PT-91M on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
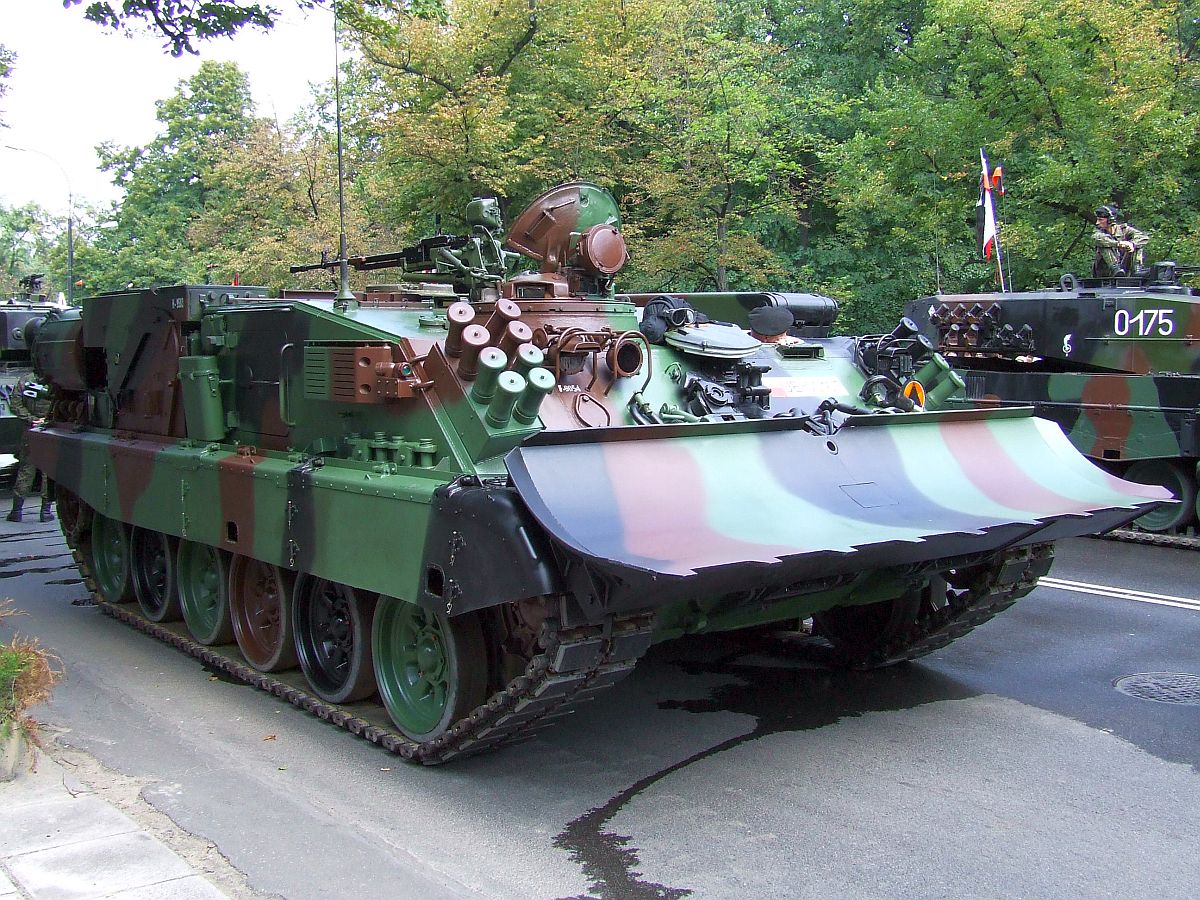
The PT-91 Twardy (, en, Tough, link=no) is a
 The
The
 The new ' dynamic armour, developed by the Poland Military-Technical Institute, increased the main battle tank's protection from
The new ' dynamic armour, developed by the Poland Military-Technical Institute, increased the main battle tank's protection from 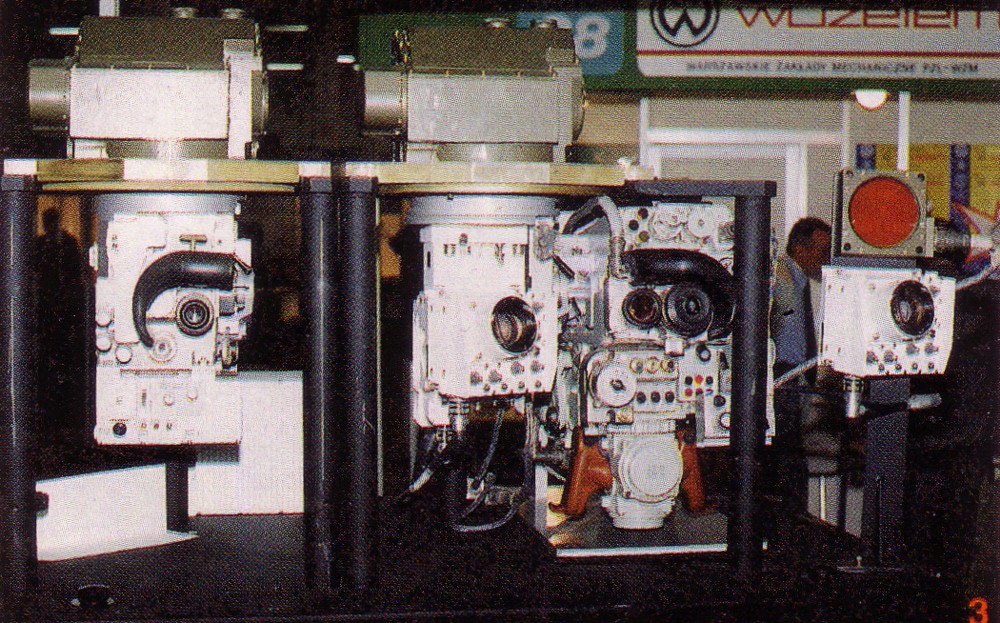 The
The
 (''E'' for ''Export'') Renamed prototypes of the PT-91M used as demonstrators of the export variant shown at military exhibitions. The PT-91E is an initial prototype, initially named SP1 (it is the same vehicle that was shown on military parade in Kuala Lumpur in 2005). PT-91Ex is the second prototype, named SP2.Nowa Technika Wojskowa – November 2007 page 15 – Pokaz "Malaja" i CV90120-T na Drawsku – by Andrzej Kliński Both vehicles faced a number of tests in Malaysia. SP1 was used for traction tests and was driven 7000 km offroad in Malaysia. SP2 achieved 2000 km with 500 firings of the main cannon. The PT-91Ex is very similar to PT-91M, and is offered for export to other countries.
