Power to gas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Power-to-gas (often abbreviated P2G) is a technology that uses
 In December 2013,
In December 2013,
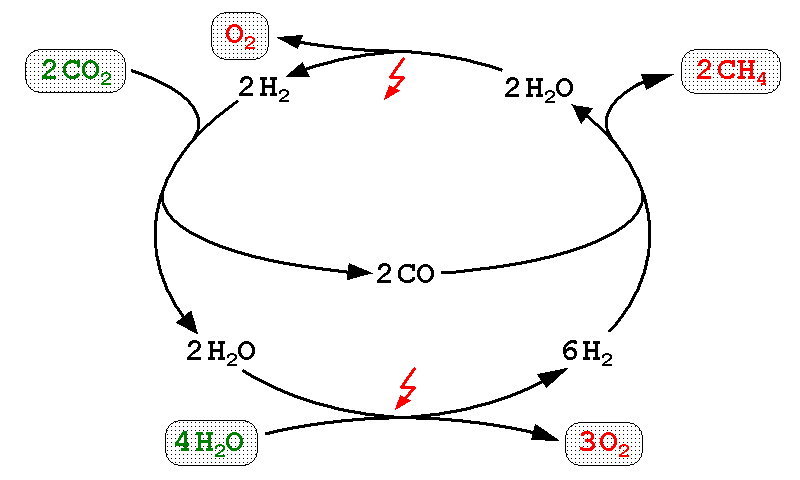 A power-to-methane system combines hydrogen from a power-to-hydrogen system with carbon dioxide to produce methane (see
A power-to-methane system combines hydrogen from a power-to-hydrogen system with carbon dioxide to produce methane (see  In April 2014 the
In April 2014 the
/ref> As a cooling medium for the exothermic reaction boiling water is used at up to 300 °C, which corresponds to a water vapour pressure of about 87 bar. The SOEC works with a pressure of up to 15 bar, steam conversions of up to 90% and generates one
Three minute explainer video
by the
Zentrum für Sonnenenergie-und Wasserstoff-Forschung (ZSW) Baden-Württemberg
* Smedley, Tim
Power-to-gas energy storage could help displace use of fossil fuels
''
Presentation of the prototype installation in Zürich Werdehölzli
(in German). Energy storage
electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by ...
power to produce a gaseous fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy b ...
. When using surplus power from wind generation
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller impact on the environment than burning fossil fuels. Historically, w ...
, the concept is sometimes called windgas.
Most P2G systems use electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from n ...
to produce hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
. The hydrogen can be used directly, or further steps (known as two-stage P2G systems) may convert the hydrogen into syngas
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, in various ratios. The gas often contains some carbon dioxide and methane. It is principly used for producing ammonia or methanol. Syngas is combustible and can be used as ...
, methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
, or LPG.
Single-stage P2G systems to produce methane also exist, such as reversible solid oxide cell (rSOC) technology.
The gas may be used as chemical feedstock, or converted back into electricity using conventional generators such as gas turbines. Power-to-gas allows energy from electricity to be stored and transported in the form of compressed gas, often using existing infrastructure for long-term transport and storage of natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon d ...
. P2G is often considered the most promising technology for seasonal renewable energy storage.
Energy storage and transport
Power-to-gas systems may be deployed as adjuncts to wind parks orsolar power plant
A photovoltaic power station, also known as a solar park, solar farm, or solar power plant, is a large-scale grid-connected photovoltaic power system (PV system) designed for the supply of merchant power. They are different from most building ...
s. The excess power or off-peak power generated by wind generators or solar array
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and ...
s may then be used hours, days, or months later to produce electrical power for the electrical grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power ...
. In the case of Germany, before switching to natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon d ...
, the gas networks were operated using towngas
Coal gas is a flammable gaseous fuel made from coal and supplied to the user via a piped distribution system. It is produced when coal is heated strongly in the absence of air. Town gas is a more general term referring to manufactured gaseous ...
, which for 50–60 % consisted of hydrogen. The storage capacity of the German natural gas network is more than 200,000 GWh which is enough for several months of energy requirement. By comparison, the capacity of all German pumped-storage hydroelectricity
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing. The method stores energy in the form of gravitational potent ...
plants amounts to only about 40 GWh.
Natural gas storage
Natural gas is a commodity that can be stored for an indefinite period of time in natural gas storage facilities for later consumption.
