Principality of Dalmatian Croatia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Duchy of Croatia (; also Duchy of the Croats, hr , Kneževina Hrvata; ) was a
Hrvatski rani srednji vijek
Zagreb, 1995, p. 198 In Byzantine sources the entity was usually called just "Croatia" ().Ferdo Šišić: Pregled povijesti hrvatskoga naroda 600. - 1526. - prvi dio, p. 156 The first known duke, Borna of Croatia, Borna, was named "Duke of Dalmatia" ( la, Dux Dalmatiae)''Annales regni Francorum'' DCCCXVIIII (year 819) and later "Duke of Dalmatia and Liburnia" ( la, Dux Dalmatiae atque Liburniae)''Annales regni Francorum'' DCCCXXI (year 821) in the Annales regni Francorum. The Croatian name is recorded in contemporary charters of Croatian dukes from the second half of the 9th century. Trpimir I was named "Duke of the Croats" ( la, Dux Chroatorum) in a Latin charter issued in 852, while Branimir was defined as "Duke of the Croats" ( la, Dux Cruatorvm) on a preserved Branimir Inscription, inscription from Šopot near Benkovac.Florin Curta: Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500-1250, p. 139-140
/ref>

 Most of Dalmatia in the 7th century was under the Avar Khaganate, a nomadic confederacy led by the Pannonian Avars, Avars who subjugated surrounding Slavic tribes. In 614 the Avars and Slavs sacked and destroyed the capital of the province of Dalmatia, Salona, and retained direct control of the region for a few decades until they were driven out by the Croats. The earliest recorded Croatian leader, referred to by the Emperor Constantine Porphyrogenitus, was Porga of Croatia, Porga. After their participation in Samo’s and of Kubrat's Old Great Bulgaria, Bulgarian defeat of the Avars in 632,
Most of Dalmatia in the 7th century was under the Avar Khaganate, a nomadic confederacy led by the Pannonian Avars, Avars who subjugated surrounding Slavic tribes. In 614 the Avars and Slavs sacked and destroyed the capital of the province of Dalmatia, Salona, and retained direct control of the region for a few decades until they were driven out by the Croats. The earliest recorded Croatian leader, referred to by the Emperor Constantine Porphyrogenitus, was Porga of Croatia, Porga. After their participation in Samo’s and of Kubrat's Old Great Bulgaria, Bulgarian defeat of the Avars in 632, '' '' , until they rebelled and defeated the Franks after a seven-year war, but it is not known on which specific war and time span this refers to.
Although the Christianization of Croats began right after their arrival to Dalmatia, in the early 9th century a part of the Croats were still pagan.

 The Duchy of Croatia was located between two major powers of the Middle Ages: the Eastern Roman Empire in the East which controlled the Dalmatian cities and islands and aimed to extend their rule over the entire former Roman province of Dalmatia, and the Franks in the West seeking to control the northern and northwestern lands. The Byzantine influence on Croatia was also reflected on the creation of Croatian law and in trade with the Byzantine coastal cities.
In the second quarter of the 9th century the Croats began developing a navy. Along with the Narentines, who were still pagan at the time and occupied the territory of the river Neretva mouth, they were active in the Adriatic Sea and made shipping and traveling in the area hazardous, especially for Venice. Therefore, in 839 the Republic of Venice, Venetians under Doge of Venice, Doge Pietro Tradonico attacked the eastern coast of the Adriatic, including Croatia, but during the assault they signed peace with their ruler, ''princeps'' Mislav of Croatia, Mislav ( la, principe Muisclavo), who ruled from Klis near Split. The peace treaty was signed at a place named St. Martin. The Doge also attacked Narentine islands, but failed to defeat them and made peace with their leader, who is mentioned as count ''Drosaico'' by the chronicler John the Deacon (Venetian chronicler), John the Deacon. However, the peace treaty was short-lasting and next year the Venetians were defeated by the Narentines under count ''Diuditum''. Piracy continued in the Adriatic, as well as hostility towards Venice, which is seen from the contract between Emperor Lothair I and Doge Tradonico, in which the Doge committed himself to defend the cities in Italy and Istria from Slavic attacks.
Duke Mislav was succeeded around 845 by Trpimir I of Croatia, Trpimir I, who continued the formal legacy of being the vassal of the Francia, Frankish king Lothair I (840–855), although he managed to strengthen his personal rule in Croatia. Arab campaigns thoroughly weakened the Byzantine Empire and Venice, which was used in the advance of the Croatian duke in 846 and 848. In 846 Trpimir successfully attacked the Byzantine coastal cities and their ''patricius''. Between 854 and 860, he successfully defended his land from the Bulgarian invasion under Knyaz Boris I of Bulgaria, somewhere in Northeastern Bosnia, concluding a peace treaty with Boris and exchanging gifts. Constantine Porphyrogenitus mentions the traditional friendship between the Bulgarians and Croatians, who coexisted peacefully up to that time.''De Administrando Imperio'', XXXI. Of the Croats and of the country they now dwell inNada Klaić, Povijest Hrvata u ranom srednjem vijeku, Zagreb 1975., p. 227-231
In a Latin charter preserved in a rewrite from 1568, dated to 4 March 852 or, according to a newer research, about 840, Trpimir refers to himself as "leader of the Croats with the help of God" ( la, dux Croatorum iuvatus munere divino); his land, called "Kingdom of Croatia (medieval), Kingdom of the Croats" ( la, regnum Croatorum), can simply be interpreted as the "Realm of the Croats", since Trpimir was not a king. The term ''regnum'' was also used by other dukes of that time as a sign of their independence. This charter also documents his ownership of the Klis Fortress, from where his rule was centered, and mentions Mislav's donations to the Archbishopric of Split. In the proximity of his court in Klis, in Rižinice, Trpimir built a church and the first Order of Saint Benedict, Benedictine monastery in Croatia. Trpimir's name is inscribed on a stone fragment from an altar screen of the Rižinice monastery church. He is more expressly remembered as the founder of the House of Trpimirović, a native Croat dynasty that ruled, with interruptions, from 845 until 1091 in Croatia.
