Panthera pardus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant

 ''Felis pardus'' was the
''Felis pardus'' was the
 Results of
Results of
species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
in the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
''Panthera
''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae that was named and described by Lorenz Oken in 1816 who placed all the spotted cats in this group. Reginald Innes Pocock revised the classification of this genus in 1916 as comprising the tig ...
'', a member of the cat family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
, Felidae
Felidae () is the family of mammals in the order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a felid (). The term "cat" refers both to felids in general and specifically to the dom ...
. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
, in some parts of Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
, Southern Russia
Southern Russia or the South of Russia (russian: Юг России, ''Yug Rossii'') is a colloquial term for the southernmost geographic portion of European Russia generally covering the Southern Federal District and the North Caucasian Feder ...
, and on the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
to Southeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
and East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biolo ...
because leopard populations are threatened by habitat loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby ...
and fragmentation, and are declining in large parts of the global range. The leopard is considered locally extinct
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, refers to a species (or other taxon) of plant or animal that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinct ...
in Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a List of cities in China, city and Special administrative regions of China, special ...
, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to A ...
, Togo
Togo (), officially the Togolese Republic (french: République togolaise), is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to the west, Benin to the east and Burkina Faso to the north. It extends south to the Gulf of Guinea, where its c ...
, the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia (Middle East, The Middle East). It is ...
, Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lie ...
, Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
, Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Ku ...
, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and most likely in North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
, Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
, Laos
Laos (, ''Lāo'' )), officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic ( Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ, French: République démocratique populaire lao), is a socialist s ...
, Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked as an enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the highest mountains in Southern Africa. It has an area of over and has a population ...
, Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
, Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
and Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
.
Contemporary records suggest that the leopard occurs in only 25% of its historical global range.
Compared to other wild cats, the leopard has relatively short legs and a long body with a large skull. Its fur is marked with rosettes. It is similar in appearance to the jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus ''Panthera'' native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the th ...
(''Panthera onca''), but has a smaller, lighter physique, and its rosettes are generally smaller, more densely packed and without central spots. Both leopards and jaguars that are melanistic
The term melanism refers to black pigment and is derived from the gr, μελανός. Melanism is the increased development of the dark-colored pigment melanin in the skin or hair.
Pseudomelanism, also called abundism, is another variant of pi ...
are known as black panther
A black panther is the melanistic colour variant of the leopard (''Panthera pardus'') and the jaguar (''Panthera onca''). Black panthers of both species have excess black pigments, but their typical rosettes are also present. They have been ...
s. The leopard is distinguished by its well-camouflaged fur, opportunistic
Opportunism is the practice of taking advantage of circumstances – with little regard for principles or with what the consequences are for others. Opportunist actions are expedient actions guided primarily by self-interested motives. The term ...
hunting behaviour, broad diet, strength, and its ability to adapt to a variety of habitats ranging from rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
to steppe, including arid and montane areas. It can run at speeds of up to . The earliest known leopard fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s excavated in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
are estimated 600,000 years old, dating to the late Early Pleistocene
The Early Pleistocene is an unofficial sub-epoch in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently estimated to span the time ...
. Leopard fossils were also found in Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
.
Etymology
The English name 'leopard' comes from fro, leupart or frm, liepart, that derives from la, leopardus and grc, λέοπάρδος (''leopardos''). ''Leopardos'' could be acompound
Compound may refer to:
Architecture and built environments
* Compound (enclosure), a cluster of buildings having a shared purpose, usually inside a fence or wall
** Compound (fortification), a version of the above fortified with defensive struc ...
of (''leōn''), meaning lion, and (''pardos''), meaning spotted. The word ''λέοπάρδος'' originally referred to a cheetah
The cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus'') is a large cat native to Africa and central Iran. It is the fastest land animal, estimated to be capable of running at with the fastest reliably recorded speeds being , and as such has evolved specialized ...
(''Acinonyx jubatus'').
'Panther' is another common name, derived from la, panther and grc, πάνθηρ (''pánthēr''); The generic name ''Panthera'' originates in la, panthera, which refers to a hunting net for catching wild beasts that were used by the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
s in combats. ''Pardus'' is the masculine singular form.
Characteristics
The leopard's fur is generally soft and thick, notably softer on the belly than on the back. Its skin colour varies between individuals from pale yellowish to dark golden with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its belly is whitish and its ringed tail is shorter than its body. Its pupils are round. Leopards living in arid regions are pale cream, yellowish to ochraceous and rufous in colour; those living in forests and mountains are much darker and deep golden. Spots fade toward the white underbelly and the insides and lower parts of the legs. Rosettes are circular in East African leopard populations, and tend to be squarish in Southern African and larger in Asian leopard populations. The fur tends to be grayish in colder climates, and dark golden inrain forest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainforest ...
habitats. The pattern of the rosettes is unique in each individual. This pattern is thought to be an adaptation to dense vegetation with patchy shadows, where it serves as camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
.
Its white-tipped tail is about long, white underneath and with spots that form incomplete bands toward the tail's end.
The guard hairs protecting the basal hairs are short, in face and head, and increase in length toward the flanks and the belly to about . Juveniles have woolly fur, and appear to be dark-coloured due to the densely arranged spots.
Its fur tends to grow longer in colder climates.
The leopard's rosettes differ from those of the jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus ''Panthera'' native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the th ...
(''Panthera onca''), which are darker and with smaller spots inside.
The leopard has a diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectiv ...
chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
number of 38.
The chromosomes include four acrocentric
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers ...
, five metacentric
Metacentric may refer to:
* Metacentric height, the distance between the center of gravity of a ship and its metacenter
* Metacentric centromere, the position of a centromere on a chromatid
{{disambiguation ...
, seven submetacentric
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers ...
and two telocentric
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers ...
pairs.
Size and weight
The leopard issexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
with males larger and heavier than females. It is slender and muscular, with relatively short limbs and a broad head. Males stand at the shoulder, while females are tall. The head-and-body length ranges between with a long tail. Sizes vary geographically. Males weigh , and females .
Some leopards in North Africa allegedly were as large as Barbary lion
The Barbary lion, also called the North African lion, Berber lion, Atlas lion, and Egyptian lion, is an extinct population of the lion subspecies '' Panthera leo leo''. It lived in the mountains and deserts of the Barbary Coast of North Africa, ...
s (''Panthera leo leo''). In 1913, an Algerian newspaper reported a leopard killed that allegedly measured about in total length.