Usage
Gas storage is principally used to meet load variations. Gas is injected into storage during periods o ...
is a mature industry that has been in existence since Victorian times. The storage/retrieval power rate requirement in Germany is estimated at 16 GW in 2023, 80 GW in 2033 and 130 GW in 2050. The storage costs per kilowatt hour are estimated at €0.10 for hydrogen and €0.15 for methane.
The existing natural gas transport infrastructure conveys massive amounts of gas for long distances profitably using pipelines. It is now profitable to ship natural gas between continents using LNG carrier
An LNG carrier is a tank ship designed for transporting liquefied natural gas (LNG).
History
The first LNG carrier '' Methane Pioneer'' () carrying , classed by Bureau Veritas, left the Calcasieu River on the Louisiana Gulf coast on 25 January ...
s. The transport of energy through a gas network is done with much less loss (<0.1%) than in an electrical transmission network (8%). This infrastructure can transport methane produced by P2G without modification.
It may also be possible to use it for hydrogen. The use of the existing natural gas pipeline
Pipeline transport is the long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas through a system of pipes—a pipeline—typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countr ...
s for hydrogen was studied by the EU NaturalHy project and the United States Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United States ...
(DOE). Blending technology is also used in HCNG
HCNG or H2CNG (hydrogen compressed natural gas) is a mixture of compressed natural gas and 4–9 percent hydrogen by energy. It may be used as a fuel gas for internal combustion engines and home appliances.
(regarding the acronyms in the above em ...
.
Efficiency
In 2013, theround-trip efficiency
Round trip may refer to:
Science and technology
* Round-trip delay time, in communications
*Round-trip engineering, automatic synchronization of related software development artifacts
* Round-trip format conversion, in document conversion
*Round- ...
of power-to-gas-storage was well below 50%, with the hydrogen path being able to reach a maximum efficiency of ~ 43% and methane of ~ 39% by using combined-cycle powerplants. If cogeneration
Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time.
Cogeneration is a more efficient use of fuel or heat, because otherwise- wasted heat from elec ...
plants are used that produce both electricity and heat, efficiency can be above 60%, but is still less than pumped hydro
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing. The method stores energy in the form of gravitational potential ...
or battery storage. However, there is potential to increase the efficiency of power-to-gas storage. In 2015 a study published in Energy and Environmental Science
''Energy & Environmental Science'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing original (primary) research and review articles. The journal covers work of an interdisciplinary nature in the biochemical and biophysical sciences and ch ...
found that by using reversible solid oxide cells and recycling waste heat in the storage process, electricity-to-electricity round-trip efficiencies exceeding 70% can be reached at low cost. In addition, a 2018 study using pressurized reversible solid oxide cells and a similar methodology found that round-trip efficiencies (power-to-power) of up to 80% might be feasible.
Electrolysis technology
*Relative advantages and disadvantages of electrolysis technologies.Power-to-hydrogen
All current P2G systems start by using electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen by means of electrolysis. In a "power-to-hydrogen" system, the resulting hydrogen is injected into the natural gas grid or is used in transport or industry rather than being used to produce another gas type.ITM Power
ITM Power plc is an energy storage and clean fuel company founded in the UK in 2001. It designs, manufactures, and integrates electrolysers based on proton exchange membrane (PEM) technology to produce green hydrogen using renewable electricity an ...
won a tender in March 2013 for a Thüga Group project, to supply a 360 kW self-pressurising high-pressure electrolysis
High-pressure electrolysis (HPE) is the electrolysis of water by decomposition of water (H2O) into oxygen (O2) and hydrogen gas (H2) due to the passing of an electric current through the water. The difference with a standard proton exchange m ...
rapid response proton exchange membrane
A proton-exchange membrane, or polymer-electrolyte membrane (PEM), is a semipermeable membrane generally made from ionomers and designed to conduct protons while acting as an electronic insulator and reactant barrier, e.g. to oxygen and hydrogen g ...
(PEM) electrolyser
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of c ...
''Rapid Response Electrolysis'' Power-to-Gas energy storage plant. The unit produces 125 kg/day of hydrogen gas and incorporates AEG
Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft AG (AEG; ) was a German producer of electrical equipment founded in Berlin as the ''Deutsche Edison-Gesellschaft für angewandte Elektricität'' in 1883 by Emil Rathenau. During the Second World War, ...
power electronics. It will be situated at a Mainova
Mainova AG ( FWBMNV6 is one of the largest regional energy suppliers in Germany and supplies about one million people in Hessen
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a s ...
