Polish corridor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

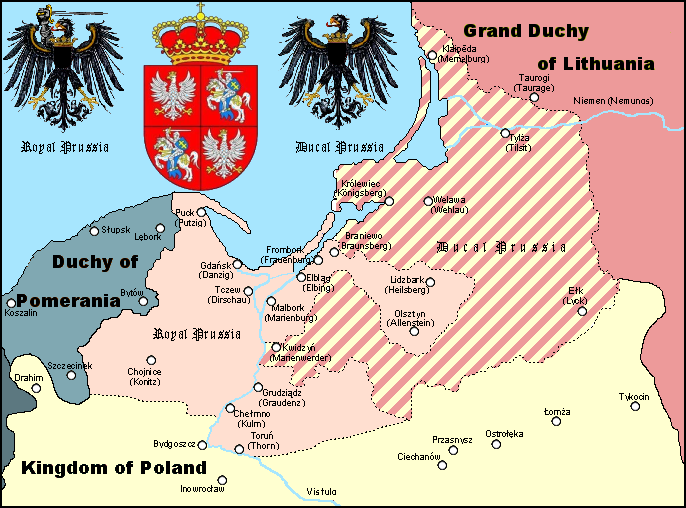

 The Polish Corridor (german: Polnischer Korridor; pl, Pomorze, Polski Korytarz), also known as the Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia (
The Polish Corridor (german: Polnischer Korridor; pl, Pomorze, Polski Korytarz), also known as the Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia (
Google Print, p.15
/ref> As the Polish commission report to the Allied Supreme Council noted on 12 March 1919: "Finally the fact must be recognised that 600,000 Poles in West Prussia would under any alternative plan remain under German rule". Also, as
 The German author Christian Raitz von Frentz writes that after First World War ended, the Polish government tried to reverse the systematic
The German author Christian Raitz von Frentz writes that after First World War ended, the Polish government tried to reverse the systematic
(Appendix B. German Population of Western Poland by Province and Country)
German political scientist
/ref> In the winter of 1938-1939, Germany placed increasing pressure on Poland and Hungary to sign the Anti-Comintern Pact.Weinberg, Gerhard ''Hitler's Foreign Policy, 1933-1939 The Road to World War II'', New York: Engima Books, 2010 p.668 Initially, the main concern of Germany diplomacy was not Danzig or the Polish Corridor, but rather having Poland sign the Anti-Comintern Pact, which as the American historian
/ref> German newspapers in Danzig and Nazi Germany played an important role in inciting nationalist sentiment: headlines buzzed about how Poland was misusing its economic rights in Danzig and German Danzigers were increasingly subjugated to the will of the Polish state. At the same time, Hitler also offered Poland additional territory as an enticement, such as the possible annexation of
Robert Coulondre, the French ambassador in Berlin in a dispatch to the Foreign Minister
 At the 1945
At the 1945


 The Polish Corridor (german: Polnischer Korridor; pl, Pomorze, Polski Korytarz), also known as the Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia (
The Polish Corridor (german: Polnischer Korridor; pl, Pomorze, Polski Korytarz), also known as the Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia (Pomeranian Voivodeship
Pomeranian Voivodeship, Pomorskie Region, or Pomerania Province ( Polish: ''Województwo pomorskie'' ; ( Kashubian: ''Pòmòrsczé wòjewództwò'' ), is a voivodeship, or province, in northwestern Poland. The provincial capital is Gdańsk.
Th ...
, eastern Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
, formerly part of West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kin ...
), which provided the Second Republic of Poland
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First Worl ...
(1920–1939) with access to the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
, thus dividing the bulk of Germany (Weimar Republic) from the province of East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
. At its narrowest point, the Polish territory was just 30 km wide. The Free City of Danzig
The Free City of Danzig (german: Freie Stadt Danzig; pl, Wolne Miasto Gdańsk; csb, Wòlny Gard Gduńsk) was a city-state under the protection of the League of Nations between 1920 and 1939, consisting of the Baltic Sea port of Danzig (now Gda ...
(now the Polish cities of Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
, Sopot
Sopot is a seaside resort city in Pomerelia on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland, with a population of approximately 40,000. It is located in Pomeranian Voivodeship, and has the status of the county, being the smallest ci ...
and the surrounding areas), situated to the east of the corridor, was a semi-independent German speaking city-state forming part of neither Germany nor Poland, though united with the latter through an imposed union covering customs, mail, foreign policy, railways as well as defence.
A similar territory, also occasionally referred to as a corridor, was originally connected to the Polish Crown
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, incl ...
until 1308, and was later reclaimed as part of Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
during the period 1466–1772.
Terminology
According to German historian Hartmut Boockmann the term "Corridor" was first used by Polish politicians, while Polish historian Grzegorz Lukomski writes that the word was coined by German nationalist propaganda of the 1920s. Internationally the term was used in the English language already as early as March 1919 and whatever its origins, it became a widespread term in English language usage. The equivalent German term is ''Polnischer Korridor''. Polish names include ''korytarz polski'' ("Polish corridor") and ''korytarz gdański'' ("Gdańsk corridor"); however, reference to the region as a corridor came to be regarded as offensive by interwar Polish diplomats. Among the harshest critics of the term ''corridor'' was Polish Foreign MinisterJózef Beck
Józef Beck (; 4 October 1894 – 5 June 1944) was a Polish statesman who served the Second Republic of Poland as a diplomat and military officer. A close associate of Józef Piłsudski, Beck is most famous for being Polish foreign minister in ...
, who in his May 5, 1939 speech in Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland ( Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of ...
(Polish parliament) said: "I am insisting that the term ''Pomeranian Voivodeship'' should be used. The word ''corridor'' is an artificial idea, as this land has been Polish for centuries, with a small percentage of German settlers". Poles would commonly refer to the region as ''Pomorze Gdańskie'' ("Gdańsk Pomerania, Pomerelia") or simply ''Pomorze'' ("Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
"), or as ''województwo pomorskie'' ("Pomeranian Voivodeship
Pomeranian Voivodeship, Pomorskie Region, or Pomerania Province ( Polish: ''Województwo pomorskie'' ; ( Kashubian: ''Pòmòrsczé wòjewództwò'' ), is a voivodeship, or province, in northwestern Poland. The provincial capital is Gdańsk.
Th ...
"), which was the administrative name for the region.
Background
History of the area
In the 10th century, Pomerelia was settled by Slavic Pomeranians, ancestors of theKashubians
The Kashubians ( csb, Kaszëbi; pl, Kaszubi; german: Kaschuben), also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ( West Slavic) ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in nor ...
, who were subdued by Bolesław I of Poland. In the 11th century, they created an independent duchy.James Minahan, ''One Europe, Many Nations: A Historical Dictionary of European National Groups'', Greenwood Publishing Group, 2000, p.375, In 1116/1121, Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
was again conquered by Poland. In 1138, following the death of Duke Bolesław III, Poland was fragmented into several semi-independent principalities. The Samborides
The Samborides () or House of Sobiesław () were a ruling dynasty in the historic region of Pomerelia. They were first documented about 1155 as governors (''princeps'') in the Eastern Pomeranian lands serving the royal Piast dynasty of Poland ...
