Potassium gold cyanide on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Potassium dicyanoaurate is an
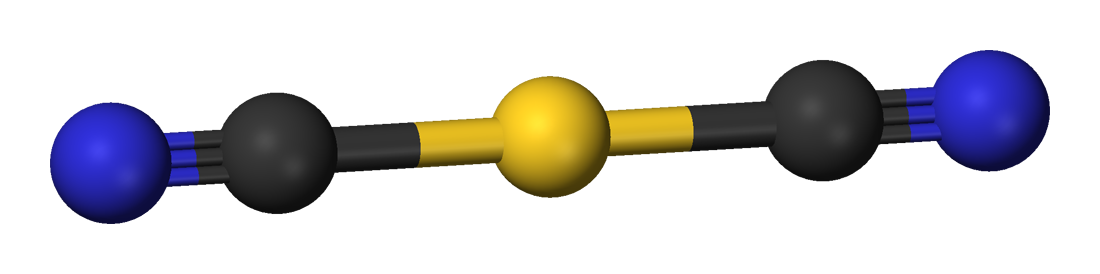 Potassium dicyanoaurate is a salt. The dicyanoaurate anion is linear according to
Potassium dicyanoaurate is a salt. The dicyanoaurate anion is linear according to
inorganic compound
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as '' inorganic chemis ...
with formula K u(CN)2 It is a colorless to white solid that is soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The salt itself is often not isolated, but solutions of the dicyanoaurate ion ( u(CN)2sup>−) are generated on a large scale in the extraction of gold from its ores.
Production
In mining of gold from dilute sources, gold is selectively extracted by dissolution in aqueous solutions of cyanide, provided by dissolving sodium cyanide,potassium cyanide
Potassium cyanide is a compound with the formula KCN. This colorless crystalline salt, similar in appearance to sugar, is highly soluble in water. Most KCN is used in gold mining, organic synthesis, and electroplating. Smaller applications inc ...
and/or calcium cyanide. The reaction for the dissolution of gold, the "Elsner Equation", is:
:4 Au + 8 KCN + O2 + 2 H2O → 4 K u(CN)2+ 4 KOH
In this process, oxygen is the oxidant.
It can also be produced by reaction of gold(I) salts with excess potassium cyanide.
:AuCl + 2 KCN → K u(CN)2 + KCl
Structure
: Potassium dicyanoaurate is a salt. The dicyanoaurate anion is linear according to
Potassium dicyanoaurate is a salt. The dicyanoaurate anion is linear according to X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
. On the basis of infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functi ...
, the dicyanoaurate anion adopts a very similar structure in sodium dicyanoaurate (NaAu(CN)2).
Uses
Dicyanoaurate is the soluble species that is the focus ofgold cyanidation
Gold cyanidation (also known as the cyanide process or the MacArthur-Forrest process) is a hydrometallurgical technique for extracting gold from low-grade ore by converting the gold to a water-soluble coordination complex. It is the most commonl ...
, the hydrometallurgical process for winning gold from dilute ores. In fact, sodium cyanide, not the potassium salt, is more widely used in commercial processes.
Aside from its major use as an intermediate in the extraction of gold, potassium dicyanoaurate is often used in gold plating
Gold plating is a method of depositing a thin layer of gold onto the surface of another metal, most often copper or silver (to make silver-gilt), by chemical or electrochemical plating. This article covers plating methods used in the modern elec ...
applications.
Related compounds
The compound containing gold(III) cyanide is also known: potassium tetracyanoaurate(III), K u(CN)4 Its use is less common. The potassium ion can be replaced withquaternary ammonium
In chemistry, quaternary ammonium cations, also known as quats, are positively charged polyatomic ions of the structure , R being an alkyl group or an aryl group. Unlike the ammonium ion () and the primary, secondary, or tertiary ammonium cations ...
cations as in tetrabutylammonium
Tetrabutylammonium is a quaternary ammonium cation with the formula (C4H9)4sup>+. It is used in the research laboratory to prepare lipophilic salts of inorganic anions. Relative to tetraethylammonium derivatives, tetrabutylammonium salts are mor ...
dicyanoaurate.
Safety
The ingestion of a gram quantities of potassium dicyanoaurate has led to death.References
{{Cyanides Cyanides Aurates Gold(I) compounds Potassium compounds Cyanometallates