The maximum weight of a wild leopard in Southern Africa was about . It measured . An Indian leopard killed in Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several pea ...
in 2016 measured with an estimated weight of ; it was perhaps the largest known wild leopard in India.
The largest skull of a leopard was recorded in India in 1920 and measured in basal length, in breadth, and weighed . The skull of an African leopard measured in basal length, and in breadth, and weighed .
Variant colouration
Melanistic
The term melanism refers to black pigment and is derived from the gr, μελανός. Melanism is the increased development of the dark-colored pigment melanin in the skin or hair.
Pseudomelanism, also called abundism, is another variant of pi ...
leopards are also called black panther
A black panther is the melanistic colour variant of the leopard (''Panthera pardus'') and the jaguar (''Panthera onca''). Black panthers of both species have excess black pigments, but their typical rosettes are also present. They have been ...
s. Melanism in leopards is caused by a recessive allele and inherited as a recessive trait
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
. Interbreeding in melanistic leopards produces a significantly smaller litter size than is produced by normal pairings.
The black leopard is common foremost in tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
and subtropical moist forests like the equatorial rainforest
Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests (TSMF), also known as tropical moist forest, is a subtropical and tropical forest habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature.
Description
TSMF is generally found in large, discon ...
of the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula ( Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The ar ...
and the tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equator ...
on the slopes of some African mountains such as Mount Kenya
Mount Kenya (Kikuyu language, Kikuyu: ''Kĩrĩnyaga'', Kamba language, Kamba, ''Ki Nyaa'') is the highest mountain in Kenya and the Highest mountain peaks of Africa, second-highest in Africa, after Mount Kilimanjaro, Kilimanjaro. The highest pea ...
.
Between January 1996 and March 2009, leopards were photographed at 16 sites in the Malay Peninsula in a sampling effort of more than 1,000 camera trap
A camera trap is a camera that is automatically triggered by a change in some activity in its vicinity, like presence of an animal or a human being. It is typically equipped with a motion sensor – usually a passive infrared (PIR) senso ...
nights. Of the 445 photographs of melanistic leopards, 410 were taken in study sites south of the Kra Isthmus
The Kra Isthmus ( th, คอคอดกระ, ) in Thailand is the narrowest part of the Malay Peninsula. The western part of the isthmus belongs to Ranong Province and the eastern part to Chumphon Province, both in Southern Thailand. The ...
, where the non-melanistic morph was never photographed. These data indicate the near-fixation of the dark allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chrom ...
in the region. The expected time for the fixation of this recessive allele due to genetic drift
Genetic drift, also known as allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance.
Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and there ...
alone ranged from about 1,100 years to about 100,000 years. Pseudomelanistic leopards have also been reported.
In India, nine pale and white leopards were reported between 1905 and 1967.
Leopards exhibiting erythrism
Erythrism or erythrochroism refers to an unusual reddish pigmentation of an animal's hair, skin, feathers, or eggshells.
Causes of erythrism include:
* Genetic mutations which cause an absence of a normal pigment and/or excessive production of ot ...
were recorded between 1990 and 2015 in South Africa's Madikwe Game Reserve
The Madikwe Game Reserve is a protected area in South Africa, part of the latest park developments in the country. Named after the Madikwe or Marico River, on whose basin it is located, it was opened in 1991 and comprises 750 km² of bushland ...
and in Mpumalanga
Mpumalanga () is a province of South Africa. The name means "East", or literally "The Place Where the Sun Rises" in the Swazi, Xhosa, Ndebele and Zulu languages. Mpumalanga lies in eastern South Africa, bordering Eswatini and Mozambique. ...
. The cause of this morph known as a "strawberry leopard" or "pink panther" is not well understood.
Taxonomy
 ''Felis pardus'' was the
''Felis pardus'' was the scientific name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bo ...
proposed by Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, ...
in 1758.
The generic name ''Panthera
''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae that was named and described by Lorenz Oken in 1816 who placed all the spotted cats in this group. Reginald Innes Pocock revised the classification of this genus in 1916 as comprising the tig ...
'' was first used by Lorenz Oken
Lorenz Oken (1 August 1779 – 11 August 1851) was a German naturalist, botanist, biologist, and ornithologist.
Oken was born Lorenz Okenfuss (german: Okenfuß) in Bohlsbach (now part of Offenburg), Ortenau, Baden, and studied natural history and ...
in 1816, who included all the known spotted cats into this group.
Oken's classification was not widely accepted, and ''Felis
''Felis'' is a genus of small and medium-sized cat species native to most of Africa and south of 60° latitude in Europe and Asia to Indochina. The genus includes the domestic cat. The smallest ''Felis'' species is the black-footed cat with a h ...
'' or ''Leopardus
''Leopardus'' is a genus comprising eight species of small cats native to the Americas. This genus is considered the oldest branch of a genetic lineage of small cats in the Americas whose common ancestor crossed the Bering land bridge from Asia ...
'' was used as the generic name until the early 20th century.
The leopard was designated as the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specim ...
of ''Panthera'' by Joel Asaph Allen
Joel Asaph Allen (July 19, 1838 – August 29, 1921) was an American zoologist, mammalogist, and ornithologist. He became the first president of the American Ornithologists' Union, the first curator of birds and mammals at the American Museum of ...
in 1902.
In 1917, Reginald Innes Pocock
Reginald Innes Pocock Fellow of the Royal Society, F.R.S. (4 March 1863 – 9 August 1947) was a British zoologist.
Pocock was born in Clifton, Bristol, the fourth son of Rev. Nicholas Pocock (historian), Nicholas Pocock and Edith Prichard. He ...
also subordinated the tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living Felidae, cat species and a member of the genus ''Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily pr ...
(''P. tigris''), lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large cat of the genus '' Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adu ...
(''P. leo''), and jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus ''Panthera'' native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the th ...
(''P. onca'') to ''Panthera''.
