The population of the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
was estimated at over 67.0 million in 2020. It is the
21st most populated country in the world and has a population density of 270 people per square kilometre (700 people per square mile), with
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
having significantly greater density than
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
,
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
, and
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
. Almost a third of the population lives in
South East England
South East England is one of the nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It consists of the counties of Buckinghamshire, East Sussex, Hampshire, the Isle of Wight, Kent, Oxfordshire, Berkshi ...
, which is predominantly urban and suburban, with about 9 million in the capital city, London, whose population density is just over 5,200 per square kilometre (13,468 per sq mi).
The population of the UK has undergone
demographic transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory which refers to the historical shift from high birth rates and high death rates in societies with minimal technology, education (especially of women) and economic development, to l ...
—that is, the transition from a (typically) pre-industrial population, with high
birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
and
mortality rates and slow population growth, through a stage of falling mortality and faster rates of population growth, to a stage of low birth and mortality rates with, again, lower rates of growth. This growth through 'natural change' has been accompanied in the past two decades by growth through net
migration into the United Kingdom, which since 1999 has exceeded natural change.
The United Kingdom's high
literacy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, hum ...
rate (99% at age 15 and above) is attributable to
universal state education, introduced at the primary level in 1870 (
Scotland 1872, free 1890) and at the secondary level in 1900. Parents are obliged to have their children educated from the ages of 5 to 16 years (18 in England from 2013), and can continue education free of charge in the form of
A-Levels
The A-Level (Advanced Level) is a subject-based qualification conferred as part of the General Certificate of Education, as well as a school leaving qualification offered by the educational bodies in the United Kingdom and the educational au ...
,
vocational training
Vocational education is education that prepares people to work as a technician or to take up employment in a skilled craft or trade as a tradesperson or artisan. Vocational Education can also be seen as that type of education given to an in ...
, and apprenticeship until the age of 18.
The United Kingdom's population is predominantly
White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population ...
(81.88% at the
2011 Census), but due to migration from
Commonwealth nations, Britain has become
ethnically diverse
The term multiculturalism has a range of meanings within the contexts of sociology, political philosophy, and colloquial use. In sociology and in everyday usage, it is a synonym for " ethnic pluralism", with the two terms often used interchang ...
. The second and third largest non-white racial groups are
Asian British
British Asians (also referred to as Asian Britons) are British citizens of Asian descent. They constitute a significant and growing minority of the people living in the United Kingdom, with 6.9% of the population identifying as Asian/Asian Bri ...
at 7% of the population, followed by
Black British people
Black British people are a multi-ethnic group of British citizens of either African or Afro-Caribbean descent.Gadsby, Meredith (2006), ''Sucking Salt: Caribbean Women Writers, Migration, and Survival'', University of Missouri Press, pp. 76–7 ...
at 3%.
The main language of the country is
British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
. Some
Celtic languages
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edwar ...
, namely
Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well ...
and
Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
, are still spoken by minorities in
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
and
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
, respectively, and
Cornish has been revived to a limited degree in
Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
; but the predominant language in all these areas is English.
Welsh is widely spoken as a first language in parts of
North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and
West Wales
West Wales ( cy, Gorllewin Cymru) is not clearly defined as a particular region of Wales. Some definitions of West Wales include only Pembrokeshire, Ceredigion and Carmarthenshire, which historically comprised the Welsh principality of ''Deheub ...
, and to lesser extent in
South East Wales
South East Wales is a loosely defined region of Wales generally corresponding to the preserved counties of Mid Glamorgan, South Glamorgan and Gwent. Highly urbanised, it includes the cities of Cardiff and Newport as well as large towns in th ...
, where English is the dominant first language.
History
Before the census, 200–1800
Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered wa ...
had an estimated population between 2.8 million and 3 million at the end of the second century AD. At the end of the fourth century, it had an estimated population of 3.6 million, of whom 125,000 consisted of the
Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
and their families and dependents.
[ Joan P. Alcock]
''A Brief History of Roman Britain'', page 260
Hachette UK
Hachette () is a French publisher. Founded in 1826 by Louis Hachette as Brédif, the company later became L. Hachette et Compagnie, Librairie Hachette, Hachette SA and Hachette Livre in France. After acquiring an Australian publisher, Hachette ...
The urban population of Roman Britain was about 240,000 people at the end of the fourth century.
Roman Britain's capital city,
Londinium, is estimated to have had a population of about 60,000.
Following the Roman withdrawal from Britain, Germanic tribes from continental Europe such as the
Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
,
Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
and
Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nation ...
began a period of significant migration to the southeastern part of the island, notably bringing their language,
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
. Nevertheless, the overall population is believed to have fallen precipitously due to political upheavals and plagues. By the time of the compilation of the
Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manus ...
in the eleventh century, there may have between 1.25 and 2 million people living in England. Though the Domesday Book did not count the English population, it has been regarded as one of the first attempts to produce a census of the country.
Between the years of 1086 and 1750, the English population fluctuated in size due to civil war, famines and plagues.
By the end of the 13th century, the population was estimated to have reached between four to six million people, but a combination of factors such as widespread famine and disease in the following century collapsed the population dramatically. An agricultural crisis in 1315 to 1322 and the
Black Death in 1348 to 1350 collapsed the population by over a third of its pre-existing number, and the growth rate.
By 1377, the population was estimated on a poll-tax of all people aged 14 and over, depending on the population amount of those under 14, to be around 2.2 million to 3.1 million.
Periods of instability over the 15th century such as the
War of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These wars were fought bet ...
caused the population to, while grow, increase at a slowed pace.
The general factors behind the slow increase was a high mortality rate due to war, less marriages within the population and late marriages, keeping fertility levels lower then they should have been for the time and a net emigration of English people out of the country.
However in contrast to the preceding century, by the 16th century, this situation has elevated itself due to political stability under the
Tudor monarchy and little civil unrest which would have resulted in a higher mortality rate.
While this was overturned with the English Civil War in 17th century, it allowed the population to grow at a faster pace, causing the population of England to reach a pre-collapse total of 5.74 million by 1750.
In
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
, population growth was not to the same extent as it was in England, which resulted in being significantly lower in the late 17th and early 18th centuries, which is often ascribed to similar factors halting it such as a high mortality rate, especially for infants, and later marriage and childbearing patterns.
Ireland on the other hand before the 19th century consistently had rapid population growth, which has been ascribed to higher fertility rates and earlier marriage than England. Furthermore the
Plantation of Ulster in the 17th century also affected the population total of Scotland with an estimated 100,000 Scots migrating to
Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''Cúige Uladh'' ; sco, label= Ulster Scots, Ulstèr or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional Irish provinces. It is made up of nine counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kin ...
, additionally, the
Jacobite rebellion in 1745 also caused significant emigration.
The estimated population total of Scotland in 1691 was 1.23 million.
The impetus to collect population data was reinforced due to food supply concerns and war against
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
in the late 18th century and then beginning of the early 19th century.
In 1800, the
Census Act was passed, authorising the first modern census in British history to be conducted.
Census established and the demographic transition, 1800 – 2000

The first
Census in 1801 revealed that the population of Great Britain was 10.5 million. Of this, England's population had grown to 8.3 million, Wales population rested at 0.6 million while Scotland had a population of 1.6 million.
In Ireland, the population rested at an estimate of between 4.5 and 5.5 million inhabitants. Since 1801, a census has been conducted every decade, in Ireland this was conducted for the first time in 1821.
During the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, the
demographic transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory which refers to the historical shift from high birth rates and high death rates in societies with minimal technology, education (especially of women) and economic development, to l ...
started to occur within the United Kingdom, going from a pre-industrial society demographically to one of a industrialised society. By
1841 Census, the population of England and Wales rested at 15.9 million,
[1841: A window on Victorian Britain](_blank)
The Independent, 25 April 2006 doubling in the space of 40 years, for Ireland 8.2 million
and for Scotland 2.6 million.
This slowed rate of growth for Scotland may be attributed to higher net emigration of Scottish people out of the nation, and two typhus epidemics in 1837 and 1847.
Factors often associated with the beginning of the demographic transition began to change dramatically as well, which contributed to the rapid increase. For example,
Child mortality decreased dramatically, the proportion of children born in London who died before the age of five decreased from 74.5 per thousand in 1730–1749 to 31.8 per thousand in 1810–1829. General mortality was thought to have declined as well, especially after 1850 as well as a increased birth rate caused the English population to sustain itself in the second phase of the transition from 1750 to 1870.
Due to this, in the second half of the 19th century the
population of England
The demography of England has since 1801 been measured by the decennial national census, and is marked by centuries of population growth and urbanization. Due to the lack of authoritative contemporary sources, estimates of the population o ...
continued to grow quickly from 16.8 million in 1851 to 30.5 million in 1901.
This rapid growth was also seen in the other constituent nations. In Wales, the population increased from 0.6 million in 1801 to 2 million in 1901, in Scotland, the population increased from 1.6 million to 4.5 million in 1901. In contrast however and due to the
Great Irish Famine, which began in the 1840s, caused the deaths of 1 million
Irish people
The Irish ( ga, Muintir na hÉireann or ''Na hÉireannaigh'') are an ethnic group and nation native to the island of Ireland, who share a common history and Culture of Ireland, culture. There have been humans in Ireland for about 33,000 years ...
, and caused well over a million to emigrate.
Mass emigration became entrenched as a result of the famine, and Ireland's population decreased rapidly, from 8.2 million in 1841 to 3.2 million in 1901.
However this massive population collapse did not effect
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
to the same extent, due to being more industrialised and urbanised and while the population did decline, it had recovered itself by the beginning of the 20th century.
This prolonged period of emigration and net population decline in Irish history was only reversed by the middle of the 20th century.
By the 1870s, the total fertility rate of the UK population declined from 4.88 children per woman in 1871, to 2.4 by 1921, representing a transition to the third stage of the demographic transition.
Traditional means of birth control were used such as abstinence and withdrawal facilitated the collapse of the birth rate,
this was also hastened by the 1930s by more modern methods of contraception which were beginning to be used with increased acceptance.
From 1840 to 1930 there was a net emigration of English people out of the country which resulted in the population being stunted in the capacity it could have grown to.
During the first half of the 20th century, the United Kingdom began to approach the 4th stage of the demographic transition.
The end of the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and the loss of lives of troops, coupled with an
influenza outbreak is estimated to have caused the death of upwards of 900,000 people in the United Kingdom.
This as a consequence shrunk the male population of the
Lost Generation
The Lost Generation was the social generational cohort in the Western world that was in early adulthood during World War I. "Lost" in this context refers to the "disoriented, wandering, directionless" spirit of many of the war's survivors in th ...
and altered the sex ratio, which slowed the growth rate of the population down.
By the end of the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, this transition had been completed and the society had a low but fluctuating birth rate, a low death rate and a slowed growth rate of the population.
In 1948, the
British Nationality Act
British Nationality Act is a stock short title used for legislation in the United Kingdom relating to nationality.
The Bill for an Act with this short title will have been known as a British Nationality Bill during its passage through Parliame ...
was signed which allowed the access of the peoples of the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
's colonies to migrate to the country being classed in nationality as the same as a native of the United Kingdom. This law, while a unintentional side-effect, led to the start of
modern migration to the United Kingdom.
The move into the 4th stage also took place during major social change in the United Kingdom throughout the 1960s.
Liberalisation of society during the decade led to the
1967 Abortion Act which legalised abortion in the United Kingdom for the first time, and the
1969 Divorce Reform Act, which liberalised the circumstances under which someone can get a divorce.
Between these years, the population fluctuated; from the 1950s onwards the population increased through natural growth but by the time of the mid 1970s the population decreased due to emigration, which took net migration to a negative, and deaths exceeding births.
For the first time in 1973, the birth rate of the country fell below
replacement level, due to the previous liberalising acts.
By the 1980s, the decline of population growth had recovered to a extent due to a reversal of net emigration.
In the 1990s, international migration began to contribute more proportionally to population growth,
and by 1998 this had passed natural increase as the main provider of growth.
Liberalisation of immigration rules under the new government allowed rapid increase of the number of migrants arriving, quadrupling the number from a net migration rate of 50,000 a year, to 200,000 a year.
Modern century, 2000–present
By the beginning of the 21st century, the population of the United Kingdom rested at a total of 59,113,000 people. In each constituent nation, the population of England was 49,449,700, Scotland had a population of 5,064,200, Wales had a population of 2,910,200 and Northern Ireland a population of 1,689,300.
Increased international migration which began to rapidly increase at the end of the 20th century also has brought increased ethnic heterogenization to the British population, not only in ethnicity and race, but also in country of birth. In 2001, the
White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population ...
population was registered to be 88.52% of the total population, but by 2011, this proportion of the population had dropped to 81.88%, with other ethnic groups either rising by 50% of their respective total population in 2001 or doubling entirely.
Such rapid immigration growth boosted population growth in the United Kingdom. In 2011, the population sat at around 63 million people.
Population

