Pre-Modern Aliyah on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Aliyah (, ; he, עֲלִיָּה ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of
 ''Aliyah'' is an important Jewish cultural concept and a fundamental component of
''Aliyah'' is an important Jewish cultural concept and a fundamental component of
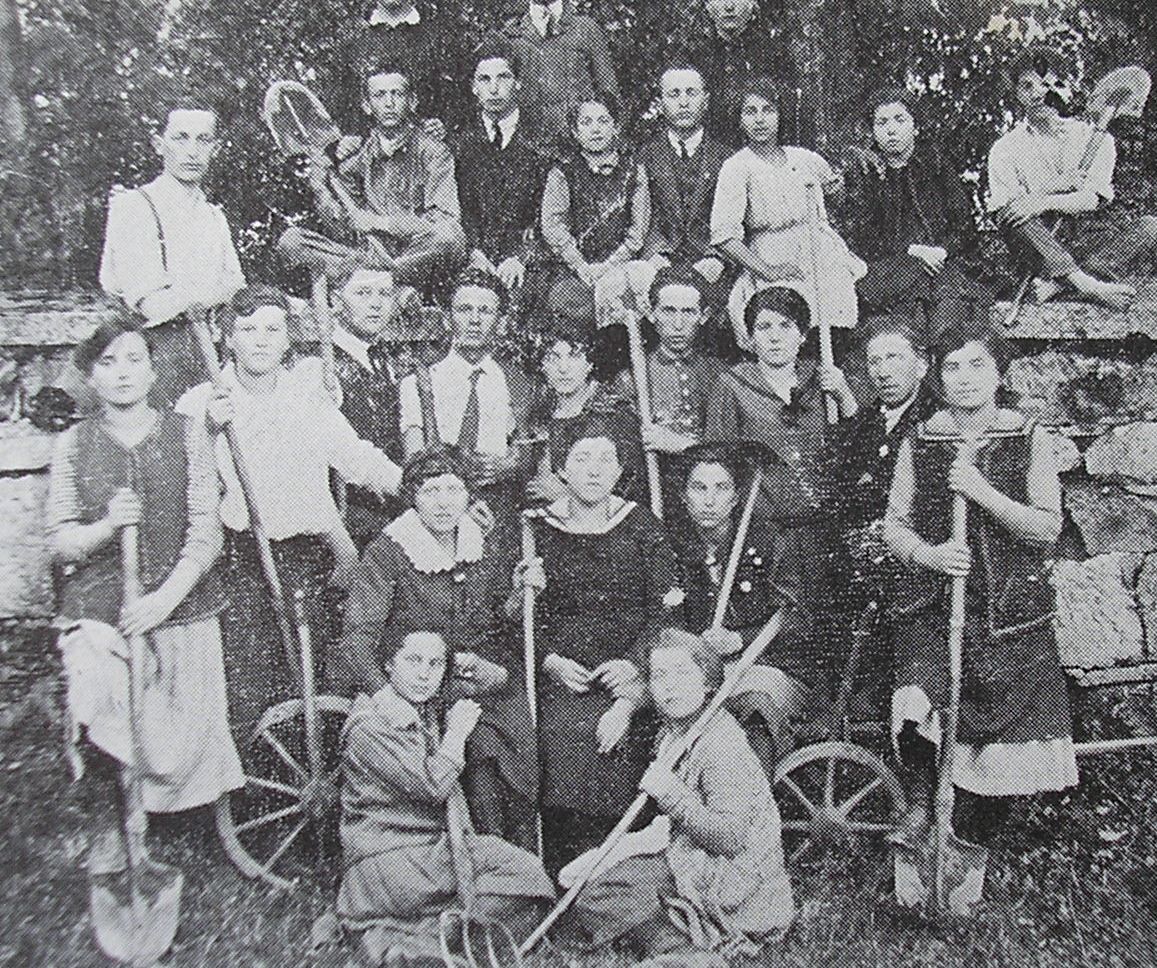 Between 1919 and 1923, 40,000 Jews, mainly from
Between 1919 and 1923, 40,000 Jews, mainly from
 Between 1929 and 1939, with the rise of
Between 1929 and 1939, with the rise of
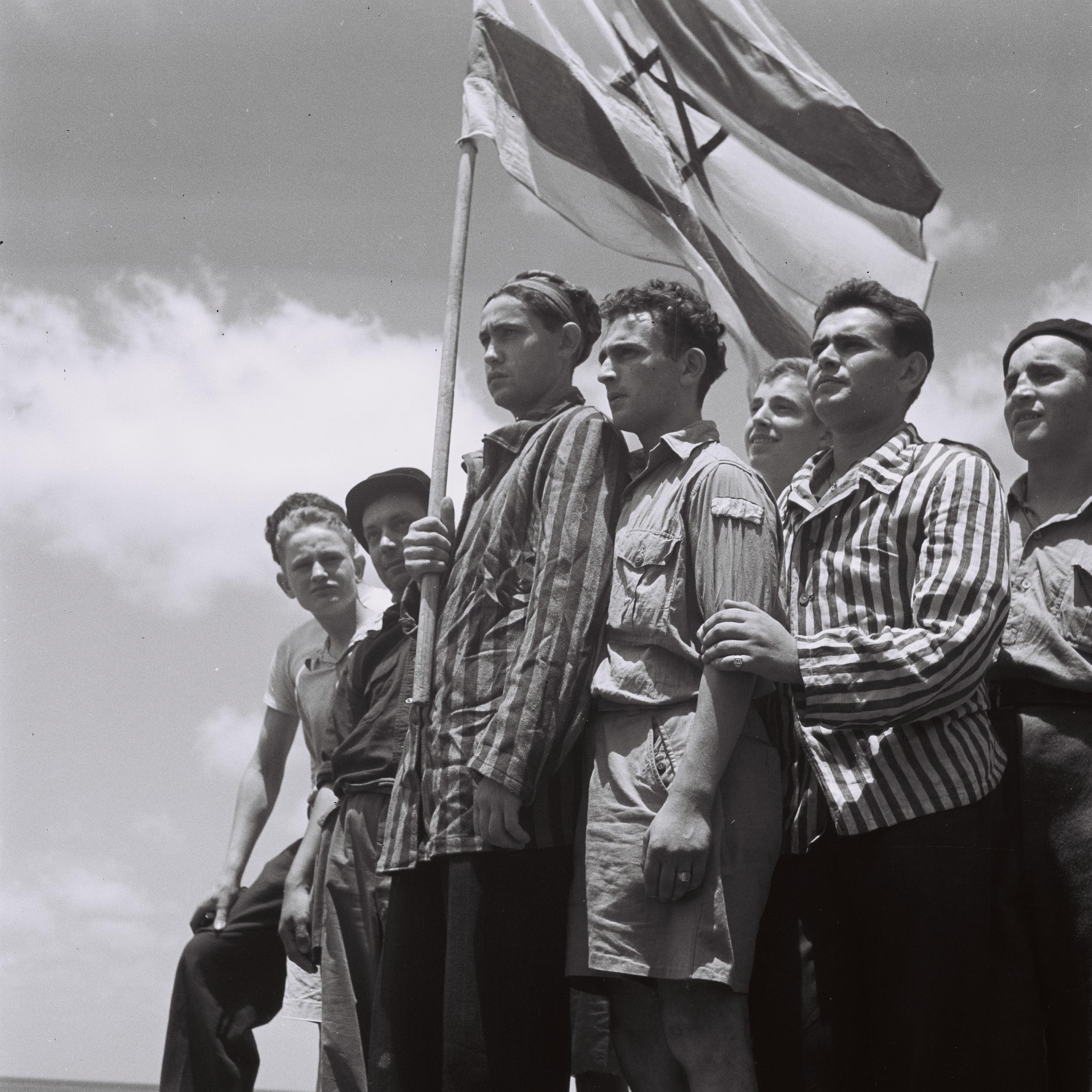 The British government limited Jewish immigration to Mandatory Palestine with quotas, and following the rise of
The British government limited Jewish immigration to Mandatory Palestine with quotas, and following the rise of
''Post-Holocaust politics: Britain, the United States & Jewish refugees, 1945-1948.'' Page 15.
The
- Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs The last ''ma'abarot'' closed in 1963. In the mid-1950s, a smaller wave of immigration began from North African countries such as
 From 1948 until the early 1970s, around 900,000 Jews from Arab lands left, fled, or were expelled from various Arab nations.Malka Hillel Shulewitz, ''The Forgotten Millions: The Modern Jewish Exodus from Arab Lands'', Continuum 2001, pp. 139 and 155.Ada Aharoni]
From 1948 until the early 1970s, around 900,000 Jews from Arab lands left, fled, or were expelled from various Arab nations.Malka Hillel Shulewitz, ''The Forgotten Millions: The Modern Jewish Exodus from Arab Lands'', Continuum 2001, pp. 139 and 155.Ada Aharoni]
"The Forced Migration of Jews from Arab Countries
, Historical Society of Jews from Egypt website. Accessed February 1, 2009. In the course of
 More than 200,000 North American immigrants live in Israel. There has been a steady flow of immigration from North America since Israel's inception in 1948.
Several thousand American Jews moved to Mandate Palestine before the State of Israel was established. From Israel's establishment in 1948 to the
More than 200,000 North American immigrants live in Israel. There has been a steady flow of immigration from North America since Israel's inception in 1948.