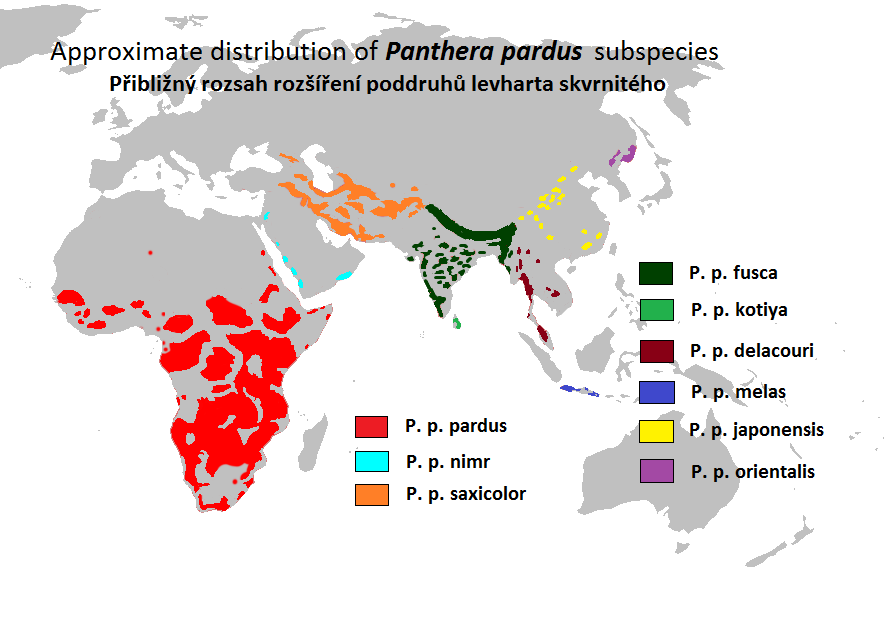
Subspecies
Following Linnaeus' first description, 27 leopardsubspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics ( morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all specie ...
were proposed by naturalists between 1794 and 1956. Since 1996, only eight subspecies have been considered valid on the basis of mitochondrial
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used t ...
analysis. Later analysis revealed a ninth valid subspecies, the Arabian leopard
The Arabian leopard (''Panthera pardus nimr'') is a leopard subspecies native to the Arabian Peninsula. It has been listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List since 1996 as fewer than 200 wild individuals were estimated to be alive i ...
.
In 2017, the Cat Classification Task Force of the Cat Specialist Group recognized the following eight subspecies as valid taxa:
Results of an analysis of molecular variance and pairwise fixation index
The fixation index (FST) is a measure of population differentiation due to genetic structure. It is frequently estimated from genetic polymorphism data, such as single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) or microsatellites. Developed as a special case o ...
of 182 African leopard museum specimens showed that some African leopards exhibit higher genetic differences than Asian leopard subspecies.
Evolution
phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups ...
studies based on nDNA
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. I ...
and mtDNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA ...
analysis showed that the last common ancestor
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. All living beings are in fact descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal comm ...
of the ''Panthera'' and ''Neofelis'' genera is thought to have lived about . ''Neofelis'' diverged about from the ''Panthera'' lineage
Lineage may refer to:
Science
* Lineage (anthropology), a group that can demonstrate its common descent from an apical ancestor or a direct line of descent from an ancestor
* Lineage (evolution), a temporal sequence of individuals, populat ...
. The tiger diverged about , followed by the snow leopard about and the leopard about . The leopard is a sister taxon
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
to a clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English ter ...
within ''Panthera'', consisting of the lion and the jaguar.
Results of a phylogenetic analysis of chemical secretion 440px
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classic ...
s amongst cats indicated that the leopard is closely related to the lion.
The geographic origin of the ''Panthera'' is most likely northern Central Asia. The leopard-lion clade was distributed in the Asian and African Palearctic
The Palearctic or Palaearctic is the largest of the eight biogeographic realms of the Earth. It stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
The realm consists of several bioregions: the Euro-Sib ...
since at least the early Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58 Additionally, a 2016 study revealed that the mitochondrial genomes of the leopard, lion and
 Leopards are active mainly from dusk till dawn and rest for most of the day and for some hours at night in thickets, among rocks or over tree branches. Leopards have been observed walking across their range at night; they may even wander up to if disturbed. In some regions, they are
Leopards are active mainly from dusk till dawn and rest for most of the day and for some hours at night in thickets, among rocks or over tree branches. Leopards have been observed walking across their range at night; they may even wander up to if disturbed. In some regions, they are
 In parts of its global range, the leopard is
In parts of its global range, the leopard is
IUCN/SSC Cat Specialist Group: ''Panthera pardus'' in Africa
an
''Panthera pardus'' in Asia
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Leopard Articles containing video clips Big cats Felids of Africa Felids of Asia Mammals described in 1758 National symbols of Benin National symbols of Malawi National symbols of Somalia National symbols of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Panthera Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus
snow leopard
The snow leopard (''Panthera uncia''), also known as the ounce, is a felid in the genus '' Panthera'' native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because the global population is es ...
are more similar to each other than their nuclear genome
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. I ...
s, indicating that their ancestors hybridized with the snow leopard at some point in their evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
.
Fossils of leopard ancestors were excavated in East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
and South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
, dating back to the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
between 2 and . The modern leopard is suggested to have evolved in Africa about and to have radiated across Asia about 0.2 and .
Fossil cat teeth collected in Sumatra's Padang Highlands were assigned to the leopard. It has since been hypothesized that it became extirpated on the island due to the Toba eruption
The Youngest Toba eruption was a supervolcano eruption that occurred around 74,000 years ago at the site of present-day Lake Toba in Sumatra, Indonesia. It is one of the Earth's largest known explosive eruptions. The Toba catastrophe theory hold ...
about 75,000 years ago, and due to competition with the Sunda clouded leopard
The Sunda clouded leopard (''Neofelis diardi'') is a medium-sized wild cat native to Borneo and Sumatra. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List since 2015, as the total effective population probably consists of fewer than 10,000 mature ...
(''Neofelis diardi'') and the dhole
The dhole (''Cuon alpinus''; ) is a canid native to Central, South, East and Southeast Asia. Other English names for the species include Asian wild dog, Asiatic wild dog, Indian wild dog, whistling dog, red dog, red wolf, and mountain wolf. It ...
(''Cuon alpinus'').
In Europe, the leopard occurred at least since the Pleistocene. Leopard-like fossil bones and teeth possibly dating to the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Perrier
Perrier ( , also , ) is a French brand of natural bottled mineral water obtained at its source in Vergèze, located in the Gard ''département''. Perrier is known for its carbonation and its distinctive green bottle.
Perrier was part of th ...
in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, northeast of London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, and in Valdarno
The Valdarno is the valley of the river Arno, although this name does not apply to the entire river basin. Usage of the term generally excludes Casentino and the valleys formed by major tributaries.
