Phenobarbital on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Phenobarbital, also known as phenobarbitone or phenobarb, sold under the brand name Luminal among others, is a
 The second approach utilizes
The second approach utilizes 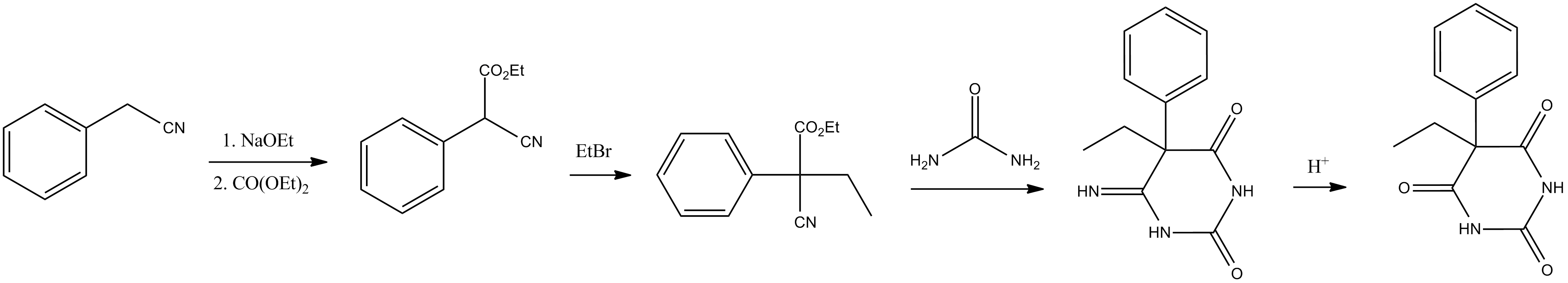 A new synthetic route based on diethyl 2-ethyl-2-phenylmalonate and urea has been described.
A new synthetic route based on diethyl 2-ethyl-2-phenylmalonate and urea has been described.
medication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
of the barbiturate
Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential a ...
type. It is recommended by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
(WHO) for the treatment of certain types of epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
. In the developed world, it is commonly used to treat seizures in young children, while other medications are generally used in older children and adults. In developed countries it is used for veterinary purposes. It may be used intravenously, injected into a muscle, or taken by mouth. The injectable form may be used to treat status epilepticus
Status epilepticus (SE), or status seizure, is a single seizure lasting more than 5 minutes or 2 or more seizures within a 5-minute period without the person returning to normal between them. Previous definitions used a 30-minute time limit. The s ...
. Phenobarbital is occasionally used to treat trouble sleeping
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder in which people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy, ...
, anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
, and drug withdrawal
Drug withdrawal, drug withdrawal syndrome, or substance withdrawal syndrome, is the group of symptoms that occur upon the abrupt discontinuation or decrease in the intake of pharmaceutical or recreational drugs.
In order for the symptoms of w ...
and to help with surgery. It usually begins working within five minutes when used intravenously and half an hour when administered by mouth. Its effects last for between four hours and two days.
Side effects include a decreased level of consciousness
An altered level of consciousness is any measure of arousal other than normal. Level of consciousness (LOC) is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to stimuli from the environment.
A mildly depressed level of consciousne ...
along with a decreased effort to breathe. There is concern about both abuse
Abuse is the improper usage or treatment of a thing, often to unfairly or improperly gain benefit. Abuse can come in many forms, such as: physical or verbal maltreatment, injury, assault, violation, rape, unjust practices, crimes, or other t ...
and withdrawal following long-term use. It may also increase the risk of suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and ...
. It is pregnancy category
The pregnancy category of a medication is an assessment of the risk of fetal injury due to the pharmaceutical, if it is used as directed by the mother during pregnancy. It does ''not'' include any risks conferred by pharmaceutical agents or their ...
B or D (depending on how it is taken) in the United States and category D in Australia, meaning that it may cause harm when taken by pregnant women. If used during breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that bre ...
it may result in drowsiness in the baby. A lower dose is recommended in those with poor liver or kidney function, as well as elderly people. Phenobarbital, like other barbiturates works by increasing the activity of the inhibitory neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neu ...
GABA.
Phenobarbital was discovered in 1912 and is the oldest still commonly used anti-seizure medication. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.
