Plains Tribes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
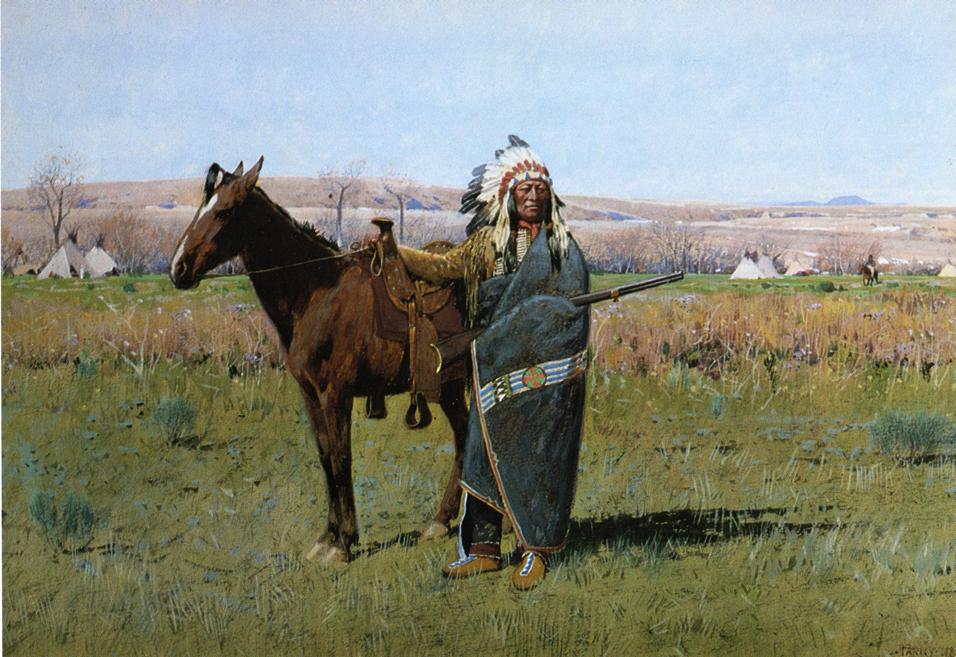

 Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and
Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and

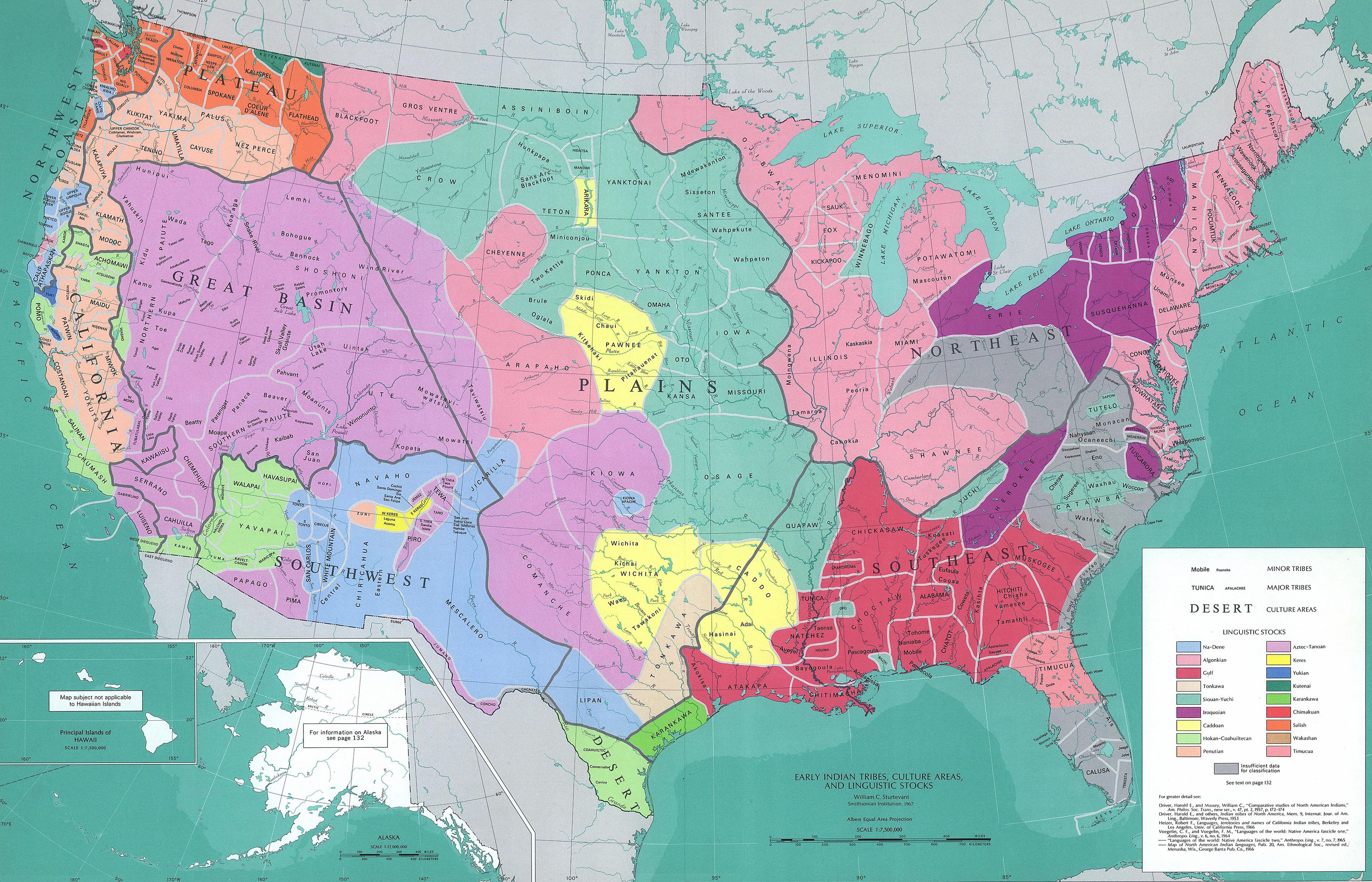 The earliest people of the Great Plains mixed hunting and gathering wild plants. The cultures developed horticulture, then agriculture, as they settled in sedentary villages and towns. Maize, originally from Mesoamerica and spread north from the
The earliest people of the Great Plains mixed hunting and gathering wild plants. The cultures developed horticulture, then agriculture, as they settled in sedentary villages and towns. Maize, originally from Mesoamerica and spread north from the
 The Plains Indians found by Coronado had not yet obtained horses; it was the introduction of the horse that revolutionized Plains culture. When horses were obtained, the Plains tribes rapidly integrated them into their daily lives. People in the southwest began to acquire horses in the 16th century by trading or stealing them from Spanish colonists in New Mexico. As horse culture moved northward, the Comanche were among the first to commit to a fully mounted nomadic lifestyle. This occurred by the 1730s, when they had acquired enough horses to put all their people on horseback.
The horse enabled the Plains Indians to gain their subsistence with relative ease from the seemingly limitless bison herds. Riders were able to travel faster and farther in search of bison herds and to transport more goods, thus making it possible to enjoy a richer material environment than their pedestrian ancestors. For the Plains peoples, the horse became an item of prestige as well as utility. They were extravagantly fond of their horses and the lifestyle they permitted.
The first Spanish conqueror to bring horses to the new world was Hernán Cortés in 1519. However, Cortés only brought about sixteen horses with his expedition. Coronado brought 558 horses with him on his 1539–1542 expedition. At the time, the Indians of these regions had never seen a horse. Only two of Coronado's horses were mares, so he was highly unlikely to have been the source of the horses that Plains Indians later adopted as the cornerstone of their culture.Haines, Francis. "The Northward Spread of Horses among the Plains Indians. ''American Anthropologist'', Vol 40, No. 3 (1988) In 1592, however, Juan de Oñate brought 7,000 head of livestock with him when he came north to establish a colony in New Mexico. His horse herd included mares as well as stallions.
The Plains Indians found by Coronado had not yet obtained horses; it was the introduction of the horse that revolutionized Plains culture. When horses were obtained, the Plains tribes rapidly integrated them into their daily lives. People in the southwest began to acquire horses in the 16th century by trading or stealing them from Spanish colonists in New Mexico. As horse culture moved northward, the Comanche were among the first to commit to a fully mounted nomadic lifestyle. This occurred by the 1730s, when they had acquired enough horses to put all their people on horseback.
The horse enabled the Plains Indians to gain their subsistence with relative ease from the seemingly limitless bison herds. Riders were able to travel faster and farther in search of bison herds and to transport more goods, thus making it possible to enjoy a richer material environment than their pedestrian ancestors. For the Plains peoples, the horse became an item of prestige as well as utility. They were extravagantly fond of their horses and the lifestyle they permitted.
The first Spanish conqueror to bring horses to the new world was Hernán Cortés in 1519. However, Cortés only brought about sixteen horses with his expedition. Coronado brought 558 horses with him on his 1539–1542 expedition. At the time, the Indians of these regions had never seen a horse. Only two of Coronado's horses were mares, so he was highly unlikely to have been the source of the horses that Plains Indians later adopted as the cornerstone of their culture.Haines, Francis. "The Northward Spread of Horses among the Plains Indians. ''American Anthropologist'', Vol 40, No. 3 (1988) In 1592, however, Juan de Oñate brought 7,000 head of livestock with him when he came north to establish a colony in New Mexico. His horse herd included mares as well as stallions.