The population of the UK in the last recorded census in
2011 was 63 million, of whom 31 million were male and 32 million female. The 2011 census recorded the population of England as 53.0 million, Scotland as 5.3 million, Wales as 3.1 million, and Northern Ireland as 1.8 million. At the last recorded population estimate, it was estimated that the UK population was at a total of 67,081,234 people.
There are 13 urban areas that exceed 500,000 inhabitants: they are centred on
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
,
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1. ...
,
Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popul ...
,
Leeds and Bradford,
Southampton and Portsmouth,
Sheffield
Sheffield is a city in South Yorkshire, England, whose name derives from the River Sheaf which runs through it. The city serves as the administrative centre of the City of Sheffield. It is historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire a ...
,
Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a populat ...
,
Leicester,
Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
,
Belfast
Belfast ( , ; from ga, Béal Feirste , meaning 'mouth of the sand-bank ford') is the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast. It is the 12th-largest city in the United Kingdom ...
,
Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
,
Newcastle upon Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne ( RP: , ), or simply Newcastle, is a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. The city is located on the River Tyne's northern bank and forms the largest part of the Tyneside built-up area. Newcastle is ...
and
Nottingham
Nottingham ( , locally ) is a city and unitary authority area in Nottinghamshire, East Midlands, England. It is located north-west of London, south-east of Sheffield and north-east of Birmingham. Nottingham has links to the legend of Robi ...
.
According to the World Population Review,
in 2019 there was:
* One birth every 39 seconds
* One death every 52 seconds
* A net gain of one person every minute
* One net migrant every 3 minutes
Population by constituent country
File:Population of England over time.svg, England
File:Population of Scotland over time.svg, Scotland
File:Population of Wales over time.svg, Wales
File:Population of NI over time.svg, Northern Ireland
Population change over time

The following table shows the total UK population estimated at
census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses in ...
dates. Pre 1901 figures include the whole of Ireland, whereas from 1901 onwards only the population of Northern Ireland is included.
Population density calculated on:
* Pre-1901:
243,820 km2 total land area for the United Kingdom plus 70,273 km
2 land area of the
Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 Counties of Ireland, counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern ...
.
* Post-1901: its current boundaries.
Future projections

The UK government first began publishing population projections for the country in the 1920's under the
Government Actuary’s Department (GAD) which were mainly produced to be used for long-term financial estimates for pensions and other schemes of social insurance.
However since the Second World War, population projections have taken an expanded role in all areas of influencing government policy. The GAD produced population projections every year from 1955 to 1979 and then switched it to every 2 years up to 1991. The Office of National Statistics took control of producing population projections for the country in 2006.
The British
Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; cy, Swyddfa Ystadegau Gwladol) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible for t ...
' 2016-based National Population Projections indicated that, if recent trends continue, the UK's population would increase by 3.6 million between mid-2016 and mid-2026. This represents an average annual growth rate of 0.5%. Over the same period, the population of England is projected to grow by 5.9%; for Wales, this figure is 3.1%, while for Scotland and Northern Ireland the figures are 3.2% and 4.2% respectively. These projections did not allow for any possible effects of the UK
leaving the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
.
[National Population Projections, 2016-based](_blank)
retrieved 29 October 2017
Fertility


Since 1838, it has been compulsory to register a birth or death in the United Kingdom.
First official data on the
fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were ...
of the country was first made available in 1938,
However estimates of the total fertility rate can be made back all the way till 1541.
The fertility rate of the country before the 19th century maintained itself at an average of around 5 children per woman. This fertility rate within the United Kingdom has been falling since 1870, when the country began into transition into the 3rd stage of the
demographic transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory which refers to the historical shift from high birth rates and high death rates in societies with minimal technology, education (especially of women) and economic development, to l ...
.
This transition represents the change in reproductive strategy from how many children a mother 'needs' to more of how many she 'wants' and a substitution of quality over quantity in the offspring produced.
From the 1880s onwards, the birth rate began to decline rapidly from the levels it had previous sustained itself at.
In England this crude birth rate decline represented a 44% decrease over a period from 1875 to 1920.
A number of factors have been argued to have contributed to this ranging from four broad spectrums of biological, technological changes and developments in the society,
socio-economic reasons and cultural considerations.
In the context of the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, a large number of socio-economic developments occurred; large scale urbanisation of the population caused mass internal movements of people to high density population centres, income per capita of citizens rose significantly especially in the last half of the 19th century, coupled with large scale economic growth improved the livelihoods of the working and middle classes of the United Kingdom, this growth in the standard of living led also to the collapse of
mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
s, which had been in decline since the early 18th century and more especially the
infant mortality.
This development came about with the decline of
child labour at the same time as well which meant there was less of a need for a quantity of children to uphold the household economically,
educational quality of the country rose during the same time period which meant that children held more a economical potential through educated labour means.
The decline and equalling out of the gender gap in terms of place in the workforce meant that women were beginning in the 19th century to become a larger part of the workforce which also contributed to the birth rate decline.
Improvements in public diets and nutritional quality increases, which are linked to biological factors such as a decline in lactation, have also been included as a potential factor in the decline of the fertility rate.
Technological developments within the society also began to have an effect; contraceptive use become somewhat usable on a mass scale in the latter half of the 19th century due to technological developments in the production of rubber.
Abortion, while illegal during the 19th century, was also used by women, however to what extent at the time is unknown.
Cultural considerations such as decline in religious adherence (albeit little data on this matter during the 19th century) have also been considered as reasons.
While these factors altogether are debated by demographers as to which were more important then each other, it is generally accepted that due to these factors overall, mothers could begin to invest more time and nurture 'quality' into their offspring rather then having a increased 'quantity' of children that were needed in the past for various such reasons, and that this development led to the decrease of the total fertility rate.
By 1914, the birthrate sat at around 2.88 children per woman, however by 1918 had collapsed proportionally by almost 50% due to
World War One
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and sank to 2.03 children.
In the
post-World War One period, while the birthrate of the country boomed at the very end of the war reaching a peak of 3.08 children in 1920,
this began to endure a rapid decline and had slumped to historic lows by the 1930s, for the first time in the country's history falling below a replacement level fertility rate.
This did not recover in-till the end of the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
in 1945.
In the
post-World War Two period, the fertility rate of the country boomed once again, bringing itself out of the below replacement level in the 1930s to levels not seen since the late 19th century. This peaked in 1964, with a TFR of 2.95.
However by 1973, the fertility rate of the country collapsed again below replacement, and has not since in the present day reached a replacement level again.
However population issues such as the sub-replacement level fertility rate have often been categorised as something in which the government does not view as a major issue.
Little incentives were made and have been made to increase the birth rate throughout the UK's post war period.
However
Wendy Singe argues that, while compared to other countries, the United Kingdom managed to retain a similarly 'high' (for post-war European standards) fertility rate with a quote; 'liberal market economy and residual approach to welfare, a combination of high female employment and relatively high fertility has been achieved without a coherent or generous set of work-family reconciliation policies.'
Family planning policies were enacted during the 1970s due to concerns of rapid population growth during the 1960s.
The
1973 NHS Reorganisation Act is an example of such policies, within this act family planning advice and supplies were first issued to the public.
Over this time period, with previous liberalising acts such as the
Abortion Act and the
Divorce Reform Act, and scientific developments such as increased access to contraceptive methods to reduce pregnancies, such as the
contraceptive pill Oral contraceptives, abbreviated OCPs, also known as birth control pills, are medications taken by mouth for the purpose of birth control.
Female
Two types of female oral contraceptive pill, taken once per day, are widely available:
* The combin ...
, it is generally ascribed that these social changes were the major contributors to the decline of the fertility rate below replacement level in the latter half of the 20th century.
With these changes also, pre-marital conceptions fell to 1950 levels by the late 1970s.
This pattern of decline of the birth rate is similar to other European countries.
The government's position was further presented and then re-iterated in 1984 at the
UN Conference on Population in Mexico;
The United Kingdom('s) government does not pursue a population policy in the sense of actively trying to influence the overall size of the population, its age-structure, or the components of change except in the field of immigration. Nor has it expressed a view about the size of population, or the age-structure, that would be desirable. ...The current level of births has not been the cause of general anxiety. The prevailing view is that decisions about fertility and childbearing are for people themselves to make, but that it is proper for government to provide individuals with the information and the means necessary to make their decisions effective. To this end, the government provides assistance with family planning as part of the National Health Service. The ‘ageing’ of the population does raise social and economic issues. However, it is believed that these will prove manageable; and also, to a degree, that society will adapt....’
In 2003, Right to Request was setup which allowed the parents of small children to request flexible working times which included shorter working hours for parents to care for their children.
However, although a majority of requests for Right to Request are accepted, a report in 2006 found that its impact was negligible as mothers tended to switch employers to get reduced hours regardless.
Due to migration beginning in the late 90s and especially during the 2000s lead to the overall total fertility rate of the country to rise by 0.1 in the period of 2004 to 2011.
In 2012, the UK's
total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were t ...
(TFR) was 1.92 children per woman,
below the
replacement rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were t ...
, which in the UK is 2.075. In 2001, the TFR was at a record low of 1.63, but it then increased every year until it reached a peak of 1.96 in 2008, before decreasing again.
In 2012 and 2013, England and Wales's TFR decreased to 1.85.
In Scotland however TFR is lower: it decreased from 1.75 in 2010 to 1.67 in 2012.
Northern Ireland has the highest TFR in the UK, standing at 2.02 in 2010 and 2.03 in 2012.

