Polabian Slavs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Polabian Slavs ( dsb, Połobske słowjany, pl, Słowianie połabscy, cz, Polabští slované) is a collective term applied to a number of Lechitic ( West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today


 The Polabian Slavs replaced the
The Polabian Slavs replaced the 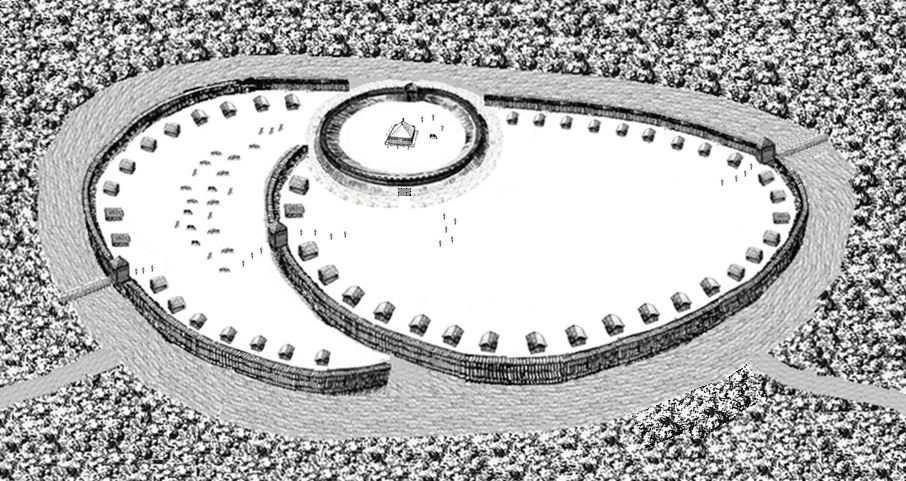
 From 1140 to 1143 Holsatian nobles advanced into Wagria to permanently settle in the lands of the pagan Wagri. Count Adolf II of Holstein and Henry of Badewide took control of Polabian settlements at
From 1140 to 1143 Holsatian nobles advanced into Wagria to permanently settle in the lands of the pagan Wagri. Count Adolf II of Holstein and Henry of Badewide took control of Polabian settlements at
Map of the lands inhabited by Polabian Slavs
{{Slavic ethnic groups (VII-XII century) Slavic ethnic groups
eastern Germany
The new states of Germany () are the five re-established states of the former German Democratic Republic (GDR) that unified with the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) with its 10 states upon German reunification on 3 October 1990.
The new st ...
. The approximate territory stretched from the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
in the north, the Saale and the ''Limes Saxoniae
The Limes Saxoniae (Latin for "Limit of Saxony"), also known as the Limes Saxonicus or Sachsenwall ("Saxon Dyke"), was an unfortified limes or border between the Saxons and the Slavic Obotrites, established about 810 in present-day Schleswig ...
''Christiansen, 18 in the west, the Ore Mountains and the Western Sudetes in the south, and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
in the east. They have also been known as Elbe Slavs (german: Elbslawen) or Wends
Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people ...
. Their name derives from the Slavic ''po'', meaning "by/next to/along", and the Slavic name for the ''Elbe'' (''Labe'' in Czech and ''Łaba'' in Polish).
The Polabian Slavs started settling in the territory of modern Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
in the 6th century. They were largely conquered by Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
and Danes since the 9th century and were subsequently included and gradually assimilated within the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
. The tribes were gradually Germanized and assimilated in the following centuries; the Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Branden ...
are the only descendants of the Polabian Slavs to have retained their identity and culture.
The Polabian language is now extinct. However, the two Sorbian languages are spoken by approximately 22,000-30,000 inhabitants of the region and the languages are regarded by the government of Germany as official languages of the region.
Tribes
TheBavarian Geographer The epithet "Bavarian Geographer" ( la, Geographus Bavarus) is the conventional name for the anonymous author of a short Latin medieval text containing a list of the tribes in Central- Eastern Europe, headed ().
The name "Bavarian Geographer" was ...
, an anonymous medieval document compiled in Regensburg in 830, contains a list of the tribes in Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
to the east of the Elbe. Among other tribes it lists the Uuilci (Veleti
The Veleti, also known as Wilzi, Wielzians, and Wiltzes, were a group of medieval Lechitic tribes within the territory of Hither Pomerania, related to Polabian Slavs. They had formed together the Confederation of the Veleti, a loose monarchic c ...
