Potato starch on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Potato starch is starch extracted from
Potato starch is starch extracted from
 Starch derivatives are used in many cooking recipes, for example in
Starch derivatives are used in many cooking recipes, for example in
 Many types of potatoes are grown for the production of potato starch, potato varieties with high starch content and high starch yields are selected. Recently, a new type of potato plant was developed that only contains one type of starch molecule:
Many types of potatoes are grown for the production of potato starch, potato varieties with high starch content and high starch yields are selected. Recently, a new type of potato plant was developed that only contains one type of starch molecule:
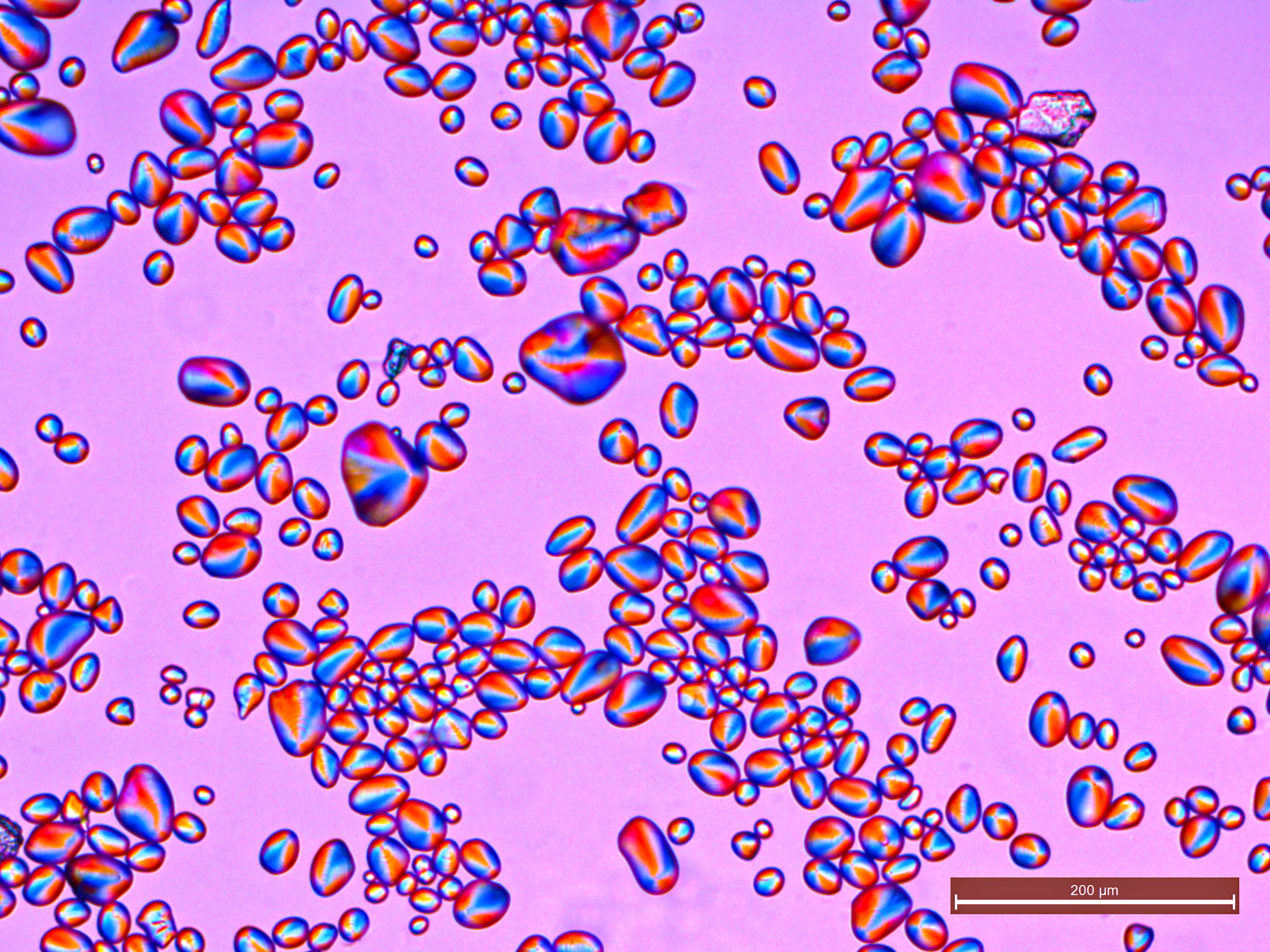 Examined under a microscope using a mixture of equal volumes of glycerol and distilled water, potato starch presents transparent, colorless granules, either irregularly shaped, ovoid or pear-shaped, usually 30 μm to 100 μm in size but occasionally exceeding 100 μm, or rounded, 10 μm to 35 μm in size. Starch granules exhibit characteristic dark crosses in polarized light. If potato starch is wetted it becomes sticky.
