships.
Aboard ships and large boats
On water craft, the superstruct ...
. The four guns were supplied with a total of 340 rounds of ammunition, or 85 shells per gun. The turrets could depress to −5° and elevate to 30°, which provided a maximum range of . The 21 cm gun fired a shell at a muzzle velocity
Muzzle velocity is the speed of a projectile (bullet, pellet, slug, ball/shots or shell) with respect to the muzzle at the moment it leaves the end of a gun's barrel (i.e. the muzzle). Firearm muzzle velocities range from approximately to i ...
of per second. The ships' secondary armament consisted of ten SK L/40 guns, all placed in the sides of the hulls. Three guns were mounted in casemates amidships on either side, with a pair of gun turrets above them. These guns were provided with a total of 1,400 shells, or 140 per gun. These guns fired an projectile at a muzzle velocity of per second. The guns could elevate to 30°, allowing a maximum range of .
The ships also carried twelve 8.8 cm SK L/35 guns for close in defense; these were arranged in groups of four in shielded pivot mounts. Four guns were mounted around the forward conning tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armored, from which an officer in charge can conn the vessel, controlling movements of the ship by giving orders to those responsible for the ship's engine, rudder, lines, and gro ...
, four were located around the rear two funnels amidships, with the last four guns placed on top of the rear superstructure. These guns fired a shell at a muzzle velocity of per second. They could elevate to 25° and could engage targets out to . The vessels' armament system was rounded out by four submerged torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes.
There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboa ...
s. They were mounted in the bow, stern, and on each broadside
Broadside or broadsides may refer to:
Naval
* Broadside (naval), terminology for the side of a ship, the battery of cannon on one side of a warship, or their near simultaneous fire on naval warfare
Printing and literature
* Broadside (comic ...
, and supplied with eleven torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, su ...
es.
Armor
The steel armor used on the two ships was produced by theKrupp
The Krupp family (see pronunciation), a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, is notable for its production of steel, artillery, ammunition and other armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG (Friedrich Krup ...
firm. The main belt armor
Belt armor is a layer of heavy metal armor plated onto or within the outer hulls of warships, typically on battleships, battlecruisers and cruisers, and aircraft carriers.
The belt armor is designed to prevent projectiles from penetrating to ...
consisted of a layer of teak
Teak (''Tectona grandis'') is a tropical hardwood tree species in the family Lamiaceae. It is a large, deciduous tree that occurs in mixed hardwood forests. ''Tectona grandis'' has small, fragrant white flowers arranged in dense clusters (panicl ...
that was thick, covered by thick steel plating in the central section, which covered the ships' machinery spaces and ammunition magazine
A magazine is a periodical publication, generally published on a regular schedule (often weekly or monthly), containing a variety of content. They are generally financed by advertising, purchase price, prepaid subscriptions, or by a combinatio ...
s. The belt was reduced to on either ends of the central portion; the bow and stern were unprotected. The armored deck ranged in thickness from to 80 mm. Sloped armor, which ranged in thickness from 50 to 80 mm, connected the deck to the armored belt. The ships' casemate guns, which were placed above the main belt, were protected by 100 mm thick armor plating, as were the 15 cm turret guns. The two 21 cm guns had 150 mm thick sides and 30 mm roofs. The forward conning tower was protected by sides and had a thick roof. The rear conning tower was much less thoroughly protected, with only worth of armor protection.
Ships
Service history
''Prinz Adalbert'' went into service as a gunnery training vessel for the fleet after her commissioning, while ''Friedrich Carl'' served with the reconnaissance squadron of the Active Battle Fleet, initially as itsflagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the fi ...
. ''Friedrich Carl'' also went on foreign cruises during this period, including to escort Kaiser Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor (german: Kaiser) and King of Prussia, reigning from 15 June 1888 until his abdication on 9 November 1918. Despite strengthening the German Empir ...
's yacht
A yacht is a sailing or power vessel used for pleasure, cruising, or racing. There is no standard definition, though the term generally applies to vessels with a cabin intended for overnight use. To be termed a , as opposed to a , such a pleasu ...
''Hohenzollern'' on foreign visits. One of these included the Kaiser's visit to Morocco in 1905 that led to the First Moroccan Crisis
The First Moroccan Crisis or the Tangier Crisis was an international crisis between March 1905 and May 1906 over the status of Morocco. Germany wanted to challenge France's growing control over Morocco, aggravating France and Great Britain. The ...
