Geography of Kenya on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
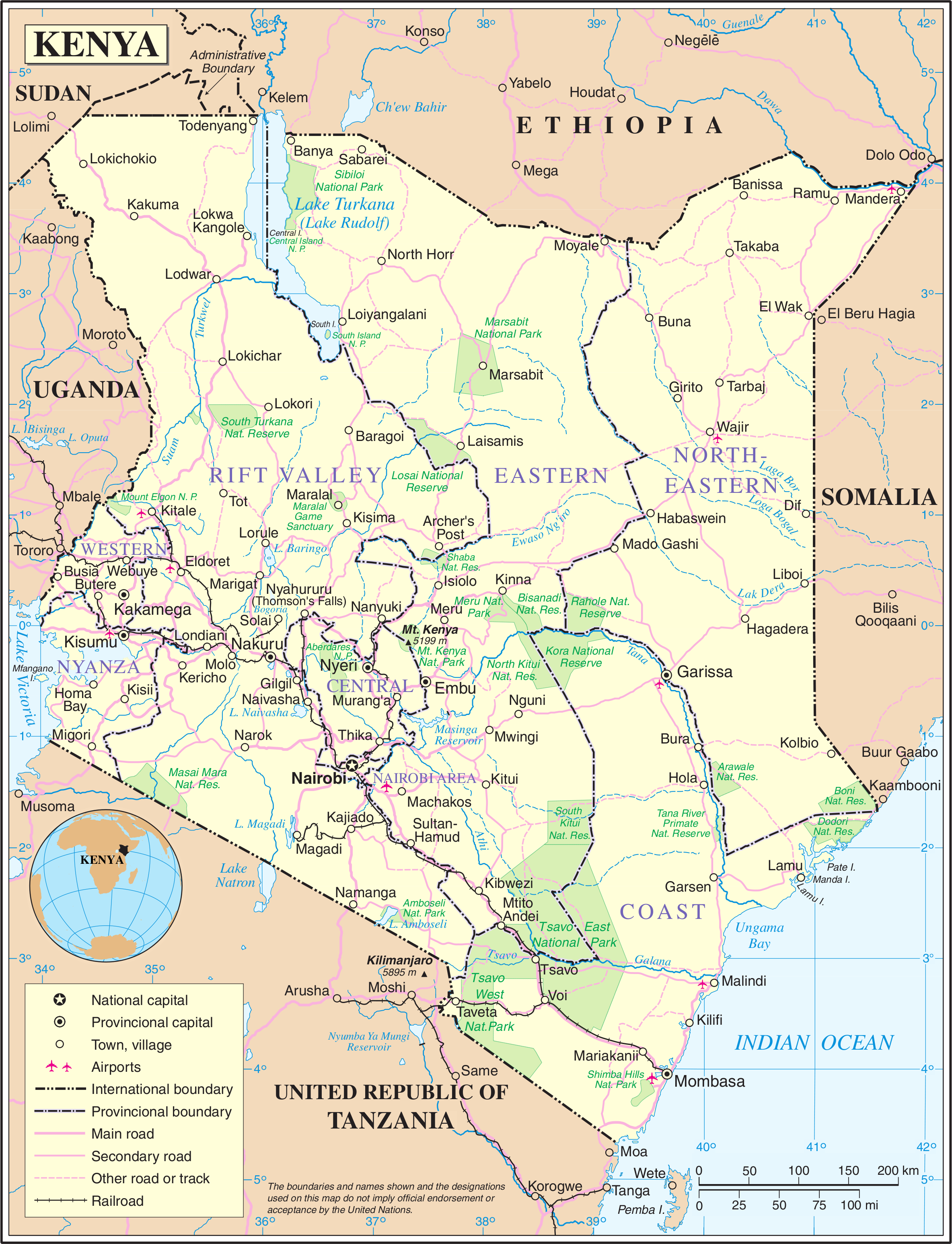
 The Geography of
The Geography of
/ref>
/ref> The southeast corner of the country is underlain by sediments of the
 The climate of Kenya varies by location, from mostly cool every day, to always warm/hot. The climate along the coast is tropical. This means rainfall and temperatures are higher throughout the year. At the coastal cities,
The climate of Kenya varies by location, from mostly cool every day, to always warm/hot. The climate along the coast is tropical. This means rainfall and temperatures are higher throughout the year. At the coastal cities,  Elevation is the major factor in temperature levels, with the higher areas, on average, as 11 °C (20 °F) cooler, day or night."NairobiDagoretti, Kenya: Climate, Global Warming, and
Daylight Charts and Data", Climate-Charts.com, 2008, web:
Elevation is the major factor in temperature levels, with the higher areas, on average, as 11 °C (20 °F) cooler, day or night."NairobiDagoretti, Kenya: Climate, Global Warming, and
Daylight Charts and Data", Climate-Charts.com, 2008, web:
CC741
: compare
CC661
. The many cities over a kilometre in elevation have temperature swings from roughly . Nairobi, at , ranges from , and
File:Pt Thomson Batian Nelion Mt Kenya.JPG, Thompson (4955 m), Batian (5199 m) and Nelion (5188 m) on Mt Kenya
File:Africa6_006.jpg, The Great Rift Valley as it is visible near Eldoret, Kenya
File:Lake turkana.jpg,

Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
is diverse, varying amongst its 47 counties. Kenya has a coastline on the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
, which contains swamps of East African mangroves
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
. Inland are broad plains and numerous hills. Kenya borders South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of th ...
