Peace plans proposed before and during the Bosnian War on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Four major international peace plans were proposed before and during the Bosnian War by
 The original Carrington–Cutileiro peace plan, named for its authors Lord Carrington and
The original Carrington–Cutileiro peace plan, named for its authors Lord Carrington and
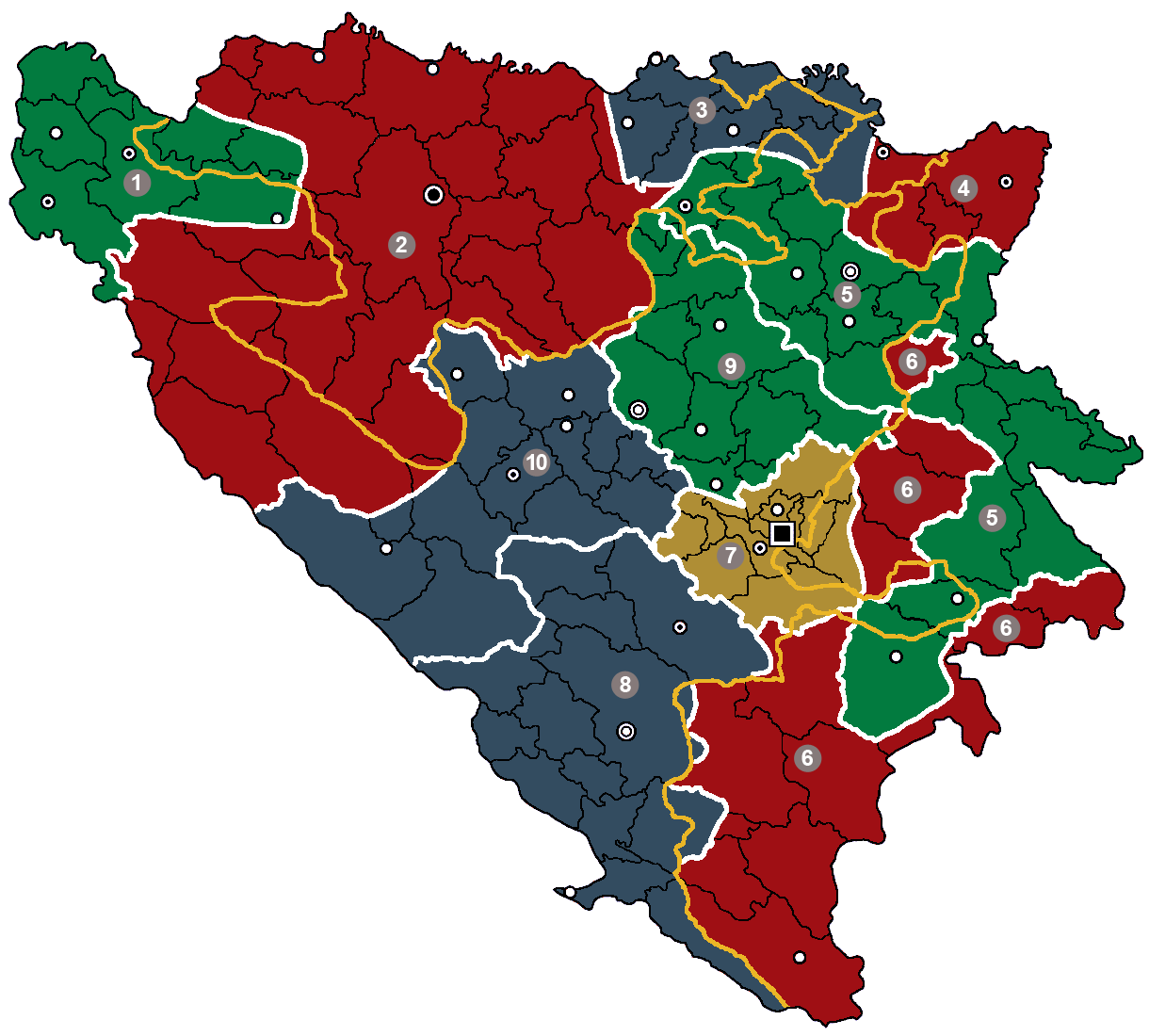 In early January 1993, the UN Special Envoy Cyrus Vance and EC representative Lord Owen began negotiating a peace proposal with the leaders of Bosnia's warring factions. The proposal, which became known as the "Vance-Owen peace plan", involved the division of Bosnia into ten semi-autonomous regions and received the backing of the UN. The President of the
In early January 1993, the UN Special Envoy Cyrus Vance and EC representative Lord Owen began negotiating a peace proposal with the leaders of Bosnia's warring factions. The proposal, which became known as the "Vance-Owen peace plan", involved the division of Bosnia into ten semi-autonomous regions and received the backing of the UN. The President of the
Direct Democracy although mediators referred to the referendum as a "sham". On 18 June, Lord Owen declared that the plan was "dead". Given the pace at which territorial division, fragmentation and ethnic cleansing had occurred, the plan was already obsolete by the time it was announced. It became the last proposal that sought to salvage a mixed, united Bosnia-Herzegovina; subsequent proposals either re-enforced or contained elements of partition of Bosnia and Herzegovina. On 1 April, Cyrus Vance announced his resignation as Special Envoy to the UN Secretary-General. He was replaced by Norwegian Foreign Minister
 In late July, representatives of Bosnia-Herzegovina's three warring factions entered into a new round of negotiations. On 20 August, the U.N. mediators
In late July, representatives of Bosnia-Herzegovina's three warring factions entered into a new round of negotiations. On 20 August, the U.N. mediators
The_first_Muslim_proposal_on_cantonisation_of_Bosnia_and_Herzegovina.png, Map of the first Bosniak proposal on federalisation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, from 25 June 1991.
Joint_cantonisation_proposal_of_HDZ-SDA_of_August_1992.png, Bosniak
European Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
(EC) and United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
(UN) diplomats before the conflict was settled by the Dayton Agreement
The General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina, also known as the Dayton Agreement or the Dayton Accords ( Croatian: ''Daytonski sporazum'', Serbian and Bosnian: ''Dejtonski mirovni sporazum'' / Дејтонски миро ...
in 1995.
Background
The Bosnian war which lasted from 1992 to 1995 was fought among its three main ethnicities Bosniaks,Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, ...
and Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
. Whilst the Bosniak plurality had sought a nation state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may i ...
