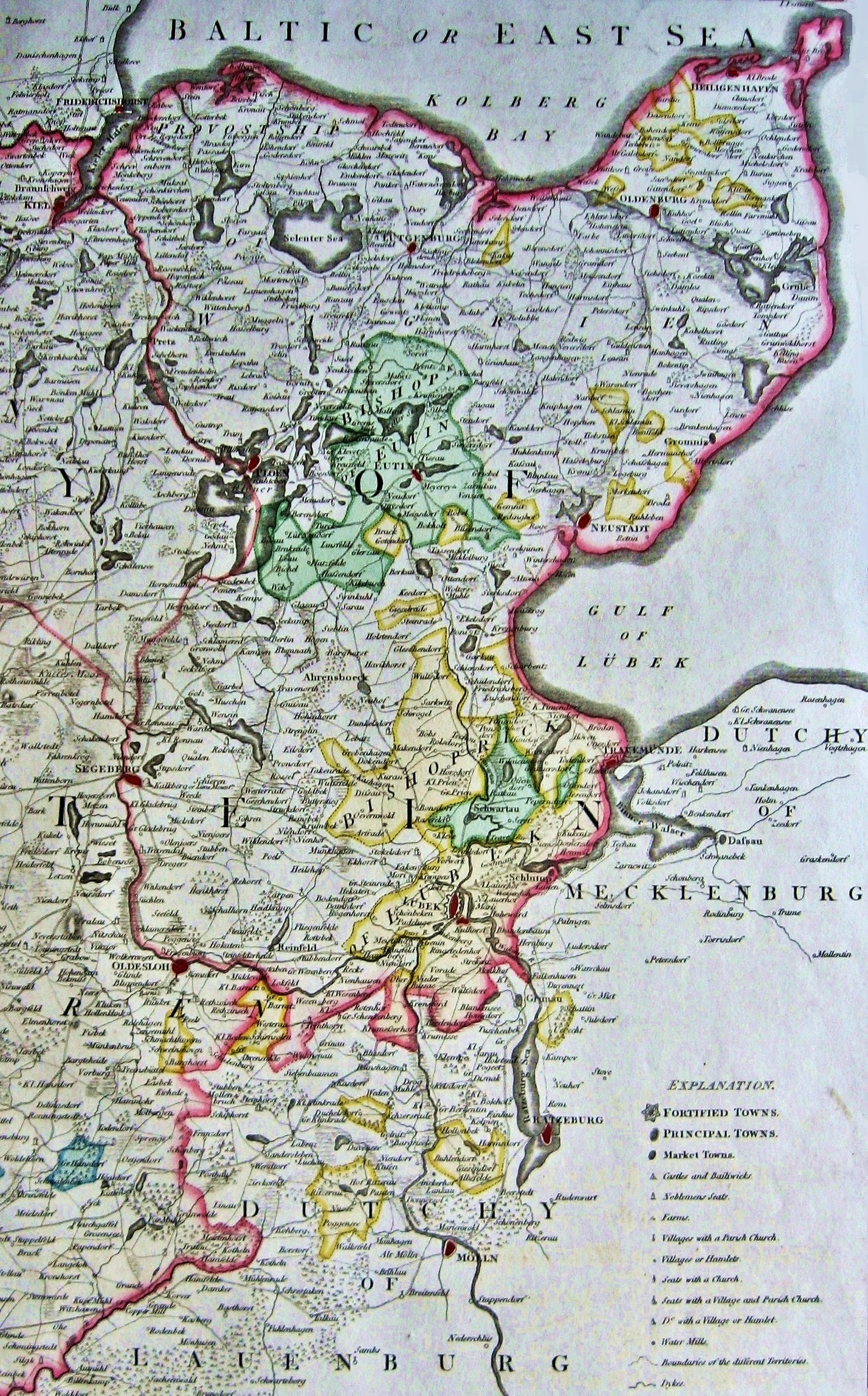
Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck, (german: Hochstift Lübeck; Fürstbistum Lübeck; Bistum Lübeck) was an ecclesiastical principality of the
 The original diocese was founded about 970 by
The original diocese was founded about 970 by  The Bishopric did not attempt to fight the
The Bishopric did not attempt to fight the
 Between 1810 and 1814 the principality was annexed to
Between 1810 and 1814 the principality was annexed to  Following the Austro-Prussian War in 1867 the principality was enlarged by the prior Holsteinian bailiwick of
Following the Austro-Prussian War in 1867 the principality was enlarged by the prior Holsteinian bailiwick of  In 1937 the region was incorporated into the Prussian
In 1937 the region was incorporated into the Prussian
At ''Meyers Konversationslexikon'', 4th ed., 1885-92
{{DEFAULTSORT:Lubeck States and territories established in 1160 Prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire in Germany Lower Saxon Circle Roman Catholic dioceses in the Holy Roman Empire Former Roman Catholic dioceses in Germany History of Lübeck Dioceses established in the 10th century 1180s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1180 establishments in Europe 1803 disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire Former states and territories of Schleswig-Holstein
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
until 1803. Originally ruled by Roman-Catholic bishops, after 1586 it was ruled by lay administrators and bishops who were members of the Protestant Holstein-Gottorp
Holstein-Gottorp or Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp () is the historiographical name, as well as contemporary shorthand name, for the parts of the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, also known as Ducal Holstein, that were ruled by the dukes of Schlesw ...