Several thousand American Jews moved to Mandate Palestine before the State of Israel was established. From Israel's establishment in 1948 to the
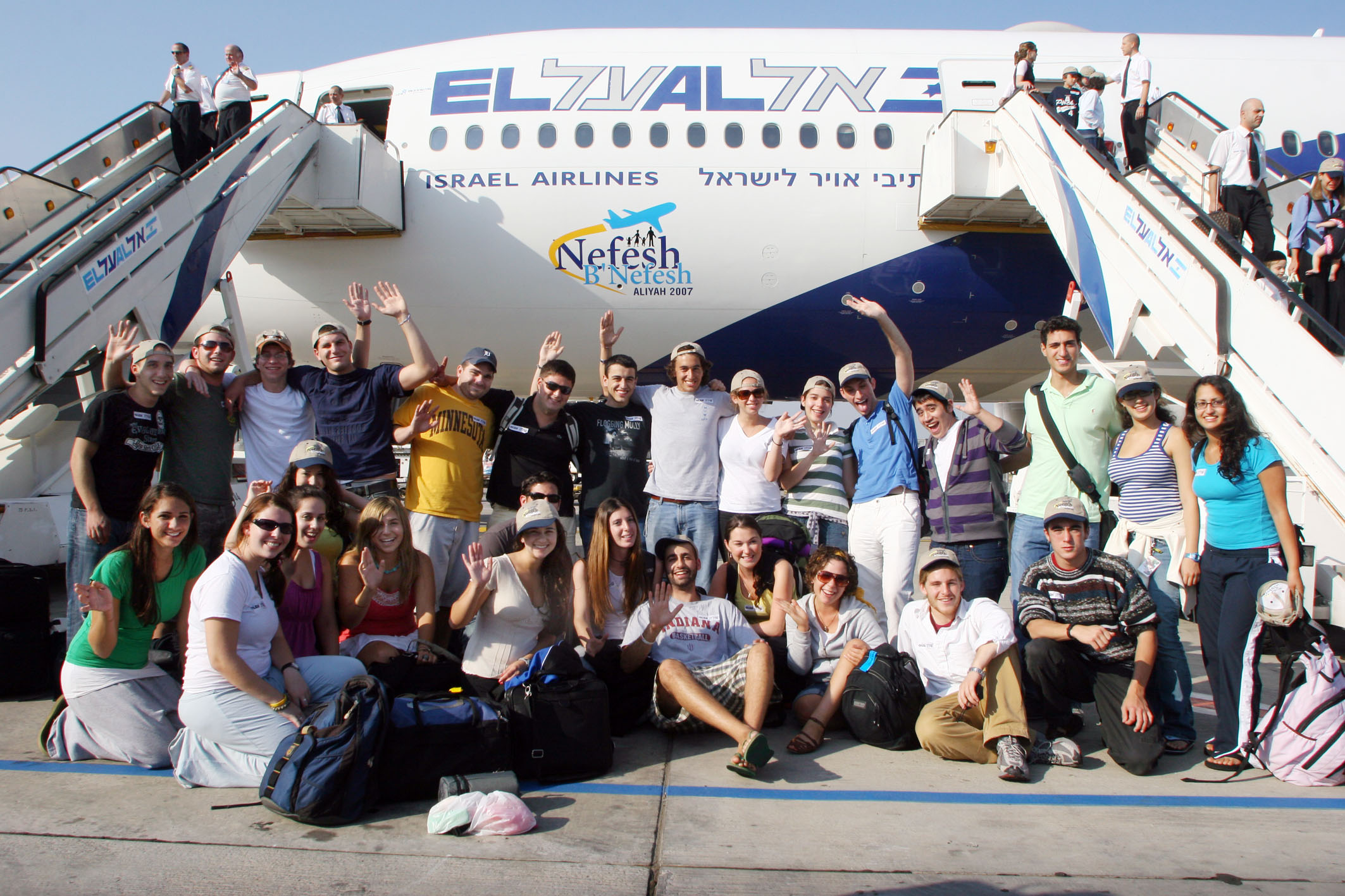 Since the mid-1990s, there has been a steady stream of History of the Jews in South Africa, South African Jews, American Jews, and French Jews who have either made aliyah, or purchased property in Israel for potential future immigration. Over 2,000 French Jews moved to Israel each year between 2000 and 2004 due to Antisemitism in 21st-century France, anti-Semitism in France. The Bnei Menashe Jews from
Since the mid-1990s, there has been a steady stream of History of the Jews in South Africa, South African Jews, American Jews, and French Jews who have either made aliyah, or purchased property in Israel for potential future immigration. Over 2,000 French Jews moved to Israel each year between 2000 and 2004 due to Antisemitism in 21st-century France, anti-Semitism in France. The Bnei Menashe Jews from
 Yom HaAliyah (Aliyah Day) ( he, יום העלייה) is an Israeli national holiday celebrated annually according to the Jewish calendar on the tenth of the
Yom HaAliyah (Aliyah Day) ( he, יום העלייה) is an Israeli national holiday celebrated annually according to the Jewish calendar on the tenth of the
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
from the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel, which is in the modern era chiefly represented by the State of Israel. Traditionally described as "the act of going up" (towards the Jewish holy city of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
), moving to the Land of Israel or "making aliyah" is one of the most basic tenets of Zionism
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
. The opposite action—emigration by Jews from the Land of Israel—is referred to in the Hebrew language
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
as ''yerida
Yerida ( he, ירידה ''yerida'', "descent") is emigration by Jews from the State of Israel (or in religious texts, Land of Israel). Yerida is the opposite of aliyah (, lit. "ascent"), which is immigration by Jews to Israel. Zionists are gener ...
'' (). The Law of Return
The Law of Return ( he, חֹוק הַשְׁבוּת, ''ḥok ha-shvūt'') is an Israeli law, passed on 5 July 1950, which gives Jews, people with one or more Jewish grandparent, and their spouses the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Isr ...
that was passed by the Israeli parliament
The Knesset ( he, הַכְּנֶסֶת ; "gathering" or "assembly") is the unicameral legislature of Israel. As the supreme state body, the Knesset is sovereign and thus has complete control of the entirety of the Israeli government (with ...
in 1950 gives all diaspora Jews, as well as their children and grandchildren, the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Israeli citizenship
Israeli citizenship law details the conditions by which a person holds citizenship of Israel. The two primary pieces of legislation governing these requirements are the 1950 Law of Return and 1952 Citizenship Law.
Every Jew in the world has ...
on the basis of connecting to their Jewish identity
Jewish identity is the objective or subjective state of perceiving oneself as a Jew and as relating to being Jewish. Under a broader definition, Jewish identity does not depend on whether a person is regarded as a Jew by others, or by an exter ...
.
For much of their history, most Jews have lived in the diaspora outside of the Land of Israel due to various historical conflicts that led to their persecution alongside multiple instances of expulsions and exoduses, with the most recent such event being the Jewish–Roman wars. Despite its historical value as a national aspiration for the Jewish people, aliyah was acted upon by few prior to the rise of a national awakening among Jews worldwide and the subsequent development of the Zionist movement in the late 19th century; the large-scale immigration of Jews to Palestine had consequently begun by 1882. Since the Israeli Declaration of Independence in 1948, more than 3 million Jews have made aliyah. , Israel and the Israeli-occupied territories
Israeli-occupied territories are the lands that were captured and occupied by Israel during the Six-Day War of 1967. While the term is currently applied to the Palestinian territories and the Golan Heights, it has also been used to refer to a ...
contain approximately 42.9 percent of the world's Jewish population.
Historical overview
Throughout the years of dispersion, a small-scale return migration ofDiaspora Jews
The Jewish diaspora ( he, תְּפוּצָה, təfūṣā) or exile (Hebrew: ; Yiddish: ) is the dispersion of Israelites or Jews out of their ancient ancestral homeland (the Land of Israel) and their subsequent settlement in other parts of th ...
to the Land of Israel is characterized as the Pre-Modern Aliyah. Successive waves of Jewish settlement are an important aspect of the history of Jewish life in Israel. The "Land of Israel" (''Eretz Yisrael
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine (see also Israe ...
'') is the Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
name for the region commonly known in English through the middle of the twentieth century, from the ancient Roman designation, as Palestine. This traditional Hebrew toponym, in turn, has lent its name to the modern State of Israel. Since the birth of Zionism
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
in the late 19th century, the advocates of aliyah have striven to facilitate the settlement of Jewish refugees
This article lists expulsions, refugee crises and other forms of displacement that have affected Jews.
Timeline
The following is a list of Jewish expulsions and events that prompted significant streams of Jewish refugees.
Assyrian captivity
; ...
in Ottoman Palestine
Ottoman Syria ( ar, سوريا العثمانية) refers to divisions of the Ottoman Empire within the region of Syria, usually defined as being east of the Mediterranean Sea, west of the Euphrates River, north of the Arabian Desert and south ...
, Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
, and the sovereign State of Israel.
The following waves of migration have been identified: the First Aliyah
The First Aliyah (Hebrew: העלייה הראשונה, ''HaAliyah HaRishona''), also known as the agriculture Aliyah, was a major wave of Jewish immigration (''aliyah'') to Ottoman Syria between 1881 and 1903. Jews who migrated in this wave came ...
and the Second Aliyah
The Second Aliyah ( he, העלייה השנייה, ''HaAliyah HaShniya'') was an aliyah (Jewish emigration to Palestine) that took place between 1904 and 1914, during which approximately 35,000 Jews immigrated into Ottoman-ruled Palestine, mos ...
to Ottoman Palestine; the Third, Fourth, and Fifth Aliyah
The Fifth Aliyah ( he, העלייה החמישית, ''HaAliyah HaHamishit'') refers to the fifth wave of the Jewish immigration to Palestine from Europe and Asia between the years 1929 and 1939, with the arrival of 225,000 to 300,000 Jews. The F ...
to Mandatory Palestine including Aliyah Bet
''Aliyah Bet'' ( he, עלייה ב', " Aliyah 'B'" – bet being the second letter of the Hebrew alphabet) was the code name given to illegal immigration by Jews, most of whom were refugees escaping from Nazi Germany, and later Holocau ...
(immigration done in spite of restrictive Mandatory law) between 1934 and 1948 and the Bericha of the Holocaust survivors
Holocaust survivors are people who survived the Holocaust, defined as the persecution and attempted annihilation of the Jews by Nazi Germany and its allies before and during World War II in Europe and North Africa. There is no universally accep ...