, ''principes'' in Pomerelia, gradually evolved into independent dukes, who ruled the duchy until 1294. Before Pomerelia regained independence in 1227, their dukes were vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerai ...
s of Poland and Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
. Since 1308-1309, following succession wars between Poland and Brandenburg, Pomerelia was subjugated by the Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights
The State of the Teutonic Order (german: Staat des Deutschen Ordens, ; la, Civitas Ordinis Theutonici; lt, Vokiečių ordino valstybė; pl, Państwo zakonu krzyżackiego), also called () or (), was a medieval Crusader state, located in Cen ...
in Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
. In 1466, with the second Peace of Thorn
The Peace of Thorn or Toruń of 1466, also known as the Second Peace of Thorn or Toruń ( pl, drugi pokój toruński; german: Zweiter Friede von Thorn), was a peace treaty signed in the Hanseatic city of Thorn (Toruń) on 19 October 1466 betwe ...
, Pomerelia became part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
as a part of autonomous Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
. After the First Partition of Poland in 1772 it was annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
and named West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kin ...
, and became a constituent part of the new German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
in 1871. Thus the Polish Corridor was not an entirely new creation: the territory assigned to Poland had been an integral part of Poland prior to 1772, but with a large degree of autonomy.
Historical population
Perhaps the earliest census data onethnic
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established fo ...
or national structure of West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kin ...
(including areas which later became the Polish Corridor) is from 1819.
Karl Andree
Karl Andree (20 October 1808 – 10 August 1875) was a German geographer.
Biography
Andree was born in Braunschweig. He was educated at Jena, Göttingen, and Berlin. After having been implicated in a students' political agitation he became a ...
, "Polen: in geographischer, geschichtlicher und culturhistorischer Hinsicht" (Leipzig 1831), gives the total population of West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kin ...
as 700,000 inhabitants - including 50% Poles (350,000), 47% Germans (330,000) and 3% Jews (20,000).
Data from the 19th century and early 20th century show the following ethnic changes in four "core" counties of the Corridor ( Puck, Wejherowo
Wejherowo ( csb, Wejrowò; german: Neustadt in Westpreußen, formerly Weyhersfrey) is a city in Gdańsk Pomerania, northern Poland, with 48,735 inhabitants (2021). It has been the capital of Wejherowo County in Pomeranian Voivodeship since 19 ...
- directly at the Baltic Sea coast - and Kartuzy, Kościerzyna - between Provinz Pommern and Free City Danzig):
Allied plans for a corridor after World War I
During theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, both sides made bids for Polish support, and in turn Polish leaders were active in soliciting support from both sides. Roman Dmowski
Roman Stanisław Dmowski (Polish: , 9 August 1864 – 2 January 1939) was a Polish politician, statesman, and co-founder and chief ideologue of the National Democracy (abbreviated "ND": in Polish, "''Endecja''") political movement. He saw th ...
, a former deputy in the Russian State Duma
The State Duma (russian: Госуда́рственная ду́ма, r=Gosudárstvennaja dúma), commonly abbreviated in Russian as Gosduma ( rus, Госду́ма), is the lower house of the Federal Assembly of Russia, while the upper hous ...
and the leader of the ''Endecja'' movement was especially active in seeking support from the Allies. Dmowski argued that an independent Poland needed access to the sea on demographic, historical and economic grounds as he maintained that a Poland without access to the sea could never be truly independent. After the war Poland was to be re-established as an independent state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
. Since a Polish state had not existed since the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
, the future republic's territory had to be defined.
Giving Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
access to the sea was one of the guarantees proposed by United States President
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United Stat ...
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
in his Fourteen Points
U.S. President Woodrow Wilson
The Fourteen Points was a statement of principles for peace that was to be used for peace negotiations in order to end World War I. The principles were outlined in a January 8, 1918 speech on war aims and peace terms ...
of January 1918. The thirteenth of Wilson's points was:
: "An independent Polish state should be erected which should include the territories inhabited by indisputably Polish populations, which should be assured a free and secure access to the sea, and whose political and economic independence and territorial integrity should be guaranteed by international covenant."
The following arguments were behind the creation of the corridor:
Ethnographic reasons
The ethnic situation was one of the reasons for returning the area to the restored Poland. The majority of the population in the area was Polish.Anna M. Cienciala, Natalia Sergeevna Lebedeva, Wojciech Materski, Maia A. Kipp, ''Katyn: A Crime without Punishment'', Yale University Press, 2008,Google Print, p.15
/ref> As the Polish commission report to the Allied Supreme Council noted on 12 March 1919: "Finally the fact must be recognised that 600,000 Poles in West Prussia would under any alternative plan remain under German rule". Also, as
David Hunter Miller
David Hunter Miller (1875–1961) was a US lawyer and an expert on treaties who participated in the drafting of the covenant of the League of Nations.
He practiced law in New York City from 1911 to 1929; served on the Inquiry, a body of exper ...
from president Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
's group of experts and academics (known as The Inquiry) noted in his diary from the Paris Peace Conference: "If Poland does not thus secure access to the sea, 600,000 Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in ...
in West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kin ...
will remain under German rule and 20,000,000 Poles in Poland proper will probably have but a hampered and precarious commercial outlet". The Prussian census of 1910 showed that there were 528,000 Poles (including West Slavic Kashubians
The Kashubians ( csb, Kaszëbi; pl, Kaszubi; german: Kaschuben), also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ( West Slavic) ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in nor ...
, who had supported the Polish national lists in German elections) in the region, compared with 385,000 Germans (including troops and officials stationed in the area)."Principles and Problems of International Relations" page 608 H. Arthur Steiner – 1940 The province of West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kin ...
as a whole had between 36% and 43% ethnic Poles in 1910, depending on the source (the lower number is based directly on German 1910 census figures, while the higher number is based on calculations according to which a large part of those people counted as Catholic Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, image = Hohe_Domkirche_St._Petrus.jpg
, imagewidth = 200px
, alt =
, caption = Cologne Cathedral, Cologne
, abbreviation =
, type = Nat ...
in the official census in fact identified as Poles). The Poles did not want the Polish population to remain under the control of the German state, which had in the past treated the Polish population and other minorities as second-class citizens and had pursued Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In ling ...
. As Professor Lewis Bernstein Namier
Sir Lewis Bernstein Namier (; 27 June 1888 – 19 August 1960) was a British historian of Polish-Jewish background. His best-known works were '' The Structure of Politics at the Accession of George III'' (1929), ''England in the Age of the Amer ...
(1888–1960) -- born to Jewish parents in Lublin Governorate
Lublin Governorate (russian: Люблинская губерния, pl, Gubernia lubelska) was an administrative unit (governorate) of Congress Poland.
History
The Lublin Governorate was created in 1837 from the Lublin Voivodeship, and had th ...
(Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
, former Congress Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. I ...
) and later a British citizen, a former member of the British Intelligence Bureau throughout World War I and the British delegation at the Versailles conference
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed ...
, known for his anti-Polish
Polonophobia, also referred to as anti-Polonism, ( pl, Antypolonizm), and anti-Polish sentiment are terms for negative attitudes, prejudices, and actions against Poles as an ethnic group, Poland as their country, and their culture. These incl ...
Niepodległość, Tom 21 Pilsudski Institute of America Instytut Józefa Piłsudskiego Poświecony Badaniu Najnowszej Historii Polski., 1988 page 58 and anti-German attitude -- wrote in the ''Manchester Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and '' The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the G ...