Examined under a microscope using a mixture of equal volumes of glycerol and distilled water, potato starch presents transparent, colorless granules, either irregularly shaped, ovoid or pear-shaped, usually 30 μm to 100 μm in size but occasionally exceeding 100 μm, or rounded, 10 μm to 35 μm in size. Starch granules exhibit characteristic dark crosses in polarized light. If potato starch is wetted it becomes sticky.
Memorandum on potato starch, International Starch Institute
Potato starch gelatinization film, Youtube
{{DEFAULTSORT:Potato Starch Potatoes Edible thickening agents Starch Passover foods
 Potato starch is starch extracted from
Potato starch is starch extracted from potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
es. The cells of the root tuber
Tubers are a type of enlarged structure used as storage organs for nutrients in some plants. They are used for the plant's perennation (survival of the winter or dry months), to provide energy and nutrients for regrowth during the next growin ...
s of the potato plant contain leucoplast
Leucoplasts (λευκός leukós "white", πλαστός plastós "formed, molded") are a category of plastid and as such are organelles found in plant cells. They are non-pigmented, in contrast to other plastids such as the chloroplast.
Lacki ...
s (starch grains). To extract the starch, the potatoes are crushed, and the starch grains are released from the destroyed cells. The starch is then left to settle out of solution or separated by hydrocyclones, then dried to powder.
Potato starch contains typical large oval spherical granules ranging in size from 5 to 100 μm. Potato starch is a refined starch, containing minimal protein or fat. This gives the powder a clear white colour, and the cooked starch typical characteristics of neutral taste, good clarity, high binding strength, long texture, and minimal tendency to foaming or yellowing of the solution.
Potato starch contains approximately 800 ppm phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
bound to the starch; this increases the viscosity and gives the solution a slightly anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
ic character, a low gelatinisation temperature of approximately , and high swelling power.
These properties are used in food and technical applications.
Use
 Starch derivatives are used in many cooking recipes, for example in
Starch derivatives are used in many cooking recipes, for example in noodles
Noodles are a type of food made from unleavened dough which is either rolled flat and cut, stretched, or extruded, into long strips or strings. Noodles are a staple food in many cultures (for example, Chinese noodles, Filipino noodles, Ind ...
, wine gums
Wine gums (or winegums) are chewy, firm pastille-type sweets similar to gumdrops without the sugar coating, originating from the United Kingdom. All brands have their own recipes containing various sweeteners, flavourings, and colourings. Wine ...
, cocktail nuts, potato chips
A potato chip (North American English; often just chip) or crisp (British and Irish English) is a thin slice of potato that has been either deep fried, baked, or air fried until crunchy. They are commonly served as a snack, side dish, or ap ...
, hot dog
A hot dog (uncommonly spelled hotdog) is a food consisting of a grilled or steamed sausage served in the slit of a partially sliced bun. The term hot dog can refer to the sausage itself. The sausage used is a wiener ( Vienna sausage) or a f ...
sausages, bakery cream and instant soup
Instant soup is a type of soup designed for fast and simple preparation. Some are homemade, and some are mass-produced on an industrial scale and treated in various ways to preserve them. A wide variety of types, styles and flavors of instant soup ...
s and sauces, in gluten
Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain cereal grains. Although "gluten" often only refers to wheat proteins, in medical literature it refers to the combination of prolamin and glutelin proteins naturally occurring in all grai ...
-free recipes, in kosher foods for Passover
Passover, also called Pesach (; ), is a major Jewish holiday that celebrates the Biblical story of the Israelites escape from slavery in Egypt, which occurs on the 15th day of the Hebrew month of Nisan, the first month of Aviv, or spring. ...
and in Asian cuisine
Asian cuisine includes several major regional cuisines: Central Asian, East Asian, North Asian, South Asian, Southeast Asian, and West Asian. A cuisine is a characteristic style of cooking practices and traditions, usually associated with ...
. In pastry
Pastry is baked food made with a dough of flour, water and shortening (solid fats, including butter or lard) that may be savoury or sweetened. Sweetened pastries are often described as '' bakers' confectionery''. The word "pastries" sugges ...