In 864 Duke Domagoj of Croatia, Domagoj, founder of the House of Domagojević, usurped the throne after the death of Trpimir and forced his sons, including Zdeslav of Croatia, Zdeslav, to flee to Constantinople. During the rule of Domagoj piracy was a common practice in the Adriatic. The pirates attacked Christian sailors, including a ship with papal legates returning from the Fourth Council of Constantinople (Roman Catholic), Eighth Catholic Ecumenical Council, thus forcing the Pope to intervene by asking Domagoj to stop piracy, but his efforts were of no avail. Domagoj waged wars with the
The Duchy of Croatia was located between two major powers of the Middle Ages: the Eastern Roman Empire in the East which controlled the Dalmatian cities and islands and aimed to extend their rule over the entire former Roman province of Dalmatia, and the Franks in the West seeking to control the northern and northwestern lands. The Byzantine influence on Croatia was also reflected on the creation of Croatian law and in trade with the Byzantine coastal cities.
In the second quarter of the 9th century the Croats began developing a navy. Along with the Narentines, who were still pagan at the time and occupied the territory of the river Neretva mouth, they were active in the Adriatic Sea and made shipping and traveling in the area hazardous, especially for Venice. Therefore, in 839 the Republic of Venice, Venetians under Doge of Venice, Doge Pietro Tradonico attacked the eastern coast of the Adriatic, including Croatia, but during the assault they signed peace with their ruler, ''princeps'' Mislav of Croatia, Mislav ( la, principe Muisclavo), who ruled from Klis near Split. The peace treaty was signed at a place named St. Martin. The Doge also attacked Narentine islands, but failed to defeat them and made peace with their leader, who is mentioned as count ''Drosaico'' by the chronicler John the Deacon (Venetian chronicler), John the Deacon. However, the peace treaty was short-lasting and next year the Venetians were defeated by the Narentines under count ''Diuditum''. Piracy continued in the Adriatic, as well as hostility towards Venice, which is seen from the contract between Emperor Lothair I and Doge Tradonico, in which the Doge committed himself to defend the cities in Italy and Istria from Slavic attacks.
Duke Mislav was succeeded around 845 by Trpimir I of Croatia, Trpimir I, who continued the formal legacy of being the vassal of the Francia, Frankish king Lothair I (840–855), although he managed to strengthen his personal rule in Croatia. Arab campaigns thoroughly weakened the Byzantine Empire and Venice, which was used in the advance of the Croatian duke in 846 and 848. In 846 Trpimir successfully attacked the Byzantine coastal cities and their ''patricius''. Between 854 and 860, he successfully defended his land from the Bulgarian invasion under Knyaz Boris I of Bulgaria, somewhere in Northeastern Bosnia, concluding a peace treaty with Boris and exchanging gifts. Constantine Porphyrogenitus mentions the traditional friendship between the Bulgarians and Croatians, who coexisted peacefully up to that time.''De Administrando Imperio'', XXXI. Of the Croats and of the country they now dwell inNada Klaić, Povijest Hrvata u ranom srednjem vijeku, Zagreb 1975., p. 227-231
In a Latin charter preserved in a rewrite from 1568, dated to 4 March 852 or, according to a newer research, about 840, Trpimir refers to himself as "leader of the Croats with the help of God" ( la, dux Croatorum iuvatus munere divino); his land, called "Kingdom of Croatia (medieval), Kingdom of the Croats" ( la, regnum Croatorum), can simply be interpreted as the "Realm of the Croats", since Trpimir was not a king. The term ''regnum'' was also used by other dukes of that time as a sign of their independence. This charter also documents his ownership of the Klis Fortress, from where his rule was centered, and mentions Mislav's donations to the Archbishopric of Split. In the proximity of his court in Klis, in Rižinice, Trpimir built a church and the first Order of Saint Benedict, Benedictine monastery in Croatia. Trpimir's name is inscribed on a stone fragment from an altar screen of the Rižinice monastery church. He is more expressly remembered as the founder of the House of Trpimirović, a native Croat dynasty that ruled, with interruptions, from 845 until 1091 in Croatia.