'' on November 7, 1933: "The Poles are the Nation of the Vistula, and their settlements extend from the sources of the river to its estuary. … It is only fair that the claim of the river-basin should prevail against that of the seaboard."
Economic reasons
The Poles held the view that without direct access to theBaltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
, Poland's economic independence would be illusory.''Out of the Ashes'' James Thorburn Muirhead 1941, page 54 Around 60.5% of Polish import trade and 55.1% of exports went through the area. The report of the Polish Commission presented to the Allied Supreme Council said:
:"1,600,000 Germans in East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
can be adequately protected by securing for them freedom of trade across the corridor, whereas it would be impossible to give an adequate outlet to the inhabitants of the new Polish state (numbering 25,000,000) if this outlet had to be guaranteed across the territory of an alien and probably hostile Power."
The United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
eventually accepted this argument. The suppression of the Polish Corridor would have abolished the economic ability of Poland to resist dependence on Germany. As Lewis Bernstein Namier
Sir Lewis Bernstein Namier (; 27 June 1888 – 19 August 1960) was a British historian of Polish-Jewish background. His best-known works were '' The Structure of Politics at the Accession of George III'' (1929), ''England in the Age of the Amer ...
, Professor of Modern History at the University of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public university, public research university in Manchester, England. The main campus is south of Manchester city centre, Manchester City Centre on Wilmslow Road, Oxford Road. The university owns and operates majo ...
and known for both his "legendary hatred of Germany" and Germanophobia as well as his anti-Polish attitude directed against what he defined as the "aggressive, antisemitic and warmongerily imperialist" part of Poland, wrote in a newspaper article in 1933:
:"The whole of Poland's transport system ran towards the mouth of the Vistula....
:"90% of Polish exports came from her western provinces.
:"Cutting through of the Corridor has meant a minor amputation for Germany; its closing up would mean strangulation for Poland.".
By 1938, 77.7% of Polish exports left either through Gdańsk (31.6%) or the newly built port of Gdynia
Gdynia ( ; ; german: Gdingen (currently), (1939–1945); csb, Gdiniô, , , ) is a city in northern Poland and a seaport on the Baltic Sea coast. With a population of 243,918, it is the 12th-largest city in Poland and the second-largest in th ...
(46.1%)
The Inquiry's opinion
David Hunter Miller
David Hunter Miller (1875–1961) was a US lawyer and an expert on treaties who participated in the drafting of the covenant of the League of Nations.
He practiced law in New York City from 1911 to 1929; served on the Inquiry, a body of exper ...
in his diary from the Paris Peace Conference noted, that the problem of Polish access to the sea was very difficult because leaving entire Pomerelia under German control meant cutting off millions of Poles from their commercial outlet and leaving several hundred thousand Poles under German rule, while granting such access meant cutting off East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
from the rest of Germany. The Inquiry recommended, that both the Corridor and Danzig should have been ceded directly to Poland.
Quote: ''"It is believed that the lesser of these evils is preferable, and that the Corridor and Danzig should othbe ceded to Poland, as shown on map 6. East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
, though territorially cut off from the rest of Germany, could easily be assured railroad transit across the Polish corridor (a simple matter as compared with assuring port facilities to Poland), and has, in addition, excellent communication via Königsberg
Königsberg (, ) was the historic Prussian city that is now Kaliningrad, Russia. Königsberg was founded in 1255 on the site of the ancient Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teutonic Knights during the Northern Crusades, and was ...
and the Baltic Sea. In either case a people is asked to entrust large interests to the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
. In the case of Poland they are vital interests; in the case of Germany, aside from Prussian sentiment, they are quite secondary".''
In the end, The Inquiry's recommendations were implemented only partially: most of West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kin ...
was given to Poland, but Danzig became a Free City Free city may refer to: Historical places
* Free city (antiquity) a self-governed city during the Hellenistic and Roman Imperial eras
* Free imperial city, self-governed city in the Holy Roman Empire subordinate only to the emperor
** Free City of ...
.
Incorporation into the Second Polish Republic
DuringWorld War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
had forced the Imperial Russian
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. Th ...
troops out of Congress Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. I ...
and Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
, as manifested in the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
on 3 March 1918. Following the military defeat of Austria-Hungary, an independent Polish republic was declared in Western Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
on 3 November 1918, the same day Austria signed the armistice. The collapse of Imperial Germany
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
's Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
* Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a maj ...
, and the subsequent withdrawal of her remaining occupation forces after the Armistice of Compiègne on 11 November allowed the republic led by Roman Dmowski
Roman Stanisław Dmowski (Polish: , 9 August 1864 – 2 January 1939) was a Polish politician, statesman, and co-founder and chief ideologue of the National Democracy (abbreviated "ND": in Polish, "''Endecja''") political movement. He saw th ...
and Józef Piłsudski
Józef Klemens Piłsudski (; 5 December 1867 – 12 May 1935) was a Polish statesman who served as the Naczelnik państwa, Chief of State (1918–1922) and Marshal of Poland, First Marshal of Second Polish Republic, Poland (from 1920). He was ...
to seize control over the former Congress Polish areas. Also in November, the revolution in Germany forced the Kaiser
''Kaiser'' is the German word for "emperor" (female Kaiserin). In general, the German title in principle applies to rulers anywhere in the world above the rank of king (''König''). In English, the (untranslated) word ''Kaiser'' is mainly ap ...
's abdication and gave way to the establishment of the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a Constitutional republic, constitutional federal republic for the first time in ...
. Starting in December, the Polish-Ukrainian War expanded the Polish republic's territory to include Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
and parts of Eastern Galicia, while at the same time the German Province of Posen
The Province of Posen (german: Provinz Posen, pl, Prowincja Poznańska) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1848 to 1920. Posen was established in 1848 following the Greater Poland Uprising as a successor to the Grand Duchy of Posen, ...
(where even according to the German made 1910 census 61,5% of the population was Polish) was severed by the Greater Poland uprising, which succeeded in attaching most of the province's territory to Poland by January 1919. This led Weimar's Otto Landsberg
Otto Landsberg (4 December 1869 – 9 December 1957) was a German jurist, politician and diplomat. He was a member of the revolutionary Council of the People's Deputies that took power during the German Revolution of 1918–19 and then served as ...
and Rudolf Breitscheid
Rudolf Breitscheid (2 November 1874 – 28 August 1944) was a German politician and leading member of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) during the Weimar Republic. Once leader of the liberal Democratic Union, he joined the SPD in ...
to call for an armed force to secure Germany's remaining eastern territories (some of which contained significant Polish minorities, primarily on the former Prussian partition territories). The call was answered by the minister of defense Gustav Noske, who decreed support for raising and deploying volunteer " Grenzschutz" forces to secure East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
, Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
and the Netze District
The Netze District or District of the Netze (german: link=no, Netzedistrikt or '; pl, Obwód Nadnotecki) was a territory in the Kingdom of Prussia from 1772 until 1807. It included the urban centers of Bydgoszcz (''Bromberg''), Inowrocław (''In ...
.
On 18 January, the Paris peace conference opened, resulting in the draft of the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1 ...
28 June 1919. Articles 27 and 28 of the treaty ruled on the territorial shape of the corridor, while articles 89 to 93 ruled on transit, citizenship and property issues. Per the terms of the Versailles treaty, which was put into effect on 20 January 1920, the corridor was established as Poland's access to the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
from 70% of the dissolved province of West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kin ...