) with 95 civitates, the Nortabtrezi ( Obotrites) with 53 civitates, the Milzane ( Milceni) with 30 civitates, and the Hehfeldi ( Hevelli) with 14 civitates.
The Great Soviet Encyclopedia classifies the Polabian Slavs in three main tribes, the Obotrites, the Veleti
The Veleti, also known as Wilzi, Wielzians, and Wiltzes, were a group of medieval Lechitic tribes within the territory of Hither Pomerania, related to Polabian Slavs. They had formed together the Confederation of the Veleti, a loose monarchic c ...
, and the Lusatian Sorbs.
The main tribes of the Obotritic confederation were the Obotrites proper ( Wismar Bay to the Schweriner See); the Wagrians
The Wagri, Wagiri, or Wagrians were a tribe of Polabian Slavs inhabiting Wagria, or eastern Holstein in northern Germany, from the ninth to twelfth centuries. They were a constituent tribe of the Obodrite confederacy.
In the Slavic uprisings of 9 ...
(eastern Holstein
Holstein (; nds, label=Northern Low Saxon, Holsteen; da, Holsten; Latin and historical en, Holsatia, italic=yes) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of German ...
); the Warnabi (''Warnower'') (the upper Warnow
The Warnow () is a river in the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in Germany. It flows into the Baltic Sea near the town of Rostock, in its borough Warnemünde.
The source of the Warnow is in Grebbin, a small village north of Parchim, at the wes ...
and Mildenitz); and the Polabians proper (between the Trave
The Trave () is a river in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is approximately long, running from its source near the village of Gießelrade in Ostholstein to Travemünde, where it flows into the Baltic Sea. It passes through Bad Segeberg, Bad Old ...
and the Elbe). Other tribes associated with the confederation include the Linones (''Linonen
The Linones were a small Slavic people first recorded in the early 9th century. They lived north and east of the Elbe, across from Höhbeck in the region around Lenzen, south of the Wilzi and Obotrites, north of the Hevelli and northeast of the S ...
'') near Lenzen
Lenzen (Elbe) is a small town in the district of Prignitz, in Brandenburg, Germany. The town lies to the north of the Löcknitz River, not far from where the Löcknitz flows into the Elbe. It is part of the ''Amt'' Lenzen-Elbtalaue.
Overview
Len ...
, the Travnjane near the Trave
The Trave () is a river in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is approximately long, running from its source near the village of Gießelrade in Ostholstein to Travemünde, where it flows into the Baltic Sea. It passes through Bad Segeberg, Bad Old ...
, and the Drevani in the Hanoverian Wendland and the northern Altmark :''See German tanker Altmark for the ship named after Altmark and Stary Targ for the Polish village named Altmark in German.''
The (English: Old MarchHansard, ''The Parliamentary Debates from the Year 1803 to the Present Time ...'', Volume 32. ...
.Herrmann, 8
The Veleti
The Veleti, also known as Wilzi, Wielzians, and Wiltzes, were a group of medieval Lechitic tribes within the territory of Hither Pomerania, related to Polabian Slavs. They had formed together the Confederation of the Veleti, a loose monarchic c ...
, also known as the Liutizians or Wilzians, included the Kessinians The Kessinians, also known as Kessini, Chizzini, ''Kcynianie'' and ''Chyżanie'', were a medieval West Slavs, West Slavic tribe in what is now northeastern Germany. They inhabited the territory between the Warnow and Recknitz rivers, today split bet ...
(''Kessiner'', ''Chyzzini'') along the lower Warnow and Rostock; the Circipani
Circipania (german: Circipanien, Zirzipanien) was a medieval territory in what is now northeastern Germany. The name derives from Latin ''circum'' (around) and ''Pane'' (the Peene River). The region was enclosed roughly by the upper Recknitz, Treb ...
(''Zirzipanen'') between the Recknitz
The Recknitz (historically known as ''Raxa'') is a river in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in northeastern Germany. The Recknitz's glacial valley stretches as far south as the heights at Glasewitz near Güstrow. The river has no definite source, but rath ...
, Trebel
Trebel is a municipality in the district Lüchow-Dannenberg, in Lower Saxony, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russ ...
