Orion Arm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Orion Arm is a minor Shen, j., and Zheng, X.
Shen, j., and Zheng, X., 2020, RAA, Vol.20, No.10,159

 The Orion Arm contains a number of
The Orion Arm contains a number of
Image:Orion Arm.JPG, frame, center, Orion and neighboring arms (clickable map)
rect 126 149 188 182 Rosette Nebula
rect 285 116 327 145 Crab Nebula
rect 243 245 284 274 Orion Nebula
rect 299 288 345 312
Image:Nearest Nebulae and Star clusters.gif, 800px, center, The nearest nebulae and star clusters (clickable map)
rect 396 142 447 173 Rosette Nebula
rect 376 230 426 258
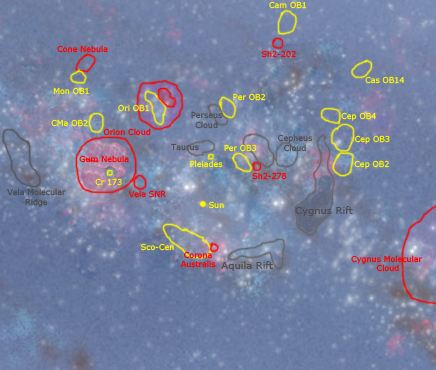
Messier Objects in the Milky Way (SEDS)A 3D map of the Milky Way Galaxy
{{Authority control Milky Way arms Galactic astronomy Spiral galaxies
spiral arm
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''Milky Way Galaxy
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
that is across and approximately in length, containing the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
, including Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
. It is also referred to by its full name, the Orion–Cygnus Arm, as well as Local Arm, Orion Bridge, and formerly, the Local Spur and Orion Spur.
The arm is named for the Orion Constellation, which is one of the most prominent constellations of Northern Hemisphere winter (Southern Hemisphere summer). Some of the brightest stars and most famous celestial objects of the constellation (e.g. Betelgeuse, Rigel
Rigel is a blue supergiant star in the constellation of Orion. It has the Bayer designation β Orionis, which is Latinized to Beta Orionis and abbreviated Beta Ori or β Ori. Rigel is the brightest and most massive componentand ...
, the three stars of Orion's Belt
Orion's Belt or the Belt of Orion, also known as the Three Kings or Three Sisters, is an asterism in the constellation Orion. It consists of the three bright stars Alnitak, Alnilam and Mintaka.
Looking for Orion's Belt is the easiest way to ...
, the Orion Nebula) are within it as shown on the interactive map below.
The arm is between the Carina–Sagittarius Arm
The Carina–Sagittarius Arm (also known as the Sagittarius Arm or Sagittarius–Carina Arm, labeled -I) is generally thought to be a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way galaxy. Each spiral arm is a long, diffuse curving streamer of stars that ra ...
(the local portions of which are toward the Galactic Center
The Galactic Center or Galactic Centre is the rotational center, the barycenter, of the Milky Way galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact ra ...
) and the Perseus Arm
The Perseus Arm is one of two major spiral arms of the Milky Way galaxy. The second major arm is called the Scutum–Centaurus Arm. The Perseus Arm begins from the distal end of the long Milky Way central bar. Previously thought to be 13,000 lig ...
(the local portion of which is the main outer-most arm and one of two major arms of the galaxy).
Long thought to be a minor structure, namely a "spur" between the two arms mentioned, evidence was presented in mid 2013 that the Orion Arm might be a branch of the Perseus Arm, or possibly an independent arm segment.
Within the arm, the Solar System is close to its inner rim, in a relative cavity in the arm's interstellar medium known as the Local Bubble
The Local Bubble, or Local Cavity, is a relative cavity in the interstellar medium (ISM) of the Orion Arm in the Milky Way. It contains the closest of celestial neighbours and among others, the Local Interstellar Cloud (which contains the Sol ...
, about halfway along the arm's length, approximately from the Galactic Center.