, e.g. sponge cake
Sponge cake is a light cake made with egg whites, flour and sugar, sometimes leavened with baking powder. Some sponge cakes do not contain egg yolks, like angel food cake, but most of them do. Sponge cakes, leavened with beaten eggs, originated ...
, it is used to keep the cake moist and give a soft texture. It is also occasionally used in the preparation of pre-packed grated cheese
Grated cheese is cheese that has been grated. Typically, aged hard cheeses are used. Cheese can be grated by hand using a hand grater, and can be bought already grated. Commercial grated cheeses are often blends of cheeses.
Shredded cheese i ...
, to reduce sweating and binding.
Other examples are '' helmipuuro'', a porridge made from monodisperse grains of potato starch and milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modula ...
, and '' papeda'' (the Moluccan
Moluccans are the Austronesian-speaking and Papuan-speaking ethnic groups indigenous to the Maluku Islands (also called the Moluccas), Indonesia. The region was historically known as the Spice Islands, and today consists of two Indonesian prov ...
community in the Netherlands uses potato starch to make ''papeda''). It is also used in non-food applications as wallpaper adhesive, for textile finishing and textile sizing
Sizing or size is a substance that is applied to, or incorporated into, other materials—especially papers and textiles—to act as a protective filler or glaze. Sizing is used in papermaking and textile manufacturing to change the absorption ...
, in paper coating and sizing, and as an adhesive in paper sack
A paper sack is a packaging type that can be constructed of one or several layers of high quality kraft paper, usually produced from virgin fibre. Paper sacks can also be referred to as industrial paper bags, industrial paper sacks or multi-wall ...
s and gummed tape.
Potato starch was also used in one of the earlier color photography processes, the Lumière brothers' Autochrome Lumière, until the arrival of other colour film processes in the mid-1930s.
Potato varieties
 Many types of potatoes are grown for the production of potato starch, potato varieties with high starch content and high starch yields are selected. Recently, a new type of potato plant was developed that only contains one type of starch molecule:
Many types of potatoes are grown for the production of potato starch, potato varieties with high starch content and high starch yields are selected. Recently, a new type of potato plant was developed that only contains one type of starch molecule: amylopectin Amylopectin is a water-insoluble polysaccharide and highly branched polymer of α-glucose units found in plants. It is one of the two components of starch, the other being amylose.
Plants store starch within specialized organelles called amyloplas ...
, the waxy potato starch
Waxy potato starch is a variety of commercially available starch composed almost entirely of amylopectin molecules, extracted from new potato varieties. Standard starch extracted from traditional potato varieties contains both amylose and amylopect ...
. Waxy starches, after starch gelatinisation, retrograde less during storage.
The cultivation of potatoes for starch mainly takes place in Germany, the Netherlands, China, Japan, France, Denmark, and Poland, but also in Sweden, Finland, Austria, the Czech Republic, Ukraine, Canada, and India.
Some potato starch is also produced as a byproduct from the potato processing industry, recovered from the potato cutting circuit during the production of French fries and potato chip
A potato chip (North American English; often just chip) or crisp (British and Irish English) is a thin slice of potato that has been either deep fried, baked, or air fried until crunchy. They are commonly served as a snack, side dish, or ap ...
s.
Identification
 Examined under a microscope using a mixture of equal volumes of glycerol and distilled water, potato starch presents transparent, colorless granules, either irregularly shaped, ovoid or pear-shaped, usually 30 μm to 100 μm in size but occasionally exceeding 100 μm, or rounded, 10 μm to 35 μm in size. Starch granules exhibit characteristic dark crosses in polarized light. If potato starch is wetted it becomes sticky.
Examined under a microscope using a mixture of equal volumes of glycerol and distilled water, potato starch presents transparent, colorless granules, either irregularly shaped, ovoid or pear-shaped, usually 30 μm to 100 μm in size but occasionally exceeding 100 μm, or rounded, 10 μm to 35 μm in size. Starch granules exhibit characteristic dark crosses in polarized light. If potato starch is wetted it becomes sticky.
See also
* Corn starch *Katakuri
''Erythronium japonicum'', known as Asian fawn lily, Oriental fawn lily, Japanese fawn lily is a pink-flowered species trout lily, belonging to the Lily family and native to Japan, Korea, the Russian Far East (Sakhalin Island, Kuril Islands) an ...
* Potato starch production
* Potato flour
* Autochrome Lumière
References
External links
Memorandum on potato starch, International Starch Institute
Potato starch gelatinization film, Youtube
{{DEFAULTSORT:Potato Starch Potatoes Edible thickening agents Starch Passover foods