across all ethnic lines, the Croats had created an autonomous community that functioned independently of central Bosnian rule, and the Serbs declared independence for the region's eastern and northern regions relevant to the Serb population. All peace plans were proposed with the view to observing Bosnia and Herzegovina as a sovereign state entire of its territorial integrity (as it had been in Yugoslavia as the SR Bosnia and Herzegovina
The Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Socijalistička Republika Bosna i Hercegovina, Социјалистичка Pепублика Босна и Херцеговина), commonly referred to as Socia ...
) and without an imbalance of greater devolution and autonomy awarded to any community or region.
Carrington–Cutileiro plan
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
ambassador José Cutileiro
José Cutileiro (20 November 1934 – 17 May 2020) was a Portuguese diplomat and writer. He was a representative to the Council of Europe, Secretary General of the Western European Union (WEU), and an envoy to the UN Commissioner for Human Rig ...
, resulted from the EC Peace Conference held in February 1992 in an attempt to prevent Bosnia-Herzegovina sliding into war. It was also referred to as the Lisbon Agreement ( sh, Lisabonski sporazum). It proposed ethnic power-sharing on all administrative levels and the devolution of central government to local ethnic communities. However, all Bosnia-Herzegovina's districts would be classified as Bosniak, Serb
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
or Croat
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, Ge ...
under the plan, even where no ethnic majority was evident. In later negotiations, there were compromises about changing district borders. On 3 March 1992, Bosnia and Herzegovina was declared independent following a referendum held days earlier on February 29 and 1 March.
On 11 March 1992, the Assembly of the Serb People of Republika Srpska (the self-proclaimed parliament of the Bosnian Serbs) unanimously rejected the original peace plan, putting forth their own map which claimed almost two thirds of Bosnia's territory, with a series of ethnically split cities and isolated enclaves and leaving the Croats and Bosniaks with a disjointed strip of land in the centre of the republic. That plan was rejected by Cutileiro. However, he put forth a revised draft of the original which stated that the three constituent units would be "based on national principles and taking into account economic, geographic, and other criteria."
On 18 March 1992, all three sides signed the agreement; Alija Izetbegović
Alija Izetbegović (; ; 8 August 1925 – 19 October 2003) was a Bosnian politician, lawyer, Islamic philosopher and author, who in 1992 became the first president of the Presidency of the newly independent Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovin ...
for the Bosniaks, Radovan Karadžić
Radovan Karadžić ( sr-cyr, Радован Караџић, ; born 19 June 1945) is a Bosnian Serb politician, psychiatrist and poet. He was convicted of genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes by the International Criminal Tr ...
for the Bosnian Serbs and Mate Boban for the Bosnian Croats.