Recently, the parallax and proper motion of more than 30 methanol (6.7-GHz) and water (22-GHz) masers in high-mass star-forming regions within a few kiloparsecs of the Sun were measured. Measurement accuracy was better than ±10% and even 3%, the best parallax measurement in the BeSSeL project ( Bar and Spiral Structure Legacy Survey). The accuracy locations of interstellar masers in HMSFRs (high-mass star-forming regions) have been shown that the Local Arm appears to be an orphan segment of an arm between the Sagittarius and Perseus arms that wraps around less than a quarter of the Milky Way. The segment has the length of ~20,000 ly and the width of ~3,000 ly with the pitch angle from 10.1° ± 2.7° to 11.6° ± 1.8°. These results reveal that the Local Arm is larger than previously thought, and both its pitch angle and star formation rate are comparable to those of the Galaxy’s major spiral arms. The Local Arm is reasonably referred to as the fifth feature in the Milky Way. The “spur” interpretation may be incorrect.
To understand the form of the Local Arm between the Sagittarius and Perseus arms, the stellar density of a specific population of stars with about 1 Gyr of age between 90° ≤ l ≤ 270° have been mapped using the Gaia DR2. The 1 Gyr population have been employed because they are significantly more-evolved objects than the gas in HMSFRs tracing the Local Arm. Investigations have been carried out to compare both the stellar density and gas distribution along the Local Arm. Researchers have found a marginally significant arm-like stellar overdensity close to the Local Arm, identified with the HMSFRs especially in the region of 90° ≤ l ≤ 190°. They have concluded that the Local Arm is the arm segment associated with only the gas and star-forming clouds, with a significant stellar overdensity. Additionally, they have found that the pitch angle of the stellar arm is slightly larger than the gas-defined arm, and also there is an offset between gas-defined and stellar arm. The offset and different pitch angles between the stellar and HMSFR-defined spiral arms are consistent with the expectation that star formation lags the gas compression in a spiral density wave lasting longer than the typical star formation timescale of 107 − 108 years.Shen, j., and Zheng, X., 2020, RAA, Vol.20, No.10,159

Messier objects
 The Orion Arm contains a number of
The Orion Arm contains a number of Messier objects
The Messier objects are a set of 110 astronomical objects catalogued by the French astronomer Charles Messier in his ''Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des Amas d'Étoiles'' (''Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters'').
Because Messier was only in ...
:
*The Butterfly Cluster
The Butterfly Cluster (cataloged as Messier 6 or M6, and as NGC 6405) is an open cluster of stars in the southern constellation of Scorpius. Its name derives from the vague resemblance of its shape to a butterfly. The Trumpler classification of ...
(M6)
*The Ptolemy Cluster (M7)
* Open Cluster M23
* Open Cluster M25
*The Dumbbell Nebula
The Dumbbell Nebula (also known as the Apple Core Nebula, Messier 27, and NGC 6853) is a planetary nebula (nebulosity surrounding a white dwarf) in the constellation Vulpecula, at a distance of about 1360 light-years. It was the first such nebula ...
(M27)
* Open Cluster M29
* Open Cluster M34
* Open Cluster M35
* Open Cluster M39
*Winnecke 4
Winnecke 4 (also known as Messier 40 or WNC 4) is an optical double star consisting of two unrelated stars in a northerly zone of the sky, Ursa Major.
The pair were discovered by Charles Messier in 1764 while he was searching for a neb ...
(M40)
* Open Cluster M41
*The Orion Nebula (M42)
*The De Mairan's Nebula (M43)
*The Beehive Cluster
The Beehive Cluster (also known as Praesepe (Latin for "manger" or "crib"), M44, NGC 2632, or Cr 189), is an open cluster in the constellation Cancer. One of the nearest open clusters to Earth, it contains a larger population of stars than oth ...
(M44)
*The Pleiades
The Pleiades (), also known as The Seven Sisters, Messier 45 and other names by different cultures, is an asterism and an open star cluster containing middle-aged, hot B-type stars in the north-west of the constellation Taurus. At a distance ...
(M45)
* Open Cluster M46
* Open Cluster M47
* Open Cluster M48
* Open Cluster M50
*The Ring Nebula (M57)
* Open Cluster M67
* M73
*The Little Dumbbell Nebula (M76)
* Diffuse Nebula M78
* Open Cluster M93
*The Owl Nebula (M97)
Interactive maps
Trifid Nebula
The Trifid Nebula (catalogued as Messier 20 or M20 and as NGC 6514) is an H II region in the north-west of Sagittarius in a star-forming region in the Milky Way's Scutum-Centaurus Arm.