; the aliyah from elsewhere in the Middle East and North Africa as well as the aliyah from Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Communist countries
A communist state, also known as a Marxist–Leninist state, is a one-party state that is administered and governed by a communist party guided by Marxism–Leninism. Marxism–Leninism was the state ideology of the Soviet Union, the Cominte ...
following the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states (primarily Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 Ju ...
with the 1968 Polish political crisis
The Polish 1968 political crisis, also known in Poland as March 1968, Students' March, or March events ( pl, Marzec 1968; studencki Marzec; wydarzenia marcowe), was a series of major student, intellectual and other protests against the ruling Pol ...
, as well as the aliyah from post-Soviet states in the 1990s. Today, most aliyah consists of voluntary migration for ideological, economic, or family reunification
Family reunification is a recognized reason for immigration in many countries because of the presence of one or more family members in a certain country, therefore, enables the rest of the divided family or only specific members of the family to e ...
purposes.
Etymology
''Aliyah'' inHebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
means "ascent" or "going up". Jewish tradition views traveling to the Land of Israel as an ascent, both geographically and metaphysically. In one opinion, the geographical sense preceded the metaphorical one, as most Jews going on pilgrimage to Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, which is situated at approximately 750 meters (2,500 feet) above sea level, had to climb to a higher geographic elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Ver ...
. The reason is that many Jews in early rabbinic times used to live either in Egypt's Nile Delta and on the plains of Babylonia, which lay relatively low; or somewhere the Mediterranean Basin, from where they arrived by ship.
Religious, ideological and cultural concept
 ''Aliyah'' is an important Jewish cultural concept and a fundamental component of
''Aliyah'' is an important Jewish cultural concept and a fundamental component of Zionism
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
. It is enshrined in Israel's Law of Return
The Law of Return ( he, חֹוק הַשְׁבוּת, ''ḥok ha-shvūt'') is an Israeli law, passed on 5 July 1950, which gives Jews, people with one or more Jewish grandparent, and their spouses the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Isr ...
, which accords any Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
(deemed as such by halakha
''Halakha'' (; he, הֲלָכָה, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical commandm ...
and/or Israeli secular law) and eligible non-Jews (a child and a grandchild of a Jew, the spouse of a Jew, the spouse of a child of a Jew and the spouse of a grandchild of a Jew), the legal right
Some philosophers distinguish two types of rights, natural rights and legal rights.
* Natural rights are those that are not dependent on the laws or customs of any particular culture or government, and so are ''universal'', ''fundamental'' and ...
to assisted immigration and settlement in Israel, as well as Israeli citizenship.
Someone who "makes ''aliyah''" is called an ''oleh'' (m.; pl. ''olim'') or ''olah'' (f.; pl. ''olot''). Many religious Jews espouse ''aliyah'' as a return to the Promised land
The Promised Land ( he, הארץ המובטחת, translit.: ''ha'aretz hamuvtakhat''; ar, أرض الميعاد, translit.: ''ard al-mi'ad; also known as "The Land of Milk and Honey"'') is the land which, according to the Tanakh (the Hebrew ...
, and regard it as the fulfillment of God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
's biblical promise to the descendants of the Hebrew patriarchs Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
, Isaac
Isaac; grc, Ἰσαάκ, Isaák; ar, إسحٰق/إسحاق, Isḥāq; am, ይስሐቅ is one of the three patriarchs of the Israelites and an important figure in the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He was th ...
, and Jacob
Jacob (; ; ar, يَعْقُوب, Yaʿqūb; gr, Ἰακώβ, Iakṓb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. J ...
. Nachmanides (the Ramban) includes making aliyah in his enumeration of the 613 commandments.
In the Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the ce ...
, at the end of tractate Ketubot, the Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
says: "A man may compel his entire household to go up with him to the land of Israel, but may not compel one to leave." The discussion on this passage in the Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
emphasizes the importance of living in Israel: "One should always live in the Land of Israel, even in a town most of whose inhabitants are idolaters, but let no one live outside the Land, even in a town most of whose inhabitants are Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
; for whoever lives in the Land of Israel may be considered to have a God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
, but whoever lives outside the Land may be regarded as one who has no God."
Sifre
Sifre ( he, סִפְרֵי; ''siphrēy'', ''Sifre, Sifrei'', also, ''Sifre debe Rab'' or ''Sifre Rabbah'') refers to either of two works of '' Midrash halakha'', or classical Jewish legal biblical exegesis, based on the biblical books of Number ...
says that the mitzvah (commandment) of living in Eretz Yisrael
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine (see also Israe ...
is as important as all the other mitzvot put together. There are many mitzvot such as shmita, the sabbatical year for farming, which can only be performed in Israel.
In Zionist
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
discourse, the term ''aliyah'' (plural ''aliyot'') includes both voluntary immigration for ideological, emotional, or practical reasons and, on the other hand, mass flight of persecuted populations of Jews. The vast majority of Israeli Jews today trace their family's recent roots to outside the country. While many have actively chosen to settle in Israel rather than some other country, many had little or no choice about leaving their previous home countries. While Israel is commonly recognized as "a country of immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, a ...
", it is also, in large measure, a country of refugees, including internal refugees. Israeli citizens who marry individuals of Palestinian heritage, born within the Israeli-occupied territories and carrying Palestinian IDs, must renounce Israeli residency themselves in order to live and travel together with their spouses.
According to the traditional Jewish ordering of books of the Tanakh
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' jussive The jussive (abbreviated ) is a grammatical mood of verbs for issuing orders, commanding, or exhorting (within a subjunctive framework). English verbs are not marked for this mood. The mood is similar to the ''cohortative'' mood, which typically a ...
verb form derived from the same '' jussive The jussive (abbreviated ) is a grammatical mood of verbs for issuing orders, commanding, or exhorting (within a subjunctive framework). English verbs are not marked for this mood. The mood is similar to the ''cohortative'' mood, which typically a ...
root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
as ''aliyah'', meaning "and let him go up" (to Jerusalem in Judah).
2 Chronicles 36:23 (KJV) Thus saith Cyrus king of Persia, All the kingdoms of the earth hath the God of heaven given me; and he hath charged me to build him an house in Jerusalem, which '' s' in Judah. Who '' s there' among you of all his people? The LORD his God '' e' with him, and let him go up.
Historical background
Return to the land of Israel is a recurring theme in Jewish prayers recited every day, three times a day, and holiday services onPassover
Passover, also called Pesach (; ), is a major Jewish holiday that celebrates the Biblical story of the Israelites escape from slavery in Egypt, which occurs on the 15th day of the Hebrew month of Nisan, the first month of Aviv, or spring. ...
and Yom Kippur
Yom Kippur (; he, יוֹם כִּפּוּר, , , ) is the holiest day in Judaism and Samaritanism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, the first month of the Hebrew calendar. Primarily centered on atonement and repentance, the day' ...
traditionally conclude with the words "Next year in Jerusalem
''L'Shana Haba'ah B'Yerushalayim'' ( he, לשנה הבאה בירושלים), lit. "Next year in Jerusalem", is a phrase that is often sung at the end of the Passover Seder_and_at_the_end_of_the_'' isan_in_the__Hebrew_..._and_at_the_end_of_the_' ...
". Because Jewish lineage can provide a right to Israeli citizenship, ''aliyah'' (returning to Israel) has both a secular and a religious significance.
For generations of religious Jews, ''aliyah'' was associated with the coming of the Jewish Messiah
The Messiah in Judaism () is a savior and liberator figure in Jewish eschatology, who is believed to be the future redeemer of the Jewish people. The concept of messianism originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible a messiah is a king or ...
. Jews prayed for their Messiah to come, who was to redeem the land of Israel from gentile rule and return world Jewry to the land under a Halachic
''Halakha'' (; he, הֲלָכָה, ), also transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Jewish religious laws which is derived from the written and Oral Torah. Halakha is based on biblical comman ...
theocracy
Theocracy is a form of government in which one or more deities are recognized as supreme ruling authorities, giving divine guidance to human intermediaries who manage the government's daily affairs.
Etymology
The word theocracy originates fr ...
.
Pre-Modern Aliyah
Biblical
TheHebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Abraham Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
came to the Land of '' Abraham Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Je ...
Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
with his family and followers in approximately 1800 BC. His grandson Jacob
Jacob (; ; ar, يَعْقُوب, Yaʿqūb; gr, Ἰακώβ, Iakṓb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. J ...
went down to Egypt with his family, and after several centuries there, the Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
went back to Canaan under Moses and Joshua
Joshua () or Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' lit. 'Yahweh is salvation') ''Yēšūaʿ''; syr, ܝܫܘܥ ܒܪ ܢܘܢ ''Yəšūʿ bar Nōn''; el, Ἰησοῦς, ar , يُوشَعُ ٱبْنُ نُونٍ '' Yūšaʿ ...
, entering it in about 1300 BC.
A few decades after the fall of the Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah ( he, , ''Yəhūdā''; akk, 𒅀𒌑𒁕𒀀𒀀 ''Ya'údâ'' 'ia-ú-da-a-a'' arc, 𐤁𐤉𐤕𐤃𐤅𐤃 ''Bēyt Dāwīḏ'', " House of David") was an Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. C ...
and the Babylonian exile of the Jewish people, approximately 50,000 Jews returned to Zion following the Cyrus Declaration from 538 BC. The Jewish priestly scribe Ezra
Ezra (; he, עֶזְרָא, '; fl. 480–440 BCE), also called Ezra the Scribe (, ') and Ezra the Priest in the Book of Ezra, was a Jewish scribe ('' sofer'') and priest (''kohen''). In Greco-Latin Ezra is called Esdras ( grc-gre, Ἔσδρα ...
led the Jewish exiles living in Babylon to their home city of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
in 459 BC.