Some towns in the area:
*Rignano sull'Arno
*Fi ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
. Until 1940, similar fossils dating back to the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
were excavated mostly in loess
Loess (, ; from german: Löss ) is a clastic, predominantly silt-sized sediment that is formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. Ten percent of Earth's land area is covered by loess or similar deposits.
Loess is a periglacial or aeoli ...
and caves at 40 sites in Europe, including Furninha
Furninha, also known as Dominique's cave, is a natural cave on the southern slope of the Peniche peninsula in Portugal. The cave is situated on the cliffs between the Peniche Fortress and the Cape Carvoeiro.
The cave is located furthest west of ...
Cave near Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administrative limits w ...
, Genista Caves in Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
, and Santander Province
Cantabria (, also , , Cantabrian: ) is an autonomous community in northern Spain with Santander as its capital city. It is called a ''comunidad histórica'', a historic community, in its current Statute of Autonomy. It is bordered on the eas ...
in northern Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
to several sites across France, Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, Italy, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, in the north up to Derby
Derby ( ) is a city and unitary authority area in Derbyshire, England. It lies on the banks of the River Derwent in the south of Derbyshire, which is in the East Midlands Region. It was traditionally the county town of Derbyshire. Derby g ...
in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
, in the east to Přerov
Přerov (; german: Prerau) is a city in the Olomouc Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 41,000 inhabitants. It lies on the Bečva River. In the past it was a major crossroad in the heart of Moravia in the Czech Republic. The historic cent ...
in the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
and the Baranya Baranya or Baranja may refer to:
* Baranya (region) or Baranja, a region in Hungary and Croatia
* Baranya County, a county in modern Hungary
* Baranya County (former), a county in the historic Kingdom of Hungary
* Baranya, Hungarian name of villag ...
in southern Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
, Leopard fossils dating to the Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as Upper Pleistocene from a stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of the Pleistocene Epoch withi ...
were found in Biśnik Cave in south-central Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. The oldest known leopard fossils excavated in Europe are about 600,000 years old and were found in the Grotte du Vallonnet in France and near Mauer in Germany. Four European Pleistocene leopard subspecies were proposed. ''P. p. begoueni'' from the beginning of the Early Pleistocene
The Early Pleistocene is an unofficial sub-epoch in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently estimated to span the time ...
was replaced about by ''P. p. sickenbergi'', which in turn was replaced by ''P. p. antiqua'' around 0.3 million years ago. The most recent, ''P. p. spelaea'', appeared at the beginning of the Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as Upper Pleistocene from a stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of the Pleistocene Epoch withi ...
and survived until about 24,000 years ago in several parts of Europe. Leopard fossils dating to the Pleistocene were also excavated in the Japanese archipelago
The Japanese archipelago (Japanese: 日本列島, ''Nihon rettō'') is a group of 6,852 islands that form the country of Japan, as well as the Russian island of Sakhalin. It extends over from the Sea of Okhotsk in the northeast to the East Chin ...
.
Hybrids
In 1953, a male leopard and a lioness werecrossbred
A crossbreed is an organism with purebred parents of two different breeds, varieties, or populations. ''Crossbreeding'', sometimes called "designer crossbreeding", is the process of breeding such an organism, While crossbreeding is used to main ...
in Hanshin Park in Nishinomiya, Japan
270px, Nishinomiya City Hall
270px, Aerial view of Nishinomiya city center
270px, Hirota Shrine
is a city located in Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 484,368 in 218948 households and a population density of 4 ...
. Their offspring known as a leopon
A leopon (portmanteau of ''leopard'' and ''lion'') is the hybrid offspring of a male leopard and a female lion. The head of the animal is similar to that of a lion while the rest of the body carries similarities to leopards. These hybrids are p ...
was born in 1959 and 1961, all cubs were spotted and bigger than a juvenile leopard. Attempts to mate a leopon with a tigress were unsuccessful.
Distribution and habitat
The leopard has the largest distribution of all wild cats, occurring widely in Africa, theCaucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
and Asia, although populations are fragmented and declining. It is considered to be extirpated
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, refers to a species (or other taxon) of plant or animal that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinct ...
in North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
. It inhabits foremost savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland- grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground ...
and rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
, and areas where grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses ( Poaceae). However, sedge ( Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur na ...
s, woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see ...
s, and riverine forests remain largely undisturbed. In sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
, it is still numerous and surviving in marginal habitats where other large cats have disappeared. There is considerable potential for human-leopard conflict due to leopards preying on livestock.
Leopard populations on the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plat ...
are small and fragmented. In southeastern Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
, a leopard killed in 2017 was the first record in this area in 65 years.
In western and central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
, it avoids deserts, areas with long snow cover and proximity to urban centres.
In the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, In ...
, the leopard is still relatively abundant, with greater numbers than those of other ''Panthera'' species. As of 2020, the leopard population within forested habitats in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
's tiger range landscapes was estimated at 12,172 to 13,535 individuals. Surveyed landscapes included elevations below in the Shivalik Hills
The Sivalik Hills, also known as the Shivalik Hills and Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas that stretches over about from the Indus River eastwards close to the Brahmaputra River, spanning the northern parts of the Ind ...
and Gangetic plains
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of northern and eastern India, around half of Pakistan, virtually all of Ba ...
, Central India
Central India is a loosely defined geographical region of India. There is no clear official definition and various ones may be used. One common definition consists of the states of Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh, which are included in al ...
and Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through Odisha, Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu in the south passing some parts of Karnataka as well as Telangana. They are eroded and ...
, Western Ghats, the Brahmaputra River
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, northeast India, and Bangladesh. It is also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, Luit in Assamese, and Jamuna River in Bangla. I ...
basin and hills in Northeast India
, native_name_lang = mni
, settlement_type =
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption =
, motto =
, image_map = Northeast india.png
, ...
. Some leopard populations in the country live quite close to human settlements and even in semi-developed areas. Although adaptable to human disturbances, leopards require healthy prey populations and appropriate vegetative cover for hunting for prolonged survival and thus rarely linger in heavily developed areas. Due to the leopard's stealth, people often remain unaware that it lives in nearby areas.
In Nepal's Kanchenjunga Conservation Area
Kanchenjunga Conservation Area is a protected area in the Himalayas of eastern Nepal that was established in 1997. It covers in the Taplejung District and comprises two peaks of Kanchenjunga. In the north it adjoins the Qomolangma National Nature ...