Medical uses
Phenobarbital is used in the treatment of all types of seizures, exceptabsence seizure
Absence seizures are one of several kinds of generalized seizures. These seizures are sometimes referred to as petit mal seizures (from the French for "little illness", a term dated in the late 18th century). Absence seizures are characterized by ...
s.British National Formulary
The ''British National Formulary'' (BNF) is a United Kingdom (UK) pharmaceutical reference book that contains a wide spectrum of information and advice on prescribing and pharmacology, along with specific facts and details about many medici ...
51 It is no less effective at seizure control than phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence seizures. The in ...
, but phenobarbital is not as well tolerated. Phenobarbital may provide a clinical advantage over carbamazepine
Carbamazepine (CBZ), sold under the trade name Tegretol among others, is an anticonvulsant medication used primarily in the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It is used as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia along with other m ...
for treating partial onset seizures. Carbamazepine may provide a clinical advantage over phenobarbital for generalized onset tonic-clonic seizures. Its very long active half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ...
(53–118 hours) means for some people doses do not have to be taken every day, particularly once the dose has been stabilized over a period of several weeks or months, and seizures are effectively controlled.
The first-line drugs for treatment of status epilepticus
Status epilepticus (SE), or status seizure, is a single seizure lasting more than 5 minutes or 2 or more seizures within a 5-minute period without the person returning to normal between them. Previous definitions used a 30-minute time limit. The s ...
are benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, ...
s, such as lorazepam
Lorazepam, sold under the brand name Ativan among others, is a benzodiazepine medication. It is used to treat anxiety disorders, trouble sleeping, severe agitation, active seizures including status epilepticus, alcohol withdrawal, and che ...
or diazepam. If these fail, then phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence seizures. The in ...
may be used, with phenobarbital being an alternative in the US, but used only third-line in the UK. Failing that, the only treatment is anaesthesia in intensive care. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
(WHO) gives phenobarbital a first-line recommendation in the developing world and it is commonly used there.
Phenobarbital is the first-line choice for the treatment of neonatal seizure
A neonatal seizure is a seizure in a baby younger than age 4-weeks that is identifiable by an electrical recording of the brain. It is an occurrence of abnormal, paroxysmal, and persistent ictal rhythm with an amplitude of 2 microvolts in the elec ...
s. Concerns that neonatal seizures in themselves could be harmful make most physicians treat them aggressively. No reliable evidence, though, supports this approach.
Phenobarbital is sometimes used for alcohol detoxification and benzodiazepine detoxification for its sedative and anti-convulsant properties. The benzodiazepines chlordiazepoxide (Librium) and oxazepam (Serax) have largely replaced phenobarbital for detoxification.
Phenobarbital is useful for insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder in which people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy, ...
and anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
.
Other uses
Phenobarbital properties can effectively reduce tremors and seizures associated with abrupt withdrawal from benzodiazepines. Phenobarbital is acytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various co ...
inducer, and is used to reduce the toxicity of some drugs.
Phenobarbital is occasionally prescribed in low doses to aid in the conjugation of bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) ( Latin for "red bile") is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from t ...
in people with Crigler–Najjar syndrome, type II, or in people with Gilbert's syndrome.
Phenobarbital can also be used to relieve cyclic vomiting syndrome
Cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS) is a chronic functional condition of unknown pathogenesis. CVS is characterized as recurring episodes lasting a single day to multiple weeks. Each episode is divided into four phases: inter-episodic, prodrome, vo ...
symptoms.
Phenobarbital is a commonly used agent in high purity and dosage for lethal injection
Lethal injection is the practice of injecting one or more drugs into a person (typically a barbiturate, paralytic, and potassium solution) for the express purpose of causing rapid death. The main application for this procedure is capital puni ...
of "death row" criminals.
In infants suspected of neonatal biliary atresia
Biliary atresia, also known as extrahepatic ductopenia and progressive obliterative cholangiopathy, is a childhood disease of the liver in which one or more bile ducts are abnormally narrow, blocked, or absent. It can be congenital or acquired. I ...
, phenobarbital is used in preparation for a 99mTc-IDA hepatobiliary ( HIDA; hepatobiliary 99mTc-iminodiacetic acid) study that differentiates atresia from hepatitis
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes ( jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal ...
or cholestasis.