AG site in the Schielestraße, Frankfurt
Frankfurt, officially Frankfurt am Main (; Hessian: , " Frank ford on the Main"), is the most populous city in the German state of Hesse. Its 791,000 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located on it ...
in the state of Hessen
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt. Two other major historic cities are Darms ...
. The operational data will be shared by the whole Thüga group – the largest network of energy companies in Germany with around 100 municipal utility members. The project partners include: badenova AG & Co. kg, Erdgas Mittelsachsen GmbH, Energieversorgung Mittelrhein GmbH, erdgas schwaben GmbH, Gasversorgung Westerwald GmbH, Mainova
Mainova AG ( FWBMNV6 is one of the largest regional energy suppliers in Germany and supplies about one million people in Hessen
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a s ...
Aktiengesellschaft, Stadtwerke Ansbach GmbH, Stadtwerke Bad Hersfeld GmbH, Thüga Energienetze GmbH, WEMAG AG, e-rp GmbH, ESWE Versorgungs AG with Thüga Aktiengesellschaft as project coordinator. Scientific partners will participate in the operational phase. It can produce 60 cubic metres of hydrogen per hour and feed 3,000 cubic metres of natural gas enriched with hydrogen into the grid per hour. An expansion of the pilot plant is planned from 2016, facilitating the full conversion of the hydrogen produced into methane to be directly injected into the natural gas grid.
 In December 2013,
In December 2013, ITM Power
ITM Power plc is an energy storage and clean fuel company founded in the UK in 2001. It designs, manufactures, and integrates electrolysers based on proton exchange membrane (PEM) technology to produce green hydrogen using renewable electricity an ...
, Mainova
Mainova AG ( FWBMNV6 is one of the largest regional energy suppliers in Germany and supplies about one million people in Hessen
Hesse (, , ) or Hessia (, ; german: Hessen ), officially the State of Hessen (german: links=no, Land Hessen), is a s ...
, and NRM Netzdienste Rhein-Main GmbH began injecting hydrogen into the German gas distribution network using ITM Power
ITM Power plc is an energy storage and clean fuel company founded in the UK in 2001. It designs, manufactures, and integrates electrolysers based on proton exchange membrane (PEM) technology to produce green hydrogen using renewable electricity an ...
HGas, which is a rapid response proton exchange membrane
A proton-exchange membrane, or polymer-electrolyte membrane (PEM), is a semipermeable membrane generally made from ionomers and designed to conduct protons while acting as an electronic insulator and reactant barrier, e.g. to oxygen and hydrogen g ...
electrolyser
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of c ...
plant. The power consumption of the electrolyser is 315 kilowatts. It produces about 60 cubic meters per hour of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
and thus in one hour can feed 3,000 cubic meters of hydrogen-enriched natural gas into the network.
On August 28, 2013, E.ON Hanse, Solvicore, and Swissgas inaugurated a commercial power-to-gas unit in Falkenhagen, Germany. The unit, which has a capacity of two megawatts, can produce 360 cubic meters of hydrogen per hour. The plant uses wind power and Hydrogenics
Hydrogenics is a developer and manufacturer of hydrogen generation and fuel cell products based on water electrolysis and proton exchange membrane (PEM) technology. Hydrogenics is divided into two business units: OnSite Generation and Power Syst ...
electrolysis equipment to transform water into hydrogen, which is then injected into the existing regional natural gas transmission system. Swissgas, which represents over 100 local natural gas utilities, is a partner in the project with a 20 percent capital stake and an agreement to purchase a portion of the gas produced. A second 800 kW power-to-gas project has been started in Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
/Reitbrook district and is expected to open in 2015.
In August 2013, a 140 MW wind park in Grapzow, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV; ; nds, Mäkelborg-Vörpommern), also known by its anglicized name Mecklenburg–Western Pomerania, is a state in the north-east of Germany. Of the country's sixteen states, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern ranks 14th in po ...
owned by E.ON received an electrolyser. The hydrogen produced can be used in an internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal co ...
or can be injected into the local gas grid. The hydrogen compression and storage system stores up to 27 MWh of energy and increases the overall efficiency of the wind park by tapping into wind energy that otherwise would be wasted. The electrolyser produces 210 Nm3/h of hydrogen and is operated by RH2-WKA.
The INGRID project started in 2013 in Apulia
it, Pugliese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographic ...