Second Temple period
Jews returned to the Land of Israel throughout the Second Temple period.Herod the Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renova ...
also encouraged aliyah and often gave key posts, such as the position of High Priest to returnees.
200–500 AD
In late antiquity, the two hubs of rabbinic learning were Babylonia and the land of Israel. Throughout the Amoraic period, many Babylonian Jews immigrated to the land of Israel and left their mark on life there, as rabbis and leaders.10th–11th century
In the 10th century, leaders of the Karaite Jewish community, mostly living under Persian rule, urged their followers to settle in Eretz Yisrael. The Karaites established their own quarter inJerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, on the western slope of the Kidron Valley
The Kidron Valley ( classical transliteration, ''Cedron'', from he, נחל קדרון, ''Naḥal Qidron'', literally Qidron River; also Qidron Valley) is the valley originating slightly northeast of the Old City of Jerusalem, which then separate ...
. During this period, there is abundant evidence of pilgrimages to Jerusalem by Jews from various countries, mainly in the month of Tishrei
Tishrei () or Tishri (; he, ''tīšrē'' or ''tīšrī''; from Akkadian ''tašrītu'' "beginning", from ''šurrû'' "to begin") is the first month of the civil year (which starts on 1 Tishrei) and the seventh month of the ecclesiastical year ...
, around the time of the Sukkot holiday.
1200–1882
The number of Jews migrating to the land of Israel rose significantly between the 13th and 19th centuries, mainly due to a general decline in the status of Jews across Europe and an increase in religious persecution. The expulsion of Jews from England (1290), France (1391),Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
(1421), and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
(the Alhambra decree of 1492) were seen by many as a sign of approaching redemption and contributed greatly to the messianic spirit of the time.
Aliyah was also spurred during this period by the resurgence of messianic fervor among the Jews of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, the Germanic states, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, and North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
. The belief in the imminent coming of the Jewish Messiah
The Messiah in Judaism () is a savior and liberator figure in Jewish eschatology, who is believed to be the future redeemer of the Jewish people. The concept of messianism originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible a messiah is a king or ...
, the ingathering of the exiles and the re-establishment of the kingdom of Israel encouraged many who had few other options to make the perilous journey to the land of Israel.
Pre-Zionist resettlement in Palestine met with various degrees of success. For example, little is known of the fate of the 1210 "aliyah of the three hundred rabbis" and their descendants. It is thought that few survived the bloody upheavals caused by the Crusader invasion in 1229 and their subsequent expulsion by the Muslims in 1291. After the fall of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
in 1453 and the expulsion of Jews from Spain (1492) and Portugal (1498), many Jews made their way to the Holy Land. Some Ukrainian Jewish refugees fleeing the pogroms of the Khmelnytsky Uprising of the mid-17th century also settled in the Holy Land. Then the immigration in the 18th and early 19th centuries of thousands of followers of various Kabbalist and Hassidic rabbis, as well as the disciples of the Vilna Gaon and the disciples of the Chattam Sofer, added considerably to the Jewish populations in Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; he, טְבֶרְיָה, ; ar, طبريا, Ṭabariyyā) is an Israeli city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's F ...
, Hebron
Hebron ( ar, الخليل or ; he, חֶבְרוֹן ) is a Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies above sea level. The second-largest city in the West Bank (after Eas ...
, and Safed.
The messianic dreams of the Gaon of Vilna
Gaon may refer to
* Gaon (Hebrew), a non-formal title given to certain Jewish Rabbis
** Geonim, presidents of the two great Talmudic Academies of Sura and Pumbedita
** Vilna Gaon, known as ''the'' Gaon of Vilnius.
* Gaon Music Chart, record chart ...
inspired one of the largest pre-Zionist waves of immigration to Eretz Yisrael. In 1808 hundreds of the Gaon's disciples, known as Perushim
The ''perushim'' ( he, פרושים) were Jewish disciples of the Vilna Gaon, Elijah ben Solomon Zalman, who left Lithuania at the beginning of the 19th century to settle in the Land of Israel, which was then part of Ottoman Syria under Otto ...
, settled in Tiberias and Safed, and later formed the core of the Old Yishuv
The Old Yishuv ( he, היישוב הישן, ''haYishuv haYashan'') were the Jewish communities of the southern Syrian provinces in the Ottoman period, up to the onset of Zionist aliyah and the consolidation of the New Yishuv by the end of Wor ...
in Jerusalem. This was part of a larger movement of thousands of Jews from countries as widely spaced as Persia and Morocco, Yemen and Russia, who moved to Israel beginning in the first decade of the nineteenth century—and in even larger numbers after the conquest of the region by Muhammad Ali of Egypt
Muhammad Ali Pasha al-Mas'ud ibn Agha, also known as Muhammad Ali of Egypt and the Sudan ( sq, Mehmet Ali Pasha, ar, محمد علي باشا, ; ota, محمد علی پاشا المسعود بن آغا; ; 4 March 1769 – 2 August 1849), was ...
in 1832—all drawn by the expectation of the arrival of the Messiah in the Jewish year 5600, Christian year 1840, a movement documented in Arie Morgenstern's '' Hastening Redemption''.
There were also those who like the British mystic Laurence Oliphant tried to lease Northern Palestine to settle the Jews there (1879).
Zionist Aliyah (1882 on)
In Zionist history, the different waves of ''aliyah'', beginning with the arrival of the '' Biluim'' fromRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
in 1882, are categorized by date and the country of origin of the immigrants.
The first modern period of immigration to receive a number in common speech was the Third Aliyah, which in the World War I period was referred to as the successor to the First and Second Aliyot from Babylonia in the Biblical period. Reference to earlier modern periods as the First and Second Aliyot appeared first in 1919 and took a while to catch on.
Ottoman Palestine (1881–1914)
The pronounced persecution of Russian Jews between 1881 and 1910 led to a large wave of emigration. Since only a small portion of East European Jews had adopted Zionism by then, between 1881 and 1914 only 30–40,000 emigrants went to Ottoman Palestine, while over one and a half million Russian Jews and 300,000 from Austria-Hungary reached Northern America.First Aliyah (1882–1903)
Between 1882 and 1903, approximately 35,000 Jews immigrated to theOttoman Palestine
Ottoman Syria ( ar, سوريا العثمانية) refers to divisions of the Ottoman Empire within the region of Syria, usually defined as being east of the Mediterranean Sea, west of the Euphrates River, north of the Arabian Desert and south ...
, joining the pre-existing Jewish population which in 1880 numbered 20,000-25,000. The Jews immigrating arrived in groups that had been assembled, or recruited. Most of these groups had been arranged in the areas of Romania and Russia in the 1880s. The migration of Jews from Russia correlates with the end of the Russian pogroms, with about 3 percent of Jews emigrating from Europe to Palestine. The groups who arrived in Palestine around this time were called ''Hibbat Tsiyon'', which is a Hebrew word meaning "fondness for Zion." They were also called ''Hovevei Tsiyon'' or "enthusiasts for Zion" by the members of the groups themselves. While these groups expressed interest and "fondness" for Palestine, they were not strong enough in number to encompass an entire mass movement as would appear later on in other waves of migration. The majority, belonging to the Hovevei Zion
Hovevei Zion ( he, חובבי ציון, lit. '' hose who areLovers of Zion''), also known as Hibbat Zion ( he, חיבת ציון), refers to a variety of organizations which were founded in 1881 in response to the Anti-Jewish pogroms in the Russ ...
and Bilu movements, came from the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
with a smaller number arriving from Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
. Many established agricultural communities. Among the towns that these individuals established are Petah Tikva (already in 1878), Rishon LeZion, Rosh Pinna
Rosh Pina or Rosh Pinna ( he, רֹאשׁ פִּנָּה, lit. ''Cornerstone'') is a local council in the Korazim Plateau in the Upper Galilee on the eastern slopes of Mount Kna'an in the Northern District of Israel. It was established as Gei ...
, and Zikhron Ya'akov
Zikhron Ya'akov ( he, זִכְרוֹן יַעֲקֹב, ''lit.'' "Jacob's Memorial"; often shortened to just ''Zikhron'') is a town in Israel, south of Haifa, and part of the Haifa District. It is located at the southern end of the Carmel mounta ...
. In 1882 the Yemenite Jews
Yemenite Jews or Yemeni Jews or Teimanim (from ''Yehudei Teman''; ar, اليهود اليمنيون) are those Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Is ...
settled in the Arab village of Silwan
Silwan or Siloam ( ar, سلوان, translit=Silwan; gr, Σιλωὰμ, translit=Siloam; he, כְּפַר הַשִּׁילוֹחַ, translit=''Kfar ha-Shiloaḥ'') is a predominantly Palestinian neighborhood in East Jerusalem, on the outskir ...
located south-east of the walls of the Old City of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
on the slopes of the Mount of Olives
The Mount of Olives or Mount Olivet ( he, הַר הַזֵּיתִים, Har ha-Zeitim; ar, جبل الزيتون, Jabal az-Zaytūn; both lit. 'Mount of Olives'; in Arabic also , , 'the Mountain') is a mountain ridge east of and adjacent to Jeru ...
. Kurdish Jews
, image = File:RABBI MOSHE GABAIL.jpg
, caption = Rabbi Moshe Gabai, head of the Jewish community of Zakho, with Israeli President Yitzhak Ben-Zvi in 1951
, pop = 200,000–300,000
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
settled in Jerusalem starting around 1895.