Mother's mean age at first birth
The first available data on when a mother gives birth for the first time was in 1920.
The reduction of the total fertility rate of the United Kingdom has also had a effect on the mean age in which a mother gives birth to her first child.
The age in which a mother gives birth to her first child has changed depending on the time period, but since the 1970s the age in which someone gives birth has been trending upwards.
Family size
The reduction of the fertility rate has also had an effect on the general family size of mothers in the United Kingdom, with the two being interlinked with each other.
The family size of the average UK family can be estimated with a
completed family size (CFS), which is an estimate of the amount of children a woman has birthed by the end of her childbearing years.
Family size within the UK has shifted towards two or one children in recent decades, rather then in the past when larger family sizes were more prominent and sought after.
This pattern is similar to other European countries, where couples are having fewer children.
Increasingly, there are also more couples who are completely childless; this has been increasing since the 1950s.
Life expectancy

Life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
has increased in the United Kingdom since the 18th century due to the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
and then the
Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, was a phase of rapid scientific discovery, standardization, mass production and industrialization from the late 19th century into the early 20th century. The Fi ...
which has vastly increased quality of life of the country's citizens.
At the start of the 20th century, the life expectancy at birth was only 45.6 years.
By 1950, life expectancy at birth had risen to 68.6 years.
During the latter half of the century, further factors influenced the increase of life expectancy: diseases and the improvement of healthcare in the 1950s, decline in smoking in the mid-1970s and improvements in treating heart disease in the 1990s contributed to its decline.
At the start of the 21st century, the life expectancy at birth was 77.8 years.
In 2011 the life expectancy at birth of the UK was around 80.4 years,
but the rate of increase has been stalling.
Potential factors behind this may be austerity measures imposed in the beginning of the 2010s,
which coincidentally since then mortality rates have slowed down in decline
or older people dying off at faster rates then expected.
On the topic of austerity measures, Professor Richard Faragher has said that "It is possible to have high or rising life expectancy during austerity, as is the case in Japan. Similarly, you can have rising life expectancy despite high levels of inequality – this was the case in Britain from 1900-1950."
but noted that austerity measures to social services like the
NHS
The National Health Service (NHS) is the umbrella term for the publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom (UK). Since 1948, they have been funded out of general taxation. There are three systems which are referred to using the " ...
, especially social care support for the elderly may be causing a stalling of life expectancy increase due to a decreased quality of life for older generations.
Infant mortality
 Infant mortality
Infant mortality has been on the decline since the Second Industrial Revolution, although the majority of the decline came around from the start to the end of the 20th century.
In raw terms for example, infant mortality in England sat around 151 deaths to 1000 live births in 1901 but by the end of the century it had plummeted down to only 6 deaths per 1000 births.
There are two general lines of thought which are usually taken from into analysing the decline of infant mortality rates, the first line of thought comes from social historians, who ascribe the decline of infant mortality to social phenomenons of the time such as the need for a healthy population for the sake of the nation's fighting capabilities and political issues surrounding women.
The second line of thought comes from demographers themselves which more or less ascribe the decline of infant mortality itself more to the general decline of mortality altogether in the society then any particular reason why.
Physical unfitness during the
Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the Sou ...
came into national prominence as many recruits came back to be too medically unfit for service.
With this, In 1904, the ''
Report of the Inter-Departmental Committee on Physical Deterioration'' was published
which listed large amounts of details of the failings of the British population, and for that matter government, in sustaining a healthy population.
The current rate of infant mortality in the United Kingdom is roughly around 3.82 deaths per 1,000 live births.
Age structure
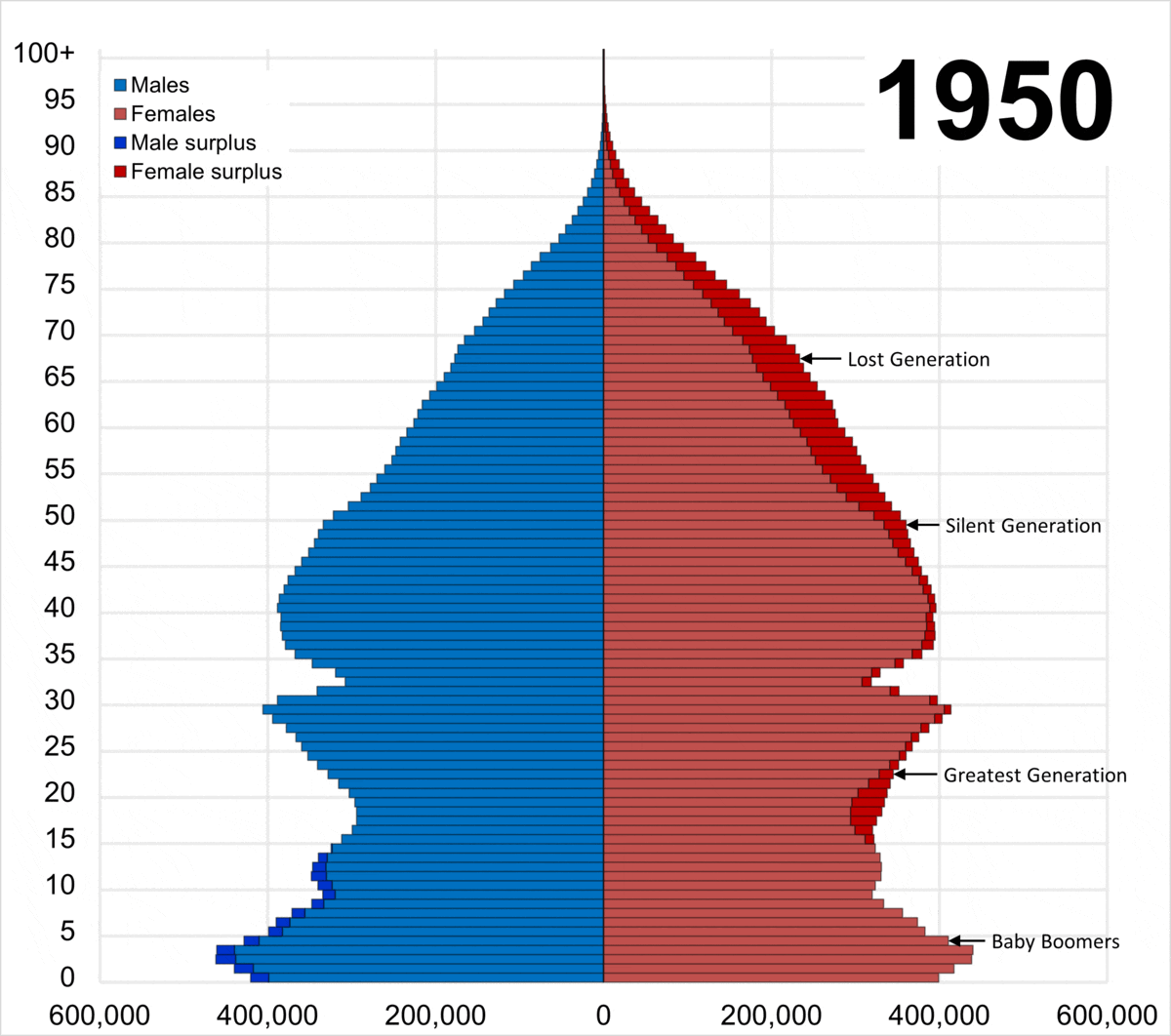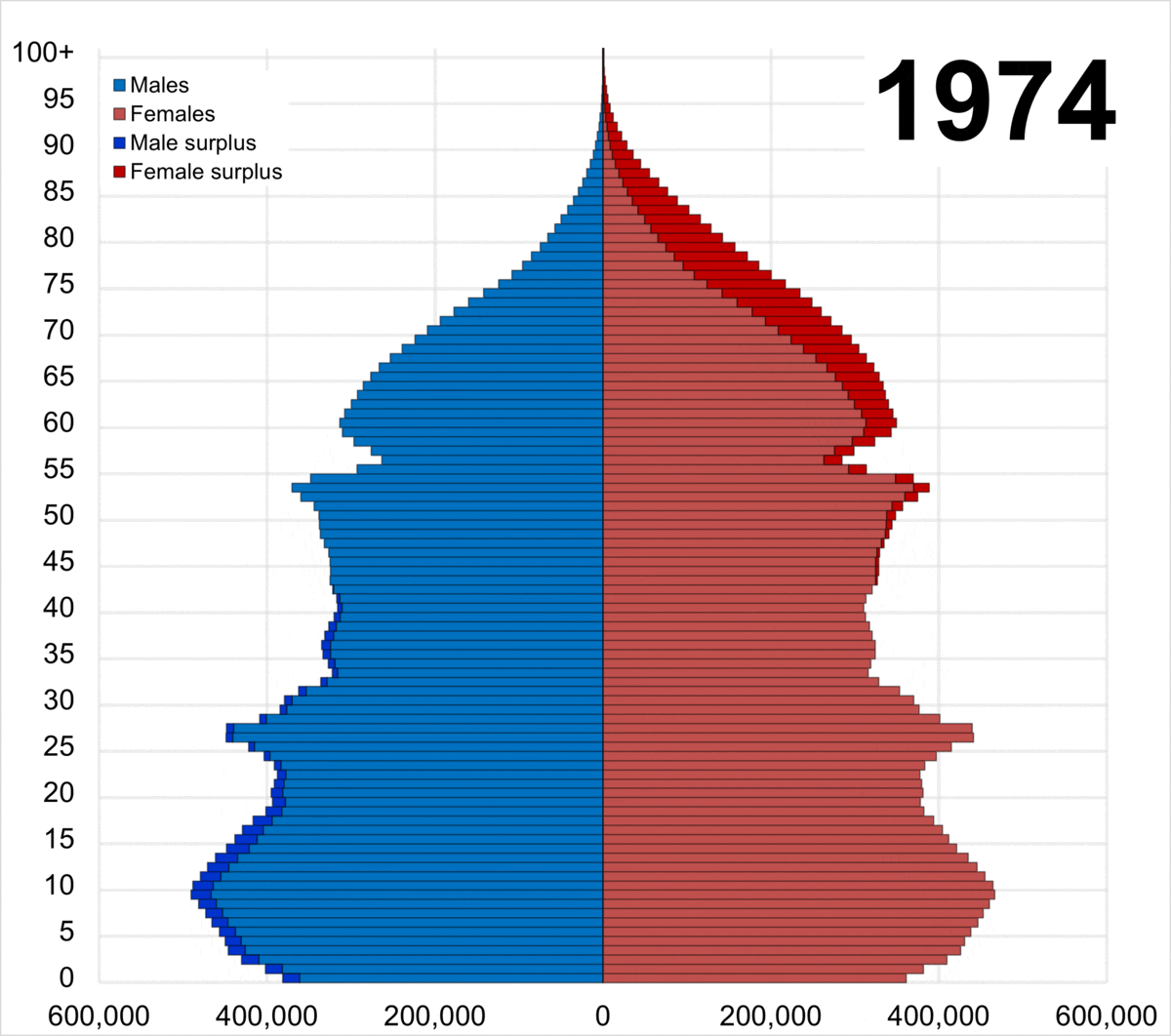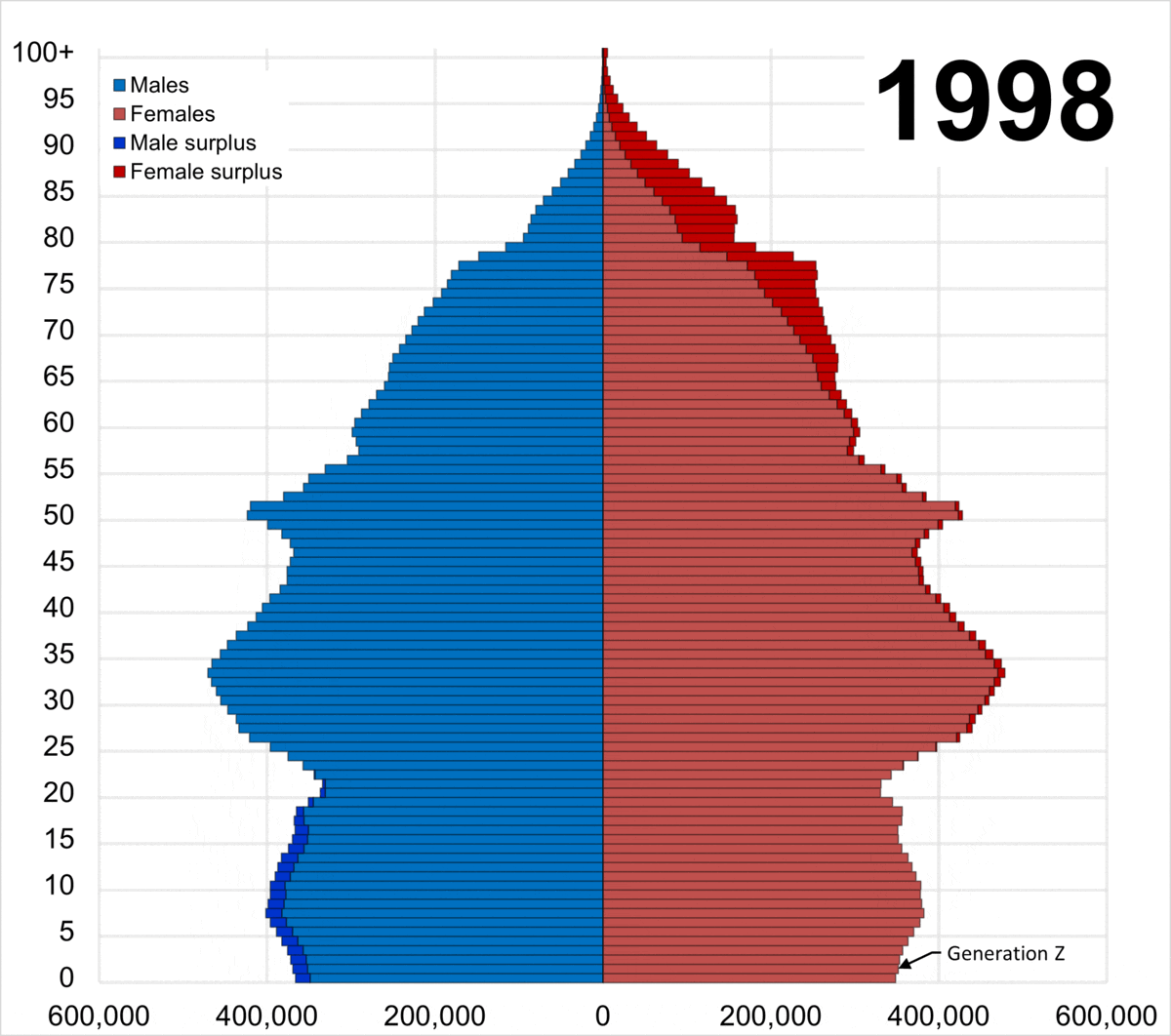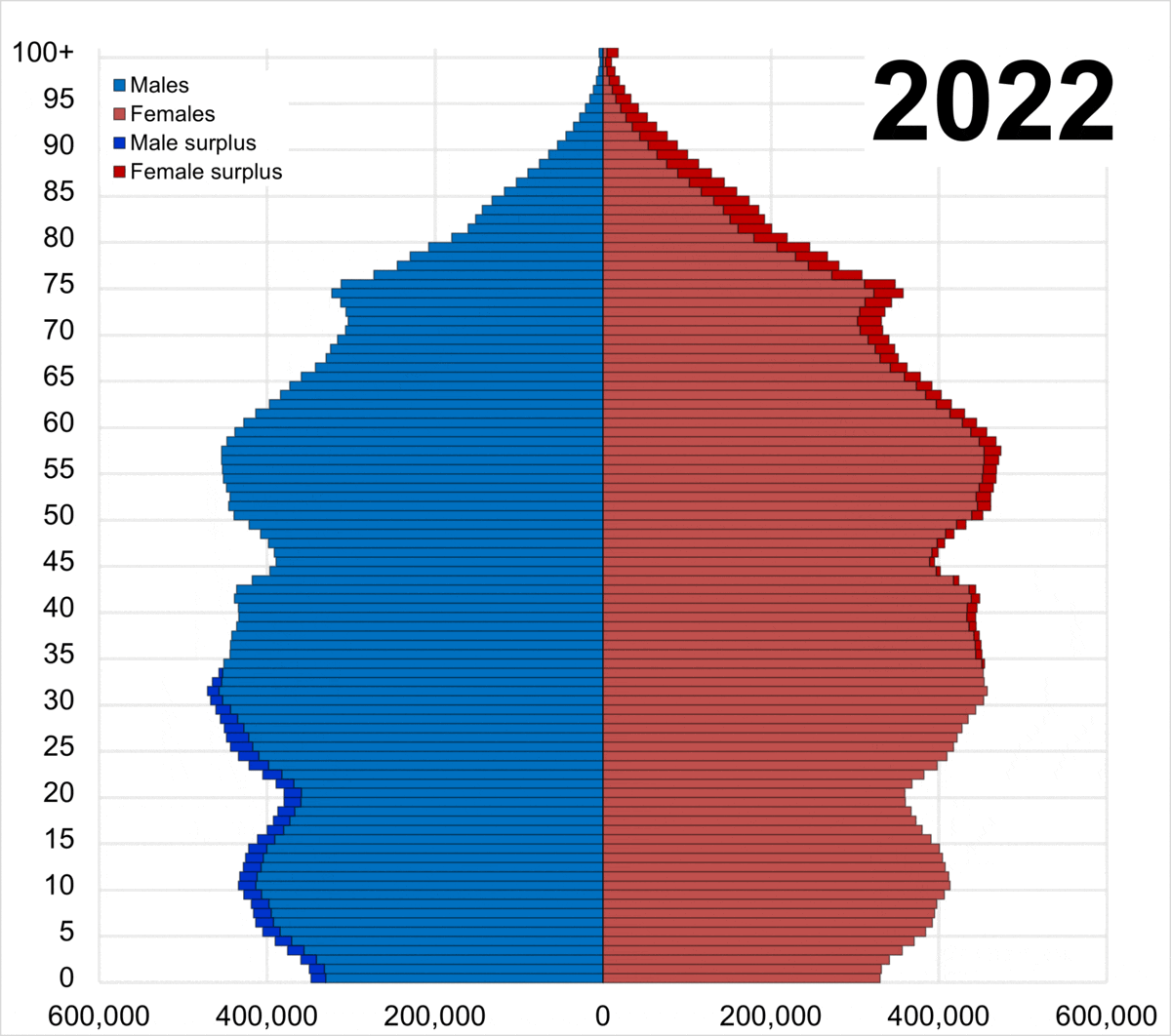

