Pacific Islander American on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pacific Islander Americans (also known as
 Migration from
Migration from
The American Presidency Project. Retrieved September 1, 2019. and signed an agreement with
The Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander Population: 2010 Census
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20100105031601/http://imdiversity.com/Villages/Asian/reference/census_2000_pac_islanders.asp Pacific Islander Populations, Census 2000 {{Authority control Ethnic groups in the United States American people of Micronesian descent American people of Melanesian descent American people of Polynesian descent Pacific Islands American
Oceanian Americans
Oceanian Americans or Oceanic Americans are Americans whose ancestors came from Oceania, a region which is compose of the Australian continent and the Pacific Islands.
There are basically two Oceanian American groups, that well represent the ra ...
) are Americans
Americans are the citizens and nationals of the United States of America.; ; Although direct citizens and nationals make up the majority of Americans, many dual citizens, expatriates, and permanent residents could also legally claim Ame ...
who are of Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/ racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of O ...
ancestry (or are descendants of the indigenous peoples of Oceania
The indigenous peoples of Oceania are Aboriginal Australians, Papuans, and Austronesians (Melanesians (including Torres Strait Islanders), Micronesians, and Polynesians). These indigenous peoples have a historical continuity with pre-colonia ...
or of Austronesian descent). For its purposes, the United States census also counts Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples ...
as part of this group.
Pacific Islander Americans make up 0.5% of the U.S. population including those with partial Pacific Islander ancestry, enumerating about 1.4 million people. The largest ethnic subgroups of Pacific Islander Americans are Native Hawaiians
Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, Kānaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, First Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians) ( haw, kānaka, , , and ), are the indigenous ethnic group of Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.
Hawa ...
, Samoans
Samoans or Samoan people ( sm, tagata Sāmoa) are the indigenous Polynesian people of the Samoan Islands, an archipelago in Polynesia, who speak the Samoan language. The group's home islands are politically and geographically divided between t ...
, Chamorros
The Chamorro people (; also CHamoru) are the indigenous people of the Mariana Islands, politically divided between the United States territory of Guam and the encompassing Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands in Micronesia. Today, signif ...
, Fijians
Fijians ( fj, iTaukei, lit=Owners (of the land)) are a nation and ethnic group native to Fiji, who speak Fijian and share a common history and culture.
Fijians, or ''iTaukei'', are the major indigenous people of the Fiji Islands, and live i ...
, Marshalleses, Tongans
Tongans, a Polynesian group, represent more than 98% of the inhabitants of Tonga. The rest are European (the majority are British), mixed European, and other Pacific Islanders. There also are several hundred Chinese. Almost two-thirds of the po ...
, and Tahitians
The Tahitians ( ty, Māohi; french: Tahitiens) are the Polynesian ethnic group indigenous to Tahiti and thirteen other Society Islands in French Polynesia. The numbers may also include the modern population in these islands of mixed Polynesia ...
.
American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internatio ...
, Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, and the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonw ...
are insular area
In the law of the United States, an insular area is a U.S.-associated jurisdiction that is not part of the 50 states or the District of Columbia. This includes fourteen U.S. territories administered under U.S. sovereignty, as well as three so ...
s ( U.S. territories), while Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
is a state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
.
History
First stage: Hawaiian migration (18th-19th centuries)
 Migration from
Migration from Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
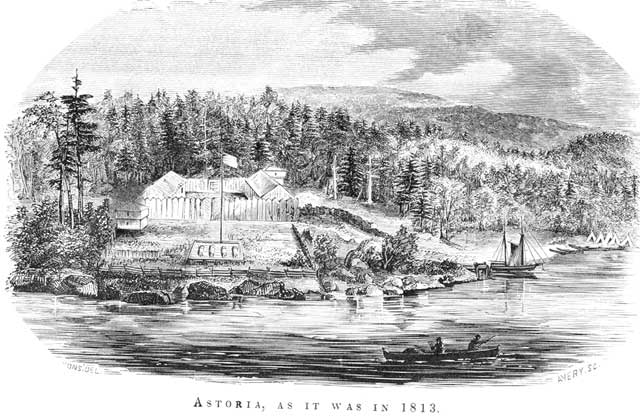
to the United States began in the last decade of the 18th century, but the first migrants to arrive in the country were natives of Hawaii. People from other Oceanian backgrounds (except Australians and Māori) did not migrate to the United States until the late 19th century. The first Native Hawaiians to live in the present-day United States were fur traders. They were hired by British fur traders in Hawaii and taken to the northwestern United States, from where trade networks developed with Honolulu. However, they charged less than Americans for doing the same jobs and returned to Hawaii when their contracts ended. The first Native Hawaiians to live permanently in the United States settled in the Astoria colony (in present-day Oregon) in 1811, having been brought there by its founder, fur merchant John Jacob Astor. Astor created the Pacific Fur Company
The Pacific Fur Company (PFC) was an American fur trade venture wholly owned and funded by John Jacob Astor that functioned from 1810 to 1813. It was based in the Pacific Northwest, an area contested over the decades between the United Kingdom o ...