(''E'' for ''Export'') Renamed prototypes of the PT-91M used as demonstrators of the export variant shown at military exhibitions. The PT-91E is an initial prototype, initially named SP1 (it is the same vehicle that was shown on military parade in Kuala Lumpur in 2005). PT-91Ex is the second prototype, named SP2.Nowa Technika Wojskowa – November 2007 page 15 – Pokaz "Malaja" i CV90120-T na Drawsku – by Andrzej Kliński Both vehicles faced a number of tests in Malaysia. SP1 was used for traction tests and was driven 7000 km offroad in Malaysia. SP2 achieved 2000 km with 500 firings of the main cannon. The PT-91Ex is very similar to PT-91M, and is offered for export to other countries.


 The ''PZA'' (''Przeciwlotniczy Zestaw Artyleryjski'', meaning "AA Artillery System"; “Loara” means “
The ''PZA'' (''Przeciwlotniczy Zestaw Artyleryjski'', meaning "AA Artillery System"; “Loara” means “
WB Electronics
Artillery Fire Control Syste
Topaz
In 2014, this configuration was abandoned due to manufacturing flaws (microfractures detected in the vehicle's welded steel plates), numerous reliability concerns related to the automotive performance of the chassis and the loss of the Polish manufacturing line for the S-12U engine, and was replaced by the Korean-made K9 tracked chassis.
 Units equipped with the PT-91 Twardy:
* 1 Warszawska Brygada Pancerna (1st Armoured Brigade) – one battalion, Warsaw district –
Units equipped with the PT-91 Twardy:
* 1 Warszawska Brygada Pancerna (1st Armoured Brigade) – one battalion, Warsaw district –
: 27 PT-91MA
: 113 PT-91MA1 * : 48 PT-91M ''Pendekar''. * : Unknown number donated by Poland starting in July 2022.
PT-91 on Bumar-Łabędy Web Site
PT-91Ex on Bumar-Łabędy Web Site
at globalsecurity.org
at armyrecognition.com {{ModernPOLAFVsNav , style= wide Post–Cold War main battle tanks Main battle tanks of Poland Science and technology in Poland Tanks with autoloaders Military vehicles introduced in the 1990s T-72
Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
main battle tank
A main battle tank (MBT), also known as a battle tank or universal tank, is a tank that fills the role of armor-protected direct fire and maneuver in many modern armies. Cold War-era development of more powerful engines, better suspension sys ...
. A development of the T-72M1
The T-72 is a family of Soviet/Russian main battle tanks that entered production in 1969. The T-72 was a development of the T-64, which was troubled by high costs and its reliance on immature developmental technology. About 25,000 T-72 tanks ha ...
, it entered service in 1995. The PT-91 was designed at the OBRUM (''Ośrodek Badawczo-Rozwojowy Urządzeń Mechanicznych'', or ''Research and Development Centre for Mechanical Appliances'') and is produced by the Bumar Łabędy company, part of the Bumar Group, a Polish technical military consortium. Changes from the T-72M include a new dual-axis stabilized fire-control system, reactive armour
Reactive armour is a type of vehicle armour that reacts in some way to the impact of a weapon to reduce the damage done to the vehicle being protected. It is most effective in protecting against shaped charges and specially hardened kinetic ener ...
, a more powerful engine, transmission and new automatic loader.
Unlike many other T-72 upgrades, Polish Army PT-91s feature elements created almost exclusively by domestic companies, including the new engine, fire control system, and all communication system elements. Many of the elements were used to upgrade existing fleets of T-72 tanks in countries including the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
( T-72M4 CZ), Georgia (T-72SIM-1), and India (T-72 Ajeya Mk. 2). A total of 232 PT-91 tanks were delivered to the Polish Land Forces: 92 newly built vehicles and 140 from refurbished T-72A and T-72M1 tanks, designated PT-91M1 and PT-91MA1, respectively.
History
In the late 1980s, thePolish Army
The Land Forces () are the land forces of the Polish Armed Forces. They currently contain some 62,000 active personnel and form many components of the European Union and NATO deployments around the world. Poland's recorded military history stre ...
modernized all of its obsolete T-55
The T-54 and T-55 tanks are a series of Soviet main battle tanks introduced in the years following the Second World War. The first T-54 prototype was completed at Nizhny Tagil by the end of 1945.Steven Zaloga, T-54 and T-55 Main Battle Tank ...
tanks to the T-55AM ''Mérida'' standard. The successful conversion convinced the General Staff that similar modernization programs could be applied to other Soviet-designed tanks made in Poland and used by the Polish Armed Forces. In late 1988, the decision was made to prepare the modernization of the T-72M1, using experience gained from the production of licensed T-72M (obiekt 172M-E3 – Polish army designation T-72), T-72M1 (obiekt 172M-E5) and T-72M1K (Polish army designation T-72M1D).
 The
The Gliwice
Gliwice (; german: Gleiwitz) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. The city is located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Kłodnica river (a tributary of the Oder). It lies approximately 25 km west from Katowice, the regional capi ...
-based OBRUM, the ''Research and Development Centre of Mechanical Systems'' ( pl, Ośrodek Badawczo-Rozwojowy Urządzeń Mechanicznych) was chosen as the main design bureau. However, initially, the work progressed at a very slow pace, mainly because the Polish General Staff was also considering the purchase of a newer version of the T-72 (T-72
The T-72 is a family of Soviet/Russian main battle tanks that entered production in 1969. The T-72 was a development of the T-64, which was troubled by high costs and its reliance on immature developmental technology. About 25,000 T-72 tanks h ...