Interlinked with
fertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Fertili ...
and
mortality, The age structure of the United Kingdom has varied with how rates of fertility and mortality have changed throughout the country's history. Due to the transition to an
industrialised society, the United Kingdom has also undergone a '
demographic transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory which refers to the historical shift from high birth rates and high death rates in societies with minimal technology, education (especially of women) and economic development, to l ...
': that is to say, that it has gone from a high birth rate, high mortality rate society to a low birth rate, low mortality rate society over the space of two centuries.
Before the 18th century, the United Kingdom retained an age structure universal to societies in the first stage of the transition theory, with high fertility rates and high mortality rates,
in the late 18th century, the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
began, kickstarting the country's transition into the second phase: mortality rates declined but birth rates stayed at the same level;
by 1870, the country had begun to transition into the third phase:
the birth rate began to decline from around near 5 children per woman to below replacement level in the 1930s.
The fourth phase of the transition began in the 1960s, when the fertility rate rose, and peaked during the middle of the decade, and then collapsed by 1973 to a below replacement level rate. Since then, the rate has not risen to an above replacement level fertility rate; this has resulted in a population which is currently ageing:
in 2007, for the first time in the country's history, there were more people over the age of 60 then there were under the age of 16.
Peaks and bands within the population represent different periods in which people were born, for example, a large peak of people in particularly for those aged 70–74 born following the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
and a wide band for those aged 50–59, born during the 1960s baby boom. Those aged 80 upwards would have been born in the 1930s baby dearth when the birth rate was below replacement level. On the younger band of the population there is a noticeable gap between the ages of 14 to 20, this due to at the beginning of the 21st century a lower number of children being born (and a subsequent lower TFR), however in the years following the birth rate rose during the 2010s and a 'broadening' of the pyramid began for those in the younger years leading to more children in those age cohorts. In relation to the sex ratio of the country, in the higher ages of the population, there are more women then men reflecting the higher life expectancies of women in the population, in the lower ages there are more men then women because there are slightly more boys then girls born each year. In relation to the older age brackets, In 2015, there were estimated to be over half a million people (556,270) aged 90 and over living in the UK, up from 194,670 people in 1985, and there were estimated to be 14,570
centenarian
A centenarian is a person who has reached the age of 100 years. Because life expectancies worldwide are below 100 years, the term is invariably associated with longevity. In 2012, the United Nations estimated that there were 316,600 living centen ...
s (people aged 100 or over) and 850 people aged 105 or over. The
Office of National Statistics
An office is a space where an organization's employees perform administrative work in order to support and realize objects and goals of the organization. The word "office" may also denote a position within an organization with specific du ...
has also wrote in their mid-2016 report on population projections that the median age of the British population was 40 years of age, and this will continue to rise as more people in the population age and a below-replacement level fertility level not refilling the population. This will make the number of people aged 85 and over double from 1.6 million in mid-2016 to 3.2 million in mid-2041.
The demographic ageing of the population is not evenly spread geographically, as people in rural areas are typically of a higher age then those living in metropolitan areas such as
Greater London for example.
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
(2020 estimate)
File:Scotland Population pyramid estimate 2020.svg, alt=, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
(2020 estimate)
File:Wales Population pyramid estimate 2020.svg, alt=, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
(2020 estimate)
File:Northern Ireland Population pyramid estimate 2020.svg, alt=, Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
(2020 estimate)
File:Under 15s across the UK.svg, Under 15 years old
File:Working age population distributed across the UK 2021.svg, 16 to 64 years old (working age)
File:Above the age of 65 years old across the UK.svg, Above the age of 65 years old

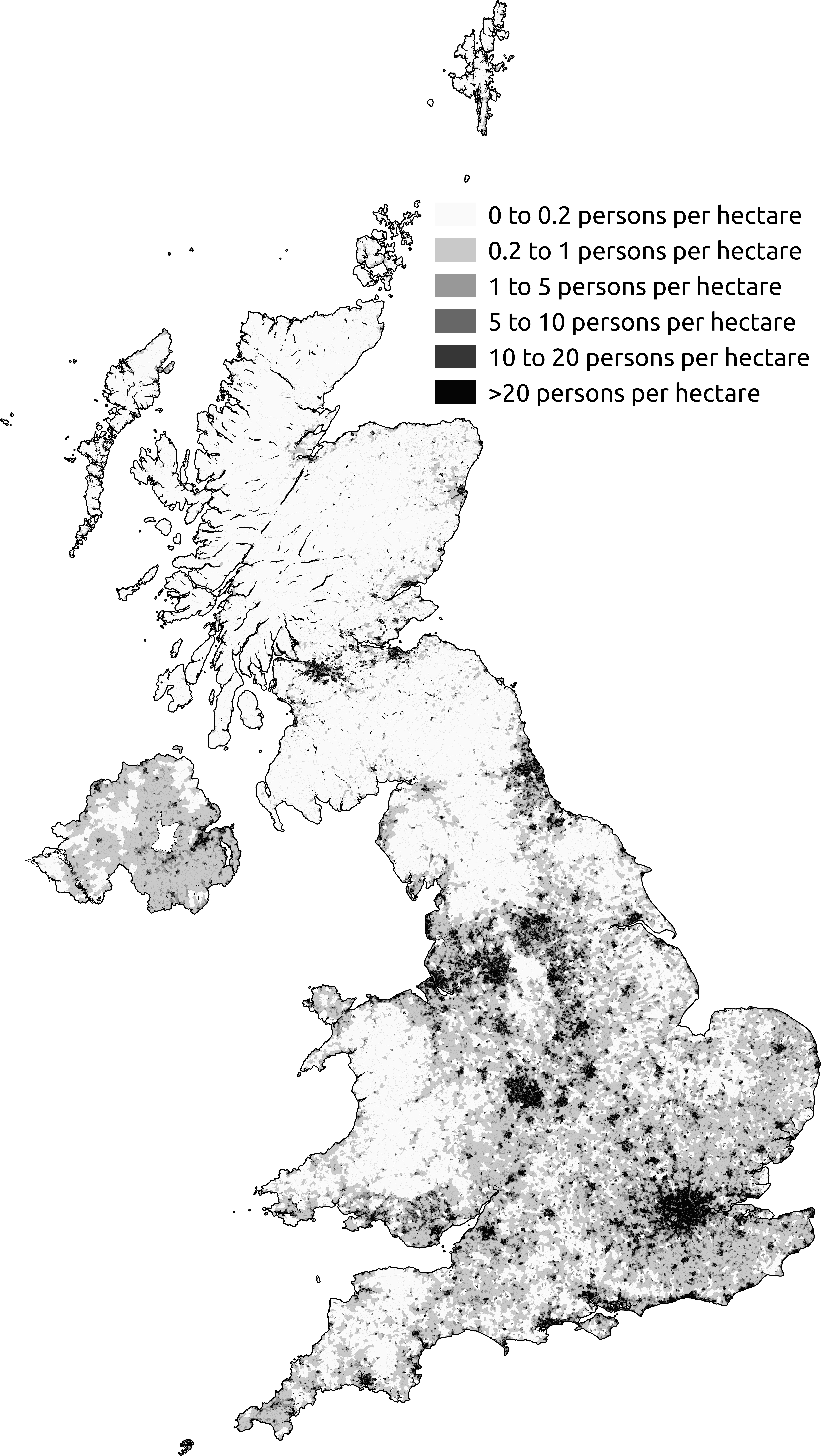
Urbanisation and population density
Population density
The United Kingdom is one of the most densely populated countries in Europe, in 2020 it was the 8th most densely populated country.
The current largest metropolitan areas are listen below:
Urbanisation