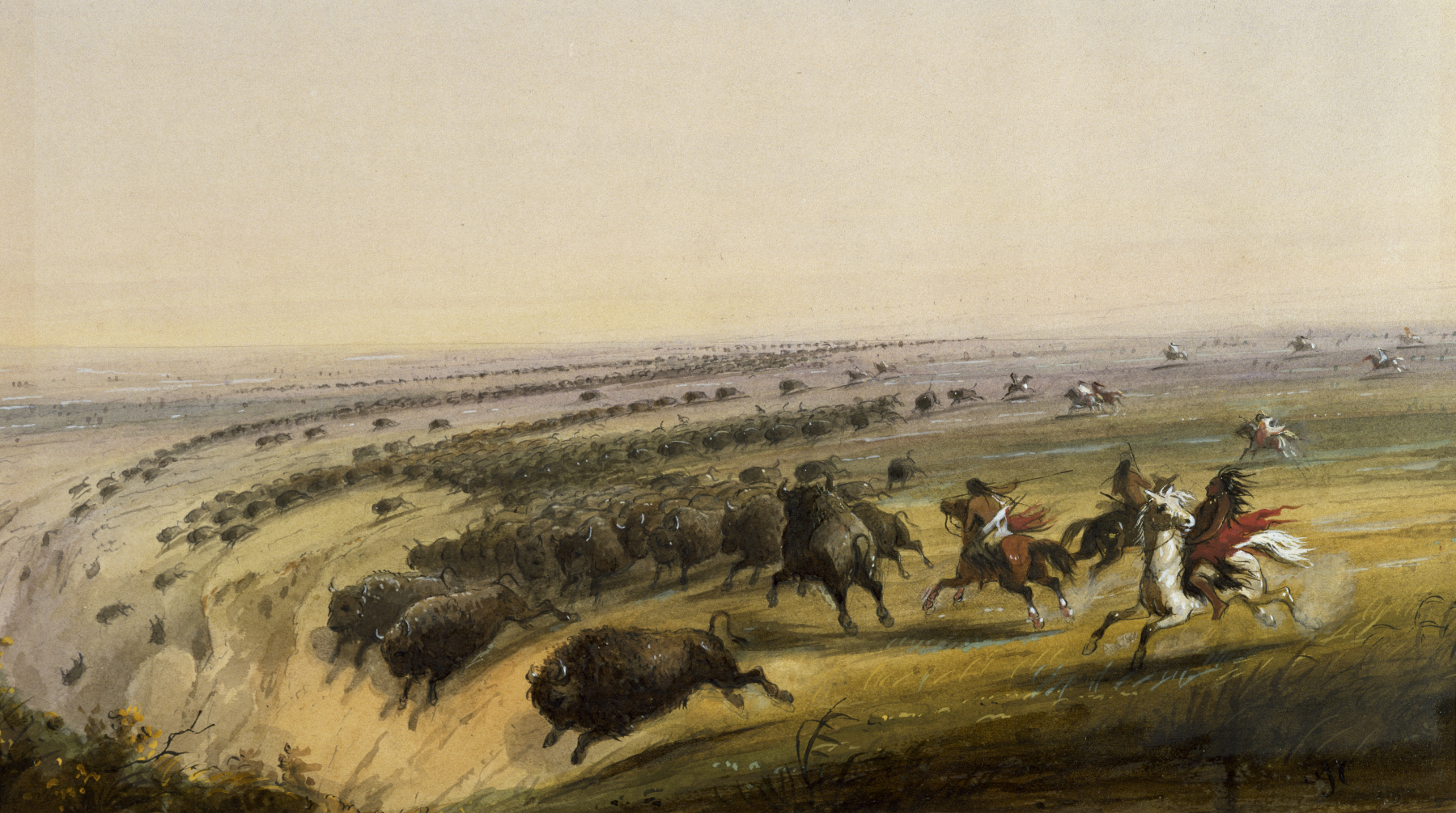 It was the Comanche, coming to the attention of the Spanish in New Mexico in 1706, who first realized the potential of the horse. As nomads, hunters, and pastoralists, well supplied with horses, they swept most of the mixed-economy Apaches from the plains and by the 1730s were dominant in the Great Plains south of the Arkansas River. The success of the Comanche encouraged other Indian tribes to adopt a similar lifestyle. The southern Plains Indians acquired vast numbers of horses. By the 19th century, Comanche and Kiowa families owned an average of 35 horses and mules each – and only six or seven were necessary for transport and war. The horses extracted a toll on the environment as well as required labor to care for the herd. Formerly egalitarian societies became more divided by wealth with a negative impact on the role of women. The richest men would have several wives and captives who would help manage their possessions, especially horses.
The milder winters of the southern Plains favored a pastoral economy by the Indians. On the northeastern Plains of Canada, the Indians were less favored, with families owning fewer horses, remaining more dependent upon dogs for transporting goods, and hunting bison on foot. The scarcity of horses in the north encouraged raiding and warfare in competition for the relatively small number of horses that survived the severe winters.
The Lakota, also called Teton Sioux, enjoyed the happy medium between North and South and became a dominant Plains tribe by the mid-19th century. They had relatively small horse herds, thus having less impact on their ecosystem. At the same time, they occupied the heart of prime bison range which was also an excellent region for furs, which could be sold to French and American traders for goods such as guns. The Lakota became a highly powerful Plains tribe.
It was the Comanche, coming to the attention of the Spanish in New Mexico in 1706, who first realized the potential of the horse. As nomads, hunters, and pastoralists, well supplied with horses, they swept most of the mixed-economy Apaches from the plains and by the 1730s were dominant in the Great Plains south of the Arkansas River. The success of the Comanche encouraged other Indian tribes to adopt a similar lifestyle. The southern Plains Indians acquired vast numbers of horses. By the 19th century, Comanche and Kiowa families owned an average of 35 horses and mules each – and only six or seven were necessary for transport and war. The horses extracted a toll on the environment as well as required labor to care for the herd. Formerly egalitarian societies became more divided by wealth with a negative impact on the role of women. The richest men would have several wives and captives who would help manage their possessions, especially horses.
The milder winters of the southern Plains favored a pastoral economy by the Indians. On the northeastern Plains of Canada, the Indians were less favored, with families owning fewer horses, remaining more dependent upon dogs for transporting goods, and hunting bison on foot. The scarcity of horses in the north encouraged raiding and warfare in competition for the relatively small number of horses that survived the severe winters.
The Lakota, also called Teton Sioux, enjoyed the happy medium between North and South and became a dominant Plains tribe by the mid-19th century. They had relatively small horse herds, thus having less impact on their ecosystem. At the same time, they occupied the heart of prime bison range which was also an excellent region for furs, which could be sold to French and American traders for goods such as guns. The Lakota became a highly powerful Plains tribe.
 By the 19th century, the typical year of the Lakota and other northern nomads was a communal buffalo hunt as early in spring as their horses had recovered from the rigors of the winter. In June and July the scattered bands of the tribes gathered together into large encampments, which included ceremonies such as the
By the 19th century, the typical year of the Lakota and other northern nomads was a communal buffalo hunt as early in spring as their horses had recovered from the rigors of the winter. In June and July the scattered bands of the tribes gathered together into large encampments, which included ceremonies such as the
history.msu.edu
The bison herds formed the basis of the economies of the Plains tribes. Without bison, they were forced to move onto reservations or starve. Bison were slaughtered for their skins, with the rest of the animal left behind to decay on the ground. After the animals rotted, their bones were collected and shipped back east in large quantities. The railroad industry also wanted bison herds culled or eliminated. Herds of bison on tracks could damage locomotives when the trains failed to stop in time. Herds often took shelter in the artificial cuts formed by the grade of the track winding through hills and mountains in harsh winter conditions. As a result, bison herds could delay a train for days.
As the great herds began to wane, proposals to protect the bison were discussed. Buffalo Bill Cody, among others, spoke in favor of protecting the bison because he saw that the pressure on the species was too great. But these were discouraged since it was recognized that the Plains Indians, often at war with the United States, depended on bison for their way of life. In 1874, President Ulysses S. Grant " pocket vetoed" a federal bill to protect the dwindling bison herds, and in 1875 General Philip Sheridan pleaded to a joint session of Congress to slaughter the herds, to deprive the Plains Indians of their source of food. This meant that the bison were hunted almost to extinction during the 19th century and were reduced to a few hundred by the early 1900s.
The railroad industry also wanted bison herds culled or eliminated. Herds of bison on tracks could damage locomotives when the trains failed to stop in time. Herds often took shelter in the artificial cuts formed by the grade of the track winding through hills and mountains in harsh winter conditions. As a result, bison herds could delay a train for days.
As the great herds began to wane, proposals to protect the bison were discussed. Buffalo Bill Cody, among others, spoke in favor of protecting the bison because he saw that the pressure on the species was too great. But these were discouraged since it was recognized that the Plains Indians, often at war with the United States, depended on bison for their way of life. In 1874, President Ulysses S. Grant " pocket vetoed" a federal bill to protect the dwindling bison herds, and in 1875 General Philip Sheridan pleaded to a joint session of Congress to slaughter the herds, to deprive the Plains Indians of their source of food. This meant that the bison were hunted almost to extinction during the 19th century and were reduced to a few hundred by the early 1900s.
