Population of Canada on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 During the late 18th and early 19th century
During the late 18th and early 19th century
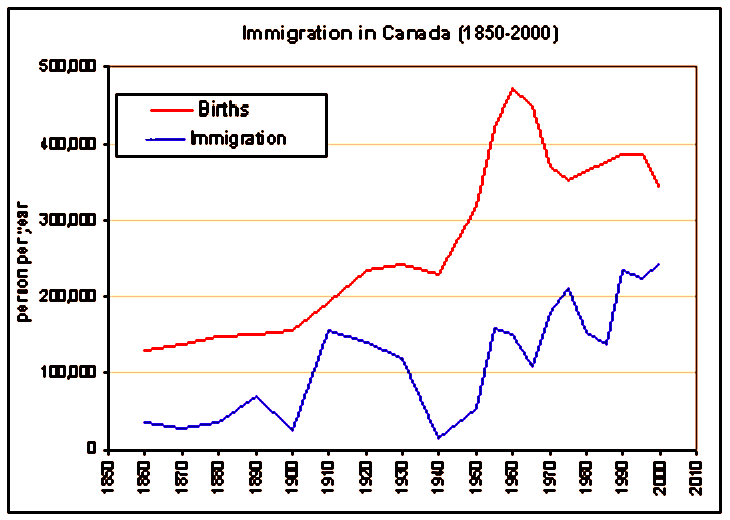 The 1911 census was a detailed enumeration of the population showing a count of 7,206,643 individuals. This was an increase of 34% over the 1901 census of 5,371,315. The year with the most population growth was during the peak of the
The 1911 census was a detailed enumeration of the population showing a count of 7,206,643 individuals. This was an increase of 34% over the 1901 census of 5,371,315. The year with the most population growth was during the peak of the

Population of Canada
- The Daily (Statistics Canada)
- Statistics Canada
Canada Population
– Worldometers
Annual Estimates of Population for Canada, Provinces and Territories, from July 1, 1971 to July 1, 2014
- Economics and Statistics Branch (Newfoundland & Labrador Statistics Agency)
Population and Dwelling Count, 2011 Census
– Statistics Canada
– Statistics Canada
– Statistics Canada (Archived)
Population Institute of Canada
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Population Of Canada By Years Demographics of Canada

Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
ranks 37th by population, comprising about 0.5% of the world's total, with over 39 million Canadians
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
as of 2022. Being, however, the fourth-largest country by land area (second-largest by total area), the vast majority of the country is sparsely inhabited, with most of its population south of the 55th parallel north
The 55th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 55 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
At this latitude the sun is visible for 17 hours, ...
and just over 60 percent of Canadians live in just two provinces: Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
and Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
. Though Canada's population density
Population density (in agriculture: Stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical ...
is low, many regions in the south, such as the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor, have population densities higher than several European countries
The list below includes all entities falling even partially under any of the regions of Europe, various common definitions of Europe, geographical or political. Fifty generally recognised sovereign states, Kosovo with limited, but substantial, ...
. Canada's largest population centres are Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
, Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
, Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the ...
, Calgary, Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city ancho ...
and Ottawa, with those six being the only ones with more than one million people.
The large size of Canada's north, which is not at present arable, and thus cannot support large human populations, significantly lowers the country's carrying capacity. In 2021, the population density
Population density (in agriculture: Stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical ...
of Canada was 4.2 people per square kilometre. As contrast, Russia's similar figure was 8.4 people per square kilometre.
The historical growth of Canada's population is complex and has been influenced in many different ways, such as indigenous populations, expansion of territory, and human migration. Being a new world
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
country, immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, a ...
has been, and remains, the most important factor in Canada's population growth. The 2021 Canadian census counted a total population of 36,991,981, an increase of around 5.2 percent over the 2016 figure. Between 1990 and 2008, the population increased by 5.6 million, equivalent to 20.4 percent overall growth.