In 864 Duke Domagoj of Croatia, Domagoj, founder of the House of Domagojević, usurped the throne after the death of Trpimir and forced his sons, including Zdeslav of Croatia, Zdeslav, to flee to Constantinople. During the rule of Domagoj piracy was a common practice in the Adriatic. The pirates attacked Christian sailors, including a ship with papal legates returning from the Fourth Council of Constantinople (Roman Catholic), Eighth Catholic Ecumenical Council, thus forcing the Pope to intervene by asking Domagoj to stop piracy, but his efforts were of no avail. Domagoj waged wars with the

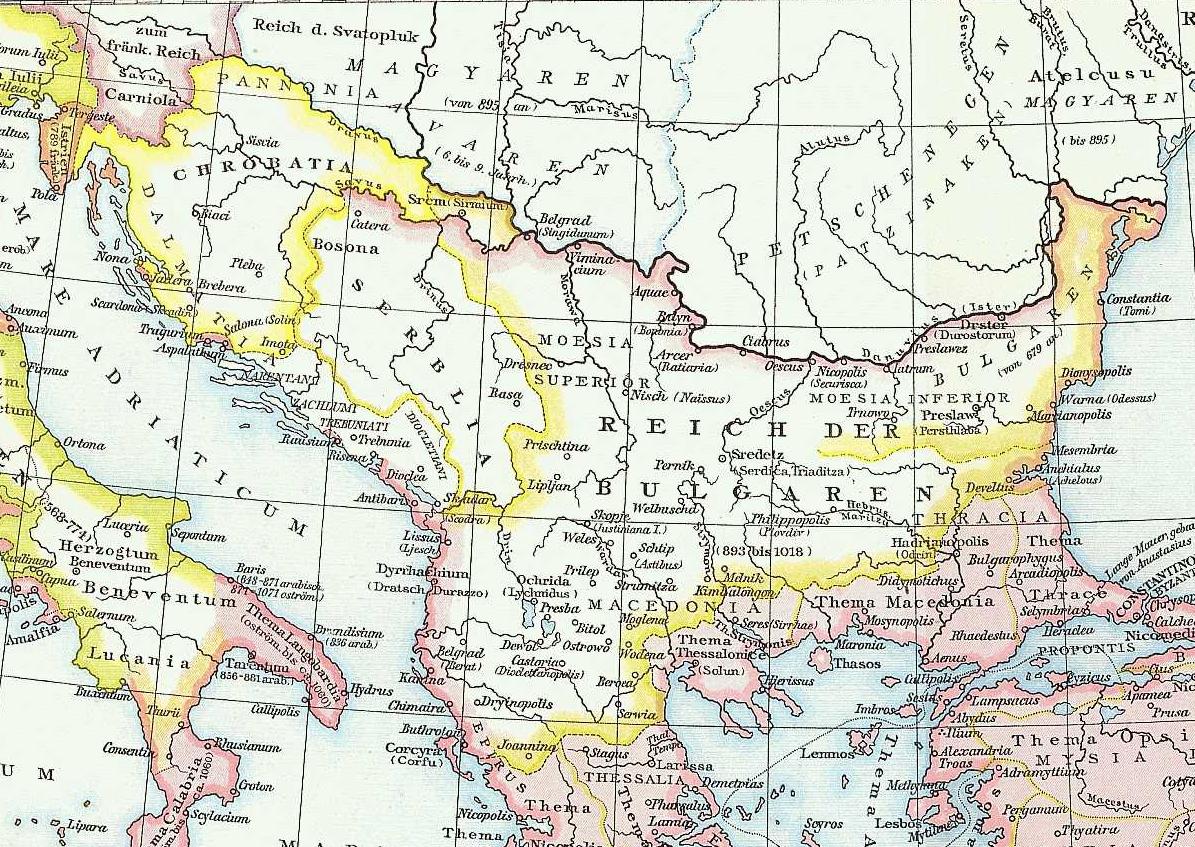 Duke Zdeslav's reign was short and ended in 879 when Branimir of Croatia, Branimir of the House of Domagojević killed him and usurped the throne. Branimir was unlike Zdeslav a proponent of Rome and returned the country to the Roman fold. He had regular contacts with Pope John VIII, to whom he sent a letter revealing his intentions to entrust his people and his country to the Apostolic See. The Pope replied to his requests, praising his initiative and in 879 the Duchy under Branimir, now free of Frankish suzerainty, received papal recognition as a state.Maddalena Betti: The Making of Christian Moravia (858-882), 2013, p. 130
Duke Zdeslav's reign was short and ended in 879 when Branimir of Croatia, Branimir of the House of Domagojević killed him and usurped the throne. Branimir was unlike Zdeslav a proponent of Rome and returned the country to the Roman fold. He had regular contacts with Pope John VIII, to whom he sent a letter revealing his intentions to entrust his people and his country to the Apostolic See. The Pope replied to his requests, praising his initiative and in 879 the Duchy under Branimir, now free of Frankish suzerainty, received papal recognition as a state.Maddalena Betti: The Making of Christian Moravia (858-882), 2013, p. 130
/ref> The second half of the 9th century marked a significant increase in papal influence in the Southeastern Europe. Pope John VIII complained to Domagoj about the obstinacy of Ignatios of Constantinople, Patriarch Ignatius who denied his jurisdiction over Bulgaria and appointed a new Archbishop. The Pope also requested from Dukes Zdeslav and Branimir assistance and protection for his legates who were crossing Croatia on their way to First Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria. Although the exact geographical extent of the Duchy is not known, these requests confirm geographical contiguity between Croatia and Bulgaria, which bordered probably somewhere in Bosnia. Muncimir of Croatia, Muncimir (also called Mutimir), the youngest son of Trpimir, came to throne after the death of Branimir (c. 892), which marked the return of the House of Trpimirović to power. A Latin charter from Biaći near Trogir dated to 28 September 892 named Muncimir "Duke of the Croats" ( la, Croatorum dux). During his rule, in the late 9th century the Hungarians crossed the Carpathians and entered the Carpathian Basin. They invaded northern Italy and also defeated Duke Braslav of Pannonia, Braslav from the Duchy of Pannonia, endangering Croatia.John Van Antwerp Fine: The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century, 1991, p. 262 Muncimir ruled until about 910 when he was succeeded by Tomislav of Croatia, Tomislav, the last duke and the first king of Croatia. Venetian chronicler John the Deacon wrote that in 912 a Venetian ambassador, returning from Bulgaria, passed through Croatian territory before reaching the land of Zahumlje, which suggests that Croatia at the time also bordered Bulgaria, then under the rule of Simeon I of Bulgaria, Simeon I. In Historia Salonitana, a chronicle from the 13th century written by Thomas the Archdeacon from Split, Tomislav was mentioned as Duke of Croatia in 914. According to ''De Administrando Imperio'', Croatia at the time had 100,000 infantrymen and 60,000 horsemen, 80 large ships and 100 smaller vessels, but these numbers are viewed as a clear exaggeration and an overemphasis of the Croatian forces. Croatia also waged battles with the Magyars during the early 10th century. According to the Palaeography, palaeographic analysis of the original manuscript of ''De Administrando Imperio'', assumed number of inhabitants in medieval Croatia estimated between 440,000 and 880,000 people, and military numbers of Franks and Byzantines, the military force was most probably composed of 20,000-100,000 infantrymen, and 3,000-24,000 horsemen organized in 60 allagions. During the Byzantine–Bulgarian wars#Simeon I.27s Imperial ambitions, war between the Byzantium and Bulgaria of Simeon I, in about 923, the Byzantines concluded an alliance with Croatia. Prior to that the Bulgarians had several decisive victories against the Byzantines, capturing Adrianople and endangering Constantinople. In 924 Simeon I deposed Zaharija of Serbia, Zaharija from rule in Principality of Serbia (early medieval), Serbia, who fled to Croatia. In 926, Simeon's troops invaded Croatia, but were severely defeated in the Battle of the Bosnian Highlands. In 927 Pope John X sent his legates to mediate a peace treaty between Croats and Bulgarians.Florin Curta: Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500-1250, p. 196