 Armed conflicts intensified in the late 19th century between Native American nations on the plains and the U.S. government, through what were called generally the Indian Wars. Notable conflicts in this period include the Dakota War,
Armed conflicts intensified in the late 19th century between Native American nations on the plains and the U.S. government, through what were called generally the Indian Wars. Notable conflicts in this period include the Dakota War,
 The semi-sedentary, village-dwelling Plains Indians depended upon agriculture for a large share of their livelihood, particularly those who lived in the eastern parts of the Great Plains which had more precipitation than the western side. Corn was the dominant crop, followed by
The semi-sedentary, village-dwelling Plains Indians depended upon agriculture for a large share of their livelihood, particularly those who lived in the eastern parts of the Great Plains which had more precipitation than the western side. Corn was the dominant crop, followed by
 Although people of the Plains hunted other animals, such as elk or
Although people of the Plains hunted other animals, such as elk or
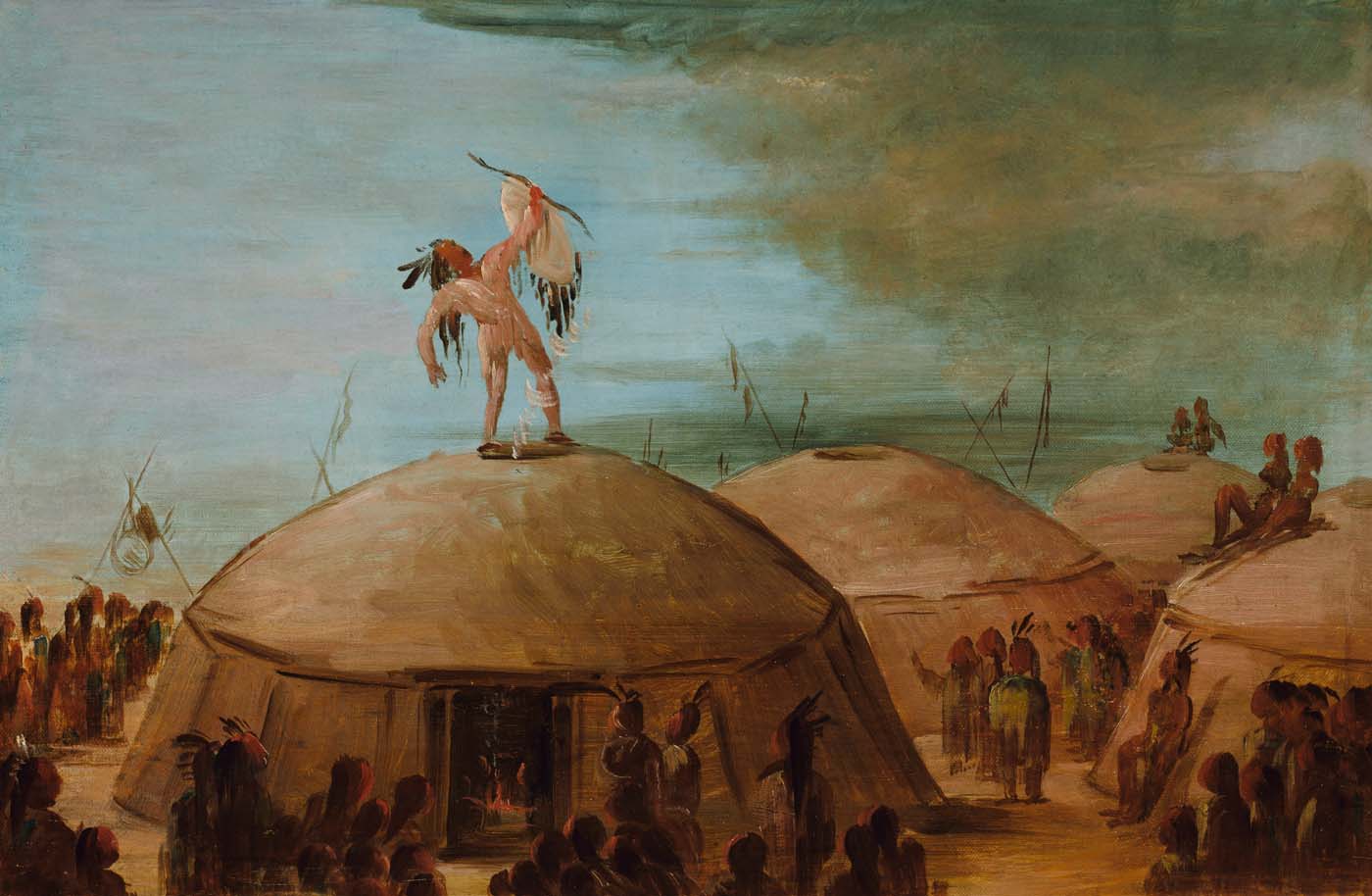
 While there are some similarities among linguistic and regional groups, different tribes have their own cosmologies and world views. Some of these are animist in nature, with aspects of polytheism, while others tend more towards monotheism or panentheism. Prayer is a regular part of daily life, for regular individuals as well as spiritual leaders, alone and as part of group ceremonies. One of the most important gatherings for many of the Plains tribes is the yearly
While there are some similarities among linguistic and regional groups, different tribes have their own cosmologies and world views. Some of these are animist in nature, with aspects of polytheism, while others tend more towards monotheism or panentheism. Prayer is a regular part of daily life, for regular individuals as well as spiritual leaders, alone and as part of group ceremonies. One of the most important gatherings for many of the Plains tribes is the yearly
"Native American Gender Roles."
''Encyclopedia of the Great Plains.'' Retrieved 15 Oct 2013. In traditional culture, women tanned hides, tended crops, gathered wild foods, prepared food, made clothing, and took down and erected the family's tepees. In the present day, these customs are still observed when lodges are set up for ceremonial use, such as at pow wows. Historically, Plains women were not as engaged in public political life as were the women in the coastal tribes. However, they still participated in an advisory role and through the women's societies. In contemporary Plains cultures, traditionalists work to preserve the knowledge of these traditions of everyday life and the values attached to them. Plains women in general have historically had the right to divorce and keep custody of their children. Because women own the home, an unkind husband can find himself homeless. A historical example of a Plains woman divorcing is Making Out Road, a Cheyenne woman, who in 1841 married non-Native frontiersman
 The earliest 16th-century Spanish explorers did not find the Plains Indians especially warlike. The Wichita in Kansas and Oklahoma lived in dispersed settlements with few defensive works. The Spanish initially had friendly contacts with the Apache (
The earliest 16th-century Spanish explorers did not find the Plains Indians especially warlike. The Wichita in Kansas and Oklahoma lived in dispersed settlements with few defensive works. The Spanish initially had friendly contacts with the Apache ( Due to their mobility, endurance, horsemanship, and knowledge of the vast plains that were their domain, the Plains Indians were often victors in their battles against the U.S. army in the American era from 1803 to about 1890. However, although Indians won many battles, they could not undertake lengthy campaigns. Indian armies could only be assembled for brief periods of time as warriors also had to hunt for food for their families. The exception to that was raids into Mexico by the Comanche and their allies in which the raiders often subsisted for months off the riches of Mexican haciendas and settlements. The basic weapon of the Indian warrior was the short, stout bow, designed for use on horseback and deadly, but only at short range. Guns were usually in short supply and ammunition scarce for Native warriors. The U.S. government through the Indian Agency would sell the Plains Indians guns for hunting, but unlicensed traders would exchange guns for buffalo hides. The shortages of ammunition together with the lack of training to handle firearms meant the preferred weapon was the bow and arrow.
Due to their mobility, endurance, horsemanship, and knowledge of the vast plains that were their domain, the Plains Indians were often victors in their battles against the U.S. army in the American era from 1803 to about 1890. However, although Indians won many battles, they could not undertake lengthy campaigns. Indian armies could only be assembled for brief periods of time as warriors also had to hunt for food for their families. The exception to that was raids into Mexico by the Comanche and their allies in which the raiders often subsisted for months off the riches of Mexican haciendas and settlements. The basic weapon of the Indian warrior was the short, stout bow, designed for use on horseback and deadly, but only at short range. Guns were usually in short supply and ammunition scarce for Native warriors. The U.S. government through the Indian Agency would sell the Plains Indians guns for hunting, but unlicensed traders would exchange guns for buffalo hides. The shortages of ammunition together with the lack of training to handle firearms meant the preferred weapon was the bow and arrow.
"Standing Tall: Plains Indians Enjoyed Height, Health Advantage"
, Jeff Grabmeier, Ohio State
''Constitution of the Pawnee Nation of Oklahoma.''
Retrieved 5 Dec 2012. ** Kitkehakhi, Oklahoma ** Pitahawirata, Oklahoma ** Skidi, Oklahoma * Ponca, Nebraska, Oklahoma *
Great Plains Indians Musical Instruments
on the Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History,
"American Indian Contributions To Science and Technology"
, Chris R. Landon, Portland Public Schools, 1993
"Buffalo and the Plains Indians"
South Dakota State Historical Society Education Kit {{DEFAULTSORT:Plains Indians


 Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and
Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and First Nation
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
band governments who have historically lived on the Interior Plains (the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies
The Canadian Prairies (usually referred to as simply the Prairies in Canada) is a region in Western Canada. It includes the Canadian portion of the Great Plains and the Prairie Provinces, namely Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These provin ...
) of North America. While hunting-farming cultures have lived on the Great Plains for centuries prior to European contact, the region is known for the horse culture
A horse culture is a tribal group or community whose day-to-day life revolves around the herding and breeding of horses. Beginning with the domestication of the horse on the steppes of Eurasia, the horse transformed each society that adopted it ...
s that flourished from the 17th century through the late 19th century. Their historic nomadism and armed resistance to domination by the government and military forces of Canada and the United States have made the Plains Indian culture groups an archetype in literature and art for Native Americans everywhere.
The Plains tribes are usually divided into two broad classifications which overlap to some degree. The first group became a fully nomadic horse culture during the 18th and 19th centuries, following the vast herds of American bison, although some tribes occasionally engaged in agriculture. These include the Arapaho
The Arapaho (; french: Arapahos, ) are a Native American people historically living on the plains of Colorado and Wyoming. They were close allies of the Cheyenne tribe and loosely aligned with the Lakota and Dakota.
By the 1850s, Arapaho ba ...
, Assiniboine
The Assiniboine or Assiniboin people ( when singular, Assiniboines / Assiniboins when plural; Ojibwe: ''Asiniibwaan'', "stone Sioux"; also in plural Assiniboine or Assiniboin), also known as the Hohe and known by the endonym Nakota (or Nakod ...
, Blackfoot, Cheyenne, Comanche, Crow
A crow is a bird of the genus '' Corvus'', or more broadly a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. Crows are generally black in colour. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not pinned scientifica ...
, Gros Ventre, Kiowa, Lakota
Lakota may refer to:
* Lakota people, a confederation of seven related Native American tribes
*Lakota language, the language of the Lakota peoples
Place names
In the United States:
* Lakota, Iowa
* Lakota, North Dakota, seat of Nelson County
* La ...
, Lipan, Plains Apache (or Kiowa Apache
The Plains Apache are a small Southern Athabaskan group who live on the Southern Plains of North America, in close association with the linguistically unrelated Kiowa Tribe. Today, they are centered in Southwestern Oklahoma and Northern Texas a ...
), Plains Cree, Plains Ojibwe, Sarsi, Nakoda (Stoney), and Tonkawa
The Tonkawa are a Native American tribe indigenous to present-day Oklahoma. Their Tonkawa language, now extinct, is a linguistic isolate.
Today, Tonkawa people are enrolled in the federally recognized Tonkawa Tribe of Indians of Oklahoma. ...
. The second group were sedentary and semi-sedentary, and, in addition to hunting bison, they lived in villages, raised crops, and actively traded with other tribes. These include the Arikara
Arikara (), also known as Sahnish,
''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011)
, Hidatsa, Iowa, Kaw (or Kansa), Kitsai, Mandan, ''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011)
Missouria
The Missouria or Missouri (in their own language, Niúachi, also spelled Niutachi) are a Native American tribe that originated in the Great Lakes region of what is now the United States before European contact.May, John D"Otoe-Missouria"''Oklaho ...
, Omaha, Osage, Otoe
The Otoe (Chiwere: Jiwére) are a Native American people of the Midwestern United States. The Otoe language, Chiwere, is part of the Siouan family and closely related to that of the related Iowa, Missouria, and Ho-Chunk tribes.
Historically, t ...
, Pawnee Pawnee initially refers to a Native American people and its language:
* Pawnee people
* Pawnee language
Pawnee is also the name of several places in the United States:
* Pawnee, Illinois
* Pawnee, Kansas
* Pawnee, Missouri
* Pawnee City, Nebraska ...
, Ponca, Quapaw
The Quapaw ( ; or Arkansas and Ugahxpa) people are a tribe of Native Americans that coalesced in what is known as the Midwest and Ohio Valley of the present-day United States. The Dhegiha Siouan-speaking tribe historically migrated from the Oh ...
, Wichita, and the Santee Dakota
The Dakota (pronounced , Dakota language: ''Dakȟóta/Dakhóta'') are a Native American tribe and First Nations band government in North America. They compose two of the three main subcultures of the Sioux people, and are typically divided int ...
, Yanktonai
The Dakota (pronounced , Dakota language: ''Dakȟóta/Dakhóta'') are a Native American tribe and First Nations band government in North America. They compose two of the three main subcultures of the Sioux people, and are typically divided into ...
and Yankton Dakota.
History

 The earliest people of the Great Plains mixed hunting and gathering wild plants. The cultures developed horticulture, then agriculture, as they settled in sedentary villages and towns. Maize, originally from Mesoamerica and spread north from the
The earliest people of the Great Plains mixed hunting and gathering wild plants. The cultures developed horticulture, then agriculture, as they settled in sedentary villages and towns. Maize, originally from Mesoamerica and spread north from the Southwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
, became widespread in the south of the Great Plains around 700 CE.
Numerous Plains peoples hunted the American bison (or buffalo) to make items used in everyday life, such as food, cups, decorations, crafting tools, knives, and clothing. The tribes followed the seasonal grazing and migration of the bison. The Plains Indians lived in tipi
A tipi , often called a lodge in English, is a conical tent, historically made of animal hides or pelts, and in more recent generations of canvas, stretched on a framework of wooden poles. The word is Siouan, and in use in Dakhótiyapi, Lakȟó ...
s because they were easily disassembled and allowed the nomadic life of following game.
The Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
explorer Francisco Vásquez de Coronado was the first European to describe the Plains Indian culture. He encountered villages and cities of the Plains village cultures. While searching for a reputedly wealthy land called Quivira in 1541, Coronado came across the Querechos
The Querechos were a Native American people.
In 1541 the Spanish conquistador Francisco Vásquez de Coronado and his army journeyed east from the Rio Grande Valley in search of a rich land called Quivira. Passing through what would later be the ...
in the Texas panhandle. The Querechos were the people later called Apache. According to the Spaniards, the Querechos lived "in tents made of the tanned skins of the cows (bison). They dry the flesh in the sun, cutting it thin like a leaf, and when dry they grind it like meal to keep it and make a sort of sea soup of it to eat. ... They season it with fat, which they always try to secure when they kill a cow. They empty a large gut and fill it with blood, and carry this around the neck to drink when they are thirsty." Coronado described many common features of Plains Indians culture: skin tepees, travois
A travois (; Canadian French, from French , a frame for restraining horses; also obsolete travoy or travoise) is a historical frame structure that was used by indigenous peoples, notably the Plains Aboriginals of North America, to drag loads ove ...
pulled by dogs, Plains Indian Sign Language
Plains Indian Sign Language (PISL), also known as Hand Talk, Plains Sign Talk, and First Nation Sign Language, is a trade language, formerly trade pidgin, that was once the lingua franca across what is now central Canada, the central and weste ...
, and staple foods such as jerky
Jerky is lean trimmed meat cut into strips and dried (dehydrated) to prevent spoilage. Normally, this drying includes the addition of salt to prevent bacteria growth before the meat has finished the dehydrating process. The word "jerky" derive ...
and pemmican
Pemmican (also pemican in older sources) is a mixture of tallow, dried meat, and sometimes dried berries. A calorie-rich food, it can be used as a key component in prepared meals or eaten raw. Historically, it was an important part of indigenou ...
.
Siouan language
Siouan or Siouan–Catawban is a language family of North America that is located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east.
Name
Authors who call the entire ...
speakers may have originated in the lower Mississippi River region. They were agriculturalists and may have been part of the Mound Builder civilization during the 9th–12th centuries. Wars with the Ojibwe and Cree peoples pushed the Lakota
Lakota may refer to:
* Lakota people, a confederation of seven related Native American tribes
*Lakota language, the language of the Lakota peoples
Place names
In the United States:
* Lakota, Iowa
* Lakota, North Dakota, seat of Nelson County
* La ...
(Teton Sioux) west onto the Great Plains in the mid- to late 17th century. The Shoshone originated in the western Great Basin and spread north and east into present-day Idaho and Wyoming. By 1500, some Eastern Shoshone had crossed the Rocky Mountains into the Great Plains. After 1750, warfare and pressure from the Blackfoot, Crow, Lakota, Cheyenne, and Arapaho pushed Eastern Shoshone south and westward. Some of them migrated as far south as Texas, emerging as the Comanche by 1700.
The settlers brought diseases against which the Indians had no resistance. Between a half and two-thirds of the Plains Indians are thought to have died of smallpox by the time of the Louisiana Purchase. The 1837 Great Plains smallpox epidemic
The 1837 Great Plains smallpox epidemic spanned 1836 through 1840, but reached its height after the spring of 1837 when an American Fur Company steamboat, the S.S. ''St. Peter'', carried infected people and supplies into the Missouri Valley.''Ratio ...
spread across the Great Plains, killing many thousands between 1837 and 1840. In the end, it is estimated that two-thirds of the Blackfoot population died, along with half of the Assiniboines
The Assiniboine or Assiniboin people ( when singular, Assiniboines / Assiniboins when plural; Ojibwe: ''Asiniibwaan'', "stone Sioux"; also in plural Assiniboine or Assiniboin), also known as the Hohe and known by the endonym Nakota (or Nakod ...
and Arikaras, a third of the Crows, and a quarter of the Pawnees.
Horses
 The Plains Indians found by Coronado had not yet obtained horses; it was the introduction of the horse that revolutionized Plains culture. When horses were obtained, the Plains tribes rapidly integrated them into their daily lives. People in the southwest began to acquire horses in the 16th century by trading or stealing them from Spanish colonists in New Mexico. As horse culture moved northward, the Comanche were among the first to commit to a fully mounted nomadic lifestyle. This occurred by the 1730s, when they had acquired enough horses to put all their people on horseback.
The horse enabled the Plains Indians to gain their subsistence with relative ease from the seemingly limitless bison herds. Riders were able to travel faster and farther in search of bison herds and to transport more goods, thus making it possible to enjoy a richer material environment than their pedestrian ancestors. For the Plains peoples, the horse became an item of prestige as well as utility. They were extravagantly fond of their horses and the lifestyle they permitted.
The first Spanish conqueror to bring horses to the new world was Hernán Cortés in 1519. However, Cortés only brought about sixteen horses with his expedition. Coronado brought 558 horses with him on his 1539–1542 expedition. At the time, the Indians of these regions had never seen a horse. Only two of Coronado's horses were mares, so he was highly unlikely to have been the source of the horses that Plains Indians later adopted as the cornerstone of their culture.Haines, Francis. "The Northward Spread of Horses among the Plains Indians. ''American Anthropologist'', Vol 40, No. 3 (1988) In 1592, however, Juan de Oñate brought 7,000 head of livestock with him when he came north to establish a colony in New Mexico. His horse herd included mares as well as stallions.
The Plains Indians found by Coronado had not yet obtained horses; it was the introduction of the horse that revolutionized Plains culture. When horses were obtained, the Plains tribes rapidly integrated them into their daily lives. People in the southwest began to acquire horses in the 16th century by trading or stealing them from Spanish colonists in New Mexico. As horse culture moved northward, the Comanche were among the first to commit to a fully mounted nomadic lifestyle. This occurred by the 1730s, when they had acquired enough horses to put all their people on horseback.
The horse enabled the Plains Indians to gain their subsistence with relative ease from the seemingly limitless bison herds. Riders were able to travel faster and farther in search of bison herds and to transport more goods, thus making it possible to enjoy a richer material environment than their pedestrian ancestors. For the Plains peoples, the horse became an item of prestige as well as utility. They were extravagantly fond of their horses and the lifestyle they permitted.
The first Spanish conqueror to bring horses to the new world was Hernán Cortés in 1519. However, Cortés only brought about sixteen horses with his expedition. Coronado brought 558 horses with him on his 1539–1542 expedition. At the time, the Indians of these regions had never seen a horse. Only two of Coronado's horses were mares, so he was highly unlikely to have been the source of the horses that Plains Indians later adopted as the cornerstone of their culture.Haines, Francis. "The Northward Spread of Horses among the Plains Indians. ''American Anthropologist'', Vol 40, No. 3 (1988) In 1592, however, Juan de Oñate brought 7,000 head of livestock with him when he came north to establish a colony in New Mexico. His horse herd included mares as well as stallions.
Pueblo Indians
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Z ...
learned about horses by working for Spanish colonists. The Spanish attempted to keep knowledge of riding away from Native people, but nonetheless, they learned and some fled their servitude to their Spanish employers—and took horses with them. Some horses were obtained through trade in spite of prohibitions against it. Other horses escaped captivity for a feral
A feral () animal or plant is one that lives in the wild but is descended from domesticated individuals. As with an introduced species, the introduction of feral animals or plants to non-native regions may disrupt ecosystems and has, in some ...
existence and were captured by Native people. In all cases, the horse was adopted into their culture and herds multiplied. By 1659, the Navajo from northwestern New Mexico were raiding the Spanish colonies to steal horses. By 1664, the Apache were trading captives from other tribes to the Spanish for horses. The real beginning of the horse culture of the plains began with the Pueblo Revolt of 1680 in New Mexico and the capture of thousands of horses and other livestock. They traded many horses north to the Plains Indians. In 1683 a Spanish expedition into Texas found horses among Native people. In 1690, a few horses were found by the Spanish among the Indians living at the mouth of the Colorado River of Texas and the Caddo of eastern Texas had a sizeable number.
The French explorer Claude Charles Du Tisne Claude may refer to:
__NOTOC__ People and fictional characters
* Claude (given name), a list of people and fictional characters
* Claude (surname), a list of people
* Claude Lorrain (c. 1600–1682), French landscape painter, draughtsman and etcher ...
found 300 horses among the Wichita on the Verdigris River
The Verdigris River is a tributary of the Arkansas River in southeastern Kansas and northeastern Oklahoma in the United States. It is about long.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, ...
in 1719, but they were still not plentiful. Another Frenchman, Bourgmont, could only buy seven at a high price from the Kaw
Kaw or KAW may refer to:
Mythology
* Kaw (bull), a legendary bull in Meitei mythology
* Johnny Kaw, mythical settler of Kansas, US
* Kaw (character), in ''The Chronicles of Prydain''
People
* Kaw people, a Native American tribe
Places
* Kaw, Fr ...
in 1724, indicating that horses were still scarce among tribes in Kansas. While the distribution of horses proceeded slowly northward on the Great Plains, it moved more rapidly through the Rocky Mountains and the Great Basin. The Shoshone in Wyoming had horses by about 1700 and the Blackfoot people
The Blackfoot Confederacy, ''Niitsitapi'' or ''Siksikaitsitapi'' (ᖹᐟᒧᐧᒣᑯ, meaning "the people" or " Blackfoot-speaking real people"), is a historic collective name for linguistically related groups that make up the Blackfoot or Bla ...
, the most northerly of the large Plains tribes, acquired horses in the 1730s. By 1770, Plains horse culture
A horse culture is a tribal group or community whose day-to-day life revolves around the herding and breeding of horses. Beginning with the domestication of the horse on the steppes of Eurasia, the horse transformed each society that adopted it ...
was established, consisting of mounted bison-hunting nomads from Saskatchewan and Alberta southward nearly to the Rio Grande. Soon afterward, pressure from Europeans and Euro-Americans on all sides and European diseases caused its decline.
 It was the Comanche, coming to the attention of the Spanish in New Mexico in 1706, who first realized the potential of the horse. As nomads, hunters, and pastoralists, well supplied with horses, they swept most of the mixed-economy Apaches from the plains and by the 1730s were dominant in the Great Plains south of the Arkansas River. The success of the Comanche encouraged other Indian tribes to adopt a similar lifestyle. The southern Plains Indians acquired vast numbers of horses. By the 19th century, Comanche and Kiowa families owned an average of 35 horses and mules each – and only six or seven were necessary for transport and war. The horses extracted a toll on the environment as well as required labor to care for the herd. Formerly egalitarian societies became more divided by wealth with a negative impact on the role of women. The richest men would have several wives and captives who would help manage their possessions, especially horses.
The milder winters of the southern Plains favored a pastoral economy by the Indians. On the northeastern Plains of Canada, the Indians were less favored, with families owning fewer horses, remaining more dependent upon dogs for transporting goods, and hunting bison on foot. The scarcity of horses in the north encouraged raiding and warfare in competition for the relatively small number of horses that survived the severe winters.
The Lakota, also called Teton Sioux, enjoyed the happy medium between North and South and became a dominant Plains tribe by the mid-19th century. They had relatively small horse herds, thus having less impact on their ecosystem. At the same time, they occupied the heart of prime bison range which was also an excellent region for furs, which could be sold to French and American traders for goods such as guns. The Lakota became a highly powerful Plains tribe.
It was the Comanche, coming to the attention of the Spanish in New Mexico in 1706, who first realized the potential of the horse. As nomads, hunters, and pastoralists, well supplied with horses, they swept most of the mixed-economy Apaches from the plains and by the 1730s were dominant in the Great Plains south of the Arkansas River. The success of the Comanche encouraged other Indian tribes to adopt a similar lifestyle. The southern Plains Indians acquired vast numbers of horses. By the 19th century, Comanche and Kiowa families owned an average of 35 horses and mules each – and only six or seven were necessary for transport and war. The horses extracted a toll on the environment as well as required labor to care for the herd. Formerly egalitarian societies became more divided by wealth with a negative impact on the role of women. The richest men would have several wives and captives who would help manage their possessions, especially horses.
The milder winters of the southern Plains favored a pastoral economy by the Indians. On the northeastern Plains of Canada, the Indians were less favored, with families owning fewer horses, remaining more dependent upon dogs for transporting goods, and hunting bison on foot. The scarcity of horses in the north encouraged raiding and warfare in competition for the relatively small number of horses that survived the severe winters.
The Lakota, also called Teton Sioux, enjoyed the happy medium between North and South and became a dominant Plains tribe by the mid-19th century. They had relatively small horse herds, thus having less impact on their ecosystem. At the same time, they occupied the heart of prime bison range which was also an excellent region for furs, which could be sold to French and American traders for goods such as guns. The Lakota became a highly powerful Plains tribe.
Slaughter of the bison
Sun Dance
The Sun Dance is a ceremony practiced by some Native Americans in the United States and Indigenous peoples in Canada, primarily those of the Plains cultures. It usually involves the community gathering together to pray for healing. Individua ...
. These gatherings afforded leaders to meet to make political decisions, plan movements, arbitrate disputes, and organize and launch raiding expeditions or war parties. In the fall, people would split up into smaller bands to facilitate hunting to procure meat for the long winter. Between the fall hunt and the onset of winter was a time when Lakota warriors could undertake raiding and warfare. With the coming of winter snows, the Lakota settled into winter camps, where activities of the season ceremonies and dances as well as trying to ensure adequate winter feed for their horses. On the southern plains, with their milder winters, the fall and winter was often the raiding season. Beginning in the 1830s, the Comanche and their allies often raided for horses and other goods deep into Mexico, sometimes venturing 1,000 miles (1,600 km) south from their homes near the Red River in Texas and Oklahoma.
The U.S. federal government and local governments promoted bison hunting for various reasons: to allow ranchers to range their cattle without competition from other bovines and to starve and weaken the Plains Indian population to pressure them to remain on reservations. PDFhistory.msu.edu
The bison herds formed the basis of the economies of the Plains tribes. Without bison, they were forced to move onto reservations or starve. Bison were slaughtered for their skins, with the rest of the animal left behind to decay on the ground. After the animals rotted, their bones were collected and shipped back east in large quantities.
 The railroad industry also wanted bison herds culled or eliminated. Herds of bison on tracks could damage locomotives when the trains failed to stop in time. Herds often took shelter in the artificial cuts formed by the grade of the track winding through hills and mountains in harsh winter conditions. As a result, bison herds could delay a train for days.
As the great herds began to wane, proposals to protect the bison were discussed. Buffalo Bill Cody, among others, spoke in favor of protecting the bison because he saw that the pressure on the species was too great. But these were discouraged since it was recognized that the Plains Indians, often at war with the United States, depended on bison for their way of life. In 1874, President Ulysses S. Grant " pocket vetoed" a federal bill to protect the dwindling bison herds, and in 1875 General Philip Sheridan pleaded to a joint session of Congress to slaughter the herds, to deprive the Plains Indians of their source of food. This meant that the bison were hunted almost to extinction during the 19th century and were reduced to a few hundred by the early 1900s.
The railroad industry also wanted bison herds culled or eliminated. Herds of bison on tracks could damage locomotives when the trains failed to stop in time. Herds often took shelter in the artificial cuts formed by the grade of the track winding through hills and mountains in harsh winter conditions. As a result, bison herds could delay a train for days.
As the great herds began to wane, proposals to protect the bison were discussed. Buffalo Bill Cody, among others, spoke in favor of protecting the bison because he saw that the pressure on the species was too great. But these were discouraged since it was recognized that the Plains Indians, often at war with the United States, depended on bison for their way of life. In 1874, President Ulysses S. Grant " pocket vetoed" a federal bill to protect the dwindling bison herds, and in 1875 General Philip Sheridan pleaded to a joint session of Congress to slaughter the herds, to deprive the Plains Indians of their source of food. This meant that the bison were hunted almost to extinction during the 19th century and were reduced to a few hundred by the early 1900s.
Indian Wars
 Armed conflicts intensified in the late 19th century between Native American nations on the plains and the U.S. government, through what were called generally the Indian Wars. Notable conflicts in this period include the Dakota War,
Armed conflicts intensified in the late 19th century between Native American nations on the plains and the U.S. government, through what were called generally the Indian Wars. Notable conflicts in this period include the Dakota War, Great Sioux War
The Great Sioux War of 1876, also known as the Black Hills War, was a series of battles and negotiations that occurred in 1876 and 1877 in an alliance of Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne against the United States. The cause of the war was the ...
, Snake War and Colorado War
The Colorado War was an Indian War fought in 1864 and 1865 between the Southern Cheyenne, Arapaho, and allied Brulé and Oglala Sioux (or Lakota) peoples versus the U.S. army, Colorado militia, and white settlers in Colorado Territory and ad ...
. Comanche power peaked in the 1840s when they conducted large-scale raids hundreds of miles into Mexico proper, while also warring against the Anglo-Americans and Tejanos
Tejanos (, ; singular: ''Tejano/a''; Spanish for "Texan", originally borrowed from the Caddo ''tayshas'') are the residents of the state of Texas who are culturally descended from the Mexican population of Tejas and Coahuila that lived in th ...
who had settled in independent Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
. Expressing the frontier anti-Indian sentiment, Theodore Roosevelt believed the Indians were destined to vanish under the pressure of white civilization, stating in an 1886 lecture:
Among the most notable events during the wars was the Wounded Knee Massacre in 1890. In the years leading up to it the U.S. government had continued to seize Lakota
Lakota may refer to:
* Lakota people, a confederation of seven related Native American tribes
*Lakota language, the language of the Lakota peoples
Place names
In the United States:
* Lakota, Iowa
* Lakota, North Dakota, seat of Nelson County
* La ...
lands. A Ghost Dance ritual on the Northern Lakota reservation at Wounded Knee, South Dakota, led to the U.S. Army's attempt to subdue the Lakota. The dance was part of a religious movement founded by the Northern Paiute spiritual leader Wovoka
Wovoka (c. 1856 - September 20, 1932), also known as Jack Wilson, was the Paiute religious leader who founded a second episode of the Ghost Dance movement. Wovoka means "cutter" or "wood cutter" in the Northern Paiute language.
Biography
Wovo ...
that told of the return of the Messiah to relieve the suffering of Native Americans and promised that if they would live righteous lives and perform the Ghost Dance properly, the European American colonists would vanish, the bison would return, and the living and the dead would be reunited in an Edenic world. On December 29 at Wounded Knee, gunfire erupted, and U.S. soldiers killed up to 300 Indians, mostly old men, women, and children.
Material culture
Agriculture and plant foods
 The semi-sedentary, village-dwelling Plains Indians depended upon agriculture for a large share of their livelihood, particularly those who lived in the eastern parts of the Great Plains which had more precipitation than the western side. Corn was the dominant crop, followed by
The semi-sedentary, village-dwelling Plains Indians depended upon agriculture for a large share of their livelihood, particularly those who lived in the eastern parts of the Great Plains which had more precipitation than the western side. Corn was the dominant crop, followed by squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
and beans
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes thr ...
. Tobacco, sunflower, plums and other plants were also cultivated or gathered in the wild. Among the wild crops gathered the most important were probably berries to flavor pemmican
Pemmican (also pemican in older sources) is a mixture of tallow, dried meat, and sometimes dried berries. A calorie-rich food, it can be used as a key component in prepared meals or eaten raw. Historically, it was an important part of indigenou ...
and the Prairie Turnip.
The first indisputable evidence of maize cultivation on the Great Plains is about 900 AD. The earliest farmers, the Southern Plains villagers were probably Caddoan speakers, the ancestors of the Wichita, Pawnee Pawnee initially refers to a Native American people and its language:
* Pawnee people
* Pawnee language
Pawnee is also the name of several places in the United States:
* Pawnee, Illinois
* Pawnee, Kansas
* Pawnee, Missouri
* Pawnee City, Nebraska ...
, and Arikara
Arikara (), also known as Sahnish,
''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011)
of today. Plains farmers developed short-season and drought resistant varieties of food plants. They did not use irrigation but were adept at water harvesting and siting their fields to receive the maximum benefit of limited rainfall. The Hidatsa and Mandan of North Dakota cultivated maize at the northern limit of its range.
The farming tribes also hunted buffalo, deer, elk, and other game. Typically, on the southern Plains, they planted crops in the spring, left their permanent villages to hunt buffalo in the summer, returned to harvest crops in the fall, and left again to hunt bison in the winter. The farming Indians also traded corn to the nomadic tribes for dried buffalo meat.
With the arrival of the horse, some tribes, such as the Lakota and Cheyenne, gave up agriculture to become full-time, buffalo-hunting nomads.
By the 1870s bison herds were depleted and beef, cereal grains, fats and starchy vegetables became more important in the diet of Plains Indians. Fruits and nuts were, especially plums and grapes were dried as winter store. Flour was made from the Indian breadroot (''Pediomelum esculentum''). Indian tea (''''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011)
lespedeza
''Lespedeza'' is a genus of some 40 species (including nothospecies) of flowering plants in the pea family (Fabaceae), commonly known as bush clovers or (particularly East Asian species) Japanese clovers (''hagi''). The genus is native to warm t ...
'') is still sometimes consumed by Plains Indians who have retained these cultural traditions. Plums were one of the most important wild plant foods on the Oklahoma reservation.
Hunting
 Although people of the Plains hunted other animals, such as elk or
Although people of the Plains hunted other animals, such as elk or pronghorn
The pronghorn (, ) (''Antilocapra americana'') is a species of artiodactyl (even-toed, hoofed) mammal indigenous to interior western and central North America. Though not an antelope, it is known colloquially in North America as the American a ...
, buffalo was the primary game food source. Before horses were introduced, hunting was a more complicated process. Hunters would surround the bison, and then try to herd them off cliffs or into confined places where they could be more easily killed. The Plains Indians constructed a v-shaped funnel, about a mile long, made of fallen trees or rocks. Sometimes bison could be lured into a trap by a person covering himself with a bison skin and imitating the call of the animals.
Before their adoption of guns, the Plains Indians hunted with spears, bows, and various forms of club
Club may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Club'' (magazine)
* Club, a '' Yie Ar Kung-Fu'' character
* Clubs (suit), a suit of playing cards
* Club music
* "Club", by Kelsea Ballerini from the album ''kelsea''
Brands and enterprises ...
s. The use of horses by the Plains Indians made hunting (and warfare) much easier. With horses, the Plains Indians had the means and speed to stampede or overtake the bison. The Plains Indians reduced the length of their bows to three feet to accommodate their use on horseback. They continued to use bows and arrows after the introduction of firearms because guns took too long to reload and were too heavy. In the summer, many tribes gathered for hunting in one place. The main hunting seasons were fall, summer, and spring. In winter, adverse weather such as snow and blizzards made it more difficult to locate and hunt bison.
Clothing
Hides, with or without fur, provided material for much clothing. Most of the clothing consisted of the hides of buffalo and deer, as well as numerous species of birds and other small game. Plains moccasins tended to be constructed with soft braintanned hide on the vamps and tough rawhide for the soles. Men's moccasins tended to have flaps around the ankles, while women's had high tops, which could be pulled up in the winter and rolled down in the summer. Honored warriors and leaders earn the right to wear war bonnets, headdresses with feathers, often of golden or bald eagles.Society and culture
Religion

 While there are some similarities among linguistic and regional groups, different tribes have their own cosmologies and world views. Some of these are animist in nature, with aspects of polytheism, while others tend more towards monotheism or panentheism. Prayer is a regular part of daily life, for regular individuals as well as spiritual leaders, alone and as part of group ceremonies. One of the most important gatherings for many of the Plains tribes is the yearly
While there are some similarities among linguistic and regional groups, different tribes have their own cosmologies and world views. Some of these are animist in nature, with aspects of polytheism, while others tend more towards monotheism or panentheism. Prayer is a regular part of daily life, for regular individuals as well as spiritual leaders, alone and as part of group ceremonies. One of the most important gatherings for many of the Plains tribes is the yearly Sun Dance
The Sun Dance is a ceremony practiced by some Native Americans in the United States and Indigenous peoples in Canada, primarily those of the Plains cultures. It usually involves the community gathering together to pray for healing. Individua ...
, an elaborate spiritual ceremony that involves personal sacrifice, multiple days of fasting and prayer for the good of loved ones and the benefit of the entire community.
Certain people are considered to be ''wakan'' (Lakota
Lakota may refer to:
* Lakota people, a confederation of seven related Native American tribes
*Lakota language, the language of the Lakota peoples
Place names
In the United States:
* Lakota, Iowa
* Lakota, North Dakota, seat of Nelson County
* La ...
: "holy"), and go through many years of training to become medicine men
A medicine man is a traditional healer and spiritual leader among the indigenous people of the Americas.
Medicine Man or The Medicine Man may also refer to:
Films
* ''The Medicine Man'' (1917 film), an American silent film directed by Clifford S ...
or women, entrusted with spiritual leadership roles in the community. The buffalo and eagle are particularly sacred to many of the Plains peoples, and may be represented in iconography, or parts used in regalia
Regalia is a Latin plurale tantum word that has different definitions. In one rare definition, it refers to the exclusive privileges of a sovereign. The word originally referred to the elaborate formal dress and dress accessories of a sovereig ...
. In Plains cosmology, certain items may possess spiritual power, particularly medicine bundles which are only entrusted to prominent religious figures of a tribe, and passed down from keeper to keeper in each succeeding generation.
Gender roles
Historically, Plains Indian women had distinctly defined gender roles that were different from, but complementary to, men's roles. They typically owned the family's home and the majority of its contents.Wishart, David J"Native American Gender Roles."
''Encyclopedia of the Great Plains.'' Retrieved 15 Oct 2013. In traditional culture, women tanned hides, tended crops, gathered wild foods, prepared food, made clothing, and took down and erected the family's tepees. In the present day, these customs are still observed when lodges are set up for ceremonial use, such as at pow wows. Historically, Plains women were not as engaged in public political life as were the women in the coastal tribes. However, they still participated in an advisory role and through the women's societies. In contemporary Plains cultures, traditionalists work to preserve the knowledge of these traditions of everyday life and the values attached to them. Plains women in general have historically had the right to divorce and keep custody of their children. Because women own the home, an unkind husband can find himself homeless. A historical example of a Plains woman divorcing is Making Out Road, a Cheyenne woman, who in 1841 married non-Native frontiersman
Kit Carson
Christopher Houston Carson (December 24, 1809 – May 23, 1868) was an American frontiersman. He was a fur trapper, wilderness guide, Indian agent, and U.S. Army officer. He became a frontier legend in his own lifetime by biographies and ...
. The marriage was turbulent and formally ended when Making Out Road threw Carson and his belongings out of her tepee (in the traditional manner of announcing a divorce). She later went on to marry, and divorce, several additional men, both European-American and Indian.
Warfare
Main article: Plains Indians Warfare The earliest 16th-century Spanish explorers did not find the Plains Indians especially warlike. The Wichita in Kansas and Oklahoma lived in dispersed settlements with few defensive works. The Spanish initially had friendly contacts with the Apache (
The earliest 16th-century Spanish explorers did not find the Plains Indians especially warlike. The Wichita in Kansas and Oklahoma lived in dispersed settlements with few defensive works. The Spanish initially had friendly contacts with the Apache (Querechos
The Querechos were a Native American people.
In 1541 the Spanish conquistador Francisco Vásquez de Coronado and his army journeyed east from the Rio Grande Valley in search of a rich land called Quivira. Passing through what would later be the ...
) in the Texas Panhandle.
Three factors led to a growing importance of warfare in Plains Indian culture. First, was the Spanish colonization of New Mexico which stimulated raids and counter-raids by Spaniards and Indians for goods and slaves. Second, was the contact of the Indians with French fur traders which increased rivalry among Indian tribes to control trade and trade routes. Third, was the acquisition of the horse and the greater mobility it afforded the Plains Indians. What evolved among the Plains Indians from the 17th to the late 19th century was warfare as both a means of livelihood and a sport. Young men gained both prestige and plunder by fighting as warriors, and this individualistic style of warfare ensured that success in individual combat and capturing trophies of war were highly esteemed Robinson, Charles ''The Plains Wars 1757-1900'', London: Osprey, 2003
The Plains Indians raided each other, the Spanish colonies, and, increasingly, the encroaching frontier of the Anglos for horses, and other property. They acquired guns and other European goods primarily by trade. Their principal trading products were buffalo hides and beaver pelts. The most renowned of all the Plains Indians as warriors were the Comanche whom ''The Economist'' noted in 2010: "They could loose a flock of arrows while hanging off the side of a galloping horse, using the animal as protection against return fire. The sight amazed and terrified their white (and Indian) adversaries." The American historian S. C. Gwynne called the Comanche "the greatest light cavalry on the earth" in the 19th century whose raids in Texas terrified the American settlers.
Although they could be tenacious in defense, Plains Indians warriors took the offensive mostly for material gain and individual prestige. The highest military honors were for "counting coup
Among the Plains Indians of North America, counting coup is the warrior tradition of winning prestige against an enemy in battle. It is one of the traditional ways of showing bravery in the face of an enemy and involves intimidating him, and, it ...
"—touching a live enemy. Battles between Indians often consisted of opposing warriors demonstrating their bravery rather than attempting to achieve concrete military objectives. The emphasis was on ambush and hit and run actions rather than closing with an enemy. Success was often counted by the number of horses or property obtained in the raid. Casualties were usually light. "Indians consider it foolhardiness to make an attack where it is certain some of them will be killed." Given their smaller numbers, the loss of even a few men in battle could be catastrophic for a band, and notably at the battles of Adobe Walls in Texas in 1874 and Rosebud in Montana in 1876, the Indians broke off battle despite the fact that they were winning as the casualties were not considered worth a victory. The most famous victory ever won by the Plains Indians over the United States, the Battle of Little Bighorn, in 1876, was won by the Lakota (Sioux) and Cheyenne fighting on the defensive. Decisions whether to fight or not were based on a cost-benefit ratio; even the loss of one warrior was not considered to be worth taking a few scalps, but if a herd of horses could be obtained, the loss of a warrior or two was considered acceptable. Generally speaking, given the small sizes of the bands and the vast population of the United States, the Plains Indians sought to avoid casualties in battle, and would avoid fighting if it meant losses.
 Due to their mobility, endurance, horsemanship, and knowledge of the vast plains that were their domain, the Plains Indians were often victors in their battles against the U.S. army in the American era from 1803 to about 1890. However, although Indians won many battles, they could not undertake lengthy campaigns. Indian armies could only be assembled for brief periods of time as warriors also had to hunt for food for their families. The exception to that was raids into Mexico by the Comanche and their allies in which the raiders often subsisted for months off the riches of Mexican haciendas and settlements. The basic weapon of the Indian warrior was the short, stout bow, designed for use on horseback and deadly, but only at short range. Guns were usually in short supply and ammunition scarce for Native warriors. The U.S. government through the Indian Agency would sell the Plains Indians guns for hunting, but unlicensed traders would exchange guns for buffalo hides. The shortages of ammunition together with the lack of training to handle firearms meant the preferred weapon was the bow and arrow.
Due to their mobility, endurance, horsemanship, and knowledge of the vast plains that were their domain, the Plains Indians were often victors in their battles against the U.S. army in the American era from 1803 to about 1890. However, although Indians won many battles, they could not undertake lengthy campaigns. Indian armies could only be assembled for brief periods of time as warriors also had to hunt for food for their families. The exception to that was raids into Mexico by the Comanche and their allies in which the raiders often subsisted for months off the riches of Mexican haciendas and settlements. The basic weapon of the Indian warrior was the short, stout bow, designed for use on horseback and deadly, but only at short range. Guns were usually in short supply and ammunition scarce for Native warriors. The U.S. government through the Indian Agency would sell the Plains Indians guns for hunting, but unlicensed traders would exchange guns for buffalo hides. The shortages of ammunition together with the lack of training to handle firearms meant the preferred weapon was the bow and arrow.
Research
The people of the Great Plains have been found to be the tallest people in the world during the late 19th century, based on 21st century analysis of data collected by Franz Boas for theWorld Columbian Exposition
The World's Columbian Exposition (also known as the Chicago World's Fair) was a world's fair held in Chicago in 1893 to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1492. The centerpiece of the Fair, hel ...
. This information is significant to anthropometric
Anthropometry () refers to the measurement of the human individual. An early tool of physical anthropology, it has been used for identification, for the purposes of understanding human physical variation, in paleoanthropology and in various atte ...
historians, who usually equate the height of populations with their overall health and standard of living., Jeff Grabmeier, Ohio State
Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies
Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains are often separated into Northern and Southern Plains tribes. * Anishinaabe (Anishinape, Anicinape, Neshnabé, Nishnaabe) (see also Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands) ** Saulteaux (Nakawē), Manitoba, Minnesota and Ontario; later Alberta, British Columbia, Montana, Saskatchewan * Apache (see alsoSouthwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
)
**Lipan Apache
Lipan Apache are a band of Apache, a Southern Athabaskan Indigenous people, who have lived in the Southwest and Southern Plains for centuries. At the time of European and African contact, they lived in New Mexico, Colorado, Oklahoma, Texas, and ...