Rapid urbanisation began with the onset of the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
in the mid to late
18th century, shifting jobs and more importantly people away from rural Britain's dominance at the time which was primarily agricultural, to manufacturing jobs within urban areas which started to spring up.
In 1750, an estimated total of around only 1 million people lived in some sort of urban area such as a town or city,
which was around 1/6th of the estimated total population but a century later this had risen to 8 million people in 1850,
equating to just over half of the nation.
While this mass urbanisation affected pre-existing cities to a large degree such as
London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, smaller and 'newer' towns were in particular effected by the re-distribution of the population and exploded in raw population growth.
Cities such as
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1. ...
,
Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
,
Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of t ...
,
Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated popul ...
,
Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a populat ...
,
Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
,
Leeds
Leeds () is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds district in West Yorkshire, England. It is built around the River Aire and is in the eastern foothills of the Pennines. It is also the third-largest settlement (by popula ...
,
Sheffield
Sheffield is a city in South Yorkshire, England, whose name derives from the River Sheaf which runs through it. The city serves as the administrative centre of the City of Sheffield. It is historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire a ...
and
Newcastle Newcastle usually refers to:
*Newcastle upon Tyne, a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England
*Newcastle-under-Lyme, a town in Staffordshire, England
*Newcastle, New South Wales, a metropolitan area in Australia, named after Newcastle ...
for example had an explosive expansion in population numbers around the middle of the 19th century due to the industrial expansion of said cities bringing jobs and again people in for work.
London during the
19th century become noted as the 'premier city' of the world, being the most populated city from 1825 to 1900
and being the first city in
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
and one of the first in the world to reach the figure of one million inhabitants,
and then 5 million inhabitants.
This urbanisation in the 19th century has had two phases. David Herbert describes the process of the late 19th century and then early 20th century as a "maker and breaker" of the cities in the United Kingdom.
This mass influx of the population into the cities resulted in a centralisation of the population into the inner city areas however by the time of the late 19th century and early 20th century when technological advancements in transport kicked off allowing cities to expand their 'peripherals' from the inner areas to create large scale 'city regions' of their own.
London in particular, is a great example of this in effect, during the 19th century, the majority of people within the city lived in the inner part, however by the 20th century a massive expansion of '
Outer London
Outer London is the name for the group of London boroughs that form a ring around Inner London. Together, the inner and outer boroughs form London, the capital city of the United Kingdom.
These were areas that were not part of the County of Londo ...
' began which slowly became larger in population size by the middle of the century then
Inner London
Inner London is the name for the group of London boroughs which form the interior part of Greater London and are surrounded by Outer London. With its origins in the bills of mortality, it became fixed as an area for statistics in 1847 and was u ...
.
By the end of the 20th century this figure was 80% of the country.
However importance of the capital declined, by the end of the 20th century, London's ranking on the most populated cities of the world had fell down to not even being in the top 20.
The current classification of an 'urban' area, also termed as a 'built-up area' (BUA)
in the 2011 census, is a settlement which takes variables from both numerical population numbers and population density; in population numbers this is roughly more than or 10,000 people living in a area.
Anything below that is classified as 'rural', having several levels of distinction to define a rural town and fringe, village or hamlet which is usually taken from population density figures.
These areas are then defined within 'output areas' (OA's) themselves, which are geographic areas of the United Kingdom.
The population which resides within classified 'urban' areas was 84.4% of total population in 2022 and the annual rate of urbanisation change is estimated to be around 0.8% between 2020 and 2025.

Vital statistics (1900–2021)
Current vital statistics
* Deaths from January – May 2021 = 293,309
* Deaths from January – May 2022 = 276,227
Social issues
Marriage, divorce, families and household types
Marriage and divorce

In 2004, 58% of births were conceived within a married couple, 35% by non-married couples registered by both parents and 7% by non-married mothers who registered the birth alone.
This varied from each constituent nation, Wales for example had the highest births outside of marriage at 51% in 2004, In England this percentage was 42% and in Scotland 47%. Northern Ireland had the lowest of 35% in 2004.
Household and family type
File:Total household's by type in the UK 2021.svg, alt=, Type of households out of total households in 2021
File:Total families by type in the UK 2021.svg, alt=, Family types out of total families in 2021
File:Age of people living with parents within the UK by percentage of age group.svg, Percentage of age group living with parents in 2021
Sexual orientation

The Integrated Household Survey, published by the Office for National Statistics, provides the following estimates for the adult British population as of 2011:
* 1.1 per cent (approximately 545,000 adults at the time of the survey) identify as gay or lesbian.
* 0.4 per cent (approximately 220,000 adults) identify as bisexual.
* 0.3 per cent identify as "other".
* 3.6 per cent of those surveyed replied "don't know" or refused to answer the question.
* 0.6 per cent of those surveyed provided "no response" to the question.
* An estimated 2.7 per cent of 16-year-olds to 24-year-olds in the UK identify as gay, lesbian or bisexual compared with 0.4 per cent of those aged over 65.
Other sources provide alternative estimates of the population by sexual orientation. For example, one British journal published in 2004 estimated that approximately 5% of the British population is gay. A government figure estimated in 2005 that there are 3.6 million gay people in Britain equating to 6 per cent of the population, though a report by the Equality and Human Rights Commission described that estimate as 'of questionable validity' when set against available survey estimates.
The Gender Identity Research and Education Society (GIRES) estimated in 2009 that "56,000 might potentially be transsexual people", noting that it is very difficult to make a reliable estimate which would have been 0.09% of the population at the time of the report.
Out of the 600,000 people in the UK that applied to go to university through
UCAS
The Universities and Colleges Admissions Service (UCAS ) is a UK-based organisation whose main role is to operate the application process for British universities. It operates as an independent charity, funded by fees charged to applicants an ...
in 2020, 7.2%, or 40,000, described themselves as LGBT on their application form. UCAS estimates this to be a rate 2.5 times higher than the overall UK population. The UCAS report in collaboration with
Stonewall also found LGBT students were more likely to come from disadvantaged backgrounds (compared to those who identified as heterosexual or didn't specify), have a disability (compared to non-LGBT students) and have a mental health condition (compared to non-LGBT students).
Abortion
Abortion in the United Kingdom (however not
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
) was officially legalised in 1967 under the
Abortion Act of that year, allowing women for the first time to get an abortion under numerous medical grounds outlined within the act. Previously, this was outlawed under the
Offences against the Person Act of 1861 and then the updated
Infant Life (Preservation) Act of 1929 which only permitted an abortion if the death of a child was "done in good faith for the purpose only of preserving the life of the mother".
In 2020, the amount of conceptions which led to an abortion was around 25.3%
Health
Death rate and cause
File:Leading causes of death within the United Kingdom.svg, alt=, Leading causes of death for males
File:Leading causes of deaths for females within the United Kingdom.svg, alt=, Leading causes of death for females
Health issues
File:Obesity in the UK.svg, alt=, Obesity rates from 1975 to 2016
File:Smoking consumption over time for all adults in the United Kingdom.svg, alt=, Smoking rates from 1974 to 2020
File:Percentage of the population who consumes alcohol weekly overtime in the United Kingdom.svg, alt=, Percentage of the public who consume alcohol weekly from 2005 to 2017
File:Suicides in England and Wales per 100000 population.svg, alt=, Suicide rate
The following are lists of countries by suicide rate as published by the World Health Organization (WHO) and other sources.
About one person in 5,000–15,000 dies by suicide every year, with an estimated global rate of 10.5 per 100,000 popula ...
in England and Wales per 100,000 people from 1981 to 2020
File:Suicide rates within the United Kingdom per 100,000 people in 2020.png, alt=, Suicide rates regionally in 2020
File:Deaths to drug misuse in England and Wales.svg, alt=, Total deaths to drug misuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
in England and Wales
File:Drug misuse crude death rate UK 2019.png, alt=, Drug misuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
crude death rate regionally in 2019
Employment and income
The unemployment rate for the youth age bracket of 15–24 was 11.2% in 2019 – 13% for males and 9.2% for females.
File:UK unemployment rate.png, alt=, Unemployment rate 1881–2017
File:Percentage of labour force working in each sector of the economy from 1841 to 2011.svg, Percentage of labour force working in each (broad) sector
File:UK employment by broad sector range.svg, UK employment by broad industry sector
File:UK employment of population in private and public sectors by percentage.svg, UK employment by public or private sector
File:Average weekly earnings over time seasonally adjusted in the UK.svg, Average weekly earnings over time (seasonally adjusted)
File:Average household income in the UK from 1977 to 2021.svg, alt=, Average household income 1977–2021
File:Percentage of young people who are not in education, employment or training (NEET).svg, alt=, Percentage of young people who are not in education, employment or training (NEET)
Migration

Historical and present net numbers

Net migration to the United Kingdom has been in fluctuation throughout its history.
Through the 1970s and 1980s, migration to the United Kingdom was often a net negative in terms of numbers, with more people leaving the country, then entering in total.
Since 1994, net migration in numbers has been in the positives, with more people entering the country, rather then leaving.
Country of birth

In the 1980s to 1990s, around 12 to 13% of births were born to foreign born mothers. In 2004, this had risen to 20% of births being born to foreign born mothers.

Below is the number of births in England and Wales in 2011 by mother's country of birth, as well as their total fertility rate.
In 2014, 27% of births were to mothers born outside the UK, a 0.5-point increase since 2013. The 2014 fertility rate was higher for foreign-born mothers (2.09) than British-born mothers (1.76). In the 2010–14 time period, the most common countries of birth for mothers (excluding the UK) were Poland, Pakistan and India; and Poland and India for fathers. Within the UK,
Newham
The London Borough of Newham is a London borough created in 1965 by the London Government Act 1963. It covers an area previously administered by the Essex county boroughs of West Ham and East Ham, authorities that were both abolished by the ...
, London had the highest rate of births to non-UK mothers (76.7%) and
Torfaen
Torfaen (; cy, Torfaen ) is a county borough in the south-east of Wales. Torfaen is bordered by the county of Monmouthshire to the east, the city of Newport to the south, and the county boroughs of Caerphilly and Blaenau Gwent to the south-w ...
, Wales the lowest (3.2%). The fertility rate among non-UK born women was 1.98 and among UK born women 1.50 in 2020.
File:Counties of the UK Polish.svg, Born in Poland
File:Counties of the UK Lithuanian.svg, Born in Lithuania
File:Counties of the UK French.svg, Born in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
File:Counties of the UK South African.svg, Born in South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
Internal
Population movements of the country have fluctuated over time, in the 19th century with the urbanisation of the country, large amounts of people moved to the capital and the nearby industrial cities, but in recent years there has been a general trend of 'de-urbanisation' as parts of the population have moved back to the countryside. An example of recent large scale internal movement in the 21st century has been the departure of 220,000
White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population ...
Londoners to other areas of rural England and
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
over the 2000s and over the 2010s around a total of 550,000 people left the city.
Demographically by age, the people leaving the city more than entering tend to be in their 30s and 40s while people entering in their 20s.
Ethnicity
Ethnic demographic breakdown