, consisting of a small part of Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
with around 140 km of coastline including the Hel Peninsula
Hel Peninsula (; pl, Mierzeja Helska, Półwysep Helski; csb, Hélskô Sztremlëzna; german: Halbinsel Hela or ''Putziger Nehrung'') is a sand bar peninsula in northern Poland separating the Bay of Puck from the open Baltic Sea. It is l ...
, and 69 km without it.
The primarily German-speaking seaport of Danzig (Gdańsk), controlling the estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
of the main Polish waterway, the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
river, became the Free City of Danzig
The Free City of Danzig (german: Freie Stadt Danzig; pl, Wolne Miasto Gdańsk; csb, Wòlny Gard Gduńsk) was a city-state under the protection of the League of Nations between 1920 and 1939, consisting of the Baltic Sea port of Danzig (now Gda ...
and was placed under the protection of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
without a plebiscite. After the dock workers of Danzig harbour went on strike during the Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (Polish–Bolshevik War, Polish–Soviet War, Polish–Russian War 1919–1921)
* russian: Советско-польская война (''Sovetsko-polskaya voyna'', Soviet-Polish War), Польский фронт (' ...
, refusing to unload ammunition, the Polish Government decided to build an ammunition depot at Westerplatte, and a seaport at Gdynia
Gdynia ( ; ; german: Gdingen (currently), (1939–1945); csb, Gdiniô, , , ) is a city in northern Poland and a seaport on the Baltic Sea coast. With a population of 243,918, it is the 12th-largest city in Poland and the second-largest in th ...
in the territory of the Corridor, connected to the Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, locate ...
n industrial centers by the newly constructed Polish Coal Trunk Line railways.
Exodus of the German population
 The German author Christian Raitz von Frentz writes that after First World War ended, the Polish government tried to reverse the systematic
The German author Christian Raitz von Frentz writes that after First World War ended, the Polish government tried to reverse the systematic Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In ling ...
from former decades. Frederick the Great
Frederick II (german: Friedrich II.; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was King in Prussia from 1740 until 1772, and King of Prussia from 1772 until his death in 1786. His most significant accomplishments include his military successes in the Sil ...
( King in/of Prussia from 1740 to 1786) settled around 300,000 colonists in the eastern provinces of Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
and aimed at a removal of the Polish nobility
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in ...
, which he treated with contempt. Frederick also described Poles as "slovenly Polish trash" and compared them to the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
. On the other hand, he encouraged administrators and teachers who could speak both German and Polish.
Compare:
Prussia pursued a second colonization
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
aimed at Germanisation after 1832. The Prussians passed laws aiming at Germanisation of the provinces of Posen and West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a Provinces of Prussia, province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kin ...
in the late 19th century. The Prussian Settlement Commission established a further 154,000 colonists, including locals, in the provinces of Posen and West Prussia before World War I. Military personnel were included in the population census. A number of German civil servants and merchants were introduced to the area, which influenced the population status.
According to Richard Blanke, 421,029 Germans lived in the area in 1910, making up 42.5% of the population. Blanke has been criticised by Christian Raitz von Frentz, who has classified his book as part of a series on the subject that has an anti-Polish bias; additionally Polish professor A. Cienciala has described Blanke's views as sympathetic to Germany. In addition to the military personnel included in the population census, a number of German civil-servants and merchants were introduced to the area, which influenced the population mix, according to Andrzej Chwalba.Historia Polski 1795-1918. Andrzej Chwalba. Page 444. By 1921 the proportion of Germans had dropped to 18.8% (175,771). Over the next decade, the German population decreased by another 70,000 to a share of 9.6%.
Page 24(Appendix B. German Population of Western Poland by Province and Country)
German political scientist
Stefan Wolff
Stefan Wolff is a German political scientist. He is a specialist in international security, particularly in the management, settlement and prevention of ethnic conflicts. He is currently Professor of International Security at the University of ...
, Professor at the University of Birmingham
, mottoeng = Through efforts to heights
, established = 1825 – Birmingham School of Medicine and Surgery1836 – Birmingham Royal School of Medicine and Surgery1843 – Queen's College1875 – Mason Science College1898 – Mason Univers ...
, says that the actions of Polish state officials after the corridor's establishment followed "a course of assimilation and oppression".Stefan Wolff, ''The German Question Since 1919: An Analysis with Key Documents'', Greenwood Publishing Group, 2003, p.33, As a result, a large number of Germans left Poland after 1918: according to Wolff, 800,000 Germans had left Poland by 1923, according to Gotthold Rhode, 575,000 left the former province of Posen and the corridor after the war, according to Herrmann Rauschning, 800,000 Germans had left between 1918 and 1926, contemporary author Alfons Krysinski estimated 800,000 plus 100,000 from East Upper Silesia, the contemporary German statistics say 592,000 Germans had left by 1921, other Polish scholars say that up to a million Germans left. Polish author Władysław Kulski says that a number of them were civil servants with no roots in the province and around 378,000, and this is to a lesser degree is confirmed by some German sources such as Hermann Rauschning.
Lewis Bernstein Namier raised the question as to whether many of the Germans who left were actually settlers without roots in the area - Namier remarked in 1933 "a question must be raised how many of those Germans had originally been planted artificially in that country by the Prussian Government."
The above-mentioned Richard Blanke, in his book ''Orphans of Versailles'', gives several reasons for the exodus of the German population:
* A number of former settlers from the Prussian Settlement Commission who settled in the area after 1886 in order to germanise it were in some cases given a month to leave, in other cases they were told to leave at once.
* Poland found itself under threat during the Polish-Bolshevik war of 1919-1921, and the German population feared that Bolshevik forces would control Poland. Migration to Germany was a way to avoid conscription and participation in the war.
* State-employed Germans such as judges, prosecutors, teachers and officials left as Poland did not renew their employment contracts. German industrial workers also left due to fear of lower-wage competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, ind ...
. Many Germans had become economically dependent on Prussian state aid as Prussia had fought the "Polish problem" in its provinces.
* Germans refused to accept living in a Polish state. As Lewis Bernstein Namier
Sir Lewis Bernstein Namier (; 27 June 1888 – 19 August 1960) was a British historian of Polish-Jewish background. His best-known works were '' The Structure of Politics at the Accession of George III'' (1929), ''England in the Age of the Amer ...
said: "Some Germans undoubtedly left because they would not live under the dominion of a race which they had previously oppressed and despised."
* Germans feared that the Poles would seek reprisals after over a century of harassment and discrimination
Discrimination is the act of making unjustified distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong. People may be discriminated on the basis of Racial discrimination, r ...
by the Prussian and German state against the Polish population.
* Social and linguistic isolation: While the population was mixed, only Poles were required to be bilingual. The Germans usually did not learn Polish. When Polish became the only official language in Polish-majority provinces, their situation became difficult. The Poles shunned Germans, which contributed to their isolation.
* Lower standards of living. Poland was a much poorer country than Germany.
* Former Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
politician and later opponent Hermann Rauschning wrote that 10% of Germans were unwilling to remain in Poland regardless of their treatment, and another 10% were workers from other parts of the German Empire with no roots in the region.
Blanke says that official encouragement by the Polish state played a secondary role in the German exodus.
''Orphans of Versailles: The Germans in Western Poland, 1918-1939'' pages 32-48 Richard Blanke
University Press of Kentucky, 1993 Christian Raitz von Frentz notes "that many of the repressive measures were taken by local and regional Polish authorities in defiance of Acts of Parliament and government decrees, which more often than not conformed with the minorities treaty, the Geneva Convention
upright=1.15, Original document in single pages, 1864
The Geneva Conventions are four treaties, and three additional protocols, that establish international legal standards for humanitarian treatment in war. The singular term ''Geneva Conve ...
and their interpretation by the League council - though it is also true that some of the central authorities tacitly tolerated local initiatives against the German population."''A Lesson Forgotten: Minority Protection Under the League of Nations: The Case of the German Minority in Poland, 1920-193'' page 8 LIT Verlag Berlin-Hamburg-Münster, 1999 While there were demonstrations and protests and occasional violence against Germans, they were at a local level, and officials were quick to point out that they were a backlash against former discrimination against Poles. There were other demonstrations when Germans showed disloyalty during the Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (Polish–Bolshevik War, Polish–Soviet War, Polish–Russian War 1919–1921)
* russian: Советско-польская война (''Sovetsko-polskaya voyna'', Soviet-Polish War), Польский фронт (' ...
as the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
announced the return to the pre-war borders of 1914. Despite popular pressure and occasional local actions, perhaps as many as 80% of Germans emigrated more or less voluntarily.
Helmut Lippelt writes that Germany used the existence of German minority in Poland
The registered German minority in Poland at the 2011 national census consisted of 148,000 people, of whom 64,000 declared both German and Polish ethnicities and 45,000 solely German ethnicity.Przynależność narodowo-etniczna ludności – wyni ...
for political ends and as part of its revisionist demands, which resulted in Polish countermeasures. Polish Prime Minister Władysław Sikorski
Władysław Eugeniusz Sikorski (; 20 May 18814 July 1943) was a Polish military and political leader.
Prior to the First World War, Sikorski established and participated in several underground organizations that promoted the cause for Polish i ...
stated in 1923 that the de-Germanization of these territories had to be ended by vigorous and quick liquidation of property and eviction of German "Optanten" (Germans who refused to accept Polish citizenship
Polish nationality law is based primarily on the principle of jus sanguinis. Children born to at least one Polish parent acquire Polish citizenship irrespective of place of birth. Besides other things, Polish citizenship entitles the person to ...
and per the Versailles Treaty
The Treaty of Versailles (french: Traité de Versailles; german: Versailler Vertrag, ) was the most important of the peace treaties of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 19 ...
were to leave Poland) so that German nationalists would realise that their view of the temporary state of Polish western border was wrong.
To Lippelt this was partially a reaction to the German claims and partially Polish nationalism
Polish nationalism is a form of nationalism which asserts that the Poles are a nation and promotes the cultural unity of Poles. Norman Davies, in the context of Polish nationalism, generally defined nationalism as "a doctrine ... to create a na ...
, urging to exclude the German element. In turn, anti-Polish prejudice fueled German policy.
Impact on the East Prussian plebiscite
In the period leading up to theEast Prussian plebiscite
The East Prussian plebiscite (german: Abstimmung in Ostpreußen), also known as the Allenstein and Marienwerder plebiscite or Warmia, Masuria and Powiśle plebiscite ( pl, Plebiscyt na Warmii, Mazurach i Powiślu), was a plebiscite organised in a ...
in July 1920, the Polish authorities tried to prevent traffic through the Corridor, interrupting postal, telegraphic and telephone communication. On March 10, 1920, the British representative on the Marienwerder Plebiscite Commission, H.D. Beaumont, wrote of numerous continuing difficulties being made by Polish officials and added "as a result, the ill-will between Polish and German nationalities and the irritation due to Polish intolerance towards the German inhabitants in the Corridor (now under their rule), far worse than any former German intolerance of the Poles, are growing to such an extent that it is impossible to believe the present settlement (borders) can have any chance of being permanent.... It can confidently be asserted that not even the most attractive economic advantages would induce any German to vote Polish. If the frontier is unsatisfactory now, it will be far more so when it has to be drawn on this side (of the river) with no natural line to follow, cutting off Germany from the river bank and within a mile or so of Marienwerder
Kwidzyn (pronounced ; german: Marienwerder; Latin: ''Quedin''; Old Prussian: ''Kwēdina'') is a town in northern Poland on the Liwa River, with 38,553 inhabitants (2018). It is the capital of Kwidzyn County in the Pomeranian Voivodeship.
Geog ...
, which is certain to vote German. I know of no similar frontier created by any treaty."Butler, Rohan, MA., Bury, J.P.T., MA., & Lambert M.E., MA., editors, Documents on British Foreign Policy 1919-1939, 1st Series, Her Majesty's Stationery Office, London, 1960, vol.x, Chapter VIII, "The Plebiscites in Allenstein and Marienwerder January 21 - September 29, 1920", p.726-7
Impact on German through-traffic
The German Ministry for Transport established the ''Seedienst Ostpreußen
The Seedienst Ostpreussen or Sea Service East Prussia was a ferry connection between the German provinces of Pomerania and, later, Schleswig-Holstein and the German exclave of East Prussia from 1920 to 1939.
Political background
After the end ...
'' ("Sea Service East Prussia") in 1922 to provide a ferry connection to East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
, now a German exclave, so that it would be less dependent on transit through Polish territory.
Connections by train were also possible by "sealing" the carriages ('' Korridorzug''), i.e. passengers were not forced to apply for an official Polish visa in their passport; however, the rigorous inspections by the Polish authorities before and after the sealing were strongly feared by the passengers.
In May 1925 a train, passing through the Corridor on its way to East Prussia, crashed because the spikes had been removed from the tracks for a short distance and the fishplate
A fishplate joins two lengths of track
A fishplate, splice bar or joint bar is a metal connecting plate used to bolt the ends of two rails into a continuous track. The name is derived from ''fish'', a wooden reinforcement of a "built-up" ship's ...
s unbolted. 25 persons, including 12 women and 2 children, were killed, some 30 others were injured.
Land reform of 1925
According to Polish Historian Andrzej Chwalba, during the rule of theKingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
and the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
various means were used to increase the amount of land owned by Germans at the expense of the Polish population. In Prussia, the Polish nobility
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in ...
had its estates confiscated after the Partitions
Partition may refer to:
Computing Hardware
* Disk partitioning, the division of a hard disk drive
* Memory partition, a subdivision of a computer's memory, usually for use by a single job
Software
* Partition (database), the division of ...
, and handed over to German nobility
The German nobility (german: deutscher Adel) and royalty were status groups of the medieval society in Central Europe, which enjoyed certain privileges relative to other people under the laws and customs in the German-speaking area, until the b ...
.Historia Polski 1795-1918. Andrzej Chwalba. Page 177 The same applied to Catholic monasteries. Later, the German Empire bought up land in an attempt to prevent the restoration of a Polish majority in Polish inhabited areas in its eastern provinces. Andrzej Chwalba - Historia Polski 1795-1918 page 461-463
Christian Raitz von Frentz notes that measures aimed at reversing past Germanization included the liquidation of farms settled by the German government during the war under the 1908 law.
In 1925 the Polish government enacted a land reform program with the aim of expropriating landowners. While only 39% of the agricultural land in the Corridor was owned by Germans, the first annual list of properties to be reformed included 10,800 hectares from 32 German landowners and 950 hectares from seven Poles. The voivode
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the me ...
of Pomorze, Wiktor Lamot, stressed that "the part of Pomorze through which the so-called corridor runs must be cleansed of larger German holdings". The coastal region "must be settled with a nationally conscious Polish population.... Estates belonging to Germans must be taxed more heavily to encourage them voluntarily to turn over land for settlement. Border counties... particularly a strip of land ten kilometers wide, must be settled with Poles. German estates that lie here must be reduced without concern for their economic value or the views of their owners'.
Prominent politicians and members of the German minority were the first to be included on the land reform list and to have their property expropriated.
Weimar German interests
The creation of the corridor aroused great resentment in Germany, and all interwar governments of theWeimar Republic
The Weimar Republic (german: link=no, Weimarer Republik ), officially named the German Reich, was the government of Germany from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a Constitutional republic, constitutional federal republic for the first time in ...
refused to recognize the eastern borders agreed at Versailles, and refused to follow Germany's acknowledgment of its western borders in the Locarno Treaties
The Locarno Treaties were seven agreements negotiated at Locarno, Switzerland, during 5 to 16 October 1925 and formally signed in London on 1 December, in which the First World War Western European Allied powers and the new states of Central a ...
of 1925 with a similar declaration with respect to its eastern borders.
Institutions in Weimar Germany supported and encouraged German minority organizations in Poland, in part radicalized by the Polish policy towards them, in filing close to 10,000 complaints about violations of minority rights to the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
.
Poland in 1931 declared her commitment to peace, but pointed out that any attempt to revise its borders would mean war. Additionally, in conversation with U.S. President Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was an American politician who served as the 31st president of the United States from 1929 to 1933 and a member of the Republican Party, holding office during the onset of the Gre ...
, Polish delegate Filipowicz noted that any continued provocations by Germany could tempt the Polish side to invade, in order to settle the issue once and for all.
Nazi German and Polish diplomacy
TheNazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
, led by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
, took power in Germany in 1933. Hitler at first ostentatiously pursued a policy of rapprochement
In international relations, a rapprochement, which comes from the French word ''rapprocher'' ("to bring together"), is a re-establishment of cordial relations between two countries. This may be done due to a mutual enemy, as was the case with Germ ...
with Poland, culminating in the ten-year Polish-German Non-Aggression Pact of 1934. In the years that followed, Germany placed an emphasis on rearmament, as did Poland and other European powers. Despite this, the Nazis were able to achieve their immediate goals without provoking armed conflict: firstly, in March 1938 Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
annexed Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, and at the beginning of October the Sudetenland
The Sudetenland ( , ; Czech and sk, Sudety) is the historical German name for the northern, southern, and western areas of former Czechoslovakia which were inhabited primarily by Sudeten Germans. These German speakers had predominated in the ...
after the Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement ( cs, Mnichovská dohoda; sk, Mníchovská dohoda; german: Münchner Abkommen) was an agreement concluded at Munich on 30 September 1938, by Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy. It provided "cession to Germany ...
; together with Germany Poland also made an advance against Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918–19391945–1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
and annexed Zaolzie (1 October 1938). Germany tried to get Poland to join the Anti-Comintern Pact
The Anti-Comintern Pact, officially the Agreement against the Communist International was an anti-Communist pact concluded between Nazi Germany and the Empire of Japan on 25 November 1936 and was directed against the Communist International (C ...
. Poland refused, as the alliance was rapidly becoming a sphere of influence of an increasingly powerful Germany.
On 24 October 1938, the German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ribbentrop
Ulrich Friedrich Wilhelm Joachim von Ribbentrop (; 30 April 1893 – 16 October 1946) was a German politician and diplomat who served as Minister of Foreign Affairs of Nazi Germany from 1938 to 1945.
Ribbentrop first came to Adolf Hitler's not ...
asked the Polish ambassador Józef Lipski to have Poland sign the Anti-Comintern Pact.Weinberg, Gerhard ''Hitler's Foreign Policy, 1933-1939 The Road to World War II'', New York: Enigma Books, 2010 p.669 During a visit to Rome on 27–28 October 1938, Ribbentrop told the Italian Foreign Minister Count Galeazzo Ciano that he wanted to turn the Anti-Comintern Pact into a military alliance, and spoke of his desire to have Poland, Yugoslavia, Hungary and Romania sign the Anti-Comintern Pact so "all our energies can be directed against the Western democracies". In a secret speech before a group of 200 German journalists on 10 November 1938, Hitler complained that his peace propaganda stressing that his foreign policy was based upon the peaceful revision of the Treaty of Versailles had been too successful with the German people, and he called for a new propaganda campaign intended to stoke a bellicose mood in the ''Reich''. Notably, the enemies Hitler had in mind in his speech was not Poland, but rather France and Britain.
Following negotiations with Hitler on the Munich Agreement, British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain
Arthur Neville Chamberlain (; 18 March 18699 November 1940) was a British politician of the Conservative Party who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from May 1937 to May 1940. He is best known for his foreign policy of appeaseme ...
reported that, "He told me privately, and last night he repeated publicly, that after this Sudeten German
German Bohemians (german: Deutschböhmen und Deutschmährer, i.e. German Bohemians and German Moravians), later known as Sudeten Germans, were ethnic Germans living in the Czech lands of the Bohemian Crown, which later became an integral part o ...
question is settled, that is the end of Germany's territorial claims in Europe". Almost immediately following the agreement, however, Hitler reneged on it. The Nazis increased their requests for the incorporation of the Free City of Danzig into the Reich, citing the "protection" of the German majority as a motive.
In November 1938, Danzig's district administrator, Albert Forster
Albert Maria Forster (26 July 1902 – 28 February 1952) was a Nazi German politician, member of the SS and war criminal. Under his administration as the ''Gauleiter'' and ''Reichsstatthalter'' of Danzig-West Prussia (the other German-anne ...
, reported to the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
that Hitler had told him Polish frontiers would be guaranteed if the Poles were "reasonable like the Czechs." German State Secretary Ernst von Weizsäcker
Ernst Heinrich Freiherr von Weizsäcker (25 May 1882 – 4 August 1951) was a German naval officer, diplomat and politician. He served as State Secretary at the Foreign Office of Nazi Germany from 1938 to 1943, and as its Ambassador to ...
reaffirmed this alleged guarantee in December 1938.Anna M/ref> In the winter of 1938-1939, Germany placed increasing pressure on Poland and Hungary to sign the Anti-Comintern Pact.Weinberg, Gerhard ''Hitler's Foreign Policy, 1933-1939 The Road to World War II'', New York: Engima Books, 2010 p.668 Initially, the main concern of Germany diplomacy was not Danzig or the Polish Corridor, but rather having Poland sign the Anti-Comintern Pact, which as the American historian
Gerhard Weinberg
Gerhard Ludwig Weinberg (born 1 January 1928) is a German-born American diplomatic and military historian noted for his studies in the history of Nazi Germany and World War II. Weinberg is the William Rand Kenan, Jr. Professor Emeritus of History ...
noted was "...a formal gesture of political and diplomatic obeisance to Berlin, separating them from any other past or prospective international ties, and having nothing to do with the Soviet Union at all". In late 1938-early 1939, Hitler had decided upon war with Britain and France, and having Poland sign the Anti-Comintern Pact was intended to protect the ''Reichs eastern border while the Wehrmacht turned west. In November 1938, Hitler ordered his Foreign Minister Ribbentrop to convert the Anti-Comintern Pact, which had been signed with the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent form ...
in 1936 and joined by Fascist Italy in 1937 into an anti-British military alliance. Starting in October 1938, the main focus on German military planning was for a war against Britain with Hitler ordering the Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabt ...
to start building a strategical bombing force capable of bombing British cities.Weinberg, Gerhard ''Hitler's Foreign Policy, 1933-1939 The Road to World War II'', New York: Engima Books, 2010 p.676 On 17 January 1939, Hitler approved of the famous Z Plan that called for a gigantic fleet to take on the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
and on 27 January 1939 he ordered that henceforward the ''Kriegsmarine
The (, ) was the navy of Germany from 1935 to 1945. It superseded the Imperial German Navy of the German Empire (1871–1918) and the inter-war (1919–1935) of the Weimar Republic. The was one of three official branches, along with the a ...
'' was to have first priority for defense spending.
The situation regarding the Free City and the Polish Corridor created a number of headaches for German and Polish Customs. The Germans requested the construction of an extra-territorial '' Reichsautobahn'' freeway (to complete the ''Reichsautobahn Berlin-Königsberg'') and railway through the Polish Corridor, effectively annexing Polish territory and connecting East Prussia to Danzig and Germany proper, while cutting off Poland from the sea and its main trade route. If Poland agreed, in return they would extend the non-aggression pact for 25 years.
This seemed to conflict with Hitler's plans to turn Poland into a satellite state and with Poland's rejection of the Anti-Comintern Pact, and his desire either to isolate or to gain support against the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
.Joachim C. Fest
Joachim Clemens Fest (8 December 1926 – 11 September 2006) was a German historian, journalist, critic and editor who was best known for his writings and public commentary on Nazi Germany, including a biography of Adolf Hitler and books about ...
, ''Hitler'', Harcourt Trade, 2002, pp.575-577,/ref> German newspapers in Danzig and Nazi Germany played an important role in inciting nationalist sentiment: headlines buzzed about how Poland was misusing its economic rights in Danzig and German Danzigers were increasingly subjugated to the will of the Polish state. At the same time, Hitler also offered Poland additional territory as an enticement, such as the possible annexation of
Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, the Memel Territory
Memel, a name derived from the Couronian-Latvian ''memelis, mimelis, mēms'' for "mute, silent", may refer to:
*Memel, East Prussia, Germany, now Klaipėda, Lithuania
**Memelburg, ( Klaipėda Castle), the ''Ordensburg'' in Memel, a castle built in ...
, Soviet Ukraine
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
and parts of the Czech lands
The Czech lands or the Bohemian lands ( cs, České země ) are the three historical regions of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia. Together the three have formed the Czech part of Czechoslovakia since 1918, the Czech Socialist Republic sin ...
.
However, Polish leaders continued to fear for the loss of their independence and a fate like that of Czechoslovakia, which had yielded the Sudetenland
The Sudetenland ( , ; Czech and sk, Sudety) is the historical German name for the northern, southern, and western areas of former Czechoslovakia which were inhabited primarily by Sudeten Germans. These German speakers had predominated in the ...
to Germany in October 1938, only to be invaded by Germany in March 1939. Some felt that the Danzig question was inextricably tied to the problems in the Polish Corridor and any settlement regarding Danzig would be one step towards the eventual loss of Poland's access to the sea. Hitler's credibility outside Germany was very low after the occupation of Czechoslovakia, though some British and French politicians approved of a peaceful revision of the corridor's borders.
In 1939, Nazi Germany made another attempt to renegotiate the status of Danzig; Poland was to retain a permanent right to use the seaport if the route through the Polish Corridor was to be constructed. However, the Polish administration distrusted Hitler and saw the plan as a threat to Polish sovereignty, practically subordinating Poland to the Axis and the Anti-Comintern Bloc while reducing the country to a state of near-servitude as its entire trade would be dependent on Germany.
Avalon Project : The French Yellow Book : No. 113 - M. Coulondre, French Ambassador in Berlin, to M. Georges Bonnet, Minister for Foreign Affairs. Berlin, April 30, 1939Robert Coulondre, the French ambassador in Berlin in a dispatch to the Foreign Minister
Georges Bonnet
Georges-Étienne Bonnet (22/23 July 1889 – 18 June 1973) was a French politician who served as foreign minister in 1938 and 1939 and was a leading figure in the Radical Party.
Early life
Bonnet was born in Bassillac, Dordogne, the son of ...
wrote on 30 April 1939 that Hitler sought: "...a mortgage on Polish foreign policy, while itself retaining complete liberty of action allowing the conclusion of political agreements with other countries. In these circumstances, the new settlement proposed by Germany, which would link the questions of Danzig and of the passage across the Corridor with counterbalancing questions of a political nature, would only serve to aggravate this mortgage and practically subordinate Poland to the Axis and the Anti-Comintern Bloc. Warsaw refused this in order to retain its independence."
Hitler used the issue of the status city as pretext for attacking Poland, while explaining during a high-level meeting of German military officials in May 1939 that his real goal is obtaining ''Lebensraum
(, ''living space'') is a German concept of settler colonialism, the philosophy and policies of which were common to German politics from the 1890s to the 1940s. First popularized around 1901, '' lso in:' became a geopolitical goal of Imper ...
'' for Germany, isolating Poles from their Allies in the West and afterwards attacking Poland, thus avoiding the repeat of the Czech situation, where the Western powers became involved.
Ultimatum of 1939
A revised and less favorable proposal came in the form of an ultimatum delivered by the Nazis in late August, after the orders had already been given to attack Poland on September 1, 1939. Nevertheless, at midnight on August 29, von Ribbentrop handed British Ambassador SirNeville Henderson
Sir Nevile Meyrick Henderson (10 June 1882 – 30 December 1942) was a British diplomat who served as the ambassador of the United Kingdom to Germany from 1937 to 1939.
Early life and education
Henderson was born at Sedgwick Park, near Hor ...
a list of terms that would allegedly ensure peace in regard to Poland. Danzig was to return to Germany and there was to be a plebiscite in the Polish Corridor; Poles who had been born or had settled there since 1919 would have no vote, while all Germans born but not living there would. An exchange of minority populations between the two countries was proposed. If Poland accepted these terms, Germany would agree to the British offer of an international guarantee, which would include the Soviet Union. A Polish plenipotentiary
A ''plenipotentiary'' (from the Latin ''plenus'' "full" and ''potens'' "powerful") is a diplomat who has full powers—authorization to sign a treaty or convention on behalf of his or her sovereign. When used as a noun more generally, the wor ...
, with full powers, was to arrive in Berlin and accept these terms by noon the next day. The British Cabinet viewed the terms as "reasonable," except the demand for a Polish Plenipotentiary, which was seen as similar to Czechoslovak President Emil Hácha
Emil Dominik Josef Hácha (12 July 1872 – 27 June 1945) was a Czech lawyer, the president of Czechoslovakia from November 1938 to March 1939. In March 1939, after the breakup of Czechoslovakia, Hácha was the nominal president of the newly pro ...
accepting Hitler's terms in mid-March 1939.
When Ambassador Józef Lipski went to see Ribbentrop on August 30, he was presented with Hitler’s demands. However, he did not have the full power to sign and Ribbentrop ended the meeting. News was then broadcast that Poland had rejected Germany's offer.