Phenobarbital is used as a secondary agent to treat newborns with neonatal abstinence syndrome, a condition of withdrawal symptoms from exposure to opioid drugs '' in utero''.
In massive doses, phenobarbital is prescribed to terminally ill people to allow them to end their life through physician-assisted suicide
Assisted suicide is suicide undertaken with the aid of another person. The term usually refers to physician-assisted suicide (PAS), which is suicide that is assisted by a physician or other healthcare provider. Once it is determined that the p ...
.
Like other barbiturates, phenobarbital can be used recreationally, but this is reported to be relatively infrequent.
The synthesis of a photoswitchable analog (DASA-barbital) and phenobarbital has been described for use as research compound in photopharmacology.
Side effects
Sedation and hypnosis are the principal side effects (occasionally, they are also the intended effects) of phenobarbital.Central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
effects, such as dizziness, nystagmus and ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements. Ataxia is a clinical manifestation indicating dysfunction of ...
, are also common. In elderly patients, it may cause excitement and confusion, while in children, it may result in paradoxical hyperactivity.
Phenobarbital is a cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various co ...
hepatic enzyme inducer. It binds transcription factor receptors that activate cytochrome P450 transcription, thereby increasing its amount and thus its activity. Due to this higher amount of CYP450, drugs that are metabolized by the CYP450 enzyme system will have decreased effectiveness. This is because the increased CYP450 activity increases the clearance of the drug, reducing the amount of time they have to work.
Caution is to be used with children. Among anti-convulsant drugs, behavioural disturbances occur most frequently with clonazepam and phenobarbital.
Contraindications
Acute intermittent porphyria, hypersensitivity to any barbiturate, prior dependence on barbiturates, severe respiratory insufficiency (as withchronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce ...
), severe liver failure, pregnancy, and breastfeeding are contraindications for phenobarbital use.
Overdose
Phenobarbital causes a depression of the body's systems, mainly thecentral
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
and peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brai ...
s. Thus, the main characteristic of phenobarbital overdose is a "slowing" of bodily functions, including decreased consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scien ...
(even coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
), bradycardia
Bradycardia (also sinus bradycardia) is a slow resting heart rate, commonly under 60 beats per minute (BPM) as determined by an electrocardiogram. It is considered to be a normal heart rate during sleep, in young and healthy or elderly adults, ...
, bradypnea
Bradypnea is abnormally slow breathing. The respiratory rate at which bradypnea is diagnosed depends on the age of the person, with the limit higher during childhood.
Age ranges
* Age 0–1 year < 30 breaths per minute
* Age 1–3 years < 25 br ...
, hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe ...
, and hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the di ...
(in massive overdoses). Overdose may also lead to pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive liquid accumulation in the tissue and air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia and respiratory failure. It is due ...
and acute renal failure as a result of shock
Shock may refer to:
Common uses Collective noun
*Shock, a historic commercial term for a group of 60, see English numerals#Special names
* Stook, or shock of grain, stacked sheaves
Healthcare
* Shock (circulatory), circulatory medical emerge ...
, and can result in death.
The electroencephalogram
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex ...
(EEG) of a person with phenobarbital overdose may show a marked decrease in electrical activity, to the point of mimicking brain death
Brain death is the permanent, irreversible, and complete loss of brain function which may include cessation of involuntary activity necessary to sustain life. It differs from persistent vegetative state, in which the person is alive and some aut ...
. This is due to profound depression of the central nervous system, and is usually reversible.
Treatment of phenobarbital overdose is supportive, and mainly consists of the maintenance of airway
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose t ...
patency (through endotracheal intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequentl ...
and mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move a ...
), correction of bradycardia and hypotension (with intravenous fluids
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutri ...
and vasopressor
An antihypotensive agent, also known as a vasopressor agent or simply vasopressor, or pressor, is any substance, whether endogenous or a medication, that tends to raise low blood pressure. Some antihypotensive drugs act as vasoconstrictors to i ...
s, if necessary), and removal of as much drug as possible from the body. In very large overdoses, multi-dose activated charcoal is a mainstay of treatment as the drug undergoes enterohepatic recirculation. Urine alkalization (achieved with sodium bicarbonate) enhances renal excretion. Hemodialysis is effective in removing phenobarbital from the body, and may reduce its half-life by up to 90%. No specific antidote for barbiturate poisoning is available.