Second Aliyah (1904–1914)
Between 1904 and 1914, 35–40,000 Jews immigrated to Ottoman Palestine. The vast majority came from theRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, in particular from the Pale of Settlement
The Pale of Settlement (russian: Черта́ осе́длости, '; yi, דער תּחום-המושבֿ, '; he, תְּחוּם הַמּוֹשָב, ') was a western region of the Russian Empire with varying borders that existed from 1791 to 19 ...
in Eastern Europe. Jews from other countries in Eastern Europe such as Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
and Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
also joined. Jewish emigration from Eastern Europe was largely due to pogrom
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russia ...
s and outbreaks of anti-Semitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
there. However, Mountain Jews
Mountain Jews or Caucasus Jews also known as Juhuro, Juvuro, Juhuri, Juwuri, Juhurim, Kavkazi Jews or Gorsky Jews ( he, יהודי קווקז ''Yehudey Kavkaz'' or ''Yehudey he-Harim''; russian: Горские евреи, translit=Gorskie Yevrei ...
from the Caucasus and Jews from other countries including Yemen, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, and Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
also arrived at this time. The Eastern European Jewish immigrants of this period, greatly influenced by socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
ideals, established the first kibbutz, Degania Alef, in 1909 and formed self-defense organizations, such as Hashomer, to counter increasing Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
hostility and to help Jews to protect their communities from Arab marauders. Ahuzat Bayit, a new suburb of Jaffa established in 1909, eventually grew to become the city of Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the ...
. During this period, some of the underpinnings of an independent nation-state arose: Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
, the ancient national language, was revived as a spoken language; newspapers and literature written in Hebrew were published; political parties and workers organizations were established. The First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
effectively ended the period of the Second Aliyah.
It is estimated that over half of those who arrived during this period ended up leaving; Ben Gurion stated that nine out of ten left.
British Palestine (1919–1948)
Third Aliyah (1919–1923)
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
arrived in the wake of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. The British occupation of Palestine and the establishment of the British Mandate created the conditions for the implementation of the promises contained in the Balfour Declaration. Many of the Jewish immigrants were ideologically driven pioneers, known as '' halutzim'', trained in agriculture and capable of establishing self-sustaining economies. In spite of immigration quotas established by the British administration, the Jewish population reached 90,000 by the end of this period. The Jezreel Valley
The Jezreel Valley (from the he, עמק יזרעאל, translit. ''ʿĒmeq Yīzrəʿēʿl''), or Marj Ibn Amir ( ar, مرج ابن عامر), also known as the Valley of Megiddo, is a large fertile plain and inland valley in the Northern Distr ...
and the Hefer Plain marshes were drained and converted to agricultural use. Additional national institutions arose such as the Histadrut (General Labor Federation); an elected assembly; national council; and the Haganah, the forerunner of the Israel Defense Forces.
Fourth Aliyah (1924–1929)
Between 1924 and 1929, 82,000 Jews arrived, many as a result of increasinganti-Semitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
and throughout Europe. The vast majority of Jewish immigrants arrived from Europe mostly from Poland, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, Romania, and Lithuania, but about 12% came from Asia, mostly Yemen and Iraq. The immigration quotas of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
kept Jews out. This group contained many middle-class families that moved to the growing towns, establishing small businesses, and light industry. Of these approximately 23,000 left the country.
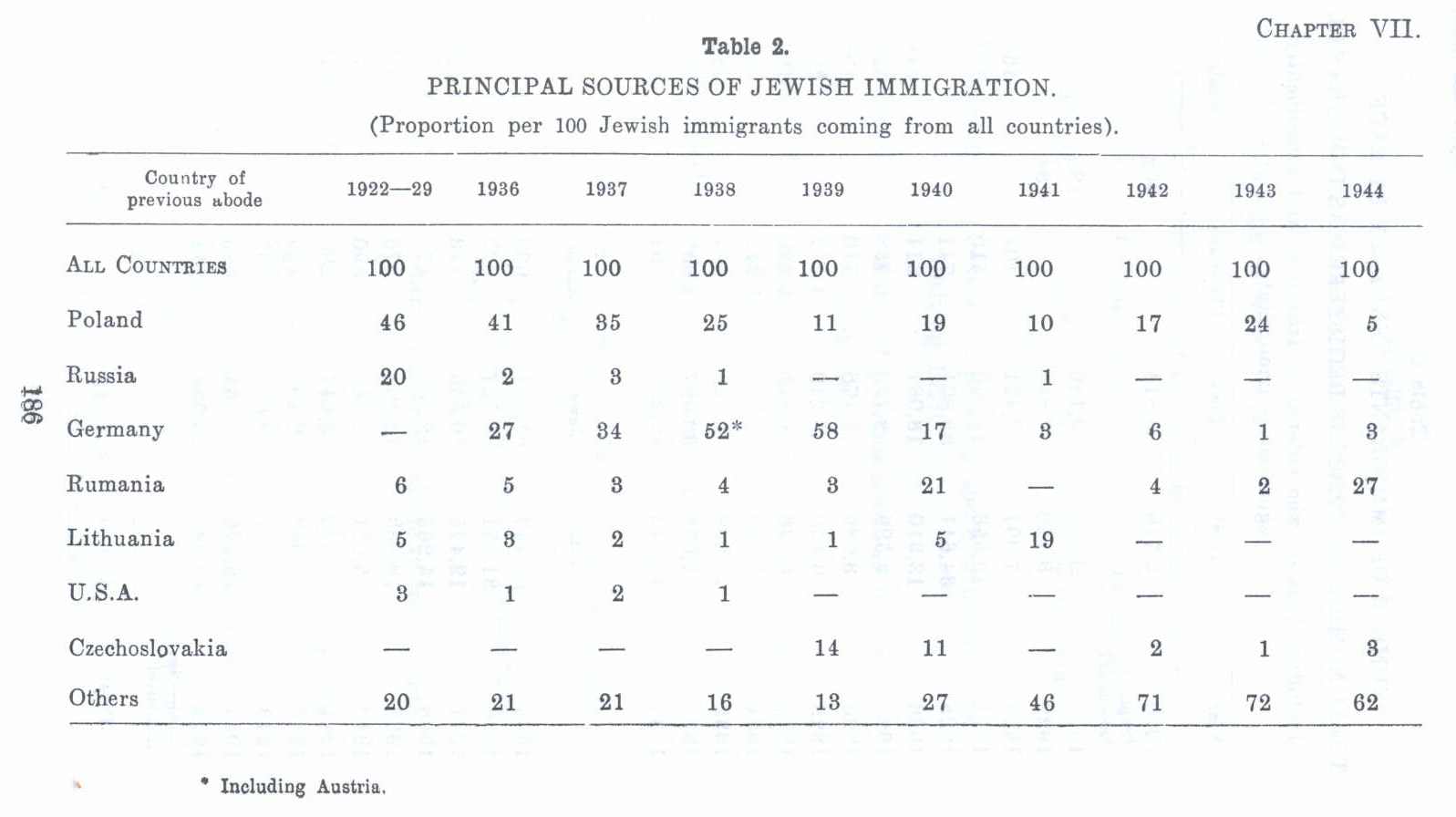
Fifth Aliyah (1929–1939)

 Between 1929 and 1939, with the rise of
Between 1929 and 1939, with the rise of Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) i ...
in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, a new wave of 250,000 immigrants arrived; the majority of these, 174,000, arrived between 1933 and 1936, after which increasing restrictions on immigration by the British made immigration clandestine and illegal, called ''Aliyah Bet''. The Fifth Aliyah was again driven almost entirely from Europe, mostly from Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
(particularly from Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, and Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
), but also from Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
. Some Jewish immigrants also came from other countries such as Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, and Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
. The Fifth Aliyah contained large numbers of professionals, doctors, lawyers, and professors, from Germany. Refugee architects and musicians introduced the Bauhaus
The Staatliches Bauhaus (), commonly known as the Bauhaus (), was a German art school operational from 1919 to 1933 that combined crafts and the fine arts.Oxford Dictionary of Art and Artists (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 4th edn., 20 ...
style (the White City of Tel Aviv has the highest concentration of International Style architecture in the world with a strong element of Bauhaus) and founded the Palestine Philharmonic Orchestra. With the completion of the port at Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
and its oil refineries
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, lique ...
, significant industry was added to the predominantly agricultural economy. The Jewish population reached 450,000 by 1940.
At the same time, tensions between Arabs and Jews grew during this period, leading to a series of Arab riots against the Jews in 1929 that left many dead and resulted in the depopulation of the Jewish community in Hebron
Hebron ( ar, الخليل or ; he, חֶבְרוֹן ) is a Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies above sea level. The second-largest city in the West Bank (after Eas ...
. This was followed by more violence during the " Great Uprising" of 1936–1939. In response to the ever-increasing tension between the Arabic and Jewish communities married with the various commitments the British faced at the dawn of World War II, the British issued the White Paper of 1939
The White Paper of 1939Occasionally also known as the MacDonald White Paper (e.g. Caplan, 2015, p.117) after Malcolm MacDonald, the British Colonial Secretary, who presided over its creation. was a policy paper issued by the British governmen ...
, which severely restricted Jewish immigration to 75,000 people for five years. This served to create a ''relatively'' peaceful eight years in Palestine while the Holocaust unfolded in Europe.
Shortly after their rise to power, the Nazis negotiated the Ha'avara or "Transfer" Agreement with the Jewish Agency under which 50,000 German Jews and $100 million worth of their assets would be moved to Palestine.
Aliyah Bet: Illegal immigration (1933–1948)
 The British government limited Jewish immigration to Mandatory Palestine with quotas, and following the rise of
The British government limited Jewish immigration to Mandatory Palestine with quotas, and following the rise of Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) i ...
to power in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, illegal immigration to Mandatory Palestine commenced. The illegal immigration was known as ''Aliyah Bet'' ("secondary immigration"), or ''Ha'apalah'', and was organized by the Mossad Le'aliyah Bet, as well as by the Irgun
Irgun • Etzel
, image = Irgun.svg , image_size = 200px
, caption = Irgun emblem. The map shows both Mandatory Palestine and the Emirate of Transjordan, which the Irgun claimed in its entirety for a future Jewish state. The acronym "Etzel" i ...
. Immigration was done mainly by sea, and to a lesser extent overland through Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
and Syria. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
and the years that followed until independence, ''Aliyah Bet'' became the main form of Jewish immigration to Mandatory Palestine.