S) or the modern T-80
The T-80 is a main battle tank (MBT) that was designed and manufactured in the former Soviet Union and manufactured in Russia. The T-80 is based on the T-64, while incorporating features from the later T-72. The chief designer of the T-80 was S ...
.
After the political upheaval of 1989 and dissolution of the Soviet bloc, Polish-Soviet talks on purchase of modern tanks came to a halt and support for designing a new Polish tank gained momentum. The first design proposed by the bureau was code-named ''Wilk'' (Polish for ''wolf''), but the project was canceled. Instead, priority was shifted to a different project named ''Twardy''.
The basic aim of the T-72 conversion was to adapt it to the reality of modern warfare and fix its most visible deficiencies. Among those were low mobility, insufficient armour, lack of a fire control system and poor stabilisation of the main gun, which resulted in poor firing accuracy. An additional problem was the lack of passive night vision aiming systems.
Development
Starting in July 1991,T-72
The T-72 is a family of Soviet/Russian main battle tanks that entered production in 1969. The T-72 was a development of the T-64, which was troubled by high costs and its reliance on immature developmental technology. About 25,000 T-72 tanks h ...
modernization programs were implemented by the Bumar-Labedy
Bumar-Labedy is an arms manufacturer based in Poland. It is a division of the Polish Armaments Group.
In 2010 the firm won the contract to build Hitfist OWS remote-controlled turrets for Polish armored vehicles.
In 2016 the firm was awarded the ...
factory, which had been producing T-72
The T-72 is a family of Soviet/Russian main battle tanks that entered production in 1969. The T-72 was a development of the T-64, which was troubled by high costs and its reliance on immature developmental technology. About 25,000 T-72 tanks h ...
s under Soviet license. The modernized main battle tank was designated the PT-91 ''Twardy''. Bumar-Labedy enhanced the tank's armour protection, fire control system and the engine. In 1993, the Polish Defense Ministry ordered 20 PT-91 tanks, to be used for field trials and armed forces tests.
 The new ' dynamic armour, developed by the Poland Military-Technical Institute, increased the main battle tank's protection from
The new ' dynamic armour, developed by the Poland Military-Technical Institute, increased the main battle tank's protection from high-explosive anti-tank
High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is the effect of a shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armor. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity ...
(HEAT) projectiles and missiles. The protection consisted of 394 tiles with explosives, which would detonate in case of a direct hit. The tiles cover 9 m2 of the tank: 108 are placed on the turret, 118 on the hull and 84 on each side's anti-HEAT screens. The ''Twardy'' uses steel anti-HEAT screens instead of the rubber one used on the T-72.
The ERAWA tiles fit together almost without gaps, unlike the gaps on the modernized Soviet T-72 which measure up to 10–15 mm, noticeably decreasing their defensive effectiveness. There are two ERAWA modifications: ''ERAWA''-1 and -2, differing in weight of the explosives. Experiments showed that the ERAWA dynamic defense decreases the high-explosive jet impact depth by 50–70% and that of penetrator (APFSDS) projectiles by 30–40%. Furthermore, ERAWA's explosive containers do not detonate when hit by a shot of up to 30 mm calibre or by shell or mine fragments, or when covered in burning napalm or petrol.
The ''Twardy'' is armed with the same 2A46
The 2A46 (also called D-81TM) is a 125 mm/L48 smoothbore cannon of Soviet origin used in several main battle tanks. It was designed by OKB-9 (Artillery Plant No. 9) in Yekaterinburg.
Description
It was developed by the Spetstekhnika Design ...
125 mm smoothbore
A smoothbore weapon is one that has a barrel without rifling. Smoothbores range from handheld firearms to powerful tank guns and large artillery mortars.
History
Early firearms had smoothly bored barrels that fired projectiles without signi ...
gun used in the T-72, fitted with an automatic reloading mechanism which reduces the tank crew by one, as it replaces the gun loader, and gives a rate of fire of 8 to 10 rounds per minute. Additional armament comprises the 7.62 mm PKT coaxial general-purpose machine gun and 12.7 mm NSVT anti-aircraft heavy machine gun. The PT-91 has a thermosmoke device that generates smoke screens from fuel, and has 24 grenade launchers fitted with smoke, anti-personnel frag, or tear gas grenades developed specifically to provide a non-lethal protection.
The modernization of the fire control system began with replacing the older Soviet 2Є28M two-plane stabilizer with a new stabilizer developed in Slovakia. The system has an electronic information block showing the tank's technical condition. Furthermore, it informs the commander when the sighted fire becomes ineffective from excessively high cross-country speed or other reasons.
 The
The fire control system
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director, and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a h ...
, developed by Polish engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the limit ...
s, contains the PCD gunner's day sight and the TES thermovision night sight developed by the Israeli company El-Op
Elbit Systems Ltd. is an Israel-based international defense electronics company engaged in a wide range of programs throughout the world. The company, which includes Elbit Systems and its subsidiaries, operates in the areas of aerospace, land ...
