Pandoh Dam on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Pandoh Dam is an

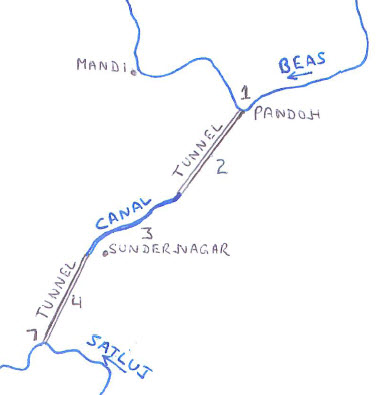 The seven components of the Dehar hydroelectric Project for diversion of 9000 cusecs of water and power generation as shown on the figures are:
# Pandoh dam - 76.25 m (250 ft) earthen dam
# Pandoh Baggi Tunnel - 7.62 m dia, 13.11 km long
# Sundernagar Hydel Channel - 11.8 km long open channel
# Sundarnagar Dehar Tunnel - 8.53 m dia, 12.53 km long
# Surge Shaft - 22.86 m dia x 125 m high
# Penstocks - Three 4.877 m split to six 3.353 m
# Dehar Power House - 6 × 165 MW
The seven components of the Dehar hydroelectric Project for diversion of 9000 cusecs of water and power generation as shown on the figures are:
# Pandoh dam - 76.25 m (250 ft) earthen dam
# Pandoh Baggi Tunnel - 7.62 m dia, 13.11 km long
# Sundernagar Hydel Channel - 11.8 km long open channel
# Sundarnagar Dehar Tunnel - 8.53 m dia, 12.53 km long
# Surge Shaft - 22.86 m dia x 125 m high
# Penstocks - Three 4.877 m split to six 3.353 m
# Dehar Power House - 6 × 165 MW
 The tall Pandoh Dam is an
The tall Pandoh Dam is an
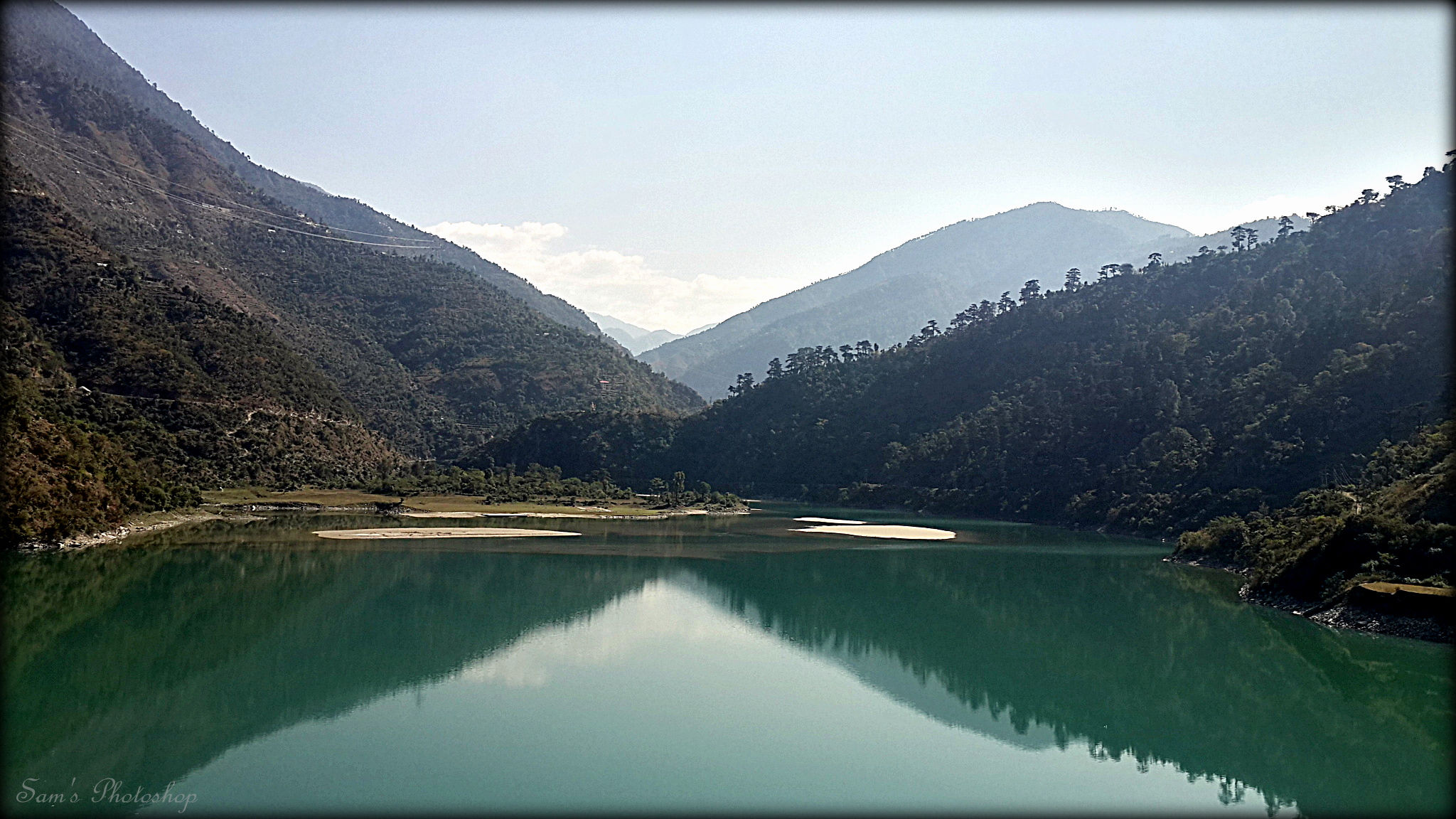 Pandoh Lake is created by Pandoh Dam and is located about upstream from Mandi on the River
Pandoh Lake is created by Pandoh Dam and is located about upstream from Mandi on the River
embankment dam
An embankment dam is a large artificial dam. It is typically created by the placement and compaction of a complex semi-plastic mound of various compositions of soil or rock. It has a semi-pervious waterproof natural covering for its surface an ...
on the Beas River