Following the war, Berihah
Bricha ( he, בריחה, translit. ''Briẖa'', "escape" or "flight"), also called the Bericha Movement, was the underground organized effort that helped Jewish Holocaust survivors escape post–World War II Europe to the British Mandate fo ...
("escape"), an organization of former partisans and ghetto fighters was primarily responsible for smuggling Jews from Eastern Europe through Poland. In 1946 Poland was the only Eastern Bloc country to allow free Jewish aliyah to Mandate Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 i ...
without visas or exit permits. By contrast, Stalin forcibly brought Soviet Jews back to USSR, as agreed by the Allies during the Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference (codenamed Argonaut), also known as the Crimea Conference, held 4–11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union to discuss the post ...
.Arieh J. Kochavi''Post-Holocaust politics: Britain, the United States & Jewish refugees, 1945-1948.'' Page 15.
The
University of North Carolina
The University of North Carolina is the multi-campus public university system for the state of North Carolina. Overseeing the state's 16 public universities and the NC School of Science and Mathematics, it is commonly referred to as the UNC Sy ...
Press. The refugees were sent to the Italian ports from which they traveled to Mandatory Palestine. More than 4,500 survivors left the French port of Sète aboard ''President Warfield'' (renamed ''Exodus''). The British turned them back to France from Haifa, and forced them ashore in Hamburg. Despite British efforts to curb the illegal immigration, during the 14 years of its operation, 110,000 Jews immigrated to Palestine. In 1945 reports of the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
with its 6 million Jewish killed, caused many Jews in Palestine to turn openly against the British Mandate, and illegal immigration escalated rapidly as many Holocaust survivors joined the aliyah.
Early statehood (1948–1960)
After Aliyah Bet, the process of numbering or naming individual aliyot ceased, but immigration did not. A major wave of Jewish immigration, mainly from post-Holocaust Europe and the Arab and Muslim world took place from 1948 to 1951. In three and a half years, the Jewish population of Israel, which was 650,000 at the state's founding, was more than doubled by an influx of about 688,000 immigrants. In 1949, the largest-ever number of Jewish immigrants in a single year - 249,954 - arrived in Israel. This period of immigration is often termed ''kibbutz galuyot'' (literally, ingathering of exiles), due to the large number of Jewish diaspora communities that made aliyah. However, ''kibbutz galuyot'' can also refer to aliyah in general. At the beginning of the immigration wave, most of the immigrants to reach Israel were Holocaust survivors from Europe, including many fromdisplaced persons camp
A refugee camp is a temporary settlement built to receive refugees and people in refugee-like situations. Refugee camps usually accommodate displaced people who have fled their home country, but camps are also made for internally displaced peop ...
s in Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, and from British detention camps on Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ge ...
. Large sections of shattered Jewish communities throughout Europe, such as those from Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
and Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
also immigrated to Israel, with some communities, such as those from Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
, being almost entirely transferred. At the same time, the number of Jewish immigrants from Arab countries greatly increased. Special operations were undertaken to evacuate Jewish communities perceived to be in serious danger to Israel, such as Operation Magic Carpet
Operation Magic Carpet was the post-World War II operation by the War Shipping Administration to repatriate over eight million American military personnel from the European, Pacific, and Asian theaters. Hundreds of Liberty ships, Victory ships ...
, which evacuated almost the entire Jewish population of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
, and Operation Ezra and Nehemiah
From 1951 to 1952, Operation Ezra and Nehemiah airlifted between 120,000 and 130,000 Iraqi Jews to Israel via Iran and Cyprus. The massive emigration of Iraqi Jews was among the most climactic events of the Jewish exodus from the Muslim World.
...
, which airlifted most of the Jews of Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
to Israel. Egyptian Jews were smuggled to Israel in Operation Goshen. Nearly the entire Jewish population of Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
left for Israel around this time, and clandestine aliyah from Syria took place, as the Syrian government prohibited Jewish emigration, in a process that was to last decades. Israel also saw significant immigration of Jews from non-Arab Muslim countries such as Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
, and Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
in this period.
This resulted in a period of austerity. To ensure that Israel, which at that time had a small economy and scant foreign currency reserves, could provide for the immigrants, a strict regime of rationing was put in place. Measures were enacted to ensure that all Israeli citizens had access to adequate food, housing, and clothing. Austerity was very restrictive until 1953; the previous year, Israel had signed a reparations agreement with West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
, in which the West German government would pay Israel as compensation for the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; ...
, due to Israel's taking in a large number of Holocaust survivors. The resulting influx of foreign capital boosted the Israeli economy and allowed for the relaxing of most restrictions. The remaining austerity measures were gradually phased out throughout the following years.
When new immigrants arrived in Israel, they were sprayed with DDT
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, commonly known as DDT, is a colorless, tasteless, and almost odorless crystalline chemical compound, an organochloride. Originally developed as an insecticide, it became infamous for its environmental impacts. ...
, underwent a medical examination, were inoculated against diseases, and were given food. The earliest immigrants received desirable homes in established urban areas, but most of the immigrants were then sent to transit camps, known initially as immigrant camps, and later as ''Ma'abarot
Ma'abarot ( he, מַעְבָּרוֹת) were immigrant and refugee absorption camps established in Israel in the 1950s, constituting one of the largest public projects planned by the state to implement its sociospatial and housing policies.
T ...
''. Many were also initially housed in reception centers in military barracks. By the end of 1950, some 93,000 immigrants were housed in 62 transit camps. The Israeli government's goal was to get the immigrants out of refugee housing and into society as speedily as possible. Immigrants who left the camps received a ration card, an identity card, a mattress, a pair of blankets, and $21 to $36 in cash. They settled either in established cities and towns, or in kibbutzim and moshavim. Many others stayed in the ''Ma'abarot'' as they were gradually turned into permanent cities and towns, which became known as development town
Development towns ( he, עיירת פיתוח, ''Ayarat Pitu'ah'') were new settlements built in Israel during the 1950s in order to provide permanent housing for a large influx of Jewish immigrants from Arab countries, Holocaust survivors from E ...
s, or were absorbed as neighborhoods of the towns they were attached to, and the tin dwellings were replaced with permanent housing.
In the early 1950s, the immigration wave subsided, and emigration increased; ultimately, some 10% of the immigrants would leave Israel for other countries in the following years. In 1953, immigration to Israel averaged 1,200 a month, while emigration averaged 700 a month. The end of the period of mass immigration gave Israel a critical opportunity to more rapidly absorb the immigrants still living in transit camps. The Israeli government built 260 new settlements and 78,000 housing units to accommodate the immigrants, and by the mid-1950s, almost all were in permanent housing.Aliyah- Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs The last ''ma'abarot'' closed in 1963. In the mid-1950s, a smaller wave of immigration began from North African countries such as
Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
, Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, many of which were in the midst of nationalist struggles. Between 1952 and 1964, some 240,000 North African Jews came to Israel. During this period, smaller but significant numbers arrived from other places such as Europe, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, and Latin America. In particular, a small immigration wave from then Polish People's Republic, communist Poland, known as the "Władysław Gomułka, Gomulka Aliyah", took place during this period. From 1956 to 1960, Poland permitted free Jewish emigration, and some 50,000 Polish Jews immigrated to Israel.
Since the founding of the State of Israel, the Jewish Agency for Israel was mandated as the organization responsible for aliyah in the diaspora.
From Arab countries
 From 1948 until the early 1970s, around 900,000 Jews from Arab lands left, fled, or were expelled from various Arab nations.Malka Hillel Shulewitz, ''The Forgotten Millions: The Modern Jewish Exodus from Arab Lands'', Continuum 2001, pp. 139 and 155.Ada Aharoni]
From 1948 until the early 1970s, around 900,000 Jews from Arab lands left, fled, or were expelled from various Arab nations.Malka Hillel Shulewitz, ''The Forgotten Millions: The Modern Jewish Exodus from Arab Lands'', Continuum 2001, pp. 139 and 155.Ada Aharoni]"The Forced Migration of Jews from Arab Countries
, Historical Society of Jews from Egypt website. Accessed February 1, 2009. In the course of
Operation Magic Carpet
Operation Magic Carpet was the post-World War II operation by the War Shipping Administration to repatriate over eight million American military personnel from the European, Pacific, and Asian theaters. Hundreds of Liberty ships, Victory ships ...
(1949–1950), nearly the entire community of Yemenite Jews (about 49,000) immigrated to Israel. Its other name, Operation On Wings of Eagles (Hebrew: כנפי נשרים, Kanfei Nesharim), was inspired by
:Exodus 19:4 - ''Ye have seen what I did unto the Egyptians, and how I bare you on eagles' wings, and brought you unto myself''. and
:Isaiah 40:31 - ''But they that wait upon the LORD shall renew their strength; they shall mount up with wings as eagles; they shall run, and not be weary; and they shall walk, and not faint''. Some 120,000 History of the Jews in Iraq, Iraqi Jews were airlifted to Israel in Operation Ezra and Nehemiah
From 1951 to 1952, Operation Ezra and Nehemiah airlifted between 120,000 and 130,000 Iraqi Jews to Israel via Iran and Cyprus. The massive emigration of Iraqi Jews was among the most climactic events of the Jewish exodus from the Muslim World.
...
.