, the POD-72Variants
PT-91 ''Twardy''
Production variant for the Polish Army, an extensively modernized development of the T-72M1. Most are equipped with an SKO-1M Drawa-1T dual-axis stabilized fire control system (with TES – Thermal Elbow Sight; the total number of delivered thermal sights is 202Andrzej Kliński, Nowa Technika Wojskowa – May 2008 page 22 – Odmłodzona Drawa.) though some early production vehicles have a SKO-1 Drawa (with NV sight), ''Erawa'' reactive armour, a PCO SSC-1 Obra-1 laser-warning system and 850 hp PZL-Wola S-12U engine.Andrzej Kliński, Nowa Technika Wojskowa – September 2007 page 14 – Jak można zmodernizować Twardego? The first 20 initial production vehicles were delivered to Polish Land Forces in 1993–1994. Another 78 full-scale production vehicles were delivered 1995–1997, 135 modernized T-72M1 tanks (made in the late 80s) were delivered between 1998 and 2002. Both new and modernized tanks have the same combat capabilities. The Polish Army uses PT-91s in 3 variants– PT-91, PT-91M and the PT-91MA1.PT-91A ''Twardy''
Development variant with a PZL-Wola S-1000 1,000 hp engine with mechanic transmission and a number of other minor changes. Used for trials and as a demonstrator on military exhibitions.PT-91Z ''Hardy''
(''Z'' for ''Zmodernizowany'' – literally ''Modernized'') Further development with a SAGEM Savan-15 fire control system. In live-fire tests the Savan-15 has a minor advantage in accuracy over the Drawa.Nowa Technika Wojskowa – November 1999 page 18 – Polskie T-72 – Co dalej? - by Tomasz Begier and Dariusz Użycki The biggest advantage is a new gun stabilization system that provides a significant increase in accuracy when the tank is on the move. Later it was used as a base to develop the PT-91M. This variant has won a number of stress tests in Malaysia over theT-90
The T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank. It uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard protective measures include a blend of steel and comp ...
, T-84
The T-84 is a Ukrainian main battle tank (MBT), based on the Soviet T-80 MBT introduced in 1976, specifically the diesel engine version: T-80UD. The T-84 was first built in 1994 and entered service in the Ukrainian Armed Forces in 1999. Its h ...
and K1 tanks, and has won the competition for a new Malaysian MBT. Only one prototype was made.
PT-91M ''Pendekar''
(''M'' for ''Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
'') Production export variant for Malaysia with a Sagem Savan-15 fire control system, a new 1,000 hp powerpack, and a Renk automatic transmission, bringing its top speed to 70 km/h. Its main gun has been changed to a ZTS 2A46MS 125 mm gun, along with a 7.62 mm FN MAG coaxial machine gun and a 12.7 mm FN Browning M2 HB AA machine gun. This variant is equipped with a Sagem panoramic sight, a Sagem laser gyro inertial navigation system, turret stabilisation system, Obra-3 laser-warning system, and is integrated with 81 mm smoke grenade launchers, CBRN
Chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear defence (CBRN defence) are protective measures taken in situations in which chemical, biological, radiological or nuclear warfare (including terrorism) hazards may be present. CBRN defence consi ...
warning and protection system, and Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; grc-gre, Θαλῆς; ) was a Greek mathematician, astronomer, statesman, and pre-Socratic philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. He was one of the Seven Sages of Greece. Many, most notably Aristotle, regarded ...
communication system. It also features ERAWA 2 Explosive Reactive Armour
Reactive armour is a type of vehicle armour that reacts in some way to the impact of a weapon to reduce the damage done to the vehicle being protected. It is most effective in protecting against shaped charges and specially hardened kinetic ener ...
, and German-made tank tracks (Diehl Defence
Diehl Defence GmbH & Co. KG is a German arms manufacturer and a division of the Diehl Stiftung with headquarters in Überlingen. Diehl Defence mainly produces missiles and ammunition. Diehl BGT Defence was founded in 2004 as result of the merge ...
). Two prototypes were made (renamed PT-91E and PT-91Ex), then 48 serial PT-91M ''Malaj'' vehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles (motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles (trains, trams), ...
s were produced from 2007–2009.Nowa Technika Wojskowa – October 2005 page 9 – Pierwsza prezentacja "Malaja" - by Andrzej Kliński
PT-91E/Ex
PT-91P
(''P'' for ''Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
'') A demonstrator for the SITDEF Peru 2009 military exhibition, the PT-91P is a cheaper alternative to the PT-91Ex. This variant is equipped with the latest PCO Drawa-TG fire control system, a thermal sight, and a modern communication system ( Radmor RRC9310 radio, WB Electronics Fonet-IP communication system and Teldat battlefield management system). The vehicle was shown at a number of South American events including the SITDEF Peru 2009 Expo.Nowa Technika Wojskowa – April 2009 page 16 – Twardy na wystawie w Peru – by Andrzej Kliński
PT-72U / PT-91U / PT-91EU
(''U'' for ''Urbanizowany'' – Tank to fight in urbanized terrain) A demonstrator for the MSPO 2011 military exhibition. This is an offer for the Polish Army which involves certain modifications of the T-72 and PT-91 tanks. The modification includes installation of such additional equipment as a remote-controlled cannon with an optical system, an omnidirectional observation system, add-on armour, and further engineering equipment. The PT-72U is equipped with a remote-controlled weapon station armed with a 12.7 mm machine gun mounted to the crew commander hatch. The system had a fire rotation of 360° and an elevation angle for the gun from -5° to 55°. The observation system is equipped with 8 day–night cameras with the observation angle 55° and a rotary passive camera FLIR which has up to 26 times optical zoom. The armour package has chassis and turret bar armour. The bottom of the chassis is equipped with reactive armour and add-on armour. The PT-72U is equipped with a full range of new modern internal and external communication tools, allowing communication also via the internet. There were plans to modernize 84 Armenian T-72s to the PT-72U standard.PT-16
A further development introduced in 2016. Upgrades include improved armour, armament, and mobility. The hull armour and cast turret have been upgraded with add-on composite armour equivalent to up to 1000 mm RHA (rolled homogeneous armour), supplied byGermany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
. The protection can be improved with Polish ERAWA explosive reactive armour. The 125 mm smoothbore cannon has been replaced with a 120 mm smoothbore cannon compatible with NATO ammunition and uses a carousel-type autoloader. This autoloader is separate from the crew compartment, where the T-72 autoloader was located. The manned 12.7 mm machine gun has been upgraded to be remotely operated.