Mechanism of action
Phenobarbital is as anallosteric modulator
In pharmacology and biochemistry, allosteric modulators are a group of substances that bind to a receptor to change that receptor's response to stimulus. Some of them, like benzodiazepines, are drugs. The site that an allosteric modulator binds to ...
which extends the amount of time the chloride ion channel is open by interacting with GABAA receptor subunits. Through this action, phenobarbital increases the flow of chloride
The chloride ion is the anion (negatively charged ion) Cl−. It is formed when the element chlorine (a halogen) gains an electron or when a compound such as hydrogen chloride is dissolved in water or other polar solvents. Chloride s ...
ions into the neuron which decreases the excitability of the post-synaptic neuron. Hyperpolarizing this post-synaptic membrane leads to a decrease in the general excitatory aspects of the post-synaptic neuron. By making it harder to depolarize the neuron, the threshold for the action potential of the post-synaptic neuron will be increased. Phenobarbital stimulates GABA to accomplish this hyperpolarization. Direct blockade of excitatory glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synt ...
signaling is also believed to contribute to the hypnotic/anticonvulsant effect that is observed with the barbiturates.
Pharmacokinetics
Phenobarbital has an oral bioavailability of about 90%.Peak plasma concentration
Cmax is the maximum (or peak) serum concentration that a drug achieves in a specified compartment or test area of the body after the drug has been administered and before the administration of a second dose. It is a standard measurement in pha ...
s (Cmax) are reached eight to 12 hours after oral administration. It is one of the longest-acting barbiturates available – it remains in the body for a very long time (half-life of two to seven days) and has very low protein binding
Plasma protein binding refers to the degree to which medications attach to proteins within the blood. A drug's efficiency may be affected by the degree to which it binds. The less bound a drug is, the more efficiently it can traverse or diffuse t ...
(20 to 45%). Phenobarbital is metabolized by the liver, mainly through hydroxylation
In chemistry, hydroxylation can refer to:
*(i) most commonly, hydroxylation describes a chemical process that introduces a hydroxyl group () into an organic compound.
*(ii) the ''degree of hydroxylation'' refers to the number of OH groups in a ...
and glucuronidation
Glucuronidation is often involved in drug metabolism of substances such as drugs, pollutants, bilirubin, androgens, estrogens, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, fatty acid derivatives, retinoids, and bile acids. These linkages involve gl ...
, and induces many isozymes of the cytochrome P450 system. Cytochrome P450 2B6 (CYP2B6
Cytochrome P450 2B6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP2B6'' gene. CYP2B6 is a member of the cytochrome P450 group of enzymes. Along with CYP2A6, it is involved with metabolizing nicotine, along with many other substances.
Func ...
) is specifically induced by phenobarbital via the CAR/ RXR nuclear receptor
In the field of molecular biology, nuclear receptors are a class of proteins responsible for sensing steroid hormone, steroids, thyroid hormone, thyroid hormones, vitamins, and certain other molecules. These receptors work with other proteins to ...
heterodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' ha ...
. It is excreted primarily by the kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
s.
Veterinary uses
Phenobarbital is one of the first line drugs of choice to treatepilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
in dogs, as well as cats.
It is also used to treat feline hyperesthesia syndrome in cats when anti-obsessional therapies prove ineffective.
It may also be used to treat seizures in horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
s when benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, ...
treatment has failed or is contraindicated.
History
The first barbiturate drug, barbital, was synthesized in 1902 by German chemists Emil Fischer andJoseph von Mering
Josef, Baron von Mering (28 February 1849, in Cologne – 5 January 1908, at Halle an der Saale, Germany) was a German physician.
Working at the University of Strasbourg, Mering was the first person to discover (in conjunction with Oskar Minkow ...
and was first marketed as Veronal by Friedr. Bayer et comp. By 1904, several related drugs, including phenobarbital, had been synthesized by Fischer. Phenobarbital was brought to market in 1912 by the drug company Bayer
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include pharmaceutic ...
as the brand Luminal. It remained a commonly prescribed sedative and hypnotic until the introduction of benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, ...
s in the 1960s.