, Italy. It is a four-year project with 39 MWh storage and a 1.2 MW electrolyser for smart grid monitoring and control. The hydrogen is used for grid balancing, transport, industry, and injection into the gas network.
The surplus energy from the 12 MW Prenzlau Windpark in Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 squ ...
, Germany will be injected into the gas grid from 2014 on.
The 6 MW Energiepark Mainz from Stadtwerke Mainz, RheinMain University of Applied Sciences, Linde
Linde may refer to:
Places
*Lindes and Ramsberg Mountain District, a former district in Sweden, see Lindesberg Municipality
* Lipka, Złotów County, a village in Poland, called Linde before World War II
Rivers
* Linde (Tollense), a river of Meck ...
and Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''E ...
in Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
(Germany) will open in 2015.
Power to gas and other energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production.
A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.
Energy comes in ...
schemes to store and utilize renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
are part of Germany's Energiewende (energy transition program).
In France, the MINERVE demonstrator of AFUL Chantrerie (Federation of Local Utilities Association) aims to promote the development of energy solutions for the future with elected representatives, companies and more generally civil society. It aims to experiment with various reactors and catalysts. The synthetic methane produced by the MINERVE demonstrator (0.6 Nm3 / h of CH4) is recovered as CNG fuel, which is used in the boilers of the AFUL Chantrerie boiler plant. The installation was designed and built by the French SME Top Industrie, with the support of Leaf. In November 2017 it achieved the predicted performance, 93.3% of CH4. This project was supported by the ADEME and the ERDF-Pays de la Loire Region, as well as by several other partners: Conseil départemental de Loire -Atlantic, Engie-Cofely, GRDF, GRTGaz, Nantes-Metropolis, Sydela and Sydev.
A full scale 1GW electrolyzer operated by EWE and Tree Energy Solutions is planned at the gas terminal in Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven (, ''Wilhelm's Harbour''; Northern Low Saxon: ''Willemshaven'') is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea, and has a population of 76,089. Wilhelmsh ...
, Germany. The first 500 MW is expected to begin operation in 2028. Wilhelmshaven can accomodate a second plant, bringing total potential capacity to 2GW.Grid injection without compression
The core of the system is aproton exchange membrane
A proton-exchange membrane, or polymer-electrolyte membrane (PEM), is a semipermeable membrane generally made from ionomers and designed to conduct protons while acting as an electronic insulator and reactant barrier, e.g. to oxygen and hydrogen g ...
(PEM) electrolyser
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of c ...
. The electrolyser converts electrical energy into chemical energy, which in turn facilitates the storage of electricity. A gas mixing plant ensures that the proportion of hydrogen in the natural gas stream does not exceed two per cent by volume, the technically permissible maximum value when a natural gas filling station is situated in the local distribution network. The electrolyser supplies the hydrogen-methane mixture at the same pressure as the gas distribution network, namely 3.5 bar.
Power-to-methane
 A power-to-methane system combines hydrogen from a power-to-hydrogen system with carbon dioxide to produce methane (see
A power-to-methane system combines hydrogen from a power-to-hydrogen system with carbon dioxide to produce methane (see natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon d ...
) using a methanation
Methanation is the conversion of carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide (COx) to methane (CH4) through hydrogenation. The methanation reactions of COx were first discovered by Sabatier and Senderens in 1902.
CO''x'' methanation has many practical ap ...
reaction such as the Sabatier reaction
The Sabatier reaction or Sabatier process produces methane and water from a reaction of hydrogen with carbon dioxide at elevated temperatures (optimally 300–400 °C) and pressures (perhaps 3 MPa ) in the presence of a nickel catalyst. It w ...
or biological methanation resulting in an extra energy conversion loss of 8%, the methane may then be fed into the natural gas grid if the purity requirement is reached.
ZSW (Center for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research) and SolarFuel GmbH (now ETOGAS GmbH) realized a demonstration project with 250 kW electrical input power in Stuttgart, Germany. The plant was put into operation on October 30, 2012.
The first industry-scale Power-to-Methane plant was realized by ETOGAS for Audi AG in Werlte, Germany. The plant with 6 MW electrical input power is using CO2 from a waste-biogas
Biogas is a mixture of gases, primarily consisting of methane, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide, produced from raw materials such as agricultural waste, manure, municipal waste, plant material, sewage, green waste and food waste. It is a ...
plant and intermittent renewable power to produce synthetic natural gas
Substitute natural gas (SNG), or synthetic natural gas, is a fuel gas (predominantly methane, CH4) that can be produced from fossil fuels such as lignite coal, oil shale, or from biofuels (when it is named bio-SNG) or using electricity with power- ...