Other improvements include an upgraded fire control system. The tank is proposed to be fitted with a new engine, options for which include an unspecified Serbian turbocharged diesel, a German 1088 hp, Serbian V46-TK, and potentially yet-to-be-developed 1200 hp engines. Other improvements include rubber skirts covering the lower hull and the tracks, and new tracks based on those found on German Leopard 2s, which can be fitted with deep wading kits to allow it to ford water obstacles up to 13 feet (4 meters) deep. The upgrade can be applied to both PT-91s and T-72M1s, of which Poland has a total of 823 (233 PT-91s, 120 active T-72M1s, and 470 reserve T-72M1s). The vehicle did not enter mass production.
PT-17
The main goals of the PT-17 tank were to increase firepower and fire maneuverability, increase mobility and survivability on the battlefield, improve crew comfort, and increase mission duration. The demonstrator was developed in cooperation with Ukrainian companies that supplied the tank turret. The PT-17's power range includes a S1000R ESM-350M engine and a reinforced suspension. Diehl rubber tracks are used. The chassis equipment includes an auxiliary power generator (APU), air conditioning, a new steering system with shuttlecock and a PCO KDN-1 Nyks day/night reversing camera. The tank turret is a Ukrainian construction, featuring the Ukrainian KBM-2 smoothbore 120 mm cannon, with a barrel length of L50, and a 22 mm ammunition-charge unit mounted in the niche of the turret. The total ammunition capacity is 50 shells. The armament is supplemented by a 7.62 mm caliber machine gun and a remotely mounted ZSMU-1276 armament module manufactured by Zakłady Mechaniczne "Tarnów" S.A. The turret was equipped with stabilized sight-and-sight optics, GOC-1 Nike and GOD-1 Iris from PCO S.A and BMS. Optionally, the manufacturer advises on the use of Safran's VIGY-15 panoramic day-observation device. The additional composite armour of both the hull and the turret is expected to increase survival of the tank on the battlefield, as is the installed PCO SSP-1 OBRA-3 universal self-propelled vehicle system and two 6-tube intermittent grenade launchers. Features installed on the demonstrator systems are just an example of the possibilities. Ultimately, they can be configured according to the needs of the potential recipient.PT-91M2
Although the PT-91M2's modernization objectives are the same as the PT-17's, the range of the PT-91M2 differs considerably. The S-12U engine is powered by an 850 horsepower engine with enhanced mechanical transmission (Cx version). Tracks come with rubber overlays developed by Obrum / Bumar. Like the PT-17, reinforced suspension (torsion shafts, shock absorbers, and elastomer bumpers) are used. Among the chassis, equipment included the auxiliary power generator (APU), the modernized rotary car charger, the PNK-72 "Radomka" night-vision, and PCO KDN-1 Nyks night-time reversing camera. Hull protection is provided by the ERAWA III reactive armour and rod armour at the rear of the chassis. Increased firepower is planned to be achieved by installing a 125 mm 2M46MS caliber Slovak cannon with a barrel length of 48 calibres. Inside the turret, there is also a change to the location of the second round of ammunition. Significantly, the PT-91M2 demonstrated a SAVAN-15 French fire control system (SAVAN-15) from Safran, previously used in PT-91M tanks in Malaysia. A TKN-3z night vision mount is available for the commander. The PT-91M2 has a SOD Observation System, a universal PCO SSP-1 OBRA-3 vehicle self-propelled system (both PCO S.A.), and two modules each of 12 902A smoke grenades. Additional protection for the turret includes ERAWA reactive armour modules.Related vehicles

WZT WZT (''Wóz Zabezpieczenia Technicznego'' – armoured recovery vehicle) was a Polish post-World War II armoured recovery vehicle series. It consists of five versions.
The first two, WZT-1 and WZT-2 were built on T-55/T-55A hull, the WZT-3 was bui ...
is the acronym of for ''Wóz Zabezpieczenia Technicznego'' literally ''Technical Support Vehicle'': it indicates a family of armoured recovery vehicle
An armoured recovery vehicle (ARV) is typically a powerful tank or armoured personnel carrier (APC) chassis modified for use during combat for military vehicle recovery (towing) or repair of battle-damaged, stuck, and/or inoperable armoured f ...
s based on the PT-91/T-72 tank hull, with over 400 vehicles delivered to the clients. It is armed with a 12.7 mm ( in) machine-gun fitted to the commander's hatch. Standard equipment includes: crane with telescopic jib that can lift a maximum load of fifteen tonnes, front-mounted stabilizing dozer blade, main and secondary winches.
* WZT-3 – A T-72 based variant for Polish Army – 20 vehicles.
* WZT-3M – A PT-91 based variant for Polish Army – 9 new vehicles and 20 WZT-3 upgraded to this standard.
* M-84AI – A M-84A based variant, made on licence in Yugoslavia – 15 vehicles for Kuwait
* ARV-3 – A T-72 based variant for Indian Army – 352 vehicles made
* WZT-4 – A PT-91M based variant for Malaysian Army (technically this vehicle is closely related to MID-M) – 6 vehicles

MID ''Bizon''-S
(''MID'' for ''Maszyna Inżynieryjno-Drogowa'' – lit. ''Engineering-Roading Machine''; ''Bizon'' isPolish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
for '' Bison'') – Polish engineering tank based on the PT-91 tank hull.
* MID – A PT-91 based variant for Polish Army – 8 vehicles
* MID-M – A PT-91M based variant for Malaysian Army – 3 vehicles
PMC
(''PMC'' for ''Pomocniczy Most Czołgowy'' – lit. ''Auxiliary Tank Bridge'') – Polish Armoured Vehicle Launched Bridge is a close-supportbridgelayer
An armoured vehicle-launched bridge (AVLB) is a combat support vehicle, sometimes regarded as a subtype of military engineering vehicle, designed to assist militaries in rapidly deploying tanks and other armoured fighting vehicles across gap- ...
. The PMC-90, developed on the basis of PT-91
The PT-91 Twardy (, en, Tough, link=no) is a Polish main battle tank. A development of the T-72M1, it entered service in 1995. The PT-91 was designed at the OBRUM (''Ośrodek Badawczo-Rozwojowy Urządzeń Mechanicznych'', or ''Research ...