It was discovered by Charles Messier on June 5, 1764. I ...
rect 343 304 384 333 Lagoon Nebula
rect 393 322 434 353 Omega Nebula
The Omega Nebula, also known as the Swan Nebula, Checkmark Nebula, Lobster Nebula, and the Horseshoe Nebula (catalogued as Messier 17 or M17 or NGC 6618) is an H II region in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Philippe Loys d ...
rect 445 322 494 353 Eagle Nebula
The Eagle Nebula (catalogued as Messier 16 or M16, and as NGC 6611, and also known as the Star Queen Nebula) is a young open cluster of stars in the constellation Serpens, discovered by Jean-Philippe de Cheseaux in 1745–46. Both the "Eagle" ...
rect 424 244 483 280 North America Nebula
rect 293 248 319 266 Rigel
Rigel is a blue supergiant star in the constellation of Orion. It has the Bayer designation β Orionis, which is Latinized to Beta Orionis and abbreviated Beta Ori or β Ori. Rigel is the brightest and most massive componentand ...
rect 225 179 299 246 Orion's Belt
Orion's Belt or the Belt of Orion, also known as the Three Kings or Three Sisters, is an asterism in the constellation Orion. It consists of the three bright stars Alnitak, Alnilam and Mintaka.
Looking for Orion's Belt is the easiest way to ...
rect 331 211 368 234 Polaris
rect 318 236 353 259 Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
poly 302 176 303 241 315 242 361 177 Betelgeuse
rect 419 222 458 245 Deneb
Deneb () is a first-magnitude star in the constellation of Cygnus, the swan. Deneb is one of the vertices of the asterism known as the Summer Triangle and the "head" of the Northern Cross. It is the brightest star in Cygnus and th ...
poly 0 123 508 118 637 160 637 217 470 163 0 178 Perseus Arm
The Perseus Arm is one of two major spiral arms of the Milky Way galaxy. The second major arm is called the Scutum–Centaurus Arm. The Perseus Arm begins from the distal end of the long Milky Way central bar. Previously thought to be 13,000 lig ...
poly 2 202 460 201 633 261 637 326 408 260 1 258 Orion Arm
poly 1 284 397 293 633 360 637 477 541 475 357 413 0 400 Sagittarius Arm
desc bottom-left
Seagull Nebula
IC 2177 is a region of nebulosity that lies along the border between the constellations Monoceros and Canis Major. It is a roughly circular H II region centered on the Be star
Be stars are a heterogeneous set of stars with B spectral types ...
rect 463 264 501 292 Cone Nebula
rect 528 284 576 322 California Nebula
rect 695 117 741 149 Heart Nebula
rect 461 301 494 339 Orion Nebula
rect 691 154 739 182 Soul Nebula
rect 568 371 625 405 North America Nebula
rect 643 366 687 402 Cocoon Nebula
rect 688 392 761 429 Gamma Cygni Nebula
rect 594 404 625 444 Veil Nebula
The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus.
It constitutes the visible portions of the Cygnus Loop,
a supernova remnant, many portions of which have acquired their own individual names and ca ...
rect 513 541 550 578 Trifid Nebula
The Trifid Nebula (catalogued as Messier 20 or M20 and as NGC 6514) is an H II region in the north-west of Sagittarius in a star-forming region in the Milky Way's Scutum-Centaurus Arm.
It was discovered by Charles Messier on June 5, 1764. I ...
poly 676 435 690 435 692 427 723 429 726 461 677 461 Crescent Nebula
rect 489 597 543 630 Lagoon Nebula
rect 555 592 595 626 Omega Nebula
The Omega Nebula, also known as the Swan Nebula, Checkmark Nebula, Lobster Nebula, and the Horseshoe Nebula (catalogued as Messier 17 or M17 or NGC 6618) is an H II region in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Philippe Loys d ...
rect 574 646 614 689 Eagle Nebula
The Eagle Nebula (catalogued as Messier 16 or M16, and as NGC 6611, and also known as the Star Queen Nebula) is a young open cluster of stars in the constellation Serpens, discovered by Jean-Philippe de Cheseaux in 1745–46. Both the "Eagle" ...