Historical population overview
Indigenous peoples
Scholars vary on the estimated size of theindigenous population
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
in what is now Canada prior to colonization and on the effects of European contact. During the late 15th century is estimated to have been between 200,000 and two million, with a figure of 500,000 currently accepted by Canada's Royal Commission on Aboriginal Health. Although not without conflict, European Canadians' early interactions with First Nations and Inuit populations were relatively peaceful. However repeated outbreaks of European infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
s such as influenza, measles and smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
(to which they had no natural immunity), combined with other effects of European contact, resulted in a twenty-five percent to eighty percent indigenous population decrease post-contact. Roland G Robertson suggests that during the late 1630s, smallpox killed over half of the Wyandot (Huron), who controlled most of the early North American fur trade in the area of New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
. In 1871 there was an enumeration of the indigenous population within the limits of Canada at the time, showing a total of only 102,358 individuals. From 2006 to 2016, the Indigenous population has grown by 42.5 percent, four times the national rate. According to the 2011 Canadian Census, indigenous peoples (First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
– 851,560, Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
– 59,445 and Métis – 451,795) numbered at 1,400,685, or 4.3% of the country's total population.
New France
The European population grew slowly under French rule, thus remained relatively low as growth was largely achieved through natural births, rather than by immigration. Most of the French were farmers, and the rate of natural increase among the settlers themselves was very high. The women had about 30 per cent more children than comparable women who remained in France. Yves Landry says, "Canadians had an exceptional diet for their time." The1666 census of New France
The 1666 census of New France was the first census conducted in Canada (and also North America). It was organized by Jean Talon, the first Intendant of New France, between 1665 and 1666.
Talon and the French Minister of the Marine Jean-Baptiste C ...
was the first census conducted in North America. It was organized by Jean Talon, the first Intendant of New France, between 1665 and 1666. According to Talon's census there were 3,215 people in New France, comprising 538 separate families. The census showed a great difference in the number of men at 2,034 versus 1,181 women. By the early 1700s the New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
settlers were well established along the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connectin ...
and Acadian Peninsula
The Acadian Peninsula (french: Péninsule acadienne) is situated in the northeastern corner of New Brunswick, Canada, encompassing portions of Gloucester and Northumberland Counties. It derives its name from the large Acadian population located ...
with a population around 15,000 to 16,000. Mainly due to natural increase and modest immigration from Northwest France (Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
, Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
, Île-de-France
The Île-de-France (, ; literally "Isle of France") is the most populous of the eighteen regions of France. Centred on the capital Paris, it is located in the north-central part of the country and often called the ''Région parisienne'' (; en, Pa ...
, Poitou-Charentes
Poitou-Charentes (; oc, Peitau-Charantas; Poitevin-Saintongese: ) is a former administrative region on the southwest coast of France. It is part of the new region Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It comprises four departments: Charente, Charente-Maritime, D ...
and Pays de la Loire) the population of New France increased to 55,000 according to the last French census of 1754. This was an increase from 42,701 in 1730.
British Canada
 During the late 18th and early 19th century
During the late 18th and early 19th century Canada under British rule
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total ...
experienced strong population growth. In the wake of the 1775 invasion of Canada by the newly formed Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, approximately 60,000 of the 80,000 Americans loyal to the Crown, designated later as United Empire Loyalists
United Empire Loyalists (or simply Loyalists) is an honorific title which was first given by the 1st Lord Dorchester, the Governor of Quebec, and Governor General of The Canadas, to American Loyalists who resettled in British North America dur ...
fled to British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestow ...
, a large portion of whom migrated to Nova Scotia and New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
(separated from Nova Scotia) in 1784. Although the exact numbers cannot be certain because of unregistered migration At least 20,000 went to Nova Scotia, 14,000 to New Brunswick; 1,500 to PEI and 6,000 to Ontario(13,000 including 5,000 blacks went to England and 5,500 to the Caribbean). For the rest of the 1780s additional immigrants arrived from the south. From 1791 An additional 30,000 Americans, called "Late Loyalists," were lured into Ontario in the 1790s by the promise of land and swearing loyalty to the Crown. As a result of the period known as the Great Migration by 1831, Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada (french: province du Bas-Canada) was a British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence (1791–1841). It covered the southern portion of the current Province of Quebec an ...