For the overwhelming majority of its established history, the United Kingdom has been ethnically homogenous society with few minorities.
Such few minorities formed in total numbers over a long period of time and the largest numerical minority which resembled over one million were Irish people.
Following the
British Nationality Act of 1948, which transformed the status of all the subjects of the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
into classified legal 'British citizens', allowed upwards of millions from Britain's colonies to migrate to the United Kingdom legally.
In the following same year, the
Empire Windrush embarked to the United Kingdom which allowed upwards of 800 West Indians marking in popular history the beginning of
modern migration to the United Kingdom, despite the fact that little migrants came afterwards until the middle of the 1950s.
Since 1948, the population of the country has gradually become more ethnically heterogenized nationally, while regionally, in areas such as metropolitan counties, this process has been more rapid. Data on ethnicity was not formally collected until 1991 when the census for the first time asked the ethnicity of the British population, however estimates can still be taken on the approximate population of the non-white/ethnic minority population for the previous decades.
From 1997 onwards, ethnic diversity has increased rapidly since the country experienced net-positive migration in 1992
and then in 1997 with the expansion and lifting of restrictions on immigration with the
New Labour government.
Note:
File:Ethnic demographics of England from 1981 - 2021.gif, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
File:Ethnic demography of Wales from 1991 - 2021.gif, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
File:Racial demography of Scotland from 1991 - 2011.gif, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
File:Northern Ireland ethnic demography 2001 to 2021.gif, Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
Geographic distribution
File:White percentage UK wide.svg, White: Total (87.12%)
File:White British percentage UK wide 2011.svg, White: British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
(81.5%)
File:Counties of the UK Irish.svg, White: Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
(0.95%)
File:Asian percentage UK wide.svg, Asian/Asian British: Total (6.92%)
File:Counties of the UK Indian.svg, Asian/Asian British: Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
(2.3%)
File:Counties of the UK Pakistani.svg, Asian/Asian British: Pakistani (1.86%)
File:Counties of the UK Bangladeshi.svg, Asian/Asian British: Bangladeshi (0.71%)
File:Counties of the UK Chinese.svg, Asian/Asian British: Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
(0.69%)
File:Counties of the UK Other Asian.svg, Asian/Asian British: Other Asian (1.36%)
File:Counties of the UK Black.svg, Black/Black British: Total (3.01%)
File:Counties of the UK Caribbean.svg, Black/Black British: Caribbean (0.94%)
File:Counties of the UK Arab.svg, Other: Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
(0.40%)
Age structure of ethnic groups
File:White population pyramid - UK 2011.svg, White: Total
File:White British in 2011.svg, alt=, White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population ...
File:White Irish - 2011.svg, alt=, White Irish
}
White Irish is an ethnicity classification used in the 2011 United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White Irish population was 1,105,673 or 1.7% of the UK total population.
This total includes the White Irish population estimate for ...
File:Other White in 2011.svg, alt=, Other White
The term Other White is a classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom and has been used in documents such as the 2011 UK Census to describe people who self-identify as white (chiefly European) persons who are not of the English, Welsh, ...
File:Ethnic minority total population pyramid UK.svg, Ethnic minority: Total
File:Asian population pyramid - UK 2011.svg, Asian/Asian British: Total
File:Asian or Asian British Indian in 2011.svg, alt=, Asian/Asian British: Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
File:Asian Pakistani - 2011.svg, alt=, Asian/Asian British: Pakistani
File:Asian Bangladeshi - 2011.svg, alt=, Asian/Asian British: Bangladeshi
File:Asian Chinese - 2011.svg, alt=, Asian/Asian British: Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
File:Other Asians 2011.svg, alt=, Other Asian
File:Black population pyramid - UK 2011.svg, Black/Black British: Total
File:Black Caribbean - 2011.svg, alt=, Black/Black British: Caribbean
File:Black Africans - 2011.svg, alt=, Black/Black British: African
File:Other Blacks 2011.svg, alt=, Other Blacks
File:Mixed population pyramid - UK 2011.svg, Mixed/British Mixed: Total
File:Other Ethnic - 2011.svg, alt=, Other ethnic groups
File:Other Arabs - 2011.svg, Other: Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
Ethnicity of school pupils
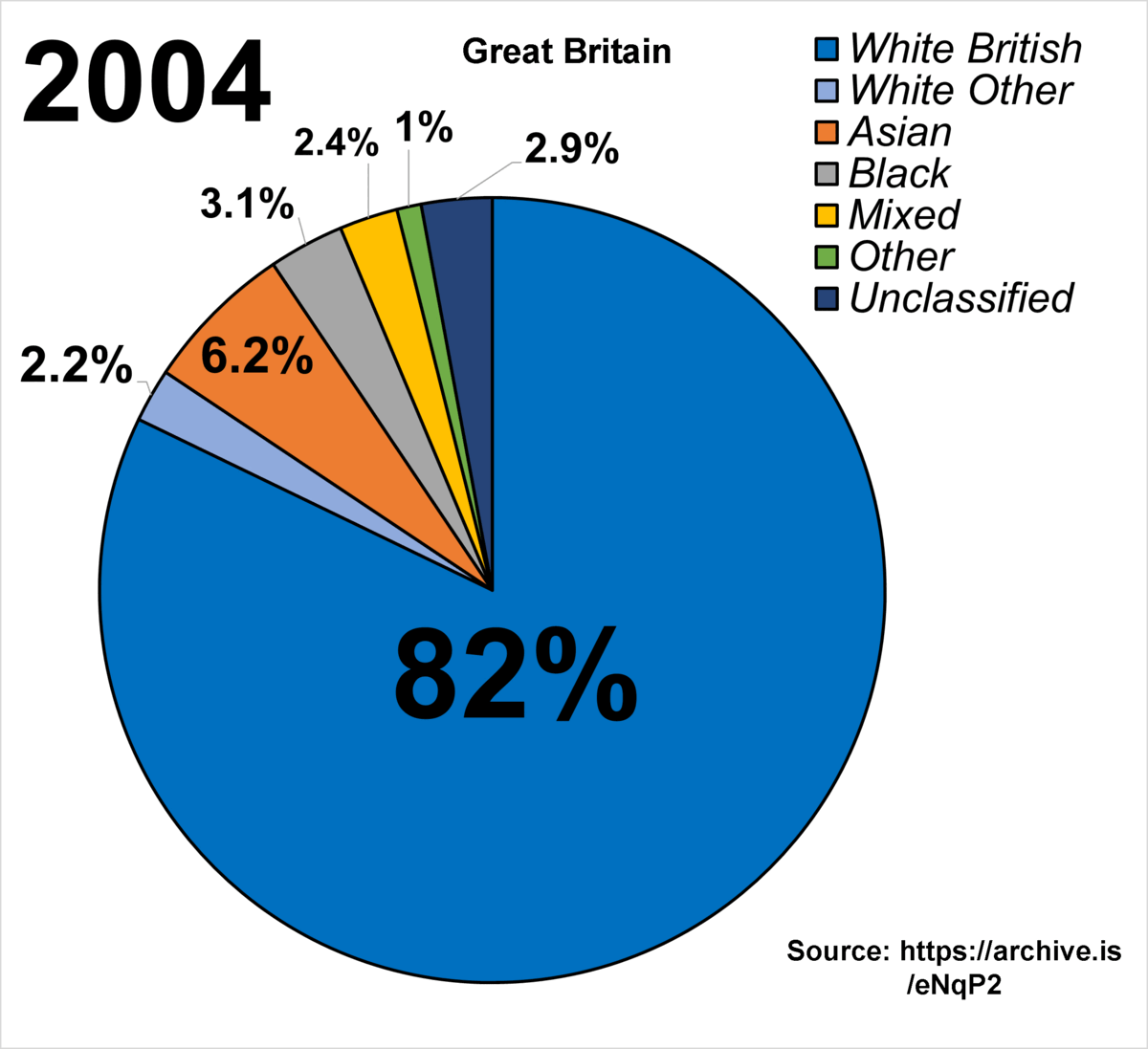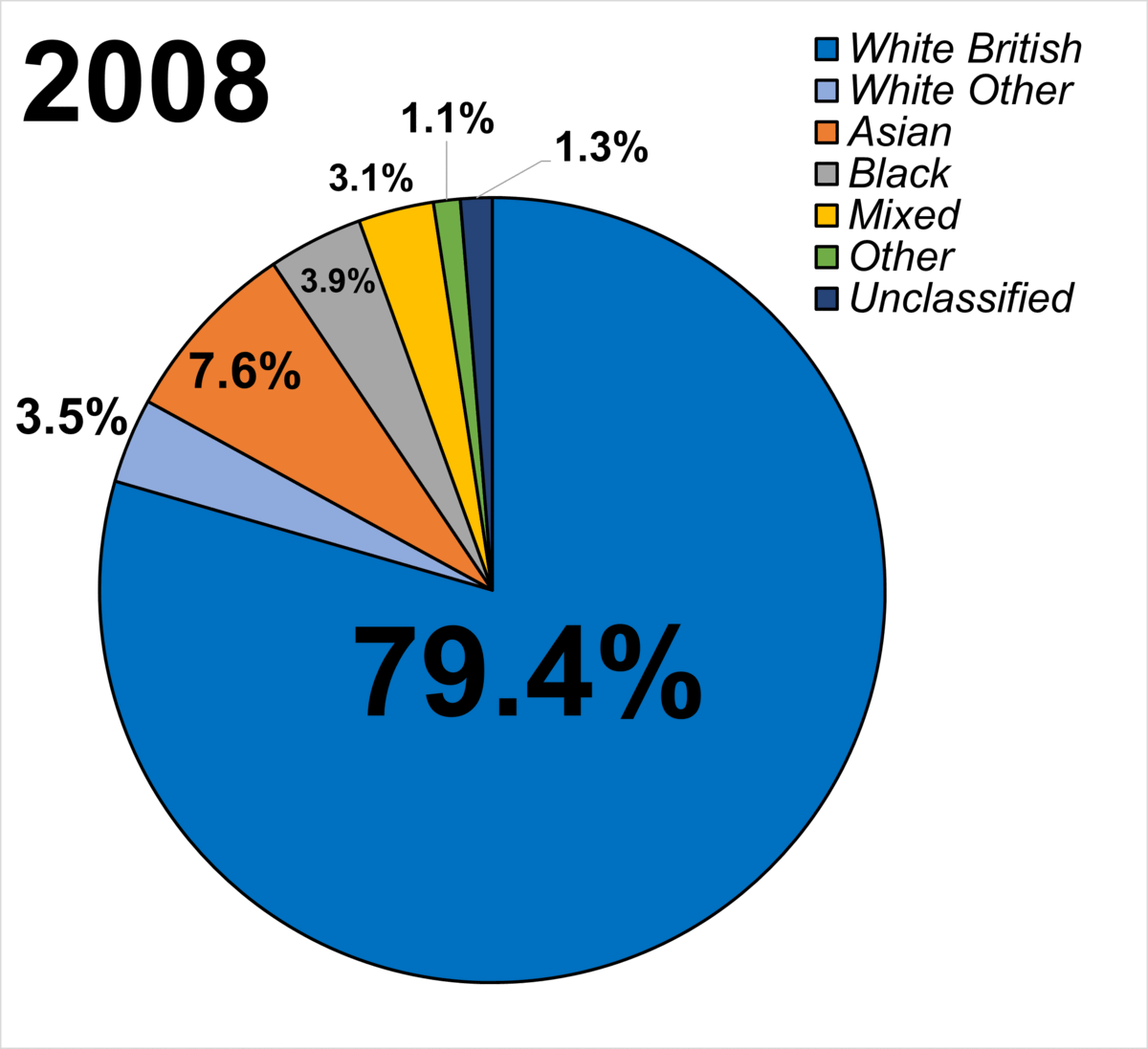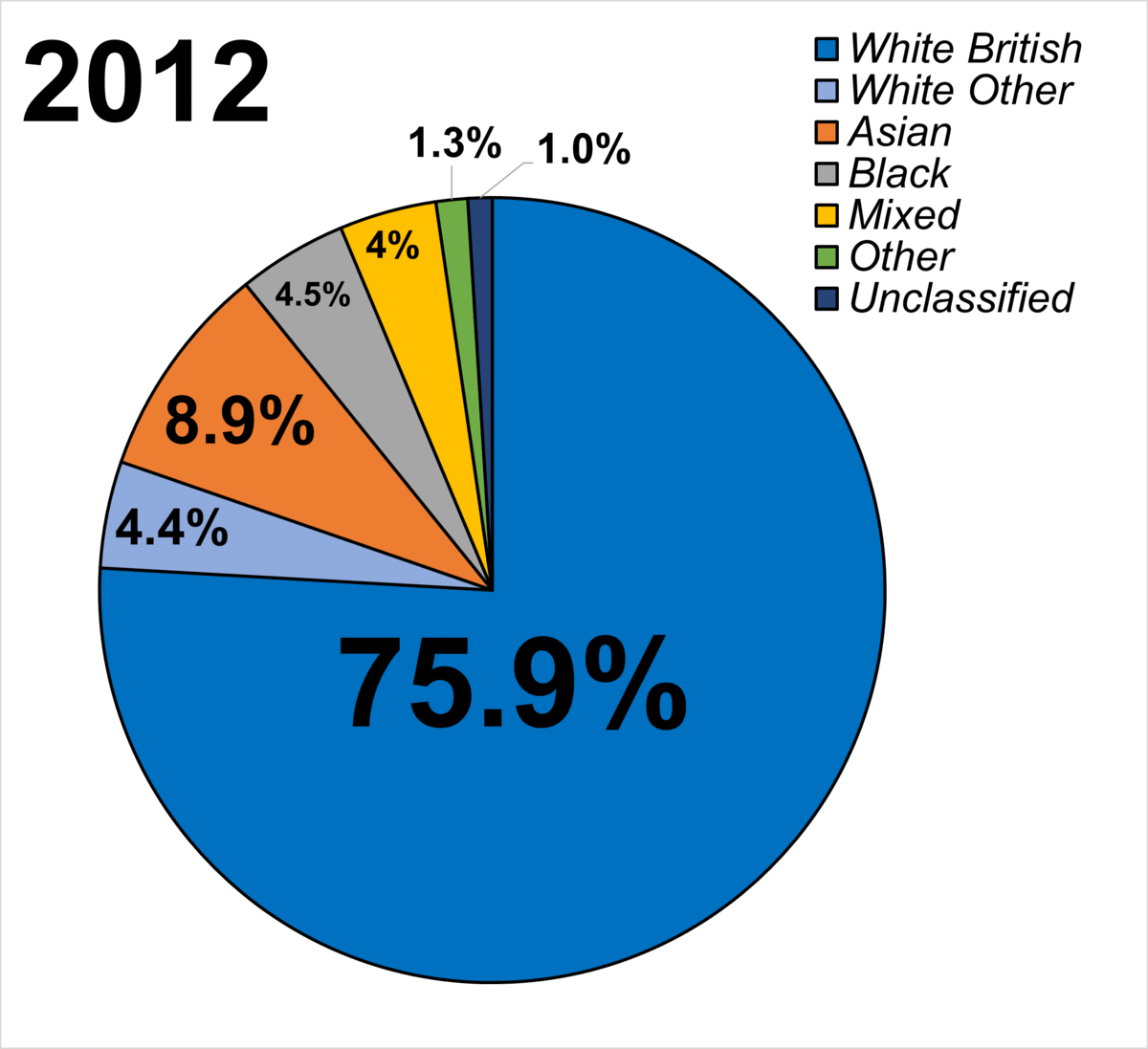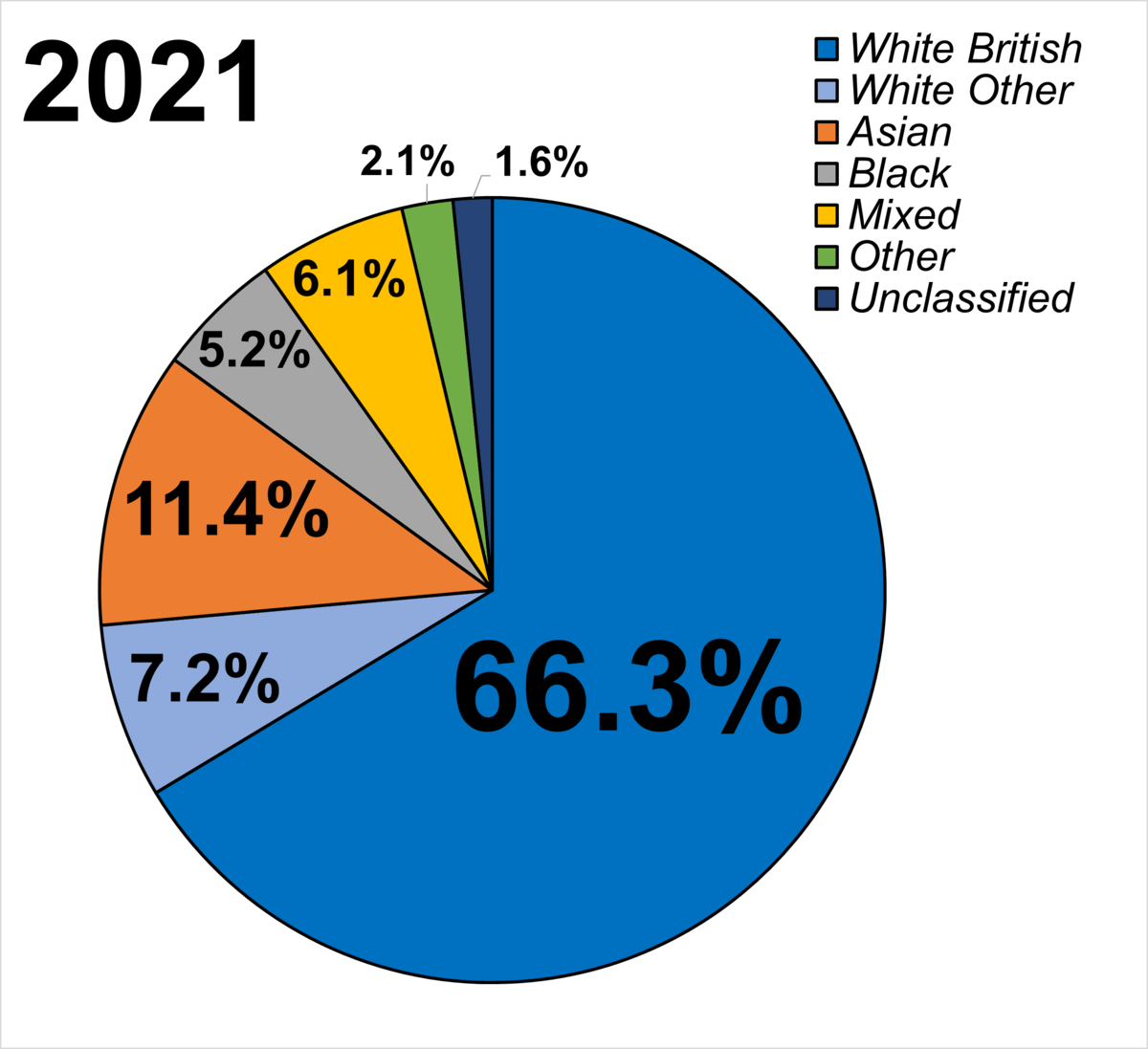 File:White total school children within England.svg, White: 71.4%
File:White British school children within England.svg, White British: 63.9%
File:White total school children within England.svg, White: 71.4%
File:White British school children within England.svg, White British: 63.9%
Ethnicity of live births and total fertility rate
Future projections