/ref> During these years Croatia was elevated to the status of a Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), kingdom. It is generally said that Duke Tomislav was crowned king in 925, but this is not certain since it is not known when and where was he crowned, or was he crowned at all. However, Tomislav was the first Croatian ruler whom the Papal chancellery honoured with the title king. Tomislav is mentioned as a king in two preserved documents published in the ''Historia Salonitana'' and by the ''Chronicle of the Priest of Duklja'', where Tomislav's rule was specified at 13 years. In a note preceding the text of the Council conclusions in Split in 925 it is written that Tomislav is the king "in the province of the Croats and in the Dalmatian regions" (''in prouintia Croatorum et Dalmatiarum finibus Tamisclao rege''). In the 12th canon of the Council conclusions in 925 the ruler of the Croats is called "king" (''rex et proceres Chroatorum''), while in a letter sent by the Pope John X Tomislav is named "King of the Croats" (''Tamisclao, regi Crouatorum'').Codex Diplomaticus Regni Croatiæ, Dalamatiæ et Slavoniæ, Vol I, p. 34 Although there are no inscriptions of Tomislav to confirm the title, later inscriptions and charters confirm that his 10th century successors called themselves "kings".
File:Crkva sv. Spasa,Cetina 0187.jpg, Church of Holy Salvation, Cetina
''Historia Salonitanorum Atque Spalatinorum Pontificum''
* Severin Binius
Concilia generalia et provincialia, quotquot reperiri potuerunt. Item Epistolae decretales et Romanorum pontificum vitae
1606
Croatia — an independent principality (Richard C. Frucht: ''Eastern Europe'', Edition 2005 /Santa Barbara, California, USA/)
Duke Branimir put the Principality of Croatia "permanently beneath the wing of the Roman Church and Western Christian civilization (879)" (Richard Barrie Dobson: ''Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages'', Edition 2000 /Cambridge, England, UK/)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Croats, Duchy of the Duchy of Croatia, History of Dalmatia Former Slavic countries Croatian principalities States and territories established in the 7th century States and territories disestablished in the 920s Former countries in the Balkans 7th-century establishments in Europe
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
state that was established by White Croats
White Croats ( hr, Bijeli Hrvati; pl, Biali Chorwaci; cz, Bílí Chorvati; uk, Білі хорвати, Bili khorvaty), or simply known as Croats, were a group of Early Slavic tribes who lived among other West and East Slavic tribes in the ar ...
who migrated into the area of the former Roman province of Dalmatia
Dalmatia was a Roman province. Its name is derived from the name of an Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae, which lived in the central area of the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It encompassed the northern part of present-day Albania, much of C ...
7th century CE. Throughout its existence the Duchy had several seats – namely, Klis, Solin
Solin (Latin and it, Salona; grc, Σαλώνα ) is a town in Dalmatia, Croatia. It is situated right northeast of Split, on the Adriatic Sea and the river Jadro.
Solin developed on the location of ancient city of ''Salona'', which was the ...
, Knin
Knin (, sr, link=no, Книн, it, link=no, Tenin) is a city in the Šibenik-Knin County of Croatia, located in the Dalmatian hinterland near the source of the river Krka, an important traffic junction on the rail and road routes between Zagr ...
, Bijaći
Bijaći ( it, Santa Marta) is a village in Croatia, northeast of Trogir, at the contact point between the Trogir part and the Lower Kaštela part of the Velo field.
It was first mentioned in two old Croatian documents from AD 852 (Byaci) and AD ...
and Nin. It comprised the '' littoral –'' the coastal part of today's Croatia ''–'' except Istria, and included a large part of the mountainous hinterland
Hinterland is a German word meaning "the land behind" (a city, a port, or similar). Its use in English was first documented by the geographer George Chisholm in his ''Handbook of Commercial Geography'' (1888). Originally the term was associated ...
as well. The Duchy was in the center of competition between the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the ...
and the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
for rule over the area. Croatian rivalry with Venice emerged in the first decades of the 9th century and would continue through the following centuries. Croatia also waged battles with the Bulgarian Empire (founded ; Bulgar-Croatian relations improved greatly afterwards) and with the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
; it also sought to extend its control over important coastal cities under the rule of Byzantium. Croatia experienced periods of vassalage to Francia , the Franks or to the Byzantines and of ''de facto'' independence until 879, when Duke Branimir of Croatia, Branimir was recognized as an independent ruler by Pope John VIII. The Duchy was ruled by the Trpimirović and Domagojević dynasties from 845 to 1091. Around 925, during the rule of Tomislav of Croatia, Tomislav, Croatia became a Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), kingdom.