, a melanistic leopard was photographed at an elevation of by a camera trap in May 2012. In Sri Lanka, leopards were recorded in Yala National Park and in unprotected forest patches, tea estate
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of ''Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of southwestern China and norther ...
s, grasslands, home gardens, pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanic ...
and eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as ...
plantations.
In Myanmar, leopards were recorded for the first time by camera traps in the hill forests of Myanmar's Karen State
Kayin State ( my, ကရင်ပြည်နယ်, ; kjp, ဖၠုံခါန်ႋကၞင့်, italics=no; ksw, ကညီကီၢ်စဲၣ်, ), also known by the endonyms Kawthoolei and Karen State, is a state of Myanmar. The ...
. The Northern Tenasserim Forest Complex in southern Myanmar is considered a leopard stronghold. In Thailand, leopards are present in the Western Forest Complex
The Western Forest Complex, straddling two countries, Thailand and Myanmar, including 19 national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, is the main biodiversity conservation corridor of the region. Covering 18,730 km2, it is one of the largest pro ...
, Kaeng Krachan Kaeng Krachan may refer to the following places in Phetchaburi Province, Thailand:
* Kaeng Krachan District
* Kaeng Krachan Dam
* Kaeng Krachan National Park
Kaeng Krachan National Park ( th, อุทยานแห่งชาติแก่� ...
- Kui Buri, Khlong Saeng-Khao Sok
Khao Sok National Park ( th, เขาสก, ) is in Surat Thani Province, Thailand. Its area is 461,712 rai ~ , and it includes the Cheow Lan Lake contained by the Ratchaprapha Dam. The park is the largest area of virgin forest in southern ...
protected area complexes and in Hala Bala Wildlife Sanctuary
300px, Hala-Bala Wildlife Sanctuary.
Hala-Bala Wildlife Sanctuary ( th, เขตรักษาพันธุ์สัตว์ป่าฮาลา-บาลา) is a wildlife sanctuary in Thailand, considered to be one of the richest forests ...
bordering Malaysia. In Peninsular Malaysia
Peninsular Malaysia ( ms, Semenanjung Malaysia; Jawi: سمننجڠ مليسيا), or the States of Malaya ( ms, Negeri-negeri Tanah Melayu; Jawi: نڬري-نڬري تانه ملايو), also known as West Malaysia or the Malaysian Peninsula, ...
, leopards are present in Belum-Temengor
Belum-Temengor is the largest continuous forest complex in Peninsular Malaysia. Specifically, it is located in the Malaysian state of Perak ( Hulu Perak) and crosses into Southern Thailand. Belum-Temenggor is divided into two sections. Belum is lo ...
, Taman Negara
Taman Negara is a national park in Peninsular Malaysia. It was established in 1938/1939 as the King George V National Park after Theodore Hubback lobbied the sultans of Pahang, Terengganu and Kelantan to set aside a piece of land that covers the ...
and Endau-Rompin National Park
Endau-Rompin National Park ( Malay: ''Taman Negara Endau-Rompin'') is a protected tropical rainforest in the southernmost prolongation of the Tenasserim Hills, Malaysia. It is south of the state of Pahang and northeast of Johor covering an area of ...
s.
In Laos, leopards were recorded in Nam Et-Phou Louey
Nam Et-Phou Louey National Protected Area (NPA) is a protected area in northern Laos, covering in three provinces: Houaphan, Luang Prabang, and Xieng Khouang. The park includes a core area where human access and wildlife harvest is prohibited an ...
National Biodiversity Conservation Area and Nam Kan National Protected Area.
In Cambodia, leopards inhabit deciduous dipterocarp forest
Dipterocarpaceae is a family of 16 genera and about 695 known species of mainly tropical lowland rainforest trees. The family name, from the type genus ''Dipterocarpus'', is derived from Greek (''di'' = two, ''pteron'' = wing and ''karpos'' = fru ...
in Phnom Prich Wildlife Sanctuary
Phnom Prich Wildlife Sanctuary ( km, ដែនជម្រកសត្វព្រៃភ្នំព្រេច) is a large protected area in eastern Cambodia that was established in 1993. It is part of maybe the largest protected area complex i ...
and Mondulkiri Protected Forest.
In southern China, leopards were recorded only in the Qinling
The Qinling () or Qin Mountains, formerly known as the Nanshan ("Southern Mountains"), are a major east–west mountain range in southern Shaanxi Province, China. The mountains mark the divide between the drainage basins of the Yangtze and Yellow ...
Mountains during surveys in 11 nature reserves between 2002 and 2009.
In Java, leopards inhabit dense tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equator ...
s and dry deciduous forest
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals ...
s at elevations from sea level to . Outside protected areas, leopards were recorded in mixed agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peopl ...
land, secondary forest
A secondary forest (or second-growth forest) is a forest or woodland area which has re-grown after a timber harvest or clearing for agriculture, until a long enough period has passed so that the effects of the disturbance are no longer evident. I ...
and production forest between 2008 and 2014.
In the Russian Far East, it inhabits temperate coniferous forest
Temperate coniferous forest is a terrestrial biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Temperate coniferous forests are found predominantly in areas with warm summers and cool winters, and vary in their kinds of plant life. In some, needle ...
s where winter temperatures reach a low of .
Behaviour and ecology
The leopard is a solitary andterritorial
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or an ...
animal. It is typically shy and alert when crossing roadways and encountering oncoming vehicles, but may be emboldened to attack people or other animals when threatened. Adults associate only in the mating season. Females continue to interact with their offspring even after weaning and have been observed sharing kills with their offspring when they can not obtain any prey. They produce a number of vocalizations, including growls, snarls, meows, and purrs. The roaring
A roar is a type of animal vocalization that is deep and resonating. Many mammals have evolved to produce roars and other roar-like vocals for purposes such as long-distance communication and intimidation. These include various species of big cat ...
sequence in leopards consists mainly of grunts, also called "sawing", as it resembles the sound of sawing wood. Cubs call their mother with a ''urr-urr'' sound.
The whitish spots on the back of its ears are thought to play a role in communication.
It has been hypothesized that the white tips of their tails may function as a 'follow-me' signal in intraspecific
Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species.
Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organis ...
communication. However, no significant association were found between a conspicuous colour of tail patches and behavioural variables in carnivores.