's population had reached approximately 553,000, with Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a part of British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of th ...
reaching about 237,000 individuals. The Great Famine of Ireland of the 1840s had significantly increased the pace of Irish immigration to Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
and the Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on th ...
, peaking in 1847 with 100,000 distressed individuals. By 1851, the population of the Maritime colonies also reached roughly 533,000 (277,000 in Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
, 194,000 in New Brunswick and 62,000 in Prince Edward Island). To the west British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
had about 55,000 individuals by 1851. Beginning in the late 1850s, the immigration of Chinese into the Colony of Vancouver Island
The Colony of Vancouver Island, officially known as the Island of Vancouver and its Dependencies, was a Crown colony of British North America from 1849 to 1866, after which it was united with the mainland to form the Colony of British Columbia ...
and Colony of British Columbia peaked with the onset of the Fraser Canyon Gold Rush
The Fraser Canyon Gold Rush, (also Fraser Gold Rush and Fraser River Gold Rush) began in 1858 after gold was discovered on the Thompson River in British Columbia at its confluence with the Nicoamen River a few miles upstream from the Thompson's c ...
. By 1861, as a result of natural births and the Great Migration of Canada from the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
, the Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on th ...
population increased to 3.1 million inhabitants. Newfoundland's population by 1861 reached approximately 125,000 individuals.
Post-confederation
The population has increased every year since the establishment of the Dominion of Canada in 1867; however, the population of Newfoundland was not included prior to its entry into confederation as Canada's tenth province in 1949. The first national census of the country was taken in 1871, with a population count around 3,689,000. The year with the least population growth (in real terms) was 1882–1883, when only 30,000 new individuals were enumerated. The 1911 census was a detailed enumeration of the population showing a count of 7,206,643 individuals. This was an increase of 34% over the 1901 census of 5,371,315. The year with the most population growth was during the peak of the
The 1911 census was a detailed enumeration of the population showing a count of 7,206,643 individuals. This was an increase of 34% over the 1901 census of 5,371,315. The year with the most population growth was during the peak of the Post-World War II baby boom
The middle of the 20th century was marked by a significant and persistent increase in fertility rates in many countries of the world, especially in the Western world. The term '' baby boom'' is often used to refer to this particular boom, general ...
in 1956–1957, when the population grew by over 529,000, in a single twelve-month period. The Canadian baby boom, defined as the period from 1947 to 1966, saw more than 400,000 babies born annually. The 1996 census recorded a total population of 28,846,761. This was a 5.7% increase over the 1991 census of 27,296,859. The 2001 census had a total population count of 30,007,094. In contrast, the official Statistics Canada population estimate for 2001 was 31,021,300.
Canada's total population enumerated by the 2006 census was 31,612,897. This count was lower than the official 1 July 2006 population estimate of 32,623,490 people. Ninety percent of the population growth between 2001 and 2006 was concentrated in the main metropolitan areas. The 2011 census was the fifteenth decennial census with a total population count of 33,476,688 up 5.9% from 2006. On average, censuses have been taken every five years since 1905. Censuses are required to be taken at least every ten years as mandated in section 8 of the Constitution Act, 1867
The ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (french: Loi constitutionnelle de 1867),''The Constitution Act, 1867'', 30 & 31 Victoria (U.K.), c. 3, http://canlii.ca/t/ldsw retrieved on 2019-03-14. originally enacted as the ''British North America Act, 186 ...
.
Components of population growth
A population estimate for 2022 put the total number of people in Canada at 38,232,593. Demographic statistics according to the World Population Review in 2022. *One birth every 1 minute *One death every 2 minutes *One net migrant every 2 minutes *Net gain of one person every 2 minutes In 2010, Canada's annual population growth rate was 1.238%, or a daily increase of 1,137 individuals. Between 1867 and 2009 Canada's population grew by 979%. Canada had the highest net migration rate (0.61%) of all G-8 member countries between 1994 and 2004. Natural growth accounts for an annual increase of 137,626 persons, at a yearly rate of 0.413%. Between 2001 and 2006, there were 1,446,080immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, a ...
and 237,418 emigrants, resulting in a net migration of just over 1.2 million people. Since 2001, immigration has ranged between 221,352 and 262,236 immigrants per annum.