, and Peene
The Peene () is a river in Germany.
Geography
The Westpeene, with the Ostpeene as its longer tributary, and the Kleine Peene/Teterower Peene (with a ''Peene '' without specification (or ''Nordpeene'') as its smaller and shorter affluent) flo ...
Rivers; the Tollenser east and south of the Peene along the Tollense River; and the Redarier south and east of the Tollensesee on the upper Havel. The Redarier were the most important of the Veleti tribes.
The Rani of Rügen, not to be confused with the older Germanic Rugians
The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians ( grc, Ρογοί, Rogoi), were a Roman-era Germanic people. They were first clearly recorded by Tacitus, in his ''Germania'' who called them the ''Rugii'', and located them near the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Some ...
, are sometimes considered to be part of the Veleti.Christiansen, 27 South of the Rani were the Ucri (''Ukranen'') along the Ucker
The Uecker () or Ucker is a river in the northeastern German states of Brandenburg, where it is known as the ''Ucker'', and of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Its source lies in the Uckermark district, one kilometer north of Ringenwalde. It flows no ...
and the Morici (''Morizani'', ''Müritzer'') along the Müritz; the former gave their name to the Uckermark
The Uckermark () is a historical region in northeastern Germany, straddles the Uckermark District of Brandenburg and the Vorpommern-Greifswald District of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Its traditional capital is Prenzlau.
Geography
The region is nam ...
. Smaller tribes included the Došane along the Dosse, the Zamzizi in the Ruppin Land, and the Rěčanen on the upper Havel. Along the lower Havel and near the confluence of the Elbe and the Havel lived the Nelětici, the Liezizi, the Zemzizi, the Smeldingi (''Smeldinger''), and the Bethenici.
The middle Havel region and the Havelland were settled by the Hevelli, a tribe loosely connected to the Veleti. East of the Hevelli lived the Sprevane of the lower Dahme and Spree rivers. Small tribes on the middle Elbe included the Moriciani, the Zerwisti, the Serimunt, and the Nicici.
South of the Hevelli lived the ancestors of the modern Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Branden ...
, the Lusici of Lower Lusatia
Lower Lusatia (; ; ; szl, Dolnŏ Łużyca; ; ) is a historical region in Central Europe, stretching from the southeast of the German state of Brandenburg to the southwest of Lubusz Voivodeship in Poland. Like adjacent Upper Lusatia in the sou ...
and the Milceni of Upper Lusatia. Near these tribes were the Selpoli and the Besunzanen. The Colodici, Siusler, Nisanen and Glomaci (''Daleminzier'') lived along the upper Elbe, while the Chutici, Plisni, Gera, Puonzowa, Tucharin, Weta, and groups of Nelětici lived near the Saale.Herrmann, 9 On the middle Oder lived the Leubuzzi, who were associated with medieval Poland. Small groups of West Slavs also lived on the Main
Main may refer to:
Geography
* Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
...
and the Regnitz
The Regnitz is a river in Franconia, Germany. It is a left tributary of the Main and is in length.
The river is formed by the confluence of the rivers Rednitz and Pegnitz, which meet in the city of Fürth. From there the Regnitz runs northwa ...
near Bamberg and in northeastern Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
.
Society

Princes
A Polabian prince was known as a '' knez''. His power was relatively greater in Slavic society than those of Danish or Swedish kings in their kingdoms, although it was not absolute. He was the general leader of his tribe and was foremost among its nobles, holding much of the forested hinterland and expecting reverence from his warriors. However, his authority largely extended only to the territory controlled by his governor, or '' voivod''. Each ''voivod'' governed small territories based around fortifications. Princely power often differed between tribes. The Obodrite prince Henryk was able to maintain a sizable army ca. 1100 at the expense of the towns, and the importance of ''knez'' within the Obodrites only increased after his death.Christiansen, 32 The prince of the Rani, on the other hand, was limited by the local senate, which was led by the high priest atCape Arkona
Cape Arkona () is a 45-metre (150-foot) high cape on the island of Rügen in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It forms the tip of the Wittow peninsula, just a few kilometres north of the Jasmund National Park. The protected landscape of Cape Arko ...