(SNG) which is directly fed into the local gas grid (which is operated by EWE). The plant is part of the Audi e-fuels program. The produced synthetic natural gas, named Audi e-gas, enables CO2-neutral mobility with standard CNG vehicles. Currently it is available to customers of Audi's first CNG car, the Audi A3 g-tron.
 In April 2014 the
In April 2014 the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
's co-financed and from the KIT
Kit may refer to:
Places
*Kitt, Indiana, US, formerly Kit
* Kit, Iran, a village in Mazandaran Province
* Kit Hill, Cornwall, England
People
* Kit (given name), a list of people and fictional characters
* Kit (surname)
Animals
* Young animal ...
coordinated HELMETH (Integrated High-Temperature ELectrolysis and METHanation for Effective Power to Gas Conversion) research project started. The objective of the project is the proof of concept of a highly efficient Power-to-Gas technology by thermally integrating high temperature electrolysis ( SOEC technology) with CO2-methanation.
Through the thermal integration of exothermal methanation and steam generation for the high temperature steam electrolysis conversion efficiency > 85% (higher heating value
The heating value (or energy value or calorific value) of a substance, usually a fuel or food (see food energy), is the amount of heat released during the combustion of a specified amount of it.
The ''calorific value'' is the total energy relea ...
of produced methane per used electrical energy) are theoretically possible. The process consists of a pressurized high-temperature steam electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from n ...
and a pressurized CO2-methanation module.
The project was completed in 2017 and achieved an efficiency of 76% for the prototype with an indicated growth potential of 80% for industrial scale plants. The operating conditions of the CO2-methanation are a gas pressure of 10 - 30 bar, a SNG production of 1 - 5.4 m3/h (NTP) and a reactant conversion that produces SNG with H2 < 2 vol.-% resp. CH4 > 97 vol.-%. Thus, the generated substitute natural gas can be injected in the entire German natural gas network without limitations.DIN EN 16723-2:2017-10 - Erdgas und Biomethan zur Verwendung im Transportwesen und Biomethan zur Einspeisung ins Erdgasnetz/ref> As a cooling medium for the exothermic reaction boiling water is used at up to 300 °C, which corresponds to a water vapour pressure of about 87 bar. The SOEC works with a pressure of up to 15 bar, steam conversions of up to 90% and generates one
standard cubic meter
A standard cubic foot (scf) is a unit used both in the natural gas industry to represent an amount of natural gas and in other industries where other gases are used. It is the unit commonly used when following the customary system, a collection ...
of hydrogen from 3.37 kWh
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bill ...
of electricity as feed for the methanation.
The technological maturity of Power to Gas is evaluated in the European 27 partner project STORE&GO, which has started in March 2016 with a runtime of four years. Three different technological concepts are demonstrated in three different European countries ( Falkenhagen/Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, Solothurn
Solothurn ( , ; french: Soleure ; it, Soletta ; rm, ) is a town, a municipality, and the capital of the canton of Solothurn in Switzerland. It is located in the north-west of Switzerland on the banks of the Aare and on the foot of the Weissens ...
/Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, Troia/Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
). The technologies involved include biological and chemical methanation
Methanation is the conversion of carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide (COx) to methane (CH4) through hydrogenation. The methanation reactions of COx were first discovered by Sabatier and Senderens in 1902.
CO''x'' methanation has many practical ap ...
, direct capture of CO2 from atmosphere, liquefaction of the synthesized methane to bio- LNG, and direct injection into the gas grid. The overall goal of the project is to assess those technologies and various usage paths under technical, economic,
and legal aspects to identify business cases on the short and on the long term. The project is co-funded by the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
's Horizon 2020
The Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, also called Framework Programmes or abbreviated FP1 to FP9, are funding programmes created by the European Union/European Commission to support and foster research in the Europea ...
research and innovation programme (18 million euro) and the Swiss government (6 million euro), with another 4 million euro coming from participating industrial partners. The coordinator of the overall project is the research center of the
DVGW located at the KIT
Kit may refer to:
Places
*Kitt, Indiana, US, formerly Kit
* Kit, Iran, a village in Mazandaran Province
* Kit Hill, Cornwall, England
People
* Kit (given name), a list of people and fictional characters
* Kit (surname)
Animals
* Young animal ...
.