Population by years
Prior toCanadian confederation
Canadian Confederation (french: Confédération canadienne, link=no) was the process by which three British North American provinces, the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, were united into one federation called the Dominion ...
in 1867 the population counts reflected only the former colonies and settlements and not the country to be as a whole with indigenous nations separated.
Ephemeral European settlements
Former colonies and territories
17th century
18th century
19th century
Canada as a whole since confederation
Census data by years
Data projections
In 2006, Statistics Canada projected for the decade 2021 to 2031 the population to grow by more than 5 million, or more than 10%. Between 1990 and 2008, the population increased by 5.6 million, equivalent to 20.4 percent overall growth. The 2016 Canadian census counted a total population of 35.1 million, or 1.5 million under the 2006 projection. In October 2020, the Trudeau government announced its plans to bring in more than 1.2 million immigrants over the subsequent three years, to catch up to the high-growth scenario.Modern population distribution
By province and territory
* List of population centres in Alberta * List of population centres in British Columbia * List of population centres in Manitoba * List of population centres in New Brunswick * List of population centres in Newfoundland and Labrador * List of population centres in the Northwest Territories *List of population centres in Nova Scotia
A population centre, in Canadian census data, is a populated place, or a cluster of interrelated populated places, which meets the demographic characteristics of an urban area, having a population of at least 1,000 people and a population density o ...
* List of population centres in Nunavut
*List of population centres in Ontario
A population centre, in Canadian census data, is a type of census unit which meets the demographic characteristics of an urban area, having a population of at least 1,000 people and a population density of no fewer than 400 persons per square km ...
* List of population centres in Prince Edward Island
* List of population centres in Quebec
* List of population centres in Saskatchewan
*List of population centres in Yukon
A population centre, in Canadian census data, is a populated place, or a cluster of interrelated populated places, which meets the demographic characteristics of an urban area, having a population of at least 1,000 people and a population density ...
By cities and municipalities
*List of largest Canadian cities by census
This is a list of the largest cities in Canada by census starting with the 1871 census of Canada, the first national census. Only communities that were incorporated as cities at the time of each census are presented. Therefore, this list does not ...
* List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population
First Nations
* List of Indian reserves in Canada by populationSee also
*Demographics of Canada
Statistics Canada conducts a country-wide census that collects demographic data every five years on the first and sixth year of each decade. The 2021 Canadian Census enumerated a Population of Canada by year, total population of 36,991,981, an i ...
*Canada immigration statistics
Since confederation in 1867 through to the contemporary era, decadal and demi-decadal census reports in Canada have compiled detailed immigration statistics. During this period, the highest annual immigration rate in Canada occurred in 1913, ...
*Immigration to Canada
According to the 2021 Canadian census, immigrants in Canada number 8.3 million persons and make up approximately 23 percent of Canada's total population. This represents the eighth-largest immigrant population in the world, while the proport ...
*Interprovincial migration in Canada
Interprovincial migration in Canada is the movement by people from one Canadian province or territory to another with the intention of settling, permanently or temporarily, in the new province or territory; it is more-or-less stable over time. I ...
* List of Canadian provinces and territories by Human Development Index
References
Further reading
* * *External links
Population of Canada
- The Daily (Statistics Canada)
- Statistics Canada
Canada Population
– Worldometers
Annual Estimates of Population for Canada, Provinces and Territories, from July 1, 1971 to July 1, 2014
- Economics and Statistics Branch (Newfoundland & Labrador Statistics Agency)
Population and Dwelling Count, 2011 Census
– Statistics Canada
– Statistics Canada
– Statistics Canada (Archived)
Population Institute of Canada
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Population Of Canada By Years Demographics of Canada