Nomenclature
"Dalmatian Croatia" (''Dalmatinska Hrvatska'') and "Littoral Croatia" (''Primorska Hrvatska'') are modern appellations amongst historians for the Duchy. The state is sometimes called a principality, i.e. the "Principality of Croatia". The first recorded name for the Duchy was "Land of the Croats" ( la, regnum Croatorum) in 852. Croatia was not yet a kingdom at the time and the term ''regnum'' is used in terms of a country in general.Ivo GoldsteinHrvatski rani srednji vijek
Zagreb, 1995, p. 198 In Byzantine sources the entity was usually called just "Croatia" ().Ferdo Šišić: Pregled povijesti hrvatskoga naroda 600. - 1526. - prvi dio, p. 156 The first known duke, Borna of Croatia, Borna, was named "Duke of Dalmatia" ( la, Dux Dalmatiae)''Annales regni Francorum'' DCCCXVIIII (year 819) and later "Duke of Dalmatia and Liburnia" ( la, Dux Dalmatiae atque Liburniae)''Annales regni Francorum'' DCCCXXI (year 821) in the Annales regni Francorum. The Croatian name is recorded in contemporary charters of Croatian dukes from the second half of the 9th century. Trpimir I was named "Duke of the Croats" ( la, Dux Chroatorum) in a Latin charter issued in 852, while Branimir was defined as "Duke of the Croats" ( la, Dux Cruatorvm) on a preserved Branimir Inscription, inscription from Šopot near Benkovac.Florin Curta: Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500-1250, p. 139-140
/ref>
Geography
Within the area of theRoman province of Dalmatia
Dalmatia was a Roman province. Its name is derived from the name of an Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae, which lived in the central area of the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It encompassed the northern part of present-day Albania, much of C ...
, various tribal groupings, which were called ''sclaviniae'' by the Byzantine Empire, Byzantines, were settled along the Adriatic coast. Croatia in the early Middle Ages was an area bounded by the Eastern Adriatic hinterland on one side, then extended to a part of western Herzegovina, western and central Bosnia (region), Bosnia, then into Lika, Gacka and Krbava, and North-West to Vinodol, Croatia, Vinodol and Labin in the Croatian Littoral area. Several coastal Dalmatian cities were under the rule of the Byzantines, including Split, Croatia, Split, Zadar, Kotor and Dubrovnik, as well as islands of Hvar and Krk. To the south Croatia bordered with the land of the Narentines, which stretched from the rivers Cetina to Neretva, and had the islands of Brač, Hvar, Korčula, Mljet, Vis and Lastovo in its possession. In the southern part of Dalmatia, there was Zahumlje (Zachumlia), Travunia and Dioclea (today Montenegro). North of Croatia there was the Pannonian Slavs#Principality, Duchy of Lower Pannonia. Croatia, as well as other early medieval states, didn't have a permanent capital and Croatian dukes resided in various places on their courts. The first important center of Croatia was Klis Fortress, Klis near Split, where Duke Trpimir I resided. Other dukes ruled from the towns of Solin, Croatia, Solin, Knin
Knin (, sr, link=no, Книн, it, link=no, Tenin) is a city in the Šibenik-Knin County of Croatia, located in the Dalmatian hinterland near the source of the river Krka, an important traffic junction on the rail and road routes between Zagr ...
, Biaći and Nin, Croatia, Nin.
History
Background

 Most of Dalmatia in the 7th century was under the Avar Khaganate, a nomadic confederacy led by the Pannonian Avars, Avars who subjugated surrounding Slavic tribes. In 614 the Avars and Slavs sacked and destroyed the capital of the province of Dalmatia, Salona, and retained direct control of the region for a few decades until they were driven out by the Croats. The earliest recorded Croatian leader, referred to by the Emperor Constantine Porphyrogenitus, was Porga of Croatia, Porga. After their participation in Samo’s and of Kubrat's Old Great Bulgaria, Bulgarian defeat of the Avars in 632,
Most of Dalmatia in the 7th century was under the Avar Khaganate, a nomadic confederacy led by the Pannonian Avars, Avars who subjugated surrounding Slavic tribes. In 614 the Avars and Slavs sacked and destroyed the capital of the province of Dalmatia, Salona, and retained direct control of the region for a few decades until they were driven out by the Croats. The earliest recorded Croatian leader, referred to by the Emperor Constantine Porphyrogenitus, was Porga of Croatia, Porga. After their participation in Samo’s and of Kubrat's Old Great Bulgaria, Bulgarian defeat of the Avars in 632, White Croats
White Croats ( hr, Bijeli Hrvati; pl, Biali Chorwaci; cz, Bílí Chorvati; uk, Білі хорвати, Bili khorvaty), or simply known as Croats, were a group of Early Slavic tribes who lived among other West and East Slavic tribes in the ar ...