line of the House of Oldenburg
The House of Oldenburg is a German dynasty with links to Denmark since the 15th century. It has branches that rule or have ruled in Denmark, Iceland, Greece, Norway, Russia, Sweden, the United Kingdom, Schleswig, Holstein, and Oldenburg. The cu ...
. The prince-bishops had seat and vote on the Ecclesiastical Bench of the College of Ruling Princes of the Imperial Diet.
The Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck, a secular state, should not be confused with the Diocese of Lübeck, which was larger and over which the bishop exercised only pastoral authority.
History
 The original diocese was founded about 970 by
The original diocese was founded about 970 by Emperor Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
in the Billung March at Oldenburg in Holstein (''Aldinborg'' or ''Starigard''), the former capital of the pagan Wagri
The Wagri, Wagiri, or Wagrians were a tribe of Polabian Slavs inhabiting Wagria, or eastern Holstein in northern Germany, from the ninth to twelfth centuries. They were a constituent tribe of the Obodrite confederacy.
In the Slavic uprisings of 9 ...
tribe. Oldenburg was then a suffragan diocese of the Archbishopric of Bremen, meant to missionize the Obotrites
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ...
. However, in the course of the 983 Slavic uprising (''see Lutici
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
''), the Wagri shook off Imperial supremacy and in 1038, the bishops were barred from entering their diocese. In 1052, the dioceses of Ratzeburg and Schwerin
Schwerin (; Mecklenburgian Low German: ''Swerin''; Latin: ''Suerina'', ''Suerinum'') is the capital and second-largest city of the northeastern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern as well as of the region of Mecklenburg, after Rostock. It ...
were split off from Oldenburg and no bishop was appointed after 1066.
After the Saxon count Henry of Badewide had campaigned in the Wagrian lands east of the Limes Saxoniae
The Limes Saxoniae (Latin for "Limit of Saxony"), also known as the Limes Saxonicus or Sachsenwall ("Saxon Dyke"), was an unfortified limes or border between the Saxons and the Slavic Obotrites, established about 810 in present-day Schleswig ...
in 1138/39, a new Bishop of Oldenburg, Vicelinus, was appointed in 1149. Duke Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German p ...
of Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
moved the seat of the diocese from Oldenburg to Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the state ...
in 1160. When the Duchy of Saxony was dissolved with Henry's deposition in 1180, the Bishopric gained the status of Imperial State (). Quarrels arose after the City of Lübeck gained imperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular pri ...
in 1226 and as the territory of the state was centered on Eutin, the town in 1309 became the residence of the bishops.
 The Bishopric did not attempt to fight the
The Bishopric did not attempt to fight the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
. In 1531 the Free City of Lübeck, instanced by Johannes Bugenhagen
Johannes Bugenhagen (24 June 1485 – 20 April 1558), also called ''Doctor Pomeranus'' by Martin Luther, was a German theologian and Lutheran priest who introduced the Protestant Reformation in the Duchy of Pomerania and Denmark in the 16th ce ...
, had turned Protestant, further inhibiting Catholic pastoring in the part of the Lübeck diocese under city rule. And in 1535 the Lübeck cathedral chapter and subsequently all its diocesan territories adopted the Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
confession. The Prince-Bishop was elected by the chapter; since 1586, all administrators of the prince-bishopric were members of the Holstein-Gottorp
Holstein-Gottorp or Schleswig-Holstein-Gottorp () is the historiographical name, as well as contemporary shorthand name, for the parts of the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, also known as Ducal Holstein, that were ruled by the dukes of Schlesw ...
line of the House of Oldenburg
The House of Oldenburg is a German dynasty with links to Denmark since the 15th century. It has branches that rule or have ruled in Denmark, Iceland, Greece, Norway, Russia, Sweden, the United Kingdom, Schleswig, Holstein, and Oldenburg. The cu ...