Nazi German invasion – end of the corridor
On September 1, 1939, Germany invaded Poland. The German Fourth Army defeated the PolishPomorze Army The Pomeranian Army ( pl, Armia Pomorze) was one of the Polish armies defending against the 1939 Invasion of Poland. It was officially created on March 23, 1939. Led by General dywizji Władysław Bortnowski, it consisted of 5 infantry divisions, ...
, which had been tasked with the defense of this region, and captured the corridor during the Battle of Tuchola Forest
The Battle of Tuchola Forest (german: Schlacht in der Tucheler Heide, pl, Bitwa w Borach Tucholskich) was one of the first battles of World War II, during the invasion of Poland. The battle occurred from 1 September to 5 September 1939 and resul ...
by September 5. The corridor was subsequently directly annexed by Germany until it was recaptured by the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
at the end of the war. Other notable battles took place at Westerplatte, the Polish post office in Danzig, Oksywie
Oksywie (german: Oxhöft, csb, Òksëwiô) is a neighbourhood of the city of Gdynia, Pomeranian Voivodeship, northern Poland. Formerly a separate settlement, it is older than Gdynia by several centuries.
Etymology
Both the Polish and then ...
, and Hel.
Ethnic composition
Most of the area was inhabited byPoles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in ...
, Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, and Kashubians
The Kashubians ( csb, Kaszëbi; pl, Kaszubi; german: Kaschuben), also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ( West Slavic) ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in nor ...
. The census of 1910 showed that there were 528,000 Poles (including West Slavic Kashubians) compared to 385,000 Germans in the region. The census included German soldiers stationed in the area as well as public officials sent to administer the area.
Since 1886, a Settlement Commission was set up by Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
to enforce German settlement while at the same time Poles, Jews and Germans migrated west during the Ostflucht
The ''Ostflucht'' (; "flight from the East") was the migration of Germans, in the later 19th century and early 20th century, from areas which were then eastern parts of Germany to more industrialized regions in central and western Germany. The ...
.
In 1921 the proportion of Germans in Pomerania (where the Corridor was located) was 18.8% (175,771). Over the next decade, the German population decreased by another 70,000 to a share of 9.6%. There was also a Jew
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
ish minority. in 1905, Kashubians numbered about 72,500.
After the occupation by Nazi Germany, a census was made by the German authorities in December 1939. 71% of people declared themselves as Poles, 188,000 people declared Kashubian as their language, 100,000 of those declared themselves Polish.
After World War II
 At the 1945
At the 1945 Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris P ...
following the German defeat in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Poland's borders were reorganized at the insistence of the Soviet Union, which occupied the entire area. Territories east of the Oder-Neisse line, including Danzig, were put under Polish administration. The Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris P ...
did not debate about the future of the territories that were part of western Poland before the war, including the corridor. It automatically became part of the reborn state in 1945.
Many German residents were executed, others were expelled to the Soviet occupation zone
The Soviet Occupation Zone ( or german: Ostzone, label=none, "East Zone"; , ''Sovetskaya okkupatsionnaya zona Germanii'', "Soviet Occupation Zone of Germany") was an area of Germany in Central Europe that was occupied by the Soviet Union as a ...
, which later became East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In t ...
.
The corridor in literature
In ''The Shape of Things to Come
''The Shape of Things to Come'' is a work of science fiction by British writer H. G. Wells, published in 1933. It takes the form of a future history which ends in 2106.
Synopsis
A long economic slump causes a major war that leaves Europe d ...
'', published in 1933, H. G. Wells correctly predicted that the corridor would be the starting point of a future Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
. He depicted the war as beginning in January 1940 and would involve heavy aerial bombing
An airstrike, air strike or air raid is an offensive operation carried out by aircraft. Air strikes are delivered from aircraft such as blimps, balloons, fighters, heavy bombers, ground attack aircraft, attack helicopters and drones. The offici ...
of civilians, but that it would result in a 10-year trench warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising Trench#Military engineering, military trenches, in which troops are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artille ...
-esque stalemate between Poland and Germany eventually leading to a worldwide societal collapse in the 1950's.
See also
Similar corridors
Other land corridors linking a country either to the sea or to a remote part of the country are: *Czech Corridor
The Czech Corridor ( cs, Český koridor; sk, Český koridor) or Czechoslovak Corridor ( cs, Československý koridor; sk, Československý koridor) was a failed proposal during the Paris Peace Conference of 1919 in the aftermath of World War I ...
(concept)
* Eilat
Eilat ( , ; he, אֵילַת ; ar, إِيلَات, Īlāt) is Israel's southernmost city, with a population of , a busy port and popular resort at the northern tip of the Red Sea, on what is known in Israel as the Gulf of Eilat and in Jorda ...
CorridorPeter Haggett, ''Geography: A Global Synthesis'', Pearson Education, 2001, p.524, (Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
)
* Jerusalem Corridor (Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
)
* Antofagasta or Atacama corridor (Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
)
* Persian Corridor (Iran 1941–1946)
* Lachin corridor (Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''O ...
/Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
)
* Siliguri Corridor
The Siliguri Corridor, also known as the Chicken's Neck, is a stretch of land around the city of Siliguri in West Bengal, India. at the narrowest section, this geo-political and geo-economical corridor connects the eight states of northeast I ...
(India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
)
* Teen Bigha Corridor
The Tin (or Teen) Bigha Corridor ( bn, তিনবিঘা করিডর) is a strip of land belonging to India on the West Bengal–Bangladesh border which, in September 2011, was leased to Bangladesh so the country could access its Dahagr ...
(Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
)
* Wakhan Corridor
The Wakhan Corridor ( ps, واخان دهلېز, translit=wāxān dahléz, fa, دالان واخان, translit=dâlân vâxân) is a narrow strip of territory in Badakhshan Province of Afghanistan, extending to Xinjiang in China and separatin ...
(Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
, this corridor was not created to link, but to separate areas)
* Bosnian Corridor
* Brčko corridor (Republika Srpska
Republika Srpska ( sr-Cyrl, Република Српска, lit=Serb Republic, also known as Republic of Srpska, ) is one of the two entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is located ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and ...
)
* Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad ( ; rus, Калининград, p=kəlʲɪnʲɪnˈɡrat, links=y), until 1946 known as Königsberg (; rus, Кёнигсберг, Kyonigsberg, ˈkʲɵnʲɪɡzbɛrk; rus, Короле́вец, Korolevets), is the largest city and ...
Post Soviet-Union rail and road links through Lithuania and Belarus to Russia proper from the now-detached Russian exclave of Kaliningrad.
* Caprivi Strip
The Caprivi Strip, also known simply as Caprivi, is a geographic salient protruding from the northeastern corner of Namibia. It is surrounded by Botswana to the south and Angola and Zambia to the north. Namibia, Botswana and Zambia meet at a s ...
(Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
, connecting the then German South West Africa
German South West Africa (german: Deutsch-Südwestafrika) was a colony of the German Empire from 1884 until 1915, though Germany did not officially recognise its loss of this territory until the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. With a total area of ...
to the Zambezi River
The Zambezi River (also spelled Zambeze and Zambesi) is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers , slightly less than hal ...
)
References
{{Authority control Aftermath of World War I in Germany History of Pomerania Second Polish Republic Treaty of Versailles Germany–Poland relations Aftermath of World War I in Poland Geopolitical corridors 1920 establishments in Poland