were either invited into Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia by the Byzantine Emperor Heraclius (r. 610-641) and allowed to settle there, or prevailing the Avars after that lengthy war the Croats migrated across the Sava from Pannonia Savia and settled Dalmatia on their own.''De Administrando Imperio'', XXX. Story of the province of Dalmatia In either case, a revised Avar alliance retook Pannonia in 677 but only as far as the Sava and Danube. By the early 9th century, Croatia emerged as a political entity with a duke as head of the state, territorially in the basins of the rivers Cetina, Krka (Croatia), Krka and Zrmanja. It was administered in 11 counties (''županija''). According to ''De Administrando Imperio'', the Croats in Pannonia were subject to the Franks for several years, Frankish vassalage
The Francia, Franks gained control of Pannonia and Dalmatia in the 790s and the first decade of the ninth century. In 788 Charlemagne, after conquering Lombardy, turned further east and subjugated Istria. In the 790s Duke Vojnomir of Pannonia accepted the Frankish overlordship, whose land the Franks placed under the March of Friuli and tried to extend their rule over the Croatians of Dalmatia. In 799 the Franks under the leadership of Eric of Friuli were defeated in the Siege of Trsat, Battle of Trsat in Liburnia. However, from 803 Frankish rule was recognized in most of northern Dalmatia.John Van Antwerp Fine: The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century, 1991, p. 251-255 The Franks also waged wars with the Byzantine Empire until a peace treaty, known as the Pax Nicephori, was signed in 812. By that treaty the Byzantines retained control of the coastal cities and islands in Dalmatia, while acknowledging Frankish rule over Istria and the Dalmatian hinterland. From c. 810 Borna, who resided in Nin, ruled most of northern Dalmatia and was a vassal of theCarolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the ...
. Borna was Duke of the Guduscani, a Croatian tribe that lived along the river Guduča near Bribir, Šibenik-Knin County, Bribir in northern Dalmatia, later the center of the Croatian state. His rule was marked by the rebellion of Ljudevit Posavski against the Franks, who defeated Borna in 819 somewhere near the River Kupa and began to ravage Dalmatia, but harsh conditions and constant attacks from Borna's men forced Ljudevit to retreat. In 821 Borna died and was succeeded by his nephew Vladislav of Croatia, Vladislav.
Between East and West

 The Duchy of Croatia was located between two major powers of the Middle Ages: the Eastern Roman Empire in the East which controlled the Dalmatian cities and islands and aimed to extend their rule over the entire former Roman province of Dalmatia, and the Franks in the West seeking to control the northern and northwestern lands. The Byzantine influence on Croatia was also reflected on the creation of Croatian law and in trade with the Byzantine coastal cities.
In the second quarter of the 9th century the Croats began developing a navy. Along with the Narentines, who were still pagan at the time and occupied the territory of the river Neretva mouth, they were active in the Adriatic Sea and made shipping and traveling in the area hazardous, especially for Venice. Therefore, in 839 the Republic of Venice, Venetians under Doge of Venice, Doge Pietro Tradonico attacked the eastern coast of the Adriatic, including Croatia, but during the assault they signed peace with their ruler, ''princeps'' Mislav of Croatia, Mislav ( la, principe Muisclavo), who ruled from Klis near Split. The peace treaty was signed at a place named St. Martin. The Doge also attacked Narentine islands, but failed to defeat them and made peace with their leader, who is mentioned as count ''Drosaico'' by the chronicler John the Deacon (Venetian chronicler), John the Deacon. However, the peace treaty was short-lasting and next year the Venetians were defeated by the Narentines under count ''Diuditum''. Piracy continued in the Adriatic, as well as hostility towards Venice, which is seen from the contract between Emperor Lothair I and Doge Tradonico, in which the Doge committed himself to defend the cities in Italy and Istria from Slavic attacks.
Duke Mislav was succeeded around 845 by Trpimir I of Croatia, Trpimir I, who continued the formal legacy of being the vassal of the Francia, Frankish king Lothair I (840–855), although he managed to strengthen his personal rule in Croatia. Arab campaigns thoroughly weakened the Byzantine Empire and Venice, which was used in the advance of the Croatian duke in 846 and 848. In 846 Trpimir successfully attacked the Byzantine coastal cities and their ''patricius''. Between 854 and 860, he successfully defended his land from the Bulgarian invasion under Knyaz Boris I of Bulgaria, somewhere in Northeastern Bosnia, concluding a peace treaty with Boris and exchanging gifts. Constantine Porphyrogenitus mentions the traditional friendship between the Bulgarians and Croatians, who coexisted peacefully up to that time.''De Administrando Imperio'', XXXI. Of the Croats and of the country they now dwell inNada Klaić, Povijest Hrvata u ranom srednjem vijeku, Zagreb 1975., p. 227-231
In a Latin charter preserved in a rewrite from 1568, dated to 4 March 852 or, according to a newer research, about 840, Trpimir refers to himself as "leader of the Croats with the help of God" ( la, dux Croatorum iuvatus munere divino); his land, called "Kingdom of Croatia (medieval), Kingdom of the Croats" ( la, regnum Croatorum), can simply be interpreted as the "Realm of the Croats", since Trpimir was not a king. The term ''regnum'' was also used by other dukes of that time as a sign of their independence. This charter also documents his ownership of the Klis Fortress, from where his rule was centered, and mentions Mislav's donations to the Archbishopric of Split. In the proximity of his court in Klis, in Rižinice, Trpimir built a church and the first Order of Saint Benedict, Benedictine monastery in Croatia. Trpimir's name is inscribed on a stone fragment from an altar screen of the Rižinice monastery church. He is more expressly remembered as the founder of the House of Trpimirović, a native Croat dynasty that ruled, with interruptions, from 845 until 1091 in Croatia.
In 864 Duke Domagoj of Croatia, Domagoj, founder of the House of Domagojević, usurped the throne after the death of Trpimir and forced his sons, including Zdeslav of Croatia, Zdeslav, to flee to Constantinople. During the rule of Domagoj piracy was a common practice in the Adriatic. The pirates attacked Christian sailors, including a ship with papal legates returning from the Fourth Council of Constantinople (Roman Catholic), Eighth Catholic Ecumenical Council, thus forcing the Pope to intervene by asking Domagoj to stop piracy, but his efforts were of no avail. Domagoj waged wars with the
The Duchy of Croatia was located between two major powers of the Middle Ages: the Eastern Roman Empire in the East which controlled the Dalmatian cities and islands and aimed to extend their rule over the entire former Roman province of Dalmatia, and the Franks in the West seeking to control the northern and northwestern lands. The Byzantine influence on Croatia was also reflected on the creation of Croatian law and in trade with the Byzantine coastal cities.
