Outline of the Solar System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the
 *
* 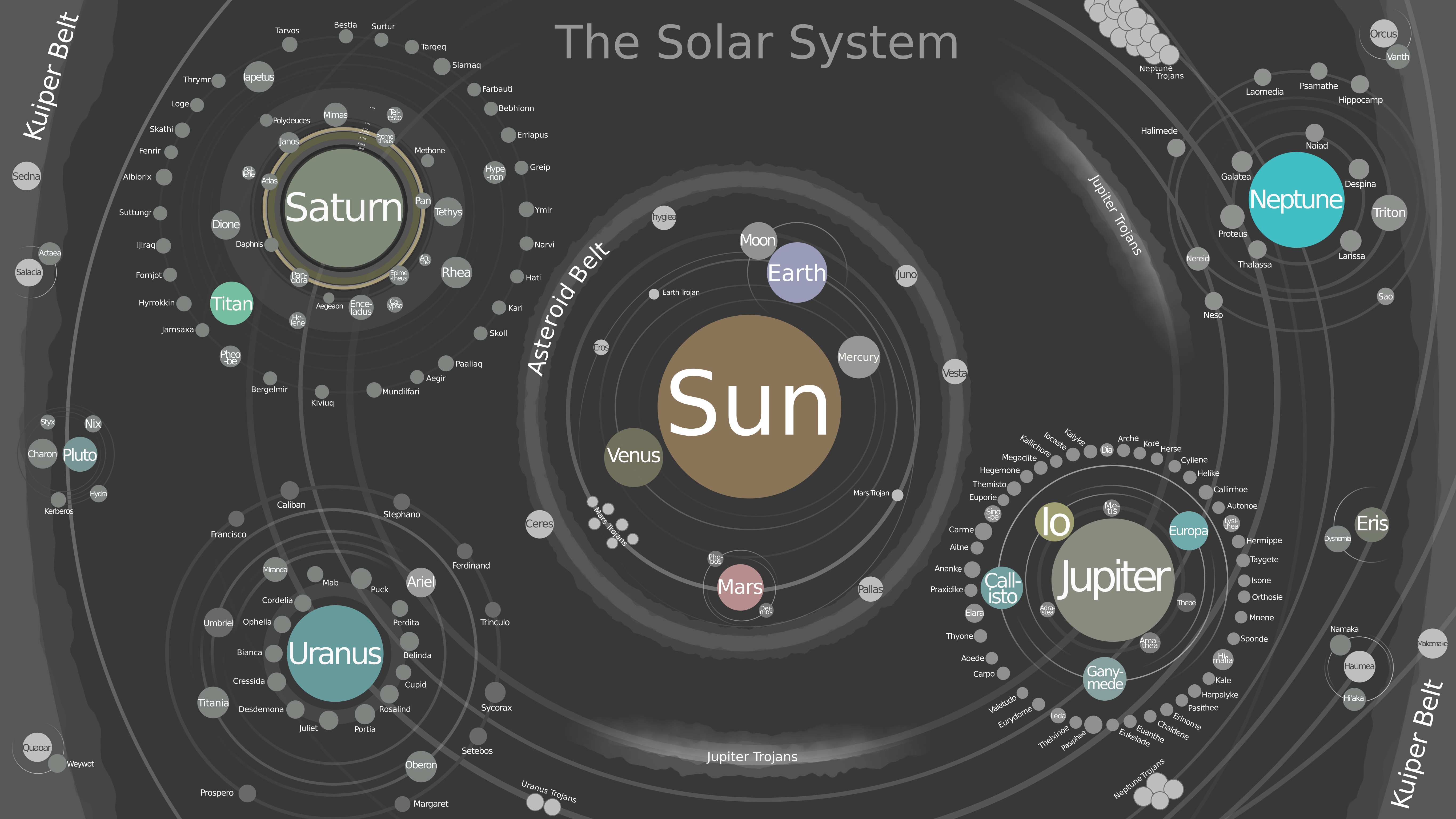 *
*
dmoz page for Solar System
*
A Cosmic History of the Solar SystemA Tediously Accurate Map of the Solar System (web based scroll map scaled to the Moon being 1 pixel)
NASA/JPL Solar System main page
*
NASA's Solar System Simulator
*
Solar System Profile
b
NASA's Solar System Exploration
{{Outline footer * Wikipedia outlines
Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
:
Solar System – gravitationally bound system comprising the Sun and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of those objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest eight are the planets (including Earth), with the remainder being significantly smaller objects, such as dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies. Of the objects that orbit the Sun indirectly, the moons, two are larger than the smallest planet, Mercury.
Regions and celestial objects of the Solar System
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
* Interplanetary medium
The interplanetary medium (IPM) or interplanetary space consists of the mass and energy which fills the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding ...
* Inner Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
** Inner planets
*** Mercury
*** Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
*** Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
**** The Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
**** Near-Earth object
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (Apsis, perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical unit ...
s
**** Van Allen radiation belt
*** Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
**** Moons of Mars
The two moons of Mars are Phobos (moon), Phobos and Deimos (moon), Deimos. They are irregular in shape. Both were discovered by American astronomer Asaph Hall in August 1877 and are named after the Greek mythology, Greek mythological twin charac ...
** Asteroid belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, located roughly between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies, of many sizes, but much smaller than planets, c ...
*** Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere. ...
s
*** Asteroid groups
*** Ceres
 *
* Outer Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
** Outer planets
***Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
**** Ganymede
**** Callisto
****Moons of Jupiter
There are 82 known moons of Jupiter, not counting a number of moonlets likely shed from the inner moons. All together, they form a satellite system which is called the Jovian system. The most massive of the moons are the four Galilean moons: ...
**** Rings of Jupiter
Ring may refer to:
* Ring (jewellery), a round band, usually made of metal, worn as ornamental jewelry
* To make a sound with a bell, and the sound made by a bell
:(hence) to initiate a telephone connection
Arts, entertainment and media Film and ...
**** Jupiter trojan
The Jupiter trojans, commonly called trojan asteroids or simply trojans, are a large group of asteroids that share the planet Jupiter's orbit around the Sun. Relative to Jupiter, each trojan librates around one of Jupiter's stable Lagrange p ...
s
*** Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
****Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
**** Rhea
**** Moons of Saturn
The moons of Saturn are numerous and diverse, ranging from tiny moonlets only tens of meters across to enormous Titan, which is larger than the planet Mercury. Saturn has 83 moons with confirmed orbits that are not embedded in its rings—of ...
**** Rings of Saturn
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entir ...
**** Shepherd moon
A shepherd moon (also herder moon or watcher moon) is a small natural satellite that clears a gap in planetary-ring material or keeps particles within a ring contained. The name is a result of the fact they limit the "herd" of the ring particle ...
s
*** Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus ( Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of ...
**** Titania
**** Oberon
Oberon () is a king of the fairies in medieval and Renaissance literature. He is best known as a character in William Shakespeare's play ''A Midsummer Night's Dream'', in which he is King of the Fairies and spouse of Titania, Queen of the Fairi ...
**** Moons of Uranus
Uranus, the seventh planet of the Solar System, has 27 known moons, most of which are named after characters that appear in, or are mentioned in, the works of William Shakespeare and Alexander Pope. Uranus's moons are divided into three groups: t ...
**** Rings of Uranus
*** Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
**** Triton
Triton commonly refers to:
* Triton (mythology), a Greek god
* Triton (moon), a satellite of Neptune
Triton may also refer to:
Biology
* Triton cockatoo, a parrot
* Triton (gastropod), a group of sea snails
* ''Triton'', a synonym of ''Triturus'' ...
**** Moons of Neptune
The planet Neptune has 14 known moons, which are named for minor water deities in Greek mythology. By far the largest of them is Triton, discovered by William Lassell on October 10, 1846, 17 days after the discovery of Neptune itself; over a ce ...
**** Rings of Neptune
** Trojans
Trojan or Trojans may refer to:
* Of or from the ancient city of Troy
* Trojan language, the language of the historical Trojans
Arts and entertainment Music
* ''Les Troyens'' ('The Trojans'), an opera by Berlioz, premiered part 1863, part 189 ...
** Centaurs
A centaur ( ; grc, κένταυρος, kéntauros; ), or occasionally hippocentaur, is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse.
Centaurs are thought of in many Greek myths as bein ...
* Ubiquitous
** Comets
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ar ...
** Meteoroid
A meteoroid () is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than this are classified as mi ...
s
** Micrometeoroid
A micrometeoroid is a tiny meteoroid: a small particle of rock in space, usually weighing less than a gram. A micrometeorite is such a particle that survives passage through Earth's atmosphere and reaches Earth's surface.
The term "micrometeor ...
s
** Cosmic dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are c ...
** Interplanetary dust cloud
The interplanetary dust cloud, or zodiacal cloud (as the source of the zodiacal light), consists of cosmic dust (small particles floating in outer space) that pervades the space between planets within planetary systems, such as the Solar System ...
* Trans-Neptunian region
** Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt () is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 tim ...
*** Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the S ...
**** Charon
In Greek mythology, Charon or Kharon (; grc, Χάρων) is a psychopomp, the ferryman of Hades, the Greek underworld. He carries the souls of those who have been given funeral rites across the rivers Acheron and Styx, which separate the ...
**** Moons of Pluto
The dwarf planet Pluto has five natural satellites. In order of distance from Pluto, they are Charon, Styx, Nix, Kerberos, and Hydra. Charon, the largest, is mutually tidally locked with Pluto, and is massive enough that Pluto–Charon is some ...
*** Haumea
, discoverer =
, discovered =
, earliest_precovery_date = March 22, 1955
, mpc_name = (136108) Haumea
, pronounced =
, adjectives = Haumean
, note = yes
, alt_names =
, named_after = Haumea
, mp_category =
, orbit_ref =
, epoc ...
*** Makemake
*** Trans-Neptunian object
A trans-Neptunian object (TNO), also written transneptunian object, is any minor planet in the Solar System that orbits the Sun at a greater average distance than Neptune, which has a semi-major axis of 30.1 astronomical units (au).
Typically ...
s
** Scattered disc
The scattered disc (or scattered disk) is a distant circumstellar disc in the Solar System that is sparsely populated by icy small solar system bodies, which are a subset of the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects. The scattered-disc obje ...
*** Eris
* Farthest regions
** Extreme trans-Neptunian objects
** Detached object
Detached objects are a dynamical class of minor planets in the outer reaches of the Solar System and belong to the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs). These objects have orbits whose points of closest approach to the Sun ( perihel ...
s
*** Sedna
** Oort cloud
The Oort cloud (), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, first described in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, is a theoretical concept of a cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging from ...
** Heliosphere
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstell ...
*** Heliopause
*** Boundaries
Boundary or Boundaries may refer to:
* Border, in political geography
Entertainment
* ''Boundaries'' (2016 film), a 2016 Canadian film
* ''Boundaries'' (2018 film), a 2018 American-Canadian road trip film
*Boundary (cricket), the edge of the pla ...
Location of the Solar System
*Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the univers ...
**Observable universe
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these ob ...
***Laniakea Supercluster
The Laniakea Supercluster (; Hawaiian for "open skies" or "immense heaven") is the galaxy supercluster that is home to the Milky Way and approximately 100,000 other nearby galaxies. It was defined in September 2014, when a group of astronom ...
****Virgo Supercluster
The Virgo Supercluster (Virgo SC) or the Local Supercluster (LSC or LS) is a mass concentration of galaxies containing the Virgo Cluster and Local Group, which itself contains the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies, as well as others. At least ...
***** Local Sheet
****** Local Group
*******Milky Way subgroup
The Milky Way has several smaller galaxies gravitationally bound to it, as part of the Milky Way subgroup, which is part of the local galaxy cluster, the Local Group.
There are 59 small galaxies confirmed to be within of the Milky Way, but not ...
********Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
*********Orion–Cygnus Arm
The Orion Arm is a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy that is across and approximately in length, containing the Solar System, including Earth. It is also referred to by its full name, the Orion–Cygnus Arm, as well as Local Arm, Orion ...
**********Gould Belt
The Gould Belt is a local, partial ring of stars in the Milky Way, about 3,000 light-years long, tilted away from the galactic plane by about 16–20 degrees. It contains many O- and B-type stars, amounting to the nearest star-forming re ...
***********Local Bubble
The Local Bubble, or Local Cavity, is a relative cavity in the interstellar medium (ISM) of the Orion Arm in the Milky Way. It contains the closest of celestial neighbours and among others, the Local Interstellar Cloud (which contains the Sol ...
************Local Interstellar Cloud
The Local Interstellar Cloud (LIC), also known as the Local Fluff, is an interstellar cloud roughly across, through which the Solar System is moving. This feature overlaps a region around the Sun referred to as the solar neighborhood. It is un ...
– immediate galactic neighborhood of the Solar System.
*************Alpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri ( Latinized from α Centauri and often abbreviated Alpha Cen or α Cen) is a triple star system in the constellation of Centaurus. It consists of 3 stars: Alpha Centauri A (officially Rigil Kentaurus), Alpha Centa ...
– star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a '' star cluster'' or ''galaxy'', although, broadly speaking ...
nearest to the Solar System, at about 4.4 light years away
*************Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
– star and planetary system
A planetary system is a set of gravitationally bound non- stellar objects in or out of orbit around a star or star system. Generally speaking, systems with one or more planets constitute a planetary system, although such systems may also consi ...
where the Earth is located.
**************Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
– the only planet known to have life, including intelligent life, including humans.
Structure and composition of the Solar System
*Interplanetary space
Interplanetary may refer to:
* Interplanetary space, the space between the planets of the Solar System
* Interplanetary spaceflight, travel between planets
*The interplanetary medium, the material that exists in interplanetary space
*The InterPl ...
* Physical characteristics of the Sun
** Structure of the Sun
* Physical characteristics of Mercury
** Structure of Mercury
** Geology of Mercury
The geology of Mercury is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mercury. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrest ...
* Physical characteristics of Venus
** Structure of Venus
** Atmosphere of Venus
The atmosphere of Venus is the layer of gases surrounding Venus. It is composed primarily of supercritical carbon dioxide and is much denser and hotter than that of Earth. The temperature at the surface is 740 K (467 °C, 872 ...
** Geology of Venus
Venus is a planet with striking geology. Of all the other planets in the Solar System, it is the one nearest to Earth and most like it in terms of mass, but has no magnetic field or recognizable plate tectonic system. Much of the ground surface ...
*** Volcanism on Venus
The surface of Venus is dominated by volcanic features and has more volcanoes than any other planet in the Solar System. It has a surface that is 90% basalt, and about 65% of the planet consists of a mosaic of volcanic lava plains, indicating that ...
* Physical characteristics of the Earth
** Figure of the Earth
Figure of the Earth is a term of art in geodesy that refers to the size and shape used to model Earth. The size and shape it refers to depend on context, including the precision needed for the model. A sphere is a well-known historical approxim ...
** Structure of the Earth
The internal structure of Earth is the solid portion of the Earth, excluding its atmosphere and hydrosphere. The structure consists of an outer silicate solid crust, a highly viscous asthenosphere and solid mantle, a liquid outer core whos ...
** Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magneti ...
** Atmosphere of Earth
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing fo ...
** Geology of Earth
*** Lithosphere of Earth
**** Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label= Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of larg ...
** Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to change in shape. This ...
of Earth
*** Water distribution on Earth
* Physical characteristics of Mars
** Structure of Mars
** Atmosphere of Mars
The atmosphere of Mars is the layer of gases surrounding Mars. It is primarily composed of carbon dioxide (95%), molecular nitrogen (2.8%), and argon (2%). It also contains trace levels of water vapor, oxygen, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and no ...
** Geology of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial g ...
*** Volcanism on Mars
Volcanic activity, or volcanism, has played a significant role in the geologic evolution of Mars. Scientists have known since the Mariner 9 mission in 1972 that volcanic features cover large portions of the Martian surface. These features incl ...
** Geography of Mars
Areography, also known as the geography of Mars, is a subfield of planetary science that entails the delineation and characterization of regions on Mars. Areography is mainly focused on what is called physical geography on Earth; that is the ...
** Water on Mars
Almost all water on Mars today exists as ice, though it also exists in small quantities as vapor in the atmosphere. What was thought to be low-volume liquid brines in shallow Martian soil, also called recurrent slope lineae, may be grains of ...
* Physical characteristics of Jupiter
** Structure of Jupiter
** Atmosphere of Jupiter
** Great Red Spot
The Great Red Spot is a persistent high-pressure region in the atmosphere of Jupiter, producing an anticyclonic storm that is the largest in the Solar System. Located 22 degrees south of Jupiter's equator, it produces wind-speeds up to 432&nb ...
* Physical characteristics of Saturn
** Structure of Saturn
** Atmosphere of Saturn
** Saturn's hexagon
Saturn's hexagon is a persistent approximately hexagonal cloud pattern around the north pole of the planet Saturn, located at about 78°N.
The sides of the hexagon are about long, which is about longer than the diameter of Earth.
The hexagon m ...
* Physical characteristics of Uranus
** Structure of Uranus
** Atmosphere of Uranus
* Physical characteristics of Neptune
** Structure of Neptune
** Atmosphere of Neptune
** Great Dark Spot
The Great Dark Spot (also known as GDS-89, for Great Dark Spot, 1989) was one of a series of dark spots on Neptune similar in appearance to Jupiter's Great Red Spot. In 1989, GDS-89 was the first Great Dark Spot on Neptune to be observed by NASA' ...
History of the Solar System
History of the Solar SystemDiscovery and exploration of the Solar System
Discovery and exploration of the Solar System – * Timeline of Solar System astronomy * Timeline of discovery of Solar System planets and their moons *Timeline of Solar System exploration
This is a timeline of Solar System exploration ordered by date of spacecraft launch. It includes:
*All spacecraft that have left Earth orbit for the purposes of Solar System exploration (or were launched with that intention but failed), includ ...
* Timeline of first images of Earth from space
* Development of hypotheses
** Geocentric model
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric models, the Sun, Moon, stars, an ...
–
** Heliocentrism
Heliocentrism (also known as the Heliocentric model) is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the center of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth ...
–
** Historical models of the Solar System
** Planets beyond Neptune
** List of former planets
** List of hypothetical Solar System objects
A hypothetical Solar System object is a planet, natural satellite, subsatellite or similar body in the Solar System whose existence is not known, but has been inferred from observational scientific evidence. Over the years a number of hypothetica ...
in astronomy
* Space exploration
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the exploration of space is carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration though is conducted both by uncrewed robo ...
– Exploration by celestial body
** Exploration of Mercury
The exploration of Mercury has a minor role in the space interests of the world. It is the least explored inner planet.JHU/APL (2006)MESSENGER: MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and RangingRetrieved on 2007-01-27 As of 2015, the ' ...
** Observations and explorations of Venus
** Exploration of the Moon
The physical exploration of the Moon began when ''Luna 2'', a space probe launched by the Soviet Union, made an impact on the surface of the Moon on September 14, 1959. Prior to that the only available means of exploration had been observation ...
** Exploration of Mars
The planet Mars has been explored remotely by spacecraft. Probes sent from Earth, beginning in the late 20th century, have yielded a large increase in knowledge about the Martian system, focused primarily on understanding its geology and habi ...
** Exploration of Ceres
** Exploration of Jupiter
The exploration of Jupiter has been conducted via close observations by automated spacecraft. It began with the arrival of ''Pioneer 10'' into the Jovian system in 1973, and, , has continued with eight further spacecraft missions. All of thes ...
** Exploration of Saturn
The exploration of Saturn has been solely performed by crewless probes. Three missions were flybys, which formed an extended foundation of knowledge about the system. The ''Cassini–Huygens'' spacecraft, launched in 1997, was in orbit from 2004 ...
** Exploration of Uranus
The exploration of Uranus has, to date, been through telescopes and a lone probe by NASA's '' Voyager 2'' spacecraft, which made its closest approach to Uranus on January 24, 1986. ''Voyager 2'' discovered 10 moons, studied the planet's cold atm ...
** Exploration of Neptune
Neptune has been directly explored by one space probe, ''Voyager 2'', in 1989. , there are no confirmed future missions to visit the Neptunian system, although a tentative Chinese mission has been planned for launch in 2024. NASA, ESA, and indep ...
** Exploration of Pluto
The exploration of Pluto began with the arrival of the ''New Horizons'' probe in July 2015, though proposals for such a mission had been studied for many decades. There are no plans as yet for a follow-up mission, though follow-up concepts have ...
* Solar System model
Solar System models, especially mechanical models, called '' orreries'', that illustrate the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons in the Solar System have been built for centuries. While they often showed relative sizes, the ...
s
Formation and evolution of the Solar System
Formation and evolution of the Solar System
The formation of the Solar System began about 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened in ...
–
* Nebular hypothesis
The nebular hypothesis is the most widely accepted model in the field of cosmogony to explain the formation and evolution of the Solar System (as well as other planetary systems). It suggests the Solar System is formed from gas and dust orbiting t ...
* Terrestrial planet
A terrestrial planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, ...
s
** Iron planets
*** Mercury
** Silicate planets
*** Geodynamics of Venus
NASA's Magellan spacecraft mission discovered that Venus has a geologically young surface with a relatively uniform age of 500±200 Ma (million years). The age of Venus was revealed by the observation of over 900 impact craters on the surface of ...
*** History of Earth
The history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geologi ...
**** Formation of Earth
*** Geological history of Mars
The geological history of Mars follows the physical evolution of Mars as substantiated by observations, indirect and direct measurements, and various inference techniques. Methods dating back to 17th century techniques developed by Nicholas Steno, ...
* Giant planet
The giant planets constitute a diverse type of planet much larger than Earth. They are usually primarily composed of low-boiling-point materials (volatiles), rather than rock or other solid matter, but massive solid planets can also exist. The ...
s
** Gas giant
A gas giant is a giant planet composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. Gas giants are also called failed stars because they contain the same basic elements as a star. Jupiter and Saturn are the gas giants of the Solar System. The term "gas giant" ...
s
*** Jupiter
*** Saturn
** Ice giant
An ice giant is a giant planet composed mainly of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, such as oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. There are two ice giants in the Solar System: Uranus and Neptune.
In astrophysics and planetary ...
s
*** Uranus
*** Neptune
See also
* Outline of astronomy * Outline of space exploration *Lists of geological features of the Solar System
This is a directory of lists of geological features on planets excepting Earth, moons and asteroids ordered by increasing distance from the Sun.
Mercury
* List of craters on Mercury
* List of geological features on Mercury
Venus
* List ...
** List of craters in the Solar System
* List of Solar System objects
The following is a list of Solar System objects by orbit, ordered by increasing distance from the Sun. Most named objects in this list have a diameter of 500 km or more.
*The Sun, a spectral class G2V main-sequence star
*The inner Solar Sy ...
* List of gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System
This is a list of most likely gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System, which are objects that have a rounded, ellipsoidal shape due to their own gravity (but are not necessarily in hydrostatic equilibrium). Apart from the Sun itself, ...
* List of possible dwarf planets
The number of dwarf planets in the Solar System is unknown. Estimates have run as high as 200 in the Kuiper belt and over 10,000 in the region beyond.
However, consideration of the surprisingly low densities of many large trans-Neptunian objects ...
* List of Solar System extremes
This article describes extreme locations of the Solar System. Entries listed in bold are Solar System-wide extremes.
By feature
By class
By object
By distance
* List of Solar System objects most distant from the Sun
See also
* ...
**By size
***List of Solar System objects by size
This article includes a list of the most massive known objects of the Solar System and partial lists of smaller objects by observed mean radius. These lists can be sorted according to an object's radius and mass and, for the most massive objects, ...
**By distance
***List of Solar System objects most distant from the Sun
These Solar System minor planets are the furthest from the Sun . The objects have been categorized by their approximate current distance from the Sun, and not by the calculated aphelion of their orbit. The list changes over time because the ob ...
*** List of Solar System objects by greatest aphelion
**Features
***List of tallest mountains in the Solar System
This is a list of the tallest mountains in the Solar System. This list includes peaks on all celestial bodies where significant mountains have been detected. For some celestial bodies, different peaks are given across different types of measure ...
*** List of largest craters in the Solar System
*** List of largest rifts, canyons and valleys in the Solar System
* List of exceptional asteroids
The following is a collection of lists of asteroids of the Solar System that are exceptional in some way, such as their size or orbit. For the purposes of this article, "asteroid" refers to minor planets out to the orbit of Neptune, and includes ...
* Planetary mnemonic
* HIP 11915
HIP 11915 is a G-type main-sequence star located about 190 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cetus. It is best known for its characteristics, which are very similar to those of the Sun, including the mass, radius, temperature, me ...
(a solar analog
Solar-type star, solar analogs (also analogues), and solar twins are stars that are particularly similar to the Sun. The stellar classification is a hierarchy with solar twin being most like the Sun followed by solar analog and then solar-type ...
whose planetary system contains a Jupiter analog)
The number of currently known, or observed, objects of the Solar System are in the hundreds of thousands. Many of them are listed in the following articles:
* List of natural satellites
* List of minor planets
The following is a list of numbered minor planets in ascending numerical order. With the exception of comets, minor planets are all small bodies in the Solar System, including asteroids, distant objects and dwarf planets. The catalog consists ...
(numbered) and List of unnumbered minor planets
The following is a list of unnumbered minor planets in chronological order of their principal provisional designation. Contrary to their numbered counterparts, unnumbered minor planets have a poorly determined orbit due to insufficient observ ...
* List of trans-Neptunian objects
This is a list of trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs), which are minor planets in the Solar System that orbit the Sun at a greater distance on average than Neptune, that is, their orbit has a semi-major axis greater than 30.1 astronomical units (AU) ...
(numbered) and List of unnumbered trans-Neptunian objects
* Lists of comets
External links
dmoz page for Solar System
*
A Cosmic History of the Solar System
NASA/JPL Solar System main page
*
NASA's Solar System Simulator
*
Solar System Profile
b
NASA's Solar System Exploration
{{Outline footer * Wikipedia outlines