; the Rani ''knez'' was essentially first among the tribe's landowners.Christiansen, 33
Towns
The power of the prince and his governors was often restricted by the river towns, known to chroniclers as civitates, especially within the territory of the Veleti. Polabian towns were centered on small earthworks arranged in circles or ovals. The '' gord'' was situated at the highest altitude of the town and held a barracks, citadel, and princely residence. It was often protected by a moat, walls, and wooden towers. Below the ''gord'', but still within the town walls, was the ''urbs'' or ''suburbium'', which held the residences for the nobility and merchants. The towns often held wooden temples for Slavic gods within the ''urbs''. Outside of the walls were homes for the peasantry.Christiansen, 29 With the exception of Arkona on Rügen, few Polabian towns on theBaltic coast
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10 ...
were built near the shore, out of concern for pirates and raiders. While not highly populated compared to Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
or Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, the Polabian towns were relatively large for the Baltic region, such as in comparison to those of Scandinavia.
Peasantry
The majority of Polabian Slavs were peasants in small villages who engaged in agriculture (rich in grains, flax) and animal husbandry (poultry, cattle). Some villagers were fishermen, beekeepers, or trappers. Farmland was divided into a unit called a ''kuritz'' ( la, uncus), for which peasants paid grain taxes to the ''voivot''.Military
Polabian society developed during the 9th and 10th centuries under pressure from theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
and the Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
s of Scandinavia. They were often forced to pay tribute to the kings of Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
, Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
bishops, and imperial margraves. Polabian society became militarized and its leaders began organizing armed forces and defenses. Many Polabian magnates lived in forest fortresses, while towns were inhabited by warriors and burghers.Christiansen, 28
The magnates often raided Germanic territories or engaged in piracy. In times of large-scale war, the ''knes'' took overall command. The prince's '' voivot'' ensured military service from the warriors and taxes from the peasantry. While the countryside provided land forces, the towns were known for their longships, which were lighter and lower than those used by the Danes and Swedes.Christiansen, 15
From a distance, Polabian fleets resembled those of the Scandinavians, although targets would recognize the Slavs' closely cropped hair and shrieking battle cries when they grew close.Christiansen, 34 Polabian cavalry used small horses which were effective in quick raiding campaigns, but less effective against the Saxon and Danish heavy cavalry
Heavy cavalry was a class of cavalry intended to deliver a battlefield charge and also to act as a tactical reserve; they are also often termed '' shock cavalry''. Although their equipment differed greatly depending on the region and histor ...
.Christiansen, 35
Religion
Religion was an important aspect of Polabian society. Much of their territory was dotted with holy places in nature to which the Slavs could pray and make offerings to Slavicgods
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater ...
. The priesthood was an important class which developed images and objects of worship. Polabian towns often included elaborate temples often visited for offerings and pilgrimages. In contrast, priests in the countryside often lived meagerly.
History
 The Polabian Slavs replaced the
The Polabian Slavs replaced the Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
who had emigrated from the 1st to 6th centuries during the Migration Period. Their settlement area was largely stable by the 8th century. Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
enlisted the Obotrites as allies in his campaign against the rebellious Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
of Holstein
Holstein (; nds, label=Northern Low Saxon, Holsteen; da, Holsten; Latin and historical en, Holsatia, italic=yes) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of German ...
. Many of the Slavic tribes became dependencies of the Carolingian Empire and the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
created the Sorbian March to defend against the Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Branden ...
. Einhard in '' Vita Karoli Magni'' describes an expedition into Slavic territory led by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
himself, in 798. The Veleti noted as Wilzi (referred to themselves as ''Welatabians'') were invaded by the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
because of their continuous expeditions into Obodrite
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ( ...
lands, with the Obodrites being allies of the Franks against the Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
.
German campaigns against the Slavs began in earnest during the Ottonian dynasty. Henry the Fowler attacked the Slavs in several campaigns with his cavalry. During the reigns of Henry and his son Otto I, several marches were established to guard the eastern acquisitions, such as the Billung March to the north and the Marca Geronis
The ''Marca Geronis'' (march of Gero) was a vast super-march in the middle of the tenth century. It was created probably for Thietmar (in the 920s) and passed to his two sons consecutively: Siegfried and Gero. On Gero's death in 965 it was divi ...
to the south. After Gero's death in 965, the Marca Geronis was divided into the Northern March, the March of Lusatia
The March or Margraviate of Lusatia (german: Mark(grafschaft) Lausitz) was as an eastern border march of the Holy Roman Empire in the lands settled by Polabian Slavs. It arose in 965 in the course of the partition of the vast '' Marca Geronis''. ...