On 28 March 1992, after a meeting with US ambassador to Yugoslavia Warren Zimmermann in Sarajevo, Izetbegović withdrew his signature and declared his opposition to any division of Bosnia.
What was said and by whom remains unclear. Warren Zimmermann denied that he told Izetbegović that if he withdrew his signature, the United States would grant recognition to Bosnia as an independent state. What is indisputable is that on the same day, Izetbegović withdrew his signature and renounced the agreement.
Vance–Owen Peace Plan
 In early January 1993, the UN Special Envoy Cyrus Vance and EC representative Lord Owen began negotiating a peace proposal with the leaders of Bosnia's warring factions. The proposal, which became known as the "Vance-Owen peace plan", involved the division of Bosnia into ten semi-autonomous regions and received the backing of the UN. The President of the
In early January 1993, the UN Special Envoy Cyrus Vance and EC representative Lord Owen began negotiating a peace proposal with the leaders of Bosnia's warring factions. The proposal, which became known as the "Vance-Owen peace plan", involved the division of Bosnia into ten semi-autonomous regions and received the backing of the UN. The President of the Republika Srpska
Republika Srpska ( sr-Cyrl, Република Српска, lit=Serb Republic, also known as Republic of Srpska, ) is one of the two entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is locat ...
, Radovan Karadžić
Radovan Karadžić ( sr-cyr, Радован Караџић, ; born 19 June 1945) is a Bosnian Serb politician, psychiatrist and poet. He was convicted of genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes by the International Criminal Tr ...
, signed the plan on 30 April. However, it was rejected by the National Assembly of Republika Srpska
The National Assembly of Republika Srpska (, abbr. НСРС/NSRS) is the legislative body of Republika Srpska, one of two entities of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The current assembly is the ninth since the founding of the entity.
History
The Natio ...
on 6 May, and subsequently referred to a referendum. The plan was rejected by 96% of voters,Republika Srpska (Bosnien-Herzegowina), 16. Mai 1993 : Vance-Owen-FriedensplanDirect Democracy although mediators referred to the referendum as a "sham". On 18 June, Lord Owen declared that the plan was "dead". Given the pace at which territorial division, fragmentation and ethnic cleansing had occurred, the plan was already obsolete by the time it was announced. It became the last proposal that sought to salvage a mixed, united Bosnia-Herzegovina; subsequent proposals either re-enforced or contained elements of partition of Bosnia and Herzegovina. On 1 April, Cyrus Vance announced his resignation as Special Envoy to the UN Secretary-General. He was replaced by Norwegian Foreign Minister
Thorvald Stoltenberg
Thorvald Stoltenberg (8 July 1931 – 13 July 2018) was a Norwegian politician and diplomat. He served as Minister of Defence from 1979 to 1981 and Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1987 to 1989 and again from 1990 to 1993 in two Labour governme ...
on 1 May.
The Vance–Owen plan was a roughly sketched map, it did not establish the definitive outline of the 10 cantons and depended on final negotiations between the three ethnic groups taking place.
Owen–Stoltenberg plan
 In late July, representatives of Bosnia-Herzegovina's three warring factions entered into a new round of negotiations. On 20 August, the U.N. mediators
In late July, representatives of Bosnia-Herzegovina's three warring factions entered into a new round of negotiations. On 20 August, the U.N. mediators Thorvald Stoltenberg
Thorvald Stoltenberg (8 July 1931 – 13 July 2018) was a Norwegian politician and diplomat. He served as Minister of Defence from 1979 to 1981 and Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1987 to 1989 and again from 1990 to 1993 in two Labour governme ...
and David Owen unveiled a map that would partition Bosnia into a union of three ethnic republics, in which Bosnian Serb forces would be given 53 percent of Bosnia-Herzegovina's territory, Muslims would be allotted 30 percent and Bosnian-Herzegovina Croats would receive 17 percent. On 28 August, in accordance with the Owen–Stoltenberg peace proposal, the Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia was proclaimed in Grude
Grude () is a town and a municipality located in West Herzegovina Canton of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, an entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Geography
Grude is located 49 kilometers from Mostar, 19 kilometers from Imotski, and 1 ...
as a "republic of the Croats in Bosnia and Herzegovina". On 29 August 1993 the Bosniak side rejected the plan.