to the northwest, Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The ...
to the west, Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
to the east, Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
to the south, and Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
to the north.
Central and Western Kenya is characterised by the Kenyan Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley is part of an intra-continental ridge system that runs through Kenya from north to south. It is part of the Gregory Rift, the eastern branch of the East African Rift, which starts in Tanzania to the south and continues ...
and central Province home to the highest mountain, Mount Kenya
Mount Kenya (Kikuyu language, Kikuyu: ''Kĩrĩnyaga'', Kamba language, Kamba, ''Ki Nyaa'') is the highest mountain in Kenya and the Highest mountain peaks of Africa, second-highest in Africa, after Mount Kilimanjaro, Kilimanjaro. The highest pea ...
and Mount Elgon
Mount Elgon is an extinct shield volcano on the border of Uganda and Kenya, north of Kisumu and west of Kitale. The mountain's highest point, named "Wagagai", is located entirely within Uganda.
on the border between Kenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
and Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The ...
. The Kakamega Forest
Kakamega Forest is a tropical rainforest situated in the Kakamega and Nandi
County of Kenya, northwest of the capital Nairobi, and near to the border with Uganda. It is Kenya's only tropical rainforest and is said to be Kenya's last remnant ...
in western Kenya is a relic of an East African rainforest. Much bigger is Mau Forest
Mau Forest is a forest complex in the Rift Valley of Kenya. It is the largest indigenous montane forest in East Africa. The Mau Forest complex has an area of .
The forest area has some of the highest rainfall rates in Kenya. Mau Forest is the lar ...
, the largest forest complex in East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
.
Geography
Location
* Eastern Africa on theIndian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
coast between Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
and Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
* Geographic coordinates
The geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical or ellipsoidal coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions directly on the Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest and most widely used of the various ...
:
Area
* Total: * Land: * Water:Land boundaries
* Total: * Border countries:Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
, South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of th ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
, Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The ...
cia.gov – The World Factbook Kenya/ref>
Coastline
* 536 km (333 mi) along the Indian Ocean.Maritime claims
* Territorial sea: * Exclusive economic zone: and * Continental shelf: 200 m depth or to the depth of exploitationGeology
Much of the western two-thirds of the country consists of thePliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
volcanics
Volcanic rock (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano. In other words, it differs from other igneous rock by being of volcanic origin. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic r ...
deposited on Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of th ...
basement rocks.Petroleum Potential of NW-Kenya Rift Basins: A Synopsis of Evidence and Issues/ref> The southeast corner of the country is underlain by sediments of the
Karoo System
The Karoo Supergroup is the most widespread stratigraphic unit in Africa south of the Kalahari Desert. The supergroup consists of a sequence of units, mostly of nonmarine origin, deposited between the Late Carboniferous and Early Jurassic, a perio ...
of Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleo ...
to Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch of the Triassic Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch ...
age and a strip of Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
age sediments along the coast in the Mombasa
Mombasa ( ; ) is a coastal city in southeastern Kenya along the Indian Ocean. It was the first capital of the British East Africa, before Nairobi was elevated to capital city status. It now serves as the capital of Mombasa County. The town ...
area. The Anza trough
The Anza trough is a rift in Kenya that was formed in the Jurassic Period of the Mesozoic Era.
The trough runs inland from the coast in the northwest direction.
The trough is an isolated graben originating from the uprising mantle-plume rift for ...
is a NW–SE trending Jurassic rift extending from the Indian Ocean coast to the Sudan northwest of Lake Turkana. The Anza Rift resulted from the break–up of Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final sta ...