Microbial methanation
The biological methanation combines both processes, theelectrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from n ...
of water to form hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
and the subsequent CO2 reduction to methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
using this hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
. During this process, methane forming microorganisms (methanogenic archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaeba ...
or methanogens
Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in hypoxic conditions. They are prokaryotic and belong to the domain Archaea. All known methanogens are members of the archaeal phylum Euryarchaeota. Methanogens are co ...
) release enzymes
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. ...
that reduce the overpotential
In electrochemistry, overpotential is the potential difference (voltage) between a half-reaction's thermodynamically determined reduction potential and the potential at which the redox event is experimentally observed. The term is directly rela ...
of a non-catalytic electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials ...
(the cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in whi ...
) so that it can produce hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
. This microbial power-to-gas reaction occurs at ambient conditions, i.e. room temperature and pH 7, at efficiencies that routinely reach 80-100%. However, methane is formed more slowly than in the Sabatier reaction due to the lower temperatures. A direct conversion of CO2 to methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
has also been postulated, circumventing the need for hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
production.
Microorganisms involved in the microbial power-to-gas reaction are typically members of the order ''Methanobacteriales
In taxonomy, the Methanobacteriales are an order of the Methanobacteria. Species within this order differ from other methanogens in that they can use fewer catabolic substrates and have distinct morphological characteristics, lipid composition ...
''. Genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclat ...
that were shown to catalyze this reaction are '' Methanobacterium'', ''Methanobrevibacter
In taxonomy, ''Methanobrevibacter'' is a genus of the Methanobacteriaceae.See the NCBIbr>webpage on Methanobrevibacter Data extracted from the The species within ''Methanobrevibacter'' are strictly anaerobic archaea that produce methane, for t ...
'', and ''Methanothermobacter
In taxonomy, ''Methanothermobacter'' is a genus of the Methanobacteriaceae.See the NCBIbr>webpage on Methanothermobacter Data extracted from the The species within this genus are thermophilic and grow best at temperatures between 55°C and ...
'' (thermophile
A thermophile is an organism—a type of extremophile—that thrives at relatively high temperatures, between . Many thermophiles are archaea, though they can be bacteria or fungi. Thermophilic eubacteria are suggested to have been among the earl ...
).
LPG production
Methane can be used to produce LPG by synthesising SNG with partial reversehydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic ...
at high pressure and low temperature. LPG in turn can be converted into alkylate
An alkylation unit (alky) is one of the conversion processes used in petroleum refineries. It is used to convert isobutane and low-molecular-weight alkenes (primarily a mixture of propene and butene) into alkylate, a high octane gasoline componen ...
which is a premium gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic c ...
blending stock because it has exceptional antiknock properties and gives clean burning.
Power to food
The synthetic methane generated from electricity can also be used for generating protein rich feed for cattle, poultry and fish economically by cultivating ''Methylococcus capsulatus
''Methylococcus capsulatus'' is an obligately methanotrophic gram-negative, non-motile coccoid bacterium. ''M. capsulatus'' are thermotolerant; their cells are encapsulated and tend to have a diplococcoid shape. In addition to methane, ' ...
'' bacteria culture with tiny land and water footprint. The carbon dioxide gas produced as by-product from these plants can be recycled in the generation of synthetic methane (SNG). Similarly, oxygen gas produced as by product from the electrolysis of water and the methanation
Methanation is the conversion of carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide (COx) to methane (CH4) through hydrogenation. The methanation reactions of COx were first discovered by Sabatier and Senderens in 1902.
CO''x'' methanation has many practical ap ...
process can be consumed in the cultivation of bacteria culture. With these integrated plants, the abundant renewable solar and wind power potential can be converted into high value food products without any water pollution or greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane ...
(GHG) emissions.
Biogas-upgrading to biomethane
In the third method the carbon dioxide in the output of a wood gas generator or a biogas plant after the biogas upgrader is mixed with the produced hydrogen from the electrolyzer to produce methane. The free heat coming from the electrolyzer is used to cut heating costs in the biogas plant. The impurities carbon dioxide, water, hydrogen sulfide, and particulates must be removed from the biogas if the gas is used for pipeline storage to prevent damage. 2014-Avedøre wastewater Services in Avedøre,Kopenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan ar ...