In the second quarter of the 9th century the Croats began developing a navy. Along with the Narentines, who were still pagan at the time and occupied the territory of the river Neretva mouth, they were active in the Adriatic Sea and made shipping and traveling in the area hazardous, especially for Venice. Therefore, in 839 the Republic of Venice, Venetians under Doge of Venice, Doge Pietro Tradonico attacked the eastern coast of the Adriatic, including Croatia, but during the assault they signed peace with their ruler, ''princeps'' Mislav of Croatia, Mislav ( la, principe Muisclavo), who ruled from Klis near Split. The peace treaty was signed at a place named St. Martin. The Doge also attacked Narentine islands, but failed to defeat them and made peace with their leader, who is mentioned as count ''Drosaico'' by the chronicler John the Deacon (Venetian chronicler), John the Deacon. However, the peace treaty was short-lasting and next year the Venetians were defeated by the Narentines under count ''Diuditum''. Piracy continued in the Adriatic, as well as hostility towards Venice, which is seen from the contract between Emperor Lothair I and Doge Tradonico, in which the Doge committed himself to defend the cities in Italy and Istria from Slavic attacks.
Duke Mislav was succeeded around 845 by Trpimir I of Croatia, Trpimir I, who continued the formal legacy of being the vassal of the Francia, Frankish king Lothair I (840–855), although he managed to strengthen his personal rule in Croatia. Arab campaigns thoroughly weakened the Byzantine Empire and Venice, which was used in the advance of the Croatian duke in 846 and 848. In 846 Trpimir successfully attacked the Byzantine coastal cities and their ''patricius''. Between 854 and 860, he successfully defended his land from the Bulgarian invasion under Knyaz Boris I of Bulgaria, somewhere in Northeastern Bosnia, concluding a peace treaty with Boris and exchanging gifts. Constantine Porphyrogenitus mentions the traditional friendship between the Bulgarians and Croatians, who coexisted peacefully up to that time.''De Administrando Imperio'', XXXI. Of the Croats and of the country they now dwell inNada Klaić, Povijest Hrvata u ranom srednjem vijeku, Zagreb 1975., p. 227-231
In a Latin charter preserved in a rewrite from 1568, dated to 4 March 852 or, according to a newer research, about 840, Trpimir refers to himself as "leader of the Croats with the help of God" ( la, dux Croatorum iuvatus munere divino); his land, called "Kingdom of Croatia (medieval), Kingdom of the Croats" ( la, regnum Croatorum), can simply be interpreted as the "Realm of the Croats", since Trpimir was not a king. The term ''regnum'' was also used by other dukes of that time as a sign of their independence. This charter also documents his ownership of the Klis Fortress, from where his rule was centered, and mentions Mislav's donations to the Archbishopric of Split. In the proximity of his court in Klis, in Rižinice, Trpimir built a church and the first Order of Saint Benedict, Benedictine monastery in Croatia. Trpimir's name is inscribed on a stone fragment from an altar screen of the Rižinice monastery church. He is more expressly remembered as the founder of the House of Trpimirović, a native Croat dynasty that ruled, with interruptions, from 845 until 1091 in Croatia.
In 864 Duke Domagoj of Croatia, Domagoj, founder of the House of Domagojević, usurped the throne after the death of Trpimir and forced his sons, including Zdeslav of Croatia, Zdeslav, to flee to Constantinople. During the rule of Domagoj piracy was a common practice in the Adriatic. The pirates attacked Christian sailors, including a ship with papal legates returning from the Fourth Council of Constantinople (Roman Catholic), Eighth Catholic Ecumenical Council, thus forcing the Pope to intervene by asking Domagoj to stop piracy, but his efforts were of no avail. Domagoj waged wars with the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Venetians and Franks. In 871 he helped the Franks, as their vassal, to seize Bari from the Arabs, but later actions of the Franks under the rule of Carloman of Bavaria led to a revolt by Domagoj against the Frankish rule. The revolt succeeded and Frankish overlordship in Dalmatia ended, but was to continue a little longer over Pannonian Slavs#Principality, Lower Pannonia.John Van Antwerp Fine: The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century, 1991, p. 261 Domagoj's rule also saw increased Byzantine influence in the area, especially reflected in the establishment of Theme of Dalmatia. After the death of Domagoj in 876 Zdeslav, who had close ties to Byzantium, returned from exile, usurped the throne from an unnamed son of Domagoj and restored peace with Venice in 878.