rect 444 633 500 678 Cat's Paw Nebula
rect 90 502 161 529 Eta Carinae Nebula
rect 442 37 491 69 Crab Nebula
rect 517 158 547 175 Messier 37
rect 527 172 559 190 Messier 36
rect 533 191 563 208 Messier 38
rect 408 257 434 280 Messier 50
rect 327 232 357 257 Messier 46
rect 422 285 454 302 Messier 67
rect 553 321 582 338 Messier 34
rect 433 305 461 321 Messier 48
rect 409 314 435 330 Messier 41
Messier 41 (also known as M41 or NGC 2287) is an open cluster in the constellation Canis Major, sometimes referred to as The Little Beehive Cluster. It was discovered by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654 and was perhaps known to Aristotle abou ...
rect 425 328 456 345 Messier 47
Messier 47 (M47 or NGC 2422) is an open cluster in the mildly southern constellation of Puppis. It was discovered by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654 and in his then keynote work re-discovered by Charles Messier on 1771. It was also independe ...
rect 474 343 500 365 Messier 44
rect 502 345 528 368 Messier 45
rect 542 378 568 399 Messier 39
rect 714 285 748 308 Messier 52
rect 352 285 379 308 Messier 93
rect 489 421 513 444 Messier 7
Messier 7 or M7, also designated NGC 6475 and sometimes known as the Ptolemy Cluster, is an open cluster of stars in the constellation of Scorpius. The cluster is easily detectable with the naked eye, close to the "stinger" of Scorpius. With a d ...
rect 495 452 518 473 Messier 6
rect 522 456 549 476 Messier 25
Messier 25, also known as IC 4725, is an open cluster of stars in the southern constellation of Sagittarius. The first recorded observation of this cluster was made by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in 1745 and it was included in Charles Messier ...
rect 512 478 539 500 Messier 23
Messier 23, also known as NGC 6494, is an open cluster of stars in the northwest of the southern constellation of Sagittarius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764. It can be found in good conditions with binoculars or a modestly sized ...
rect 531 575 555 593 Messier 21
Messier 21 or M21, also designated NGC 6531 or Webb's Cross, is an open cluster of stars located to the north-east of Sagittarius in the night sky, close to the Messier objects M20 to M25 (except M24). It was discovered and catalogued by Ch ...
rect 556 564 589 580 Messier 18
Messier 18 or M18, also designated NGC 6613, is an open cluster of stars in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764 and included in his list of comet-like objects. From the perspective of Earth, M18 is situ ...
rect 605 598 640 617 Messier 26
rect 630 618 654 639 Messier 11
rect 484 234 510 256 Messier 35
rect 287 248 316 276 NGC 2362
NGC 2362, also known as Caldwell 64, is an open cluster of stars in the southern constellation of Canis Major. It was discovered by the Italian court astronomer Giovanni Batista Hodierna, who published his finding in 1654. William Herschel called ...
rect 370 359 411 381 IC 2395
IC 2395 is an open cluster in the constellation Vela.
Observation history
It is possible that entry III.3 of the catalogue of Nicolas Louis de Lacaille, often listed as missing, is IC 2395. According to Lacaille's entry, the object consists of ...
rect 359 413 390 449 NGC 3114
rect 407 396 444 432 NGC 3532
rect 594 356 644 372 IC 1396
rect 458 392 502 406 IC 2602
IC 2602 (also known as the Southern Pleiades, Theta Carinae Cluster, or Caldwell 102) is an open cluster in the constellation Carina. Discovered by Abbe Lacaille in 1751 from South Africa, the cluster is easily visible to the unaided eye, and is on ...
rect 407 494 443 521 NGC 6087
NGC 6087 (also known as Caldwell 89 or the S Normae Cluster) is an open cluster of 40 or moreBurnham's ''Celestial Handbook'' gives the number 40, though other studies go as high as 349; see Stephen James O'Meara, ''The Caldwell Objects'', Cambri ...