, and the Thuringian March, the latter being divided into the marches of Zeitz
Zeitz ( hsb, Žič) is a town in the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the river White Elster, in the triangle of the federal states Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia and Saxony.
History
Zeitz was first recorded u ...
, Merseburg, and Meissen. Bishoprics such as Magdeburg, Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
, and Havelberg
Havelberg () is a town in the district of Stendal, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the Havel, and part of the town is built on an island in the centre of the river. The two parts were incorporated as a town in 1875. It has a populati ...
were founded to support the conversion of the Slavs to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
.
After the defeat of Otto II at the Battle of Stilo
The Battle of Stilo (also known as Cape Colonna and Crotone) was fought on 13 or 14 July 982 near Crotone in Calabria between the forces of Holy Roman Emperor Otto II and his Italo-Lombard allies and those of the Kalbid emir of Sicily, Abu'l- ...
in 982, the pagan Slavs rebelled against the Germans the following year; the Hevelli and Liutizi
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
destroyed the Bishoprics of Havelberg and Brandenburg, and Obotrites (Mstivoj) destroyed Hamburg.Barkowski, 152–155 Some Slavs advanced across the Elbe into Saxon territory, but retreated when the Christian Duke of Poland, Mieszko I, attacked them from the east. The Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
retained only nominal control over the Slavic territories between the Elbe and the Oder. Despite the efforts of Christian missionaries, most Polabian Slavs saw Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religiou ...
as a " German god" and remained pagan.
The Obotrite prince Udo
Udo is a masculine given name. It may refer to:
People Medieval era
*Udo of Neustria, 9th century nobleman
* Udo (Obotrite prince) (died 1028)
* Udo (archbishop of Trier) (c. 1030 – 1078)
* Lothair Udo II, Margrave of the Nordmark (c. 1025 � ...
and his son Gottschalk expanded their realm by unifying the Obotrite tribes and conquering some Liutizi tribes in the 11th century. They encouraged the establishments of bishoprics to support Christian missionary activity. However, a revolt in 1066 led to the murder of Gottschalk and his replacement by the pagan Kruto
Kruto the Wende (or Cruto) (died 1093), son of Grin or Grinus, was a prince of Wagria.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'' (Berlin: Akademie-Verlag, 1985), 366. James Westfall Thompson believed his family belonged to the Rani of Rugia ...
of Wagria. Gottschalk's son Henry
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
* Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
eventually killed Kruto in 1093.

 From 1140 to 1143 Holsatian nobles advanced into Wagria to permanently settle in the lands of the pagan Wagri. Count Adolf II of Holstein and Henry of Badewide took control of Polabian settlements at
From 1140 to 1143 Holsatian nobles advanced into Wagria to permanently settle in the lands of the pagan Wagri. Count Adolf II of Holstein and Henry of Badewide took control of Polabian settlements at Liubice Liubice, also known by the German name Alt-Lübeck ("Old Lübeck"), was a medieval West Slavic settlement near the site of modern Lübeck, Germany. Liubice was located at the confluence of the Schwartau with the Trave across from Teerhof Island, a ...
and Racisburg. Impressed with the success of the First Crusade, Saxons began calling for a crusade against their Slav neighbors. The Wendish Crusade
The Wendish Crusade (german: Wendenkreuzzug) was a military campaign in 1147, one of the Northern Crusades and a part of the Second Crusade, led primarily by the Kingdom of Germany within the Holy Roman Empire and directed against the Polabian Sl ...
of 1147, concurrent to the Second Crusade, was largely unsuccessful, resulting in devastation to the Liutizi lands and forced baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost ...
s. The campaign did secure Saxon control of Wagria and Polabia, however. The Obotrites were largely at peace with the Saxons during the following decade, although Slavic pirates raided Denmark.
Beginning in the late 1150s, King Valdemar the Great of Denmark enlisted the aid of Duke Henry the Lion of Saxony against the Slavs; their cooperation led to the death of the Obotrite prince, Niklot
Niklot or Nyklot (1090 – August 1160) was a chief or prince of the Slavic Obotrites and an ancestor of the House of Mecklenburg. He became chief of the Obotrite confederacy, including the Kissini and the Circipani, between the years 1130 and 1 ...