in the colony and used the Native Hawaiians to build the city's infrastructure and houses and to develop the primary sector (agriculture, hunting and fishing). The labor employment of the Native Hawaiians was done to make them serve the company (although later, most of them worked for North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great weal ...
when this company absorbed the Pacific Fur Company in 1813).
After 1813, Native Hawaiians continued to migrate to the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Thou ...
. They migrated to work in companies such as the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
(which absorbed the North West Company in 1821) and the Columbia Fishing and Trading Company, as well as in Christian missions. Chapter: ''Pacific Islander and Pacific Islander Americans, 1940-present'', written by Matthew Kester. Since 1819, some groups of Polynesian Protestant students immigrated to the United States to study theology. Since the 1830s, another group of Native Hawaiians arrived on California's shores, where they were traders and formed communities. So, they made up 10% of the population of Yerba Buena, now San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17t ...
, in 1847. During the California Gold Rush
The California Gold Rush (1848–1855) was a gold rush that began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California f ...
, many other Native Hawaiians migrated to California to work as miners.
In 1889, the first Polynesian Mormon
Mormons are a religious and cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's death in 1844, the movement split into se ...
colony was founded in Utah and consisted of Native Hawaiians, Tahitians, Samoans, and Māori. Also in the late 19th century, small groups of Pacific Islanders, usually sailors, moved to the western shores, mainly on San Francisco. Later, the U.S. occupied Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
in 1896, Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
in 1898, and American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internatio ...
in 1900. This fact diversified Oceanian emigration in the United States.
Second stage (20th-21st centuries)
However, the first record of non-Hawaiian Pacific Islanders in the United States is from 1910, with the first Guamanians living in the United States. In the following decades small groups of people from islands such as Hawaii, Guam, Tonga, or American Samoa emigrated to the United States. Many of them were Mormons (including most of Tongans and American Samoans), Chapter: ''Pacific Islander and Pacific Islander Americans, 1940-present'', written by Matthew Kester. who emigrated to help build Mormon churches, or to seek an education, either inLaie
Laie ( haw, Lāie, ) is a census-designated place (CDP) located in the Koolauloa District on the island of Oahu () in Honolulu County, Hawaii, United States. In Hawaiian, means " leaf" ( is a climbing screwpine: ''Freycinetia arborea''). The p ...
or Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the capital and most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in Utah. With a population of 200,133 in 2020, th ...
. However, the emigration of Pacific Islanders to the U.S. was small until the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, when many American Samoans, From work ''Samoan Saints: the Samoans in the mormon village of Laie, Hawaii''. Guamanians (who got the American citizenship in 1929) and Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
ns emigrated to the United States. Most of them were in the military or married with military people, but some Pacific Islanders, particularly Tongans, looked for a job in several religious and cultural centers. Since then the emigration increased and diversified every decade, with a majority emigrating to the Western urban areas and Hawaii.
This increase and diversification in the Oceanian emigration was especially true in the 1950s. In 1950, the population of Guam gained full American citizenship. In 1952, the natives of American Samoa become American nationals, although not American citizens, through the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1952
The Immigration and Nationality Act of 1952 (), also known as the McCarran–Walter Act, codified under Title 8 of the United States Code (), governs immigration to and citizenship in the United States. It came into effect on June 27, 1952. Befor ...
. Shortly thereafter, the first major waves of migration from American Samoa and Guam emerged, while other groups of places such as French Polynesia
)Territorial motto: ( en, "Great Tahiti of the Golden Haze")
, anthem =
, song_type = Regional anthem
, song = "Ia Ora 'O Tahiti Nui"
, image_map = French Polynesia on the globe (French Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of French ...
, Palau
Palau,, officially the Republic of Palau and historically ''Belau'', ''Palaos'' or ''Pelew'', is an island country and microstate in the western Pacific. The nation has approximately 340 islands and connects the western chain of the ...
or Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consis ...
began to emigrate. Over 5,100 Pacific Islanders emigrated to the United States in the 1950s, mostly from American Samoa, Guam, and Tonga. The first of them were Samoan military personnel, who had worked at the American bases of Pago Pago
Pago Pago ( ; Samoan: )Harris, Ann G. and Esther Tuttle (2004). ''Geology of National Parks''. Kendall Hunt. Page 604. . is the territorial capital of American Samoa. It is in Maoputasi County on Tutuila, which is American Samoa's main island. ...
but moved to the Honolulu's American bases when American Samoa began to be administered by the United States Department of the Interior
The United States Department of the Interior (DOI) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government headquartered at the Main Interior Building, located at 1849 C Street NW in Washington, D.C. It is responsible for the ma ...
, as well as their relatives. Most of the new Pacific Islander immigrants were Mormons and many islanders from the region emigrated to the United States seeking economic opportunities.
In 1959, Hawaii became a state and its natives got U.S. citizenship. This made more than 630,000 people Americans; many of them were Pacific Islanders, both Native Hawaiians and people of other Oceanian origins. Thus, the Hawaiian migration to the continental U.S. began to increase. In the 1960s, many more Pacific Islanders emigrated to the U.S., mainly due to increased migration from Guam, Chapter: Pacific Islanders in the U.S., written by Faye Untalan Muñoz. Fiji, Tonga, and Samoa archipelago (both independent and American Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
). The Pacific Islanders migrated by diverse reasons: Many Guamanians fled the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top:{ ...
and Typhoon Karen, and the Fijian population living in the U.S. skyrocketed from a few dozen people in the 1950s to more than 400 people. The Pacific Islander migration increased especially since 1965, when the United States government facilitated the non-European migration to the U.S. Many of them were recruited to pick fruit in California.
During the 1970s, over nine thousand Pacific Islanders migrated to the U.S., mostly from Samoa (both Western and American), Guam, Tonga, and Fiji, but also from other islands such as Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states compr ...
or Palau. Many of these people emigrated to the U.S. to study at its universities. Moreover, in the 1980s, migration from the Pacific Islands to the United States became more diversified when this country acquired the Northern Marianas Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonwea ...
in 1986"Proclamation 5564—United States Relations With the Northern Mariana Islands, Micronesia, and the Marshall Islands"The American Presidency Project. Retrieved September 1, 2019. and signed an agreement with
TTPI
The Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (TTPI) was a United Nations trust territory in Micronesia administered by the United States from 1947 to 1994.
History
Spain initially claimed the islands that later composed the territory of the T ...
(FSM, Palau and the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Inte ...
) called the Compact of Free Association
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (F ...
. The Compact of Free Association allows the inhabitants from TTPI to travel and work in the United States without visas. On the other hand, the Tyson Foods
Tyson Foods, Inc. is an American multinational corporation, based in Springdale, Arkansas, that operates in the food industry. The company is the world's second-largest processor and marketer of chicken, beef, and pork after JBS S.A. It annually ...
company, which employed a significant part of the population of the Marshall Islands, relocated many of its Marshellese employees in Springdale, Arkansas
Springdale is the fourth-largest city in Arkansas, United States. It is located in both Washington and Benton counties in Northwest Arkansas. Located on the Springfield Plateau deep in the Ozark Mountains, Springdale has long been an important ...
, where the company is based. However, most of Pacific Islanders continued to migrate to western urban areas and Hawaii. More of five thousand Pacific Islanders migrated to the United States in the 1990s, settling mostly in western cities such as Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world ...
, San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17t ...
, Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region o ...
, or Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the capital and most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in Utah. With a population of 200,133 in 2020, th ...
. In the 2000 United States census, almost all the countries of Oceania were mentioned, although only the ethnic groups mentioned in the article consisted of thousands of people. In the 2000s and 2010s, several thousands more Pacific Islanders emigrated to the United States.
Population
Demography
In the 2000 and 2010 censuses, the term "Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander" refers to people having origins in any of the original peoples of Hawaii, Guam, Tonga, Samoa, Fiji, New Zealand, and the Marshalls or other Pacific Islands. Most of the Pacific Islander Americans are ofNative Hawaiian
Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, Kānaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, First Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians) ( haw, kānaka, , , and ), are the indigenous ethnic group of Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.
Hawa ...
, Samoan and Chamorro Chamorro may refer to:
* Chamorro people, the indigenous people of the Mariana Islands in the Western Pacific
* Chamorro language, an Austronesian language indigenous to The Marianas
* Chamorro Time Zone, the time zone of Guam and the Northern Mari ...
origin.
The fact that Hawaii is a U.S. state (meaning that almost the entire native Hawaiian population lives in the U.S.), as well as the migration, high birth rate and miscegenation of the Pacific Islanders have favored the permanence and increase of this population in the U.S. (especially in the number of people who are of partial Pacific Islander descent). In the 2000 census, over 800,000 people claimed to be of Pacific Islander descent and in the 2010 census 1,225,195 Americans claimed "'Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander'" as their race alone or in combination. Most of them live in urban areas of Hawaii and California, but they also have sizeable populations in Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its ...
, Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and ...
, Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
, and New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
. On the other hand, Pacific Islander Americans represent the majority (or are the main ethnic group) in American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internatio ...
, Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, and the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonw ...
, from where many of them are natives.
Areas of origin
Melanesian Americans
Melanesian Americans areAmericans
Americans are the citizens and nationals of the United States of America.; ; Although direct citizens and nationals make up the majority of Americans, many dual citizens, expatriates, and permanent residents could also legally claim Ame ...
of Melanesian descent.
Most of them are of Fijian descent. Most of Fijian Americans are of Fijian and Indian descent. More than 32,000 people of Fijian origin live in the U.S. Most of them live in California.
Smaller communities of Papuan, Vanuatuan
Ni-Vanuatu (informally abbreviated Ni-Van) is a large group of closely related Melanesian ethnic groups native to the island country of Vanuatu. As such, ''Ni-Vanuatu'' are a mixed ethnolinguistic group with a shared ethnogenesis that speak a mu ...
, and Solomon Islander origin also live in the U.S.
Micronesian Americans
Micronesian Americans
Micronesian Americans are Americans who are descended from people of the Federated States of Micronesia. According to the 2010 census, a total of 8,185 residents self-identified as having origins in the country, which consists of four states. More ...
are Americans of Micronesian descent or are Americans whose origins are in the Federated States of Micronesia
The Federated States of Micronesia (; abbreviated FSM) is an island country in Oceania. It consists of four states from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosraethat are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states compr ...
.
There are more than 8,000 people living in the U.S. whose origins are in the Federated States of Micronesia. Most of them live in Hawaii, California, Oregon, and Texas, as well as in Mariana Islands. Another 7,000 Americans are of Palauan descent.
According to the 2010 census, the largest Chamorro Chamorro may refer to:
* Chamorro people, the indigenous people of the Mariana Islands in the Western Pacific
* Chamorro language, an Austronesian language indigenous to The Marianas
* Chamorro Time Zone, the time zone of Guam and the Northern Mari ...
populations were located in California, Washington, and Texas, but their combined number from these three states totaled less than half the number living throughout the U.S. It also revealed that the Chamorro people are the most geographically dispersed Oceanian ethnicity in the country.
Marshallese Americans or Marshallese come from the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Inte ...
. In the 2010 census, 22,434 Americans identified as being of Marshallese descent.
Because of the Marshall Islands entering the Compact of Free Association
The Compact of Free Association (COFA) is an international agreement establishing and governing the relationships of free association between the United States and the three Pacific Island sovereign states of the Federated States of Micronesia (F ...
in 1986, Marshallese have been allowed to migrate and work in the United States. There are many reasons why Marshallese came to the United States. Some Marshallese came for educational opportunities, particularly for their children. Others sought work or better health care than what is available in the islands. Massive layoffs by the Marshallese government in 2000 led to a second big wave of immigration.
Arkansas has the largest Marshallese population with over 6,000 residents. Many live in Springdale, and the Marshallese comprise over 5% of the city's population. Other significant Marshallese populations include Spokane
Spokane ( ) is the largest city and county seat of Spokane County, Washington, United States. It is in eastern Washington, along the Spokane River, adjacent to the Selkirk Mountains, and west of the Rocky Mountain foothills, south of the Ca ...
and Costa Mesa.
Smaller communities of I-Kiribati and Nauruan origins also live in the USA.
Polynesian Americans
Polynesian Americans areAmericans
Americans are the citizens and nationals of the United States of America.; ; Although direct citizens and nationals make up the majority of Americans, many dual citizens, expatriates, and permanent residents could also legally claim Ame ...
of Polynesian descent.
Large subcategories of Polynesian Americans include Native Hawaiians and Samoan Americans. In addition there are smaller communities of Tongan Americans
Tongan Americans are Americans who can trace their ancestry to Tonga, officially known as the Kingdom of Tonga. There are approximately 57,000 Tongans and Tongan Americans living in the United States, as of 2012. Tongans are considered to be Pac ...
(see Culture and diaspora of Tonga), French Polynesian Americans
French Polynesian American are Americans with French Polynesian ancestry. The number of French Polynesian Americans is unknown. According to the 2010 US census, there were 5,062 people whose origins are in Tahiti, but other origins of the French P ...
, and Māori Americans
Māori Americans are Americans of Māori descent, an ethnic group from New Zealand.
Some Māori are Mormons and are drawn to Mormon regions of Hawaii and Utah, as well as in California, Arizona and Nevada. Māori therefore were part of the fi ...
.
A Samoan American is an American who is of ethnic Samoan descent from either the independent nation Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
or the American territory of American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the Internatio ...
. Samoan American is a subcategory of Polynesian American. About 55,000 people live on American Samoa, while the U.S. censuses in 2000 and 2008 has found 4 times the number of Samoan Americans live in the mainland U.S.
California has the most Samoans; concentrations live in the San Francisco Bay Area
The San Francisco Bay Area, often referred to as simply the Bay Area, is a populous region surrounding the San Francisco, San Pablo, and Suisun Bay estuaries in Northern California. The Bay Area is defined by the Association of Bay Area G ...
, Los Angeles County
Los Angeles County, officially the County of Los Angeles, and sometimes abbreviated as L.A. County, is the List of the most populous counties in the United States, most populous county in the United States and in the U.S. state of California, ...
, and San Diego County
San Diego County (), officially the County of San Diego, is a county in the southwestern corner of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, the population was 3,298,634, making it California's second-most populous county and the f ...
. San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17t ...
has approximately 2,000 people of Samoan ancestry, and other Bay Area cities such as East Palo Alto and Daly City
Daly City () is the second most populous city in San Mateo County, California, United States, with population of 104,901 according to the 2020 census. Located in the San Francisco Bay Area, and immediately south of San Francisco (sharing its ...
have Samoan communities. In Los Angeles County, Long Beach
Long Beach is a city in Los Angeles County, California. It is the 42nd-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 466,742 as of 2020. A charter city, Long Beach is the seventh-most populous city in California.
Incorporat ...
and Carson have abundant Samoan communities, as well as in Oceanside in San Diego County. Other West Coast metropolitan areas such as Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region o ...
have strong Samoan communities, mainly in King County
King County is located in the U.S. state of Washington. The population was 2,269,675 in the 2020 census, making it the most populous county in Washington, and the 13th-most populous in the United States. The county seat is Seattle, also the st ...
and in Tacoma. Anchorage
Anchorage () is the largest city in the U.S. state of Alaska by population. With a population of 291,247 in 2020, it contains nearly 40% of the state's population. The Anchorage metropolitan area, which includes Anchorage and the neighboring ...
, Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U ...
, and Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the isla ...
, Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
, both have thousands of Samoan Americans residing in each city.
Persons born in American Samoa are United States nationals, but not United States citizens
Citizenship is a "relationship between an individual and a state to which the individual owes allegiance and in turn is entitled to its protection".
Each state determines the conditions under which it will recognize persons as its citizens, and ...
(this is the only circumstance under which an individual would be one and not the other). , there have been 10 American Samoans who have died in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
, and 2 who have died in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is borde ...
.
Pacific Islander Americans are also represented in the United States Navy SEALs
The United States Navy Sea, Air, and Land (SEAL) Teams, commonly known as Navy SEALs, are the U.S. Navy's primary special operations force and a component of the Naval Special Warfare Command. Among the SEALs' main functions are conducting s ...
, making up .6% of the enlisted and .1% of the officers.
Notes
References
External links
The Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander Population: 2010 Census
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20100105031601/http://imdiversity.com/Villages/Asian/reference/census_2000_pac_islanders.asp Pacific Islander Populations, Census 2000 {{Authority control Ethnic groups in the United States American people of Micronesian descent American people of Melanesian descent American people of Polynesian descent Pacific Islands American