Contact Group plan
Between February and October 1994, theContact Group
The Contact Group is the name for an informal grouping of great powers that have a significant interest in policy developments in the Balkans (an International Contact Group). The Contact Group is composed of United States, United Kingdom, Fran ...
(U.S., Russia, France, Britain, and Germany) made steady progress towards a negotiated settlement of the conflict in Bosnia-Herzegovina. This was known as a Contact Group plan, and a heavy pressure was put on Bosnian Serbs to accept the plan when Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
Serbia and Montenegro ( sr, Cрбија и Црна Гора, translit=Srbija i Crna Gora) was a country in Southeast Europe located in the Balkans that existed from 1992 to 2006, following the breakup of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yu ...
imposed an embargo on Drina river. It was also rejected in a referendum held on 28 August 1994.
During this period, the warring between Croats and Bosniaks came to an end as in March 1994, the two factions settled their differences in the Washington agreement
The Washington Agreement ( Croatian: ''washingtonski sporazum'' and Bosnian: ''vašingtonski sporazum'') was a ceasefire agreement between the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the Croatian Republic of Herzeg-Bosnia, signed in Washington ...
signed in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
and Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
.
Other plans by Bosnian actors
There were also Bosniak, Croat and Serb proposals for the reorganisation of Bosnia. *As ethnic tensions grew, one of the first Muslim proposals was announced on 25 June 1991. It called for the establishment of three entities (Muslim, Serb and Croat), each composed of two or three non-contiguous territories. *Another joint proposal by the BosniakParty of Democratic Action
The Party of Democratic Action ( bs, Stranka demokratske akcije; abbr. SDA) is a Bosniak nationalist, conservative political party in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
History
The Party of Democratic Action (SDA) was founded on 26 May 1990 in Sarajevo, ...
(SDA) and the Croatian Democratic Union of Bosnia and Herzegovina
The Croatian Democratic Union of Bosnia and Herzegovina ( hr, Hrvatska demokratska zajednica Bosne i Hercegovine or HDZ BiH) is a Christian democratic, nationalist political party in Bosnia and Herzegovina, representing the Croats of Bosnia and ...
(HDZ BiH) political parties was announced in August 1992. It called for establishing 12 cantons of Bosnia and Herzegovina, with autonomous rights.
SDA
SDA or sda may refer to:
Educational institutions
* San Dieguito Academy, Encinitas, California, US
* SDA Bocconi School of Management, in Milan, Italy
Science and technology Biology
* Specific dynamic action, the thermic effect of food
* Str ...
and Croat HDZ BiH
The Croatian Democratic Union of Bosnia and Herzegovina ( hr, Hrvatska demokratska zajednica Bosne i Hercegovine or HDZ BiH) is a Christian democratic, nationalist political party in Bosnia and Herzegovina, representing the Croats of Bosnia and ...
joint proposal of 12 cantons, from August 1992.
See also
* Partition of Bosnia and Herzegovina *Inter-Entity Boundary Line
The Inter-Entity Boundary Line ( sh, Međuentitetska linija), commonly abbreviated IEBL, is the administrative line that subdivides Bosnia and Herzegovina into two entities, ''Republika Srpska'' and the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. T ...
*Dayton Peace Accords
The General Framework Agreement for Peace in Bosnia and Herzegovina, also known as the Dayton Agreement or the Dayton Accords ( Croatian: ''Daytonski sporazum'', Serbian and Bosnian: ''Dejtonski mirovni sporazum'' / Дејтонски миро ...
* Croat entity in Bosnia and Herzegovina
References
Sources
*Atiyas, N.B., 1995. Mediating regional conflicts and negotiating flexibility: Peace efforts in Bosnia-Herzegovina. The Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, 542(1), pp. 185–201. *Goodby, J.E., 1996. When war won out: Bosnian peace plans before Dayton. International Negotiation, 1(3), pp. 501–523. *Klemenčić, M., 1994. Territorial proposals for the settlement of the war in Bosnia-Hercegovina. IBRU. *Leigh-Phippard, H., 1998. The Contact Group on (and in) Bosnia: an exercise in conflict mediation?. International Journal, 53(2), pp. 306–324.External links
{{Authority control Bosnian peace process Bosnian War Peace treaties Political history of Bosnia and Herzegovina Partition (politics)