(Denmark) is adding a 1 MW electrolyzer plant to upgrade the anaerobic digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a sequence of processes by which microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. The process is used for industrial or domestic purposes to manage waste or to produce fuels. Much of the ferm ...
biogas from sewage sludge. The produced hydrogen is used with the carbon dioxide from the biogas in a Sabatier reaction to produce methane. Electrochaea is testing another project outside P2G BioCat with biocatalytic methanation. The company uses an adapted strain of the thermophilic methanogen ''Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus
In taxonomy, ''Methanothermobacter'' is a genus of the Methanobacteriaceae.See the NCBIbr>webpage on Methanothermobacter Data extracted from the The species within this genus are thermophilic and grow best at temperatures between 55°C and ...
'' and has demonstrated its technology at laboratory-scale in an industrial environment. A pre-commercial demonstration project with a 10,000-liter reactor vessel was executed between January and November 2013 in Foulum
Foulum is a small Danish village with around 100 households (the settlement Formyre also included) in the Tjele parish located in Central Jutland eight kilometres east of Viborg. Foulum is a part of Region Midtjylland and a part of the Viborg ...
, Denmark.
In 2016 Torrgas, Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''E ...
, Stedin, Gasunie
N.V. Nederlandse Gasunie (short form: Gasunie) is a Dutch natural gas infrastructure and transportation company operating in the Netherlands and Germany. Gasunie owns the Netherlands gas transmission network with a total length of over and long ...
, A.Hak, Hanzehogeschool/EnTranCe and Energy Valley intend to open a 12 MW Power to Gas facility in Delfzijl
Delfzijl (; gos, Delfsiel) is a city and former municipality with a population of 25,651 in the province of Groningen in the northeast of the Netherlands. Delfzijl was a sluice between the Delf and the Ems, which became fortified settlement in ...
(The Netherlands) where biogas from Torrgas ( biocoal) will be upgraded with hydrogen from electrolysis and delivered to nearby industrial consumers.
Power-to-syngas
Syngas
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, in various ratios. The gas often contains some carbon dioxide and methane. It is principly used for producing ammonia or methanol. Syngas is combustible and can be used as ...
is a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide. It has been used since Victorian times, when it was produced from coal and known as "towngas". A power-to-syngas system uses hydrogen from a power-to-hydrogen system to produce syngas.
*1st step: Electrolysis of Water ( SOEC) −water is split into hydrogen and oxygen.
*2nd step: Conversion Reactor ( RWGSR) −hydrogen and carbon dioxide are inputs to the Conversion Reactor that outputs hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and water. 3H2 + CO2 → (2H2 + CO)syngas + H2O
*Syngas
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, in various ratios. The gas often contains some carbon dioxide and methane. It is principly used for producing ammonia or methanol. Syngas is combustible and can be used as ...
is used to produce synfuel
Synthetic fuel or synfuel is a liquid fuel, or sometimes gaseous fuel, obtained from syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, in which the syngas was derived from gasification of solid feedstocks such as coal or biomass or by reformi ...
s.
Initiatives
Other initiatives to create syngas from carbon dioxide and water may use differentwater splitting
Water splitting is the chemical reaction in which water is broken down into oxygen and hydrogen:
:2 H2O → 2 H2 + O2
Efficient and economical water splitting would be a technological breakthrough that could underpin a hydrogen economy, base ...
methods.
* CSP
**2004 Sunshine-to-Petrol —Sandia National Laboratories
Sandia National Laboratories (SNL), also known as Sandia, is one of three research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). Headquartered in Kirtland Air Force Bas ...
.
**2013 — ( IL) and Weizmann Institute of Science
The Weizmann Institute of Science ( he, מכון ויצמן למדע ''Machon Vaitzman LeMada'') is a public research university in Rehovot, Israel, established in 1934, 14 years before the State of Israel. It differs from other Israeli unive ...
.
**2014 Solar-Jet Fuels —Consortium partners ETH, SHELL
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
** Thin-shell structure
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard o ...
, DLR, Bauhaus Luftfahrt, ARTTIC.
* HTE / Alkaline water electrolysis
Alkaline water electrolysis has a long history in the chemical industry. It is a type of electrolyzer that is characterized by having two electrodes operating in a liquid alkaline electrolyte solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydr ...
**2004 Syntrolysis Fuels —Idaho National Laboratory
Idaho National Laboratory (INL) is one of the national laboratories of the United States Department of Energy and is managed by the Battelle Energy Alliance. While the laboratory does other research, historically it has been involved with nu ...
and Ceramatec, Inc. (US).
**2008 WindFuels —Doty Energy (US).
**2012 Air Fuel Synthesis —Air Fuel Synthesis Ltd (UK). Air Fuel Synthesis Ltd have become insolvent.
**2013 Green Feed — BGU and Israel Strategic Alternative Energy Foundation (I-SAEF).
**2014 E-diesel —Sunfire, a clean technology company and Audi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. As a subsidiary of its parent company, the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
...
.
The US Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is designing a power-to-liquids system using the Fischer-Tropsch Process to create fuel on board a ship at sea, with the base products carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) being derived from sea water via "An Electrochemical Module Configuration For The Continuous Acidification Of Alkaline Water Sources And Recovery Of CO2 With Continuous Hydrogen Gas Production".The total carbon content of the world's oceans is roughly 38,000 GtC. Over 95% of this carbon is in the form of dissolved bicarbonate ion (HCO3 −).
See also
*Carbon-neutral fuel
Carbon-neutral fuel is fuel which produces no net-greenhouse gas emissions or carbon footprint. In practice, this usually means fuels that are made using carbon dioxide (CO2) as a feedstock. Proposed carbon-neutral fuels can broadly be grouped in ...
* Electromethanogenesis Electromethanogenesis is a form of electrofuel production where methane is produced by direct biological conversion of electrical current and carbon dioxide.
Methane producing technologies garnered interest from the scientific community prior to 20 ...
* Electrofuel
Electrofuels, also known as e-fuels or synthetic fuels, are a type of drop-in replacement fuel. They are manufactured using captured carbon dioxide or carbon monoxide, together with hydrogen obtained from sustainable electricity sources such as ...
* Electrohydrogenesis
* Grid energy storage
Grid energy storage (also called large-scale energy storage) is a collection of methods used for energy storage on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Electrical energy is stored during times when electricity is plentiful and inex ...
* Hydrogen economy
The hydrogen economy is using hydrogen to decarbonize economic sectors which are hard to electrify, essentially, the "hard-to-abate" sectors such as cement, steel, long-haul transport etc. In order to phase out fossil fuels and limit climate ch ...
* Methanation
Methanation is the conversion of carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide (COx) to methane (CH4) through hydrogenation. The methanation reactions of COx were first discovered by Sabatier and Senderens in 1902.
CO''x'' methanation has many practical ap ...
* List of energy storage projects
This is a list of energy storage power plants worldwide, other than pumped hydro storage.
Many individual energy storage plants augment electrical grids by capturing excess electrical energy during periods of low demand and storing it in o ...
* Power-to-X
* Renewable natural gas
Renewable natural gas (RNG), also known as sustainable natural gas (SNG) or biomethane, is a biogas which has been upgraded to a quality similar to fossil natural gas and having a methane concentration of 90% or greater. By increasing the concentr ...
* Timeline of hydrogen technologies
Notes
Further reading
* {{cite journal , last1 = Götz , first1 = Manuel , last2 = Lefebvre , first2 = Jonathan , last3 = Mörs , first3 = Friedemann , last4 = McDaniel Koch , first4 = Amy , last5 = Graf , first5 = Frank , last6 = Bajohr , first6 = Siegfried , last7 = Reimert , first7 = Rainer , last8 = Kolb , first8 = Thomas , year = 2016 , title = Renewable Power-to-Gas: A technological and economic review , journal =Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
, volume = 85 , pages = 1371–1390 , doi = 10.1016/j.renene.2015.07.066 , doi-access = free
* Méziane Boudellal. "Le Power-to-Gas, Stockage de l'électricité d'origine renouvelable". 192 pages. In French only. Editor: Dunod, June 2016.
* Méziane Boudellal. "Power-to-Gas. Renewable Hydrogen Economy for the Energy Transition". 212 pages. English edition. Editor: de Gruyter, Februar 2018
External links
Three minute explainer video
by the
Institute for Energy Technology
Institute for Energy Technology (IFE) was established in 1948 as the Institute for Nuclear Energy (IFA). The name was changed in 1980. Its main office is at Kjeller, Norway, and slightly under half of the institute’s activities are based in Ha ...
(2016)Zentrum für Sonnenenergie-und Wasserstoff-Forschung (ZSW) Baden-Württemberg
* Smedley, Tim
Power-to-gas energy storage could help displace use of fossil fuels
''
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers '' The Observer'' and '' The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the ...
'', July 4, 2014. Retrieved July 21, 2014.
Presentation of the prototype installation in Zürich Werdehölzli
(in German). Energy storage