rect 437 464 472 497 NGC 6025
rect 262 478 300 506 NGC 3766
rect 513 427 554 451 IC 4665
IC 4665 (Collinder 349 / Melotte 179) is an open cluster in the constellation Ophiuchus. It was discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in 1745. The cluster began to develop less than 40 million years ago, and lies about 1,400 light years awa ...
rect 181 445 226 472 IC 2581
rect 212 506 257 526 IC 2944
IC 2944, also known as the Running Chicken Nebula, the Lambda Centauri Nebula or the λ Centauri Nebula, is an open cluster with an associated emission nebula found in the constellation Centaurus, near the star λ Centauri. It features Bok globu ...
rect 213 565 246 598 NGC 4755
rect 128 463 154 494 NGC 3293
rect 362 591 392 628 NGC 6067
NGC 6067 is an open cluster in the constellation Norma. It is located to the north of Kappa Normae, with an angular diameter of 12. Visible to the naked eye in dark skies, it is best observed with binoculars or a small telescope, and a 12-inch ...
rect 404 548 437 587 NGC 6193
rect 425 595 453 630 NGC 6231
rect 461 556 498 585 NGC 6383
rect 58 506 91 521 Tr 14
rect 77 520 108 536 Tr 16
rect 797 130 831 153 Messier 103
Messier 103 (also known as M103, or NGC 581) is an open cluster where a few hundred, mainly very faint, stars figure in Cassiopeia. It was discovered in 1781 by Charles Messier's friend and collaborator Pierre Méchain.Robert Bruce Thompson ''M ...
rect 665 408 691 434 Messier 29
Messier 29 or M29, also known as NGC 6913, is a quite small, bright open cluster of stars just south of the central bright star Gamma Cygni of a northerly zone of the sky, Cygnus. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764, and can be seen f ...
rect 746 139 782 157 hPer
rect 763 117 804 132 chi Per
rect 152 485 194 500 Col 228
rect 456 377 492 393 o Vel
poly 0 0 496 0 841 130 976 221 972 421 633 224 277 129 5 111 Perseus Arm
The Perseus Arm is one of two major spiral arms of the Milky Way galaxy. The second major arm is called the Scutum–Centaurus Arm. The Perseus Arm begins from the distal end of the long Milky Way central bar. Previously thought to be 13,000 lig ...
poly 2 230 444 239 688 340 970 495 971 639 559 452 317 387 1 380 Orion Arm
poly 2 481 423 492 694 606 922 757 470 761 234 669 1 668 Sagittarius Arm
rect 879 666 965 684 Star cluster
rect 878 684 944 699 Nebula
desc bottom-left
Other maps

See also
*Galactic disc
A galactic disc (or galactic disk) is a component of disc galaxies, such as spiral galaxies and lenticular galaxies. Galactic discs consist of a stellar component (composed of most of the galaxy's stars) and a gaseous component (mostly composed ...
* Gould Belt
The Gould Belt is a local, partial ring of stars in the Milky Way, about 3,000 light-years long, tilted away from the galactic plane by about 16–20 degrees. It contains many O- and B-type stars, amounting to the nearest star-forming regi ...
* Jon Lomberg's Milky Way painting used as background for Kepler Mission
The Kepler space telescope is a disused space telescope launched by NASA in 2009 to discover Earth-sized planets orbiting other stars. Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler, the spacecraft was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbi ...
diagram, showing our location on the Orion Spur
* Local Bubble
The Local Bubble, or Local Cavity, is a relative cavity in the interstellar medium (ISM) of the Orion Arm in the Milky Way. It contains the closest of celestial neighbours and among others, the Local Interstellar Cloud (which contains the Sol ...
* Loop I Bubble
* List of Messier objects
The Messier objects are a set of 110 astronomical objects catalogued by the French astronomer Charles Messier in his ''Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des Amas d'Étoiles'' (''Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters'').
Because Messier was only in ...
* List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs
This list covers all known stars, brown dwarfs, and sub-brown dwarfs within of the Sun. So far, 131 such objects have been found, of which only 22 are bright enough to be visible without a telescope. The visible light needs to reach or exce ...
References
External links
Messier Objects in the Milky Way (SEDS)
{{Authority control Milky Way arms Galactic astronomy Spiral galaxies