Numerous predictions and projections of the future ethnic demography of the United Kingdom have been made over the years.
In 2010, academic
David Coleman
David Robert Coleman OBE (26 April 1926 – 21 December 2013) was a British sports commentator and television presenter who worked for the BBC for 46 years. He covered eleven Summer Olympic Games from 1960 to 2000 and six FIFA World Cups from ...
produced research postulating a future demographic decline of the
White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population ...
in Britain, indicating that they would become a minority in Birmingham and London during the 2020s.
He also estimated that around 2056 to 2066, the trend of a declining share of the white populace will result in the United Kingdom having an overall white minority.
In
Prospect, he outlined four projections for a majority-minority scenario within the United Kingdom;
* If net immigration trends (in 2010) continued its overall trend of 254,000 a year and net emigration of the
White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population ...
was 74,000 a year (180,000 per year), the White British would decline to 59% of the total population by 2051, 'Other Whites' projected to be at 10% and non-Whites projected to be 31% of the population. By 2066 this would inevitably lead to the White British being a minority of the population.
* If migration to the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
was to decline to a net inflow of 80,000 per year, the
White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population ...
would be 63% of the population by 2051 and would fall below 50% in 2080.
* Using a cross-party group of MP's recommendation of 'balanced migration', where there is neither a net inflow or outflow, where immigration only consists of 74,000 a year and emigration of the White British the same, the White British would be 67% of the population by 2051 and then fall below 50% by the end of the century.
* If there is no emigration of citizens and no immigration to the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
('natural change' scenario), then the White British would remain at around 80% of the population by 2051 and would still remain the majority by the end of the century, albeit a reduced percentage (roughly around 75 - 70%)
* A fifth estimate, made by the Philip Rees and the
University of Leeds
, mottoeng = And knowledge will be increased
, established = 1831 – Leeds School of Medicine1874 – Yorkshire College of Science1884 - Yorkshire College1887 – affiliated to the federal Victoria University1904 – University of Leeds
, ...
, estimate that if assumptions about ethnic self-identification are taken into account, and that there is a net outflow of citizens at 38,000 a year, most of which are non-white and long term net migration like mentioned turns negative, this would result in the White British remaining at around 80% of the population by 2051, 20% of which would be ethnic minorities and 15% of that 20% would be non-white.
File:White population over time including projections in the UK.svg, White population over time
File:Ethnic minority population overtime including projections to 2051.svg, Ethnic minority population (non-whites)
Religion

In 2001, the question of religious adherence was asked for the first time since 1851 in the United Kingdom Census.
The traditional religion in the United Kingdom is Christianity. In England the
established church is the
Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britai ...
(
Anglican). In Scotland, the
Church of Scotland
The Church of Scotland ( sco, The Kirk o Scotland; gd, Eaglais na h-Alba) is the national church in Scotland.
The Church of Scotland was principally shaped by John Knox, in the Reformation of 1560, when it split from the Catholic Church ...
(a
Presbyterian Church) is regarded as the 'national church' but there is not an established church.
In
Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
there is no established church, with the
Church in Wales
The Church in Wales ( cy, Yr Eglwys yng Nghymru) is an Anglican church in Wales, composed of six dioceses.
The Archbishop of Wales does not have a fixed archiepiscopal see, but serves concurrently as one of the six diocesan bishops. The p ...
having been
disestablished in 1920. Likewise, in Ireland, the
Church of Ireland
The Church of Ireland ( ga, Eaglais na hÉireann, ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Kirk o Airlann, ) is a Christian church in Ireland and an autonomous province of the Anglican Communion. It is organised on an all-Ireland basis and is the secon ...
was disestablished in 1871. In Northern Ireland and parts of Western Scotland there are lingering
sectarian divides between
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
and Protestant communities.
The table below shows data regarding religion for the 2001 and 2011 censuses:
File:Christianity in the 2011 census.png, Christians (59.5%)
In the 2011 Census, rather than select one of the specified religions offered on the Census form, many people chose to write in their own religion. Some of these religions were reassigned to one of the main religions offered. In England and Wales, 241,000 people belonged to religious groups which did not fall into any of the main religions. The largest of these were
Pagans (56,620),
Spiritualists
Spiritualism is the metaphysics, metaphysical school of thought opposing physicalism and also is the category of all spiritual beliefs/views (in monism and Mind-body dualism, dualism) from ancient to modern. In the long nineteenth century, Spir ...
(39,061) and
Jains
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
(20,288).
Despite its high-profile nature there were only 2,418
Scientologist
Scientology is a set of beliefs and practices invented by American author L. Ron Hubbard, and an associated movement. It has been variously defined as a cult, a business, or a new religious movement. The most recent published census data in ...
s. The census also recorded 176,632 people stating their religion as
Jedi Knight and 6,242 people as
Heavy Metal after a campaign by ''
Metal Hammer
''Metal Hammer'' is a heavy metal music magazine and website founded in 1983, published in the United Kingdom by Future, with other language editions available in numerous other countries. ''Metal Hammer'' features news, reviews and long-form ...
''.
These returns were classified as "No religion", along with
Atheist, Agnostic,
Humanist
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "human ...
, and Free Thinker.
Those who ticked
Heathen who had been categorised as no religion in 2001 were categorised as other.
It is unclear how the ONS treated people who ticked "Other" but did not write in any religion.
In 2012 the
British Social Attitudes Survey
The British Social Attitudes Survey (BSA) is an annual statistical survey conducted in Great Britain by National Centre for Social Research since 1983. The BSA involves in-depth interviews with over 3,300 respondents, selected using random probabi ...
found the highest number to be non-religious (48%) followed by Christians (46%) with another six per cent identifying otherwise. Discrepancies found between surveys may be the result of differences in phrasing, question order, and data collection method.
Future projections
Pew Research Center has found that by 2050 on all scenario's, the Islamic population of the United Kingdom will rise, depending on the scenario the percentage of the population which will be Islamic will either be 9.7% in a zero migration scenario, 16.7% in a medium migration scenario or 17.2% in a high migration scenario.
Languages
The United Kingdom's de facto official language is English which is spoken as a
first language
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongu ...
by 95% of the population. Six regional languages—
Scots,
Ulster-Scots,
Welsh,
Cornish, Irish and
Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well ...
—are protected under the
European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages
The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) is a European treaty (CETS 148) adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe. However, th ...
. Abilities in these languages (other than Cornish) for those aged three and above were recorded in the census of 2011 as follows.
Cornish is spoken by around 2,500 people. In the 2011 census, 464 respondents aged three and over in Cornwall said that Cornish was their main language, amounting to 0.09% of the total population of Cornwall aged three and over.
After English, Polish was the second most common language given in the United Kingdom census 2011. 618,091 respondents aged three and over said that Polish was their main language, amounting to 1.01% of the total population of the United Kingdom aged three and over.
The French language is spoken in some parts of the Channel Islands although the islands, like the Isle of Man, are not part of the United Kingdom.
British Sign Language
British Sign Language (BSL) is a sign language used in the United Kingdom (UK), and is the first or preferred language among the Deaf community in the UK. Based on the percentage of people who reported 'using British Sign Language at home' on ...
is also common.
National identity
Respondents to the 2011 UK census gave their national identities as follows.
Education