Independent realm

 Duke Zdeslav's reign was short and ended in 879 when Branimir of Croatia, Branimir of the House of Domagojević killed him and usurped the throne. Branimir was unlike Zdeslav a proponent of Rome and returned the country to the Roman fold. He had regular contacts with Pope John VIII, to whom he sent a letter revealing his intentions to entrust his people and his country to the Apostolic See. The Pope replied to his requests, praising his initiative and in 879 the Duchy under Branimir, now free of Frankish suzerainty, received papal recognition as a state.Maddalena Betti: The Making of Christian Moravia (858-882), 2013, p. 130
Duke Zdeslav's reign was short and ended in 879 when Branimir of Croatia, Branimir of the House of Domagojević killed him and usurped the throne. Branimir was unlike Zdeslav a proponent of Rome and returned the country to the Roman fold. He had regular contacts with Pope John VIII, to whom he sent a letter revealing his intentions to entrust his people and his country to the Apostolic See. The Pope replied to his requests, praising his initiative and in 879 the Duchy under Branimir, now free of Frankish suzerainty, received papal recognition as a state.Maddalena Betti: The Making of Christian Moravia (858-882), 2013, p. 130/ref> The second half of the 9th century marked a significant increase in papal influence in the Southeastern Europe. Pope John VIII complained to Domagoj about the obstinacy of Ignatios of Constantinople, Patriarch Ignatius who denied his jurisdiction over Bulgaria and appointed a new Archbishop. The Pope also requested from Dukes Zdeslav and Branimir assistance and protection for his legates who were crossing Croatia on their way to First Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria. Although the exact geographical extent of the Duchy is not known, these requests confirm geographical contiguity between Croatia and Bulgaria, which bordered probably somewhere in Bosnia. Muncimir of Croatia, Muncimir (also called Mutimir), the youngest son of Trpimir, came to throne after the death of Branimir (c. 892), which marked the return of the House of Trpimirović to power. A Latin charter from Biaći near Trogir dated to 28 September 892 named Muncimir "Duke of the Croats" ( la, Croatorum dux). During his rule, in the late 9th century the Hungarians crossed the Carpathians and entered the Carpathian Basin. They invaded northern Italy and also defeated Duke Braslav of Pannonia, Braslav from the Duchy of Pannonia, endangering Croatia.John Van Antwerp Fine: The Early Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Sixth to the Late Twelfth Century, 1991, p. 262 Muncimir ruled until about 910 when he was succeeded by Tomislav of Croatia, Tomislav, the last duke and the first king of Croatia. Venetian chronicler John the Deacon wrote that in 912 a Venetian ambassador, returning from Bulgaria, passed through Croatian territory before reaching the land of Zahumlje, which suggests that Croatia at the time also bordered Bulgaria, then under the rule of Simeon I of Bulgaria, Simeon I. In Historia Salonitana, a chronicle from the 13th century written by Thomas the Archdeacon from Split, Tomislav was mentioned as Duke of Croatia in 914. According to ''De Administrando Imperio'', Croatia at the time had 100,000 infantrymen and 60,000 horsemen, 80 large ships and 100 smaller vessels, but these numbers are viewed as a clear exaggeration and an overemphasis of the Croatian forces. Croatia also waged battles with the Magyars during the early 10th century. According to the Palaeography, palaeographic analysis of the original manuscript of ''De Administrando Imperio'', assumed number of inhabitants in medieval Croatia estimated between 440,000 and 880,000 people, and military numbers of Franks and Byzantines, the military force was most probably composed of 20,000-100,000 infantrymen, and 3,000-24,000 horsemen organized in 60 allagions. During the Byzantine–Bulgarian wars#Simeon I.27s Imperial ambitions, war between the Byzantium and Bulgaria of Simeon I, in about 923, the Byzantines concluded an alliance with Croatia. Prior to that the Bulgarians had several decisive victories against the Byzantines, capturing Adrianople and endangering Constantinople. In 924 Simeon I deposed Zaharija of Serbia, Zaharija from rule in Principality of Serbia (early medieval), Serbia, who fled to Croatia. In 926, Simeon's troops invaded Croatia, but were severely defeated in the Battle of the Bosnian Highlands. In 927 Pope John X sent his legates to mediate a peace treaty between Croats and Bulgarians.Florin Curta: Southeastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 500-1250, p. 196
/ref> During these years Croatia was elevated to the status of a Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), kingdom. It is generally said that Duke Tomislav was crowned king in 925, but this is not certain since it is not known when and where was he crowned, or was he crowned at all. However, Tomislav was the first Croatian ruler whom the Papal chancellery honoured with the title king. Tomislav is mentioned as a king in two preserved documents published in the ''Historia Salonitana'' and by the ''Chronicle of the Priest of Duklja'', where Tomislav's rule was specified at 13 years. In a note preceding the text of the Council conclusions in Split in 925 it is written that Tomislav is the king "in the province of the Croats and in the Dalmatian regions" (''in prouintia Croatorum et Dalmatiarum finibus Tamisclao rege''). In the 12th canon of the Council conclusions in 925 the ruler of the Croats is called "king" (''rex et proceres Chroatorum''), while in a letter sent by the Pope John X Tomislav is named "King of the Croats" (''Tamisclao, regi Crouatorum'').Codex Diplomaticus Regni Croatiæ, Dalamatiæ et Slavoniæ, Vol I, p. 34 Although there are no inscriptions of Tomislav to confirm the title, later inscriptions and charters confirm that his 10th century successors called themselves "kings".
See also
*History of Croatia *Croatian–Bulgarian Wars *Dukes of CroatiaNotes
References
Further reading
* Rudolf Horvat, ''Povijest Hrvatske I. (od najstarijeg doba do g. 1657.)'', Zagreb 1924. * Nada Klaić, ''Povijest Hrvata u ranom srednjem vijeku'', Zagreb 1975. * Neven Budak - Prva stoljeća Hrvatske, Zagreb, 1994. * * * Thomas the Archdeacon''Historia Salonitanorum Atque Spalatinorum Pontificum''
* Severin Binius
Concilia generalia et provincialia, quotquot reperiri potuerunt. Item Epistolae decretales et Romanorum pontificum vitae
1606
External links
Croatia — an independent principality (Richard C. Frucht: ''Eastern Europe'', Edition 2005 /Santa Barbara, California, USA/)
Duke Branimir put the Principality of Croatia "permanently beneath the wing of the Roman Church and Western Christian civilization (879)" (Richard Barrie Dobson: ''Encyclopedia of the Middle Ages'', Edition 2000 /Cambridge, England, UK/)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Croats, Duchy of the Duchy of Croatia, History of Dalmatia Former Slavic countries Croatian principalities States and territories established in the 7th century States and territories disestablished in the 920s Former countries in the Balkans 7th-century establishments in Europe