The Beas River (Sanskrit: ; Hyphasis in Ancient Greek) is a river in north India. The river rises in the Himalayas in central Himachal Pradesh, India, and flows for some to the Sutlej River in the Indian state of Punjab. Its total length is ...
in Mandi district
Mandi district is one of the central districts of Himachal Pradesh state in northern India. The town of Mandi is the headquarters of the district.
The main native language is Mandeali.
As of 2011 it is the second most populous district of H ...
of Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several pea ...
, India. Under the Beas Project, the dam was completed in 1977 and its primary purpose is hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
power generation. Part of a run-of-the-river
Run-of-river hydroelectricity (ROR) or run-of-the-river hydroelectricity is a type of hydroelectric generation plant whereby little or no water storage is provided. Run-of-the-river power plants may have no water storage at all or a limited amou ...
power scheme, it diverts the waters of the Beas to the southwest through a long system of tunnels and channels. The water is used for power generation at the Dehar Power House before being discharged into the Sutlej River
The Sutlej or Satluj River () is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroads region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. The Sutlej River is also known as ''Satadru''. It is the easternmost tributary of the ...
, connecting both rivers. The power house has an installed capacity of 990 MW. The system diverts 256 cumecs (9000 cusecs) of Beas waters to the Satluj River. The project was completed in 1977.
History
The two major riversBeas
Beas is a riverfront town in the Amritsar district of the Indian state of Punjab. Beas lies on the banks of the Beas River. Beas town is mostly located in revenue boundary of Budha Theh with parts in villages Dholo Nangal and Wazir Bhullar. ...
and Satlej flow out of the himalayas and reach a point where they are separated by a crow fly distance of approximately 36 km and have an elevation difference of approximately 1099 ft. The waters of Beas flow from melting ice throughout the year. This was realized and a plan made to exploit the potential of this river system. The power potential was estimated as 1,000 MW. The plans originally called Beas Project Unit - I Beas Satluj Link Project went through several revisions for diverting the waters of Beas river. The first plan prepared by Punjab Irrigation Department in 1957. The 1957 plan contemplated a diversion dam at Pandoh, tunnel, open channel, tunnel. The 1957 report was followed by a 1960 report and the final proposal in 1961. The final proposal included diversion dam at Pandoh, a dia, Pandoh baggi tunnel, Sunder Nagar hydel channel, dia, Sundernagar Satluj tunnel, dia high surge shaft, three Dehar penstocks split to six penstocks and Dehar power plant with 6 x 165 MW generators. The system would divert of the Beas to the Satluj. An added benefit of the project was the increased inflow to Gobind Sagar thereby increasing power generation capacity at Bhakra Dam
Bhakra Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Sutlej River in Bhakra Village near Bilaspur in Bilaspur district, Himachal Pradesh in northern India. The dam forms the Gobind Sagar reservoir.
The dam, located at a gorge near the (now submerge ...
and added irrigation waters for the states of Punjab and Haryana. The project was approved in 1963 and commissioned in 1977.
Components

 The seven components of the Dehar hydroelectric Project for diversion of 9000 cusecs of water and power generation as shown on the figures are:
# Pandoh dam - 76.25 m (250 ft) earthen dam
# Pandoh Baggi Tunnel - 7.62 m dia, 13.11 km long
# Sundernagar Hydel Channel - 11.8 km long open channel
# Sundarnagar Dehar Tunnel - 8.53 m dia, 12.53 km long
# Surge Shaft - 22.86 m dia x 125 m high
# Penstocks - Three 4.877 m split to six 3.353 m
# Dehar Power House - 6 × 165 MW
The seven components of the Dehar hydroelectric Project for diversion of 9000 cusecs of water and power generation as shown on the figures are:
# Pandoh dam - 76.25 m (250 ft) earthen dam
# Pandoh Baggi Tunnel - 7.62 m dia, 13.11 km long
# Sundernagar Hydel Channel - 11.8 km long open channel
# Sundarnagar Dehar Tunnel - 8.53 m dia, 12.53 km long
# Surge Shaft - 22.86 m dia x 125 m high
# Penstocks - Three 4.877 m split to six 3.353 m
# Dehar Power House - 6 × 165 MW
Pandoh Dam
embankment dam
An embankment dam is a large artificial dam. It is typically created by the placement and compaction of a complex semi-plastic mound of various compositions of soil or rock. It has a semi-pervious waterproof natural covering for its surface an ...
on the Beas River
The Beas River (Sanskrit: ; Hyphasis in Ancient Greek) is a river in north India. The river rises in the Himalayas in central Himachal Pradesh, India, and flows for some to the Sutlej River in the Indian state of Punjab. Its total length is ...
. The dam was commissioned in 1977 and its primary purpose is hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
power generation. Part of a run-of-the-river
Run-of-river hydroelectricity (ROR) or run-of-the-river hydroelectricity is a type of hydroelectric generation plant whereby little or no water storage is provided. Run-of-the-river power plants may have no water storage at all or a limited amou ...
power scheme, it diverts the waters of the Beas to the southwest through a long system of tunnels and channels. The water is used for power generation at the Dehar Power House before being discharged into the Satluj River, connecting both rivers.
Pandoh Lake
 Pandoh Lake is created by Pandoh Dam and is located about upstream from Mandi on the River
Pandoh Lake is created by Pandoh Dam and is located about upstream from Mandi on the River Beas
Beas is a riverfront town in the Amritsar district of the Indian state of Punjab. Beas lies on the banks of the Beas River. Beas town is mostly located in revenue boundary of Budha Theh with parts in villages Dholo Nangal and Wazir Bhullar. ...
.
Operation
Water diverted by the Pandoh Dam is first sent through the 7.62 m diameter, long Pandoh-Baggi tunnel which terminates at the beginning of a long channel. At the end of the channel, the water is stored at the Sundar Nagar Balancing Reservoir at . The reservoir has a live capacity of . From the balancing reservoir, water is again sent south through the 8.53 m dia, long Sundar Nagar Slapper tunnel. The tunnel ends just before the Dehar Power Plant at . It splits into three 4.877 m dia followed by six 3.353 m diapenstock
A penstock is a sluice or gate or intake structure that controls water flow, or an enclosed pipe that delivers water to hydro turbines and sewerage systems. The term is inherited from the earlier technology of mill ponds and watermills.
H ...
s before reaching the power house. The 22.86 m dia 125 m tall surge shaft at the end of the tunnel is designed to take any backfow due to sudden shutdown of the power plant and avoid tunnel rupture due to water hammer
Hydraulic shock (colloquial: water hammer; fluid hammer) is a pressure surge or wave caused when a fluid in motion, usually a liquid but sometimes also a gas is forced to stop or change direction suddenly; a momentum change. This phenomenon com ...
.
Dehar Power Plant
The Dehar Power Plant is situated on the banks of theSatluj
The Sutlej or Satluj River () is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroads region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. The Sutlej River is also known as ''Satadru''. It is the easternmost tributary of the ...
at the Slapper bridge. Water from penstocks is fed into a six 165 MW Francis turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts. Francis turbines are the most common water turbine in use today, and can achieve over 95% efficiency.
The proc ...
-generator and then discharged in the Satluj. The power house has an installed capacity of . The change in elevation affords a hydraulic head
Hydraulic head or piezometric head is a specific measurement of liquid pressure above a vertical datum., 410 pages. See pp. 43–44., 650 pages. See p. 22.
It is usually measured as a liquid surface elevation, expressed in units of length, ...
of .
It is managed by the Bhakra Beas Management Board (BBMB), which is engaged in regulation of the supply of water and power from Bhakra Nangal Dam
Bhakra Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Sutlej River in Bhakra Village near Bilaspur in Bilaspur district, Himachal Pradesh in northern India. The dam forms the Gobind Sagar reservoir.
The dam, located at a gorge near the (now submerg ...
and Beas Projects to the states of Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi Language, Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also Romanization, romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the I ...
, Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ...
, Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a state in northern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern ...
, Himachal Pradesh and Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
.
Diverted waters from Beas also increased the generation capacity of the Bhakra Dam
Bhakra Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Sutlej River in Bhakra Village near Bilaspur in Bilaspur district, Himachal Pradesh in northern India. The dam forms the Gobind Sagar reservoir.
The dam, located at a gorge near the (now submerge ...
downstream of Dehar Power Plant.
Ecology
The Pandoh dam diverts 256 cumecs (9000 cusecs) of Beas to river Satluj. Diversion of the Beas water has done considerable damage to the towns downstream on Beas river and left a trail of misery toMandi
Mandi may refer to:
Places
* Mandı, Azerbaijan
India
* Mandi, Jammu and Kashmir, a town on the Mandi River in the Poonch district of Jammu and Kashmir
* Mandi, Himachal Pradesh, a city in Himachal Pradesh
** Mandi State, former princely s ...
. In winter the river bed almost dries and leaves a deserted look.
See also
*Pong Dam
The Pong Dam, also known as the Beas Dam, is an earth-fill embankment dam on the Beas River in the state of Himachal Pradesh, India, just upstream of Talwara. The purpose of the dam is water storage for irrigation and hydroelectric power generat ...
– located downstream, the second phase of the Beas Project
*Bhakra Dam
Bhakra Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Sutlej River in Bhakra Village near Bilaspur in Bilaspur district, Himachal Pradesh in northern India. The dam forms the Gobind Sagar reservoir.
The dam, located at a gorge near the (now submerge ...
– downstream of Dehar Power Station
References
{{Power Projects in Himachal Pradesh Dams completed in 1977 Energy infrastructure completed in 1977 Dams in Himachal Pradesh Hydroelectric power stations in Himachal Pradesh Run-of-the-river power stations Dams on the Beas River 1977 establishments in Himachal Pradesh Buildings and structures in Mandi district