.
Climate
Mombasa
Mombasa ( ; ) is a coastal city in southeastern Kenya along the Indian Ocean. It was the first capital of the British East Africa, before Nairobi was elevated to capital city status. It now serves as the capital of Mombasa County. The town ...
, Lamu
Lamu or Lamu Town is a small town on Lamu Island, which in turn is a part of the Lamu Archipelago in Kenya. Situated by road northeast of Mombasa that ends at Mokowe Jetty, from where the sea channel has to be crossed to reach Lamu Island ...
and Malindi
Malindi is a town on Malindi Bay at the mouth of the Sabaki River, lying on the Indian Ocean coast of Kenya. It is 120 kilometres northeast of Mombasa. The population of Malindi was 119,859 as of the 2019 census. It is the largest urban cent ...
, the air changes from cool to hot, almost every day. (''See chart below'').
The further inside Kenya, the more arid the climate becomes. An arid climate is nearly devoid of rainfall, and temperature swings widely according to the general time of the day/night. For many areas of Kenya, the daytime temperature rises about 12 °C (corresponding to a rise of about 22 °F), almost every day.
 Elevation is the major factor in temperature levels, with the higher areas, on average, as 11 °C (20 °F) cooler, day or night."NairobiDagoretti, Kenya: Climate, Global Warming, and
Daylight Charts and Data", Climate-Charts.com, 2008, web:
Elevation is the major factor in temperature levels, with the higher areas, on average, as 11 °C (20 °F) cooler, day or night."NairobiDagoretti, Kenya: Climate, Global Warming, and
Daylight Charts and Data", Climate-Charts.com, 2008, web:
CC741
: compare
Nairobi
Nairobi ( ) is the capital and largest city of Kenya. The name is derived from the Maasai phrase ''Enkare Nairobi'', which translates to "place of cool waters", a reference to the Nairobi River which flows through the city. The city proper ...
/Dagoretti Dagoretti is an area in the western part of Nairobi, the capital of Kenya. It straddles the Nairobi and Kiambu County boundary with the Dagoretti Road Reserve marking the psychological border point heading Northerly and North-Easterly. Administrativ ...
data with
or Mombasa
Mombasa ( ; ) is a coastal city in southeastern Kenya along the Indian Ocean. It was the first capital of the British East Africa, before Nairobi was elevated to capital city status. It now serves as the capital of Mombasa County. The town ...
charts."Kitale, Kenya: Climate, Global Warming, and Daylight
Charts and Data", Climate-Charts.com, 2008, web:
CC661
. The many cities over a kilometre in elevation have temperature swings from roughly . Nairobi, at , ranges from , and
Kitale
Kitale is an agricultural town in northern Rift Valley Kenya situated between Mount Elgon and the Cherangany Hills at an elevation of around . Its population is 106,187 as of 2009. Kitale is the headquarter town of Trans-Nzoia County. Kitale is r ...
, at , ranges from . At night, heavy clothes or blankets are needed, in the highlands, when the temperature drops to about every night.
At lower altitudes, the increased temperature is like day and night, literally: like starting the morning at the highland daytime high, and then adding the heat of the day, again. Hence, the overnight low temperatures near sea level are nearly the same as the high temperatures of the elevated Kenyan highlands. However, locations along the Indian Ocean have more moderate temperatures, as a few degrees cooler in the daytime, such as at Mombasa
Mombasa ( ; ) is a coastal city in southeastern Kenya along the Indian Ocean. It was the first capital of the British East Africa, before Nairobi was elevated to capital city status. It now serves as the capital of Mombasa County. The town ...
(''see chart below'').
There are slight seasonal variations in temperature, of , cooler in the winter months. Although Kenya is centred at the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also ...
, it shares the seasons of the Southern Hemisphere: with the warmest summer months in December–March and the coolest winter months in June–August, again with differences in temperature varying by location within the country.
On the high mountains, such as Mount Kenya
Mount Kenya (Kikuyu language, Kikuyu: ''Kĩrĩnyaga'', Kamba language, Kamba, ''Ki Nyaa'') is the highest mountain in Kenya and the Highest mountain peaks of Africa, second-highest in Africa, after Mount Kilimanjaro, Kilimanjaro. The highest pea ...
, Mount Elgon
Mount Elgon is an extinct shield volcano on the border of Uganda and Kenya, north of Kisumu and west of Kitale. The mountain's highest point, named "Wagagai", is located entirely within Uganda.
and Kilimanjaro
Mount Kilimanjaro () is a dormant volcano in Tanzania. It has three volcanic cones: Kibo, Mawenzi, and Shira. It is the highest mountain in Africa and the highest free-standing mountain above sea level in the world: above sea level and a ...
, the weather can become bitterly cold for most of the year. Some snowfall occurs on the highest mountains.
Climate change
Terrain
Kenya's terrain is composed of low plains that rise into central highlands that are, in turn, bisected by theGreat Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley is a series of contiguous geographic trenches, approximately in total length, that runs from Lebanon in Asia to Mozambique in Southeast Africa. While the name continues in some usages, it is rarely used in geology as it ...
. There is also a fertile plateau in the west of the country.
Elevation extremes
The lowest point on Kenya is at sea level on the Indian Ocean. The highest point on Kenya is 5,197 meters above sea level atMount Kenya
Mount Kenya (Kikuyu language, Kikuyu: ''Kĩrĩnyaga'', Kamba language, Kamba, ''Ki Nyaa'') is the highest mountain in Kenya and the Highest mountain peaks of Africa, second-highest in Africa, after Mount Kilimanjaro, Kilimanjaro. The highest pea ...
.
Rivers
The notable rivers in Kenya are the Athi-Galana-Sabaki River, which at a total length of about 390 kilometers while draining an area of about 70,000 square kilometers, is the second longest river in the country, the Tana River, the longest river in the country at a total length of just over 1000 kilometers, covering a catchment area of over 100,000 square kilometers, and theNzoia River
The Nzoia River is a Kenyan river, rising from Cherangany hills. It passes through Kapsara, Springer ,Moi's bridge then crosses to Kakamega county.It flows south and then west, eventually flowing into Lake Victoria near the town of Port Victoria ...
, which is a river, rising from Mount Elgon
Mount Elgon is an extinct shield volcano on the border of Uganda and Kenya, north of Kisumu and west of Kitale. The mountain's highest point, named "Wagagai", is located entirely within Uganda.
, which flows so
Natural resources
Natural resources that are found in Kenya include: limestone, soda ash, salt,gemstones
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, or semiprecious stone) is a piece of mineral crystal which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. However, certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, a ...
, fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon.
The Mohs sca ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, diatomite
Diatomaceous earth (), diatomite (), or kieselgur/kieselguhr is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous sedimentary rock that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size ranging from more than 3 μm to le ...
, oil, gas, gold, gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywa ...
, wildlife
Wildlife refers to undomesticated animal species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wild in an area without being introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game: those birds and mammals that were hunted ...
and hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of ...
.
Land use
9.8% of the land is arable; permanent crops occupy 0.9% of the land, permanent pasture occupies 37.4% of the land; forest occupies 6.1% of the land. Other uses make up the rest of Kenya's land. This is as of 2011. 1,032 km2 of Kenyan land was irrigated in 2003.Total renewable water resources
30.7 km3 (2011)Freshwater withdrawal
* Total: 2.74 km3/yr (17%/4%/79%) * Per capita: 72.96 m3/yr (2003)Gallery
Lake Turkana
Lake Turkana (), formerly known as Lake Rudolf, is a lake in the Kenyan Rift Valley, in northern Kenya, with its far northern end crossing into Ethiopia. It is the world's largest permanent desert lake and the world's largest alkaline lake. B ...
File:Fourteen_falls_Thika,Kenya.JPG, The Fourteen Falls near Thika
Thika Thika (pronounced �θika is an industrial town and a major commerce hub in Kiambu County, Kenya, lying on the A2 road 42 kilometres (26 mi) Northeast of Nairobi, near the confluence of the Thika and Chania Rivers. Although Thika town is ...
Natural hazards
Natural hazards include recurring drought and flooding during the rainy seasons. There is limited volcanic activity in the country.Barrier Volcano
The Barrier is an active shield volcano located in the north of Kenya. It is last known to have erupted in 1921.
Description
The Barrier was given its name because it forms a barrier about long across the Kenyan Rift Valley. It has a width of ...
(elev. 1,032 m) last erupted in 1921. Several others have been historically active (see List of volcanoes in Kenya
This is a short list of active and extinct volcanoes in Kenya.For a more comprehensive list of volcanoes and craters in Kenya, see :sw:Orodha ya volkeno nchini Kenya
List of volcanoes in Kenya (non-exhaustive)
References
* Volcanoes of ...
).
Environmental issues
Current issues
Current issues that threaten the environment at the moment include water pollution from urban and industrial wastes; degradation of water quality from the increased use of pesticides and fertilisers;deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated ...
; water hyacinth
''Pontederia crassipes'' (formerly ''Eichhornia crassipes''), commonly known as common water hyacinth is an aquatic plant native to South America, naturalized throughout the world, and often invasive outside its native range.Lake Victoria
Lake Victoria is one of the African Great Lakes. With a surface area of approximately , Lake Victoria is Africa's largest lake by area, the world's largest tropical lake, and the world's second-largest fresh water lake by surface area after ...
; soil erosion
Soil erosion is the denudation or wearing away of the upper layer of soil. It is a form of soil degradation. This natural process is caused by the dynamic activity of erosive agents, that is, water, ice (glaciers), snow, air (wind), plants, a ...
; desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused ...
; and poaching.
International agreements
* Party to:Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), species ('' species diversity''), and ecosystem ('' ecosystem diversity'') ...
, Climate Change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused ...
, Endangered Species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inv ...
, Hazardous Wastes
Hazardous waste is waste that has substantial or potential threats to public health or the environment. Hazardous waste is a type of dangerous goods. They usually have one or more of the following hazardous traits: ignitability, reactivity, cor ...
, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping
The Convention on the Prevention of Marine Pollution by Dumping of Wastes and Other Matter 1972, commonly called the "London Convention" or "LC '72" and also abbreviated as Marine Dumping, is an agreement to control pollution of the sea by dum ...
, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection
The Montreal Protocol is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 September 1987, and entered into force on ...
, Ship Pollution (MARPOL 73/78
The International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, 1973 as modified by the Protocol of 1978, or "MARPOL 73/78" is one of the most important international marine environmental conventions. MARPOL 73/78, MARPOL is an amalg ...
), Wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (Anoxic waters, anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in t ...
s, Whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industr ...
.
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points ofKenya
)
, national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
, the points that are further north, south, east or west than any other location.
* Northernmost point – Kalukwakerith Mountain, Turkana County
Turkana County is a county in the former Rift Valley Province of Kenya. It is Kenya's largest county by land area (followed by Marsabit County), and also its northwesternmost. It is bordered by the countries of Uganda to the west; South Sudan ...
* Easternmost point – the tripoint
A tripoint, trijunction, triple point, or tri-border area is a geographical point at which the boundaries of three countries or subnational entities meet. There are 175 international tripoints as of 2020. Nearly half are situated in rivers, l ...
with Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
and Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitut ...
, Mandera County
Mandera County is the northeasternmost county in Kenya. Its capital and largest town is Mandera. The county is bordered by Ethiopia to the north, Somalia to the east and Wajir County to the southwest. According to the 2019 census, the county ha ...
* Southernmost point – the point where the border with Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands ...
enters the Indian Ocean, Kwale County
Kwale County is a county in the former Coast Province of Kenya. Its capital is Kwale, although Ukunda is the largest town.
Kwale county has an estimated population of 649,931.
Kwale is mainly an inland county, but it has coastline south of Mo ...
* Westernmost point – unnamed land west of Port Victoria, Busia County
Busia is a county in the former Western Province of Kenya. It borders Kakamega County to the east, Bungoma County to the north, Lake Victoria and Siaya County to the south and Busia District, Uganda to the west. The county has about 893,000 pe ...
** ''Note: Kalukwakerith Mountain is in the disputed Ilemi Triangle
The Ilemi Triangle, sometimes called only Ilemi, is an area of disputed land in East Africa. Arbitrarily defined, it measures about . Named after Anuak chief Ilemi Akwon, the territory is claimed by South Sudan and Kenya. The territory also b ...
region. If this area is excluded then Kenya does not have a northernmost point, the northern border being a straight line.''
See also
*Environmental issues in Kenya
Environmental issues in Kenya include deforestation, soil erosion, desertification, water shortage and degraded water quality, flooding, poaching, and domestic and industrial pollution.
Water resources
Water resources in Kenya are under pressu ...
* List of national parks of Kenya
* Ilemi Triangle
The Ilemi Triangle, sometimes called only Ilemi, is an area of disputed land in East Africa. Arbitrarily defined, it measures about . Named after Anuak chief Ilemi Akwon, the territory is claimed by South Sudan and Kenya. The territory also b ...
* Mandera triangle
The Mandera triangle is a geographical region in Eastern Africa where the countries of Ethiopia, Kenya and Somalia meet. The tri-border region is centered on the city of Mandera in Mandera County and corresponds with the Juba and Shabelle river ba ...
References
{{Africa topic, Climate of