 Leopards are active mainly from dusk till dawn and rest for most of the day and for some hours at night in thickets, among rocks or over tree branches. Leopards have been observed walking across their range at night; they may even wander up to if disturbed. In some regions, they are
Leopards are active mainly from dusk till dawn and rest for most of the day and for some hours at night in thickets, among rocks or over tree branches. Leopards have been observed walking across their range at night; they may even wander up to if disturbed. In some regions, they are nocturnal
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed sens ...
. In western African forests, they have been observed to be largely diurnal and hunting during twilight, when their prey animals are active; activity patterns vary between seasons.
Leopards can climb trees very skillfully, often rest on tree branches and descend from trees headfirst.
They can run at over , leap over horizontally, and jump up to vertically.
Social spacing
InKruger National Park
Kruger National Park is a South African National Park and one of the largest game reserves in Africa. It covers an area of in the provinces of Limpopo and Mpumalanga in northeastern South Africa, and extends from north to south and from ea ...
, most leopards tend to keep apart. Males interact with their partners and cubs at times, and exceptionally this can extend beyond to two generations. Aggressive encounters are rare, typically limited to defending territories from intruders. In a South African reserve, a male was wounded in a male–male territorial battle over a carcass.
Males occupy home range
A home range is the area in which an animal lives and moves on a periodic basis. It is related to the concept of an animal's territory which is the area that is actively defended. The concept of a home range was introduced by W. H. Burt in 1943. He ...
s that often overlap with a few smaller female home ranges, probably as a strategy to enhance access to females. In the Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre i ...
, the home range of a female was completely enclosed within a male's. Females live with their cubs in home ranges that overlap extensively, probably due to the association between mothers and their offspring. There may be a few other fluctuating home ranges belonging to young individuals. It is not clear if male home ranges overlap as much as those of females do. Individuals try to drive away intruders of the same sex.
A study of leopards in the Namibian farmlands showed that the size of home ranges was not significantly affected by sex, rainfall patterns or season; the higher the prey availability in an area, the greater the leopard population density and the smaller the size of home ranges, but they tend to expand if there is human interference.
Sizes of home ranges vary geographically and depending on habitat and availability of prey. In the Serengeti
The Serengeti ( ) ecosystem is a geographical region in Africa, spanning northern Tanzania. The protected area within the region includes approximately of land, including the Serengeti National Park and several game reserves. The Serenget ...
, males have home ranges of and females of ; but males in northeastern Namibia of and females of . They are even larger in arid and montane areas. In Nepal's Bardia National Park, male home ranges of and female ones of are smaller than those generally observed in Africa.
Hunting and diet
The leopard is acarnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other s ...
that prefers medium-sized prey with a body mass ranging from . Prey species in this weight range tend to occur in dense habitat and to form small herds. Species that prefer open areas and have well-developed anti-predator strategies are less preferred. More than 100 prey species have been recorded. The most preferred species are ungulates
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, ca ...
, such as impala
The impala or rooibok (''Aepyceros melampus'') is a medium-sized antelope found in eastern and southern Africa. The only extant member of the genus ''Aepyceros'' and tribe Aepycerotini, it was first described to European audiences by Ger ...
(''Aepyceros melampus''), bushbuck
The Cape bushbuck (''Tragelaphus sylvaticus'') is a common and a widespread species of antelope in sub-Saharan Africa.Wronski T, Moodley Y. (2009)Bushbuck, harnessed antelope or both? ''Gnusletter'', 28(1):18-19. Bushbuck are found in a wide ran ...
(''Tragelaphus scriptus''), common duiker
The common duiker (''Sylvicapra grimmia''), also known as the grey or bush duiker, is a small antelope and the only member of the genus ''Sylvicapra''. This species is found everywhere in Africa south of the Sahara, excluding the Horn of Africa ...
(''Sylvicapra grimmia'') and chital
The chital or cheetal (''Axis axis''; ), also known as the spotted deer, chital deer, and axis deer, is a deer species native to the Indian subcontinent. It was first described and given a binomial name by German naturalist Johann Christian Po ...
(''Axis axis''). Primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter includin ...
s preyed upon include white-eyelid mangabey
The white-eyelid mangabeys are African Old World monkeys belonging to the genus ''Cercocebus''. They are characterized by their bare upper eyelids, which are lighter than their facial skin colouring, and the uniformly coloured hairs of the fur. ...
s (''Cercocebus'' sp.), guenon
The guenons (, ) are Old World monkeys of the genus ''Cercopithecus'' (). Not all members of this genus have the word "guenon" in their common names; also, because of changes in scientific classification, some monkeys in other genera may have co ...
s (''Cercopithecus'' sp.) and gray langur
Gray langurs, also called Hanuman langurs and Hanuman monkeys, are Old World monkeys native to the Indian subcontinent constituting the genus ''Semnopithecus''. Traditionally only one species ''Semnopithecus entellus'' was recognized, but since a ...
s (''Semnopithecus'' sp.). Leopards also kill smaller carnivores like black-backed jackal
The black-backed jackal (''Lupulella mesomelas),'' also called the silver-backed jackal, is a medium-sized canine native to eastern and southern Africa. These regions are separated by roughly 900 kilometers.
One region includes the southe ...
(''Lupulella mesomelas''), bat-eared fox
The bat-eared fox (''Otocyon megalotis'') is a species of fox found on the African savanna. It is the only extant species of the genus ''Otocyon'' and considered a basal canid species. Fossil records indicate this canid first appeared during t ...
(''Otocyon megalotis''), genet (''Genetta'' sp.) and cheetah.
The largest prey killed by a leopard was reportedly a male eland weighing . A study in Wolong National Nature Reserve
Wolong National Nature Reserve (), also known as Wolong Special Administrative Region (), is a protected area located in Wenchuan County, Sichuan Province, People's Republic of China. Established in 1963 with an initial size of about 20,000 hecta ...
in southern China demonstrated variation in the leopard's diet over time; over the course of seven years, the vegetative cover receded, and leopards opportunistically shifted from primarily consuming tufted deer
The tufted deer (''Elaphodus cephalophus'') is a small species of deer characterized by a prominent tuft of black hair on its forehead and fang-like canines for the males. It is a close relative of the muntjac, living somewhat further north over ...
(''Elaphodus cephalophus'') to pursuing bamboo rat
The bamboo rats are four species of rodents of the subfamily Rhizomyinae. They are the sole living representatives of the tribe Rhizomyini. All are found in South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia.
The species are:
*The Chinese bamboo rat, ''R ...
s (''Rhizomys sinense'') and other smaller prey.