From Iran
Following the establishment of Israel, about one-third of Persian Jews, Iranian Jews, most of them poor, immigrated to Israel, and immigration from Iran continued throughout the following decades. An estimated 70,000 Iranian Jews immigrated to Israel between 1948 and 1978. Following the Iranian Revolution, Islamic Revolution in 1979, most of the Iranian Jewish community left, with some 20,000 Iranian Jews immigrating to Israel. Many Iranian Jews also settled in the United States (especially in New York City and Los Angeles, California, Los Angeles).Littman (1979), p. 5.From Ethiopia
The first major wave of aliyah from Ethiopia took place in the mid-1970s. The massive airlift known as Operation Moses began to bring Ethiopian Jews to Israel on November 18, 1984, and ended on January 5, 1985. During those six weeks, some 6,500–8,000 Ethiopian Jews were flown from Sudan to Israel. An estimated 2,000–4,000 Jews died en route to Sudan or in Sudanese refugee camps. In 1991 Operation Solomon was launched to bring the Beta Israel Jews of Ethiopia. In one day, May 24, 34 aircraft landed at Addis Ababa and brought 14,325 Jews from Ethiopia to Israel. Since that time, Ethiopian Jews have continued to immigrate to Israel bringing the number of Ethiopian-Israelis today to over 100,000.From the Soviet Union and post-Soviet states
A mass emigration was politically undesirable for the Soviet regime. The only acceptable ground was family reunification, and a formal petition ("вызов", ''vyzov'') from a relative from abroad was required for the processing to begin. Often, the result was a refusenik (Soviet Union), formal refusal. The risks to apply for an exit visa compounded because the entire family had to quit their jobs, which in turn would make them vulnerable to charges of Parasitism (social offense), social parasitism, a criminal offense. Because of these hardships, Israel set up the group Lishkat Hakesher in the early 1950s to maintain contact and promote aliyah with Jews behind the Iron Curtain. From Israel's establishment in 1948 to theSix-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states (primarily Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 Ju ...
in 1967, Soviet aliyah remained minimal. Those who made aliyah during this period were mainly elderly people granted clearance to leave for family reunification purposes. Only about 22,000 Soviet Jews managed to reach Israel. In the wake of the Six-Day War, the USSR broke off the diplomatic relations with the Jewish state. An Anti-Zionism, Anti-Zionist propaganda campaign in the state-controlled mass media and the rise of Zionology were accompanied by harsher discrimination of the Soviet Jews. By the end of the 1960s, Jewish cultural and religious life in the Soviet Union had become practically impossible, and the majority of Soviet Jews were cultural assimilation, assimilated and atheist, non-religious, but this new wave of state-sponsored anti-Semitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
on one hand, and the sense of pride for victorious Jewish nation over Soviet-armed Arab armies on the other, stirred up Zionist
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after '' Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
feelings.
After the Dymshits-Kuznetsov hijacking affair and the crackdown that followed, strong international condemnations caused the Soviet authorities to increase the emigration quota. In the years 1960–1970, the USSR let only 4,000 people leave; in the following decade, the number rose to 250,000. The exodus of Soviet Jews began in 1968.
Between 1968 and 1973, almost all Soviet Jews allowed to leave settled in Israel, and only a small minority moved to other Western countries. However, in the following years, the number of those moving to other Western nations increased. Soviet Jews granted permission to leave were taken by train to Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
to be processed and then flown to Israel. There, the ones who chose not to go to Israel, called "dropouts", exchanged their immigrant invitations to Israel for refugee status in a Western country, especially the United States. Eventually, most Soviet Jews granted permission to leave became dropouts. Overall, between 1970 and 1988, some 291,000 Soviet Jews were granted exit visas, of whom 165,000 moved to Israel and 126,000 moved to the United States. In 1989 a record 71,000 Soviet Jews were granted exodus from the USSR, of whom only 12,117 immigrated to Israel.
In 1989 the United States changed its immigration policy of unconditionally granting Soviet Jews refugee status. That same year, Soviet Premier Mikhail Gorbachev ended restrictions on Jewish immigration, and the Soviet Union itself collapsed in 1991. Since then, about a million people from the former Soviet Union immigrated to Israel, including approximately 240,000 who were not Jewish according to rabbinical law, but were eligible for Israeli citizenship under the Law of Return
The Law of Return ( he, חֹוק הַשְׁבוּת, ''ḥok ha-shvūt'') is an Israeli law, passed on 5 July 1950, which gives Jews, people with one or more Jewish grandparent, and their spouses the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Isr ...
.
The number of immigrants counted as halachically non-Jewish from the former USSR has been constantly rising ever since 1989. For example, in 1990 around 96% of the immigrants were halachically Jewish and only 4% were non-Jewish family members. However, in 2000, the proportion was: Jews (includes children from non-Jewish father and Jewish mother) - 47%, Non-Jewish spouses of Jews - 14%, children from Jewish father and non-Jewish mother - 17%, Non-Jewish spouses of children from Jewish father and non-Jewish mother - 6%, non-Jews with a Jewish grandparent - 14% & Non-Jewish spouses of non-Jews with a Jewish grandparent - 2%.
Following the Russian military intervention in Ukraine (2014–present), 2014 Russian invasion of Ukraine, Ukrainian Jews making aliyah from the Ukraine reached 142% higher during the first four months of 2014 compared to the previous year. In 2014, aliyah from the former Soviet Union went up 50% from the previous year with some 11,430 people or approximately 43% of all Jewish immigrants arrived from the former Soviet Union, propelled from the increase from Ukraine with some 5,840 new immigrants have come from Ukraine over the course of the year.
The wave of aliyah from Russia since 2014 has been called "Putin's aliyah", "Putin's exodus", and "cheese aliyah" (foreign cheese was one of the first products to disappear from Russian shops because of anti-sanctions imposed by the Russian government). The number of repatriants in this wave is comparable with that coming from the USSR between 1970 and 1988.
Following 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, Israel announced "Immigrants Come Home" operation. As of June 2022, more than 25,000 people arrived in Israel from Ukraine, Russia, Belarus and Moldova.
From Latin America
In the Argentine economic crisis (1999–2002), 1999–2002 Argentine political and economic crisis that caused a run on the banks, wiped out billions of dollars in deposits and decimatedArgentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
's middle class, most of the country's estimated 200,000 Jews were directly affected. Some 4,400 chose to start over and move to Israel, where they saw opportunity.
More than 10,000 List of Argentine Jews, Argentine Jews immigrated to Israel since 2000, joining the thousands of previous Argentine immigrants already there. The crisis in Argentina also affected its neighbour country Uruguay, from which about half of its 40,000-strong Jewish community left, mainly to Israel, in the same period. During 2002 and 2003 the Jewish Agency for Israel launched an intensive public campaign to promote aliyah from the region, and offered additional economic aid for immigrants from Argentina. Although the economy of Argentina improved, and some who had immigrated to Israel from Argentina moved back following South American country's economic growth from 2003 onwards, Argentine Jews continue to immigrate to Israel, albeit in smaller numbers than before. The Argentine community in Israel is about 50,000-70,000 people, the largest Latin American group in the country.
There has also been immigration from other Latin American countries that have experienced crises, though they have come in smaller numbers and are not eligible for the same economic benefits as immigrants to Israel from Argentina.
In Venezuela, growing antisemitism in the country, including antisemitic violence, caused an increasing number of Jews to move to Israel during the 2000s. For the first time in Venezuelan history, Jews began leaving for Israel in the hundreds. By November 2010, more than half of Venezuela's 20,000-strong Jewish community had left the country.
From France
From 2000 to 2009, more than 13,000 French Jews immigrated to Israel, largely as a result of Anti-Semitism in 21st century France, growing anti-semitism in the country. A peak was reached in 2005, with 2,951 immigrants. However, between 20 and 30% eventually returned to France. After the election of Nicolas Sarkozy, French aliyah dropped due to the Jewish community's comfort with him. In 2010 only 1,286 French Jews made aliyah. In 2012, some 200,000 French citizens lived in Israel. During the same year, following the election of François Hollande and the Toulouse and Montauban shootings, Jewish school shooting in Toulouse, as well as ongoing acts of anti-semitism and the European economic crisis, an increasing number of French Jews began buying property in Israel. In August 2012, it was reported that anti-semitic attacks had risen by 40% in the five months following the Toulouse shooting, and that many French Jews were seriously considering immigrating to Israel. In 2013, 3,120 French Jews immigrated to Israel, marking a 63% increase over the previous year. In the first two months of 2014, French Jewish aliyah increased precipitously by 312% with 854 French Jews making aliyah over the first two months. Immigration from France throughout 2014 has been attributed to several factors, of which includes increasing antisemitism, in which many Jews have been harassed and attacked by a fusillade of local thugs and gangs, a stagnant European economy and concomitant high youth unemployment rates. During the first few months of 2014, The Jewish Agency of Israel has continued to encourage an increase of French aliyah through aliyah fairs, Hebrew-language courses, sessions which help potential immigrants to find jobs in Israel, and immigrant absorption in Israel. A May 2014 survey revealed that 74 percent of French Jews consider leaving France for Israel where of the 74 percent, 29.9 percent cited anti-Semitism. Another 24.4 cited their desire to “preserve their Judaism,” while 12.4 percent said they were attracted by other countries. “Economic considerations” was cited by 7.5 percent of the respondents. By June 2014, it was estimated by the end of 2014 a full 1 percent of the French Jewish community will have made aliyah to Israel, the largest in a single year. Many Jewish leaders stated the emigration is being driven by a combination of factors, including the cultural gravitation towards Israel and France's economic woes, especially for the younger generation drawn by the possibility of other socioeconomic opportunities in the more vibrant Israeli economy. During the Hebrew year 5774 (September 2013 - September 2014) for the first time ever, more Jews made aliyah from France than any other country, with approximately 6,000 French Jews making aliyah, mainly fleeing rampant antisemitism, pro-Palestinian and anti-Zionist violence and economic malaise with France becoming the top sending country for aliyah as of late September 2014. In January 2015, events such as the Charlie Hebdo shooting and Porte de Vincennes hostage crisis created a shock wave of fear across the French Jewish community. As a result of these events, the Jewish Agency planned an aliyah plan for 120,000 French Jews who wish to make aliyah. In addition, with Europe's stagnant economy as of early 2015, many affluent French Jewish skilled professionals, businesspeople and investors have sought Israel as a start-up haven for international investments, as well as job and new business opportunities. In addition, Dov Maimon, a French Jewish émigré who studies migration as a senior fellow at the Jewish People Policy Institute, expects as many as 250,000 French Jews to make aliyah by 2030. Hours after an attack and an ISIS flag was raised on a gas factory near Lyon where the severed head of a local businessman was pinned to the gates on June 26, 2015, Immigration and Absorption Minister Zeev Elkin, Ze’ev Elkin strongly urged the French Jewish community to move to Israel and made it a national priority for Israel to welcome the French Jewish community with open arms. Immigration from France is on the rise: in the first half of 2015, approximately 5,100 French Jews made aliyah to Israel marking 25% more than in the same period during the previous year when about 7,000 made aliyah during all of 2014, indicating that about 10,000 should be expected for the full year of 2015. Following the November 2015 Paris attacks committed by suspected ISIS affiliates in retaliation for Opération Chammal, one source reported that 80 percent of French Jews were considering making aliyah. According to the Jewish Agency, nearly 6500 French Jews had made aliyah between January and November 2015.From North America
 More than 200,000 North American immigrants live in Israel. There has been a steady flow of immigration from North America since Israel's inception in 1948.