Phenobarbital's soporific, sedative and hypnotic properties were well known in 1912, but it was not yet known to be an effective anti-convulsant. The young doctor Alfred Hauptmann gave it to his epilepsy patients as a tranquilizer and discovered their seizures were susceptible to the drug. Hauptmann performed a careful study of his patients over an extended period. Most of these patients were using the only effective drug then available, bromide, which had terrible side effects and limited efficacy. On phenobarbital, their epilepsy was much improved: The worst patients had fewer and lighter seizures and some patients became seizure-free. In addition, they improved physically and mentally as bromides were removed from their regimen. Patients who had been institutionalised due to the severity of their epilepsy were able to leave and, in some cases, resume employment. Hauptmann dismissed concerns that its effectiveness in stalling seizures could lead to patients developing a build-up that needed to be "discharged". As he expected, withdrawal of the drug led to an increase in seizure frequency – it was not a cure. The drug was quickly adopted as the first widely effective anti-convulsant, though World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
delayed its introduction in the U.S.
In 1939, a German family asked Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
to have their disabled son killed; the five-month-old boy was given a lethal dose of Luminal after Hitler sent his own doctor to examine him. A few days later 15 psychiatrists were summoned to Hitler's Chancellery and directed to commence a clandestine program of involuntary euthanasia.
In 1940, at a clinic in Ansbach, Germany, around 50 intellectually disabled children were injected with Luminal and killed that way. A plaque was erected in their memory in 1988 in the local hospital at Feuchtwanger Strasse 38, although a newer plaque does not mention that patients were killed using barbiturates on site. Luminal was used in the Nazi children's euthanasia program until at least 1943.
Phenobarbital was used to treat neonatal jaundice
Neonatal jaundice is a yellowish discoloration of the white part of the eyes and skin in a newborn baby due to high bilirubin levels. Other symptoms may include excess sleepiness or poor feeding. Complications may include seizures, cerebral pal ...
by increasing liver metabolism and thus lowering bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) ( Latin for "red bile") is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from t ...
levels. In the 1950s, phototherapy
Light therapy, also called phototherapy or bright light therapy is intentional daily exposure to direct sunlight or similar-intensity artificial light in order to treat medical disorders, especially seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and circad ...
was discovered, and became the standard treatment.
Phenobarbital was used for over 25 years as prophylaxis in the treatment of febrile seizures. Although an effective treatment in preventing recurrent febrile seizures, it had no positive effect on patient outcome or risk of developing epilepsy. The treatment of simple febrile seizures with anticonvulsant prophylaxis is no longer recommended.
Society and culture
Names
Phenobarbital is the INN and phenobarbitone is theBAN
Ban, or BAN, may refer to:
Law
* Ban (law), a decree that prohibits something, sometimes a form of censorship, being denied from entering or using the place/item
** Imperial ban (''Reichsacht''), a form of outlawry in the medieval Holy Roman ...
.
Synthesis
Barbiturate
Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential a ...
drugs are obtained via condensation reactions between a derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. ...
of diethyl malonate and urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Urea serves an important ...
in the presence of a strong base. The synthesis of phenobarbital uses this common approach as well but differs in the way in which this malonate derivative is obtained. The reason for this difference is due to the fact that aryl halides do not typically undergo nucleophilic substitution in Malonic ester synthesis in the same way as aliphatic
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons ( compounds composed solely of carbon and hydrogen) are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds (; G. ''aleiphar'', fat, oil). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, like hexane ...
organosulfates or halocarbon
Halocarbon compounds are chemicals in which one or more carbon atoms are linked by covalent bonds with one or more halogen atoms (fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine – ) resulting in the formation of organofluorine compounds, organochlor ...
s do. To overcome this lack of chemical reactivity two dominant synthetic approaches using benzyl cyanide as a starting material have been developed:
The first of these methods consists of a Pinner reaction
The Pinner reaction refers to the acid catalysed reaction of a nitrile with an alcohol to form an imino ester salt (alkyl imidate salt); this is sometimes referred to as a Pinner salt.
The reaction is named after Adolf Pinner, who first described ...
of benzyl cyanide, giving phenylacetic acid
Phenylacetic acid (PAA; conjugate base phenylacetate), also known by various synonyms, is an organic compound containing a phenyl functional group and a carboxylic acid functional group. It is a white solid with a strong honey-like odor. Endogen ...
ethyl ester. Subsequently, this ester undergoes cross Claisen condensation using diethyl oxalate, giving diethyl ester of phenyloxobutandioic acid. Upon heating this intermediate easily loses carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simpl ...
, yielding diethyl phenylmalonate. Malonic ester synthesis using ethyl bromide leads to the formation of α-phenyl-α-ethylmalonic ester. Finally a condensation reaction with urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Urea serves an important ...
gives phenobarbital.
 The second approach utilizes
The second approach utilizes diethyl carbonate
Diethyl carbonate (sometimes abbreviated DEC) is an ester of carbonic acid and ethanol with the formula OC(OCH2CH3)2. At room temperature (25 °C) diethyl carbonate is a colorless liquid with a low flash point.
Diethyl carbonate is used ...
in the presence of a strong base to give α-phenylcyanoacetic ester. Alkylation of this ester using ethyl bromide proceeds via a nitrile anion Nitrile anions is jargon from the organic product resulting from the deprotonation of alkylnitriles. The proton(s) α to the nitrile group are sufficiently acidic that they undergo deprotonation by strong bases, usually lithium-derived. The produc ...
intermediate to give the α-phenyl-α-ethylcyanoacetic ester. This product is then further converted into the 4-iminoderivative upon condensation with urea. Finally acidic hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysi ...
of the resulting product gives phenobarbital.
 A new synthetic route based on diethyl 2-ethyl-2-phenylmalonate and urea has been described.
A new synthetic route based on diethyl 2-ethyl-2-phenylmalonate and urea has been described.
Regulation
The level of regulation includes Schedule IV non-narcotic (depressant) ( ACSCN 2285) in the United States under the Controlled Substances Act 1970—but along with a few other barbiturates and at least one benzodiazepine, and codeine, dionine, or dihydrocodeine at low concentrations, it also has exempt prescription and had at least one exempt OTC combination drug now more tightly regulated for its ephedrine content. The phenobarbitone/phenobarbital exists in subtherapeutic doses which add up to an effective dose to counter the overstimulation and possible seizures from a deliberate overdose in ephedrine tablets for asthma, which are now regulated at the federal and state level as: a restricted OTC medicine and/or watched precursor, uncontrolled but watched/restricted prescription drug & watched precursor, a Schedule II, III, IV, or V prescription-only controlled substance & watched precursor, or a Schedule V (which also has possible regulations at the county/parish, town, city, or district as well aside from the fact that the pharmacist can also choose not to sell it, and photo ID and signing a register is required) exempt Non-Narcotic restricted/watched OTC medicine.Selected overdoses
A mysterious woman, known as theIsdal Woman
The Isdal Woman ( no, Isdalskvinnen, 1930–1945 – November 1970) is a placeholder name given to an unidentified woman who was found dead at Isdalen ("The Ice Valley") in Bergen, Norway, on 29 November 1970.
Although police at the time ruled a ...
, was found dead in Bergen
Bergen (), historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Vestland county on the Western Norway, west coast of Norway. , its population is roughly 285,900. Bergen is the list of towns and cities in Norway, secon ...
, Norway, on 29 November 1970. Her death was caused by some combination of burns, phenobarbital, and carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simpl ...
poisoning; many theories about her death have been posited, and it is believed that she may have been a spy. The story has been the subject of a BBC Podcast, "Death in Ice Valley".
British veterinarian Donald Sinclair, better known as the character Siegfried Farnon in the "All Creatures Great and Small" book series by James Herriot, committed suicide at the age of 84 by injecting himself with an overdose of phenobarbital. Activist Abbie Hoffman
Abbot Howard "Abbie" Hoffman (November 30, 1936 – April 12, 1989) was an American political and social activist who co-founded the Youth International Party ("Yippies") and was a member of the Chicago Seven. He was also a leading proponen ...
also committed suicide by consuming phenobarbital, combined with alcohol, on April 12, 1989; the residue of around 150 pills was found in his body at autopsy.
Thirty-nine members of the Heaven's Gate UFO religious group committed mass suicide in March 1997 by drinking a lethal dose of phenobarbital and vodka "and then lay down to die" hoping to enter an alien spacecraft.
References
External links
* {{Authority control Barbiturates Anxiolytics CYP3A4 inducers Hypnotics World Health Organization essential medicines IARC Group 2B carcinogens GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Bayer brands Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate