Pitching moment on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
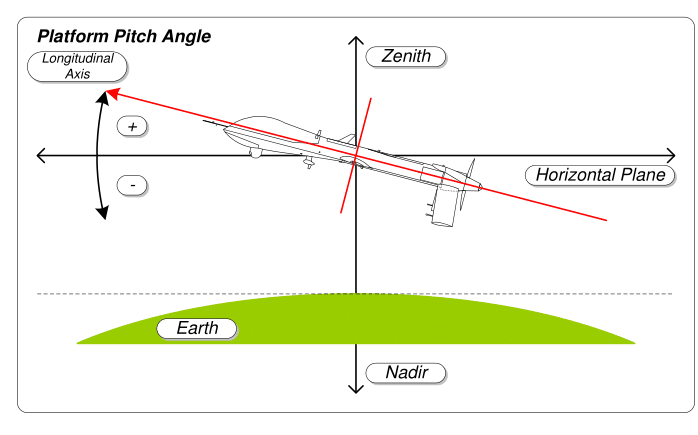
 In
In
 *
*
Low-Speed Stability
Retrieved on 2008-07-18 Aerodynamics Aerospace engineering Gliding technology

aerodynamics
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dy ...
, the pitching moment on an airfoil
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is the cross-sectional shape of an object whose motion through a gas is capable of generating significant lift, such as a wing, a sail, or the blades of propeller, rotor, or turbin ...
is the moment
Moment or Moments may refer to:
* Present time
Music
* The Moments, American R&B vocal group Albums
* ''Moment'' (Dark Tranquillity album), 2020
* ''Moment'' (Speed album), 1998
* ''Moments'' (Darude album)
* ''Moments'' (Christine Guldbrand ...
(or torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of th ...
) produced by the aerodynamic force on the airfoil if that aerodynamic force is considered to be applied, not at the center of pressure, but at the aerodynamic center
In aerodynamics, the torques or moments acting on an airfoil moving through a fluid can be accounted for by the net lift and net drag applied at some point on the airfoil, and a separate net pitching moment about that point whose magni ...
of the airfoil. The pitching moment on the wing of an airplane is part of the total moment that must be balanced using the lift on the horizontal stabilizer. More generally, a pitching moment is any moment acting on the pitch axis of a moving body.
The lift on an airfoil is a distributed force that can be said to act at a point called the center of pressure. However, as angle of attack changes on a cambered airfoil, there is movement of the center of pressure forward and aft. This makes analysis difficult when attempting to use the concept of the center of pressure. One of the remarkable properties of a cambered airfoil is that, even though the center of pressure moves forward and aft, if the lift is imagined to act at a point called the aerodynamic center
In aerodynamics, the torques or moments acting on an airfoil moving through a fluid can be accounted for by the net lift and net drag applied at some point on the airfoil, and a separate net pitching moment about that point whose magni ...
, the moment of the lift force changes in proportion to the square of the airspeed. If the moment is divided by the dynamic pressure, the area and chord of the airfoil, the result is known as the pitching moment coefficient. This coefficient changes only a little over the operating range of angle of attack of the airfoil but the change in moment slope against the AOA shown in figure below seems very steep so this should be of change in pitching moment of wing about CG rather than about AC. The combination of the two concepts of ''aerodynamic center'' and ''pitching moment coefficient'' make it relatively simple to analyse some of the flight characteristics of an aircraft.
Measurement
Theaerodynamic center
In aerodynamics, the torques or moments acting on an airfoil moving through a fluid can be accounted for by the net lift and net drag applied at some point on the airfoil, and a separate net pitching moment about that point whose magni ...
of an airfoil is usually close to 25% of the chord behind the leading edge of the airfoil. When making tests on a model airfoil, such as in a wind-tunnel, if the force sensor is not aligned with the quarter-chord of the airfoil, but offset by a distance x, the pitching moment about the quarter-chord point, is given by
:
where the indicated values of ''D'' and ''L'' are the drag and lift on the model, as measured by the force sensor.
Coefficient
The pitching moment coefficient is important in the study of the longitudinal static stability of aircraft and missiles. The ''pitching moment coefficient'' is defined as follows : where ''M'' is the pitching moment, ''q'' is the dynamic pressure, ''S'' is thewing area
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is express ...
, and ''c'' is the length of the chord of the airfoil.
is a dimensionless coefficient so consistent units must be used for ''M'', ''q'', ''S'' and ''c''.
Pitching moment coefficient is fundamental to the definition of aerodynamic center
In aerodynamics, the torques or moments acting on an airfoil moving through a fluid can be accounted for by the net lift and net drag applied at some point on the airfoil, and a separate net pitching moment about that point whose magni ...
of an airfoil. The ''aerodynamic center'' is defined to be the point on the chord line of the airfoil at which the ''pitching moment coefficient'' does not vary with angle of attack, or at least does not vary significantly over the operating range of angle of attack of the airfoil.
In the case of a symmetric airfoil, the lift force acts through one point for all angles of attack, and the ''center of pressure'' does not move as it does in a cambered airfoil. Consequently, the ''pitching moment coefficient'' about this point for a symmetric airfoil is zero.
The pitching moment is, by convention, considered to be positive when it acts to pitch the airfoil in the nose-up direction. Conventional cambered airfoils supported at the aerodynamic center pitch nose-down so the ''pitching moment coefficient'' of these airfoils is negative.Ira H. Abbott, and Albert E. Von Doenhoff (1959), ''Theory of Wing Sections'', Dover Publications Inc., New York SBN 486-60586-8See also
Aircraft flight mechanics
Aircraft flight mechanics are relevant to fixed wing ( gliders, aeroplanes) and rotary wing (helicopters) aircraft. An aeroplane (''airplane'' in US usage), is defined in ICAO Document 9110 as, "a power-driven heavier than air aircraft, deriving i ...
* Flight dynamics
Flight dynamics in aviation and spacecraft, is the study of the performance, stability, and control of vehicles flying through the air or in outer space. It is concerned with how forces acting on the vehicle determine its velocity and attitude ...
* Longitudinal static stability
* Neutral point
Ground and neutral are circuit conductors used in alternating current electrical systems. The ground circuit is connected to earth, and neutral circuit is usually connected to ground. As the neutral point of an electrical supply system is often ...
* Lift coefficient
* Drag coefficientReferences
Bibliography
* L. J. Clancy (1975), ''Aerodynamics'', Pitman Publishing Limited, London, {{ISBN, 0-273-01120-0 * Piercy, N.A.V (1943) ''Aerodynamics'', pages 384–386, English Universities Press. LondonLow-Speed Stability
Retrieved on 2008-07-18 Aerodynamics Aerospace engineering Gliding technology