, is able to carry out missions required to operations of combat forces.
* PMC-90 – PT-91 based prototype vehicle with MLC-60 bridge. Not adopted.
* PMC-''Leguan'' – PT-91M based variant for Malaysia equipped with the 26 m (87 ft) long MLC 60 Leguan bridge system
Leguan Island is a small island situated in the delta of the Essequibo River on the coast of Guyana, South America. The island is shaped like a gull wing and is nine miles (14 km) long and wide at its widest making it roughly square in area ...
. 5 vehicles for Malaysia.
* MG-20 Daglezja-G (''MG'' for ''Most Gąsienicowy'' – lit. ''Tracked Bridge'') – a tracked bridge system, based on a lengthened T-72 chassis with one additional road wheel, equipped with a MLC-70 bridge system. Closely related to a truck based MS-20 Daglezja. Currently in development phase, it is expected to replace a T-55 based BLG-67M bridges in Polish Army.
PZA ''Loara''
 The ''PZA'' (''Przeciwlotniczy Zestaw Artyleryjski'', meaning "AA Artillery System"; “Loara” means “
The ''PZA'' (''Przeciwlotniczy Zestaw Artyleryjski'', meaning "AA Artillery System"; “Loara” means “Loire
The Loire (, also ; ; oc, Léger, ; la, Liger) is the longest river in France and the 171st longest in the world. With a length of , it drains , more than a fifth of France's land, while its average discharge is only half that of the Rhône ...
” in Polish) is an armoured self-propelled anti-aircraft artillery system developed in the late 1990s. Based around the ''Twardy'' chassis, this system mounts an armoured turret holding two Oerlikon KDA 35 mm cannons linked to a radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
fire control system. It was planned that it would work closely together with PZR “Loara” (anti-aircraft rocket system) vehicles built on the basis of the PZA Loara but that project is currently on hold. The Loara is an autonomous fire unit capable of performing its tasks independently or acting as a component of a wider air defense system.
The system has two radars, 3D search radar and engagement radar. The search radar has a range of and is capable of tracking and identifying up to 64 targets at once. The radar system can be operated on the move, refreshing its data every second. The system has a laser range-finder, TV and FLIR
Forward-looking infrared (FLIR) cameras, typically used on military and civilian aircraft, use a thermographic camera that senses infrared radiation.
The sensors installed in forward-looking infrared cameras, as well as those of other thermal ...
cameras giving the system both all-weather day/night capabilities and the ability to operate entirely passively in a heavy ECM environment. The system has a reaction time less than 10 seconds. The system can engage aircraft flying at altitudes from very low altitudes up to 5,000 m (16,500 ft), and flying at speeds up to 500 m/s (1,125 mph). It is effective against infantry, lightly armoured ground and naval targets.
SJ-09
SJ-09 is one of the elements of the T-72 and PT-91 crew training system. The system is composed of both trainers teaching crew trainees how to operate different systems of the tank and simulators allowing training more advanced situations. For example, the SJ-02 is used to teach how to load the main gun. The SJ-09 is the driver training vehicle used to train drivers in operating of the vehicle as big and heavy as main battle tank. The vehicle is a tank chassis that has the turret replaced with an instructor station. All unnecessary equipment (like side skirts) were removed. The vehicle has a dummy main gun that obstructs the driver's view, like in the real tank. Vehicles used by the Polish Army were rebuilt from the few original T-72 Ural in Polish inventory delivered from Soviet Union. Another vehicle was built new for the Malaysian Army as a part of the PT-91M order.PT-94 ''Goryl''
(''Goryl'' isPolish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
for ''Gorilla
Gorillas are herbivorous, predominantly ground-dwelling great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or fi ...
'') – project of a Polish main battle tank designed using experience gained on PT-91 project. The tank would be similar in its design to Merkava
The Merkava ( he, מרכבה, , "chariot") is a series of main battle tanks used by the Israel Defense Forces and the backbone of the IDF's armored corps. The tank began development in 1970, and its first generation, the Merkava mark 1, entere ...
(engine at front), and it would feature redesigned engine, transmission and fire control system. Armour: composite + ERA, main armament: 120/125 mm gun, 60 mm mortar, secondary armament: 7.62 mm PKT coaxial machine gun, 12.7 mm NSWT AA machine gun, crew: 3. This program was also known under the name Anders
Anders is a male name in Scandinavian languages and Fering North Frisian, an equivalent of the Greek Andreas ("manly") and the English Andrew. It originated from Andres via metathesis.
In Sweden, Anders has been one of the most common names fo ...
. The program was canceled at an early stage.
PT-97 ''Gepard''
The Gepard (Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
for ''Cheetah
The cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus'') is a large cat native to Africa and central Iran. It is the fastest land animal, estimated to be capable of running at with the fastest reliably recorded speeds being , and as such has evolved specialized ...
''), sometimes known as PT-2001, is another modification project of a Polish main battle tank prepared as a future modernisation programme for the T-72 family. The programme was called for, after the first PT-91 proposition fell below requirements. Two propositions were submitted, one by Bumar which provided a project with modified frontal armour, different mortar and sporting a Leclerc–like a turret with the 2A46
The 2A46 (also called D-81TM) is a 125 mm/L48 smoothbore cannon of Soviet origin used in several main battle tanks. It was designed by OKB-9 (Artillery Plant No. 9) in Yekaterinburg.
Description
It was developed by the Spetstekhnika Design ...
main gun. OBRUM's competing project had new front and sides reactive armour and a L-44 main gun.
Despite considerable improvements, neither was approved for financial reasons, and no prototypes were built. However, design experience helped with new PT-91 versions.
Krab
The ''Krab'' (Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
for '' Crab'') is a 155 mm self-propelled howitzer designed by HSW S.A. with a OBRUM's UPG-NG chassis (a heavily modified variant of the SPG-1M vehicle) which utilizes only a handful of components from the PT-91 program such as the road wheels, suspension and S-12U power plant. It combines these with a licensed AS-90
The AS-90 ("Artillery System for the 1990s"), known officially as Gun Equipment 155 mm L131, is an armoured self-propelled artillery weapon used by the British Army.
It can fire standard charges up to using 39 calibre long barrel (com ...
M ''Braveheart'' turret armed with a 52-calibre gun anWB Electronics
Artillery Fire Control Syste
Topaz
In 2014, this configuration was abandoned due to manufacturing flaws (microfractures detected in the vehicle's welded steel plates), numerous reliability concerns related to the automotive performance of the chassis and the loss of the Polish manufacturing line for the S-12U engine, and was replaced by the Korean-made K9 tracked chassis.
Operational history
Poland
233 PT-91''s'' were delivered between 1995 and 2002. 232 vehicles remain in service. An early prototype is preserved in the Land Forces Training Center museum inPoznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
. 38 support vehicles were based on the T-72/PT-91 hull (29 WZT-3M armoured recovery vehicles, 8 MID engineering tanks, and 1 prototype PZA Loara self-propelled anti-aircraft weapon).
Wesoła
Wesoła () is one of the districts of Warsaw, and has been as such since October 27, 2002. Wesoła is located in the south-eastern part of city.
Wesoła received town privileges on December 17, 1968. Then, the town included Wola Grzybowska, W ...
* 2 Brygada Zmechanizowana Legionów (2nd Mechanised Brigade) – one battalion, Złocieniec
* 9 Brygada Kawalerii Pancernej (9th Armoured Cavalry Brigade) – two battalions, Braniewo
Braniewo () (german: Braunsberg in Ostpreußen, la, Brunsberga, Old Prussian: ''Brus'', lt, Prūsa), is a town in northern Poland, in Warmia, in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, with a population of 16,907 as of June 2021. It is the capital ...
* Centrum Szkolenia Wojsk Lądowych (Land Forces Training Center) – Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
Former units equipped with PT-91 Twardy:
* 10 Brygada Kawalerii Pancernej (10th Armoured Cavalry Brigade) – Świętoszów
Świętoszów (; german: Neuhammer am Queis) is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Osiecznica, within Bolesławiec County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland in the Lower Silesian Wilderness, on the river Kwisa.
I ...
(replaced with Leopard 2A4
The Leopard 2 is a 3rd generation main battle tank originally developed by Krauss-Maffei in the 1970s for the West German army. The tank first entered service in 1979 and succeeded the earlier Leopard 1 as the main battle tank of the West Germ ...
)
* 15 Wielkopolska Brygada Kawalerii Pancernej (15th Armoured Cavalry Brigade) – Wędrzyn (unit disbanded in June 2007)
* 17 Wielkopolska Brygada Zmechanizowana (17th Mechanized Brigade) – Międzyrzecz
Międzyrzecz (; la, Meserici, german: link=no, Meseritz) is a town in western Poland, on the Obra and Paklica river, with 17,667 inhabitants (2020). The capital of Gmina Międzyrzecz and Międzyrzecz County. Since the Local Government Reorganiz ...
(replaced with KTO Rosomak
The KTO Rosomak (Kołowy Transporter Opancerzony Rosomak) (pol. wheeled armored personnel carrier Wolverine) is an 8×8 multi-role military vehicle produced by Rosomak S.A. (formerly Wojskowe Zakłady Mechaniczne) in Siemianowice Śląskie (Up ...
)
* 34 Brygada Kawalerii Pancernej (34th Armoured Cavalry Brigade) – Żagań
Żagań ( French and german: Sagan, hsb, Zahań, la, Saganum) is a town in western Poland, on the Bóbr river, with 25,731 inhabitants (2019). The town is the capital of Żagań County in the historic region of Silesia. Previously in the Zielo ...
(replaced with Leopard 2A5)
At the introduction of PT-91, the intention of Polish General Staff was to equip all brigades of the 11th Armoured Cavalry Division with the PT-91. At the time, the division had four brigades: the 10th Armoured Cavalry, 15th Armoured Cavalry, 17th Mechanised, and 34th Armoured Cavalry.
In 2002, the 10th Armoured Cavalry brigade received Leopard 2A4 tanks donated to Poland by Germany. In 2007, the 15th Armoured Cavalry brigade was disbanded and the 17th Mechanised received the first KTO Rosomak. All these changes allowed the reallocation of PT-91s to other divisions, replacing the oldest T-72s. In early 2014, the 34th Brigade from Żagań received the first Leopard 2A5 tanks, shifting its PT-91s to the 9th Brigade in Braniewo, which previously used the T-72M1.
A typical Polish PT-91 tank battalion is equipped with 58 tanks, composed of four frontline companies with 14 vehicles each, and 2 tanks for the battalion commander and the battalion second in command. Every company of 14 tanks is composed of three platoons, with 4 tanks in each and 2 tanks for the company commander and company's second in command.
Malaysia
In 2007–2009, Bumar Łabędy delivered to Malaysia 48 PT-91M and 15 supportvehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles (motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles (trains, trams), ...
s (6 WZT-4 armoured recovery vehicle
An armoured recovery vehicle (ARV) is typically a powerful tank or armoured personnel carrier (APC) chassis modified for use during combat for military vehicle recovery (towing) or repair of battle-damaged, stuck, and/or inoperable armoured f ...
, 3 MID-M engineering tank, 5 PMC Leguan - armoured vehicle-launched bridge
An armoured vehicle-launched bridge (AVLB) is a combat support vehicle, sometimes regarded as a subtype of military engineering vehicle, designed to assist militaries in rapidly deploying tanks and other armoured fighting vehicles across gap-t ...
and one SJ-09 driver training tank), ammo
Ammunition (informally ammo) is the material fired, scattered, dropped, or detonated from any weapon or weapon system. Ammunition is both expendable weapons (e.g., bombs, missiles, grenades, land mines) and the component parts of other wea ...
, spares and support for US$370 million. Operating capability was reached 1 September 2010.
Units equipped with PT-91M:
* Rejimen ke-11 Kor Armour DiRaja – (''11th Regiment of Royal Armoured Corps'') – Gemas
Gemas (Negeri Sembilan Malay: ''Gomeh'') is a small town and a mukim in Tampin District, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia, near the Negeri Sembilan-Johor state border. It is situated 101 km northeast of Seremban, the state capital city, and 30 km no ...
Rejimen ke-11 KAD is the sole user of PT-91M in the Malaysian Army.
Georgia
Upgraded Georgian army T-72SIM-1 tanks use the Drawa-T fire control system, a development of the fire control system on the PT-91. The FCS is equipped with laser range finder and thermal imaging sensor. The system is slightly different from the one used on Polish PT-91s: the commander uses an LCD screen instead of an eyepiece. The Thermal Elbow Sight thermal imaging sensor used in Georgian tanks is of the same (Israeli) origin as the one used on the PT-91, though the external housing is different.India
In April 1999,India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
ordered 44 WZT-3 armoured recovery vehicles, followed by orders in April 2002 (80 vehicles) and July 2005 (228 vehicles) for a total of 352 WZT-3s. These vehicles are used to support the T-72
The T-72 is a family of Soviet/Russian main battle tanks that entered production in 1969. The T-72 was a development of the T-64, which was troubled by high costs and its reliance on immature developmental technology. About 25,000 T-72 tanks h ...
and T-90
The T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank. It uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard protective measures include a blend of steel and comp ...
main battle tanks. Deliveries began in 2001, and India was planning to upgrade its Ajeya Mk1 tanks (local name for T-72
The T-72 is a family of Soviet/Russian main battle tanks that entered production in 1969. The T-72 was a development of the T-64, which was troubled by high costs and its reliance on immature developmental technology. About 25,000 T-72 tanks h ...
M1) to Ajeya Mk2 standard, with some elements from PT-91, such as the Drawa-TE1 fire control system and the PZL-Wola S-1000 engine.
In October 2011, the Indian Defense Ministry announced that the state-owned BEML would produce an additional 204 WZT-3 armoured recovery vehicles – taking the total to 556 vehicles. The Ministry also clarified that no global tender was floated because it was a repeat order.
Operators

Current operators
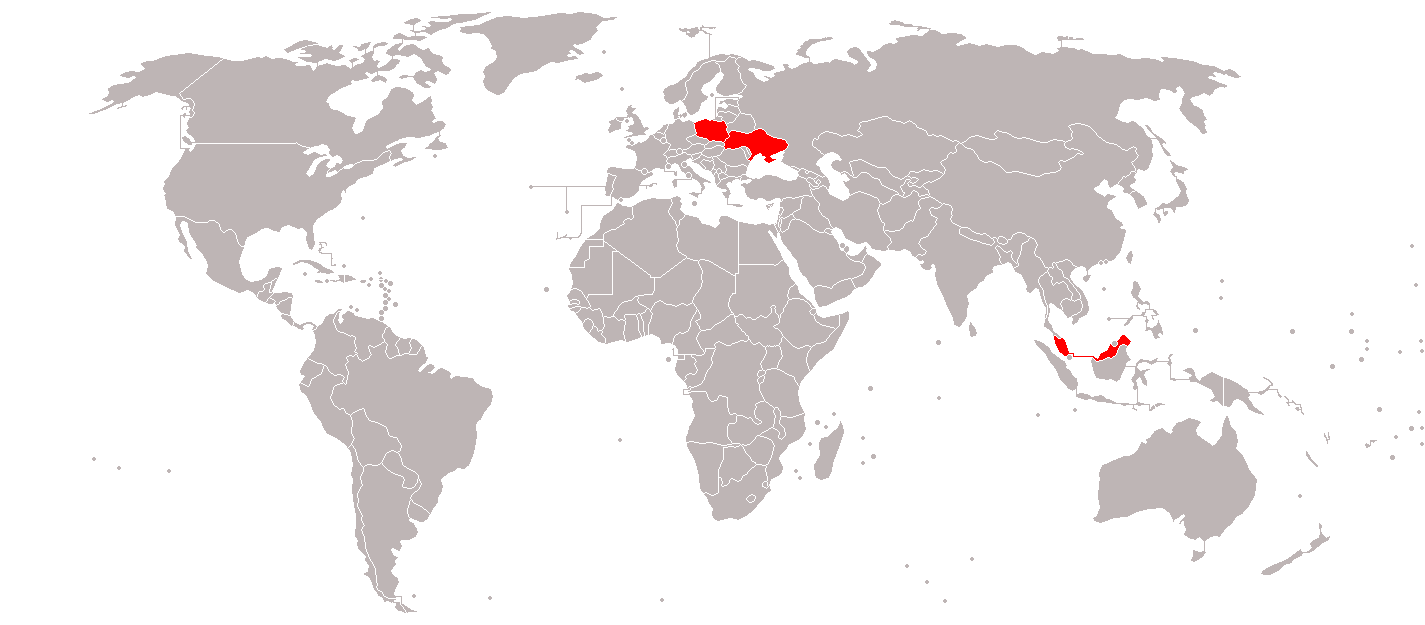
* : 92 PT-91: 27 PT-91MA
: 113 PT-91MA1 * : 48 PT-91M ''Pendekar''. * : Unknown number donated by Poland starting in July 2022.
Failed bids
* : the PT-91 was proposed to thePeruvian Army
The Peruvian Army ( es, Ejército del Perú, abbreviated EP) is the branch of the Peruvian Armed Forces tasked with safeguarding the independence, sovereignty and integrity of national territory on land through military force. Additional missi ...
to replace its T-55s, but was not selected.
References
External links
PT-91 on Bumar-Łabędy Web Site
PT-91Ex on Bumar-Łabędy Web Site
at globalsecurity.org
at armyrecognition.com {{ModernPOLAFVsNav , style= wide Post–Cold War main battle tanks Main battle tanks of Poland Science and technology in Poland Tanks with autoloaders Military vehicles introduced in the 1990s T-72