, in 1160. The two Christian lords distributed much of the conquered territory among their vassals. When Niklot's exiled son, Pribislav, engineered an Obotrite rebellion, the pair retaliated by occupying Demmin
Demmin () is a town in the Mecklenburgische Seenplatte district, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. It was the capital of the former district of Demmin.
Geography
Demmin lies on the West Pomeranian plain at the confluence of the rivers ...
and warding off Pribislav's Liutizian allies.
After conquering Wagria and Polabia during the 1140s, Saxon nobles attempted to expel the "native" Slavs and replace them with Saxon and Flemish settlers. The 1164 Obotrite revolt led by Niklot's son Pribislav convinced Henry the Lion that keeping the Slavs as allies would be less troublesome. The duke returned the Christian Pribislav to power as Prince of Mecklenburg, Kessin
Kessin is a village and a former municipality in the district of Rostock, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany.
History
Since 7 June 2009, it is part of the municipality Dummerstorf. Before this, it was within the Warnow-Ost Amt.
A group of ...
, and Rostock, and a vassal of the Saxons.
Tactics and weaponry were decisive in Denmark's campaigns against the eastern Polabian Slavs. The Danes utilized quick coastal and river raids, tactics similar to those of the Vikings. Although they lacked siege experience, the Danes were able to cripple Slavic regions by burning crops and unwalled suburbs. Slav counterattacks were repulsed by crossbows and Norwegian longbows. The Danes occupied Rugia in 1168, conquering the Rani stronghold of Arkona. Similar to Henry's reinstatement of Pribislav as a Saxon vassal, Valdemar allowed the Rani prince Jaromar to rule as a Christian Danish vassal. After Valdemar refused to share Rugia with Henry, the Saxon duke enlisted the aid of the Obotrite confederacy and the Liutizi against the Danes; Valdemar ended the conflict by paying Henry in 1171.
Alarmed at the expansion of Henry the Lion's power, Emperor Frederick Barbarossa deposed the Saxon duke and redistributed his lands in 1180/81. The withdrawal of Saxon support left the Liutizi and their Pomeranian supporters vulnerable to the Danish fleet. A Slavic fleet attempting to reclaim Rugia was crushed at the Bay of Greifswald on 19 May 1184. Danish monks engaged in missionary activity in Pomeranian abbeys, and Prince Bogislaw I surrendered to King Canute VI in 1185 to become the Danish king's vassal.
Pribislav, a Christian prince of the Hevelli, bequeathed his lands to the Saxon Albert the Bear upon his death, thereby leading to the establishment of the Margraviate of Brandenburg.
The Lusatian Sorbs remained independent to a large extent. They were temporarily subdued by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
, but upon his death the links with the Franks were broken. In a series of bloody wars between 929 and 963 their lands were conquered by King Henry the Fowler and his son Otto the Great and were incorporated into the Kingdom of Germany
The Kingdom of Germany or German Kingdom ( la, regnum Teutonicorum "kingdom of the Germans", "German kingdom", "kingdom of Germany") was the mostly Germanic-speaking East Frankish kingdom, which was formed by the Treaty of Verdun in 843, especi ...
. By the 14th century, the majority of Slavs living there had been Germanized and assimilated. However, the Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Branden ...
, the descendants of the Milceni and the Lusici, have retained their identity within Lusatia, a region divided between the German states of Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
and Saxony.
The Slavic language was spoken by the descendants of the Drevani in the area of the lower Elbe until the early 18th century.
See also
*Sukow-Dziedzice group
The Sukow or Sukow-Dziedzice group (german: Sukow-Dziedzice-Gruppe) or Sukow-Dziedzice culture ( pl, Kultura Sukow-Dziedzice, russian: Суковско-дзедзицкая культура), also known as Szeligi culture, was an archaeological cu ...
* Leipzig group
* Tornow group
* Slavic settlement of the Eastern Alps
Footnotes
References
* * * * * *External links
Map of the lands inhabited by Polabian Slavs
{{Slavic ethnic groups (VII-XII century) Slavic ethnic groups