. After the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, Lübeck was one of only two Protestant prince-bishoprics in the Empire (together with Osnabrück
Osnabrück (; wep, Ossenbrügge; archaic ''Osnaburg'') is a city in the German state of Lower Saxony. It is situated on the river Hase in a valley penned between the Wiehen Hills and the northern tip of the Teutoburg Forest. With a population ...
, which however was alternately led by Protestant and Catholic bishops).
Principality and Region of Lübeck
With the of 1803, the Prince-Bishopric was mediatized. It became the Principality of Lübeck and was given to theDuchy of Oldenburg
The Duchy of Oldenburg (german: Herzogtum Oldenburg)—named after its capital, the town of Oldenburg—was a state in the north-west of present-day Germany. The counts of Oldenburg died out in 1667, after which it became a duchy until 1810, w ...
, since the last prince-bishop ( Peter I of Holstein-Gottorp) was also prince regent of Oldenburg. In 1803 the principality comprised 9.5 German square milesOne German sq. mile () = 21.25 Eng. sq. miles or 55.05 km2. with 22,000 inhabitants. Its capital was Eutin.
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
as part of the , before it was restituted to the Duchy of Oldenburg. The Duchy of Oldenburg, named after its capital Oldenburg in Oldenburg, thus shared its name with the town of Oldenburg in Holstein, the original seat of the Bishopric, only by coincidence.
 Following the Austro-Prussian War in 1867 the principality was enlarged by the prior Holsteinian bailiwick of
Following the Austro-Prussian War in 1867 the principality was enlarged by the prior Holsteinian bailiwick of Ahrensbök
Ahrensbök (Holsatian: ''Ahrensböök'') is a municipality in the district of Ostholstein, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated approximately 17 km northwest of Lübeck, and 45 km southeast of Kiel.
History
Ahrensbök came in ...
, as a compensation for hereditary claims of the ducal House of Oldenburg
The House of Oldenburg is a German dynasty with links to Denmark since the 15th century. It has branches that rule or have ruled in Denmark, Iceland, Greece, Norway, Russia, Sweden, the United Kingdom, Schleswig, Holstein, and Oldenburg. The cu ...
to Holstein. After Oldenburg became a republic in 1918 the area remained an exclave of the Free State of Oldenburg
The Free State of Oldenburg (german: Freistaat Oldenburg) was a federated state of the Weimar Republic. It was established in 1918 following the abdication of the Grand Duke Frederick Augustus II following the German Revolution.
In 1937, it lo ...
now named Region of Lübeck (german: Landesteil Lübeck).
 In 1937 the region was incorporated into the Prussian
In 1937 the region was incorporated into the Prussian Province of Schleswig-Holstein
The Province of Schleswig-Holstein (german: Provinz Schleswig-Holstein ) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia (subsequently the Free State of Prussia after 1918) from 1868 to 1946.
History
It was created from the Duchies of Schleswig and H ...
by a territorial redeployment according to the Greater Hamburg Act
The Greater Hamburg Act (german: Groß-Hamburg-Gesetz), in full the Law Regarding Greater Hamburg and Other Territorial Readjustments (german: Gesetz über Groß-Hamburg und andere Gebietsbereinigungen), was passed by the government of Nazi Germa ...
. The Region of Lübeck then became the District of Eutin, which was merged with the neighbouring District of Oldenburg in Holstein in the new district of Eastern Holstein in 1970.
The Lutheran Church, since the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
comprising the majority of the inhabitants, remained a separate entity, named ''Evangelical Lutheran State Church of the Oldenburgian Region of Lübeck'' (german: Evangelisch-Lutherische Landeskirche des oldenburgischen Landesteils Lübeck, link=no, chaired by a land provost or bishop in Eutin) until it merged with neighbouring Landeskirchen in the new North Elbian Evangelical Lutheran Church in 1977.
Geography
The state had an area of ; as the imperial city of Lübeck was not incorporated, its only city was Eutin.Bishops of Oldenburg and Lübeck
Notes
References
At ''Meyers Konversationslexikon'', 4th ed., 1885-92
{{DEFAULTSORT:Lubeck States and territories established in 1160 Prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire in Germany Lower Saxon Circle Roman Catholic dioceses in the Holy Roman Empire Former Roman Catholic dioceses in Germany History of Lübeck Dioceses established in the 10th century 1180s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 1180 establishments in Europe 1803 disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire Former states and territories of Schleswig-Holstein