, New Mexico, Texas
** Plains Apache (Kiowa Apache
The Plains Apache are a small Southern Athabaskan group who live on the Southern Plains of North America, in close association with the linguistically unrelated Kiowa Tribe. Today, they are centered in Southwestern Oklahoma and Northern Texas a ...
), Oklahoma
** Querecho Apache, Texas
*Arapaho
The Arapaho (; french: Arapahos, ) are a Native American people historically living on the plains of Colorado and Wyoming. They were close allies of the Cheyenne tribe and loosely aligned with the Lakota and Dakota.
By the 1850s, Arapaho ba ...
(Arapahoe), formerly Colorado, currently Oklahoma and Wyoming
** Besawunena
** Nawathinehena
*Arikara
Arikara (), also known as Sahnish,
''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011)
(Arikaree, Arikari, Ree), North Dakota
* Atsina (Gros Ventre), Montana
* Blackfoot
** Kainai Nation (Káínaa, Blood), Alberta
** Northern Peigan (Aapátohsipikáni), Alberta
**''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011)
Blackfeet
The Blackfeet Nation ( bla, Aamsskáápipikani, script=Latn, ), officially named the Blackfeet Tribe of the Blackfeet Indian Reservation of Montana, is a federally recognized tribe of Siksikaitsitapi people with an Indian reservation in Mon ...
, Southern Piegan (Aamsskáápipikani), Montana
**Siksika
The Siksika Nation ( bla, Siksiká) is a First Nations in Canada, First Nation in southern Alberta, Canada. The name ''Siksiká'' comes from the Blackfoot language, Blackfoot words ''sik'' (black) and ''iká'' (foot), with a connector ''s'' bet ...
(Siksikáwa), Alberta
* Cheyenne, Montana, Oklahoma
**Suhtai
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enroll ...
, Montana, Oklahoma
* Comanche, Oklahoma, Texas
* Plains Cree, Montana, Saskatchewan, Alberta, Manitoba
*Crow
A crow is a bird of the genus '' Corvus'', or more broadly a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. Crows are generally black in colour. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not pinned scientifica ...
(Absaroka, Apsáalooke), Montana
* Escanjaques, Oklahoma
* Hidatsa, North Dakota
* Iowa (Ioway), Kansas, Nebraska, Oklahoma
*Kaw
Kaw or KAW may refer to:
Mythology
* Kaw (bull), a legendary bull in Meitei mythology
* Johnny Kaw, mythical settler of Kansas, US
* Kaw (character), in ''The Chronicles of Prydain''
People
* Kaw people, a Native American tribe
Places
* Kaw, Fr ...
(Kansa, Kanza), Kansas, Oklahoma
* Kiowa, Oklahoma
* Mandan, North Dakota
* Métis people (Canada), North Dakota, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta
* Missouri (Missouria), Oklahoma
* Omaha, Nebraska
* Osage, Oklahoma, formerly Arkansas, Missouri
*Otoe
The Otoe (Chiwere: Jiwére) are a Native American people of the Midwestern United States. The Otoe language, Chiwere, is part of the Siouan family and closely related to that of the related Iowa, Missouria, and Ho-Chunk tribes.
Historically, t ...
(Oto), Oklahoma, formerly Missouri
*Pawnee Pawnee initially refers to a Native American people and its language:
* Pawnee people
* Pawnee language
Pawnee is also the name of several places in the United States:
* Pawnee, Illinois
* Pawnee, Kansas
* Pawnee, Missouri
* Pawnee City, Nebraska ...
, Oklahoma
** Chaui, Oklahoma"Preamble.''Constitution of the Pawnee Nation of Oklahoma.''
Retrieved 5 Dec 2012. ** Kitkehakhi, Oklahoma ** Pitahawirata, Oklahoma ** Skidi, Oklahoma * Ponca, Nebraska, Oklahoma *
Quapaw
The Quapaw ( ; or Arkansas and Ugahxpa) people are a tribe of Native Americans that coalesced in what is known as the Midwest and Ohio Valley of the present-day United States. The Dhegiha Siouan-speaking tribe historically migrated from the Oh ...
, formerly Arkansas, Oklahoma
* Sioux (Očhéthi Šakówiŋ, Seven Council Fires)
**Dakota
Dakota may refer to:
* Dakota people, a sub-tribe of the Sioux
** Dakota language, their language
Dakota may also refer to:
Places United States
* Dakota, Georgia, an unincorporated community
* Dakota, Illinois, a town
* Dakota, Minnesota, ...
, Minnesota, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, South Dakota, Manitoba, Saskatchewan
*** Bdewékhaŋthuŋwaŋ (Spirit Lake Village)
*** Sisíthuŋwaŋ (Swamp/lake/fish Scale Village)
*** Waȟpékhute (Leaf Archers)
*** Waȟpéthuŋwaŋ (Leaf Village)
*** Iháŋkthuŋwaŋ (End Village)
*** Iháŋkthuŋwaŋna (Little End Village)
**Lakota
Lakota may refer to:
* Lakota people, a confederation of seven related Native American tribes
*Lakota language, the language of the Lakota peoples
Place names
In the United States:
* Lakota, Iowa
* Lakota, North Dakota, seat of Nelson County
* La ...
(Thítȟuŋwaŋ, Dwellers on the Prairies), Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Saskatchewan
*** Sičháŋǧu (Brulé, Burned Thighs)
*** Oglála (Scatters Their Own)
*** Itázipčho (Sans Arc, No Bows)
*** Húŋkpapȟa (Hunkpapa)
*** Mnikȟówožu (Miniconjou)
*** Sihásapa (Blackfoot Sioux)
*** Oóhenuŋpa (Two Kettles)
** Nakoda (Stoney), Alberta
** Nakota, Assiniboine
The Assiniboine or Assiniboin people ( when singular, Assiniboines / Assiniboins when plural; Ojibwe: ''Asiniibwaan'', "stone Sioux"; also in plural Assiniboine or Assiniboin), also known as the Hohe and known by the endonym Nakota (or Nakod ...
(Assiniboin), Montana, Saskatchewan
*Teyas
Teyas were a Native American people living near Lubbock, Texas who first made contact with Europeans in 1541 when Francisco Vásquez de Coronado traveled to them.
The tribal affiliation and language of the Teyas is unknown, although many scholars ...
, Texas
*Tonkawa
The Tonkawa are a Native American tribe indigenous to present-day Oklahoma. Their Tonkawa language, now extinct, is a linguistic isolate.
Today, Tonkawa people are enrolled in the federally recognized Tonkawa Tribe of Indians of Oklahoma. ...
, Oklahoma
* Tsuu T'ina, (Sarcee, Sarsi, Tsuut'ina), Alberta
* Wichita and Affiliated Tribes ( Kitikiti'sh), Oklahoma, formerly Texas and Kansas
** Kichai (also related to the Caddo), Oklahoma, formerly Texas and Kansas
** Taovayas ( Tawehash), Oklahoma, formerly Texas and Kansas
**Tawakoni
The Tawakoni (also Tahuacano and Tehuacana) are a Southern Plains Native American tribe, closely related to the Wichitas. They historically spoke a Wichita language of the Caddoan language family. Currently, they are enrolled in the Wichita a ...
, Oklahoma, formerly Texas and Kansas
** Waco ( Iscani, Yscani), Oklahoma, formerly Texas
** Wichita proper, Guichita
The Wichita people or Kitikiti'sh are a confederation of Southern Plains Native American tribes. Historically they spoke the Wichita language and Kichai language, both Caddoan languages. They are indigenous to Oklahoma, Texas, and Kansas.
To ...
, Rayados, Oklahoma, formerly Texas and Kansas
See also
* Comanche-Mexico Wars * Plains Standard Sign Language *Plains hide painting Plains hide painting is a traditional Plains Indian artistic practice of painting on either tanned or raw animal hides. Tipis, tipi liners, shields, parfleches, robes, clothing, drums, and winter counts could all be painted.
Genres
Art historian ...
* Hair drop, Plains men's adornment
* Native American tribes in Nebraska
* Buffalo jump
A buffalo jump, or sometimes bison jump, is a cliff formation which Indigenous peoples of North America historically used to hunt and kill plains bison in mass quantities. The broader term game jump refers to a man-made jump or cliff used for hu ...
* Southern Plains villagers
References
Further reading
* * Carlson, Paul H. (1998) ''The Plains Indians''. College Station: Texas A&M University Press. * * * * * * Sturtevant, William C., general editor, and Bruce G. Trigger, volume editor. ''Handbook of North American Indians: Northeast''. Volume 15. Washington DC: Smithsonian Institution, 1978. ASIN B000NOYRRA. * Taylor, Colin E. (1994) ''The Plains Indians: A Cultural and Historical View of the North American Plains Tribes of the Pre-Reservation Period''. Crescent. .See also
* Great Plains Indian Trading Networks before Lewis and ClarkExternal links
Great Plains Indians Musical Instruments
on the Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History,
The Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
"American Indian Contributions To Science and Technology"
, Chris R. Landon, Portland Public Schools, 1993
"Buffalo and the Plains Indians"
South Dakota State Historical Society Education Kit {{DEFAULTSORT:Plains Indians
Plains
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands.
In ...
Indigenous peoples of North America
Native American tribes
Midwestern United States
Western United States