In the present day each country of the United Kingdom has a separate education system, with power over education matters in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland being devolved.
Universal state education in England and Wales was introduced for primary level in 1870 and secondary level in 1900.
Education is mandatory from the ages of 5 to 18, The majority of children are educated in state-sector schools,
[Private school pupil numbers in decline](_blank)
guardian.co.uk 9 November 2007 only a small proportion of which select on the grounds of academic ability. Despite a fall in actual numbers, the proportion of children in England attending private schools rose slightly from 7.1% to 7.3% between 2004 and 2007.
Scotland first legislated for universal provision of education in 1696. Four percent of children in Scotland attend private schools, a rate which has remained relatively stable since 2015.
In Wales, one of the most notable distinctive features of education in Wales is the emphasis on the Welsh language – lessons in which are compulsory for all until the age of 16. Whilst a significant minority of students (15.7% in the 2014\15 academic year) are taught primarily through the medium of Welsh.
See also
*
Demography of England
The demography of England has since 1801 been measured by the decennial national census, and is marked by centuries of population growth and urbanization. Due to the lack of authoritative contemporary sources, estimates of the population of ...
*
Demography of Scotland
The demography of Scotland includes all aspects of population, past and present, in the area that is now Scotland. Scotland has a population of 5,463,300, as of 2019. The population growth rate in 2011 was estimated as 0.6% per annum according ...
*
Demography of Wales
Demographics of Wales include the numbers in population, place of birth, age, ethnicity, religion, and number of marriages in Wales.
Historical population
The population of Wales doubled from 587,000 in 1801 to 1,163,000 in 1851 and had reac ...
*
Demography of Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland is the smallest of the four components of the United Kingdom in terms of both area and population, containing 2.9% of the total population and 5.7% of the total area of the United Kingdom. It is the smaller of the two political ...
*
Demography of London
The demography of London is analysed by the Office for National Statistics and data is produced for each of the Greater London wards, the City of London and the 32 London boroughs, the Inner London and Outer London statistical sub-regions, eac ...
*
Demography of Birmingham
Birmingham, England is an ethnically and culturally diverse city. The city is the core of the second most populous urban area in the United Kingdom after London and is the largest city proper.
Population
Birmingham city's total populatio ...
*
Demography of Liverpool
*
Demography of Greater Manchester
The demography of Greater Manchester is analysed by the Office for National Statistics and data is produced for each of its ten metropolitan boroughs, each of the Greater Manchester electoral wards, the NUTS3 statistical sub-regions, each of th ...
*
City status in the United Kingdom
City status in the United Kingdom is granted by the monarch of the United Kingdom to a select group of communities. , there are 76 cities in the United Kingdom—55 in England, seven in Wales, eight in Scotland, and six in Northern Ireland. ...
*
List of cities in the United Kingdom
*
List of urban areas in the United Kingdom
*
Genetic history of the British Isles
The genetic history of the British Isles is the subject of research within the larger field of human population genetics. It has developed in parallel with DNA testing technologies capable of identifying genetic similarities and differences betwee ...
Notes and references
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
Census 2001 website*Abstract (1833). ''Abstract of the Answers and Returns made pursuant to an act passed in the eleventh year of the reign of His Majesty
King George IV
George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from the death of his father, King George III, on 29 January 1820, until his own death ten ye ...
intituled an act for taking an account of the population of Great Britain, and the increase and diminution thereof''. Population Register Abstract 1831.
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
Parliamentary Papers, 38.
*Arkell, T. (1992). ''An Examination of the Poll Taxes of the late Seventeenth Century, the Marriage Duty Act and Gregory King.''
*K. Schürer, & T. Arkell (eds.), ''Surveying the People: the interpretation and use of document sources for the study of population in the late seventeenth century'' (pp. 142–177). Oxford: Leopard's Hill Press.
*Boulton, J. (1992). "The Marriage Duty Act and parochial registration in London, 1695–1706". In: K. Schürer, & T. Arkell (eds.), ''Surveying the People: the interpretation and use of document sources for the study of population in the late seventeenth century''; pp. 222–252. Oxford: Leopard's Hill Press.
*Boulton, J. (1993). "Clandestine marriage in London: an examination of the neglected urban variable", in: ''Urban History''; 20, pp. 191–210.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Demography of the United Kingdom
 Infant mortality has been on the decline since the Second Industrial Revolution, although the majority of the decline came around from the start to the end of the 20th century. In raw terms for example, infant mortality in England sat around 151 deaths to 1000 live births in 1901 but by the end of the century it had plummeted down to only 6 deaths per 1000 births.
There are two general lines of thought which are usually taken from into analysing the decline of infant mortality rates, the first line of thought comes from social historians, who ascribe the decline of infant mortality to social phenomenons of the time such as the need for a healthy population for the sake of the nation's fighting capabilities and political issues surrounding women. The second line of thought comes from demographers themselves which more or less ascribe the decline of infant mortality itself more to the general decline of mortality altogether in the society then any particular reason why.
Physical unfitness during the
Infant mortality has been on the decline since the Second Industrial Revolution, although the majority of the decline came around from the start to the end of the 20th century. In raw terms for example, infant mortality in England sat around 151 deaths to 1000 live births in 1901 but by the end of the century it had plummeted down to only 6 deaths per 1000 births.
There are two general lines of thought which are usually taken from into analysing the decline of infant mortality rates, the first line of thought comes from social historians, who ascribe the decline of infant mortality to social phenomenons of the time such as the need for a healthy population for the sake of the nation's fighting capabilities and political issues surrounding women. The second line of thought comes from demographers themselves which more or less ascribe the decline of infant mortality itself more to the general decline of mortality altogether in the society then any particular reason why.
Physical unfitness during the 
 Interlinked with
Interlinked with 
 The Integrated Household Survey, published by the Office for National Statistics, provides the following estimates for the adult British population as of 2011:
* 1.1 per cent (approximately 545,000 adults at the time of the survey) identify as gay or lesbian.
* 0.4 per cent (approximately 220,000 adults) identify as bisexual.
* 0.3 per cent identify as "other".
* 3.6 per cent of those surveyed replied "don't know" or refused to answer the question.
* 0.6 per cent of those surveyed provided "no response" to the question.
* An estimated 2.7 per cent of 16-year-olds to 24-year-olds in the UK identify as gay, lesbian or bisexual compared with 0.4 per cent of those aged over 65.
Other sources provide alternative estimates of the population by sexual orientation. For example, one British journal published in 2004 estimated that approximately 5% of the British population is gay. A government figure estimated in 2005 that there are 3.6 million gay people in Britain equating to 6 per cent of the population, though a report by the Equality and Human Rights Commission described that estimate as 'of questionable validity' when set against available survey estimates.
The Gender Identity Research and Education Society (GIRES) estimated in 2009 that "56,000 might potentially be transsexual people", noting that it is very difficult to make a reliable estimate which would have been 0.09% of the population at the time of the report.
Out of the 600,000 people in the UK that applied to go to university through
The Integrated Household Survey, published by the Office for National Statistics, provides the following estimates for the adult British population as of 2011:
* 1.1 per cent (approximately 545,000 adults at the time of the survey) identify as gay or lesbian.
* 0.4 per cent (approximately 220,000 adults) identify as bisexual.
* 0.3 per cent identify as "other".
* 3.6 per cent of those surveyed replied "don't know" or refused to answer the question.
* 0.6 per cent of those surveyed provided "no response" to the question.
* An estimated 2.7 per cent of 16-year-olds to 24-year-olds in the UK identify as gay, lesbian or bisexual compared with 0.4 per cent of those aged over 65.
Other sources provide alternative estimates of the population by sexual orientation. For example, one British journal published in 2004 estimated that approximately 5% of the British population is gay. A government figure estimated in 2005 that there are 3.6 million gay people in Britain equating to 6 per cent of the population, though a report by the Equality and Human Rights Commission described that estimate as 'of questionable validity' when set against available survey estimates.
The Gender Identity Research and Education Society (GIRES) estimated in 2009 that "56,000 might potentially be transsexual people", noting that it is very difficult to make a reliable estimate which would have been 0.09% of the population at the time of the report.
Out of the 600,000 people in the UK that applied to go to university through  Below is the number of births in England and Wales in 2011 by mother's country of birth, as well as their total fertility rate.
In 2014, 27% of births were to mothers born outside the UK, a 0.5-point increase since 2013. The 2014 fertility rate was higher for foreign-born mothers (2.09) than British-born mothers (1.76). In the 2010–14 time period, the most common countries of birth for mothers (excluding the UK) were Poland, Pakistan and India; and Poland and India for fathers. Within the UK,
Below is the number of births in England and Wales in 2011 by mother's country of birth, as well as their total fertility rate.
In 2014, 27% of births were to mothers born outside the UK, a 0.5-point increase since 2013. The 2014 fertility rate was higher for foreign-born mothers (2.09) than British-born mothers (1.76). In the 2010–14 time period, the most common countries of birth for mothers (excluding the UK) were Poland, Pakistan and India; and Poland and India for fathers. Within the UK,  For the overwhelming majority of its established history, the United Kingdom has been ethnically homogenous society with few minorities. Such few minorities formed in total numbers over a long period of time and the largest numerical minority which resembled over one million were Irish people.
Following the British Nationality Act of 1948, which transformed the status of all the subjects of the
For the overwhelming majority of its established history, the United Kingdom has been ethnically homogenous society with few minorities. Such few minorities formed in total numbers over a long period of time and the largest numerical minority which resembled over one million were Irish people.
Following the British Nationality Act of 1948, which transformed the status of all the subjects of the 
 Numerous predictions and projections of the future ethnic demography of the United Kingdom have been made over the years.
In 2010, academic
Numerous predictions and projections of the future ethnic demography of the United Kingdom have been made over the years.
In 2010, academic  In 2001, the question of religious adherence was asked for the first time since 1851 in the United Kingdom Census.
The traditional religion in the United Kingdom is Christianity. In England the established church is the
In 2001, the question of religious adherence was asked for the first time since 1851 in the United Kingdom Census.
The traditional religion in the United Kingdom is Christianity. In England the established church is the