. In 1909, with more modern cruisers entering service with the fleet, ''Friedrich Carl'' joined her sister ship as a training vessel, being used as a torpedo training ship. Throughout their prewar careers, the ships participated in extensive fleet training.
World War I
The two ships were re-mobilized after the outbreak ofWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in August 1914. ''Prinz Adalbert'' was initially assigned to the IV Scouting Group, and alternated between the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
and Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
s for various operations, including cruising with the fleet during the Raid on Yarmouth
The Raid on Yarmouth, on 3 November 1914, was an attack by the Imperial German Navy on the British North Sea port and town of Great Yarmouth. German shells only landed on the beach causing little damage to the town, after German ships laying m ...
in early November. ''Friedrich Carl'' was sent to the Cruiser Division of the Baltic Sea commanded by ''Konteradmiral
''Konteradmiral'', abbreviated KAdm or KADM, is the second lowest naval flag officer rank in the German Navy. It is equivalent to '' Generalmajor'' in the '' Heer'' and ''Luftwaffe'' or to '' Admiralstabsarzt'' and ''Generalstabsarzt'' in the '' ...
'' (Rear Admiral) Ehler Behring, where she served as his flagship. The division was based in Neufahrwasser
Nowy Port (german: Neufahrwasser; csb, Fôrwôter) is a district of the city of Gdańsk, Poland. It borders with Brzeźno to the west, Letnica to the south, and Przeróbka to the east (over the Martwa Wisła).
The landmark of the district is ...
in Danzig. Behring was ordered to attack the Russian port of Libau, which was believed to be acting as a staging area for British submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s. On 17 November, while steaming to Libau, ''Friedrich Carl'' struck a pair of Russian naval mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive device placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Unlike depth charges, mines are deposited and left to wait until they are triggered by the approach of, or contact with, any ...
s off Memel. The ship's crew managed to keep the cruiser afloat long enough to allow nearby vessels to take off the entire crew; only seven men were killed in the attack. The operation proceeded as planned, however, and several blockship
A blockship is a ship deliberately sunk to prevent a river, channel, or canal from being used. It may either be sunk by a navy defending the waterway to prevent the ingress of attacking enemy forces, as in the case of at Portland Harbour in 1914; ...
s were sunk in the harbor entrance.
After the sinking of ''Friedrich Carl'', ''Prinz Adalbert'' was transferred to the Cruiser Division and Behring shifted his flag to the vessel. The ship conducted several operations against Russian forces in the southern Baltic in the first half of 1915, including bombardments of Libau and supporting minelayer
A minelayer is any warship, submarine or military aircraft deploying explosive mines. Since World War I the term "minelayer" refers specifically to a naval ship used for deploying naval mines. "Mine planting" was the term for installing controll ...
s around the Gulf of Riga
The Gulf of Riga, Bay of Riga, or Gulf of Livonia ( lv, Rīgas līcis, et, Liivi laht) is a bay of the Baltic Sea between Latvia and Estonia.
The island of Saaremaa (Estonia) partially separates it from the rest of the Baltic Sea. The main con ...
. She ran aground off Steinort in January but was able to free herself. After repairs were completed, she returned to active duty in March. In May, she supported the German Army attack that captured Libau. On 1 July 1915, the ship sortied to reinforce a German minelaying operation that had come under attack by a Russian cruiser flotilla. While en route with the armored cruiser ''Prinz Heinrich'', ''Prinz Adalbert'' was torpedoed by the British submarine . The damage was severe, though the cruiser was able to return to Kiel for repairs.
Repairs were finally completed by September 1915. She took part in a sortie into the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
toward the end of the month that resulted in no action. On 23 October, ''Prinz Adalbert'' was steaming some 20 miles west of Libau in company with a pair of destroyers when she was intercepted by the submarine . ''E8'' fired a spread of torpedoes at a range of approximately , which detonated the ship's ammunition magazine. The explosion destroyed the ship, which sank immediately with the loss of 672 crew. There were only three survivors. The sinking was the greatest single loss of life for the German Baltic forces for the duration of the war.
Notes
Footnotes
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* {{WWI German ships Cruiser classes World War I cruisers of Germany