Several thousand American Jews moved to Mandate Palestine before the State of Israel was established. From Israel's establishment in 1948 to the
More than 200,000 North American immigrants live in Israel. There has been a steady flow of immigration from North America since Israel's inception in 1948.
Several thousand American Jews moved to Mandate Palestine before the State of Israel was established. From Israel's establishment in 1948 to the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states (primarily Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 Ju ...
in 1967, aliyah from the United States and Canada was minimal. In 1959, a former President of the Association of Americans and Canadians in Israel estimated that out of the 35,000 American and Canadian Jews who had made aliyah, only 6,000 remained.
Following the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states (primarily Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 Ju ...
in 1967, and the subsequent euphoria among world Jewry, significant numbers arrived in the late 1960s and 1970s, whereas it had been a mere trickle before. Between 1967 and 1973, 60,000 North American Jews immigrated to Israel. However, many of them later returned to their original countries. An estimated 58% of American Jews who immigrated to Israel between 1961 and 1972 ended up returning to the United States.
Like Western European immigrants, North Americans tend to immigrate to Israel more for religious, ideological, and political purposes, and not financial or security ones. Many immigrants began arriving in Israel after the First Intifada, First and Second Intifada, with a total of 3,052 arriving in 2005 — the highest number since 1983.
Nefesh B'Nefesh, founded in 2002 by Rabbi Yehoshua Fass and Tony Gelbart, works to encourage aliyah from North America and the UK by providing financial assistance, employment services and streamlined governmental procedures. Nefesh B’Nefesh works in cooperation with the Jewish Agency and the Israeli Government in increasing the numbers of North American and British immigrants.
Following the financial crisis of 2007–2008, American Jewish immigration to Israel rose. This wave of immigration was triggered by Israel's lower unemployment rate, combined with financial incentives offered to new Jewish immigrants. In 2009, aliyah was at its highest in 36 years, with 3,324 North American Jews making aliyah.
Since the 1990s
 Since the mid-1990s, there has been a steady stream of History of the Jews in South Africa, South African Jews, American Jews, and French Jews who have either made aliyah, or purchased property in Israel for potential future immigration. Over 2,000 French Jews moved to Israel each year between 2000 and 2004 due to Antisemitism in 21st-century France, anti-Semitism in France. The Bnei Menashe Jews from
Since the mid-1990s, there has been a steady stream of History of the Jews in South Africa, South African Jews, American Jews, and French Jews who have either made aliyah, or purchased property in Israel for potential future immigration. Over 2,000 French Jews moved to Israel each year between 2000 and 2004 due to Antisemitism in 21st-century France, anti-Semitism in France. The Bnei Menashe Jews from India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, whose recent discovery and recognition by mainstream Judaism as descendants of the Ten Lost Tribes is subject to some controversy, slowly started their aliyah in the early 1990s and continue arriving in slow numbers. Organizations such as Nefesh B'Nefesh and Shavei Israel help with aliyah by supporting financial aid and guidance on a variety of topics such as finding work, learning Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
, and cultural assimilation, assimilation into Israeli culture.
In early 2007 ''Haaretz'' reported that aliyah for the year of 2006 was down approximately 9% from 2005, "the lowest number of immigrants recorded since 1988". The number of new immigrants in 2007 was 18,127, the lowest since 1988. Only 36% of these new immigrants came from the former Soviet Union (close to 90% in the 1990s) while the number of immigrants from countries like France and the United States is stable. Some 15,452 immigrants arrived in Israel in 2008 and 16,465 in 2009. On October 20, 2009, the first group of Kaifeng Jews arrived in Israel, in an aliyah operation coordinated by Shavei Israel. ''Shalom Life'' reported that over 19,000 new immigrants arrived in Israel in 2010, an increase of 16 percent over 2009.
Paternity testing
In 2013, the office of the Prime Minister of Israel announced that some people born out of wedlock, "wishing to immigrate to Israel could be subjected to DNA testing" to prove their paternity is as they claim. A Foreign Ministry spokesman said the genetic paternity testing idea is based on the recommendations of Nativ (Liaison Bureau), Nativ, an Israeli government organization that has helped Soviet Union, Soviet and Post-Soviet states, post-Soviet Jews with aliyah since the 1950s.Holiday
 Yom HaAliyah (Aliyah Day) ( he, יום העלייה) is an Israeli national holiday celebrated annually according to the Jewish calendar on the tenth of the
Yom HaAliyah (Aliyah Day) ( he, יום העלייה) is an Israeli national holiday celebrated annually according to the Jewish calendar on the tenth of the Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
month of Nisan to commemorate the Jews, Jewish people entering the Land of Israel as written in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' State of Israel, and honor the ongoing contributions of Olim, Jewish immigrants, to Israeli society. Yom HaAliyah is also observed in Israeli schools on the seventh of the Hebrew month of Cheshvan. The opening clause of the Yom HaAliyah Law states in Hebrew: English translation: The original day chosen for Yom HaAliyah, the tenth of Nisan, is laden with symbolism. Although a modern holiday created by the Knesset of Israel, the tenth of Nisan is a date of religious significance for the Jewish People as recounted in the Hebrew Bible and in traditional Jewish thought. On the tenth of Nisan, according to the biblical narrative in the Book of Joshua,
Immigration to Israel
at the Jewish Virtual Library
Making Aliyah
at the Israel Government Portal
of the Ministry of Immigrant Absorption
Official website
of Nefesh B'Nefesh, organization for aliyah from North America and UK
Aliyah to Israel
at Israel Science and Technology Homepage *
The Jewish Agency
{{DEFAULTSORT:Aliyah Aliyah, History of Mandatory Palestine History of Ottoman Syria Land of Israel Zionism Hebrew words and phrases
'' State of Israel, and honor the ongoing contributions of Olim, Jewish immigrants, to Israeli society. Yom HaAliyah is also observed in Israeli schools on the seventh of the Hebrew month of Cheshvan. The opening clause of the Yom HaAliyah Law states in Hebrew: English translation: The original day chosen for Yom HaAliyah, the tenth of Nisan, is laden with symbolism. Although a modern holiday created by the Knesset of Israel, the tenth of Nisan is a date of religious significance for the Jewish People as recounted in the Hebrew Bible and in traditional Jewish thought. On the tenth of Nisan, according to the biblical narrative in the Book of Joshua,
Joshua
Joshua () or Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' lit. 'Yahweh is salvation') ''Yēšūaʿ''; syr, ܝܫܘܥ ܒܪ ܢܘܢ ''Yəšūʿ bar Nōn''; el, Ἰησοῦς, ar , يُوشَعُ ٱبْنُ نُونٍ '' Yūšaʿ ...
and the Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
crossed the Jordan River at Gilgal into the Promised Land while carrying the Ark of the Covenant. It was thus the first documented "mass aliyah." On that day, God commanded the Israelites to commemorate and celebrate the occasion by erecting twelve stones with the text of the Torah engraved upon them. The stones represented the entirety of the Jewish nation's twelve tribes and their gratitude for God's gift of the Land of Israel () to them.
Yom HaAliyah, as a modern holiday celebration, began in 2009 as a grassroots community initiative and young Olim self-initiated movement in Tel Aviv, spearheaded by the TLV Internationals organization of the Am Yisrael Foundation. On June 21, 2016, the Twentieth Knesset voted in favor of codifying the grassroots initiative into law by officially adding Yom HaAliyah to the Israeli national calendar. The Yom HaAliyah bill was co-sponsored by Knesset members from different parties in a rare instance of cooperation across the political spectrum of the opposition and coalition.
Statistics
Recent trends
Historic data
The number of immigrants since 1882 by period, continent of birth, and country of birth is given in the table below. Continent of birth and country of birth data is almost always unavailable or nonexistent for before 1919.See also
* Galut * Yerida * History of the Jews in the Land of Israel * Homeland for the Jewish people *Law of Return
The Law of Return ( he, חֹוק הַשְׁבוּת, ''ḥok ha-shvūt'') is an Israeli law, passed on 5 July 1950, which gives Jews, people with one or more Jewish grandparent, and their spouses the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Isr ...
* Jewish population by country
* Historical Jewish population comparisons
* Demographics of Israel
* Olim L'Berlin
* Visa policy of Israel
* Israeli passport
* Israeli identity card
* Illegal immigration from Africa to Israel
* Kibbutz volunteer
* Yom HaAliyah
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
Immigration to Israel
at the Jewish Virtual Library
Making Aliyah
at the Israel Government Portal
of the Ministry of Immigrant Absorption
Official website
of Nefesh B'Nefesh, organization for aliyah from North America and UK
Aliyah to Israel
at Israel Science and Technology Homepage *
The Jewish Agency
{{DEFAULTSORT:Aliyah Aliyah, History of Mandatory Palestine History of Ottoman Syria Land of Israel Zionism Hebrew words and phrases