The leopard depends mainly on its acute senses of hearing and vision for hunting. It primarily hunts at night in most areas. In western African forests and Tsavo National Park, they have also been observed hunting by day. They usually hunt on the ground. In the Serengeti, they have been observed to ambush prey by jumping down on it from trees.
The animal stalks its prey and tries to approach as closely as possible, typically within of the target, and, finally, pounces on it and kills it by suffocation. It kills small prey with a bite to the back of the neck, but holds larger animals by the throat and strangles them. It caches kills up to apart. It is able to take large prey due to its powerful jaw muscles, and is therefore strong enough to drag carcasses heavier than itself up into trees; an individual was seen to haul a young giraffe weighing nearly up into a tree. It eats small prey immediately, but drags larger carcasses over several hundred metres and caches it safely in trees, bushes or even caves; this behaviour allows the leopard to store its prey away from rivals, and offers it an advantage over them. The way it stores the kill depends on local topography and individual preferences, varying from trees in Kruger National Park to bushes in the plain terrain of the Kalahari.
Average daily consumption rates of were estimated for males and of for females. In the southern Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for , covering much of Botswana, and parts of Namibia and South Africa.
It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African Namib coastal d ...
, leopards meet their water requirements by the bodily fluids of prey and succulent plant
In botany, succulent plants, also known as succulents, are plants with parts that are thickened, fleshy, and engorged, usually to retain water in arid climates or soil conditions. The word ''succulent'' comes from the Latin word ''sucus'', me ...
s; they drink water every two to three days and feed infrequently on moisture-rich plants such as gemsbok cucumbers (''Acanthosicyos naudinianus''), watermelon
Watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a flowering plant species of the Cucurbitaceae family and the name of its edible fruit. A scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, it is a highly cultivated fruit worldwide, with more than 1,000 varie ...
(''Citrullus lanatus'') and Kalahari sour grass (''Schmidtia kalahariensis'').
Enemies and competitors
 In parts of its global range, the leopard is
In parts of its global range, the leopard is sympatric
In biology, two related species or populations are considered sympatric when they exist in the same geographic area and thus frequently encounter one another. An initially interbreeding population that splits into two or more distinct species s ...
with other large predators such as the tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living Felidae, cat species and a member of the genus ''Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily pr ...
(''Panthera tigris''), lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large cat of the genus '' Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adu ...
(''P. leo''), cheetah, spotted hyena
The spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), also known as the laughing hyena, is a hyena species, currently classed as the sole extant member of the genus ''Crocuta'', native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as being of least concern by the IUC ...
(''Crocuta crocuta''), striped hyena (''Hyaena hyaena''), brown hyena
The brown hyena (''Parahyaena brunnea''), also called strandwolf, is a species of hyena found in Namibia, Botswana, western and southern Zimbabwe, southern Mozambique and South Africa. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Parahyaena' ...
(''Parahyaena brunnea''), African wild dog
The African wild dog (''Lycaon pictus''), also called the painted dog or Cape hunting dog, is a wild canine which is a native species to sub-Saharan Africa. It is the largest wild canine in Africa, and the only extant member of the genus '' Lyca ...
(''Lycaon pictus''), dhole
The dhole (''Cuon alpinus''; ) is a canid native to Central, South, East and Southeast Asia. Other English names for the species include Asian wild dog, Asiatic wild dog, Indian wild dog, whistling dog, red dog, red wolf, and mountain wolf. It ...
(''Cuon alpinus''), wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly un ...
(''Canis lupus'') and up to five bear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the No ...
species. Some of these species steal its kills, kill its cubs and even kill adult leopards. Leopards retreat up a tree in the face of direct aggression, and were observed when killing or preying on smaller competitors such as black-backed jackal, African civet
The African civet (''Civettictis civetta'') is a large viverrid native to sub-Saharan Africa, where it is considered common and widely distributed in woodlands and secondary forests. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 200 ...
(''Civettictis civetta''), caracal
The caracal (''Caracal caracal'') () is a medium-sized wild cat native to Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia, and arid areas of Pakistan and northwestern India. It is characterised by a robust build, long legs, a short face, long tufted ...
(''Caracal caracal'') and African wildcat
The African wildcat (''Felis lybica'') is a small wildcat species native to Africa, West and Central Asia up to Rajasthan in India and Xinjiang in China. It has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List in 2022.
In Cyprus, an African wil ...
(''Felis lybica''). Leopards generally seem to avoid encounters with adult bears, but kill vulnerable bear cubs. In Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
, a few recorded vicious fights between leopards and sloth bear
The sloth bear (''Melursus ursinus'') is a myrmecophagous bear species native to the Indian subcontinent. It feeds on fruits, ants and termites. It is listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, mainly because of habitat loss and degradation ...
s (''Melursus ursinus'') apparently result in both animals winding up either dead or grievously injured.
While interspecies killing of full-grown leopards is generally rare, given the opportunity, both tiger and lion readily kill and consume both young and adult leopards. In the Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for , covering much of Botswana, and parts of Namibia and South Africa.
It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African Namib coastal d ...
, leopards frequently lose kills to brown hyenas, if the leopard is unable to move the kill into a tree. Single brown hyenas have been observed charging at and displacing male leopards from kills. Lions occasionally fetch leopard kills from trees.
Resource partitioning
In ecology, niche differentiation (also known as niche segregation, niche separation and niche partitioning) refers to the process by which competing species use the environment differently in a way that helps them to coexist. The competitive exclu ...
occurs where leopards share their range with tigers. Leopards tend to take smaller prey, usually less than , where tigers are present.
In areas where leopard and tiger are sympatric, coexistence is reportedly not the general rule, with leopards being few where tigers are numerous. Tigers appear to inhabit the deep parts of a forest while leopards are pushed closer to the fringes. In tropical forests, leopards do not always avoid the larger cats by hunting at different times. With relatively abundant prey and differences in the size of prey selected, tigers and leopards seem to successfully coexist without competitive exclusion or interspecies dominance hierarchies that may be more common to the leopard's co-existence with the lion in savanna habitats.
Nile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed throughout sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the central, eastern, ...
s (''Crocodylus niloticus'') prey on leopards occasionally. One large adult leopard was grabbed and consumed by a large crocodile while attempting to hunt along a bank in Kruger National Park
Kruger National Park is a South African National Park and one of the largest game reserves in Africa. It covers an area of in the provinces of Limpopo and Mpumalanga in northeastern South Africa, and extends from north to south and from ea ...
. Mugger crocodile
The mugger crocodile (''Crocodylus palustris'') is a medium-sized broad-snouted crocodile, also known as mugger and marsh crocodile. It is native to freshwater habitats from southern Iran to the Indian subcontinent, where it inhabits marshe ...
s (''Crocodylus palustris'') reportedly killed an adult leopard in Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
. An adult leopard was recovered from the stomach of a Burmese python
The Burmese python (''Python bivittatus'') is one of the largest species of snakes. It is native to a large area of Southeast Asia and is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Until 2009, it was considered a subspecies of the Indian pytho ...
(''Python bivittatus''). In Serengeti National Park
The Serengeti National Park is a large national park in northern Tanzania that stretches over . It is located entirely in eastern Mara Region and north east portion of Simiyu Region and contains over of virgin savanna. The park was established ...
, troops of 30–40 olive baboon
The olive baboon (''Papio anubis''), also called the Anubis baboon, is a member of the family Cercopithecidae Old World monkeys. The species is the most wide-ranging of all baboons, being native to 25 countries throughout Africa, extending fr ...
s (''Papio anubis'') were observed while mobbing and attacking a female leopard and her cubs.
Reproduction and life cycle
In some areas, leopards mate all year round. In Manchuria and Siberia, they mate during January and February. The female'sestrous cycle
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestro ...
lasts about 46 days, and she usually is in heat for 6–7 days. The Generation time, generation length of the leopard is 9.3 years. Gestation lasts for 90 to 105 days. Cubs are usually born in a Litter (zoology), litter of 2–4 cubs. Mortality of cubs is estimated at 41–50% during the first year.
Females give birth in a cave, crevice among boulders, hollow tree or thicket. Cubs are born with closed eyes, which open four to nine days after birth. The fur of the young tends to be longer and thicker than that of adults. Their pelage is also more gray in colour with less defined spots. Around three months of age, the young begin to follow the mother on hunts. At one year of age, cubs can probably fend for themselves, but remain with the mother for 18–24 months.
The average typical life span of a leopard is 12–17 years. The oldest leopard was a captive female that died at the age of 24 years, 2 months and 13 days.
Conservation issues
The leopard is listed on CITES Appendix I, and trade is restricted to skins and body parts of 2,560 individuals in 11 sub-Saharan countries. The leopard is primarily threatened by habitat fragmentation and conversion of forest to agriculturally used land, which lead to a declining natural prey base, human–wildlife conflict with livestock herders and high leopard mortality rates. It is also threatened by trophy hunting and poaching. Between 2002 and 2012, at least four leopards were estimated to have been poached per week in India for the illegal wildlife trade of its skins and bones. In spring 2013, 37 leopard skins were found during a 7-week long market survey in major Moroccan cities. In 2014, 43 leopard skins were detected during two surveys in Morocco. Vendors admitted to have imported skins from sub-Saharan Africa. Surveys in the Central African Republic's Chinko area revealed that the leopard population decreased from 97 individuals in 2012 to 50 individuals in 2017. In this period, transhumant Pastoralism, pastoralists from the border area with Sudan moved in the area with their livestock. Rangers confiscated large amounts of poison in the camps of livestock herders who were accompanied by armed merchants. They engaged in poaching large herbivores, sale of bushmeat and trading leopard skins in Am Dafok. In Java, the leopard is threatened by illegal hunting and trade. Between 2011 and 2019, body parts of 51 Javan leopards were seized including six live individuals, 12 skins, 13 skulls, 20 canines and 22 claws.Human interaction
Cultural significance
Leopards have featured in art, mythology and folklore of many countries. In Greek mythology, it was a symbol of the god Dionysus, who was depicted wearing leopard skin and using leopards as means of transportation. In one myth, the god was captured by pirates but two leopards rescued him. During the Benin Empire, the leopard was commonly represented on engravings and sculptures and was used to symbolise the power of the king or ''Oba (ruler), oba'', since the leopard was considered the king of the forest. The Ashanti people, Ashanti also used the leopard as a symbol of leadership, and only the king was permitted to have a ceremonial leopard stool. Some African cultures considered the leopard to be a smarter, better hunter than the lion and harder to kill. In Rudyard Kipling's "How the Leopard Got His Spots", one of his ''Just So Stories'', a leopard with no spots in the Highveld, High Veldt lives with his hunting partner, the Ethiopian. When they set off to the forest, the Ethiopian changed his brown skin, and the leopard painted spots on his skin. A leopard played an important role in the 1938 Hollywood film ''Bringing Up Baby''. African chiefs, European queens, Hollywood actors and burlesque dancers wore coats made of leopard skins. The leopard is a frequently used in Leopard (heraldry), heraldry, most commonly as ''Attitude_(heraldry)#Passant, passant''. The heraldic leopard lacks spots and sports a mane, making it visually almost identical to the Lion (heraldry), heraldic lion, and the two are often used interchangeably. Naturalistic leopard-like depictions appear on the coat of arms of Benin, Coat of arms of Malawi, Malawi, Coat of arms of Somalia, Somalia, the Coat of arms of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo and Coat of arms of Gabon, Gabon, the last of which uses a black panther.Attacks on people
The Leopard of Rudraprayag killed more than 125 people; the Panar Leopard was thought to have killed more than 400 people. Both were shot by British hunter Jim Corbett. The ''spotted devil of Gummalapur'' killed about 42 people in Karnataka, India.In captivity
The Ancient Romans kept leopards in captivity to be slaughtered in Venatio, hunts as well as be used in Damnatio ad bestias, executions of criminals. In Benin, leopards were kept and paraded as mascots, totems and sacrifices to deities. Several leopards were kept in a menagerie established by King John of England at the Tower of London in the 13th century; around 1235, three of these animals were given to Henry III of England, Henry III by Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II. In modern times, leopards have been Animal training, trained and Tame animal, tamed in circuses.See also
* * Leopard pattern * List of largest cats * Panther (legendary creature)References
Further reading
* * * * * * *External links
IUCN/SSC Cat Specialist Group: ''Panthera pardus'' in Africa
an
''Panthera pardus'' in Asia
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Leopard Articles containing video clips Big cats Felids of Africa Felids of Asia Mammals described in 1758 National symbols of Benin National symbols of Malawi National symbols of Somalia National symbols of the Democratic Republic of the Congo Panthera Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus