Outline of Belarus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The following
The following
 * Pronunciation:
* Common English country name:
* Pronunciation:
* Common English country name:
 * Climate of Belarus
* Renewable energy in Belarus
* Geology of Belarus
* Protected areas of Belarus
** Biosphere reserves in Belarus
**
* Climate of Belarus
* Renewable energy in Belarus
* Geology of Belarus
* Protected areas of Belarus
** Biosphere reserves in Belarus
**
 The following
The following outline
Outline or outlining may refer to:
* Outline (list), a document summary, in hierarchical list format
* Code folding, a method of hiding or collapsing code or text to see content in outline form
* Outline drawing, a sketch depicting the outer edge ...
is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Belarus:
Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. Its strongest economic sectors are agriculture and manufacturing.
General reference
 * Pronunciation:
* Common English country name:
* Pronunciation:
* Common English country name: Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
* Official English country name: The Republic of Belarus
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
* Common endonym(s):
* Official endonym(s):
* Adjectival(s): Belarusian
* Demonym(s):
* Etymology
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the Phonological chan ...
: Name of Belarus
* International rankings of Belarus
* ISO country codes
ISO 3166-1 (''Codes for the representation of names of countries and their subdivisions – Part 1: Country codes'') is a standard defining codes for the names of countries, dependent territories, and special areas of geographical interest. It ...
: BY, BLR, 112
* ISO region codes
ISO 3166-2 is part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and defines codes for identifying the principal subdivisions (e.g., provinces or states) of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1. The ...
: See ISO 3166-2:BY
* Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
country code top-level domain
A country code top-level domain (ccTLD) is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, sovereign state, or dependent territory identified with a country code. All ASCII ccTLD identifiers are two letters long, and all ...
: .by
.by is the Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Belarus. It is administered by the Operations and Analysis Centre under the President of the Republic of Belarus (Оперативно-аналитический центр при П� ...
*Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
Internationalized country code top-level domain: .бел
.бел (abbreviation of be, Беларусь, translit=Belarus) is an approved internationalized country code top-level domain (IDN ccTLD) for Belarus. Activation of the domain was finished in late 2014. The Latin script domain for Belarus is ...
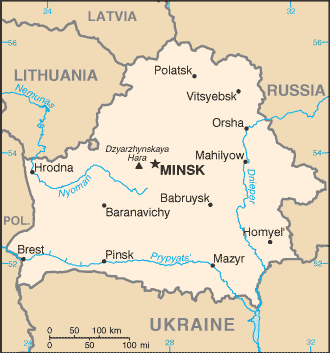
Geography of Belarus
Geography of Belarus
Belarus is a landlocked, generally flat country (the average elevation is above sea level) without natural borders, that occupies an area of . Its neighbors are Russia to the east and northeast, Latvia to the north, Lithuania to the north ...
* Belarus is: a landlocked country
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
* Location:
** Northern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
** Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago ...
*** Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
**** Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
** Time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between countries and their subdivisions instead of strictly following longitude, because it ...
: Eastern European Time
Eastern European Time (EET) is one of the names of UTC+02:00 time zone, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. The zone uses daylight saving time, so that it uses UTC+03:00 during the summer.
A number of African countries use UTC ...
(UTC+02
UTC+02:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +02:00. In ISO 8601, the associated time would be written as 2020-11-08T23:41:45+02:00. This time is used in:
As standard time (year-round)
''Principal cities: Cairo, Pretoria, Cape ...
), Eastern European Summer Time
Eastern European Summer Time (EEST) is one of the names of the UTC+03:00 time zone, which is 3 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in some European and Middle Eastern countries, which makes ...
(UTC+03
UTC+03:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +03:00. In areas using this time offset, the time is three hours later than the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
Following the ISO 8601 standard, a time with this offset would be wri ...
)
** Extreme points of Belarus
*** High: Dzyarzhynskaya Hara
Dzyarzhynskaya Hara ( Belarusian: Дзяржынская гара - ''Dziaržynskaja hara'' ) is the highest point in Belarus. The hill is 345 meters (1,130 ft) above sea level and is located west of Minsk, near Dzyarzhynsk, in the village ...
*** Low: Neman River
** Land boundaries: 3,306 km
:: 959 km
:: 891 km
:: 680 km
:: 605 km
:: 171 km
:* Coastline: ''none''
* Population of Belarus: 9,255,524 (2022) - 96th most populous country
*
* Area of Belarus: - 85th largest country
* Atlas of Belarus
Environment of Belarus
 * Climate of Belarus
* Renewable energy in Belarus
* Geology of Belarus
* Protected areas of Belarus
** Biosphere reserves in Belarus
**
* Climate of Belarus
* Renewable energy in Belarus
* Geology of Belarus
* Protected areas of Belarus
** Biosphere reserves in Belarus
** National parks of Belarus
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, ce ...
* Wildlife of Belarus
** Fauna of Belarus
*** Birds of Belarus
*** Mammals of Belarus
Natural geographic features of Belarus
*Rivers of Belarus
This is a list of rivers in Belarus.
All rivers measured in Kilometres. Inside of Belarus and the length in total.
Longest rivers
List of Rivers in Belarus
* Dnieper River
** Drut River (R)
** Sozh River (L)
***Iput River
***Pronya
***Besed ...
* World Heritage Sites in Belarus
Regions of Belarus
Regions of Belarus
At the top level of administration, Belarus is divided into six ''oblasts'' (''voblasts'' or provinces). The city of Minsk, has a special status as the capital of Belarus. Minsk is also the capital of Minsk Region.Administrative divisions of Belarus
At the top level of administration, Belarus is divided into six ''oblasts'' (''voblasts'' or provinces). The city of Minsk, has a special status as the capital of Belarus. Minsk is also the capital of Minsk Region.Provinces of Belarus
Belarus News and AnalysisPolitics and News from Belarus
News of Belarus
; Governmental websites
President's official siteEmbassy of Belarus in the United StatesMinistry of Foreign Affairs
; Informational/cultural
A Belarus MiscellanyThe Virtual Guide to BelarusBelarus Tourism and Travel InformationThe 1st Belarusian Art GalleryContemporary Belarusian Art and PaintingBelarus
''
The World Bank in BelarusPhotos of Belarus
; City and country maps
map of natural sightseeings in BelarusBelarus, topographic mapGeneral detail, downloadable PDF map of BelarusGoogle maps Belarus
{{Outline footer
=Regions (Oblasts) of Belarus
=Regions of Belarus
At the top level of administration, Belarus is divided into six ''oblasts'' (''voblasts'' or provinces). The city of Minsk, has a special status as the capital of Belarus. Minsk is also the capital of Minsk Region.Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
* Brest Oblast
Brest Region or Brest Oblast or Brest Voblasts ( be, Брэ́сцкая во́бласць ''(Bresckaja vobłasć)''; russian: Бре́стская о́бласть (''Brestskaya Oblast)'') is one of the regions of Belarus. Its administrative cent ...
* Gomel Oblast
Gomel Region or Gomel Oblast or Homiel Voblasts ( be, Го́мельская во́бласць, Homielskaja vobłasć, russian: Гомельская область, Gomelskaya oblast) is one of the regions of Belarus. Its administrative center i ...
* Grodno Oblast
Grodno Region ( pl, Grodzieńszczyzna) or Grodno Oblast or Hrodna Voblasts ( be, Гродзенская вобласць, ''Hrodzienskaja vobłasć'', , ''Haradzienščyna''; russian: Гродненская область, ''Grodnenskaya oblast' ...
* Mogilev Oblast
Mogilev Region or Mogilev Oblast or Mahiliow Voblasts ( be, link=no, Магілёўская вобласць; ''Mahiloŭskaja voblasć''; russian: link=no, Могилёвская область; ''Mogilyovskaya Oblast''), is a region (''oblast'' ...
* Minsk Oblast
Minsk Region or Minsk Oblast or Minsk Voblasts ( be, Мі́нская во́бласць, ''Minskaja voblasć'' ; russian: Минская о́бласть, ''Minskaya oblast'') is one of the regions of Belarus. Its administrative center is Minsk, ...
* Vitebsk Oblast
Vitebsk Region or Vitebsk Oblast or Viciebsk Voblasts ( be, Ві́цебская во́бласць, ''Viciebskaja voblasć'', ; rus, Ви́тебская о́бласть, Vitebskaya oblast, ˈvʲitʲɪpskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a region (oblast ...
=Districts of Belarus
=Districts of Belarus
Districts of Belarus (raion) are second-level administrative territorial entities of Belarus.
In Belarus, raions (russian: район; be, раён, rajonAccording to thInstruction on Latin Transliteration of Geographical Names of the Republic o ...
There are 118 districts in Belarus.
=Municipalities of Belarus
= Municipalities of BelarusDemography of Belarus
Demographics of Belarus
The demographics of Belarus is about the demographic features of the population of Belarus, including population growth, population density, ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the ...
Government and politics of Belarus
* Form of government: presidential republic * Capital of Belarus:Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
* Elections in Belarus
* Political parties in Belarus
This article lists political parties in Belarus.
Parties represented in the National Assembly of Belarus
The president Alexander Lukashenko is independent, and draws most of his support from non-partisan members of parliament. Most non-partisan ...
Branches of government
Government of Belarus
The Government of the Republic of Belarus ( be, Урад Рэспублікі Беларусь), which consists of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Belarus (), is the executive branch of state power in Belarus, and is appointed by the ...
Executive branch of the government of Belarus
*Head of state
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
: President of Belarus
The president of the Republic of Belarus ( be, Прэзідэнт Рэспублікі Беларусь; russian: Президент Республики Беларусь) is the head of state and head of government of Belarus. The office was cre ...
* Head of government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, ...
: Prime Minister of Belarus
The prime minister of the Republic of Belarus (; ) is the deputy head of government of Belarus. Until 1991, it was known as the Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic as the head of the government of t ...
* Cabinet of Belarus
Legislative branch of the government of Belarus
*Parliament of Belarus
The National Assembly of the Republic of Belarus ( be, Нацыянальны сход Рэспублікі Беларусь, Nacyjanalny schod Respubliki Bielaruś; russian: Национальное собрание Республики Бел ...
( bicameral)
** Upper house
An upper house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house.''Bicameralism'' (1997) by George Tsebelis The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restric ...
: Council of the Republic
** Lower house: House of Representatives of Belarus
Judicial branch of the government of Belarus
Court system of Belarus * Supreme Court of BelarusForeign relations of Belarus
Foreign relations of Belarus
The Byelorussian SSR was one of only two Soviet republics to be separate members of the United Nations (the other being the Ukrainian SSR). Both republics and the Soviet Union joined the UN when the organization was founded in 1945.
Prior to 20 ...
* Diplomatic missions in Belarus
* Diplomatic missions of Belarus
This is a list of diplomatic missions of Belarus. Belarus has been the most eager nation of the former USSR to integrate more closely and to re-engage with former Soviet states, and this is reflected in the location of its missions. The website o ...
* United States-Belarus relations
International organization membership
The Republic of Belarus is a member of: *Black Sea Economic Cooperation Zone
The Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation (BSEC) is a regional international organization focusing on multilateral political and economic initiatives aimed at fostering cooperation, peace, stability and prosperity in the Black Sea ...
(BSEC) (observer)
* Central European Initiative (CEI)
* Collective Security Treaty Organization
The Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) is an intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia consisting of six post-Soviet states: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Tajikistan. The Collective Security Treaty has ...
(CSTO)
* Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. ...
(CIS)
* Eurasian Economic Community
The Eurasian Economic Community (EAEC or EurAsEC) was a regional organisation between 2000 and 2014 which aimed for the economic integration of its member states.
The organisation originated from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) on ...
(EAEC)
* Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council
The Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC) is a post–Cold War, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) institution. The EAPC is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and Central Asi ...
(EAPC)
* European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD)
* Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an intern ...
(FAO)
* General Confederation of Trade Unions
The General Confederation of Trade Unions or GCTU (russian: Всеобщая Конфедерация Профсоюзов, ''Vseobshchya Konfederatsya Profsoyuzov'' or VKP) is an international trade union confederation. It was founded on 16 Apr ...
(GCTU)
* International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
* International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD)
* International Civil Aviation Organization
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO, ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international a ...
(ICAO)
* International Criminal Police Organization
The International Criminal Police Organization (ICPO; french: link=no, Organisation internationale de police criminelle), commonly known as Interpol ( , ), is an international organization that facilitates worldwide police cooperation and cri ...
(Interpol)
* International Development Association (IDA)
* International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRCS)
* International Finance Corporation
The International Finance Corporation (IFC) is an international financial institution that offers investment, advisory, and asset-management services to encourage private-sector development in less developed countries. The IFC is a member of ...
(IFC)
* International Labour Organization
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is the first and o ...
(ILO)
* International Mobile Satellite Organization
The International Mobile Satellite Organization (IMSO) is the intergovernmental organization that oversees certain public satellite safety and security communication services provided via the Inmarsat satellites. Some of these services concern: ...
(IMSO)
* International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
(IMF)
* International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
(IOC)
* International Organization for Migration
The International Organization for Migration (IOM) is a United Nations agency that provides services and advice concerning migration to governments and migrants, including internally displaced persons, refugees, and migrant workers.
The IOM w ...
(IOM)
* International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ) is an international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries. Membership requirements are given in Art ...
(ISO)
* International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement (ICRM)
* International Telecommunication Union
The International Telecommunication Union is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for many matters related to information and communication technologies. It was established on 17 May 1865 as the International Telegraph Unio ...
(ITU)
* International Trade Union Confederation
The International Trade Union Confederation (ITUC); german: Internationaler Gewerkschaftsbund (IGB), link=no; es, Confederación Sindical Internacional (CSI), link=no. is the world's largest trade union federation.
History
The federation w ...
(ITUC)
* Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)
* Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency
The Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) is an international financial institution which offers political risk insurance and credit enhancement guarantees. These guarantees help investors protect foreign direct investments against ...
(MIGA)
* Nonaligned Movement (NAM)
* Nuclear Suppliers Group
The Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG) is a multilateral export control regime and a group of nuclear supplier countries that seek to prevent nuclear proliferation by controlling the export of materials, equipment and technology that can be used to m ...
(NSG)
* Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
* Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons
The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) is an intergovernmental organisation and the implementing body for the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC), which entered into force on 29 April 1997. The OPCW, with its 193 member ...
(OPCW)
* Partnership for Peace
The Partnership for Peace (PfP; french: Partenariat pour la paix) is a North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) program aimed at creating trust between the member states of NATO and other states mostly in Europe, including post-Soviet state ...
(PFP)
* Permanent Court of Arbitration
The Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA) is a non-UN intergovernmental organization located in The Hague, Netherlands. Unlike a judicial court in the traditional sense, the PCA provides services of arbitral tribunal to resolve disputes that aris ...
(PCA)
* United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
(UN)
* United Nations Conference on Trade and Development
The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization within the United Nations Secretariat that promotes the interests of developing countries in world trade. It was established in 1964 by the ...
(UNCTAD)
* United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
(UNESCO)
* United Nations Industrial Development Organization
The United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) (French: Organisation des Nations unies pour le développement industriel; French/Spanish acronym: ONUDI) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that assists countries in ...
(UNIDO)
* Universal Postal Union
The Universal Postal Union (UPU, french: link=no, Union postale universelle), established by the Treaty of Bern of 1874, is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to ...
(UPU)
* World Customs Organization
The World Customs Organization (WCO) is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. The WCO works on customs-related matters including the development of international conventions, instruments, and tools on topics su ...
(WCO)
* World Federation of Trade Unions
The World Federation of Trade Unions (WFTU) is an international federation of trade unions established in 1945. Founded in the immediate aftermath of World War Two, the organization built on the pre-war legacy of the International Federation o ...
(WFTU)
* World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
(WHO)
* World Intellectual Property Organization
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO; french: link=no, Organisation mondiale de la propriété intellectuelle (OMPI)) is one of the 15 specialized agencies of the United Nations (UN). Pursuant to the 1967 Convention Establishi ...
(WIPO)
* World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Intern ...
(WMO)
* World Tourism Organization
The World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) is the United Nations specialized agency entrusted with the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism. Its headquarters are in Madrid, Spain. UNWTO is the leading internati ...
(UNWTO)
* World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and ...
(WTO) (observer)
Law and order in Belarus
Law of Belarus *Capital punishment in Belarus
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in Belarus. At least four executions were carried out in the country in 2018.
Also known as an Exceptional Measure of Punishment (russian: Исключительная Мера Наказания, ИМН), i ...
* Constitution of Belarus
The Constitution of the Republic of Belarus ( be, Канстытуцыя Рэспублікі Беларусь, russian: Конституция Республики Беларусь) is the ultimate law of Belarus. The Constitution is composed o ...
* Crime in Belarus
* Human rights in Belarus
The government of Belarus is criticized for its human rights violations and persecution of non-governmental organisations, independent journalists, national minorities, and opposition politicians. In a testimony to the United States Senate Com ...
** Censorship in Belarus
Censorship in Belarus, although prohibited by the country's constitution, is enforced by a number of laws. These include a law that makes insulting the president punishable by up to five years in prison, and another that makes criticizing Belarus ...
** LGBT rights in Belarus
** Freedom of religion in Belarus
* Law enforcement in Belarus
Law enforcement in Belarus is the responsibility of a variety of agencies such as the Militsiya, as well as other agencies such as the Presidential Guard and the State Security Agency of the Republic of Belarus, all under the authority of the coun ...
Military of Belarus
Military of Belarus
The Armed Forces of the Republic of Belarus (, ) consist of the Ground Forces and the Air Force and Air Defence Forces, all under the command of the Republic of Belarus Ministry of Defence. Being a landlocked country, Belarus has no navy.
In 2 ...
* Command
** Commander-in-chief:
*** Ministry of Defence of Belarus
* Forces
** Army of Belarus
** Navy of Belarus
** Air Force of Belarus
** Special forces of Belarus )''Anywhere, anytime, any task'' (alternative)
, battles = United Nations Interim Force in LebanonLibyan Civil War (2011) 2020 Belarusian protests
, commander1 = Major General Vadim Denisenko
, commander1 ...
* Military history of Belarus
The Armed Forces of the Republic of Belarus (, ) consist of the Ground Forces and the Air Force and Air Defence Forces, all under the command of the Republic of Belarus Ministry of Defence. Being a landlocked country, Belarus has no navy.
In 2 ...
* Military ranks of Belarus The Military ranks of Belarus are the military insignia used by the Armed Forces of Belarus. Being a former member of Soviet Union, Belarus shares a rank structure similar to that of Russia. Belarus is a landlocked country, and does not possess a n ...
Local government in Belarus
Local government in BelarusHistory of Belarus
History of Belarus
This article describes the history of Belarus. The Belarusians, Belarusian ethnos is traced at least as far in time as other East Slavs.
Belarus is a successor of some Rus' people, Ruthenian principalities (Principality of Polotsk, Polotsk, Prin ...
* Military history of Belarus
The Armed Forces of the Republic of Belarus (, ) consist of the Ground Forces and the Air Force and Air Defence Forces, all under the command of the Republic of Belarus Ministry of Defence. Being a landlocked country, Belarus has no navy.
In 2 ...
Culture of Belarus
Culture of Belarus * Architecture of Belarus **Belarusian Gothic
Belarusian Gothic () is the architectural style of ecclesiastical buildings and fortified structures of the 15th and 16th centuries in modern Belarus, Lithuania, eastern Poland and western Ukraine.
Although these buildings have features typica ...
* Cuisine of Belarus
* Festivals in Belarus
* Languages of Belarus The official languages of Belarus are Belarusian and Russian.
The pre-Slavic language of the area, as well as its geographic name was Sudovian and Sudavia, a Baltic language. Sudovian is believed to have gone extinct around the 17th century.
At p ...
* Media in Belarus
* Museums in Belarus
* National symbols of Belarus
Upon the independence of Belarus from the Soviet Union, the country resurrected national symbols that were used before the Soviet era. These included a flag of red and white stripes and a coat of arms consisting of a charging knight on horseback. ...
** Coat of arms of Belarus
The national emblem of Belarus features a ribbon in the colors of the national flag, a silhouette of Belarus, wheat ears and a red star. It is sometimes referred to as the coat of arms of Belarus, although in heraldic terms this is inaccurate ...
** Flag of Belarus
The national flag of Belarus is a red-and-green flag with a white-and-red ornament pattern placed at the hoist (staff) end. The current design was introduced in 2012 by the State Committee for Standardisation of the Republic of Belarus, and ...
** National anthem of Belarus
The "State Anthem of the Republic of Belarus" ( be, Дзяржаўны гімн Рэспублікі Беларусь ), better known as "" (; "We, Belarusians"), is the national anthem of Belarus. It was originally written in the 1940s and adopt ...
* People of Belarus
* Prostitution in Belarus
* Public holidays in Belarus
National holidays in Belarus are classified into state holidays and other holidays and commemorative days, including religious holidays. Nine of them are non-working days.
Public holidays (non-working days)
Other holidays
State
Comme ...
* Records of Belarus
* Religion in Belarus
** Christianity in Belarus
** Hinduism in Belarus
** Islam in Belarus
A continuous presence of Islam in Belarus began in the 14th century. From this time it was primarily associated with the Lipka Tatars, many of whom settled in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth while continuing their traditions and religi ...
** Judaism in Belarus
** Sikhism in Belarus
* World Heritage Sites in Belarus
Art in Belarus
* Art in Belarus * Cinema of Belarus * Literature of Belarus *Music of Belarus
Belarus is an Eastern European country with a rich tradition of folk and religious music. The country's folk music traditions can be traced back to the times of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The country's musical traditions spread with its people ...
* Television in Belarus
* Theatre in Belarus
Sports in Belarus
Sports in Belarus *Football in Belarus
Association football ( be, Асацыяцыя футбола) – commonly known as football (or soccer in the United States, Canada, Australia and Ireland, which have their own football codes) – is a popular sport in the nation of Belarus. As ...
* Belarus at the Olympics
Athletes from Belarus began their Olympic participation at the 1952 Summer Games in Helsinki, Finland, as part of the Soviet Union (IOC code: URS). After the Soviet Union disbanded in 1991, Belarus, along with four of the other fourteen former Sov ...
Economy and infrastructure of Belarus
Economy of Belarus
The economy of Belarus is an upper-middle income mixed economy. As a post-Soviet transition economy, Belarus rejected most privatisation efforts in favour of retaining centralised political and economic controls by the state. The highly centralis ...
* Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 69th (sixty-ninth)
* Agriculture in Belarus
* Banking in Belarus
** National Bank of Belarus
The National Bank of the Republic of Belarus (NBRB; be, Нацыянальны банк Рэспублікі Беларусь; rus, Национальный банк Республики Беларусь) is the central bank of Belarus, located ...
* Communications in Belarus
** Internet in Belarus
*** Internet censorship in Belarus
* Companies of Belarus
* Currency of Belarus: Rubel
** ISO 4217: BYR
A billion years or giga-annum (109 years) is a unit of time on the petasecond scale, more precisely equal to seconds (or simply 1,000,000,000 years).
It is sometimes abbreviated Gy, Ga ("giga-annum"), Byr and variants. The abbreviations Gya or ...
* Energy in Belarus
** Energy policy of Belarus
** Oil industry in Belarus
* Healthcare in Belarus
* Mining in Belarus
* Belarus Stock Exchange
* Tourism in Belarus
* Transport in Belarus
This article is about transport in Belarus.
Railways
Rail transport in Belarus is operated by Belarusskaya ChyhunkaAirports in Belarus
This is a list of airports in Belarus, grouped by type and sorted by location.
__TOC__ Airports
Airport names shown in bold indicate the airport has scheduled service on commercial airlines.
See also
* Transport in Belarus
* Belarusian A ...
** Rail transport in Belarus
** Roads in Belarus
Automobile roads in Belarus are classified into several categories.
State-owned common access roads
The state-owned roads of common access are managed by the Belavtodor department of the Ministry of Transport and Communications of Belarus."Bela ...
Education in Belarus
Education in Belarus
Education in Belarus is free at all levels except for higher education. The government ministry that oversees the running of the school systems is the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Belarus. Each of the regions inside Belarus has oversigh ...
The 2 leading establishments in the national education system:
* Academy of Public Administration under the aegis of the President of the Republic of Belarus
* Belarusian State University
Belarusian State University (BSU) ( be, links=no, Белару́скі дзяржа́ўны ўніверсітэ́т, ; russian: links=no, Белору́сский госуда́рственный университе́т) is a university in Mins ...
See also
* * * * * List of Belarus-related topics * Outline of Europe *Outline of Slavic history and culture
Topical outline of articles about Slavic history and culture. This outline is an overview of Slavic topics; for outlines related to specific Slavic groups and topics, see the links in the Other Slavic outlines section below.
Slavs are the large ...
*List of Slavic studies journals
This is a list of notable and independent English language peer-reviewed academic journals related to Slavic studies. Journals should be published by major universities, professional associations, national or regional historical societies, or n ...
References
External links
; MediaBelarus News and Analysis
News of Belarus
; Governmental websites
President's official site
; Informational/cultural
A Belarus Miscellany
''
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is availabl ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
.The World Bank in Belarus
; City and country maps
map of natural sightseeings in Belarus
{{Outline footer
Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...